Self - Concept Physical Self
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is the self-concept?
- How we think and feel about ourselves, our attributes, and our abilities
- Traits, Beliefs, roles, identities, and descriptions
- Important to our psychological and physical well-being
What is identity?
• Unique and distinctive self -descriptions situated in the context of a particular role
• Integral component of self -concept
• Developed through similar evaluative and
comparative processes to self -concept
• Identity salience leads to behavioural choices that are in accordance with the expectations attached to that identity
What is self-esteem?
• The evaluative or affective consequence of one's self concept
• The extent to which one feels positive or negative about one's self -concept
• Contingent on positive evaluations of self
What is self-compassion?
• Kind, caring and non -judgmental attitude towards the self
• Unconditional positive self -regard
• Response to negative self -evaluation
What are the three spectrums of self-compassion?
- Self-kindness vs. Self-Judgement
- Mindfulness vs. Overidentification
- Common Humanity vs. Isolation
What is self-esteem and exercise?
- Historically considered the most important psychological outcome
- Meta- analysis of the effects of exercise interventions on adults' global self - esteem found consistent but small effects
- it appears that the benefits of exercise for GSE are overstated in the literature
- Frequency, intensity, duration, type, and length of program were not significant moderators
- Increases in self - esteem were 2x larger when physical fitness improved
- Consistent findings in young, middle - aged, and older adults
What are objective changes?
in fitness may not be necessary for self - esteem to improve
What are subjective perceptions?
Subjective perceptions (e.g., physical competence) are likely more critical
What is self-compassion and Exercise?
- Linked to intrinsic motivation, external and introjected motivation
- Self - compassion predicts sustained exercise behaviour
- Promotes exercise goal reengagement after an exercise setback
What is the self-concept model?
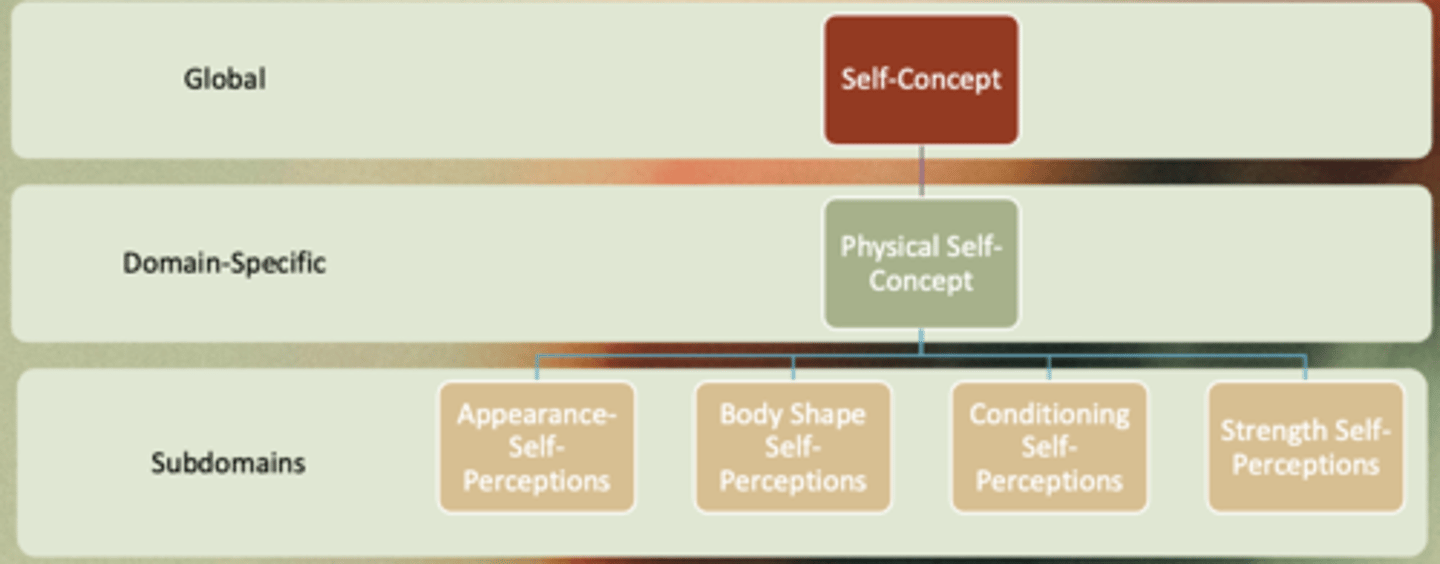
What is physical self-concept and exercise?
- Meta- analysis found positive relationship between exercise and positive physical self - concept
- Subdomains such as perceived competence and perceived fitness were comparably related to exercise as overall physical self - concept
- Limited to observational studies
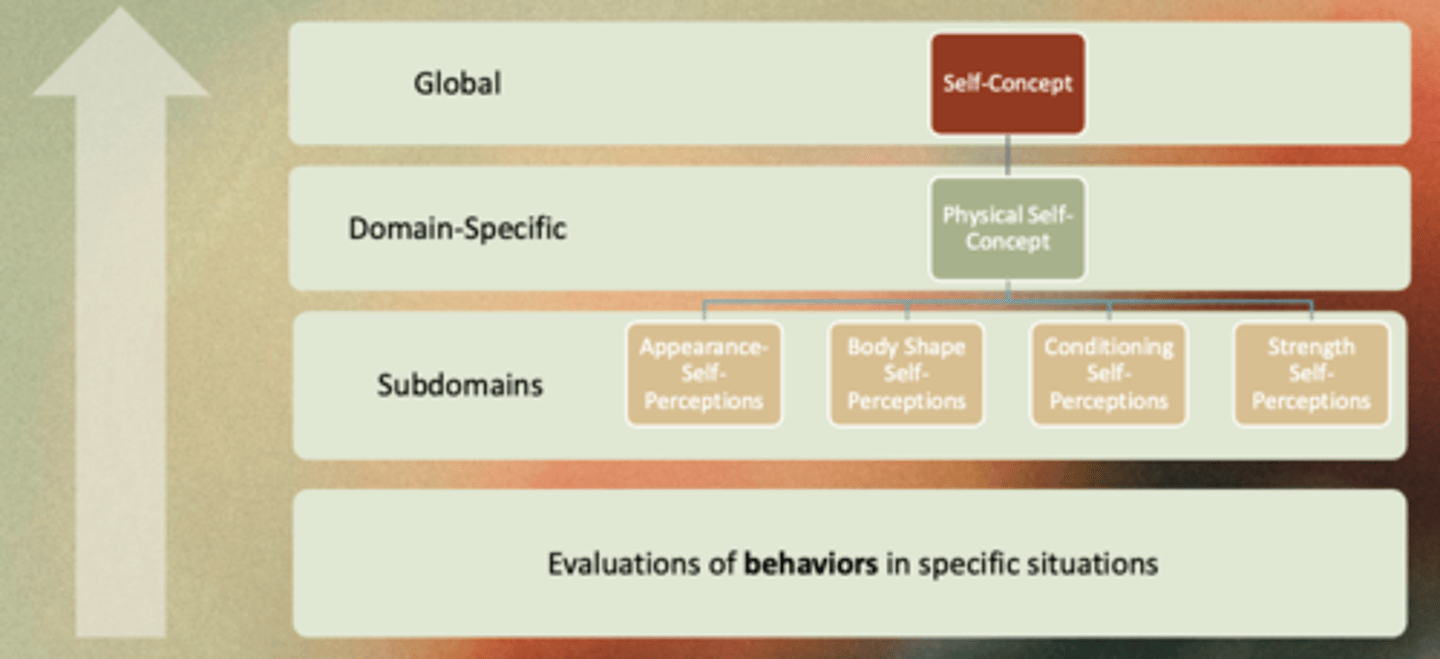
What is the bottom-up approach - Skill development hypothesis?
Exercise impacts global self - esteem by affecting domain - specific aspects of the self
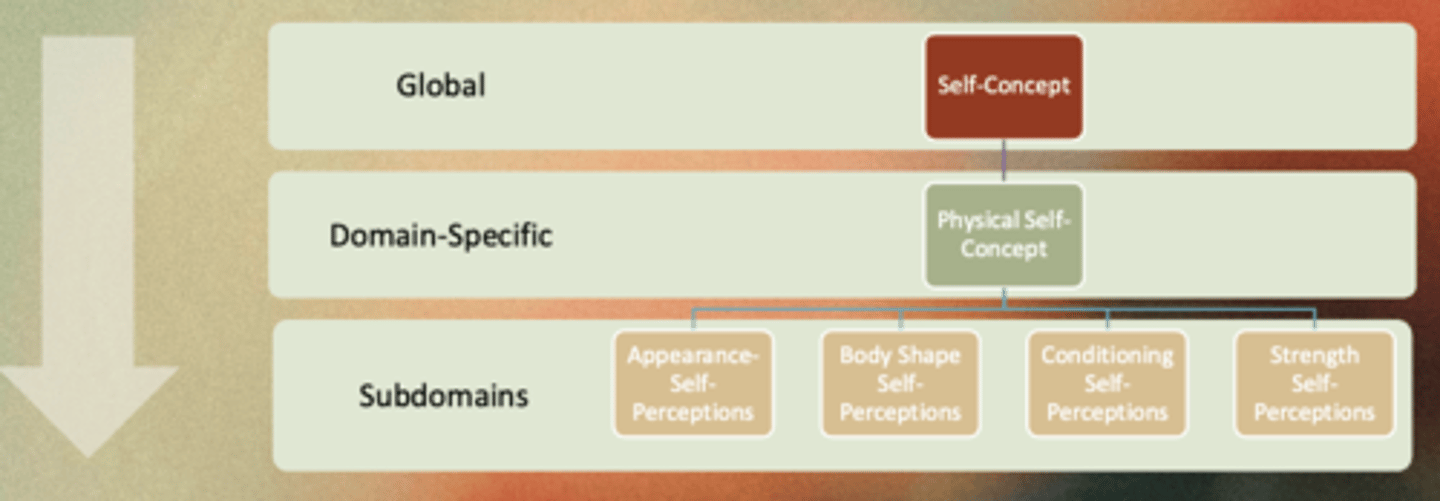
What is the top-down approach - skill - enhancement hypothesis?
Global aspects of the self influence specific self - perceptions which impact what individuals are motivated to engage in (e.g., exercise)
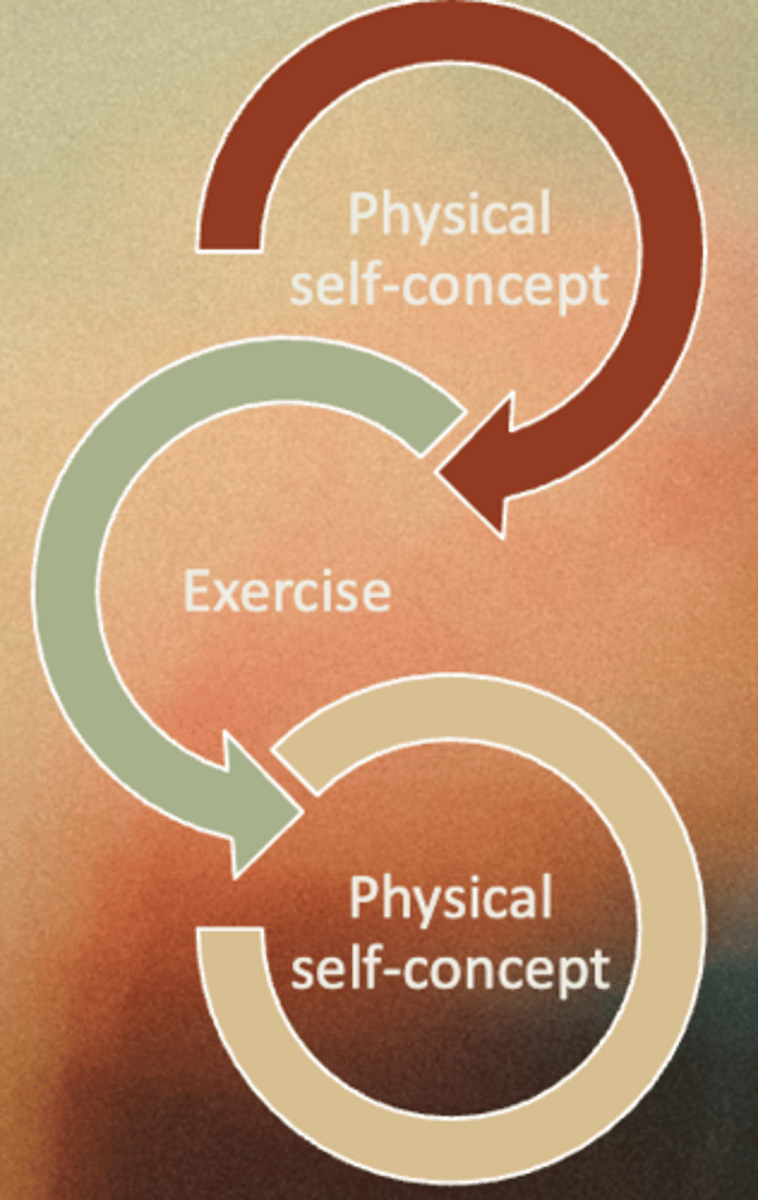
What is the reciprocal effect approach?
What type of construct is body image? What are the 4 key factors?
• Perceptual
• Cognitive
• Affective
• Behavioural
What is body image?
• Captures both the body's appearance and function
• Positive and negative facets
What are some influencing factors for body image?
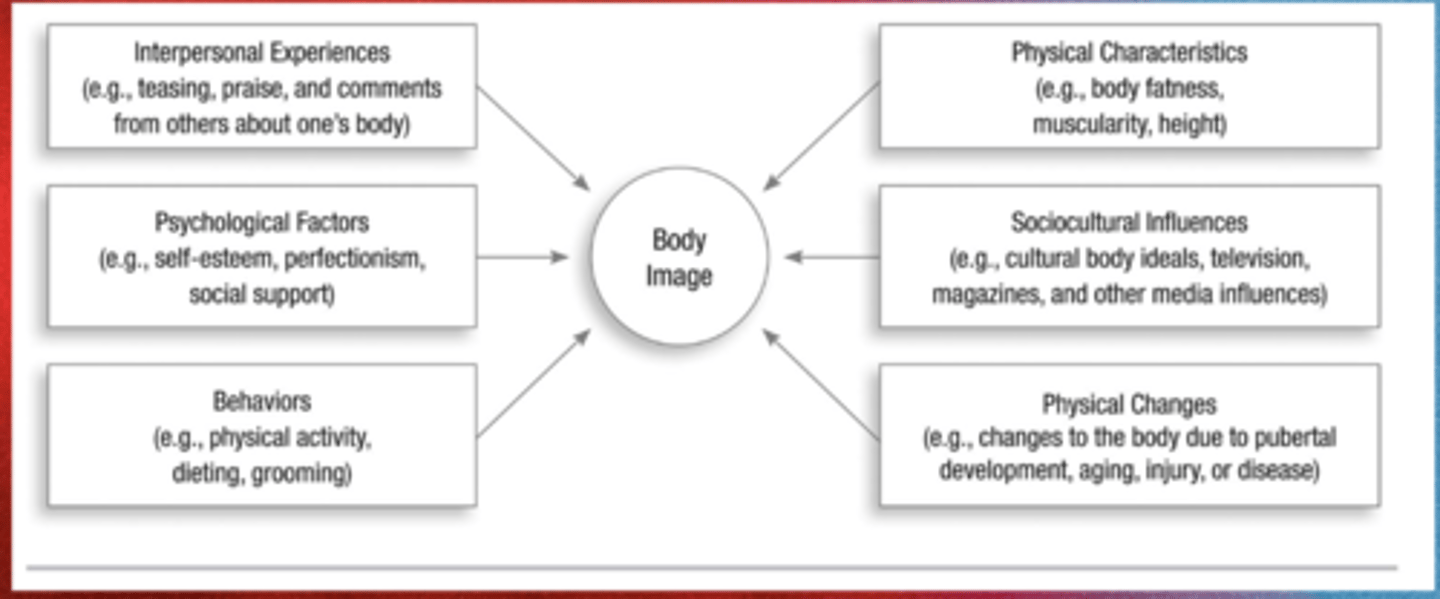
How does body image relate to exercise?
Correlate, predictor and outcome of exercise determinants and behaviour
- Exercise can lead to significant improvements in body image
What are the effects of exercise behaviour on body image?
• Strongest effects for adults
• Stronger effects for higher - weight participants
• Equal effects for men and women (Basset - Gunter et al., 2017)
• Stronger effects for higher frequency and moderate to vigorous intensity
Exercise behaviour → Body Image
• Improvements in body image regardless of change in fitness or body composition (Martin Ginis et al., 2014; Campbell & Hausenblas , 2009).
• No effect of exercise type (e.g., aerobic, resistance, etc.) or duration - acute effects possible (LePage & Crowther, 2010)
• Increased self - efficacy possible - increase in functional perceptions of what the body can do
What is the best type of exercise for body image?
Mind- body connected type exercise (e.g., yoga, belly dancing) have been associated specifically with higher positive body image (body appreciation, body pride)
• Exercise can be used to promote embodiment ("positive body connection and comfort, embodied agency and passion, and attuned self- care"
Competitive movement can:
• Capitalize on mind - body integration (i.e., flow states)
• Devote considerable effort to developing skills, strength, stamina
• Promote an internally oriented body experience
How does body image influence exercise?
• Body image concerns often cited as motive to start exercising
• Not effective for adherence
• Exercising primarily for appearance vs health motives associated with worse body image and mental health (Hurst et al., 2017)
• Fitspiration linked with worsened mood and body dissatisfaction
• Not predictive of exercise behavior
What can body image concerns lead to?
Body image concerns lead to avoidance of physique - salient exercise contexts
- Revealing exercise attire
- Physique- focused verbal cues
- Mirrors and "fitspiration" images
Physique- evaluative exercise contexts lead to psychophysiological consequences in inactive women
How does the sporting context impact body image?
• The girls sport context is considered to be physique - salient, highly evaluative towards the body, and perpetuates body and weight ideals for girls
• Outside of sport, appearance - based body talk (fat talk, teasing, compliments) reinforce attention towards the body, promotes objectification and social comparisons, and increases negative body image
• Weight and body talk is the norm is girls sport
• Maladaptive declines in body emotions over time in girl athletes
• Poor body image reduces sport enjoyment and increases risk of dropout among girl athletes
• Poor body image increases risk of mental illness, including disordered eating and depressive symptoms