Energy,work and power
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
what is energy
is a property that must be transferred to an object in order to perform work on or heat up that object. It is the ability to do work.It is measured in units of Joules (J)
what si principle of conservation of energy?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be transferred from one store to another. So total energy before
units for mass,energy,distance,speed,acceleration,force,time and power?
Mass (m)=Kilogram (kg)
Energy (E)=Joule (J)
Distance (d) or displacement (s)=Metre (m)
Speed (v) or velocity (v)=Metre per second (m/s)
Acceleration (a)=Metre per second per second (m/s2)
Force (F)=Newton (N)
Time (t)=Second (s)
Power (P)=Watt (W)
Energy stores examples
-kinetic eenrgy: energy stored by an object bcs of tis motion
-gravitational potential energy: energy stored by objects lifted upwards against the force of gravity. Released when they fall downwards.
-elastic (strain energy)-stretched rubber /elastic band and compressed spring store energy
-chemical energy: energy stored in the chemical bonds btw atoms eg fuels,foods. Can be released by chemical reactions-burning fuels
-electrostatic energy: energy stored in electric charges attracted to each other but held apart. Energy due to force of attraction or repulsion between two charges
-nucleuar energy: energy stores in nucleus and stored energy released in soem atoms if the particles inside nucleus become rearranged or split
-thermal energy: all materials contain moving particles that store energy. This is released when hot objects cool down, its particles slow releasing thermal energy (related to internal energy)
-magnetic energy: energy stored when two magnets attract eachother but are held apart. Energy due to force of attraction (or repulsion) between two magnets
what are energy transfers
Energy can be transferred between stores through different energy transfer pathways
examples of eerngy transfers
-mechanical/forces: an object movign due to a force acting on it eg when gravity accelerates an object downwards and gives it kinetic energy
-electrical currents: a chrge moving through a potential difference. Electricity can transfer energy from a power source eg cell delivering it to components within a circuit. eg when a current passes through a lamp and it emits light+heat
-heating: energy transferred from a hotter to a colder object due to temperature difference caused electrically or by chemical reaction eg fire used to heat up object. Thermal energy can be transferred by convection,conduction or radiation
-radiation: by waves eg light and soudn carry energy and can transfer this between two points eg vibration cause waves to travel throguh air as sound
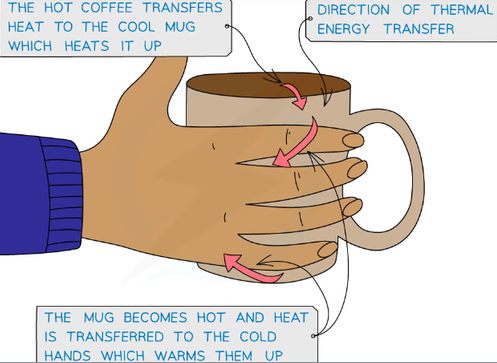
what happens to energy during an event
in an event or a process energy tends to become mreo spread out among the objects and surroundings (dissipate). energy cannot be 'lost', but it can be transferred to the thermal energy store of the surroundings.Energy can be dissipated to the surroundings by radiation (by heat, light or sound)This energy is often not useful energy, so it can be described as wasted energy. Energy will always be transferred to wasteful stores of energy due to friction.
what is kinetic energy
The amount of energy an object has as a result of its mass and speed. Equal to the work which the object could do by losing all of its speed and work done on increasing speed of object from 0 to v. Energy transferred to this store when objefct speeds up and away when it slows down.
kinetic energy equation
KE=1/2mv^2
KE = kinetic energy in Joules (J)
m = mass of the object in kilograms (kg)
v = speed of the object in metres per second (m/s)
what is gravitational potential energy?
Potential energy because of Earths gravitational pull on it and due to its height in a gravitational field. Equal to the work which coudl be done if obejct were to fall to ground or work doen in lifitng the object a distance form gorund
equation for GPE
GPE=mgh
GPE = change in gravitational potential energy, in Joules (J)
m = mass, in kilograms (kg)
g = gravitational field strength in Newtons per kilogram (N/kg)
Δh = change in height in metres (m)
what happens to GPE and KE in a fallign object if no air resistance
when somethign falls energy from its gravitational potential energy store is transferred to its kinetic energy store. For a falling object when there’s no air resistance: energy lost from the gpe store=energy gained in the kinetic energy store bcs of conservation of energy. If there is air resistance soem energy transfered to other energy stores eg thermal energy stores fo object and surroundings
how can energy stores and transfers be shown
represented using flow diagram
what are sankey diagrams
Used to represent energy transfers. The width of each arrow is proportional to the amount of energy going to each store.The end of the arrow pointing to the right represents the energy that ends up in the desired store (the useful energy output) The end(s) that point(s) down represents the wasted energy
what is work done?
when an object is moved over a distance by a force applied in the direction of its displacement.It is said that the force does work on the object.If a force is applied to an object but doesn't result in any movement, no work is done. Si unit joule (J).
work doen equation
Work done = force × distance
W = fd
how many joules in 1 nm
1 J = 1 N m
One Joule is equal to the work done by a force of one newton acting through one metre
how is energy transferred whenever work done
energy is transferred mechanically from one store to another
energy and work doen linking equation
W = fd = ΔE
energy transferred (J) = work done (J)
work doen when bird flies
The bird must travel against air resistance, therefore energy transferred from the bird's chemical energy store to its kinetic energy store and to the thermal energy store of the surroundings as some energy is dissipated as heat
energy transfer when bat hits ball
soem energy is usefully tansferred mechanically from the kinetic enregy store of the bat to the kinetic energy store of the ball.The rest of the enrgy is wasted. Some energy in the kientic eergy store of teh bat is transferred mechanically to the thermal energy stores of the bat, the abll and theri surroudnigs. The remaing energy is carried away by sound
energy transfer of a bunsen burner and beaker
energy is usually transferred by heating from the chemical energy store of the gas to the thermal enregy stores of teh beaker and the water. Energy is also wastefully transferred by heating to the thermal eenrgy stores of the stand and surrodungins. Some energy is also carried away by light.
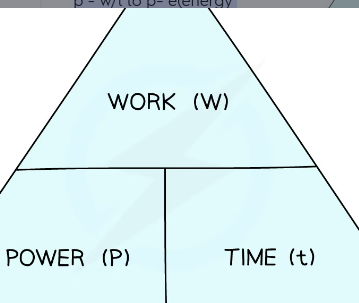
what is power
it is work done per unit time (rate at which work done) or rate at which energy is transfered. Si unit is watts
Power equation
p = w/t to p= e(energy transferred)/t
E or W = The energy transferred, or work done, measured in joules (J)
t = time measured in seconds (s)
P = power measured in watts (W)
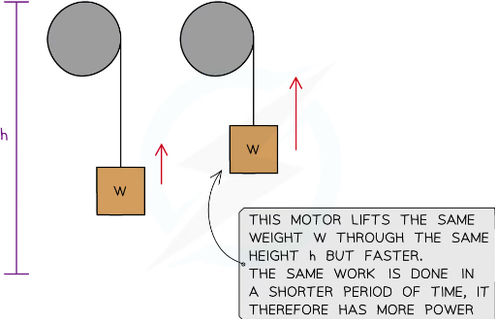
illistrate power by comparing two electric motors if they They lift the same weight.They are lifted by the same height.One lifts it faster than the other.What si their power like?
The motor that lifts the weight faster is said to have more power. This is because the work done does not depend on time, only the force (weight) and the distance lifted
What is efficency
it is the ratio of the useful work done to the total energy supplied,often expressed as a percentage
Efficency equation
Useful energy output/Total energy input/output x100%
or
useful power output/ total power input x 100 useful work done/ total energy output x100
what is the equation where power is defined as the energy transferred per unit of time?
power= energy transferred/time
what are the two ways efficiency written
Efficiency can be given in a ratio (between 0 and 1) or percentage format (between 0 and 100 %) If the question asks for efficiency as a ratio, give your answer as a fraction or decimal. If the answer is required as a percentage, remember to multiply the ratio by 100 to convert it.
how many watts in 1 kilowatt
1 kilowatt
how to increase efficiency of a system can be increased by:
-reducing waste output (lubrication,thermal insulation etc) -recycling waste output (eg absorbing thermal waste and recycling it as input energy)
what are the two types of non renewable energy sources?
-fossil fuels (eg coal,oil and natural gas) formed over a long time from remins of plants and tiny sea creatures that lived millions of years ago. Natural gas 'cleanest' of fossil fuels and is taken from the same underground rock formations tht contain oil-the gas formed with the oil and become trapped above it. when fossil fuels burn they produce gases which pollute the atmosphere eg CO2 which adds to global warming -Nuclear fuel- most contain uranium. In nuclear power stations energy is released by fission, a process in which teh nucleu of uranium atoms are split. Waste from nuclear fuel is very dangerous and stays radioactive for thousands of years. Nuclear power stations are expensive to build, and expensive to decommission (close down and dismantle)
non reneweabel eerngy disadvanatge
-Non renewable energy will run out and is harmful for environment.
-All 3 fossil fuels release CO2 into teh atmosphere when burned in power stations. This contributes to global warmign and cliamte change.
-Burning coal and oil also releases sulfur dioxide (SO2) which causes acid rain. Acid rain can harm trees and soils and can have a huge impact on wildlife
non renweable erngy advanatge
-brunign fossil fuels releases a lot of energy relatively cheaply
-energy from fossil fuels doesn’t rely on the weather. like a lot of renewabel enrgy, so its a reliabel energy source
-we have lots of fossil fuel power statiosn already so we dont need to spend moeny on new technology to use them
what are all teh different types of renewable resources?
-hydroeelctric energy -tidal energy -wind energy -wave energy -geothermal energy -solar energy -biofuels
what types of energy resources dont come from the sun and meaning
-geothermal:comes from heat produced by earths core. Water pumped down to hot rocks deep underground and rises as steam. May come naturally from hot springs or deep drilling -nucleur: comes from elements which make up a small proportion of the Earth's crust -tidal: lake fills when tide comes in and empties when goes out.Comes mainly from gravitational attraction of the moon
What is hydroelectric energy?
When water is stored above ground level it has energy in its gravitational potential store This energy can be transferred to kinetic energy if the water is allowed to flow down the slope mechanically which turns the turbine to generate electricity
What is tidal enrgy
so dam built across river where it meets the sea. When lake fills when tide comes in and empties when goes out which turns the genrators
todal barring advantages
-No pollution -Reliable and can produce a large amount of electricity at short notice -Renewable energy resource -Small systems are being developed to provide electricity for small island
disadvanateg of tidal barring
Expensive to build Damages fragile habitats Very few suitable locations The technology is not advanced enough for large scale electricity production
hydroelectric energy advantages
Can respond to demand so is reliable and available Can generate large scale amounts of electricity
hydroelectic energy disadvanatges
-Need to flood valleys to build which destroys habitats, towns and villages causes environemtnal damage -few areas suitable -expensive to build
what is geothermal energy?
Radioactive substances in Earth release energy as they decay this geothermal energy heats up the rocks. Water can be poured into shafts below the Earths surface which is heated by the rocks and returned via another shaft as steam or hot water Steam can be used to turn a turbine and generate electricity, and hot water can be used to heat homes.
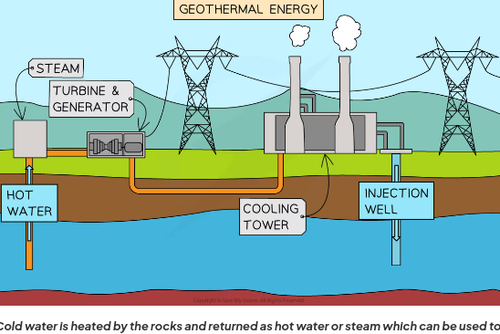
geothermal energy advantages
-Renewable resource with no real environemntal problems
-Reliable source of energy
-Geothermal power stations are usually small compared to nuclear or fossil fuel power stations
geothermal energy disadvantages
-few suitable areas so small scale production of electricity
-cost of building a power plant is often high compared to the amount of energy we can get out of it
-can result in release of greenhouse gases from underground
what si nuclear fusion
the susn energy is produced by through the process of nuclear fusion in its core. Nuclear fusion involves the collisions (and bonding) of hydrogen nuclei to form helium nuclei, releasing nuclear energy in the process.
problems with nucleur fusion
Fusion requires very high temperatures. Currently, the fusion reactions require nearly as much energy than they produce, but progress is being made toward net energy production
what is wind energy
Wind power invovles putting lots of wind turbines up in exposed places. Wind turbines use energy from the kientic energy store of movign air to genrate electricity. Wind turns the blades which turns/drives the generators inside it. Collection of aerogeneratrs-genrators driven by giant wind turbines
advanatges and disadvanategs of wind power?
Advantages:
-doesnt produce any pollutign waste and its renweable
-Runnign wind turbines is quite cheap as theyre very tough and reliable and the wind is free
Disadvanatages:
-Large,remote windy sites needed.
-Winds unreliable and may not be strogn enough to generate any power. Impossibel to icnrease supply when theres extra demand
- wind turbines noisy and can spoil landscapes as they need a lot of turbiens to genrate enoguh energrgy
what si wave energy/power?
generators are driven by the up and down motion of waves at sea. Difficult to build.
Renewable energy disadvantage
Renewable energy often more costly,much less concentrated sources of energy,often need large areas of land and less reliable.
how do thermal power stations work?
genrators turned by turbines,blown around by high pressure steam produced by heating water in the boiler.
1) Fossil fuels are burnt (in oxygen) and the energy in its chemcial energy store is transferred to teh thermal enregy store of the water by heating.
2) Once water boils to form steam the steam passes throught eh turbine and turns it transferring energy mechancially to the kinetic energy store of the turbine.
3) As the turbine revolves so does the generator which produces an electric current.The generator transfers the enrgy electrically away fromt he power station via the national grid
4) Once steam ahs passed through turbine its cooeld and condesed so it can be given back to boiler. Powerstations have huge cooling towers with drought of air up through them or use the cooling effect of nerby sea or river water
how do nuclear power stations work?
Nuclear power stations ar emostly the same as tehrmal ones however in it nuclear fission eg of uranium produces the heat to make steam to drive turbines etx rather than burning, see pg 49 og cgp
Energy is transferred from nuclear enrgy stores to thermal energy stores by ehating then mechanically to kinetic energy stores nf finally transferred electrically through the national grid.
disadvanategs of nuclear pwoer stations
-nuclear reactors are expensive to build an dmaintin and take longer to start up then fossil fuel ones
-processing the uranium before you use it causes pollution and theres always a risk of leaks of radioactive material
-uses expesnvie complex technology
-nuclear power always gives radioactive waste
-when theyre too old and insufficent, nuclear power stations have to be decommissioned-thats very expensive
-nuclear power stations cant be turned on instantly. The process of startign the fission reaction and heatign up the core of the nuclear reactor is a long oen so they cant meet sudden variations in demand
advanatges of nuclear power
-doesnt produce any of the greenhosue gases which ocntribute to global warming
-Uranium produces huge amounts of energy so the cost of energy per unit of fuel used is low
what is meant by energy spreading in thermal power stations?
Most energy in thermal power stations lost as thermal energy in the cooling water and waste gases. Most lost in turbines and some lsot in boilers,genrators and energy to run power station. As thermal energy spreads it becomes less useful
what is district heating?
when unused thermal energy from power station heats homes,offices and factories in local areas using long water pipes.
how many watts is 1MW and 1GW?
1MW= 1000000 W
1 GW= 1000 MW
what are combines cycle gas turbine power stations?
smaller units which can be sped up or shut off quickly as demand fro electricity varies. In them natural gas used as fuel for jet engine,shaft of engine turns one generator.Hot gases made from ejt used to make steam to drive another generator
what si the chemcial reaction by which msot fuels relase enregy
fuel+oxygen-->CO2+ water+thermal energy
whta do nucelar power stations produce
radioactive waste not waste gases like carbon dioxide and water
how do thermal power stations cause pollution?
-fuel burning or coal burning emits CO2 gas which adds to global warming
-Coal burning power stations emit sulfur dioxide which is harmful to health+ causes acid rain unless low sulfur coal used or desulfirization (FGD) units fitted
-transporting fuels can cause pollution eg oil leaks
-Radioactive waste from nucleur power stations highly dangerous+ takes very long to decompose and not becoem dangerous -Nucelar accidents eg when radioactive gas and dust carried thousands of kms by wind
how is energy from sun transferred to earth?
The energy from the Sun that falls on the Earth is transferred by radiation. Mostly visible light and infrared radiation
how do solar cells/photovoltaic cells work?
Solar cells transfer energy from sunlight electrically producing a current, and therefore generating electrical power. They are made of semiconducting materials. A number of cells connected together can supply electricity to homes, small-scale businesses, communication devices and satellites.Energy generated can be stored in batteries for later use
solar cells advantages
-solar energy is a renweble resource -Solar farms produce no greenhosue gases or pollution -soalr energy can be genrated in remote palces where they don't have electricity
solar cells disadvantages
-Solar farms need to be large scale to produce large amounts of electricity and solar energy is lw density energy.This is expensive to set up. Visual pollution -In many places on Earth sunlight is not a reliable energy resource (there are not enough sunshine-hours to justify the set-up costs) Inefficient
what are solar panels?
-Solar panels transfer energy from sunlight ot the thermal store of the solar panels which is used to het water in the pipes. Solar panels can be used to warm domestic water supplies This can reduce the cost of producing hot water since it is heated partially by the solar panels -Solar furnaces consist of large curved mirrors that focus the sun's rays on to a small area.These can be used to boil water, generating enough steam to turn turbines and generate electricity in a power station
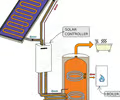
solar panels advantages
-soalr enrgy renewable resource -solar panels produce no greenhosue gases or pollution once they are operating -Solar panels cna cut the cost of enrgy bills for households
solar panel disadvantages
-solar furnaces need to be large scale to produce high temperatures -Energy is still needed to heat water to a higher temperature in domestic households -In many places on Earth sunlight is not a reliable energy resource (the sun doesn't shine regularly enough to justify the set-up costs)
how can deices reduce the enregy they dissipate/waste?
One example is lubrication being used to reduce the friction between moving parts of a machine. This reduces the thermal energy transferred.
For systems that are designed to transfer thermal energy, the wasteful dissipation of thermal energy to the surroundings can also be reduced. This is often done by using thermal insulation, for example, making a kettle from plastic, which is a thermal insulator.
what is conduction
-thermal energy in solids transferred by conduction. Conduction occurs when two solids of different temeprature come in contact with one another, thermal energy is transferred from the hotter object to the cooelr object
what are insualtors and what happens to them wehn theyre heated
non metals are ususally poor conductors known as insulators. Most insulators have packed of trapped air in them which is a poor conductor. Trapping it prevents it from circulating and forming a convection current.For thermal conduction to occur the particles need to be close together so that when they vibrate the vibrations are passed along
So both types of fluid, liquids and gases, are poor conductors of heat.
what are good conductors?
emtals are usually good conductors because htey have a mroe rapid flow of electrons
how do metals transfer energy
as the metal heated the ions/atons and electrons at the hot side vibrate more. The free electrons collide with ions/atoms throughout the metal transfering heat energy from hot to cooler parts.These collisions transfer internal energy until thermal equilibrium is achieved throughout the substance
what is thermal conductivity?
describes how well an object transfers enregy by conduction. Materials with a high thermal conductivity transfer energy between theri particles quickly.
what is thermal insulation
Thermal insulation is the reduction of heat transfer (i.e., the transfer of thermal energy between objects of differing temperature) between objectsin thermal contact or in range of radiative influence.
how to do thermal insualtion
to reduce convection you need to stop teh fluid moving and prevent convection currents from forming. Insulation such as clothes,blankets and foam cavity wall insulation all work by trapping pockets of air. The air cant mvoe so the enrgy has to conduct very slowly though the pockets of air as well as the material in betweeen both of which have low thermal conductivity
what are good emitters
good emitters re also good absorbers. Balck bodeis with dull texture
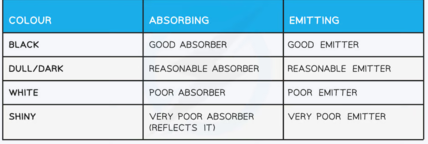
what are bad emitters/absorbers?
Shiny ,smooth objects reflect thermal radiation and so absorb very littleT.hey also emit very little, though, and so take longer to cool down
hwo to use lesli cube to investigate emission of thermal radiation
1) the Lesli cube is placed on a heat-proof mat
2) Boil water in a kettle and fill with boiling water
3) Wait for cube to warm up then hold a thermometer against each of the 4 vertical surfaces. Tehy should be the same temp
4) Hald an infrared/ thermal radiation detector at the set distance form one surface and record the amount of IR radiation detected
5) Repeat this measurement for each of the cubes vertical faces. make sure to position teh detector at the same distane from the cube each time
6) You should find you detect more infrared radiaiton from black surface and matt surfaces.
7) Repeat experiemnt
hwo to compare obsorbers using leslie cube
one way is to stick ball bearings to the back of two different surfaces with wax and see which one falls off first when the surfaces are placed equal distances from a bunsen burner
how is energy transfered in conduction,convection and radiation?
-Conduction and convection are the eerngy transfersthat involve the transfer of energy by particles
-Thermal radiation is the transfer of energy by heating by infrared electromagnetic waves
-the bigger the temp difference the faster energy is transferred between teh thermal energy stores of body to surroudngis
what is convection?
Convection occurs when more enregetic particles/moelcules in a fluid with high thermal energy (hotter region) move to an area with low thermal energy (cooler region)
liquids and gases can carry thermal energy quickly if they are free to circulate. Thermal energy in fluids is transferred by convection.
what happens durign/ in covection current?
when part of a fluid is heated it expands and becomes less dense. It therefore rises up to less dense areas in the fluid. Denser colder fluid falls down to take its place.Eventually the hot liquid/gas cools, contracts and sinks back down again
The resulting motion is called a convection current
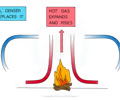
what ahppens when liquid or gas is cooeld
The molecules move together, making the liquid/gas contract
This makes the hot liquid/gas more dense than the surroundings
The cold liquid/gas falls, so that warmer liquid or gas can move into the space created
The warmer liquid or gas gets cooled and also contracts and falls down
The resulting motion is called a convection current
hwo to demonstarte convection currents
1) take a beaker of cold water and placing a few crystals of potassium permanganate in it, to one side, as shown in the diagram above
2) When the water is heated at that side, the potassium permanganate will dissolve in the heated water and rise along with the warmed water forming a birght purple solution
4) This purple solution is carried throguht he water by convection and so revealing the convection current
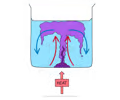
what is immersion heater? see pg 44 of cgp
1) Energy is transfered from the heater coils to the thermal energy store of the water by conduction
2) The particles near the the coils get mreo energy so they start moving around faster. They expand and beocme less dense
3) Hotter water rises above denser cooelr air
4) As hot water rises it displaces the colder water makign it sink towards heater coils
5) This cold water is then ehated by the cpils and rises. You end up with a convection cirrent above the heater only. Water below it starts cols bcs very little conduction.
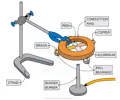
how to experiment conduction?
1) Ball bearings can be stuck to each of the emtal strips and equal distance from the centre, using a small amount of wax
2) The strips should then be turned upside down and the centre or strip with no bearings heated gently using a candle, so that each of the strips is heated at the point where they meet
3) Over time energy is transferred along to the ball bearing by conduction the wax will melt and the ball bearing will drop
4) By timing how long this takes for each of the strips, their relative thermal conductivities can be determined or if one metal bar used with beads at differnt distances it can show conduction.
where does conduction,convection and radiation happen?
-Conduction; by direct contact between the hot object and cold object
-Convection: from the surface of the hot object to the air directly above it
-Radiation: from the sides of the hot object in all directions to the surrounding air
what are biofuels?
fuels made from plant or naimlas matter eg wood,alcohol from sugar cane,methane gas from rottign waste. Stores chemical energy.