Environmental Science Final Exam
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Climate
Long term changes in meteorology
Weather
short term (daily) changes in meteorology conditions. Geographically limited
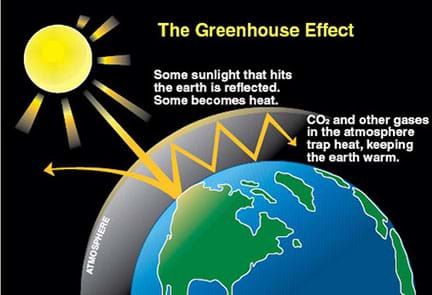
Greenhouse effect
Earth's natural warming process where atmospheric gases (like carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor) trap heat from the sun, preventing it from escaping into space
Feedback loop*
The output of a process affects the input
Positive: The output of a process increases the input

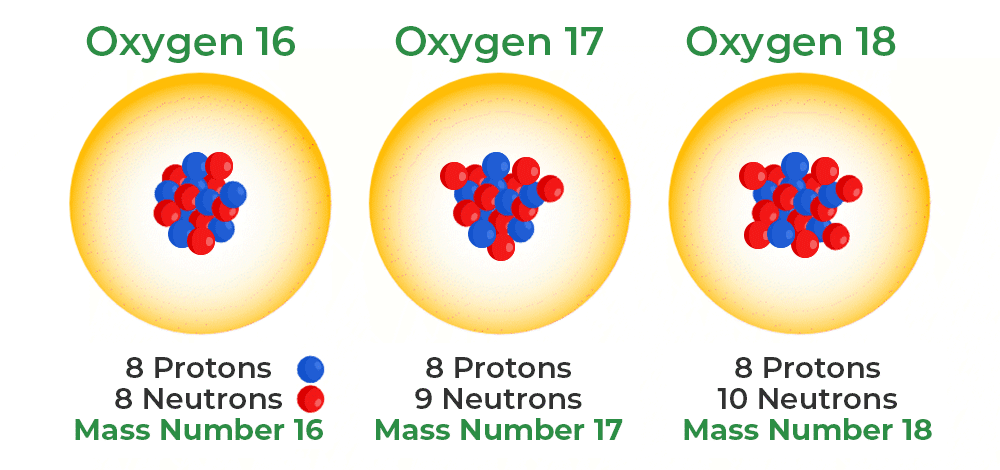
Isotope*
A chemical element in which the atoms have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in their nucleus, a radioactive form of an element
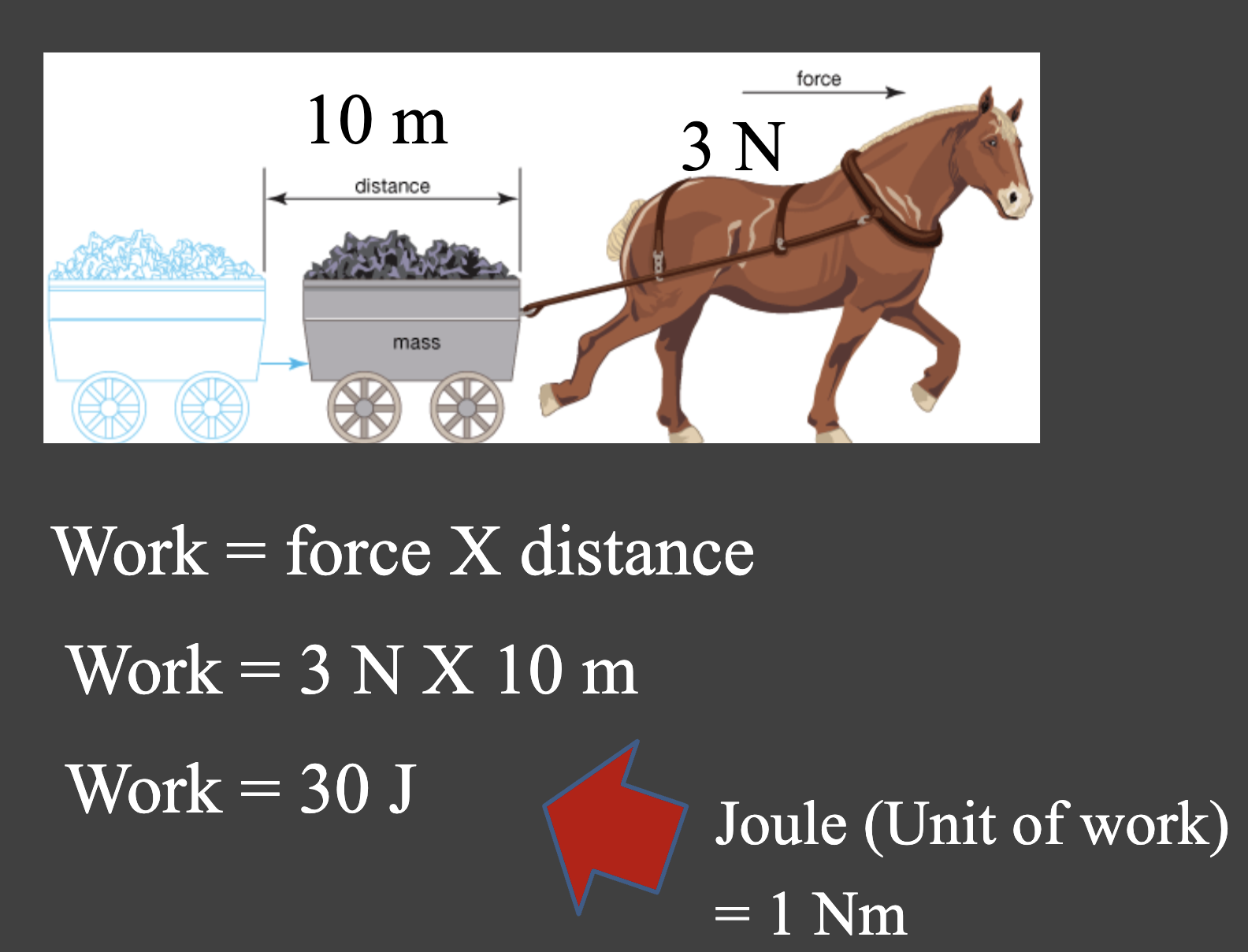
Energy*
The ability to do work
Work = Force x Distance
Force ↘
⬜ ———→ ⬜
Distance
Fossil Fuels*
Formed over millions of years from remains of dead organisms
Nuclear Energy
The immense power stored in the core (nucleus) of atoms is released through processes like fission (splitting atoms, used in reactors) or fusion (joining atoms), which generates heat to produce electricity
1. Pellets are stacked in a hollow rod
2. Rods are bundled into assemblies
3. 1000s of these fuel assemblies are
bundled together in the nuclear core
4. When struck with a neutron, Uranium
releases energy through nuclear fission
5. Chain reaction occurs, causing Uranium
to release more atoms
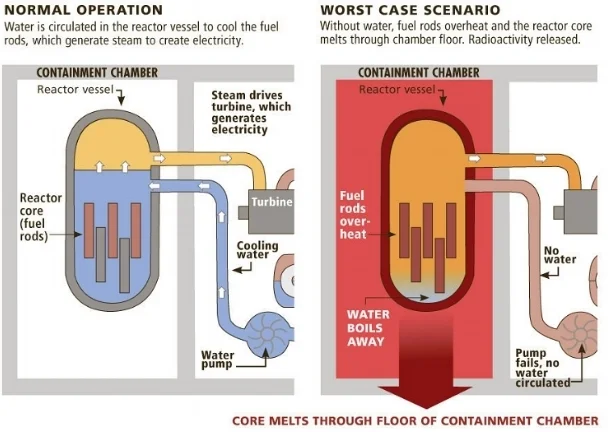
Nuclear Meltdown
a severe accident where a nuclear reactor's core overheats, causing the nuclear fuel (like uranium) and its protective cladding to melt, potentially breaching containment and releasing dangerous radioactive materials into the environment. Happens when the cooling system fails, often due to coolant loss, power loss, or human error, leading to uncontrolled heat from nuclear fission that melts the fuel rods.
Fuel rods overheat and melt (up to 5,070°F), basically turning to nuclear lava, called “corium,” which can reach temperatures of up to 9,000°F
Melted fuel rods can interact with hydrogen and explode
Loss of containment means radiation leaks
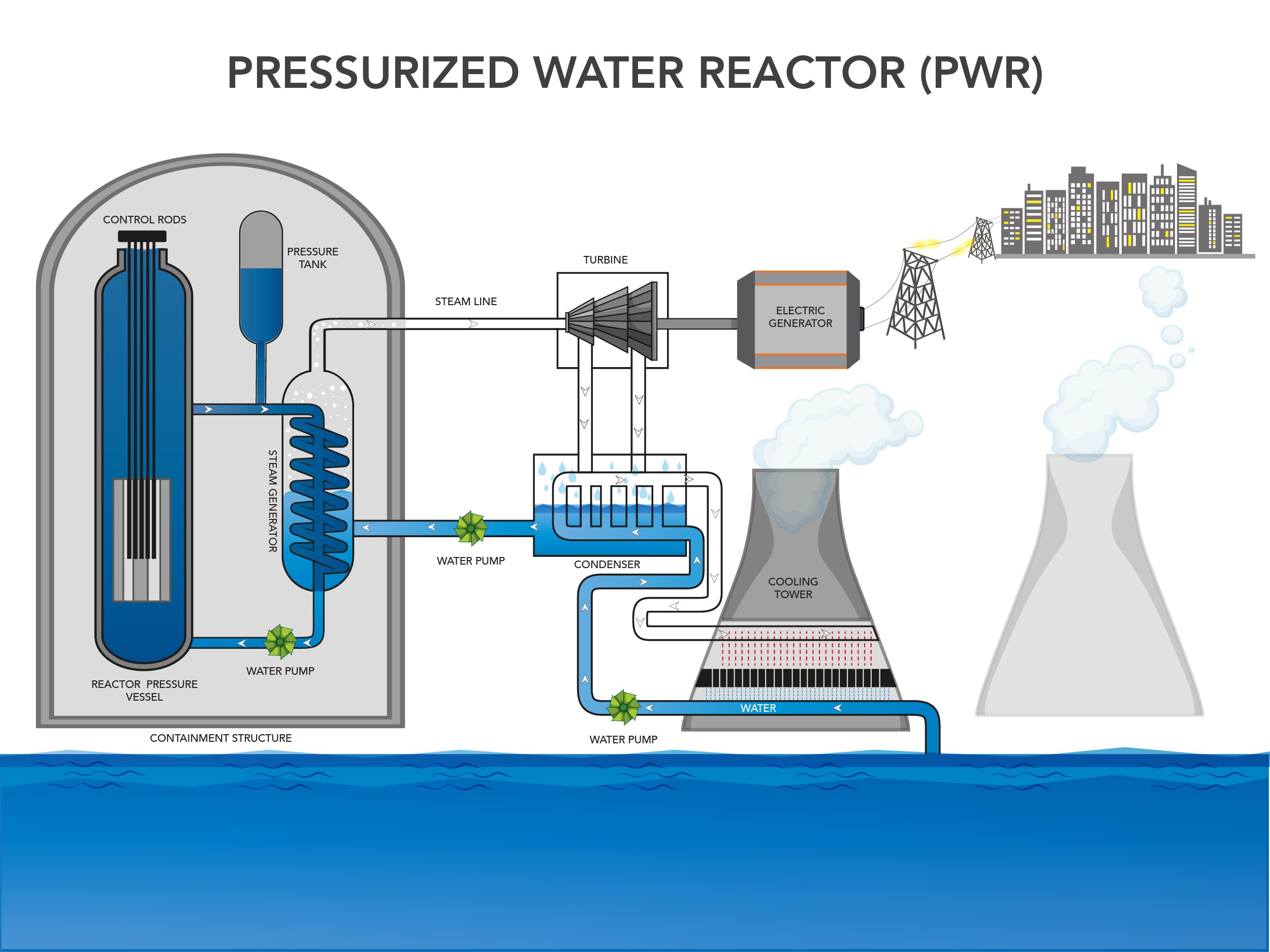
Pressurized Water Reactor (PWR)
A type of nuclear reactor that uses highly pressurized water to transfer heat from the reactor core to a steam generator (two separate circulation systems, less radioactive/safer).
- Nuclear fission in the reactor core heats the primary water to a high temperature.
- The water is kept under immense pressure, preventing it from boiling.
- This hot, pressurized water flows through tubes in a steam generator.
- The heat from the primary water is transferred to a secondary water system, causing it to boil and turn into steam.
- The steam then turns a turbine connected to a generator to produce electricity.
- The water from the primary loop remains separate from the steam in the secondary loop, which keeps most of the radioactivity contained within the primary system
Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)
A nuclear reactor that uses heat from nuclear fission to boil water directly in the reactor core, creating steam that drives a turbine to generate electricity (1 line, just heat doesn’t boil)
- Fission & Boiling: Uranium fuel in the reactor core undergoes fission, releasing heat, which boils the surrounding water, creating steam.
- Direct Cycle: The steam goes directly from the reactor vessel to the turbine, making it a "direct cycle" system.
- Power Generation: The spinning turbine turns a generator, producing electricity.
- Condensation & Recycle: After passing through the turbine, the steam is cooled in a condenser, turns back into water, and is pumped back to the reactor to repeat the cycle
Differences between PWR & BWR
- PWR creates less radiation
- PWR creates less contamination
- PWR creates less radioactive waste
- PWR is more fuel-efficient
- BWR has a higher risk of personnel contamination due to having more contaminated areas
Sustainable
Using resources in such a way that we can continue to use them indefinitly
Renewable Energy*
Able to replenish within human time scales
Example: Biomass - Fuelwood
Active Solar Technology*
Collection of the sun’s energy with electricity or moving parts
Example: solar thermal and photovoltaic solar
Passive Solar Technology*
Collection of sun’s energy with no electricity or moving parts
Example: Building Orientation - Strategically positioning a building to face the sun
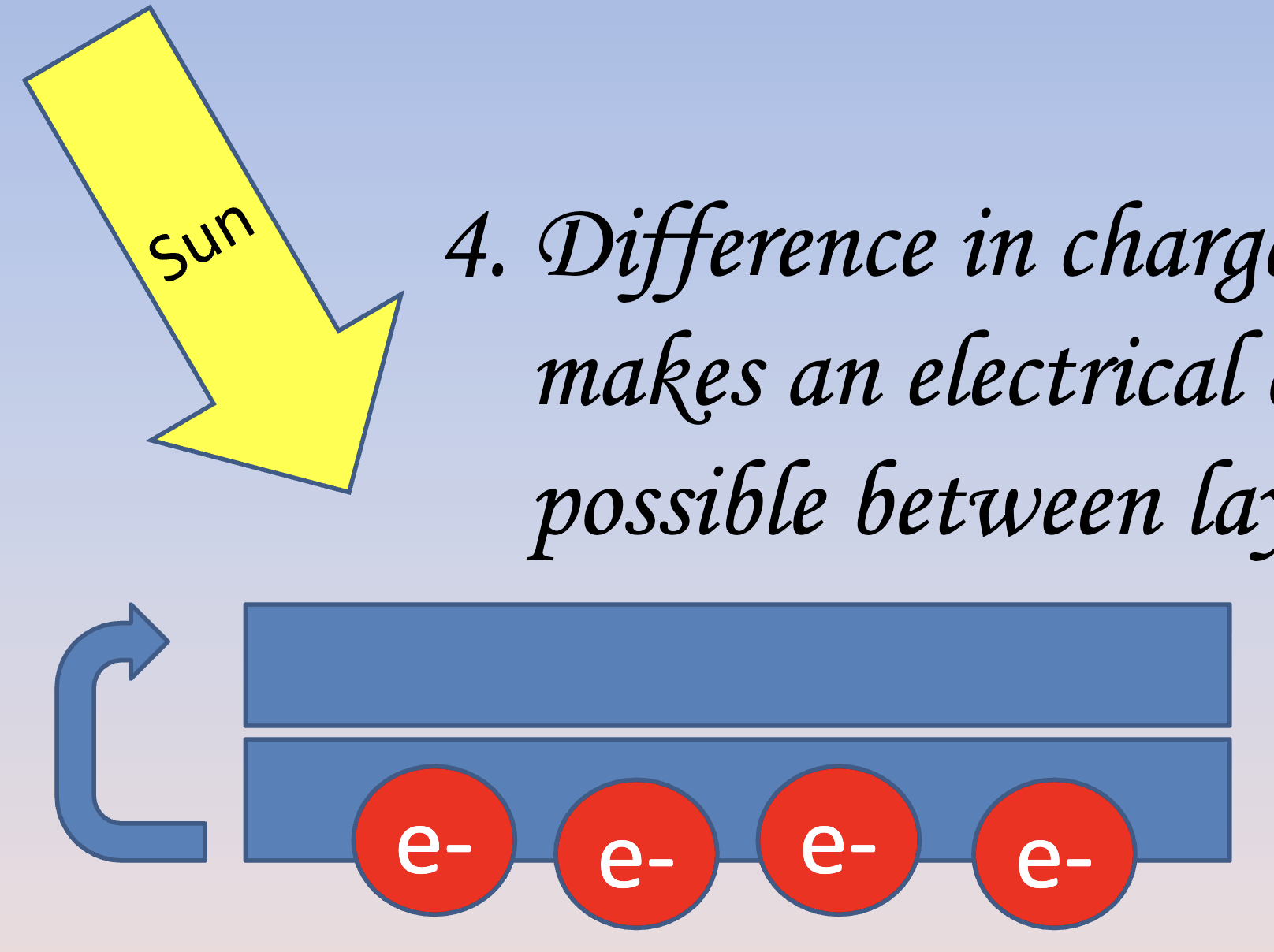
Photovoltaic cells
1. Electrons are released when sun hits the upper cell
2. Electrons move to lower layer
3. Lower layer becomes negative compared to upper layer (positive)
4. Difference in charge makes an electrical current possible between layers
Biomimicry
The design and production of materials, structures, and systems that are modeled on biological entities and processes.

Urbanization
The process of making an area more urban
Urban Flight*
Moving from the city center outward to more suburban areas
Impacts more white people while POC usually stay in city centers
Environmental Justice
The concept that access to a clean and healthy environment is a basic human right
Conspicuous consumption*
Buying things that we don’t need to impress others or compare ourselves to others
Example: buying popular designer fashion
Affluenza
The drive to have more possessions
Sustainable Development*
Improving quality of life while minimizing harm to the environment
Example: practicing sustainable agriculture
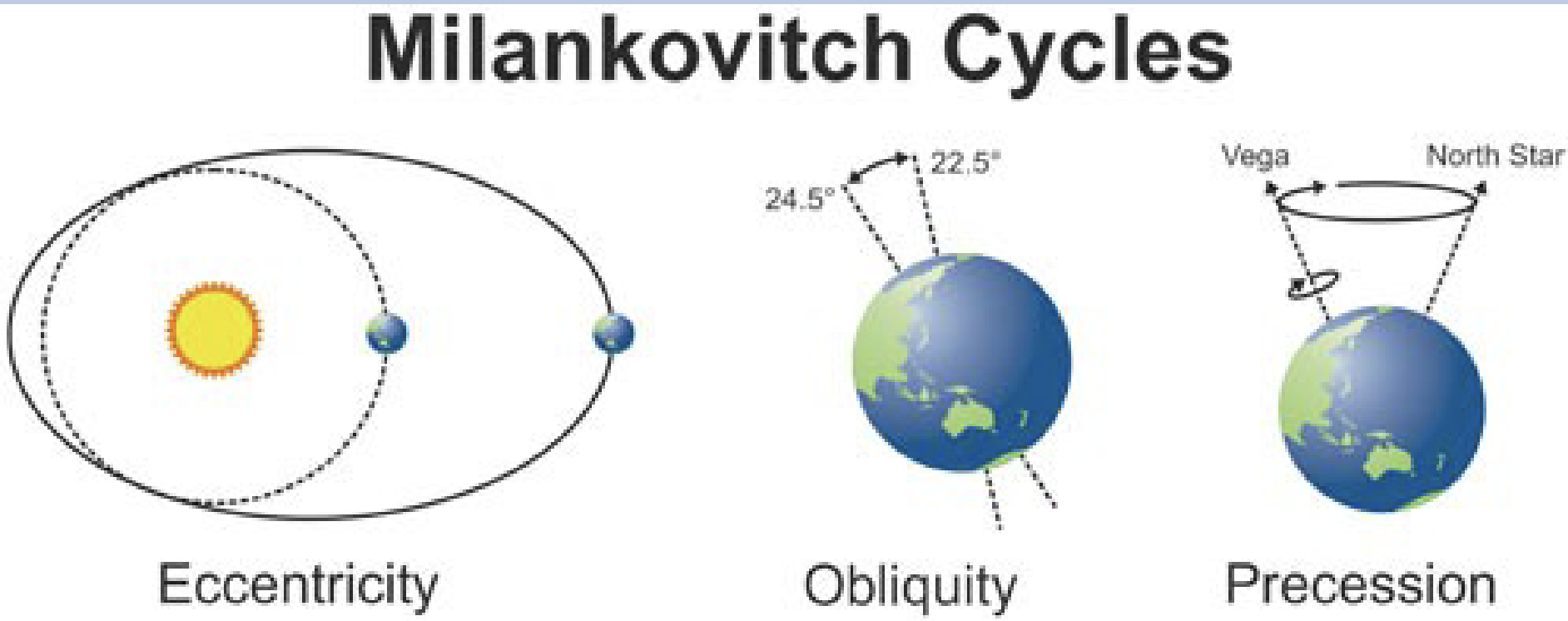
Milutin Milankovitch
His cycles are impacting CO2 distribution
tilt of axis
wobble of axis
shape of orbit
Thorstein Veblen
Created the idea of conspicuous consumption: buying things that we don’t need to impress or compare ourselves to others.
Why is the depletion of the ozone layer NOT the driver of climate change? What caused the ozone layer to deplete over time?
Ozone is not significantly altering global temp
Ozone in the stratosphere absorbs harmful solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which heats the stratosphere. The loss of this ozone layer actually causes a slight cooling effect on the Earth's surface
Different Causes: Climate change is primarily driven by the accumulation of long-lived greenhouse gases in the lower atmosphere (troposphere), mainly carbon dioxide (CO2) from burning fossil fuels.
Ozone loss due to CFCs and climate
Ozone depletion is caused by human-made chlorine and bromine-containing chemicals (like CFCs = chlorofluorocarbons) that migrate to the upper atmosphere (stratosphere).
Minor Warming Contribution: While the gases that deplete the ozone (CFCs) are themselves potent greenhouse gases, their concentrations are much lower than CO2, and their overall warming contribution is small
What isotopes are used to find out temperature and climate history from ice cores?
The primary isotopes used to determine temperature and climate history from ice cores are the stable isotopes of oxygen (18O and 16O) and hydrogen, also known as deuterium
What is the relationship between CO2 and world temperature? What has happened to the CO2 in the atmosphere in recent times?
CO2 is a heat-trapping greenhouse gas that acts like a blanket around the planet (absorbing infrared energy/heat radiating from the Earth's surface that would otherwise escape into space), and human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels, are increasing its concentration in the atmosphere, leading to a rise in global temperatures
More carbon = higher tempatures
CO2 in the atmosphere has increased to record high levels in recent times, with the annual rate of increase accelerating.
We went from 3 to 4 CO2 rates
How has climate change affected ocean organisms?
More acidic (lower pH) & reduces calcium carbonate
Climate change disrupts ecosystems, alters species' behavior and migration, and damages critical habitats like coral reefs.
It has led to a warmer ocean habitat, which in turn increases the level of acidity in the ocean.
This change in water chemistry reduces the availability of carbonate ions, making it harder for "calcifying" organisms like corals, oysters, clams, and mussels
How do the carbon isotopes released from fossil fuels differ from the natural carbon in the atmosphere?
They differ in their isotopic composition, with the relative amounts of carbon-13 and carbon-14
- At no time in the last 10,000 years have the 13C/12C ratios in the atmosphere been as low as they are today.
- Fossil fuels have lower 13C/12C ratios than the atmosphere.
Fossil fuels are derived from ancient plants and organic material that lived millions of years ago. During photosynthesis, plants preferentially take up the lighter isotope, 12C, over the heavier 13C, making the fossil fuels "lighter" in their carbon isotopic signature compared to the natural atmosphere
- Measured 13C/12C ratios in the environment began to decline dramatically just as the CO2 started to increase around 1850.
Name some economic effects of climate change
Health impacts, costal erosion/flooding, less crop productivity, drought, fire risk, climate disasters, extreme rising sea levels, heat/humidity risks to human health
What are the 3 biggest human greenhouse gas emissions from the most impact to the least?
carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide
Climate Mitigation vs. Climate Adaptation.
Mitigation: Efforts to minimize the extent or impact of a problem (reduce)
Adaptation: Adjusting as best possible (dealing with the problem)

Kyoto Protocol and Paris Agreement
Key international climate treaties under the UNFCCC
Kyoto Protocol (1997)
legally binding, U.S. did not join
Key Feature: Legally binding emission reduction targets for developed countries (Annex I) only.
Goal: Reduce greenhouse gases (GHGs) by about 5% below 1990 levels during the first commitment period (2008-2012).
Paris Agreement (2015)
Not legally binding, U.S. joined off and on
Key Feature: Universal participation; all countries submit NDCs (Nationally Determined Contributions).
Goal: Limit global warming to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels, pursuing efforts for 1.5°C.

Give examples of impactful solutions to climate change
Climate Mitigation
shifting from fossil fuels to renewables (solar, wind)
boosting energy efficiency (insulation, heat pumps, LEDs)
sustainable transport
What does work mean in terms of energy?
Energy is the ability to do work
Work = Force x Distance
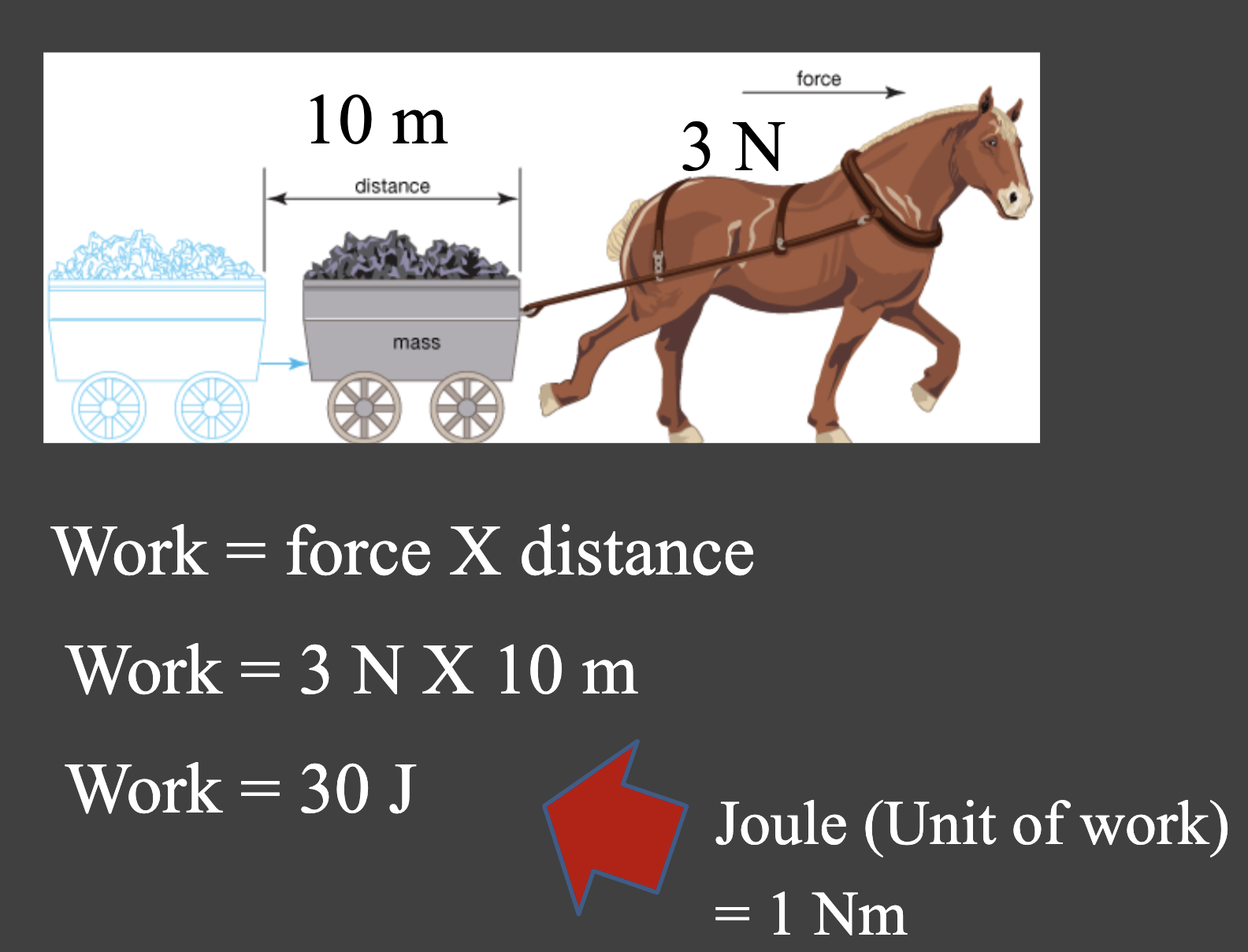
What is the unit for work?
Joule
Which fossil fuel has the most deposits?
Coal
Methods of coal mining: surface vs. subsurface
Surface mining: removes topsoil to expose shallow coal seams using large machinery, making it cost-effective for near-surface deposits, but causing greater land disruption.
Subsurface: underground mining uses shafts and tunnels to reach deeper coal, offering less surface impact but higher costs, greater risks (gas, subsidence), and lower recovery rates
Pro: fewer habitat detriments
Con: Human health risk, air pollution, black lung disease
What are some drawbacks of using coal?
severe environmental damage, including major contributions to air pollution (sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulates) and greenhouse gases (CO2), leading to acid rain, smog, climate change, and respiratory/neurological health issues like asthma and cancer
What are the 6 “criteria pollutants” that are regulated under the Clean Air Act?
- particulate matter (particles or droplets)
5 chemicals:
-sulfur oxides
-carbon monoxide
-nitrogen oxides
-ground-level ozone
-lead
What has happened to the acidity of rain in the U.S. since the Clean Air Act?
Improved
Which country do we import oil from the most?
Canada
How is fracking performed?
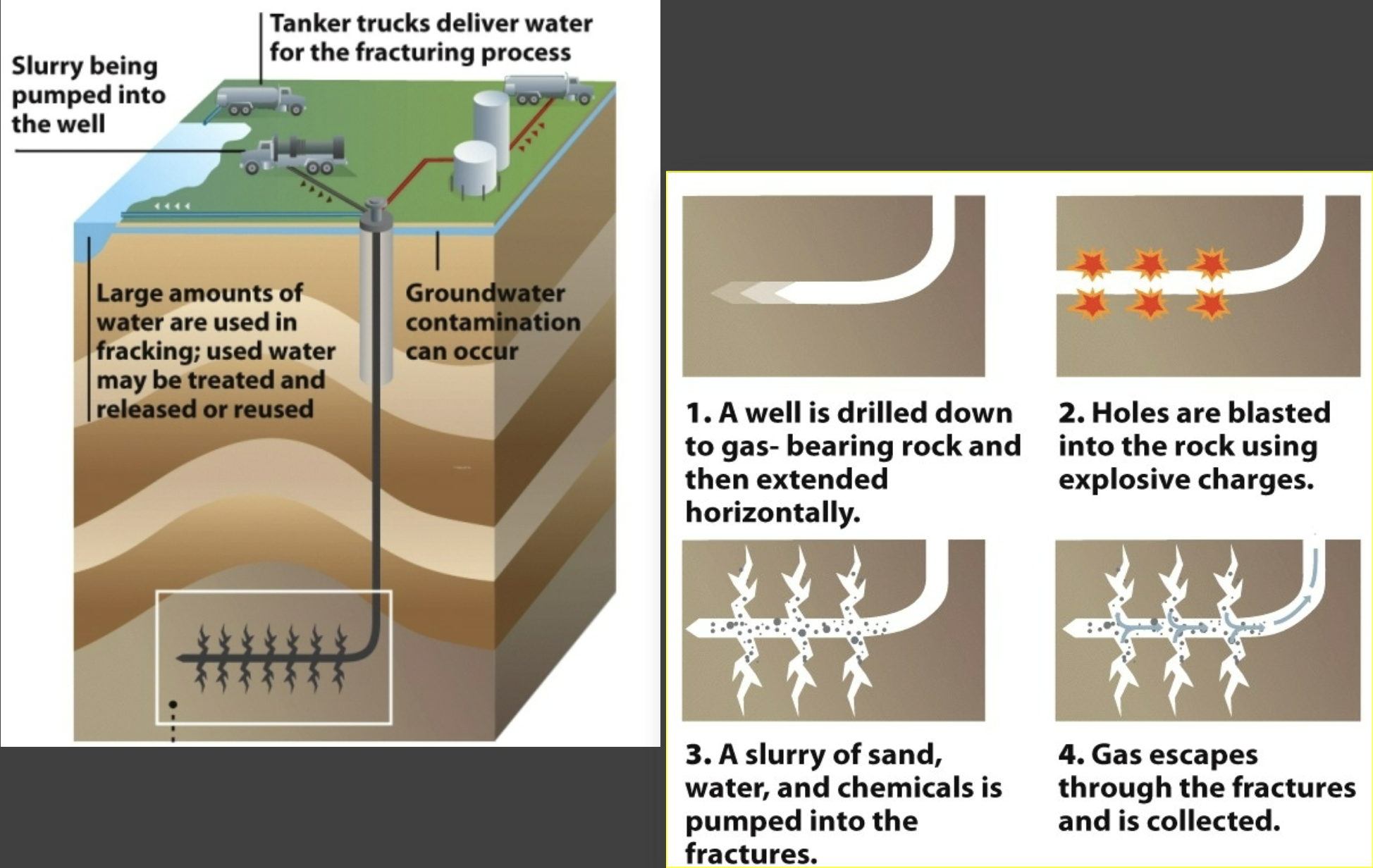
Environmental risks of fracking
Ground water contamination, earthquakes, air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, land degradation and habitat loss
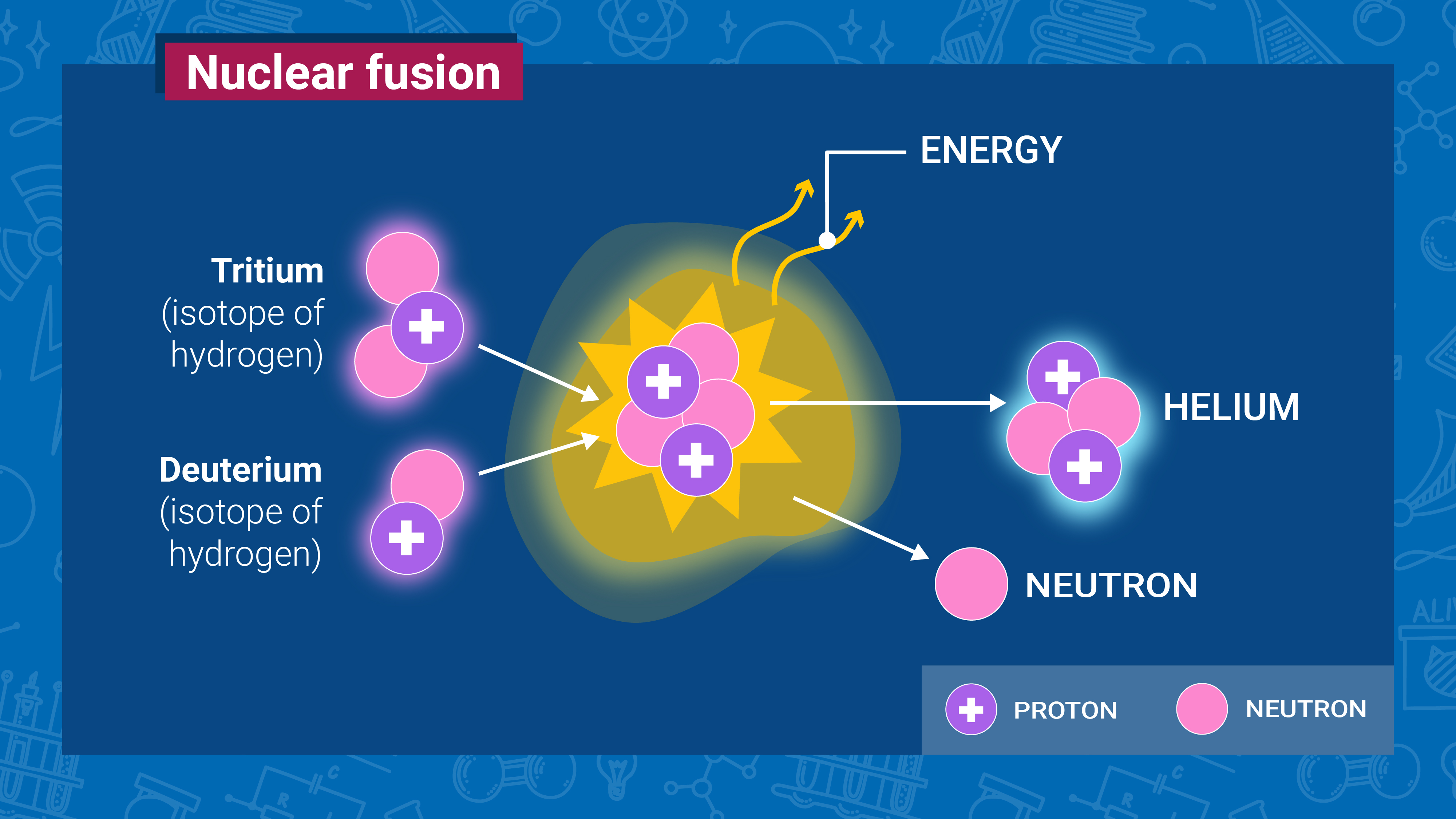
Nuclear fission
A reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei collide at very high speeds and combine to form a single, heavier nucleus. This process is accompanied by the release of a tremendous amount of energy, which is what powers stars, including our Sun
Risks of Uranium Mining
risks from heavy metals and radioactive waste, which can contaminate water sources and the surrounding environment, Radioactive dust, Radon Gas, Increased background radiation
Dangers of nuclear waste disposal
Long-term radioactivity, which can lead to genetic damage and diseases such as cancer.
Leaks that enter groundwater or soil cause environmental contamination.
Wet pools and dry casks are vulnerable to natural disasters, attacks, and accidents.
Safety with nuclear energy- Types of radiation and shielding
• Alpha: Highly ionizing. Dangerous when inside the body, but super weak penetration. You can block this with a piece of paper.
• Beta: Moderately ionizing. Can still do a lot of damage to cells. Can also cause skin burns. This is blocked with things like heavy clothing, thick cardboard, sheets of aluminum or thick plastic.
• Gamma: Not as ionizing as the others, but much worse due to penetration. This can damage your DNA, potentially leading to mutation and even cancer. This one is blocked with lead.
Pros and cons of nuclear energy
Pros: low carbon emissions and reliable, high-capacity power output, making it a key tool for combating climate change, High Energy Density
Cons: managing long-lasting radioactive waste and the high initial cost of building power plants, Risk of Accidents
Name the 2 energy renewable energy sources that are showing the most growth in the U.S.
solar energy and wind energy
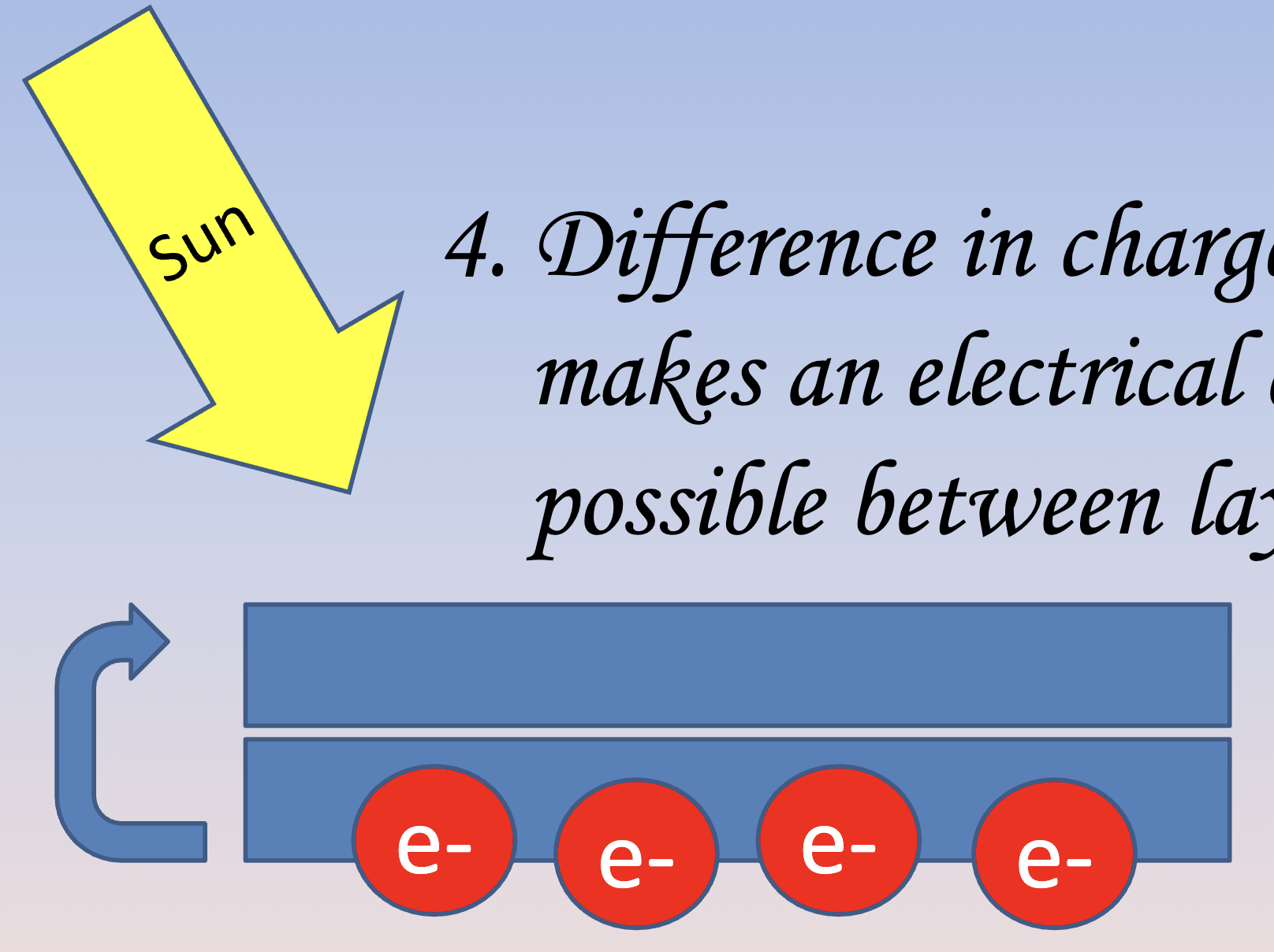
How do photovoltaic cells work?
1. Electrons are released when sun hits the upper cell
2. Electrons move to lower layer
3. Lower layer becomes negative compared to upper layer (positive)
4. Difference in charge makes an electrical current possible between layers
How does wind turbine height influence energy output
Wind turbine height significantly boosts energy output because wind speeds increase with altitude due to less ground friction, providing a stronger, more consistent resource; taller turbines access faster, smoother winds, increasing power generation, though costs rise with height
Ethanol vs. Biodiesel
Biodiesel: Glycerin from fats or oils
Ethanol: Alcohol from corn/sugarcane
List the types of energy from Earth's forces. List at least 1 positive and 1 negative about each one.
Wind Energy: electrical energy obtained from harnessing the wind with windmills or wind turbines
Pro: Can be put on existing farmland
Con: Requires a lot of open land, increases the chance of bird and bat strikes, and Noise pollution
Traditional Hydropower: Uses a dam to create a reservoir, converting gravitational potential energy into electricity through moving or falling water, which spins turbines connected to generators, transforming kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Pro: Cost-effective & high efficiency
Con: ecosystem destruction & changes water quality
Geothermal Energy: heat from within the earth is used to generate electricity, heat buildings, and cool homes by tapping into underground reservoirs of hot water or steam
Pro: Always available/consistent
Con: Risk of triggering earthquakes
Ocean Energy: power generated from the ocean's natural movements and thermal differences
Pro: Abundant, predictable, & reliable
Con: Disruptive to marine ecosystems & site-specific
List the types of energy from biomass. List at least 1 positive and 1 negative about each one.
Fuelwood: heat or electricity produced from burning wood in various forms used for cooking, heating, and power generation as an energy source
Pro: Biodegradable & easy to access
Con: Labor-intensive & air pollution
Methane from Bacteria: biogas from manure, landfills, wastewater treatment
Pro: Resourceful, utilizing already available materials
Con: Potential leaks & cannot be a primary energy source
Traditional Ethanol & Biodiesel: Biodiesel is Glycerin from fats or oils, while ethanol is Alcohol from corn/sugarcane
Pro: Non-toxic & Supports rural communities by creating jobs
Con: Deforestation
Cellulosic Ethanol: converting vegetation unsuitable for human consumption into ethanol, without sugar cane, with enzymes that break down sugar to turn into microbes (can get from any plant)
Pro: Any plant can be used, more widely available
Con: Needs controlled conditions to grow well & is not very effective as it is less productive
Algae: Algae convert sunlight and CO2 into chemical energy through photosynthesis, storing this energy in the form of natural oils and starches
Pro: Grows fast
Con: very expensive
How is cellulosic ethanol different from traditional ethanol?
Cellulosic ethanol can come from any plant while ethanol comes from corn or sugarcane
Explain the challenges to increasing renewable energy options in the future
intermittency, high costs, land use, and grid infrastructure
Pros and cons of urbanization
Pros: transportation, high-density living, economic growth, job opportunities, improved access to services like education and healthcare
Cons: Urban flight, light pollution, increased pollution and waste, higher costs of living, strain on public services
What continents will hold the most megacities in 2035?
Africa and Asia
How do race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status play a role in exposure to environmental risks?
- Urban flight usually happens to white people, while black and brown people usually stay in city centers (has to do with redlining)
City centers feel the most negative environmental impacts, leading to POC having higher health risks
- because systemic racism and poverty concentrate minority and low-income communities near hazardous facilities (factories, highways, waste sites), creating worse air/water quality, while also leading to poorer housing, hazardous jobs, and less access to healthcare, making them more vulnerable and increasing health disparities
What role can community participation play in ensuring environmental justice? How can we balance economic development with environmental protection in a way that benefits everyone?
Ensuring decisions reflect local needs, empowering marginalized groups, and creating equitable solutions, while balancing economic growth with environmental protection involves integrating community feedback early, promoting transparency, investing in green jobs and infrastructure in affected areas, and fostering inclusive, community-led initiatives for shared benefits, not just burdens. This means moving from top-down planning to collaborative governance, giving communities real power in decisions about waste sites, development, and policy, leading to more effective, just, and sustainable outcomes
Explain the connections between the consumer decisions and the environment
Consumer decisions are fundamentally linked to the environment through the entire lifecycle of products, from resource extraction and manufacturing to transportation and disposal.
Name factors that correlate with happiness from the research discussed in the lecture
Education, health, connectedness with nature, income (until basic needs are met), job satisfaction, strong relationships, & spirituality
At what point does income stop correlating with happiness?
Once basic needs are met
Feedback Loops (positive/negative)
The output of a process affects the input
Positive: output increases feedback (amplifies)
Negative: Output decreases feedback
Directional Selection
Acts against one side(trait), it does poorly, the other side does well or is favored, causing a shift
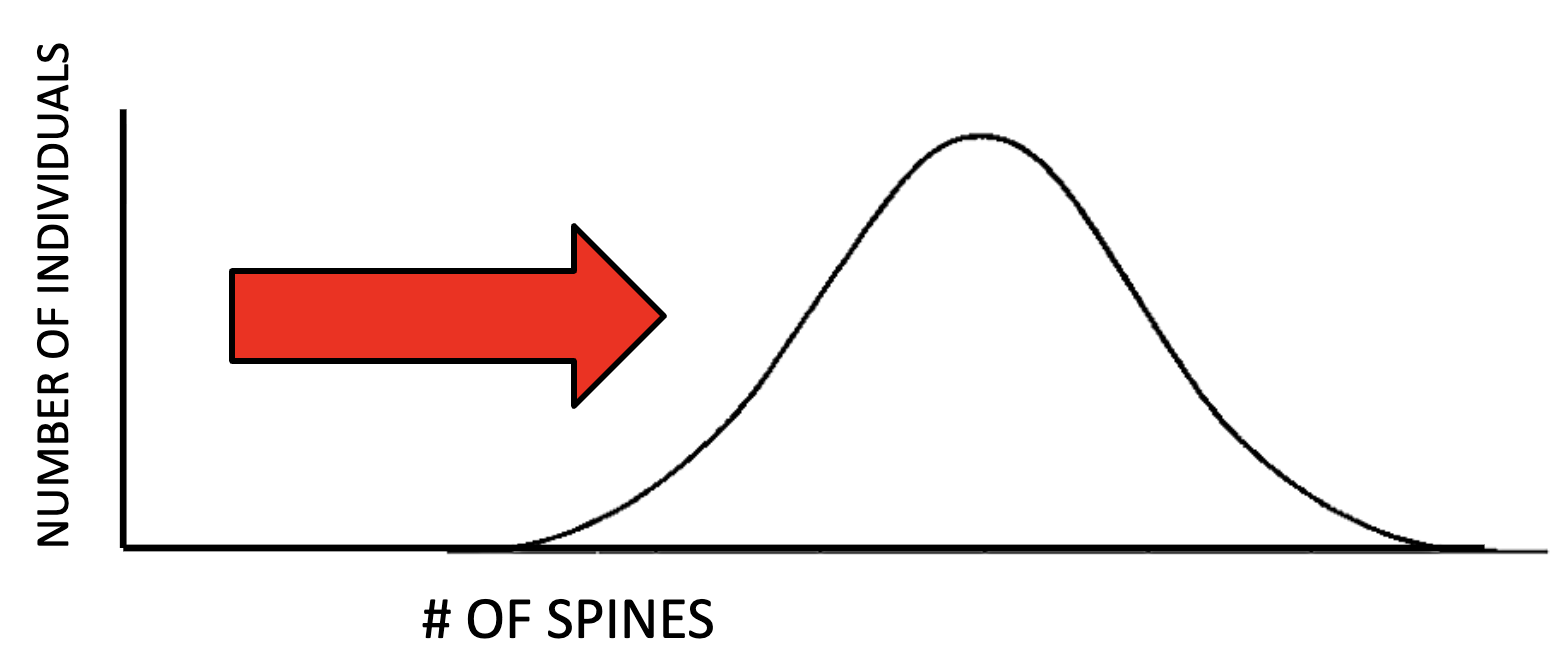
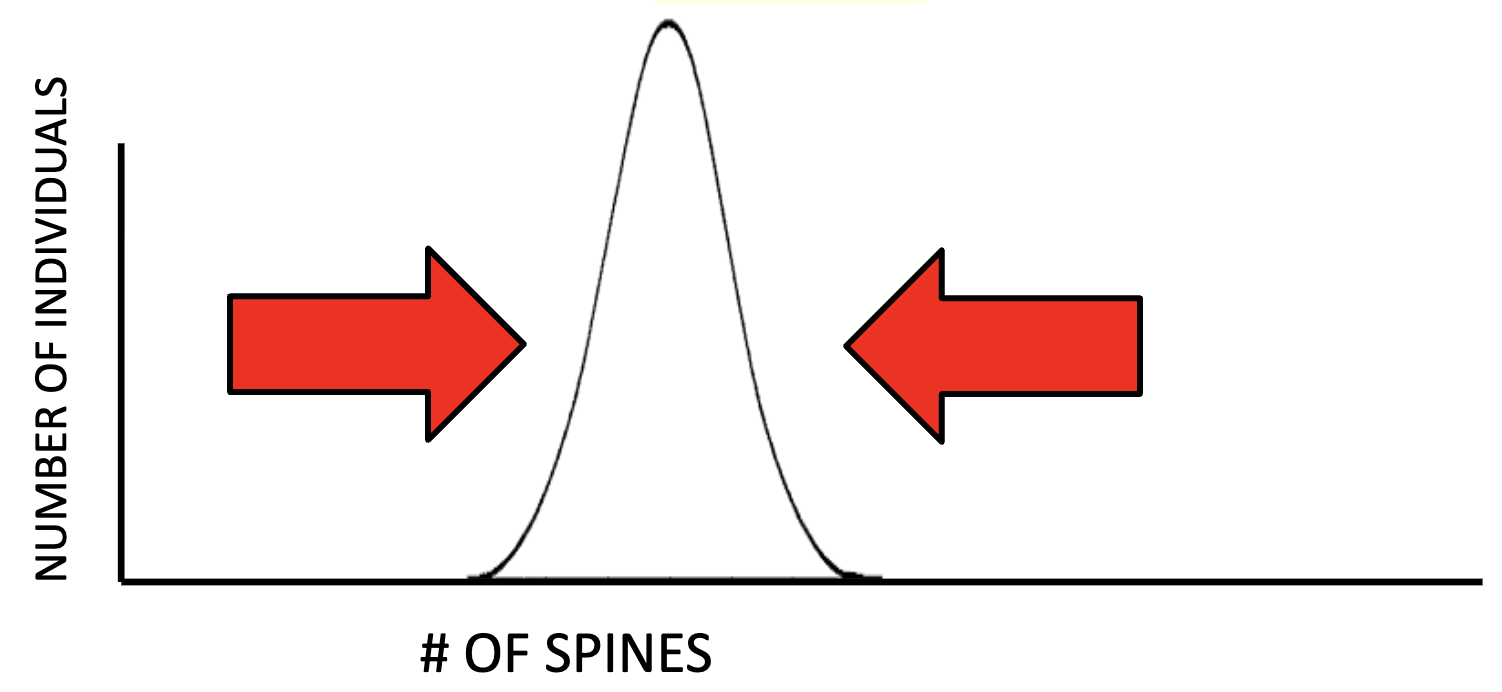
Stabilizing Selection
Acts against both extreme ends, favoring the intermediate/middle trait of the two sides
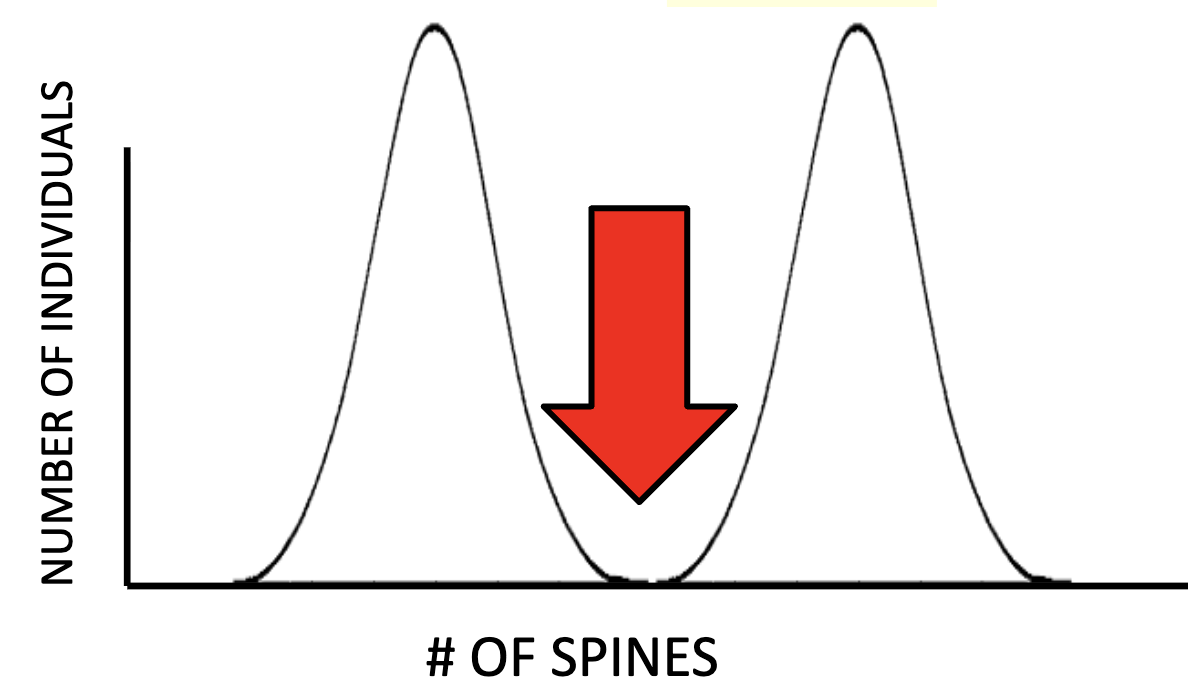
Disruptive Selection
Acts against the middle trait; the extremes do better
Organism
a living thing
Population
a group of same species in the same area
Community
a group of different species in the same area
Ecosystem
all living and non-living things in the same area
Interspecific
produced, occurring, or existing between different species
Intraspecific
produced, occurring, or existing between the same species
Indicator Species
Sensitive species that respond to environmental change first
Keystone Species
Cause significant losses to the ecosystem when removed. Top of food chain or very critical food chain link
Niche
A role played by a species in a biological community
Polyculture
A role played by a species in a biological community
Element
a pure substance that cannot be chemically broken down into simple substances, considered the simplest form of matter
Example: hydrogen & carbon
Isotope
An atom of a chemical element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons (change # of neutrons)
Biomagnification
the concentration of toxins in an organism as a result of its ingesting other plants or animals in which the toxins are more widely disbursed
r = B+I-D-E
Demographic changes
R = B + I - D - E
R = rate of population growth
B = births
D = Deaths
I = immigration
E = emmigration
Biological Species Concept
defines species by interbreeding and producing viable offspring
Phylogenetic Species Concept
defines species by DNA similaritydefines species by DNA similarity
Evolutionary Species Concept
defines species by an evolutionarily significant lineage that shares a common ancestor and niche
Allopatric speciation
Generating a new species with a geographical border
Sympatric speciation
Generating a new species without a geographical barrier
Ring Species
Populations that can interbreed with their nearest neighbors but not those far away (Brings up issues with the biological species concept).
Rotational Grazing
allows us to produce meat with a relatively small amount of land without some of the more harmful environmental costs of CAFOs
If you allow cattle to graze wherever they please, they tend to eat the softest plants first. They work from their favorite grasses to less desirable species. Over time, the diversity drops, and you could loose all your grass species.
To prevent that, we break the land into sections. All the cattle feed in just one section. The diversity of plants may drop in this section, but all the variety still exists in the other section, once they have eaten this section to a low level, You move them to the next section. Then when they get that section low, You move them again. The advantage of this, is while they are in different areas, the first section has the opportunity to regrow. And- there is seed available from the uneaten sections to help regenerate the diversity in the first spot. This way, we never fully lose the diversity of our area and the grasses survive much better.
Rainshadow Effect
A dry area forms on the downwind side of a mountain range, while the upwind side is wetter. Basically, perception happens on one side of the mountain, leaving the other side dry.
Natural Selection
the core mechanism of evolution where organisms better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully, passing advantageous traits to offspring, gradually changing the species over generations to become better suited to their surroundings
Artificial Selection
Humans choose which organisms breed in order to produce a desired trait
Fossil Fuels
a natural non renewable fuel such as coal or gas, formed in the geological past from the remains of living organisms.
Greenhouse Effect
Earth's natural process where atmospheric gases (like CO2, methane, water vapor) trap some of the Sun's heat, warming the planet to sustain life
E.O. Wilson
Created the HIPPO acronym
H = Habitat I = Invasive Species P = Pollution P = Human Population O = Over harvesting
Rachel Carson
Wrote Silent Spring in 1962, awakened the public to the threats of pollution and toxic chemicals (COBT, a form of pesticides) to humans as well as other species. Advocated for Pollution Concern.
Karl Popper
an Austrian–British philosopher, academic and social commentator who came up with the falsifiable hypothesis
↳ an educated guess that makes specific, testable predictions, allowing for the possibility of an experiment or observation to prove it wrong
Charles Darwin
British biologist, geologist, and naturalist who is celebrated for his theory of evolution and natural selection. His 1859 book, On the Origin of Species, presented his ideas on how species evolve through natural selection.
Got his idea from his time in the Galapagos Islands