Lab Practical #2
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
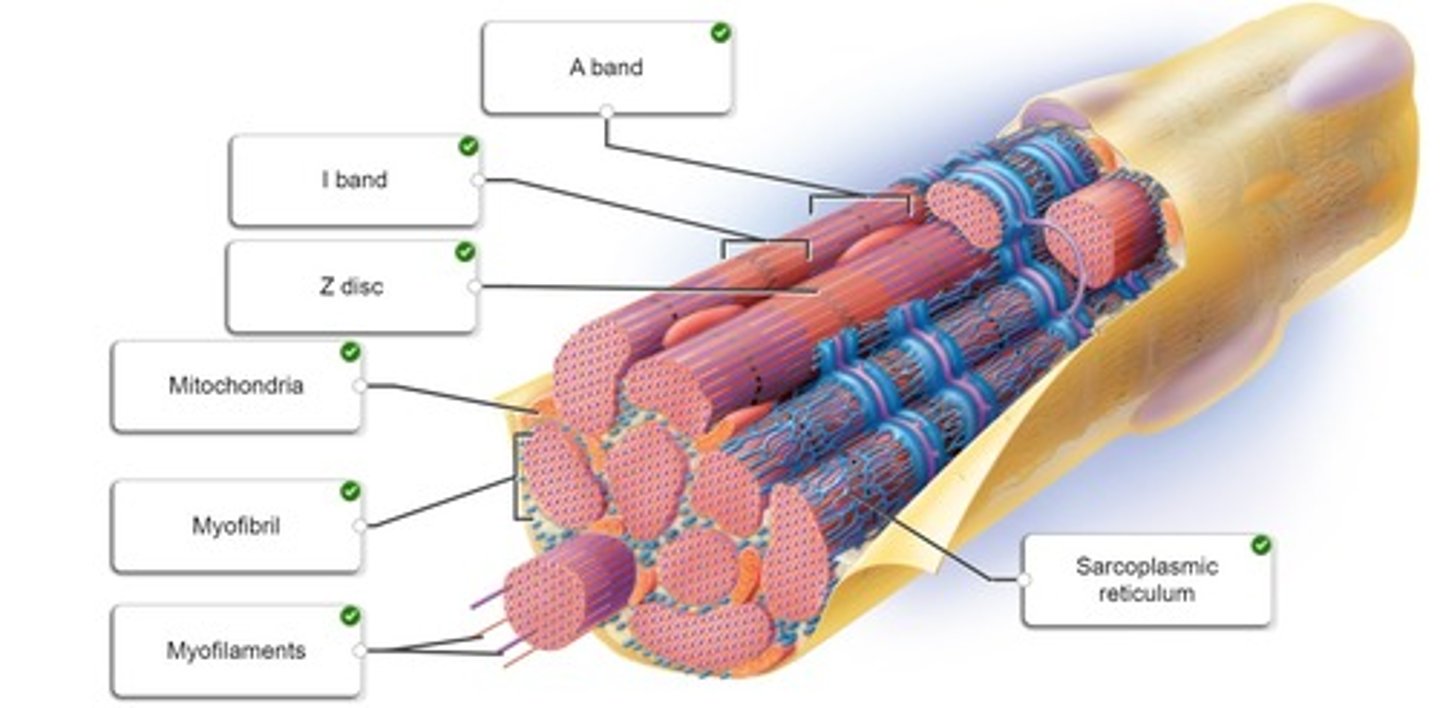
Correctly label the following parts of a skeletal muscle fiber
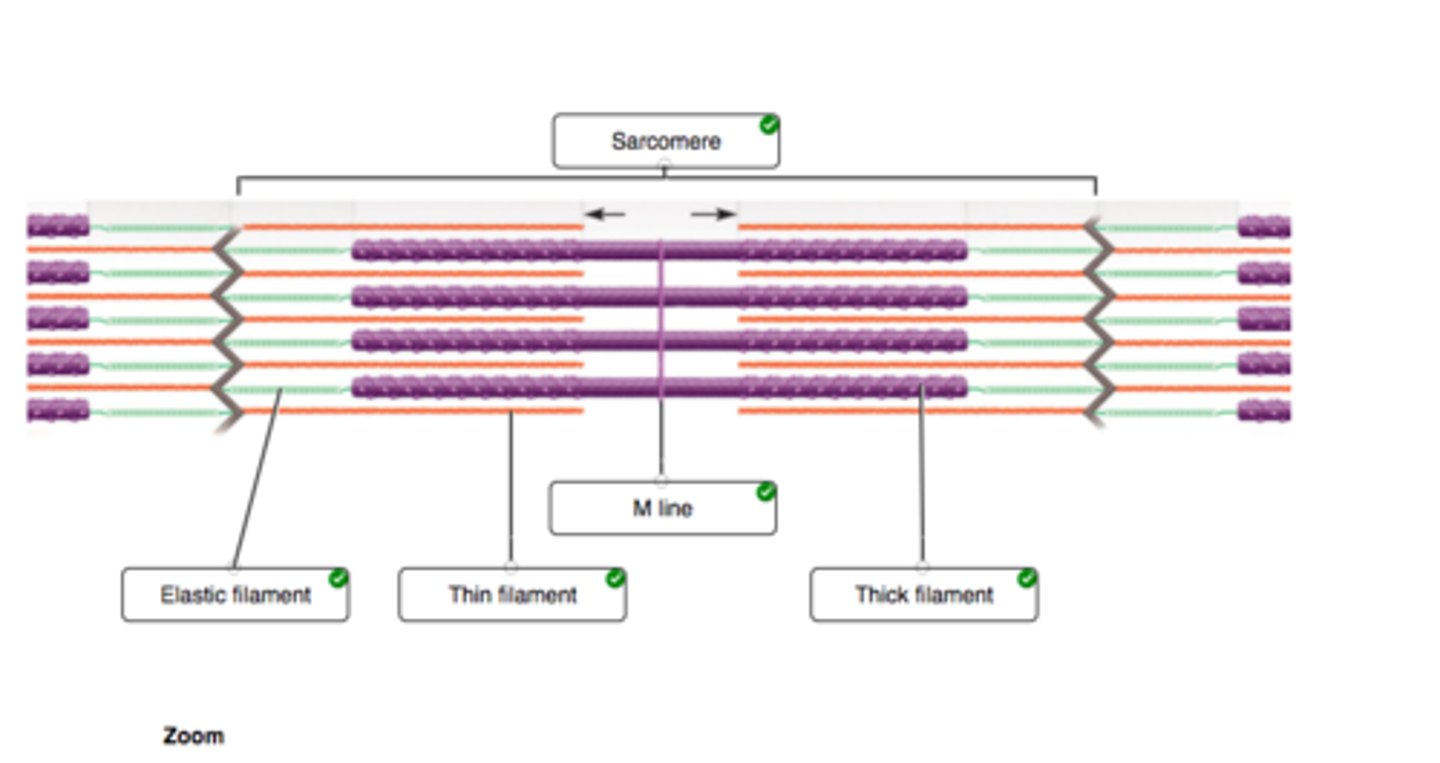
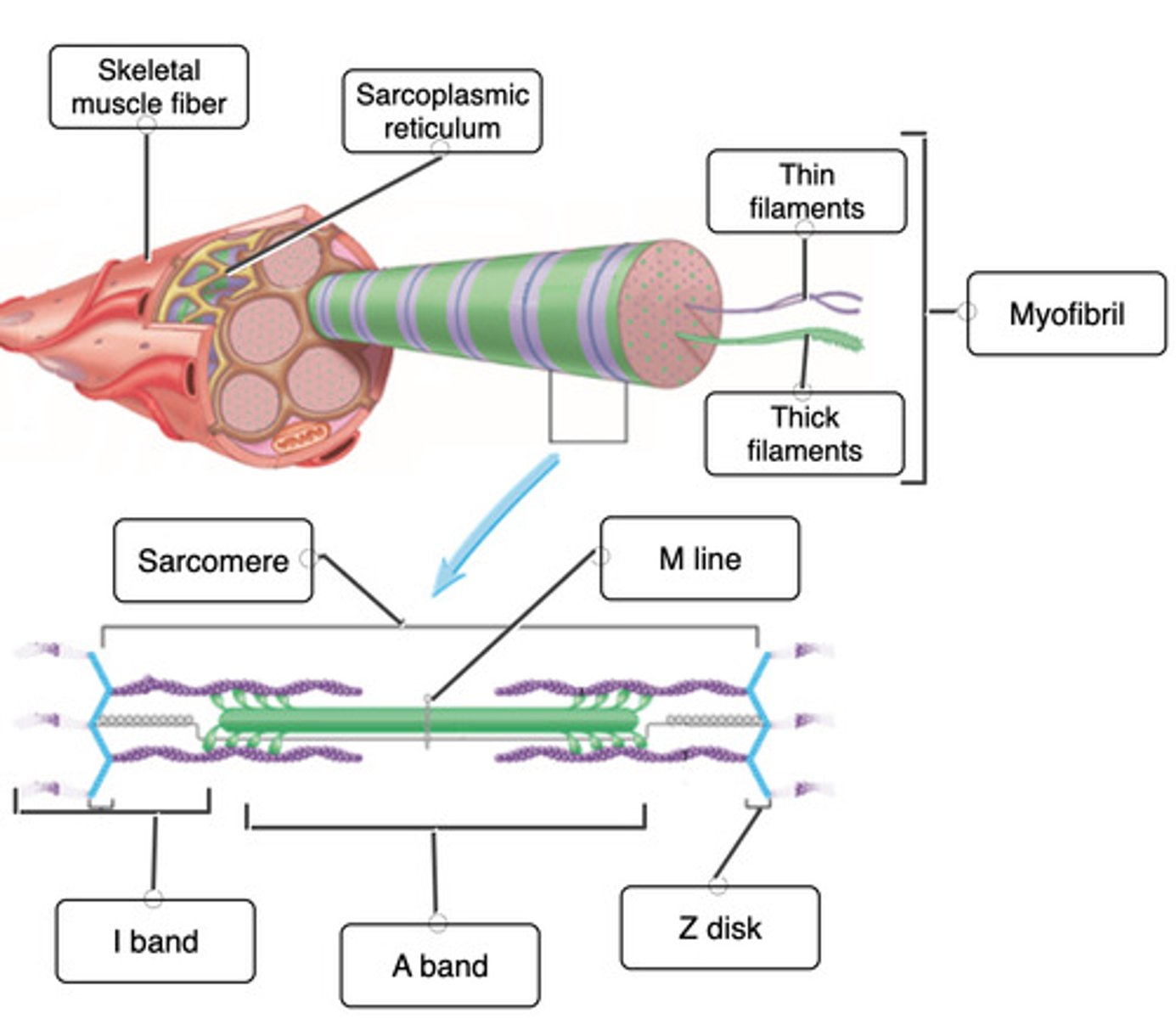
Correctly label the different filaments of a sarcomere
Excitation-contraction coupling occurs when depolarization of skeletal muscle cell results in a muscle action potential, which spreads across the cell surface and into the muscle fiber's network of _______________.
T-tubules
The sliding filament mechanism of muscle contraction describes how myosin crossbridge heads bind to and pull actin towards the center of each ____________________, effectively shortening the muscle as it contracts.
Sarcomere
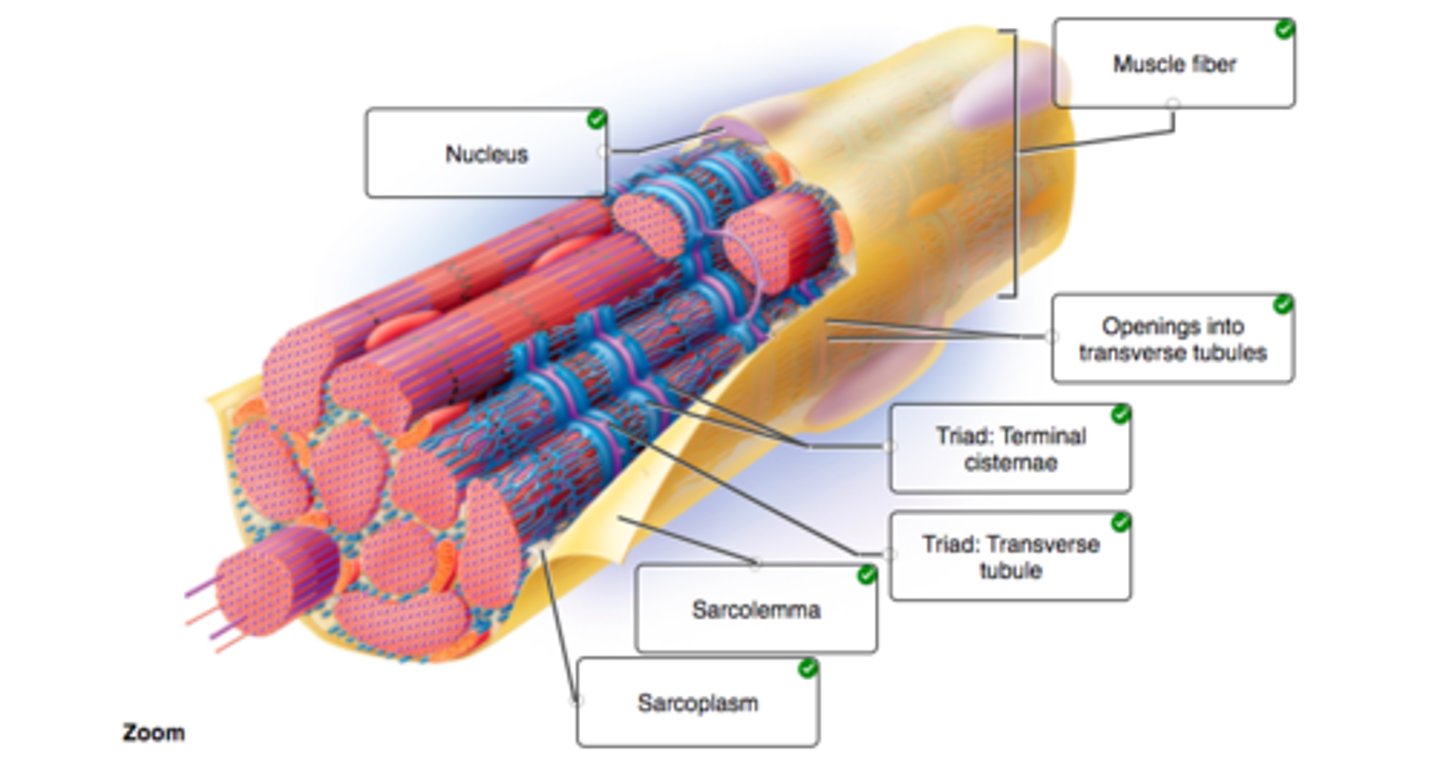
Correctly label the following parts of a skeletal muscle fiber
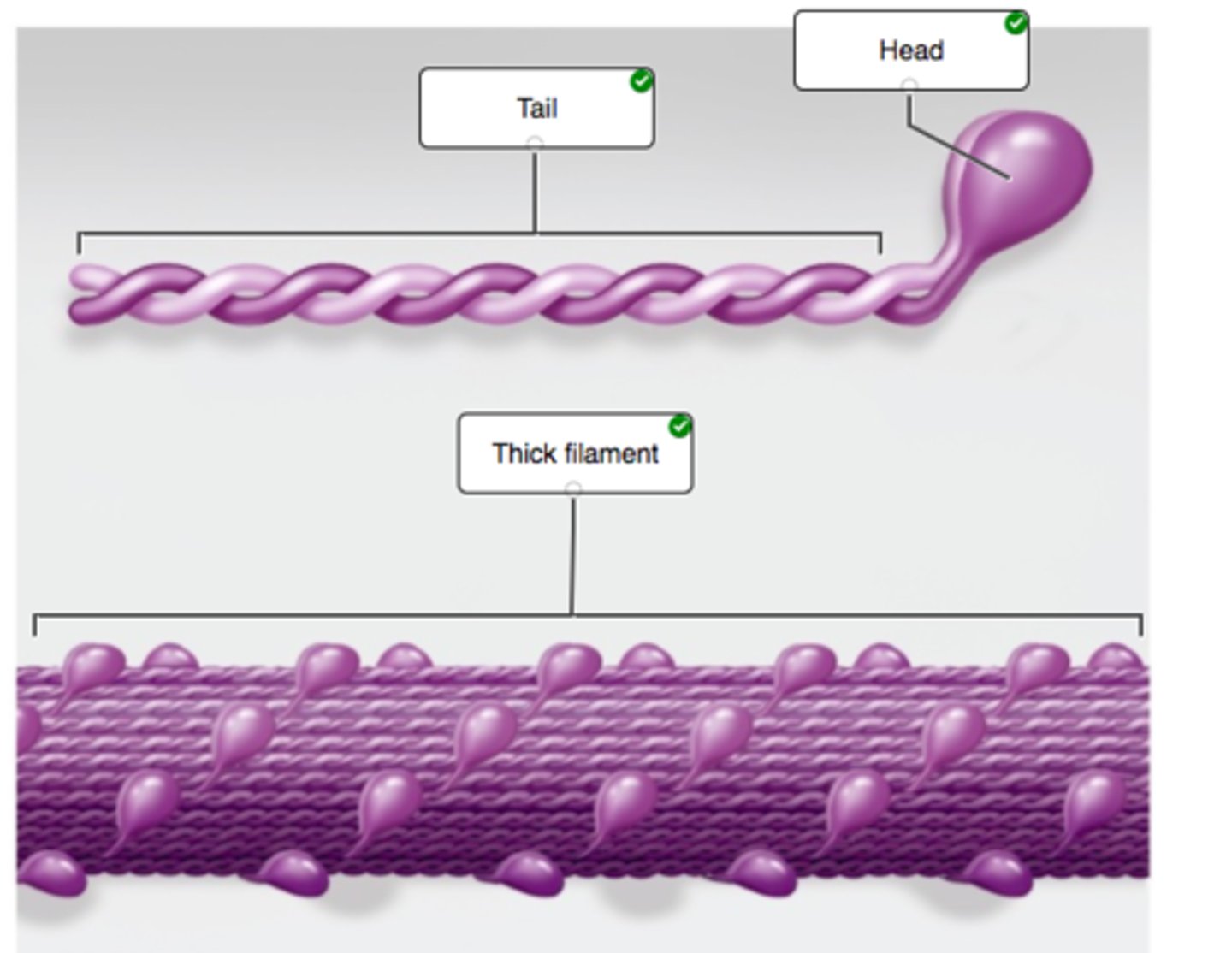
Correctly label the following features of the muscle filament
Correctly label the anatomical features of the muscle filament
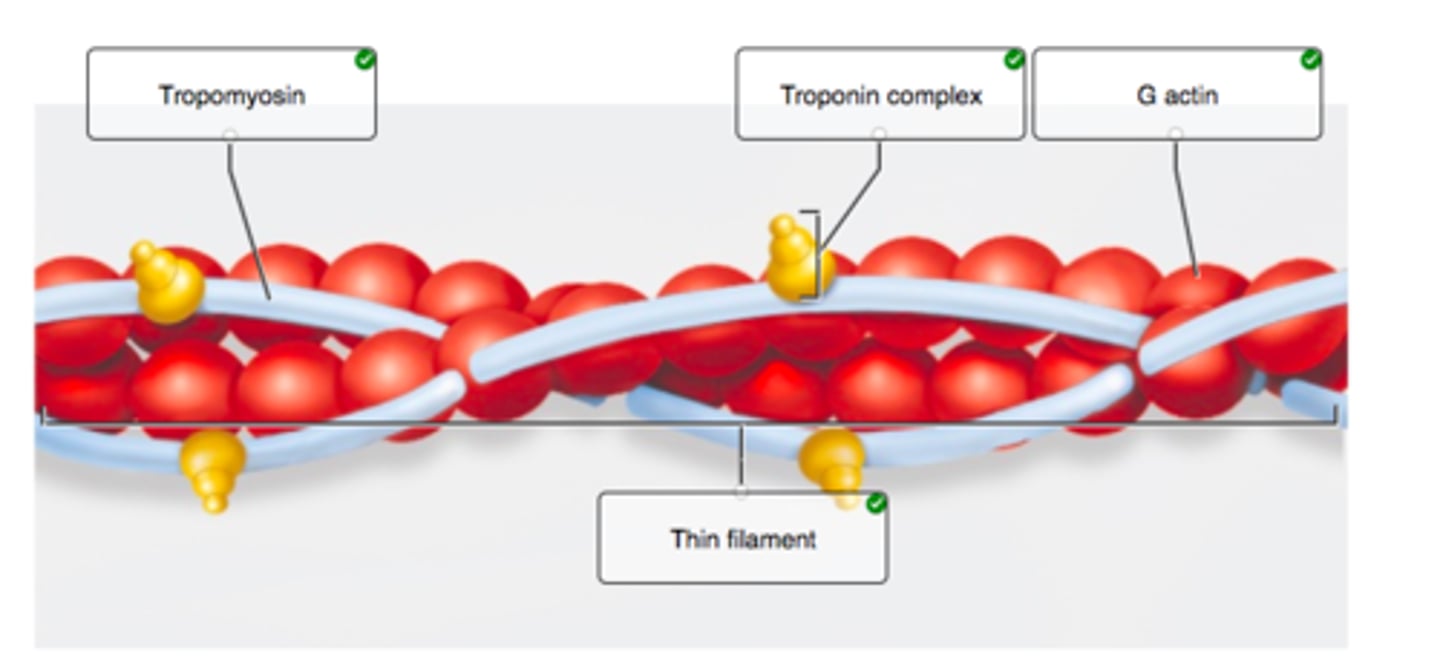
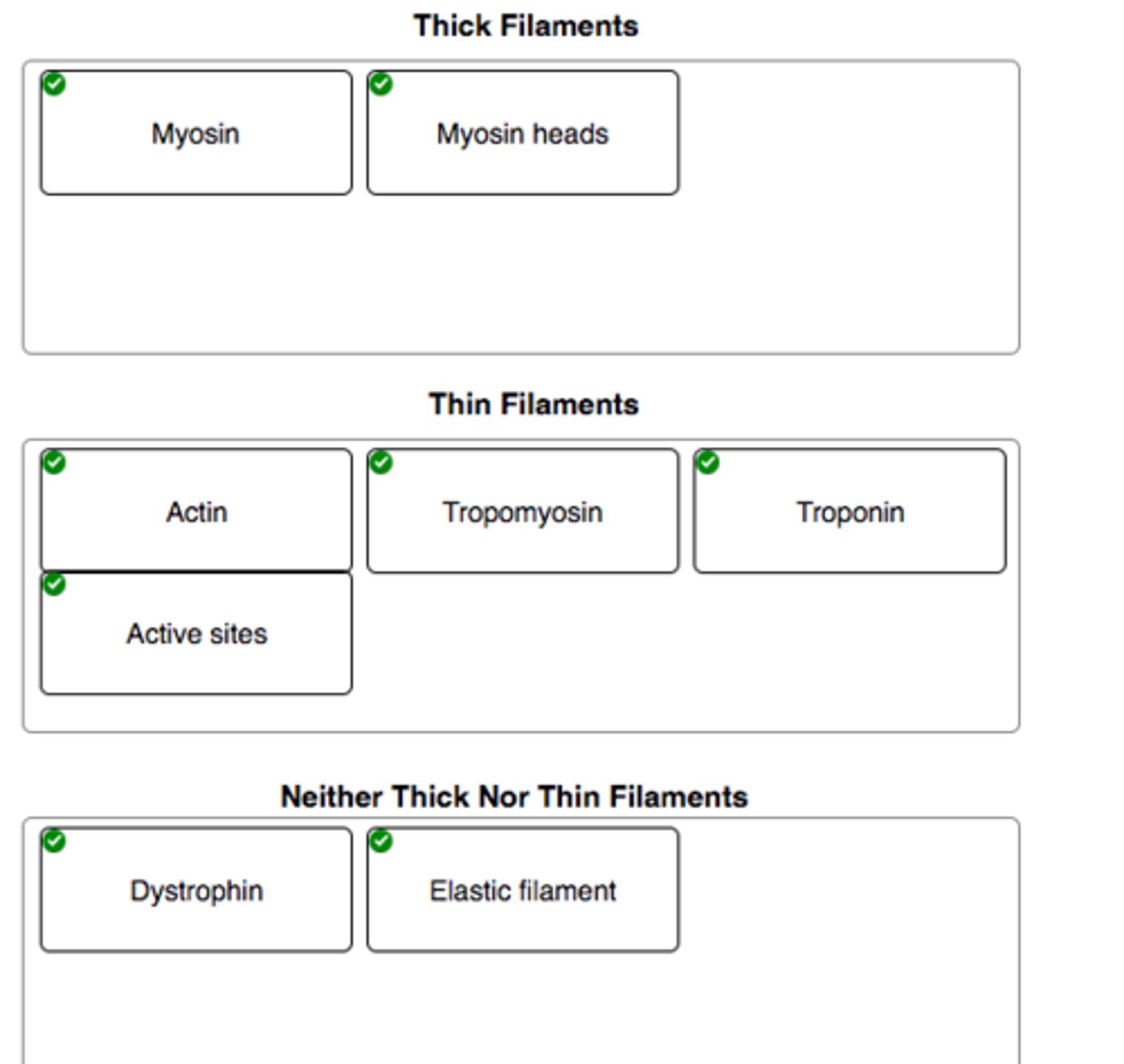
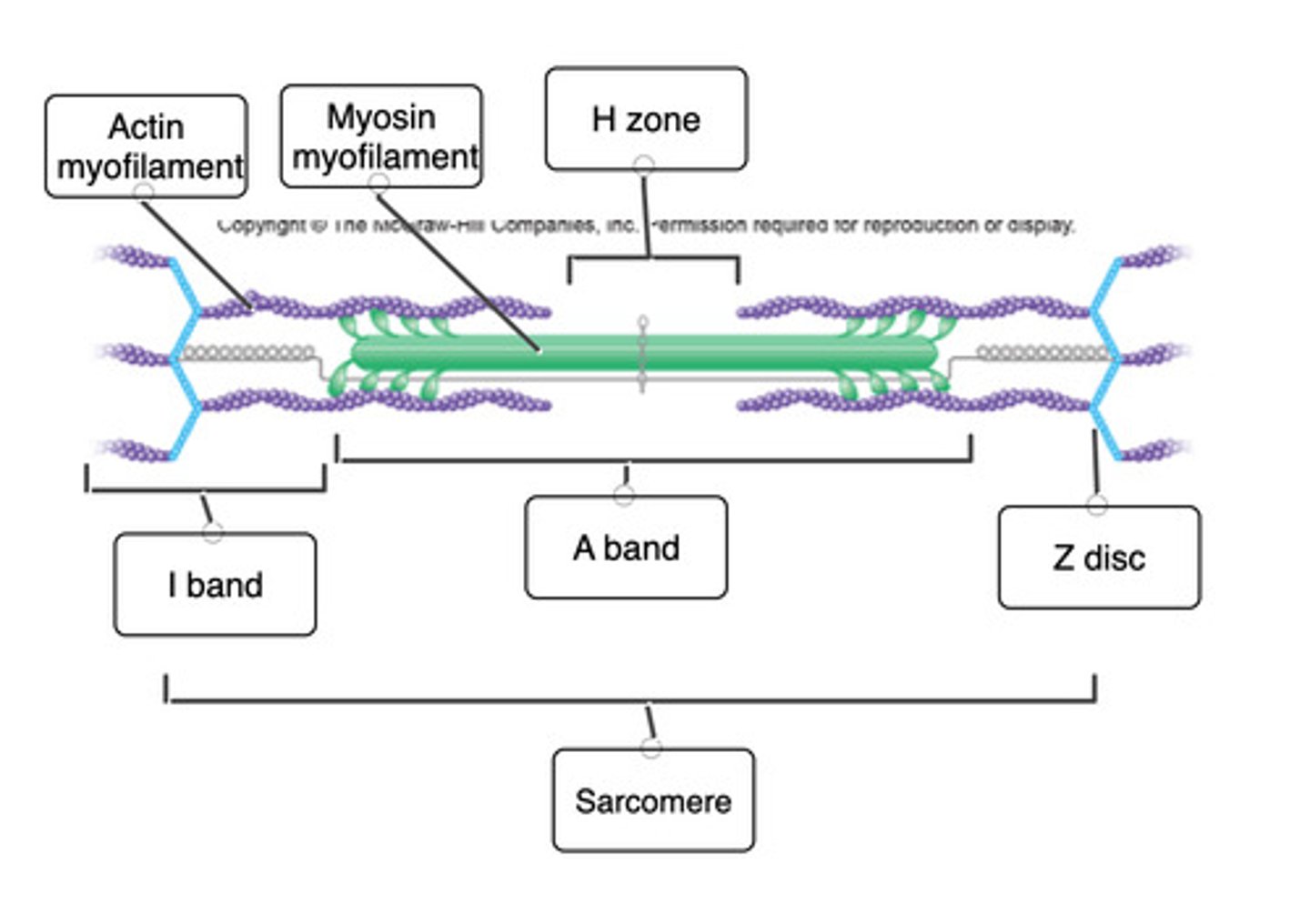
Correctly label the anatomical features of thick and thin filaments
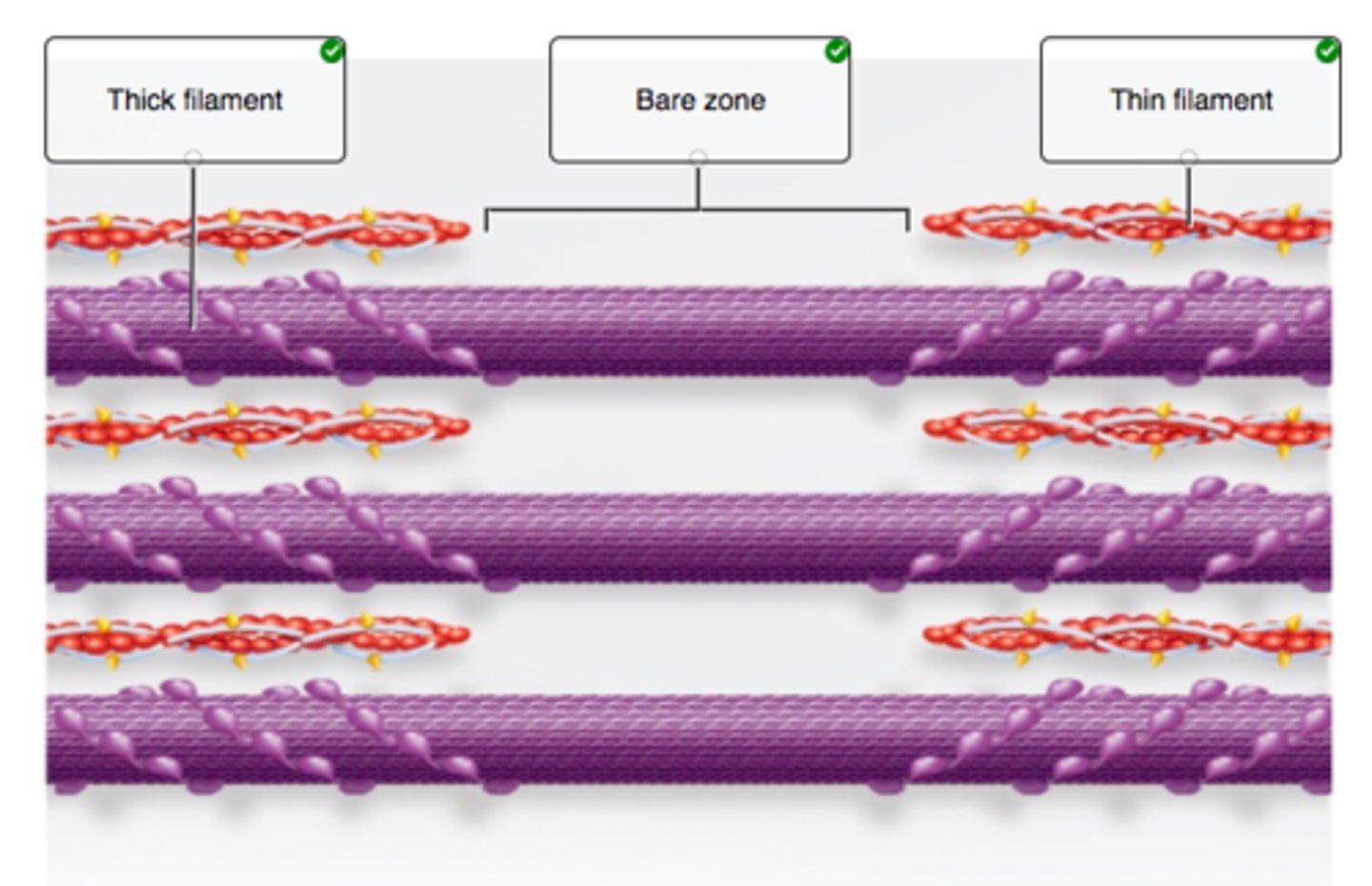
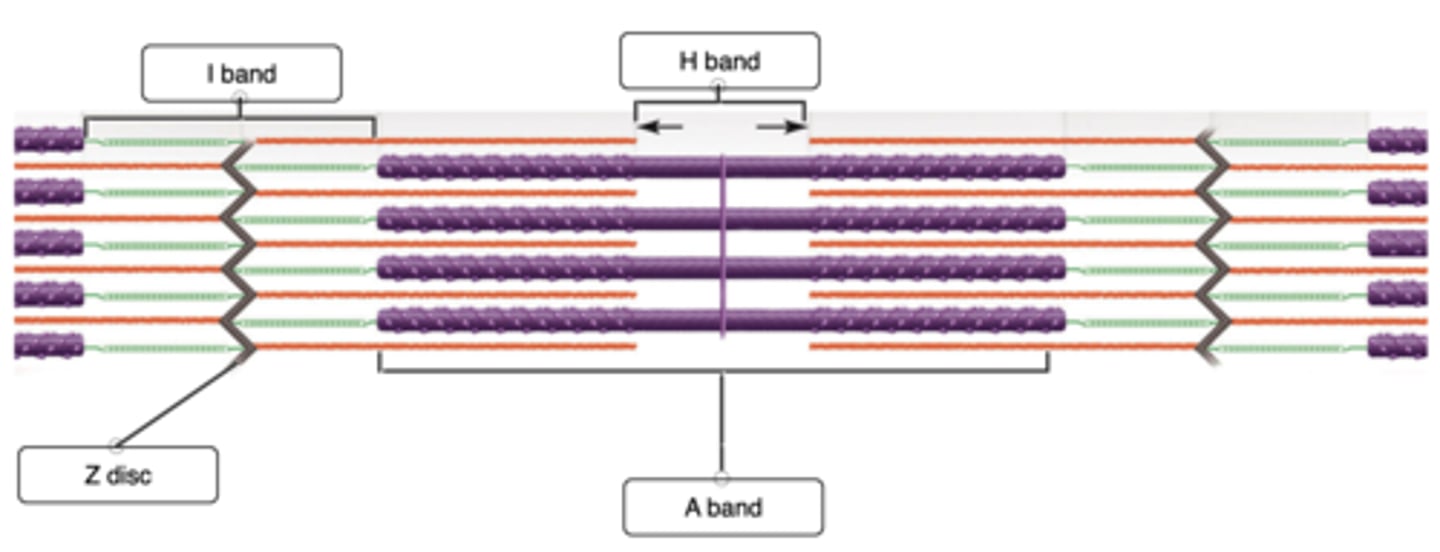
Correctly label the different bands of a sarcomere
Correctly label the anatomical features of a neuromuscular junction
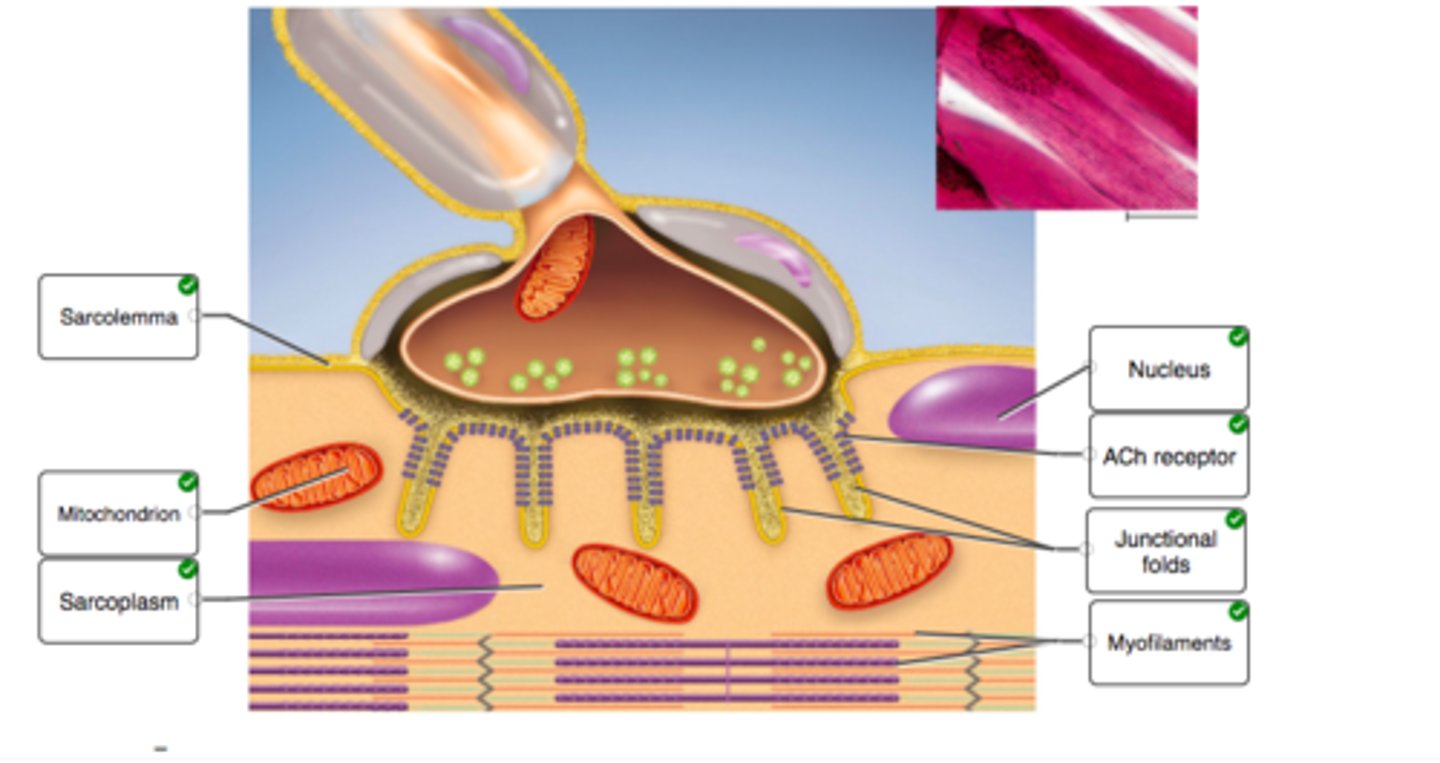
Correctly label the anatomical features of a neuromuscular junction
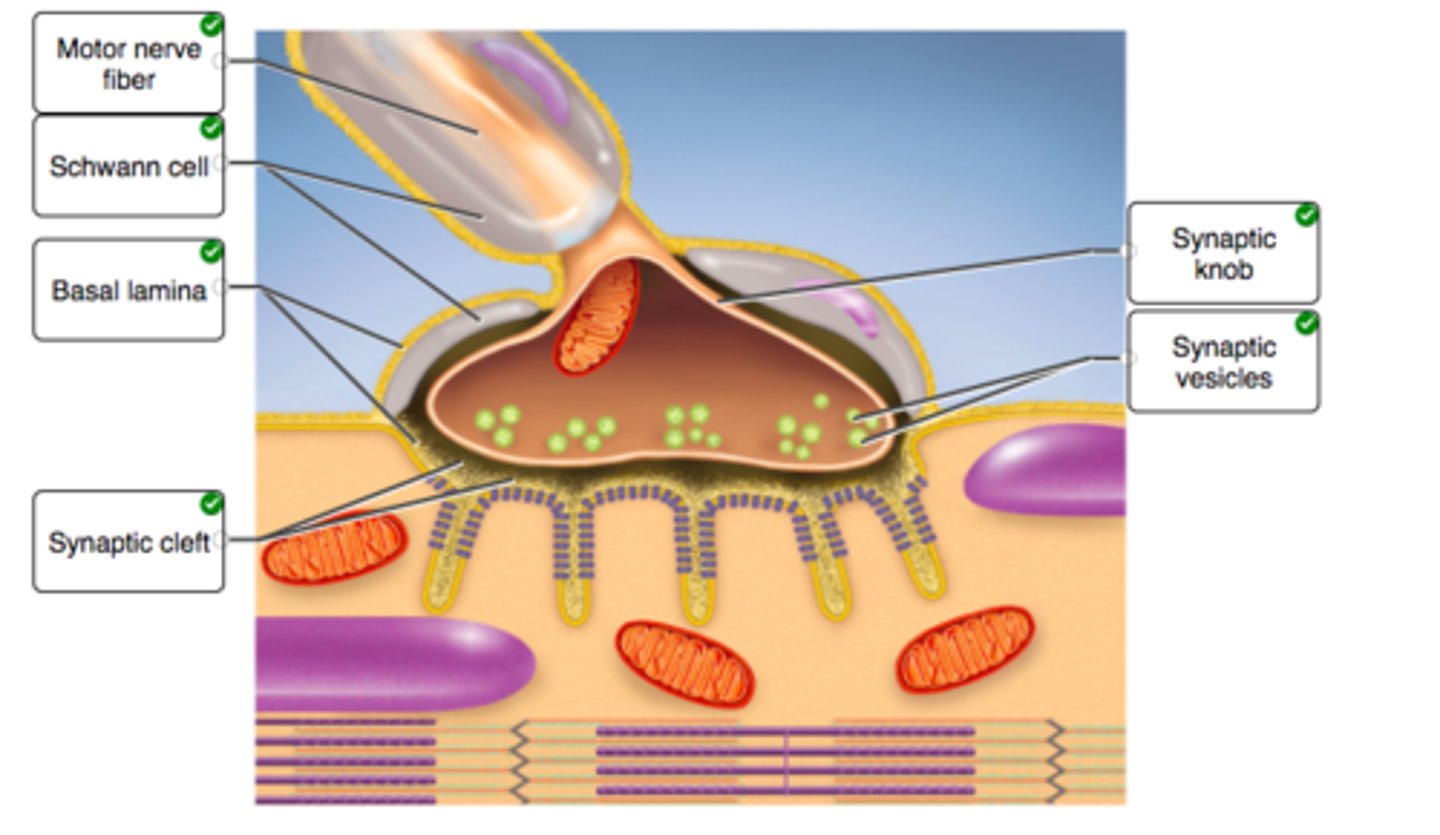
Click and drag a word from the left into each sentence on the right to accurately describe the filaments in a sarcomere

Place a single word into each sentence, then arrange the sentences into a logical paragraph order to describe the process of excitation
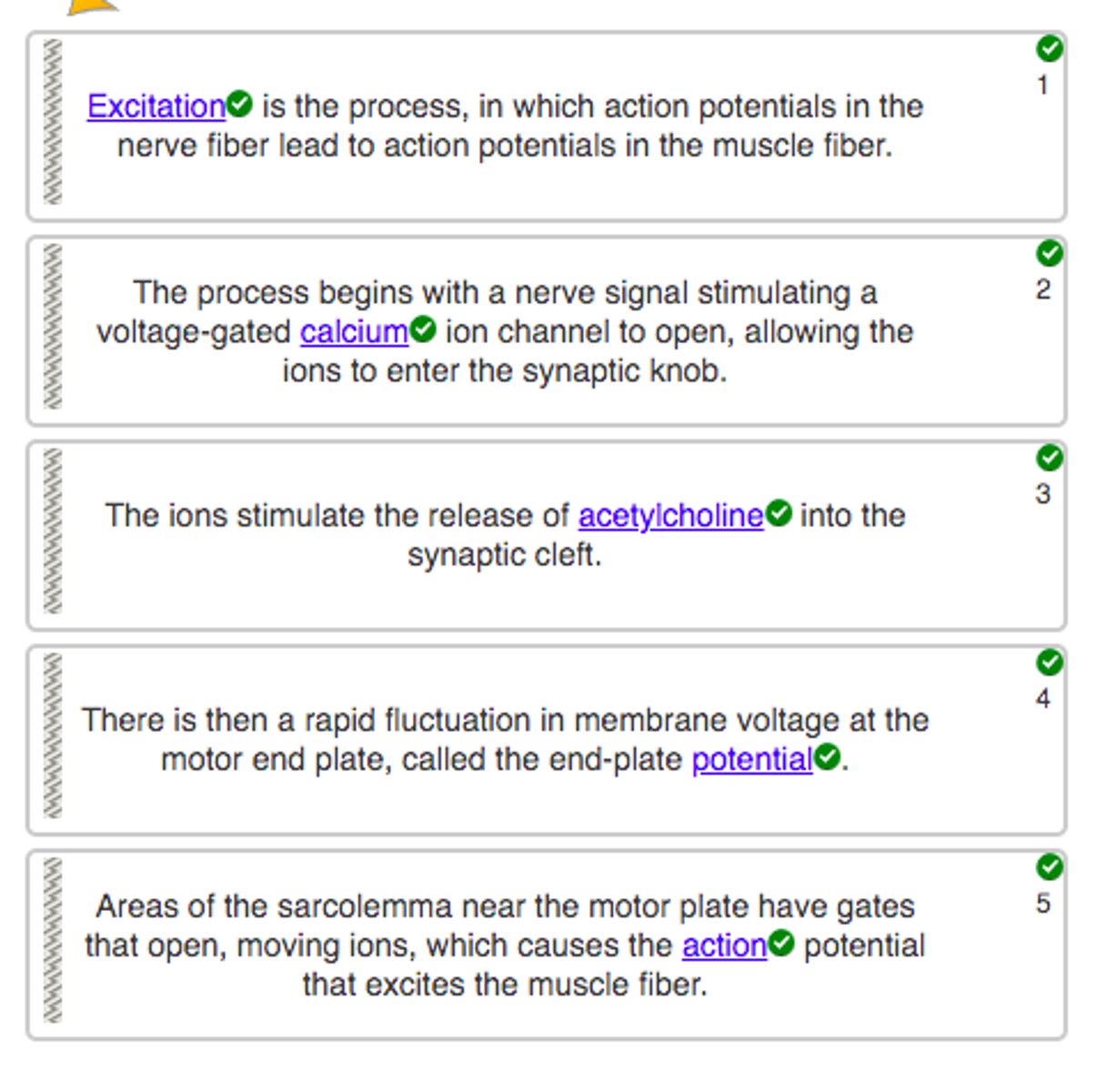
Place a single word into each sentence to make it correct, then arrange the sentences into a logical paragraph order to describe the process of excitation-contraction coupling

Place a single word into each sentence to make it correct, then arrange the sentences into a logical paragraph order to describe the process of contraction of a sarcomere

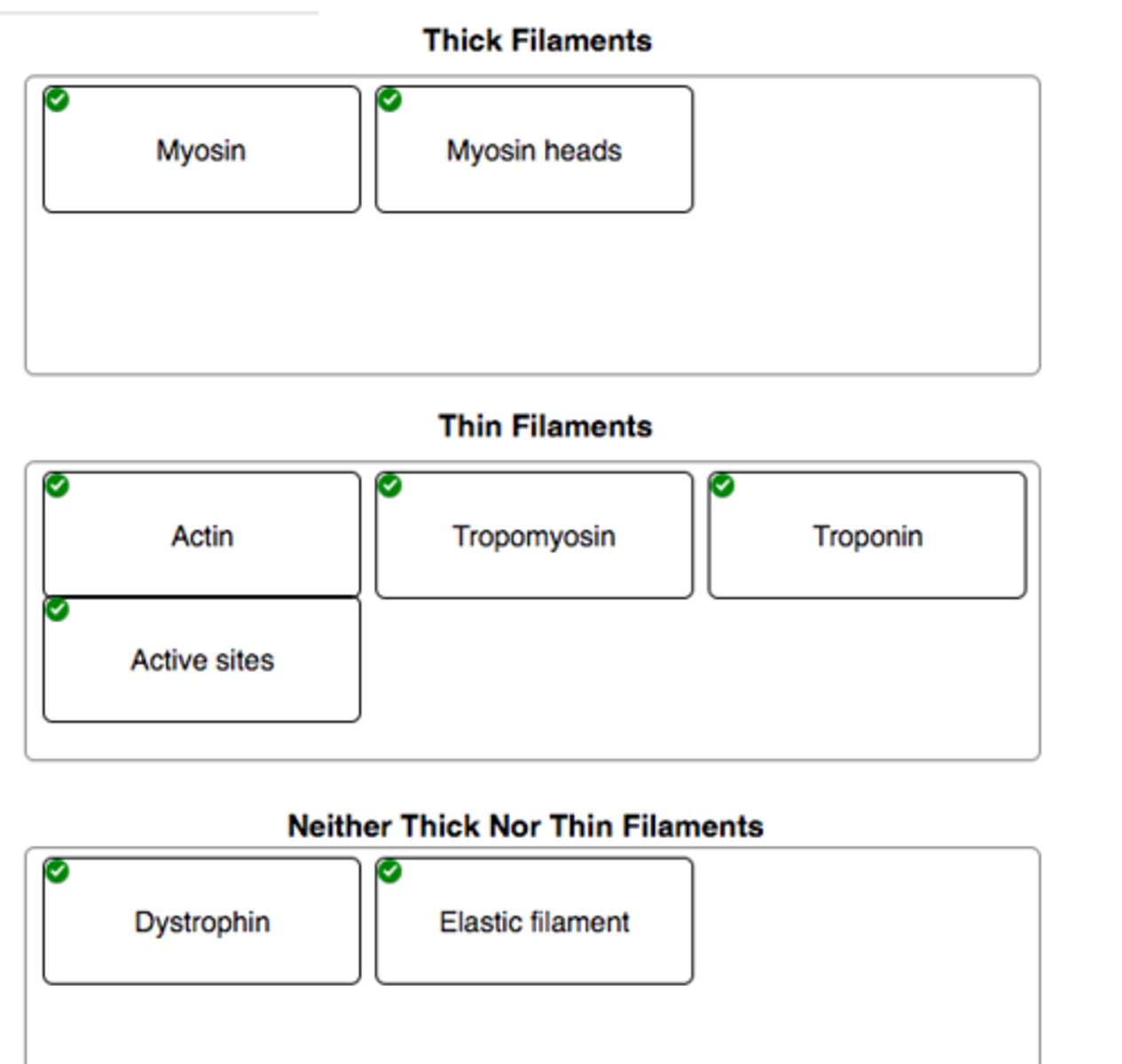
Match each protein with the appropriate filament
Match each band or line with the type of filament with which it's associated

In a fully contracted sarcomere, the actin myofilaments ____________.
Overlap
In a fully contracted sarcomere, the H zone _____________.
Disappears
The I-band of a sarcomere is widest when a muscle is relaxed - true or false?
True
Which region of the sarcomere does not change length between muscle relaxation and muscle contraction?
A band
The area between two Z discs is termed a/an ________________
Sarcomere
A fascicle:
Is surrounded by perimysium
Correctly label the following anatomical features of connective tissue of muscle.
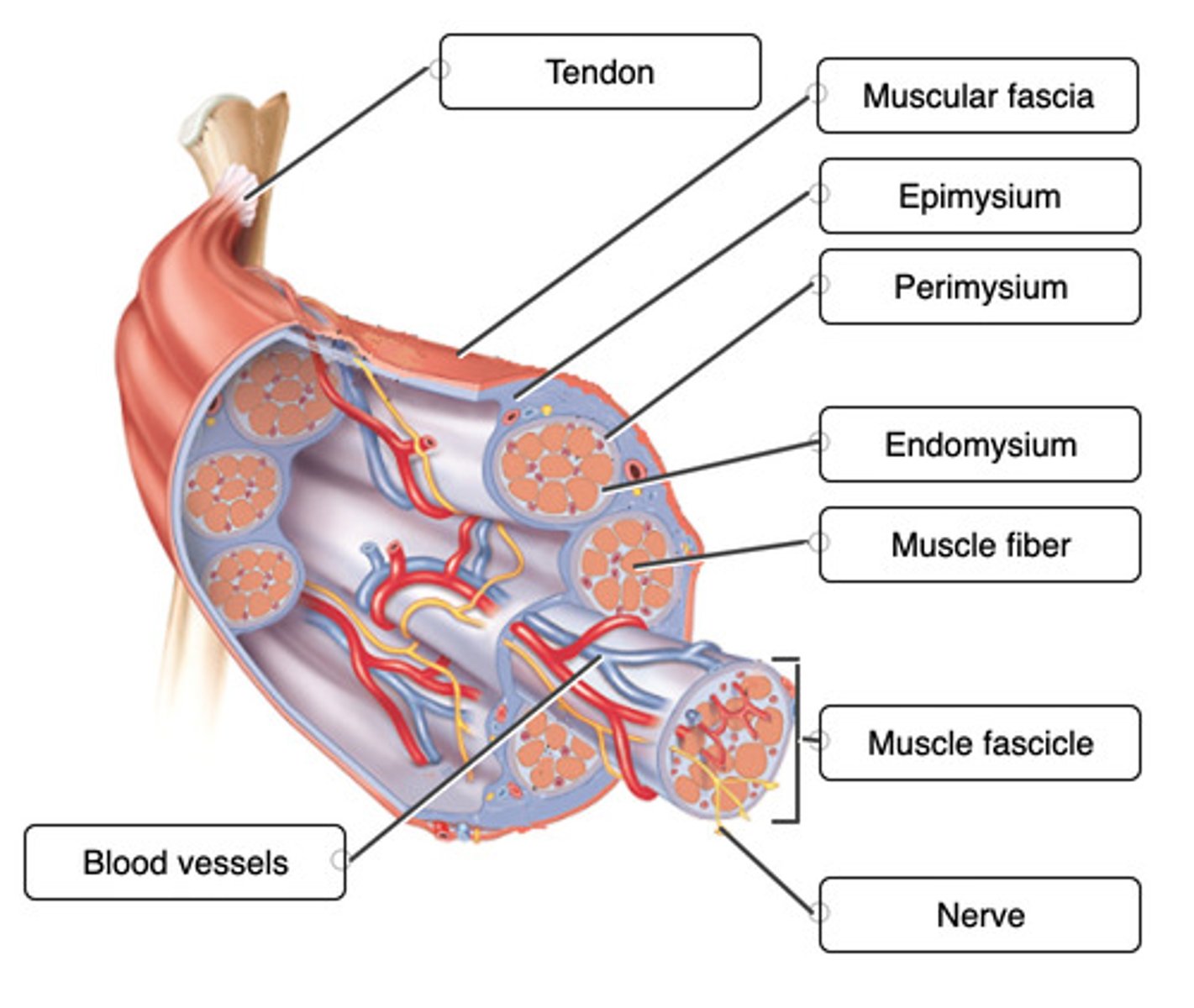
Label the microscopic structure of a skeletal muscle.
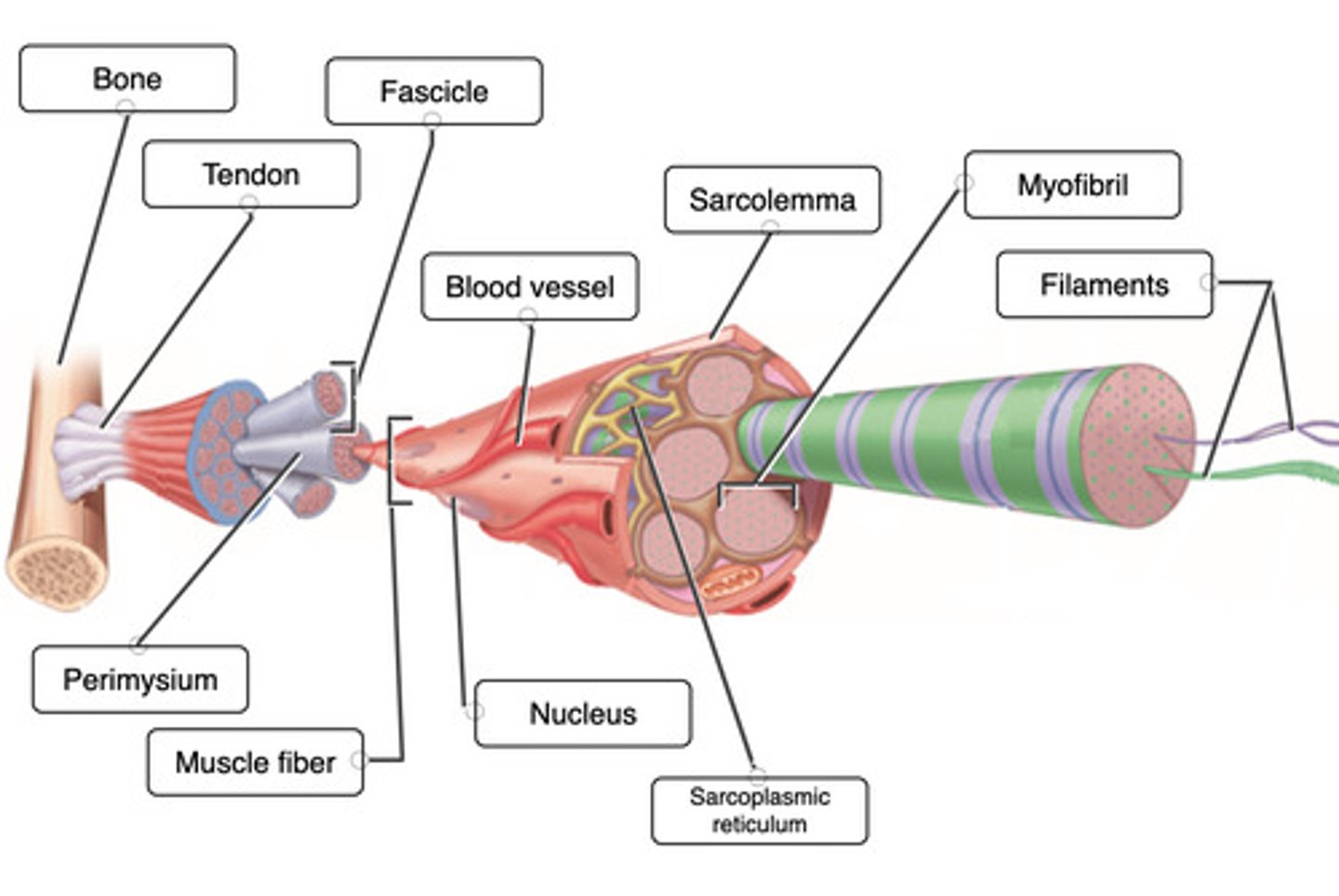
Match the muscle fiber component with its description.

Muscle myofibrils:
contain myosin and actin myofilaments
The function of the approximately 200 G actin monomers that make up the F actin strands is to:
Bind to myosin during muscle contraction
Thin myofilaments are _______ myofilaments, and thick myofilaments are _________ myofilaments.
Actin; myosin
Match each protein with the appropriate filament.
Label the skeletal muscle cell structures and features of the sarcomere.
Which of the following is not a function of the myosin heads?
Produce tropomyosin to facilitate binding to actin molecules
The myofilaments that contain two strands of F actin coiled together to form a double helix are ________ myofilaments, and the myofilaments that are composed of molecules that are shaped like golf clubs are _________ myofilaments.
Actin; myosin
Complete each sentence with the correct word from the list.

Label the parts of a skeletal muscle sarcomere.
During contraction, do myosin myofilaments shorten?
Yes
During contraction, do actin myofilaments shorten?
No
The sliding filament model explains how myofilaments slide past each other.
True
The sliding of the myofilaments past each other cause the sarcomere to shorten
True
Which of the following statements regarding the sliding filament model is false?
Both actin and myosin myofilaments shorten during contraction
Match what happens during maximum muscle contraction to the following areas of a sarcomere.

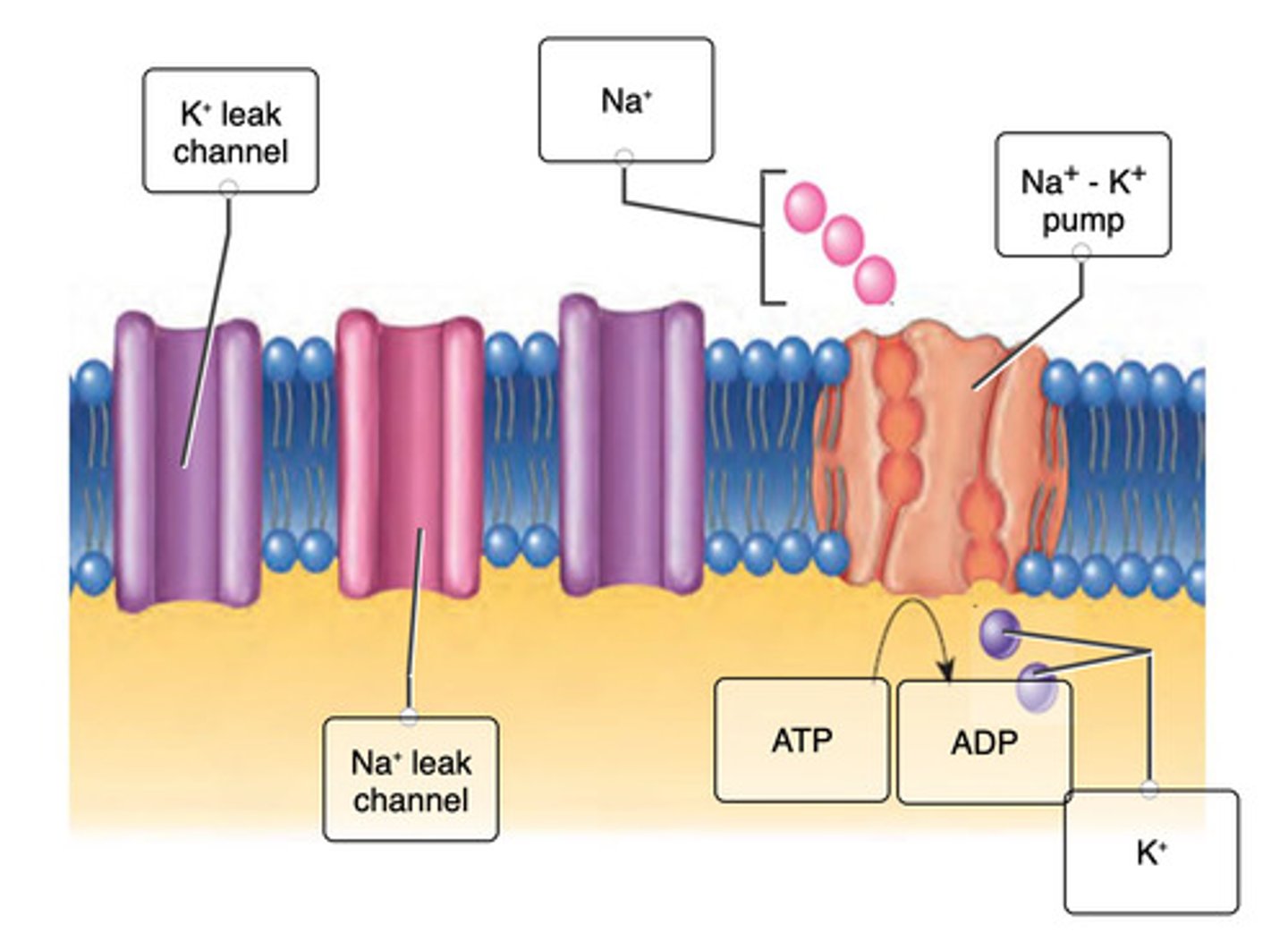
The maintenance of a resting membrane potential is due to three factors:

Use the labels to correctly identify components involved in the maintenance of the resting membrane potential.
During muscle contraction, calcium ions bind to:
Troponin
During muscle contraction, binding sites for myosin are uncovered by the movement of:
Tropomyosin
What is released when myosin heads attach to actin filaments?
Phosphate
The actin-myosin bond is broken by the attachment of:
ATP
Energy produced when ATP is converted to ADP and phosphate is stored in:
Myosin heads
Cross bridges form between binding sites on actin myofilaments and:
Myosin heads
An action potential for a muscle cell is propagated along the:
Sarcolemma
An action potential enters a muscle cell at the:
T-tubule
Uncovering binding sites for myosin on actin myofilaments is involves troponin binding to:
Calcium ions
Calcium ions released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum enter the:
Sarcoplasm
Movement of sodium ions into the muscle cell at the neuromuscular junction causes:
Depolarization of the muscle cell membrane
Choline formed from the breakdown of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft is:
Resorbed by the presynaptic terminal membrane
Increased calcium ion permeability of the presynaptic terminal cell membrane is caused by an:
Action potential
The neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction is:
Acetylcholine
The neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction increases permeability of the muscle cell membrane to:
Sodium ions
Myofibrils are composed of protein filaments called actin and myosin.
True
A bundle of muscle fibers is known as a:
Fascicle
A skeletal muscle fiber (cell) contains a single nucleus.
True
The muscle cell membrane is called the:
Sarcolemma
Which connective tissue wrapping separates individual muscle fibers?
Endomysium
In a fully contracted sarcomere, the actin myofilaments:
Overlap
In a fully contracted sarcomere, the H zone:
Disappears
The I-band of a sarcomere is widest when a muscle is relaxed
True
The area between two Z discs is termed a(an):
Sarcomere
Motor end plate
The point where the axon terminal synapses with the muscle fiber sarcolemma is called the _____________.
Neuromuscular junction
Postsynaptic membrane is located at the:
Muscle plasma membrane
Presynaptic terminal is located at the:
Axon
Synaptic cleft is located:
Between the presynaptic terminal and the muscle fiber
Complete each sentence with the correct word.
As a result of extreme muscular fatigue, muscles can become incapable of relaxing or contracting, which is called _____________.
Similarly, several hours after death, ATP levels decline, causing muscle rigidity, known as ____________.
Physiological contracture; rigor mortis
The type of muscle fatigue known as "psychological fatigue" is the result of:
The emotional state of an individual.
During ___________, muscle fibers partially relax between contractions, whereas during ___________, no relaxation occurs between contractions.
Incomplete tetanus; complete tetanus
________ occurs when a rested muscle is stimulated repeatedly, at low frequencies, allowing relaxation between contractions. This causes each contraction to be stronger than the previous one until eventually the levels of tension are equal between contractions.
Treppe
Muscle tension can be increased with _________, which involves increasing the force of contraction of the muscle fibers, as well as with __________, which involves increasing the number of muscle fibers contracting.
Summation; recruitment
Place the boxes in the numbered boxes, 1 through 8, according to the order in which these events occur.