SAM Neuro - Exam 2
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Localization of the nero system
Intracranial
Forebrain, brainstem, cerebellum
Spinal cord
C1-5, C6-T2, T3-L3, L4-S1
PNS
Somatic nerve, muscle, NMJ, autonomic nerve,
Enteric nerve
Mentation/behavior
Brainstem dx: Information processing
LOA, dull, coma
Use ascending reticular activating system (ARAS)
level of awareness
Foerbrain dx:
Confusion, disorientation, loss of learned behavior, compulsive behaviors
Ex: accidents in the house
Gait
slowly, strait, turns, fatigue, free, joint flexion or extension
Plegia: absent gait generation
Paresis: weakness, min gait generation
LMN: maintains tone, short stride, toe scuffing
UMN: gait generation, slower protraction and longer stride, ataxia
Ataxia: without order, long stride and has unpredictable foot placement
Cerebellar: hypermetric, head tilt/listing/falling, Slow nystagmus (<60 per min), sm circles, rolling, side stepping, head down, rate/range motion change
Cerebrum: Lg circles, contralateral sign, perception issues
ipsilateral forebrain localization
forebrain dose not influence gait
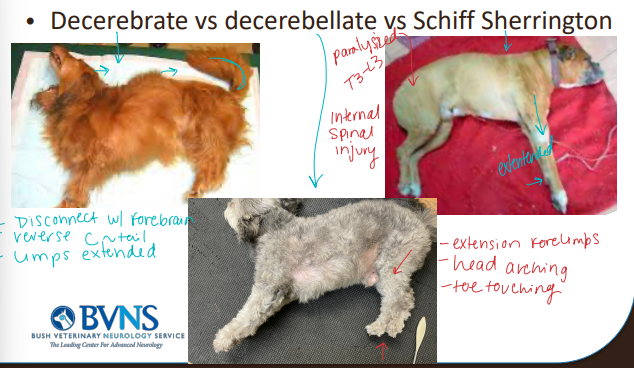
Posture
Postural Reactions: test 2x, support, do all limbs
Paw position, hopping, bracing
Muscle tone: symmetry
focal loss in 8d from nerve dx
Cranial tibial from L7-S1 disk/stenosis
Decerebrate: head up, legs strait down
Decerebellate: downward dog posture
Schiff Sherrington: extended front limbs
T3-L3
Reflex testing
Done standing or lateral
Pelvic Limb: patellar, cranial tibial, calcaneal or gastrocnemius, and withdrawal
Thoracic Limb: biceps, extensor carpi, triceps and withdrawal
Cutaneous trunci
key for localization
Perineal
Withdrawal in reflex testing
LMN stimuli to withdrawal limb
continued emotional rxn post stimuli = deep pain
Squeeze toes and watch
Which joints flex? Is it complete? does the animal kick?
Crossed extensor in lateral = UMN
LMN signs
Weakness, decreased tone, decreased reflexes
withdrawal
Short stride, ±proprioceptive deficit, toe scuffing
Slow to rise/slow to sit, dribble urine or drop stool
L7-S1
UMN Signs
Descending Tract Failure
Weakness, Increased reflex, long stride, Increased tone
Ascending Tract Failure
Proprioceptive ataxia, Postural deficit
Peripheral neuropathy/myopathy
LMN signs
Short stride, weakness, good proprioception
Frequently normal cranial nerves??
Systemic signs
WBC, temperature, malaise
Cranial Nerves
CN II: menace, tracking, obstacle course, PLR
CN III: PLR, head movement, Strabismus
CN IV: head movement, Strabismus
CN V: facial sensation/tone
CN VI: head movement, Strabismus
CN VII: facial sensation/tone
CN VIII: head movement, Strabismus
CN IX: gag reflex, resp sounds, tounge
CN X: gag reflex, resp sounds, tounge
CN XI: gag reflex, resp sounds, tounge
CN XII: gag reflex, resp sounds, tounge
Mence response
CN II
dev @ 12-16w
Forebrain dx - when deficits
Contralateral to the lesion most common
Ipsilateral if its cerebellar (rare)
Abnormal PLR and menace = Rostral to the diencephalon
Normal PLR but abnormal menace: Caudal to the diencephalon
Horner’s Syndrome
MOA: Long pathway within the CNS and periphery
Brain, cervical, thoracic, and middle ear disease
Consider both CNS and systemic diseases
can be partial or complete
CS: Miosis, Ptosis, Nictitans protrusion, Enophthalmos, Sweating (horse)
DDX: parasympathetic dx
2 branches in cat and 5 in dog
weird pupils (D in cats)
Retention/Storage of urine
Pontine storage to hypogastric nerve (T10-11) detrusor and trigone
Pudendal nerve to external urethral and anal sphincter
Voluntary control regulated by the forebrain
Cerebellar inhibition of urination
Dysfunction in different parts of the brain
Forebrain
Seizures, near normal gait, compulsive behaviours, inappropriate urination
Lg circles to lesion, contralateral sensory deficits
Brainstem
Altered gait, altered LOA, proprioception
Cerebellum
Intention tremor, postural reaction issues,
hypermetric gait, wide stance, normal strength
Vestibular
• Central: gait and proprioceptive issues - horners
• Peripheral: normal tone, proprioception, nystagmus opp lesion, head tilt, rolling to lesion
Paradoxical: the head tilt is opposite the postural deficit
Disfunction in different parts of the spine
C1-5: Long stride and ataxia, proprioceptive deficits, weakness, increased tone and reflexes to all four limbs
C6-T2: Short stride(LMN), decreased reflexes, withdrawal changes and tone in front, long stride(UMN) with ataxia, increased tone and reflexes in hind, proprioceptive deficits, in all four
T3-L3: Normal front, long stride with ataxia in hind, proprioceptive deficits, altered tone, and reflexes, cutaneous trunci changes, bladder control(UMN).
L4-S1: Normal front, short stride in hind, flopping of the distal limb, altered withdrawal, decreased reflexes and tone, slow to rise/sit, tail drop, incountenance (LMN)
Seizure-like Episodes
Cataplexy, narcolepsy, REM sleep disorder
Vestibular episodes
Panic attack
Episodes of neuromuscular disease or encephalitis
Myoclonus(twitching)
Syncope (fainting)
Cervical muscle spasm
Head bobbing & breed associated muscle disorders(bulldogs,danes)
Seizure terms
Seizure: a sudden attack or convulsion
Status epilepticus: a persistent seizure >5 min, lowers lifespan
Cluster seizures: >1 in 24hrs, lowers lifespan
Non-convulsant seizure: sensorium only, lowers lifespan, common w/ clusters, ECG req
Refractory seizure: multi tx fail
Super-refractory: ER tx fail and meds
Seizure causes
NT changes: High excitatory NT or Low inhibitory NT
Young (<1y): infectious, anomalous, metabolic, trauma, toxin
1-5y: idiopathic
>5y: neoplasia, infarct, inflam, metabolic, infection
Refractory seizure cases
MOA:
multi tx fail
Aussie, colie, Italian Spinoni
Tx:
Be aggressive >2 anticonvulsants
Rescue and emerg plan
Set expectations
6m monitoring & CBC
General treatment of seizure cases
Goal: <1seziure every 3m
Establish:
emerg, monitoring, tracking plan
maintenance, post episode tx
Consider:
Who, what, where, when, why?
Postictal phase behaviour (recovery)
takes 5 ½ lifes to reach steady state w/ meds
Phenobarbital
Use: anticonvulsant
q12h
MOA: Ca/Na channel, Gaba
Monitor:
Liver, Bone Marrow, Skin, Endocrine toxic
BW 2w after changes then 6m
high metab of T4 and P450
Loading: 16-30 mg over 24hrs in 1-6 doses
Keppra
Use: anticonvulsant
DEA not req
MOA: Ca channel, NT release
Loading: 60-100mg/kg IV - bolus
Potassium Bromide
Use: anticonvulsant - salt
not in cats: pneumonia
MOA:
Membrane stabilization/hyperpolarization
24hrs ½ life
Monitor: Pancreatitis, Esophagitis
3m after changes then yearly
high Cl
Loading: 400-600mg/kg over 5d
1/2 dose q12 to avoid nausea
Zonisamide
Use: anticonvulsant
MOA: Na channel
Monitor: idiosyncratic/acidosis
Emergency and rescue plan
Home
Repeat maintenance meds 1-3x
New med w/ short half life for 1-3d
Diazepam/midazolam: IN 80% or rectal 60%
ER/Clinic
Hospitalization after >3 till 24hrs clear
Supportive care
Load meds or new meds
Diagnostics, MRI, EEG
Benzo
AKA: Diazepam/Midazolam
Use: active seizures
Nasal: 3-6 mins - most common, carful biting
Rectal: 10-14 mins - needs cath and safer for client
MOA: Gaba
Action of 15-30min
Tolerance 1-2w (regular use)
Ketamine
Use: Refractory Status Epilepticus
no rxn w/ benzos
MOA: NMDA
Steps:
see EEG w/ active seizure
give w/ Propofol to stop movement
give ket IV then CRI
super-refractory epilepsy treatment
Meds:
Ketamine-Dexdomitor
Other:
Induce hypothermia (36.7-37.7)
Indications:
no rxn to benzos
Propofol to stop movement
continues seizure
Ket/dex
Stages of Feline seizures
Prodromal: behavior/personality change - very common
Aura: sensory type change/anticipation
Ictus: seizure phase
Post-ictal: persistent deficits min-days
High ALP/ALT, ataxia, aggression, disoriented, vison loss

Feline seizure causes
Neoplasia: meningioma #1
cats see changes in behaviour **
dogs have seizures
FIP: ventriculitis & diffuse inctercranial/spinal signs, high protien fluid
Ischemic encephalopathy FIE: Parasite migration through the brain, variable forebrain signs, sneezing
Stroke: renal, endocrinopathies, hypertension, systemic disease
Idiopathic: bimodal, normal neuro exam, 9-12y cats
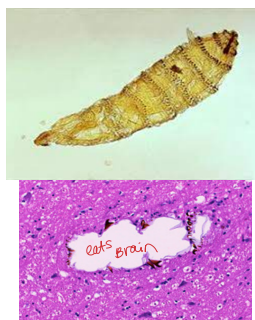
Seizures maintenance in cats
Leviteracitam, Zonisamide, Phenobarbital, Topomax
NO KBr: pneumonia (fatal)
Refractory epilepsy
Failing two medications used to maximal effect
Super-refractory SE (life threatening) not
responsive to first line ER treatments
Cluster/SE/NCSE: Decreased lifespan
SE/NCSE common in cluster pt and refractory
NCSE (Non-Convulsive Status Epilepticus), NCS (Non-Convulsive Seizure)
More common with cluster seizures
Minimal to no evidence of seizure
EEG required for diagnosis
CS: Does not look like seizure, more dull, ataxic
Treating disk disease
NSAIDS: better QOL score & recovery
Sx: best tx, timeline does not impact has recovery or success
Acupuncture: faster recovery
Physical therapy: better recovery
Glucocorticoids: contradicted
Methylprednisolone: no benefit, reduces bld flow & PMN’s
Cage rest: no benefit
Evaluating disk disease prognosis
Moderate reoccurrence for rx and low for sx
Higher grade worse rx prognosis, sx indicated
Thoracolumbar
Paraplegia/deep pain negative: poor rx, moderate sx
Paraplegia/deep pain positive: moderate rx, good sx
Non-ambulatory paraparesis: moderate rx, good sx
Ambulatory paraparesis: moderate rx, good sx
Paraspinal hyperasthesia: good rx, good sx
Cervical
Grade I-III: moderate rx, good sx
Grade IV-V: low sx, moderate sx
Testing for disk disease
Deep pain negative: eval w/ MRI
Evalute breed, focality, progressiveness
Myomalasia: diaphragm innervation issues, risk w/ acute
C6-7 keep u from heaven, C5-4 keeps you from the door (diaphragm)
DDX: Fibrocartilagenous emboli, Acute non-compressive nucleus pulposus extrusion, cancer, metabolic dx, malformations
Hydrocephalus
MOA: Active distention of ventricular system obstruction flow
breed mesencephalic stenosis, acquired
Stenosis of the mesencephalic aqueduct most common
CS: High ICP, white matter pressure, cortical atrophy, dome head, altered behavior, seizures, stupid, ataxia, circling(big), blindness, soft spots
ID:
Congenital: MRI, CT, US
Acquired: MRI, CSF
Tx: Life long pred & Omeprazole, ventriculoperitoneal shunt sx, ventriculostomy sx
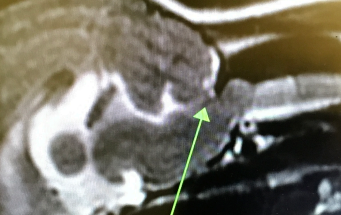
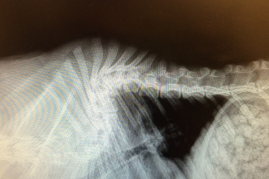
Atlanto-occipital AO or Atlanto-axial junction AA malformations
MOA:
AO: overlap, concussive, medulla compression
C1 tips foward
AA luxation: cranial/cervical spine concussion
C2 tips backwards
CS: paresis(more aute), plegia(unilateral to bilateral), vestibular signs(mild)
ID: CT, MRI, C2 rads (AA)
Tx: sx stabalization, braces (1” rolled gauze “dough nuts” in emerg)
Avoid ventroflexion
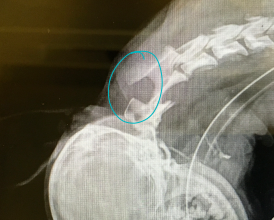
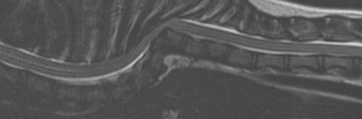
Caudal occipital junction malformations COMS
MOA: overcrowding of fossa, poor fluid dynamics, herniation, cerebellum/medulla compression
CS: hyperesthesia, phantom scratching, ataxia, vestibular signs, paresis, vocalization, face rubbing, seizures
ID: CT, MRI
Tx: Long term, NSAID, Steroid, gabapentin/lyrica, omeprazole, sx w/ short term success but reoccurs
Recurrences due to scar tissue 40-60%
Vertebral malformation
L7-S1 mosy common
MOA: segment failure or trama
transition, butterfly, block, wedge, hypoplasia (pugs/frenchies), hemivertebra
Scoliosis, lordosis, kyphosis: brachiocephalic breeds
young T3-L3 myelopathy or old w/ multi disk injuries
CS: paraspinal discomfort, paresis, plegia, incontinence, ataxia
UMN signs
ID: MRI, rads
Tx: NSAID, gabapentin, sx stabilization
gliosis/atrophy of spinal cord = guarded the prognosis,
Facet hypoplasia: Recurrent concussive injury leading to scar tissue w/in spinal cord (pugs, frenchies)
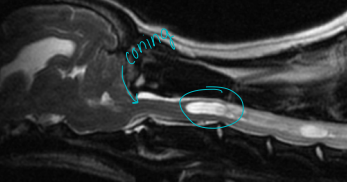
Arachnoid diverticula
MOA: unknown
Dilation of the arachnid space in caudal cervical/thoracolumbar spine
Brachycephalic, Rottie
Tx: decompressive/stabilizing sx
Localizing spinal cord/myelopathies based on CS
C1-2
UMN: all limbs and bladder
C6-T2:
UMN: hind limb and bladder
LMN: front limb
T3-L3
UMN: hind limb and bladder
L4-S1:
LMN: hind limb and bladder
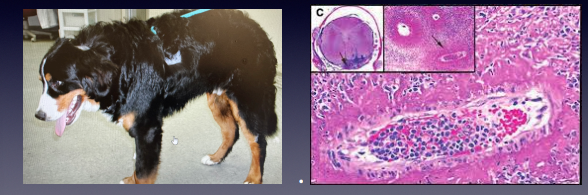
Steroid responsive meningitis arteritis SRMA
MOA: 6m-2y Beagle, Berner, Boxer
CS: low head, stiff, random vocalizing , choppy steps, walking on egg shells
Neutrophilia/IgA elevation
ID: Febrile 103-105, neutrophilia, high IGA, CSF ±MRI
Tx: Steroids, cyclosporine - 6-8m back to normal
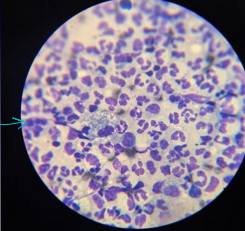
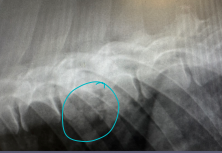
Discospondylitis
MOA: Infection of the disk/endplate
lg dogs
CS: ±Pain w/ empyema/disk extrusion
ID: difficult: rad(30%), MRI, CRP, culture(rule out), urine analysis(rule out), brucella(intact males)
Tx: C&S antibiotics (6-12m), analgesic,
euth w/ brucella
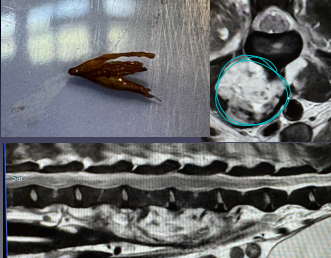
Infection/empyema of the spine
MOA: Grass awn from resp into L4 @ diaphragm
CS: Cough (weeks to months prior), pain ± lumbar myelopathy
Tx: Sx, long term antibiotics

Tetanus
MOA: 1-3w post wound or sx (AI or spay)
Travels retrograde to block interneuron
CS: rhesus sardonus, extensor rigidity, light/sound hypersensitivity, saw horse stance, lock jaw
Tx: antibiotics, clean, antitoxin, high mortality
Degenerative Myelopathy DM
>8yr start to show signs
MOA: Progressive degeneration SOD 1 mutation
GSD, Boxer, Corgi (still RARE
CS: Non painful, Ataxia
similar to T3-L3 myelopathy
ID: genetic screening (purple top MSU/OFA)
neg, carrier, affected
Tx: fucked, PT, 6-18m till euth

Trigeminal neuritis
CS: Drop jaw/bilateral
idiopathic 3-6 weeks
Tx: assist feed, 6w to fix
Infectious neuropathy
Neospora positive
Protozoal infection, young dogs
Focal granuloma
Cerebellum, spinal cord, nerve or
muscle
Do not always see eosinophils
TX: clinda, TMS
Polyradiculoneuritis
AKA: Coonhound paralysis
pelvic limbs
MOA: Rapid porgression
CS: LMN signs w/ intact sensation, Rapid atrophy 8d #1, normal cranial nerves
Tx: 4-6w recovery, can relapse, spontaneous
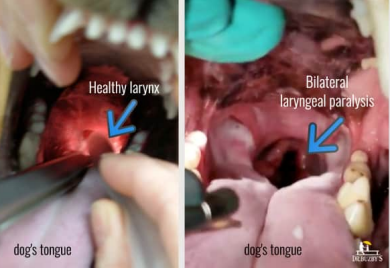
Laryngeal paralysis
degenerative dz, trauma, thyroid, cancer
MOA: Vibration of larynx causes voice and breathing changes
think horses
CS: Roaring, heat/exercise intolerance
Tx: Tie-back

Horner’s
Miosis (constriction)
Ptosis (eye lid drooping)
Nictitans protrusion (3rd eye lid)
Enophthalmos (eye dispplacment)
Sweating (horse)
Rule out causes
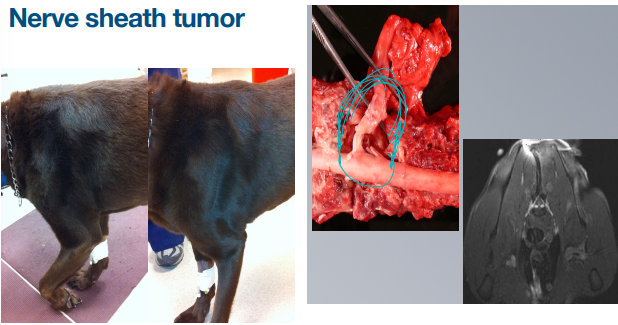
Nerve sheath tumor
MOA: Trigeminal, brachial plexus, pelvic plexus
CS: focal rapid atrophy, progressive lameness
ID: may be able to palpate, US
DDX: mononeuropathy
Mononeuropathy
Spinal cord invasion
Tonic UMN reflexes (brisk)
Other limbs
Cutaneous trunci
Horner’s (same side)

Endocrinopathies
CS: Classic Cushing’s signs, stiff stilted gait
Tx: Do not recover motor function

Immune myopathies (MMM)
MOA: location dependent, Immune attack on musle/NMJ
Masticatory muscle myositis embryo distinct
CS: swelling, pain, progresses atrophy, fibrosis - Bilateral
ocular myositis: eye bulge
Junctionopathy: aspiration
ID: AB titer(make dx), biopsy, eosinophils, high CK/CPK/AST
Poly myositis is tricky, takes weeks to dx
diffuse immune attack on muscles
Tx: Immune suppress (steroids)
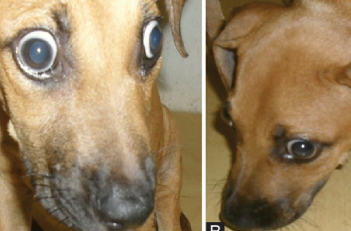
Myasthenia Gravis
MOA: acquired or congenital, thymoma
CS: Exercise intolerance, fatiguable palpebral, megaesophagus: aspiration pneumonia, regurge, sits
Tx: Tensilon, pyridostigmine, mass remvoal sx
test for monoclonal antibody
Forebrain signs
Behavior/personality changes
Loss of learned behavior
Seizures
Menace deficits
Altered sensation/proprioception
Large circles to the lesion
Cerebellum signs
Altered balance
Hypermetria
Titubation/truncal sway
Menace/PLR changes
Anxious/normal mentation
Small circles/falling/rolling
Nystagmus (slow) less then 60 bpm
Brainstem signs
LOA changes/obtunded to coma
Cranial nerve deficits; 3-12
Paresis to plegia
Small circles
Side stepping
When evaluation: Repeat frequently, patient requires
hydration
Spinal cord
Normal mentation/awareness
Paresis to plegia - tetra vs hemi
??vestibular signs??
??Horner’s??
??Breathing??
??Urination??
Dealing with Head trauma
ID:
Breathing patterns, Postures, Diaphragm, forebrain CS
Brainstem evaluation: LOA, UMN function, reflexes
Score of 1-6 for each, total >8 = 50% survival @ 48hrs
Cushing’s reflex: high ICP, low CBF, high CO2
life threatening
Tx: replace fluids, NSAIDS, fentanyl, benzodiazepines, ketamine, dexmetatomidine, propofol, anticonvulsant medications
Short acting reversible drugs
High ICP
MOA: Cushing’s reflex
high ICP, low CBF, slow HR, high CO2
life threatening brainstem issue
CS: Slow HR (<60), high BP (>150), brain stem CS
Tx: incline to 30o, lower metab (barbiturate/sedation), anticonvulsants (Keppra/phenobarbital), electrolytes (Mannitol/hypertonic saline)
Hyperosmolars
Mannitol: sugar, osmotic diuretic, decrease CSF production, draws extracellular fluid into vessels, rheologic/improve cerebral blood flow
Hypertonic saline: Salt, osmotic diuretic, draws extracellular fluid into vessels, improved cerebral blood flow, less diuretic effect
Monitoring: dehydration, electrolyte concentration
Contradictions: not for intracranial hemorrhage
Meningoencephalitis
MOA: inflam of brain/meninges
Sm dogs: pug, korkie, Maltese
CS: rapid progression (3-7d), status epileptics, blindness
Diffuse or multi-focal most common -
mentation, balance, gait changes +/-
seizure
DDX: peripheral vestibular disease
loss of balance, side stepping
Caudal Fossa
Wet dog shake
MOA: immune CNS dx
bacterial - otitis #2 (cats), fungi, viral, Tick borne (vasculitis, thrombocytopenia), cuterebra
forebrain/brain stem issue
CS: balance loss, side stepping, peripheral vestibular dx, forebrain, occular only
ID: MRI, CSF, Myringotomy
Peripheral vestibular dx
Nystagmus greater than 60bpm (fast)
Head tilt
Falling/rolling
Normal proprioception, mentation
Cranial nerve 7 dysfunction, maybe horners
Myringotomy
Via Otoscope/endoscope w/ tom cat catheter
Puncture TM
Culture material beyond TM
Otitis
ID: Culture canal or myringotomy
Tx:
Antibiotic/fungal, topical if tympanum is intact
Media/interna will require long tx (7m)
Sx VBO or TECA
Meningitis
ID: MRI, CSF(rule out)
Tx: Immune suppress (steroids, cyclosporine), initial tx chemotherapeutics
long tx 12m-18m
recheck xray/MRI b4 stopping meds