Introduction to Mendelian Genetics and Population Biology
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What did Gregor Mendel discover about inheritance in 1865?
Traits were inherited as discrete particles called alleles from both parents.
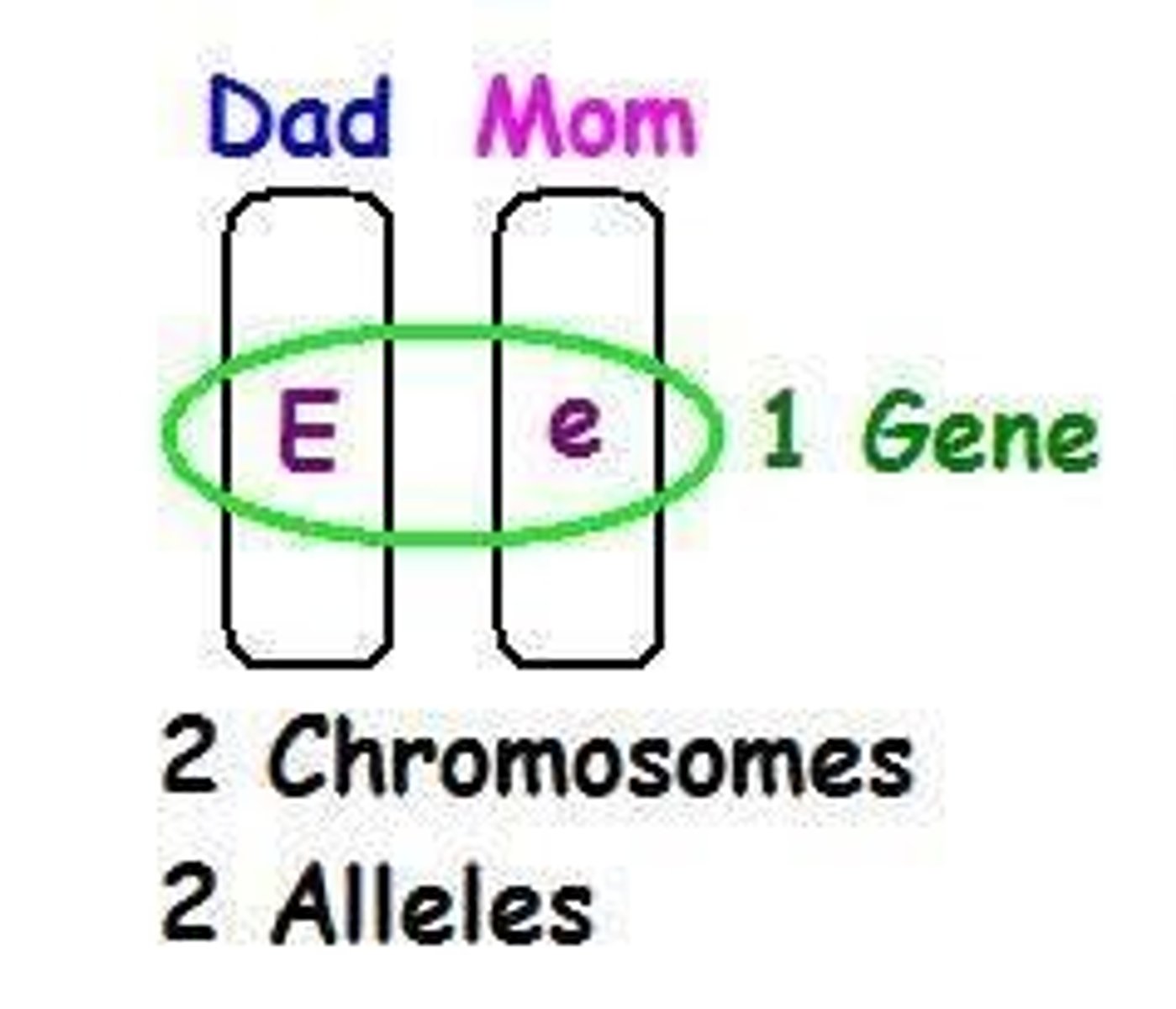
What are alleles and how do they relate to genes?
Alleles are different versions of a gene, with two alleles making up a single gene located at the same locus on two chromosomes.
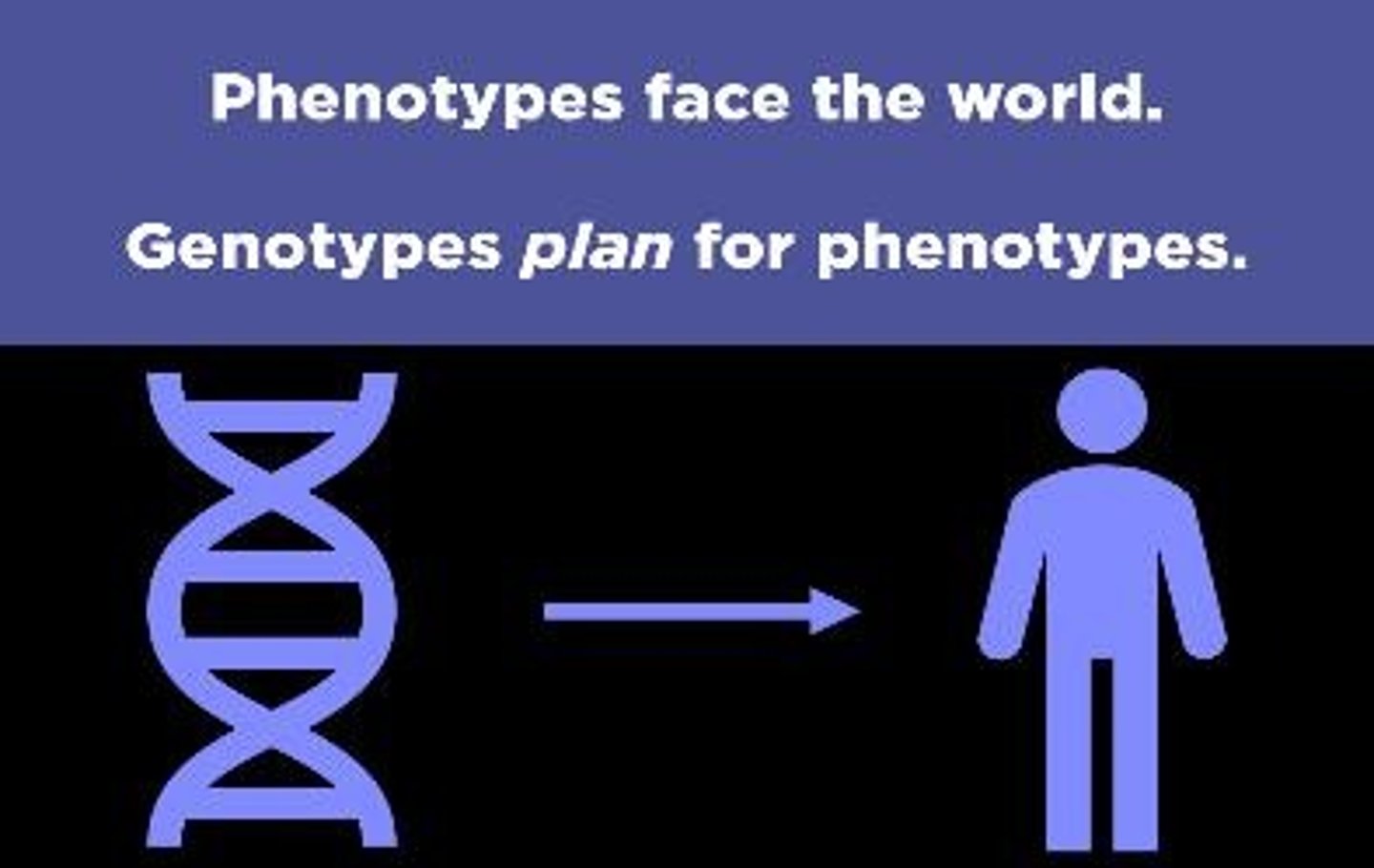
What is the difference between phenotype and genotype?
Phenotype refers to the observable physical traits of an individual, while genotype refers to the genetic makeup expressed as a list of alleles.
What does homozygous mean in genetics?
Homozygous means having two of the same type of alleles, which can be either dominant (TT) or recessive (tt).
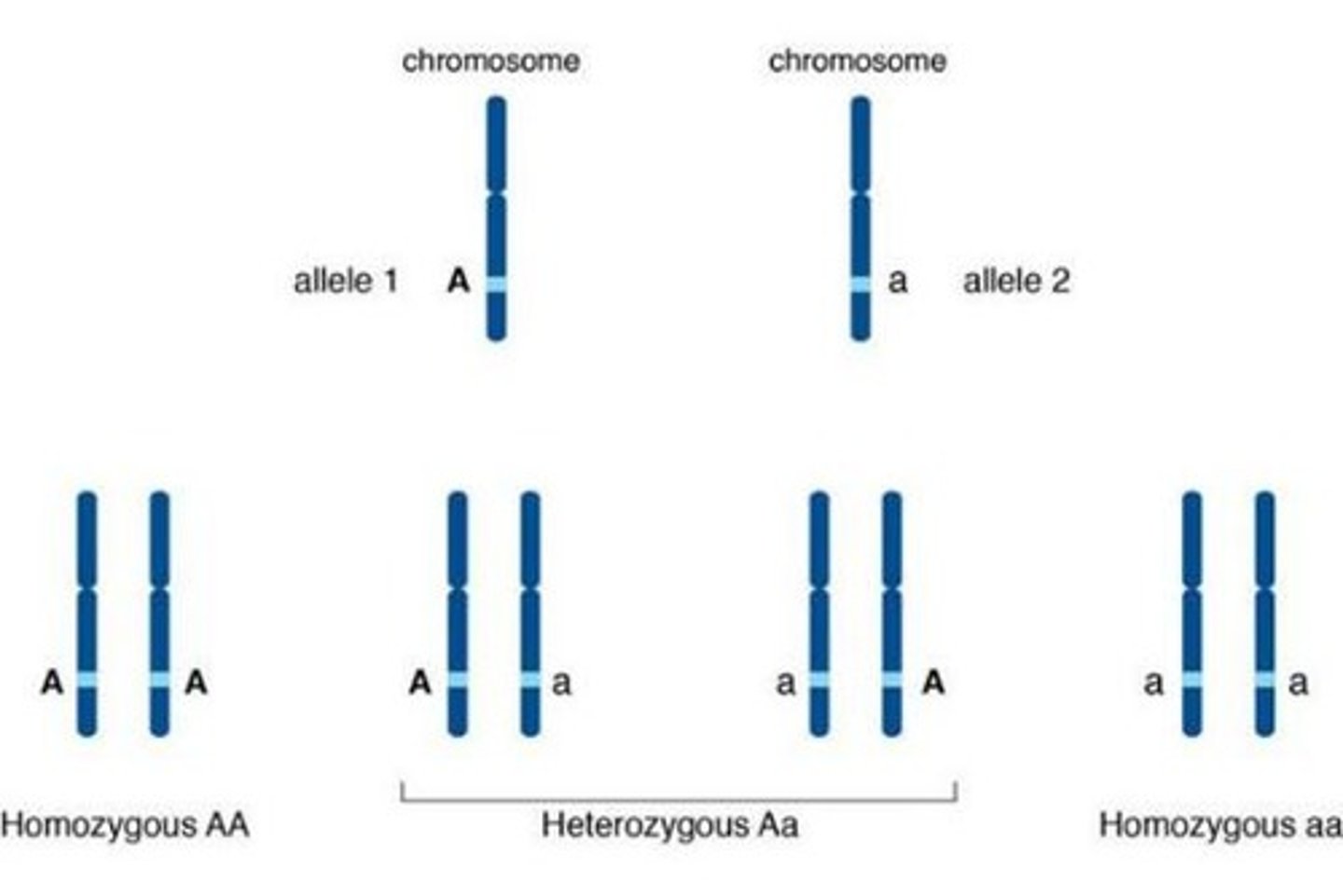
What does heterozygous mean in genetics?
Heterozygous means having two different types of alleles (Tt).
How are traits inherited from parents to offspring?
Parents randomly produce gametes and pass one allele each on to their offspring.
What is the phenotypic ratio in the F1 generation for a monohybrid cross?
The phenotypic ratio is 3 Tall : 1 Short.
What is the genotypic ratio in the F1 generation for a monohybrid cross?
The genotypic ratio is 1 TT : 2 Tt : 1 tt.
What is a Punnett square used for in genetics?
A Punnett square is used to determine the probability of parental traits being expressed in offspring.
What is the genotypic ratio from crossing two heterozygous parents (Tt)?
The genotypic ratio is 1 TT : 2 Tt : 1 tt.
What would be the phenotypic ratio if 'T' is tall and 't' is short?
The phenotypic ratio would be 3 tall : 1 short.
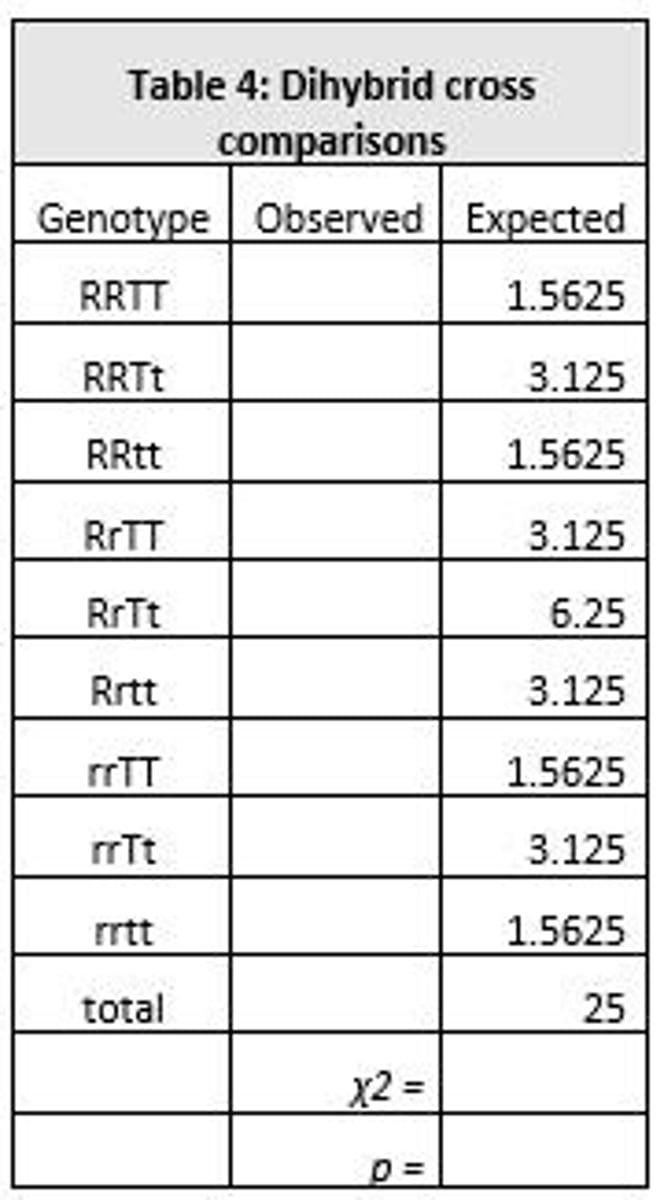
What traits are considered in a dihybrid cross?
In a dihybrid cross, traits such as seed shape (round R vs. wrinkled r) and seed color (yellow G vs. green g) are considered.

What is the genotype of the individuals crossed in the dihybrid cross example?
The genotype of the individuals crossed is RrGg x RrGg.
What is the purpose of a dihybrid cross?
A dihybrid cross is used to determine the possible allele combinations for two different traits.
What is the significance of the F2 generation in Mendelian genetics?
The F2 generation reveals recessive traits that may have been masked in the F1 generation.
How does random mating affect allele frequencies in a population?
Random mating can influence the distribution of alleles and impact biodiversity.
What is the expected outcome of random mating on biodiversity?
Random mating can enhance genetic diversity within a population.
What is the structure of a Punnett square?
A Punnett square consists of a four-square grid where traits from each parent are arranged.
What does a monohybrid cross illustrate?
A monohybrid cross illustrates the inheritance of a single trait.
What is the outcome of crossing two heterozygous parents in terms of phenotype?
The outcome would typically yield a phenotypic ratio of 3 dominant traits to 1 recessive trait.
What is a dihybrid cross in genetics?
A dihybrid cross involves a 4x4 square grid to analyze the inheritance of two traits simultaneously.
What gametes are used in the dihybrid cross example RrGg x RrGg?
The gametes are RrGg, which can produce gametes RG, Rg, rG, and rg.
How do you fill in a Punnett Square for a dihybrid cross?
Fill in each square by combining the gametes from the male and female to create potential zygotes.
How do you determine the genotypic ratio from a dihybrid cross?
List each possible genotype for the offspring and count the occurrences of each type.
What is the genotypic ratio for the cross RrGg x RrGg?
RRGG:1, RRGg:2, RrGG:2, RrGg:4, RRgg:1, Rrgg:2, rrGG:1, rrGg:2, rrgg:1.
What should the total of the genotypic and phenotypic ratios equal in a dihybrid cross?
Both the genotypic and phenotypic ratios should add up to 16.
How do you determine the phenotypic ratio from a dihybrid cross?
List the possible physical appearances for the offspring and count the occurrences of each type.
What is the phenotypic ratio for the cross RrGg x RrGg?
Round yellow: 9, round green: 3, wrinkled yellow: 3, wrinkled green: 1.
What is Mendel's first law of inheritance?
The law of segregation states that alleles are separated randomly during gamete formation.
What is Mendel's second law of inheritance?
The law of independent assortment states that gametes are produced independently of one another.
How can probabilities be used in genetics?
Probabilities can analyze the likelihood of offspring inheriting certain alleles based on expected results.
What is the significance of a p-value in statistical tests?
A p-value indicates the probability of the results occurring by random chance; a p < 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
What does a p-value greater than 0.05 indicate?
It indicates that the occurrence is not statistically significant.
How would you calculate the expected number of heads when tossing a coin four times?
The probability is calculated as p = 0.5^4 = 0.0625 (6%).
What is the expected outcome when tossing a coin five times?
If you get heads every time, it would be considered a rare event, but the probability must be analyzed against the significance threshold.
What is the purpose of statistical tests in scientific studies?
To compare expected and observed outcomes and determine if differences are statistically significant.
What is a common threshold for rare occurrences in scientific studies?
Most studies plan for rare occurrences to happen up to 5% of the time.
What happens if an experimental result has a p-value of 0.03?
It indicates that the result is statistically significant, as the probability of occurrence by random chance is lower than 5%.
What is the significance of the 4x4 grid in a dihybrid cross?
It represents the combinations of alleles from two traits being analyzed simultaneously.
What does the term 'zygote' refer to in genetics?
A zygote is the fertilized egg formed when the sperm and egg fuse together.
What is the significance of a p-value less than 0.05 in statistical testing?
It indicates that the occurrence is significant, suggesting the coin is not fair.
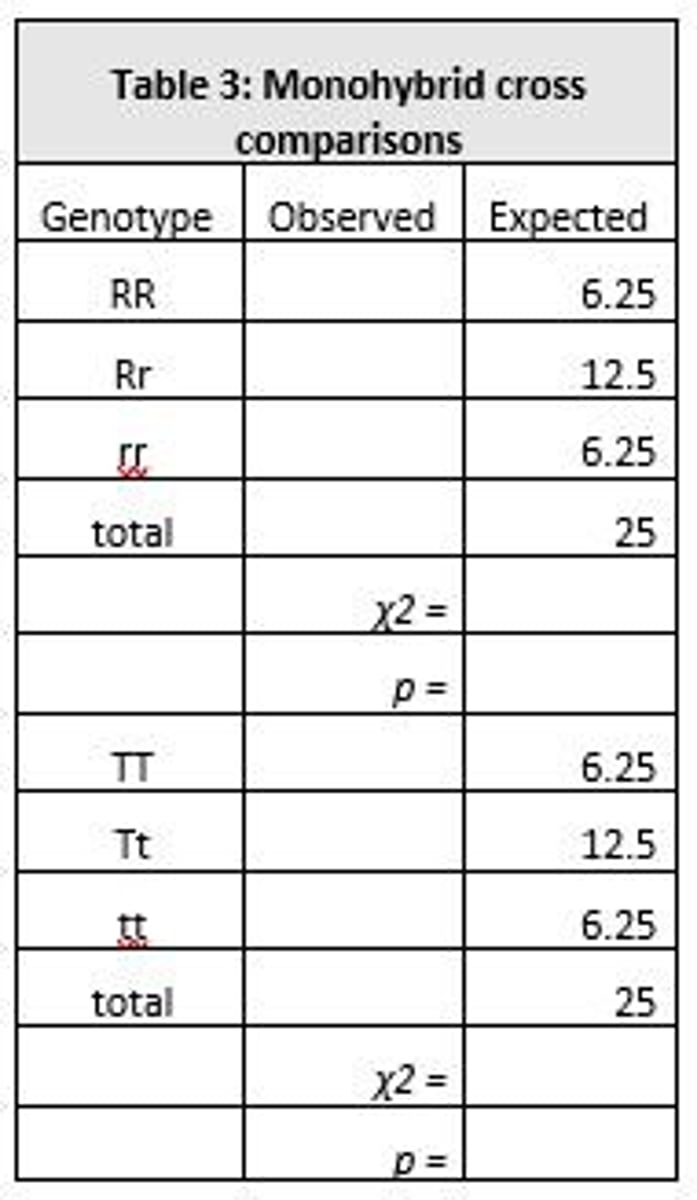
What does the chi-square (χ2) test compare?
It compares observed and expected values to determine if differences could have arisen by chance.
What is the typical acceptable error rate (alpha) in statistical tests?
Alpha is typically set at 0.05.
What is the purpose of the chi-square test in genetics?
To determine if sampled distributions are statistically the same or different.
What is allele frequency?
The proportion of alleles in a population, which always adds up to 1.
How can allele frequencies affect biodiversity?
Changes in allele frequencies can lead to evolution over time, impacting biodiversity.

What is the process for generating gametes in the lab activity?
Students randomly draw beads to represent gametes, which are then combined to create offspring.

What is the formula for calculating degrees of freedom in a chi-squared test?
Degrees of freedom equals the number of categories minus 1.
What are the basic principles of genetics that students should understand for the exam?
Students should understand alleles, genes, chromosomes, and be able to complete Punnett squares.
What is binomial nomenclature?
A naming system for organisms that uses the format 'Genus species', with the genus capitalized and species in lowercase.
Who developed the system of binomial nomenclature?
Carolus Linnaeus.
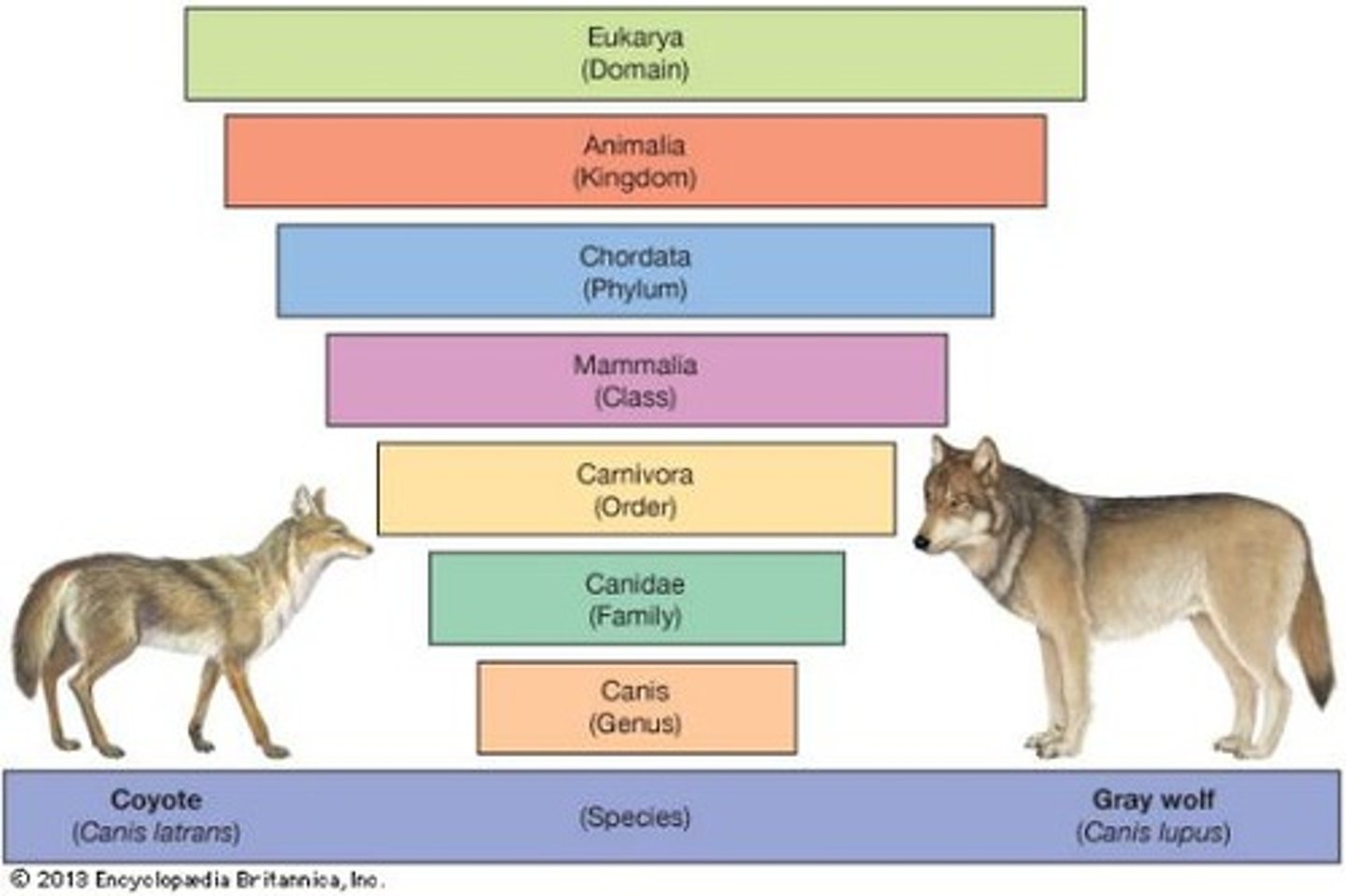
What characteristics are used in hierarchical classification?
Morphological characteristics such as color, shape, size, and placement of structures.
What is the significance of the domain Eukarya in biological classification?
It represents one of the three domains of life, encompassing all organisms with eukaryotic cells.
What is a Punnett square used for?
To calculate the expected ratios of genotypes and phenotypes in offspring from genetic crosses.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup, while phenotype refers to the observable traits.
What is the purpose of a dichotomous key?
To help identify unknown organisms based on a series of choices that lead to their classification.

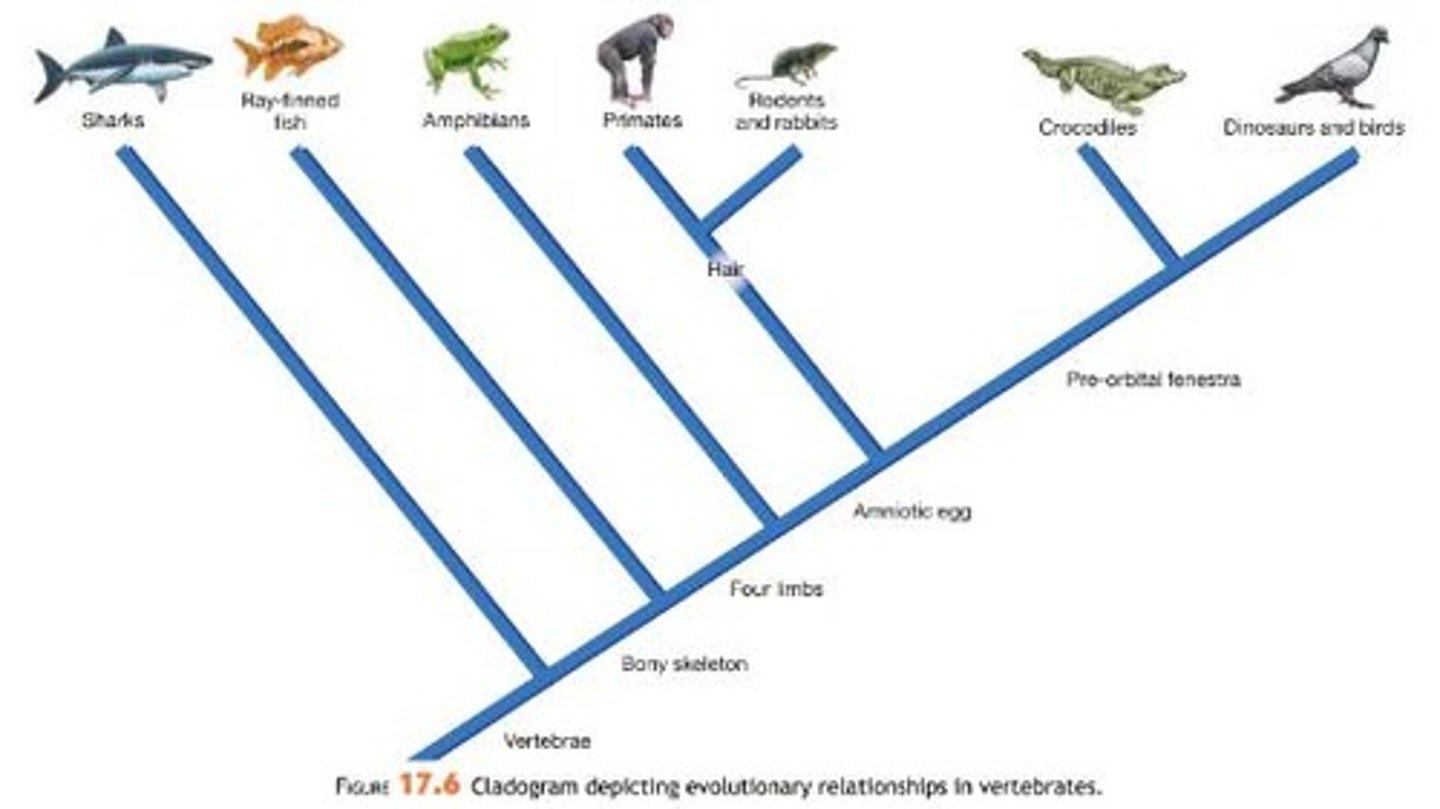
What is a phylogenetic tree/cladogram?
A diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among various biological species.
What is the role of genetic/genomic analyses in classification?
They have changed the way organisms are classified by providing molecular data.
What are the expected ratios in Mendelian genetics?
They are the ratios predicted by Mendel's laws of inheritance for traits.
What is the significance of using a chi-squared calculator in the lab?
It helps analyze the results of the genetic experiment and compare them to expected Mendelian ratios.
What is the expected allele frequency in a population with equal representation of two alleles?
0.5 for each allele.
What is the impact of random assortment of alleles on populations?
It can lead to changes in allele frequencies, affecting the population's evolution.
What is a dichotomous key used for?
To identify unknown organisms using physical characteristics through yes/no questions.
How does a dichotomous key function?
It provides only two options for each question, guiding the user through a series of decisions.
What are some alternative names for phylogenetic trees?
Phylogenetic tree, phylogeny, evolutionary tree, cladogram, dendrogram, phylogram.
What is the primary purpose of a phylogenetic tree?
To organize and approximate pathways of descent and infer relationships between groups based on traits.
What is a key aspect to interpret when analyzing a phylogenetic tree?
The pattern of branching is more important than the placement of individuals.
What does it indicate if two organisms are next to each other on a phylogenetic tree?
It does not necessarily mean they are closely related; relationships are determined by common ancestors.
How many times may seeds have evolved independently according to the example given?
Seeds may have evolved three times independently.
What is required to construct a cladogram?
A character table with characteristics for each organism.
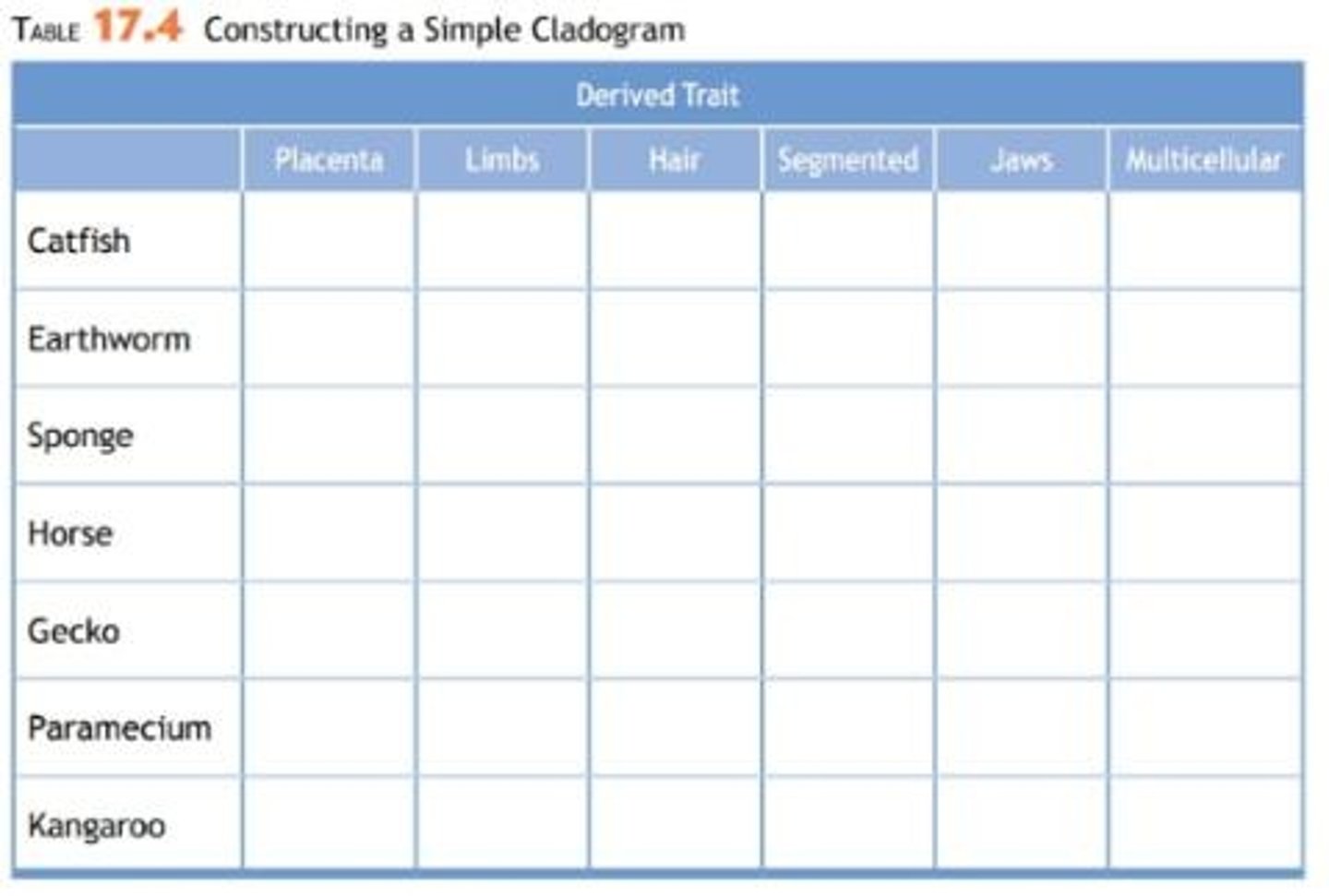
What should you do if you haven't seen the organisms needed to create a cladogram?
Ask for help if needed.
What traits do dichotomous keys rely on?
Physical characteristics of organisms.
What should you be able to do with a dichotomous key?
Use it to identify an organism.
What is expected in the study guide for the exam regarding cladograms?
Be able to create a character table and/or cladogram based on characteristics and interpret it to determine relationships.
What activity is suggested for creating a dichotomous key?
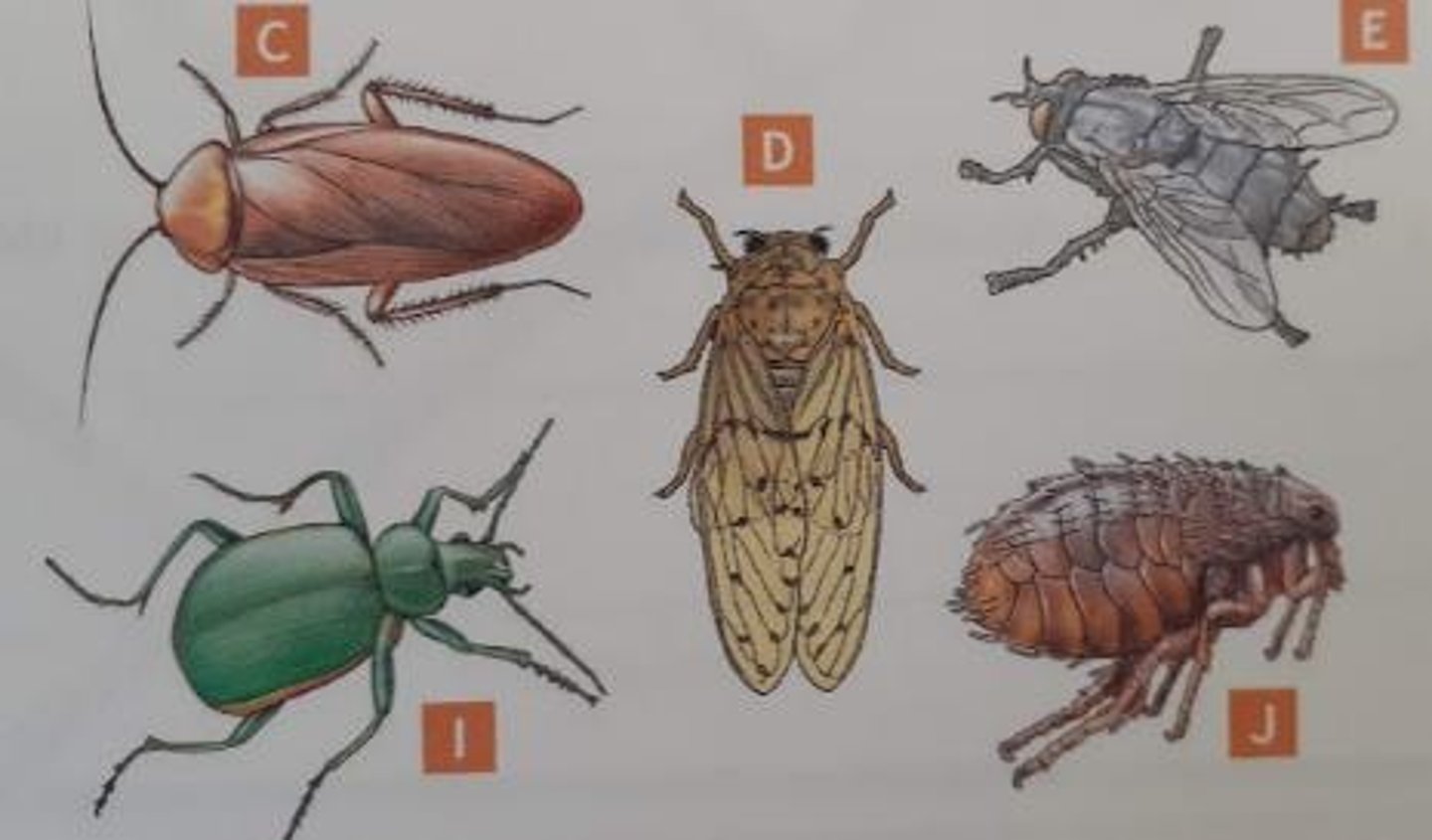
Work together to create a key to common insects and record it in your lab notebook.

What is the focus of the next week's study topics?
The Wide World of Fungi and Seedless Plants.
