AP HUG Unit 7: Industrial and Economic Development Patterns and Processes
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Agglomeration
The spatial grouping of people or activities for mutual benefit.

Assembly Line Production
Arrangement of workers, machines, and equipment in which the product being assembled passes consecutively from operation to operation until completed.
Break of bulk point
A location where goods are transferred from one type of carrier to another. (e.g. Barge to Railroad)

Bulk Gaining Industry
An industry in which the final product weighs more or comprises a greater volume than the inputs.

Bulk Reducing Industry
An industry in which the final product weighs less or comprises a lower volume than the inputs.

Comparative Advantage
The principle that an area produces the items for which it has the greatest ratio of advantage or the least ratio of disadvantage in comparison to other areas, assuming free trade exists.
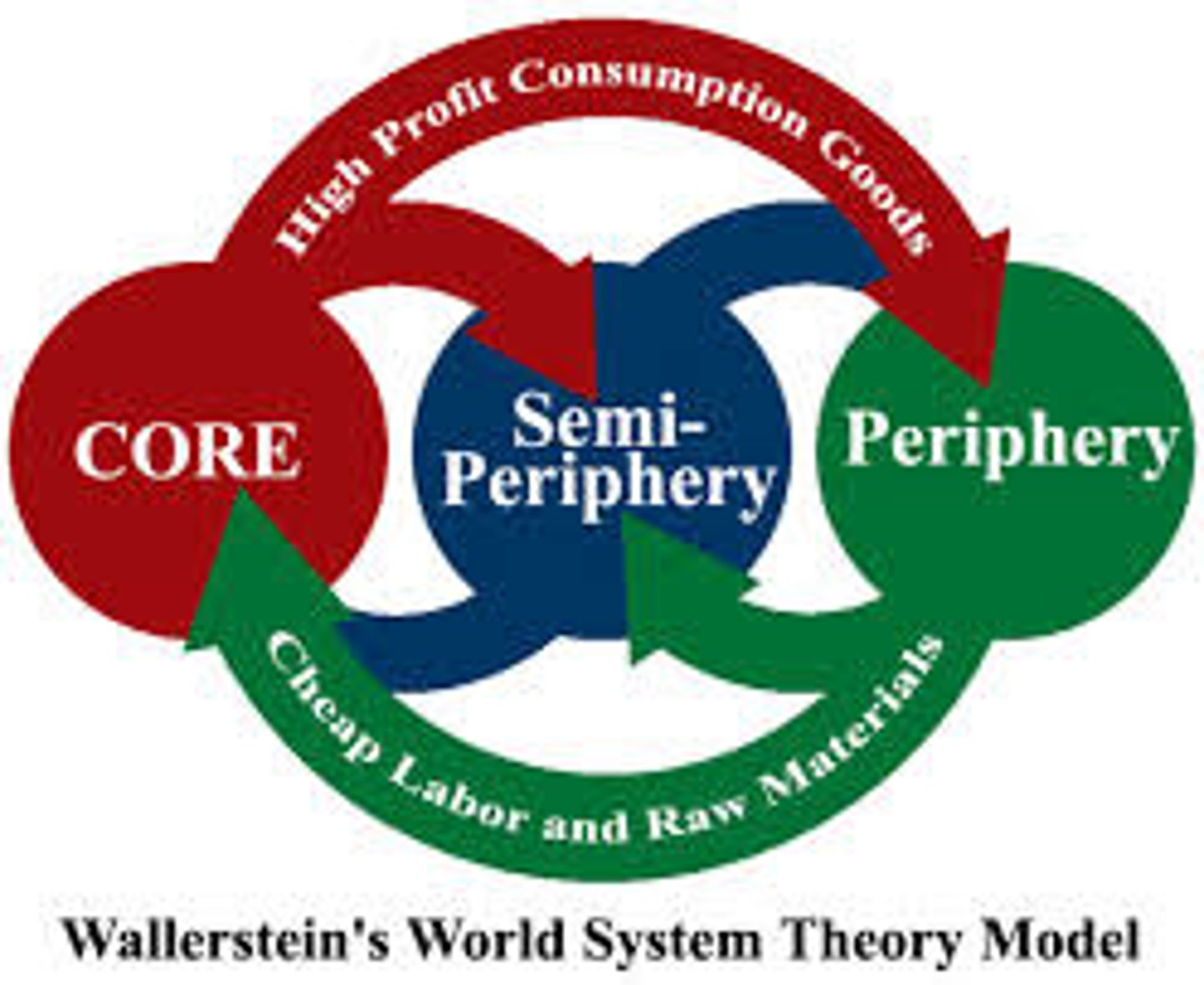
Core-Periphery Model
A model of the spatial structure of an economic system in which underdeveloped or declining peripheral areas are defined with respect to their dependence on a dominating developed core region.
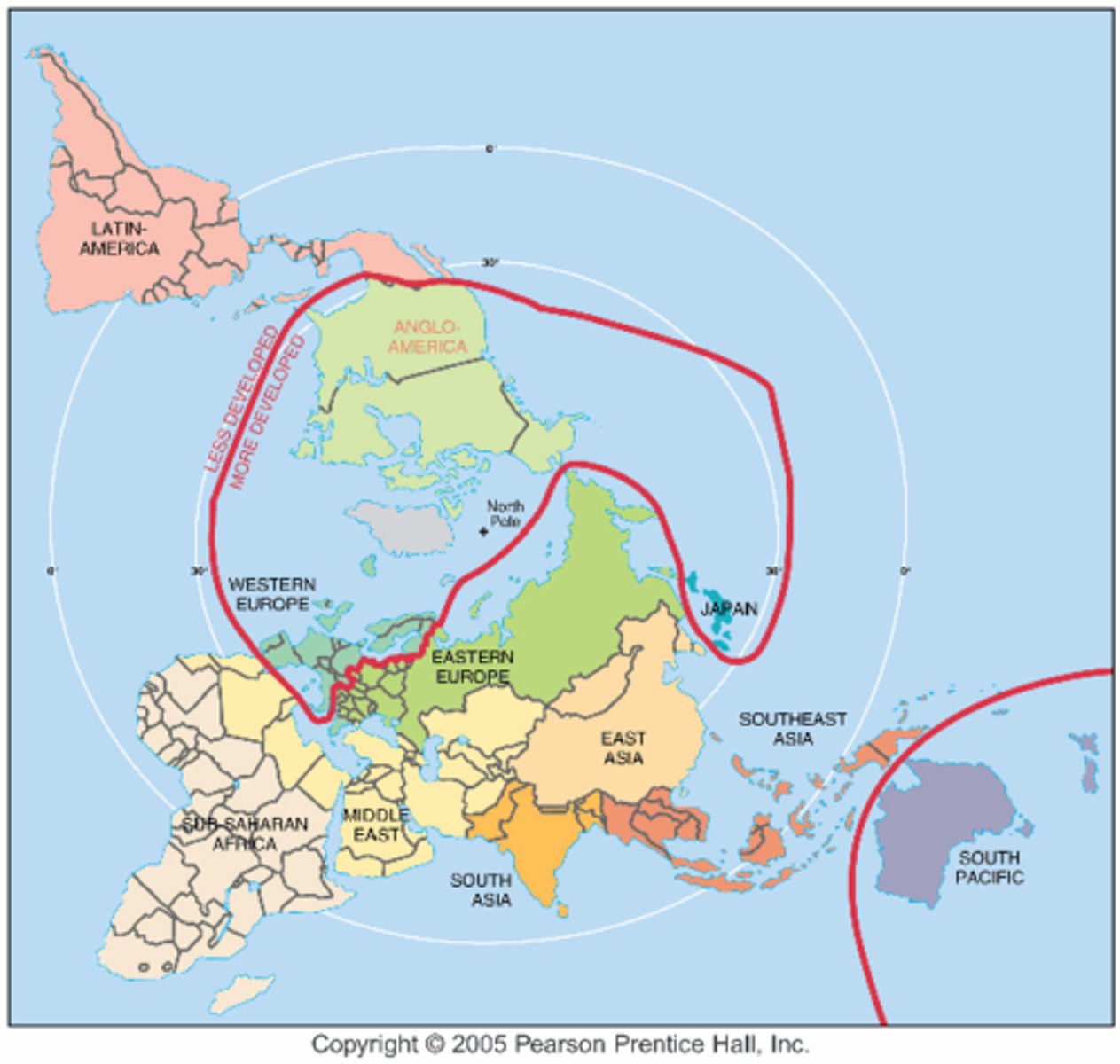
Deindustrialization
Process by which companies move industrial jobs to other regions with cheaper labor, leaving the newly deindustrialized region to switch to a service economy and to work through a period of high unemployment.
Dependency Theory
a model of economic and social development that explains global inequality in terms of the historical exploitation of poor nations by rich ones
Development
The process of growth, expansion, or realization of potential; bringing regional resources into full productive use.
Ecotourism
A form of tourism, based on the enjoyment of scenic areas or natural wonders, that aims to provide an experience of nature or culture in an environmentally sustainable way.

Friction of Distance
A measure of the retarding or restricting effect of distance on spatial interaction.
Globalization
A reference to the increasing interconnection of all parts o the world as the full range of social, cultural, political, and economic processes becomes international in scale and effect.

Gross Domestic Product
The total value of goods and services produced within the borders of a country during a specified time period, usually a calendar year.
Gross National Product (Gross National Income)
the total value of goods and services produced by a country per year plus net income earned abroad by its nations; formerly called "gross national product."
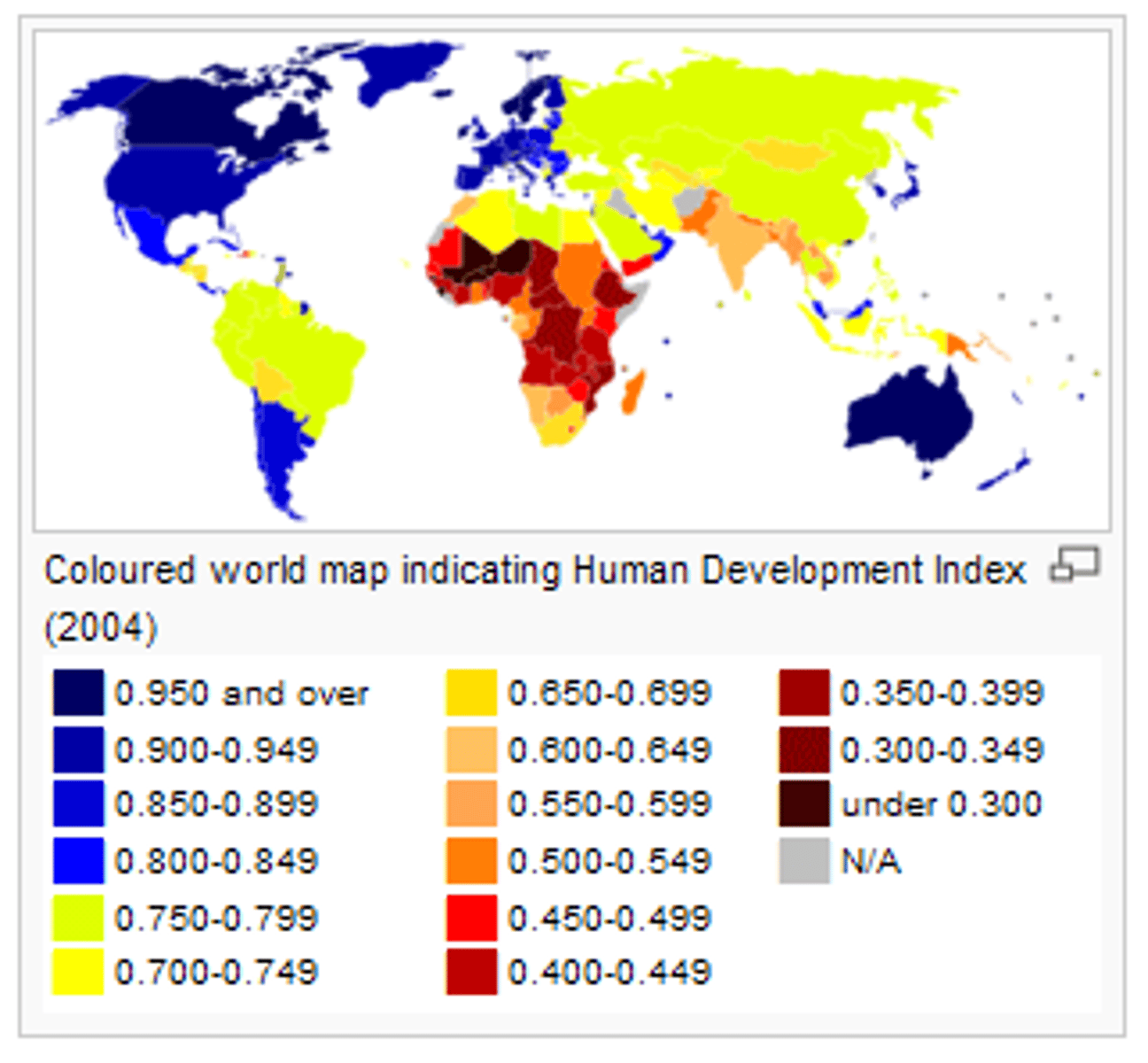
Human Development Index (HDI)
Is a composite statistic of life expectancy, education, and income indices used to rank countries into four tiers of human development.
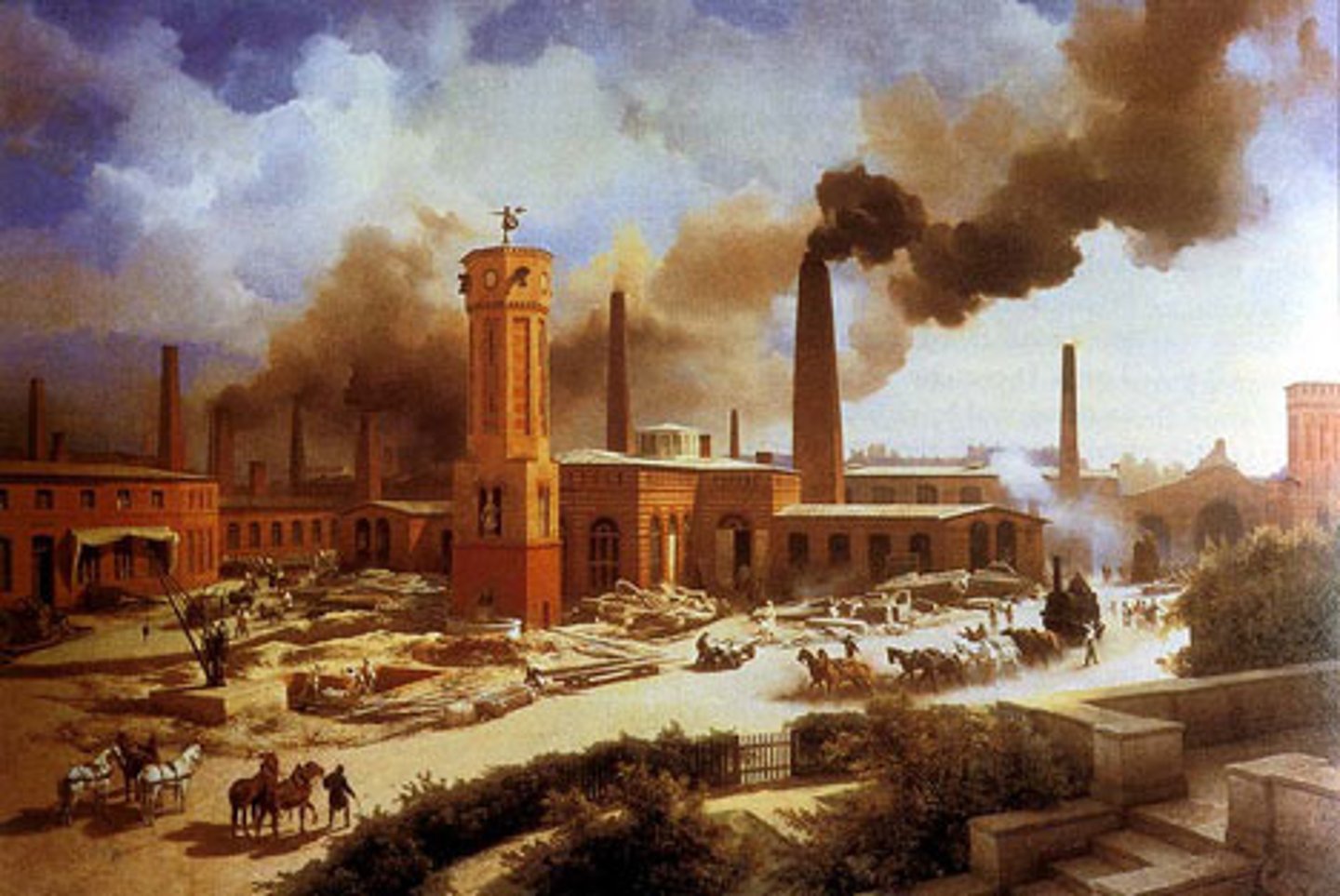
Industrial Revolution
Term for the rapid economic and social changes in agriculture and manufacturing
Followed the introduction of the factory system to the textile industry of England in the end of the 18th century.

Infrastructure
The basic structure of services, installations, and facilities needed to support industrial, agricultural, and other economic development; included are transport and communications, along with water, power, and other public utilities.
Just in Time Production
Seeks to reduce inventories for the production process by purchasing inputs for arrival just in time to use and producing output just in time to sell.
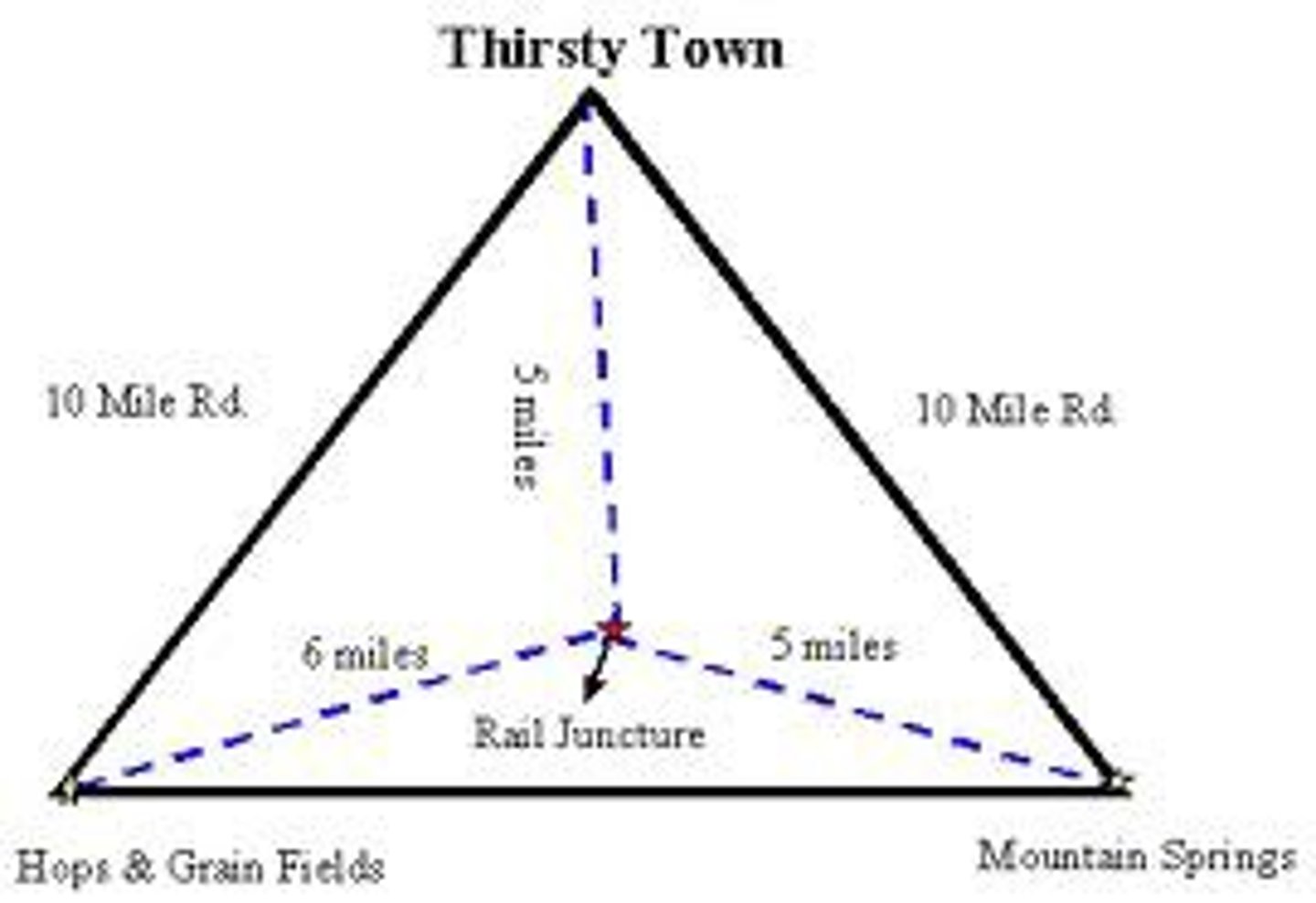
Least cost Theory
The view that the optimum location of a manufacturing establishment is at the place where the costs of transport and labor and advantages of agglomeration or deglomeration are most favorable.
Levels of Development
Levels of the quality of life in a given country. MDC, LDC, NIC. (More developed country, less developed country, newly industrialized country.)
Maquiladora
Factories built by US companies in Mexico near the US border to take advantage of much lower labor costs in Mexico.

Outsourcing
Producing abroad parts or products for domestic use or sale.

Quaternary Activities
Those parts of the economy concerned with research, with the gathering and dissemination of information, and with administration of the other economic activity levels.
Quinary Activities
A sometimes separately recognized subsection of tertiary activity management functions involving highest level decision making in all types of large organizations.
Secondary Activities
Those parts of the economy involved in the processing of raw materials derived from primary activities in altering or combing materials to produce commodities of enhanced utility and value.
Substitution Principle
In industry, the tendency to substitute one fact or production for another in order to achieve optimum plant location.
Tertiary Activities
Those parts of the economy that fulfill the exchange function, that provide market availability of commodities, and that bring together consumers and providers of services.
Third World
A term applied to countries considered not yet fully developed or in a state of underdevelopment in economic and social terms.
Transnational Corporation (TNC)
A large business organization operating in at least two separate national economies; a form of multinational corporation.

Underdevelopment
A level of economic and social achievement below what could be reached given the natural and human resources of an area where necessary capital and technology are available.
World Systems Theory
Theory originated by Immanuel Wallerstein and illuminated by his three-tier structure, proposing that social change in the developing world in inextricably linked to the economic activities of the developed world.
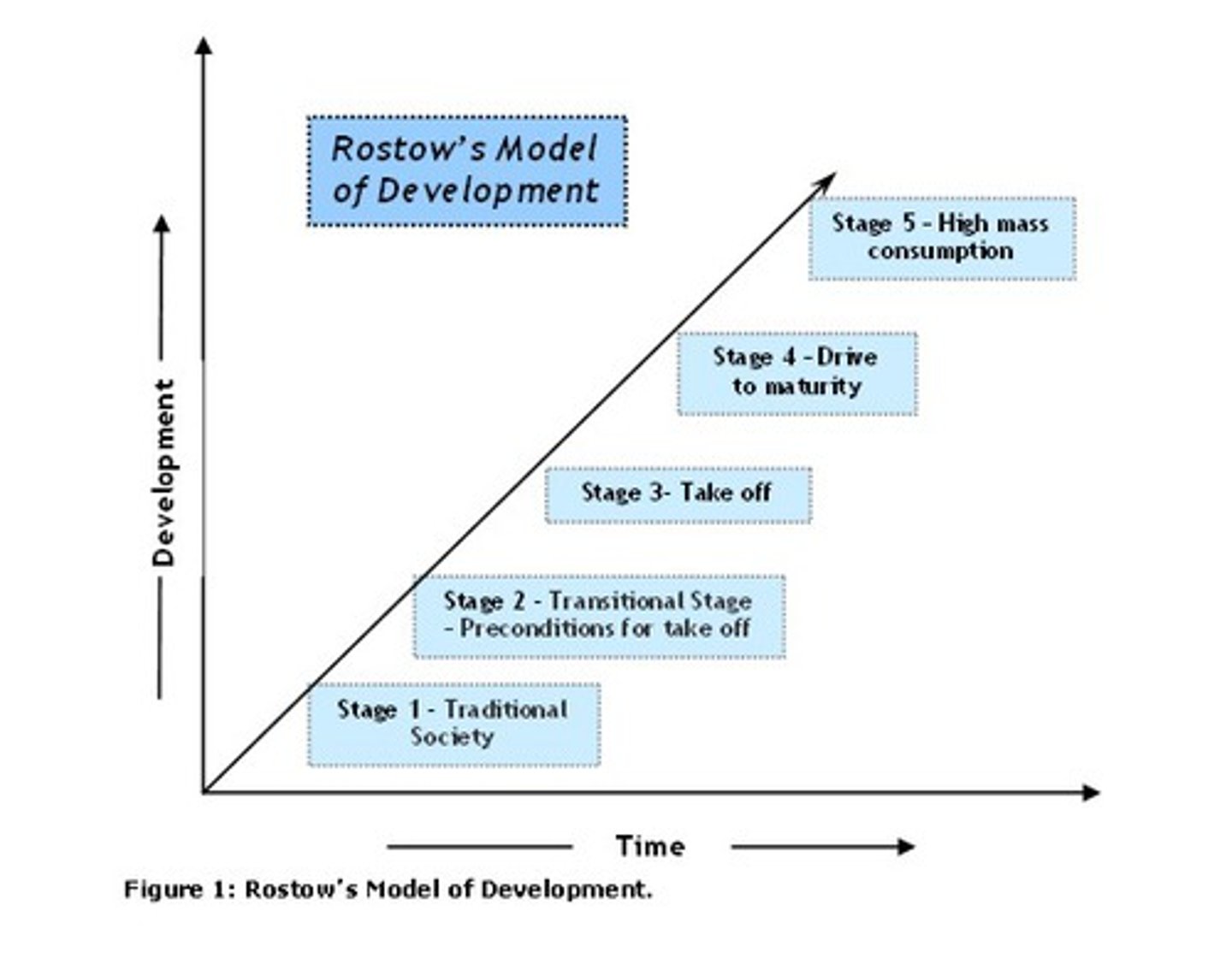
W.W Rostow
American economist who proposed his five stage model of development. 1. Traditional Society 2. Transitional Stage 3. Take off 4. Drive to Maturity 5. High Mass Consumption.
Capitalism
An economic system based on private property and free enterprise.
Raw Materials
Unprocessed natural products used in production
Colonialism/Imperialism
Attempt by one country to establish settlements and to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles in another territory.
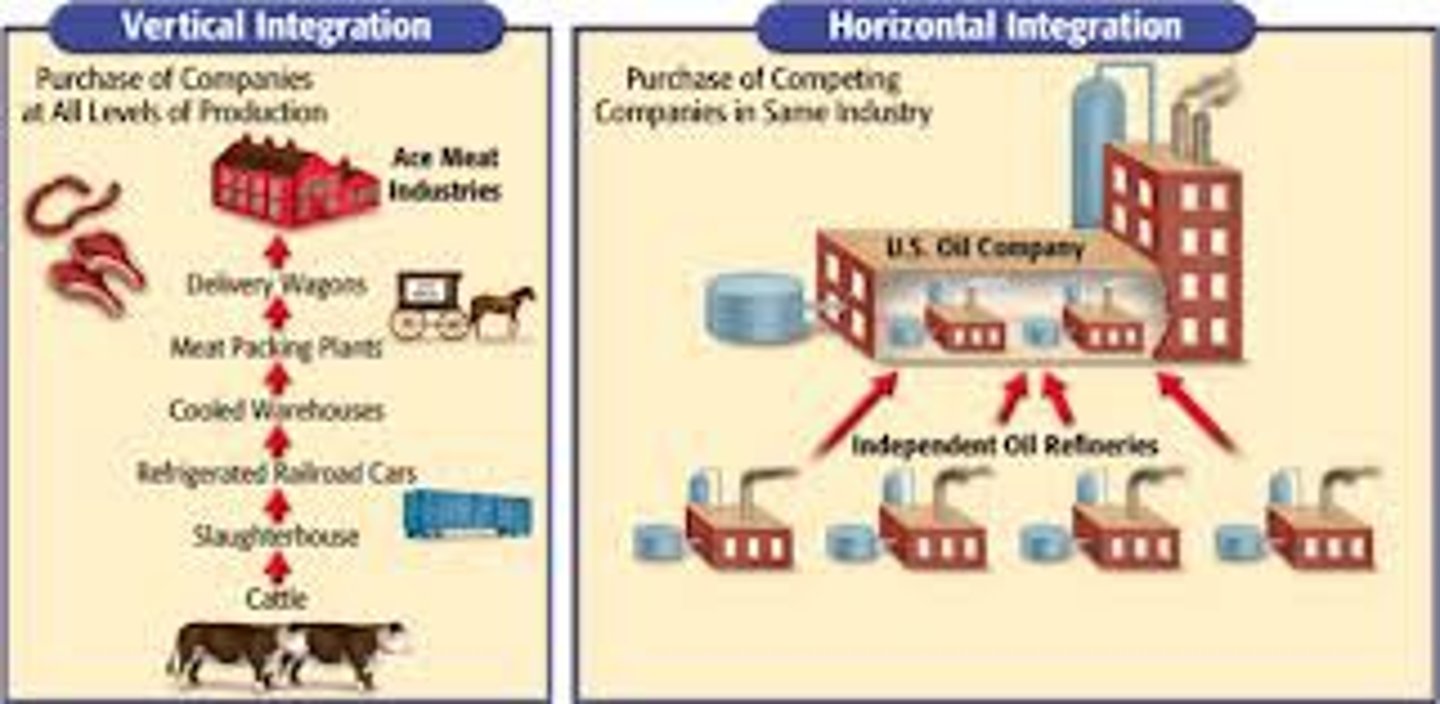
Vertical Integration
Practice where a single entity controls the entire process of a product, from the raw materials to distribution
Factors of Production
Land, labor, and capital; the three groups of resources that are used to make all goods and services
Hinterland
The market area surrounding an urban center, which that urban center serves.
Life Expectancy
A figure indicating how long, on average, a person may be expected to live

Infant Morality Rate
the number of deaths per year of infants less than one year old for every 1000 live births.
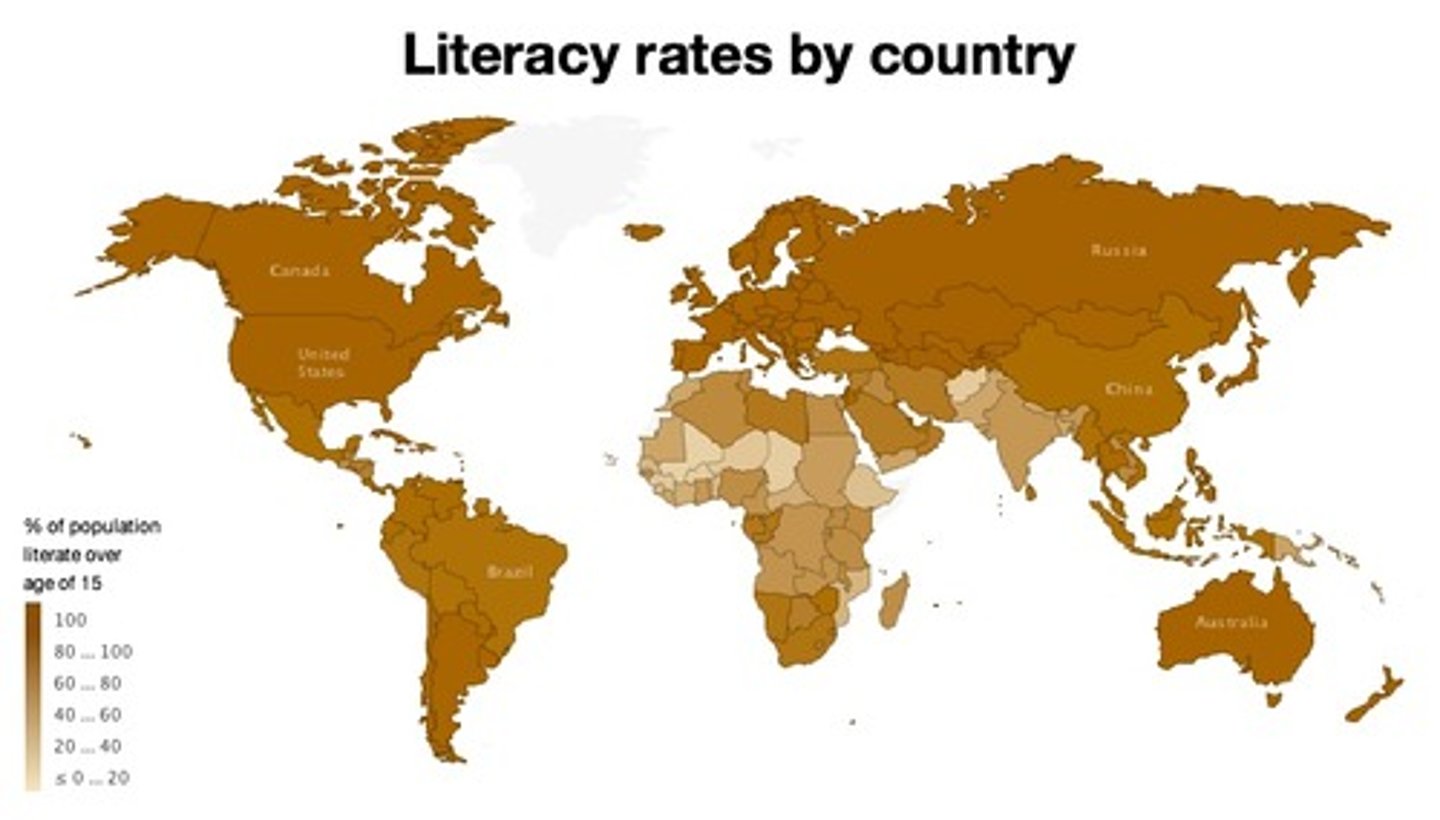
Literacy Rate
The percentage of a country's people who can read and write.
Gender Inequality Index
A United Nations index, introduced in 2010, which measures a country's loss of achievement due to gender inequality, based on reproductive health, employment, and general empowerment.
Microloans
A very small, often short-term loan made to an impoverished entrepreneur, as in an underdeveloped country

Millennium Development Goals
Goals adopted by the Millennium Declaration of 2000, consisting of 18 targets to be achieved by the year 2015.
1) eradicating extreme poverty and hunger,
2) achieving universal primary education,
3) reducing child mortality,
4) and promoting gender equality.

NAFTA
A trade agreement between Canada, the United States and Mexico that encourages free trade between these North American countries.

European Union (EU)
Europe's trading bloc free trade amount the members of the union. As well as a single European currency the euro and a central bank.
Recession
A slowdown in economic activity over a period of time.
All of the following things decline: Gross Domestic Product (GDP), employment, investment spending, capacity utilization, household incomes, business profits and inflation. Meanwhile bankruptcies and the unemployment rate rise.
Right to Work
Refers to statutes that prohibit unions from making union membership a condition of employment.

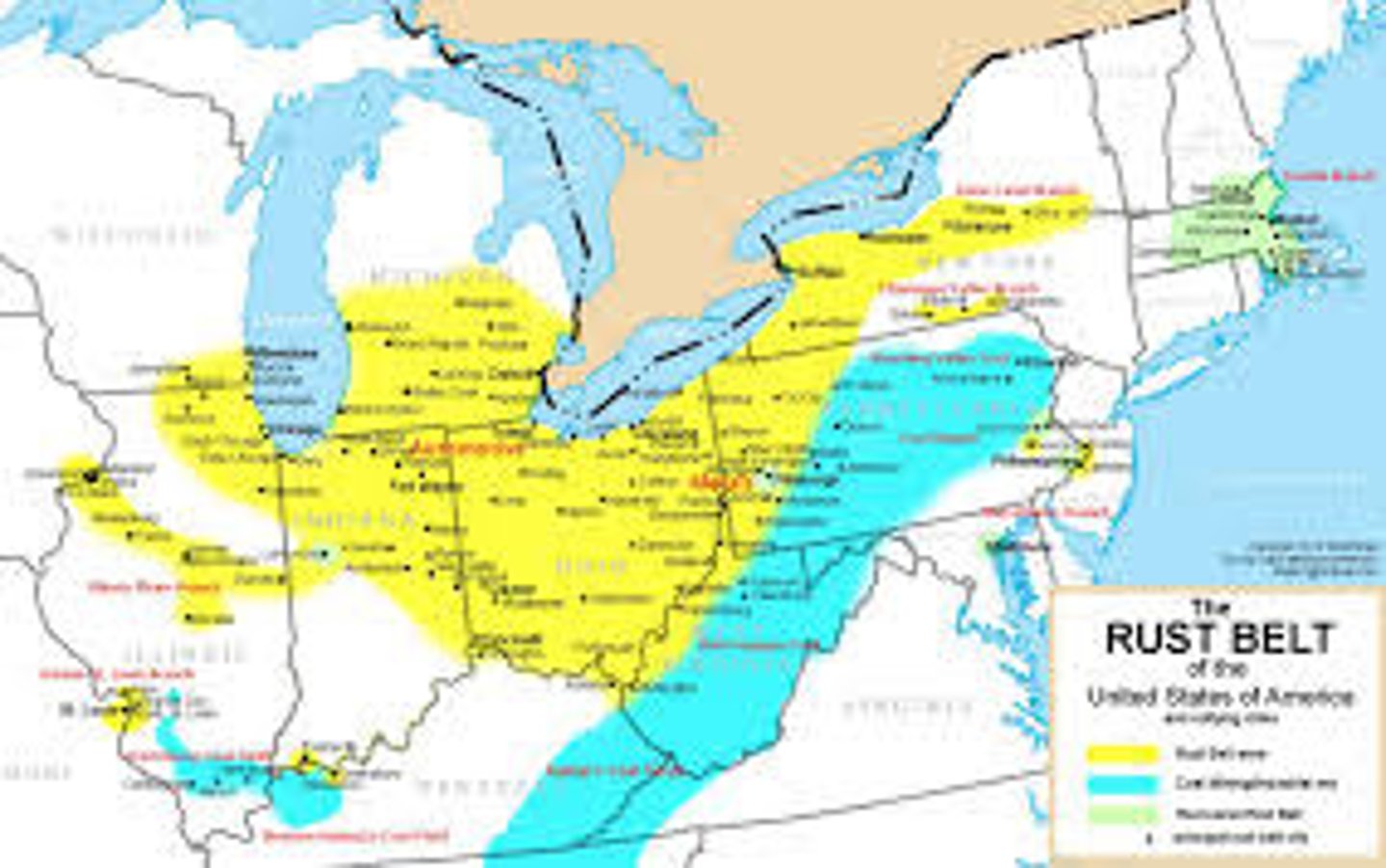
Rust Belt
The northern industrial states of the United States, including Ohio, Michigan, and Pennsylvania, in which heavy industry was once the dominant economic activity. These states lost much of their economic base to economically attractive regions of the United States and to countries where labor was cheaper, leaving old machinery to rust in the moist northern climate.
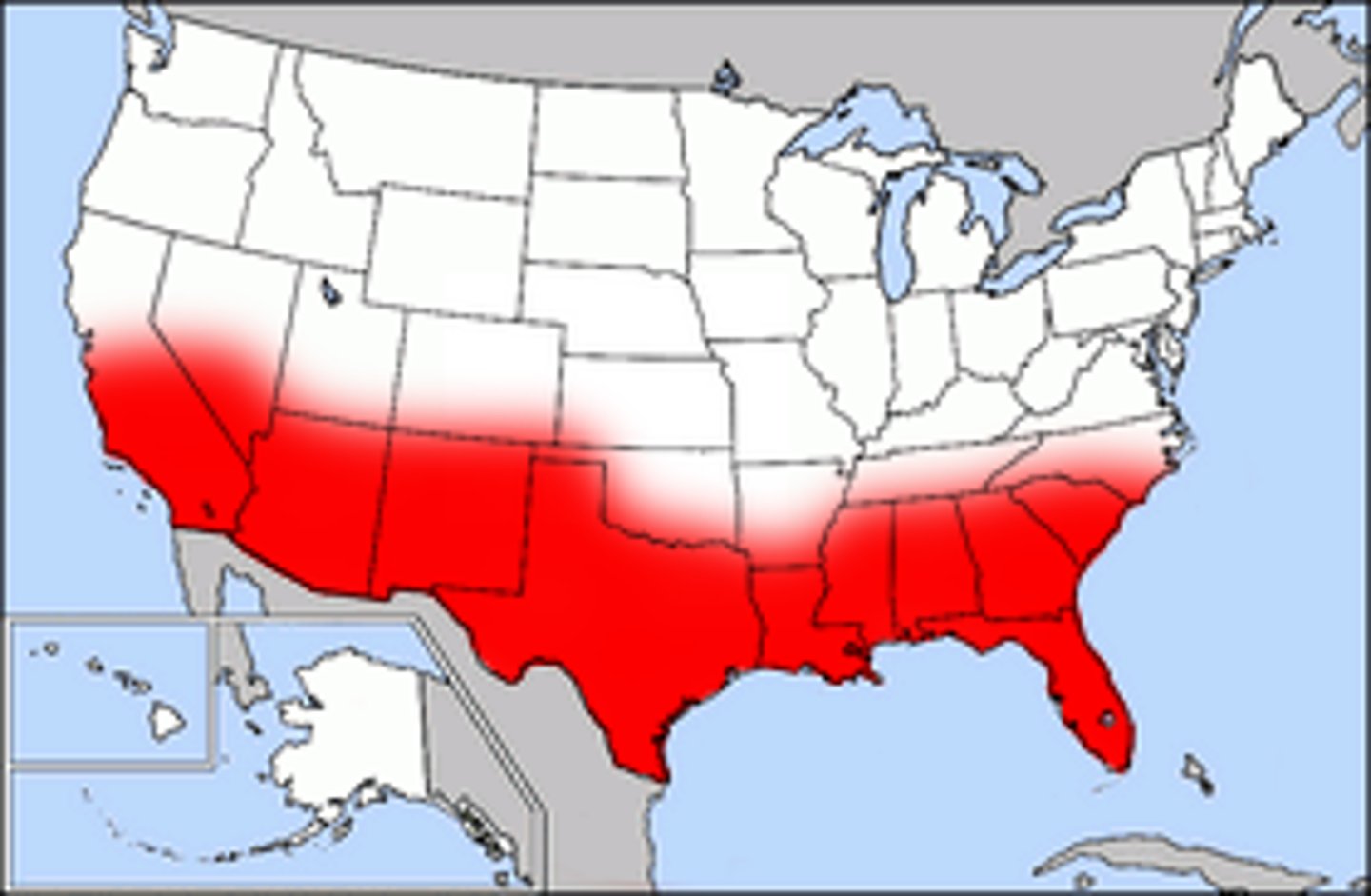
Sun Belt
U.S. region, mostly comprised of southeastern and southwestern states, which has grown most dramatically since World War II.
International Division of Labor
A division of work between rich and poor countries under which low-waged workers in the global South do assembly, manufacturing, and office work on contract to companies based in the global North.
Asian Tigers
South Korea, Singapore, Taiwan, and the then-British colony of Hong Kong: first countries to adopt the international trade alternative
IMF
International Monetary Fund//a United Nations agency to promote trade by increasing the exchange stability of the major currencies
World Bank
A specialized agency of the United Nations that makes loans to countries for economic development, trade promotion, and debt consolidation.
Its formal name is the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development.

Self-Sufficiency Model
Model encourages countries to isolate fledgling businesses from competition of large international corporations. Example--India.
Sustainable Development
Development at a rate that can be maintained and not overdeplete resources
Greenhouse Effect
Atmosphere traps some of the sun's rays
Global Warming
rising average global temperature
Commodity Chain
links materials, production, and distribution
nonrenewable resources
minerals, fossil fuels
renewable resources
solar, wind, tidal, geothermal
economies of scale
increase in the number of units produced to reduce per-unit cost
Hotellings Model
businesses located right next to each other to cut into market share (gas stations at same exit)
informal sector
business not reported to government and not calculated in GDP
Brandt Line
line on world map dividing MDCs and LDCs
structural adjustments
changes a country must make if it does not pay back development loans
closed economic state
countries, often communist, that are not open to foreign investment and limit imports
privatization
government sells industry to private corporations
nationalization
government owns major industries in a country
NGOs - Non-government Organizations
non-profit organizations like Doctors Without Borders
NIC - Newly Industrialized Country
recent and rapid development to where a country can no longer be classified a LDC
Fair Trade
producers in LDCs are compensated to a level that they can support livelihood