week 14 physics- ch. 15 CT of head, cerebral vessels, neck and spine
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
neuroradiology
The subspecialty of radiology that deals with the central nervous system (CNS) and conditions affecting the head and neck is:
cerebral infarction
What pathologic condition describes the result of a loss of adequate blood supply to a portion of the brain?
chronic subdural hematoma
Which of the following is the most common condition evaluated by repeated computed tomographic head scanning?
metastasis
Computed tomography (CT) provides rapid information about each of the following traumatic injuries except:
Select one:
a. contusions.
b. fractures.
c. hematomas.
d. metastasis.
coronal
Orbital computed tomographic images should always be available in which plane because of the pyramidal shape of the bony orbit?
acute cerebral infarction
An important use of computed tomographic angiography of the head is in the evaluation of:
polyps
Indications for a computed tomographic scan of the neck include all of the following except:
Select one:
a. carotid stenosis.
b. goiter.
c. mass.
d. polyps.
strokes
Indications for a computed tomographic scan of the spine include all of the following except:
Select one:
a. disk herniations.
b. osteomyelitis.
c. strokes.
d. spondylolisthesis.
computed tomographic scan of the head without contrast.
To ensure that no life-threatening condition exists, the first examination performed should be:
axial
Image acquisition is primarily obtained in the ___________ plane.
coronal
Which images are particularly useful for assessing bone when the plane of the bone runs parallel to the axial slice?
ventricles
Coronal images are valuable for scans of the following except:
Select one:
a. top of the cranial vault.
b. roof of the orbit.
c. skull base.
d. ventricles.
patient should not eat 6 hours prior to the exam.
Preparation of the patient for a computed tomographic scan of the head or spine should include all of the following except:
Select one:
a. metallic objects should be removed.
b. explanation of contrast media (if indicated).
c. patient should not eat 6 hours prior to the exam.
d. patient should be made comfortable.
OML
In adults, what is the preferred scanning line when imaging the head?
transverse
The __________ plane is still the most used plane for image interpretation of the skull and its contents.
computed tomographic perfusion
Which of the following is a form of computed tomographic angiography used in suspected acute brain infarction to determine the amount of brain tissue at risk for permanent damage?
thin
Studies requiring reformatted images are acquired with ________ slices.
512'512
The matrix size on most of the current equipment is:
lung
All of the following are algorithms used for the brain, neck, and spine except:
Select one:
a. bone.
b. detail.
c. lung.
d. standard.
6-8
Because enhancement persists for hours, at least ___________ hours should elapse after a contrasted examination before an unenhanced scan is obtained.
2
the nasal septum is labeled:
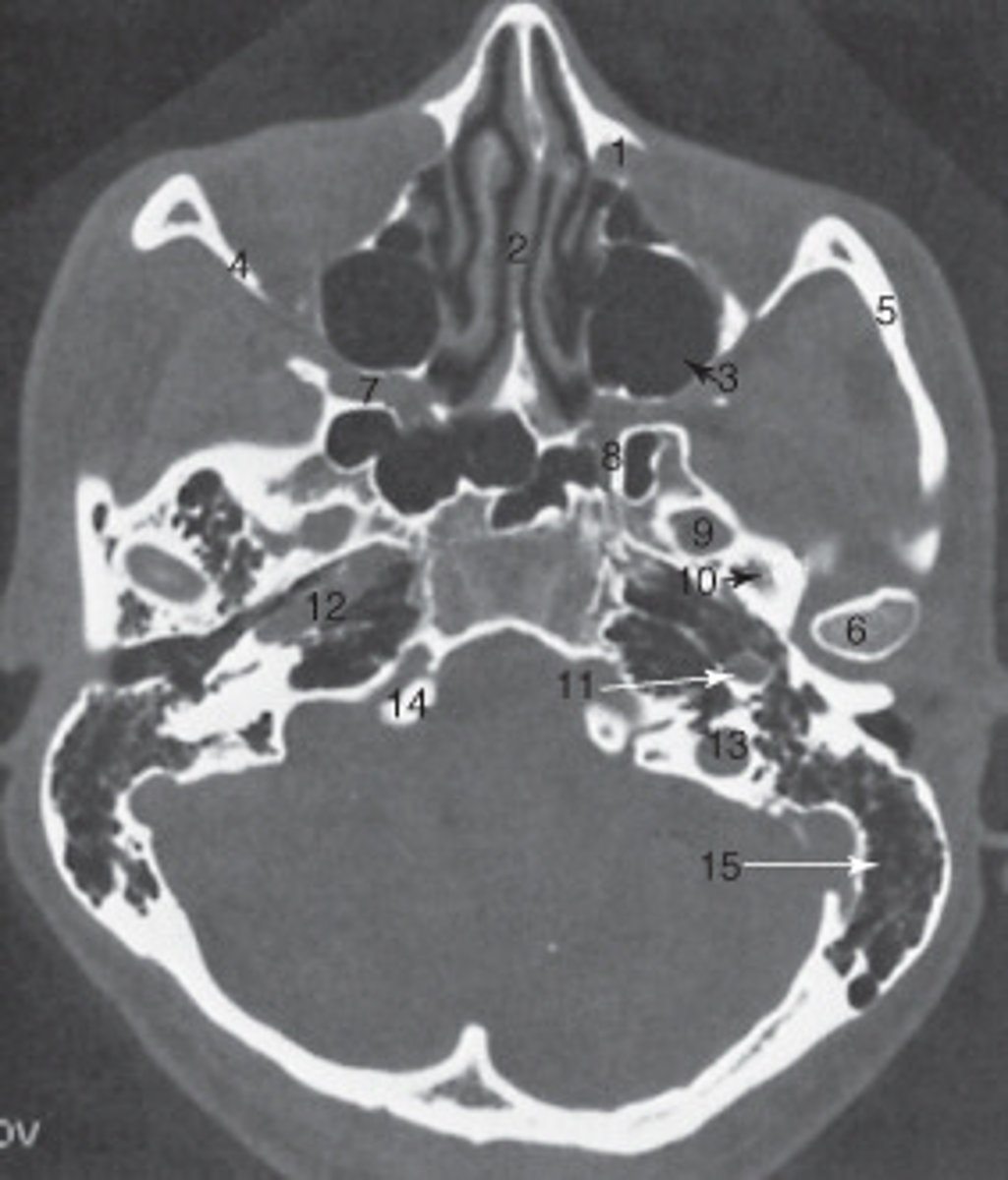
15
the mastoid air cells are labeled:
manidubular condyle
the structure labeled 6 is the:
zygomatic arch
the structure labeled 5 is the:
2
the ethmoid sinuses are labeled:
9
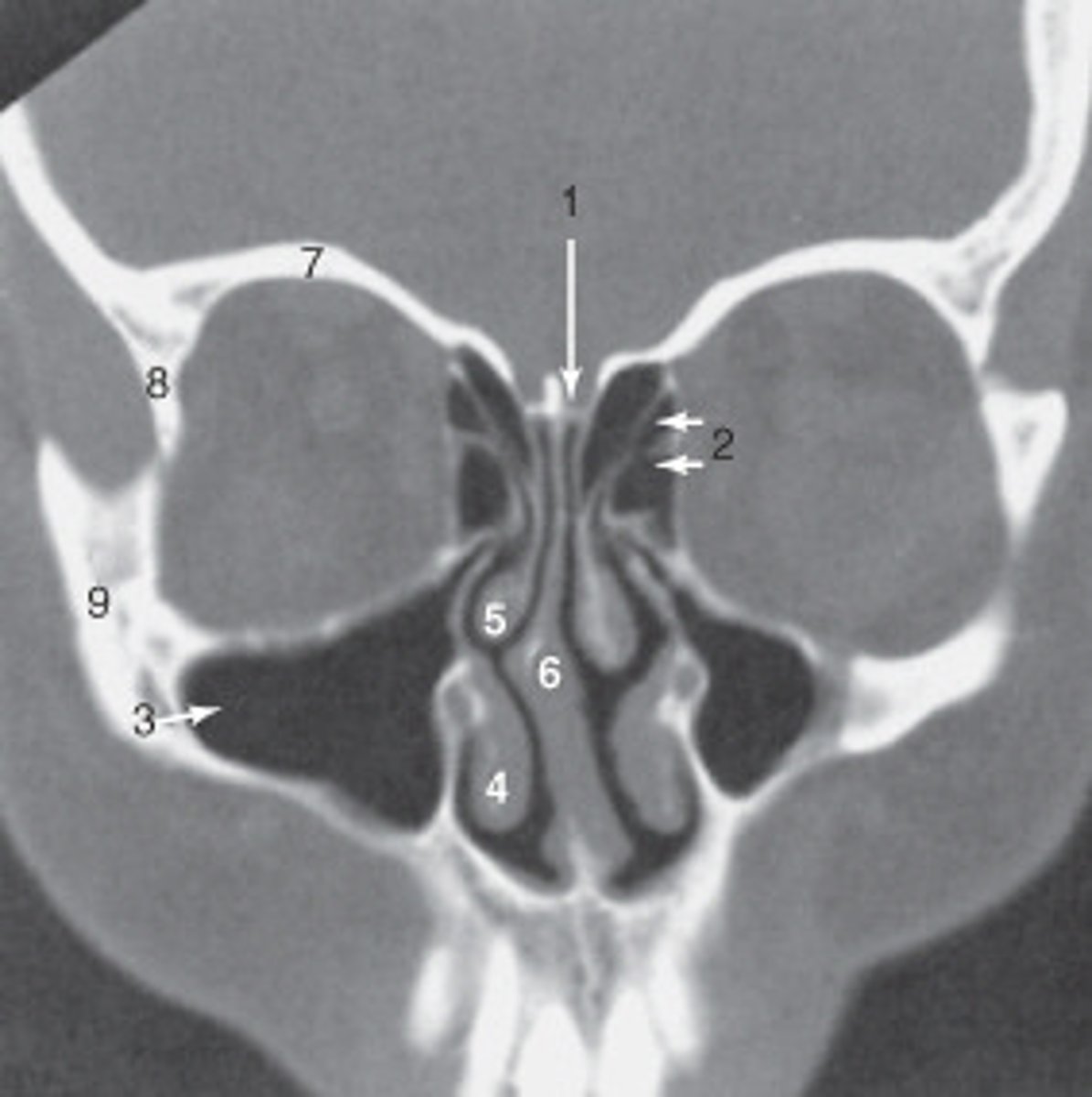
the zygoma is labeled:
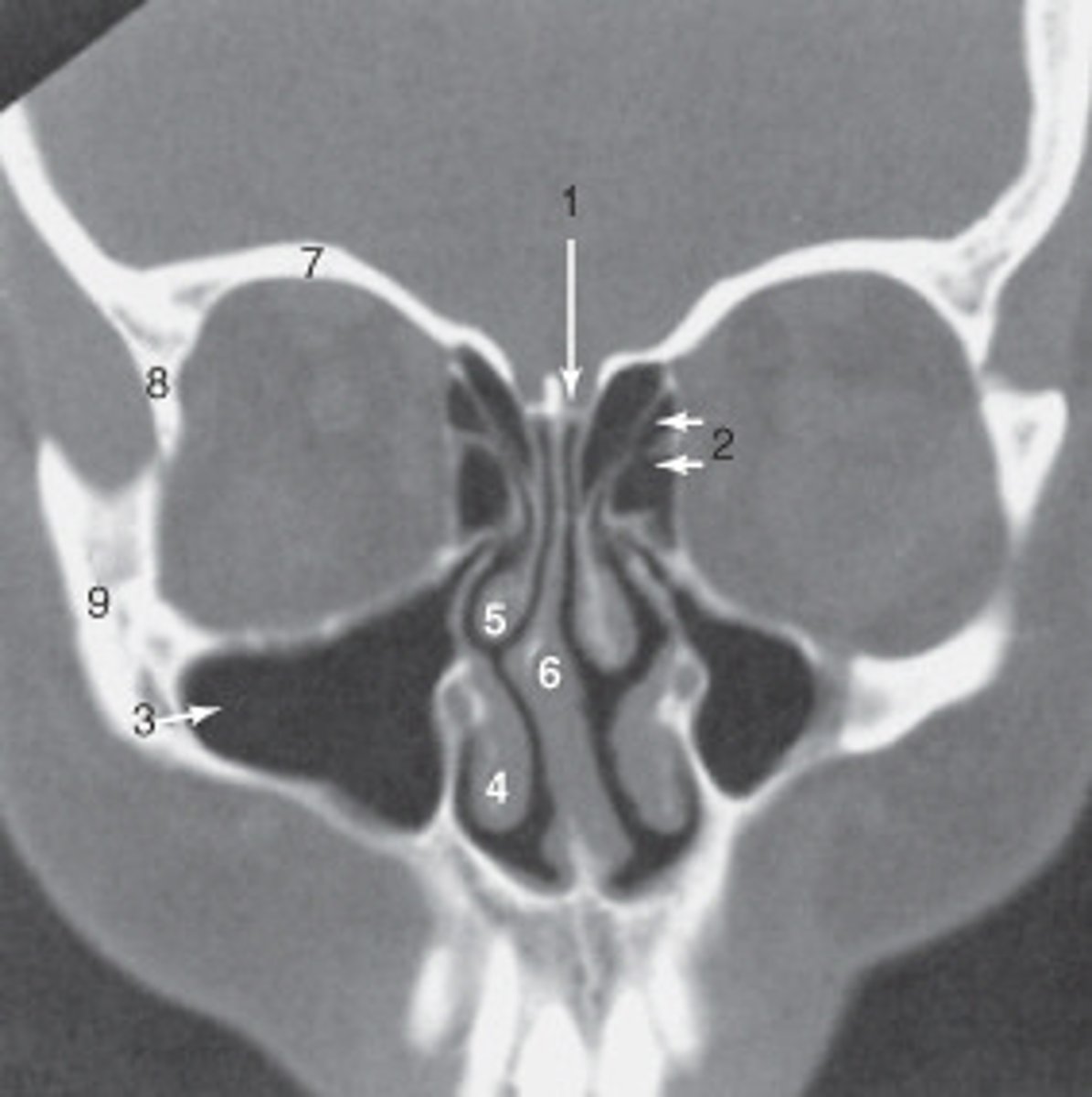
8
the lateral orbital wall is labeled:
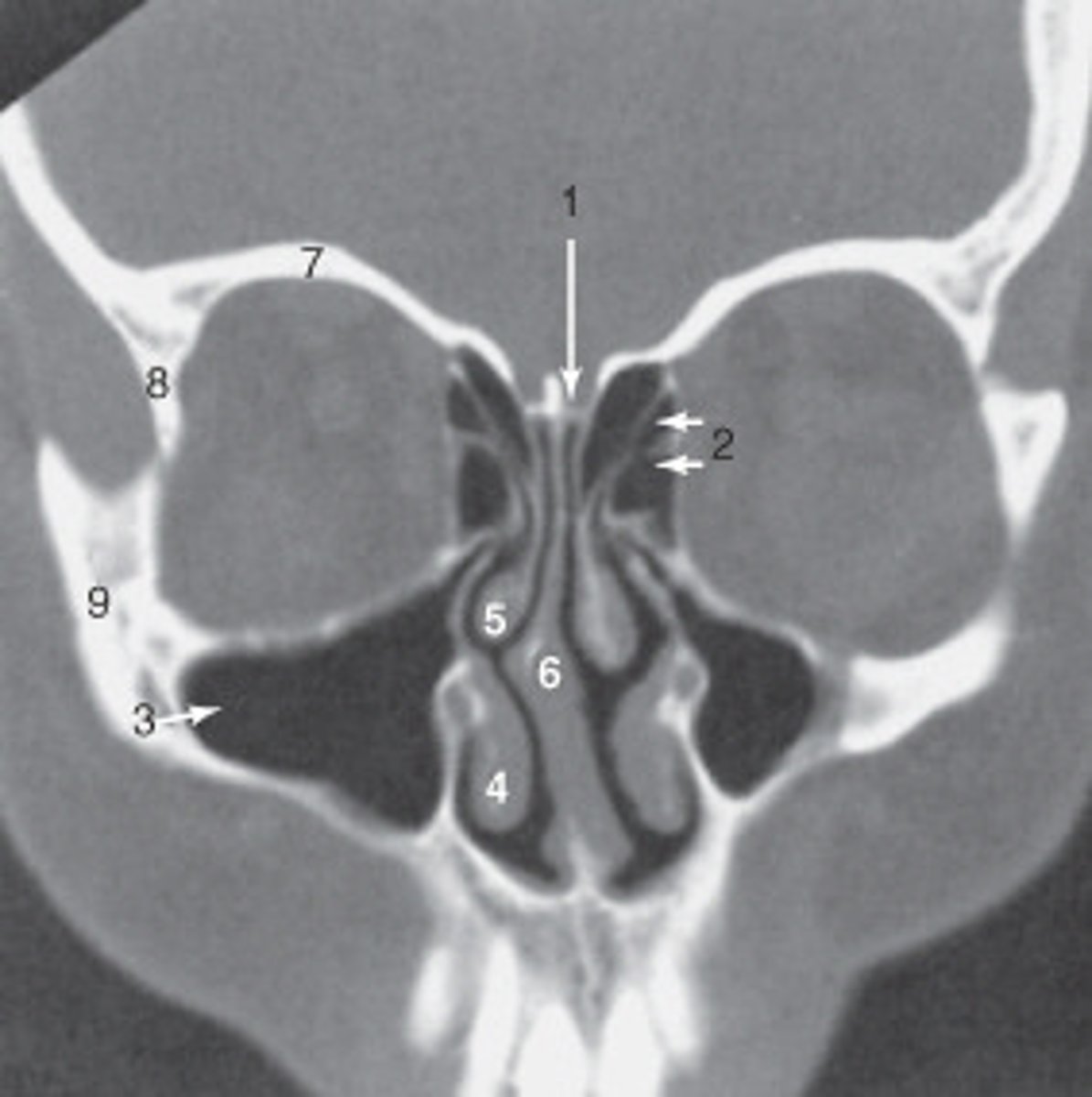
maxillary sinus
the structure labeled 3 is the:
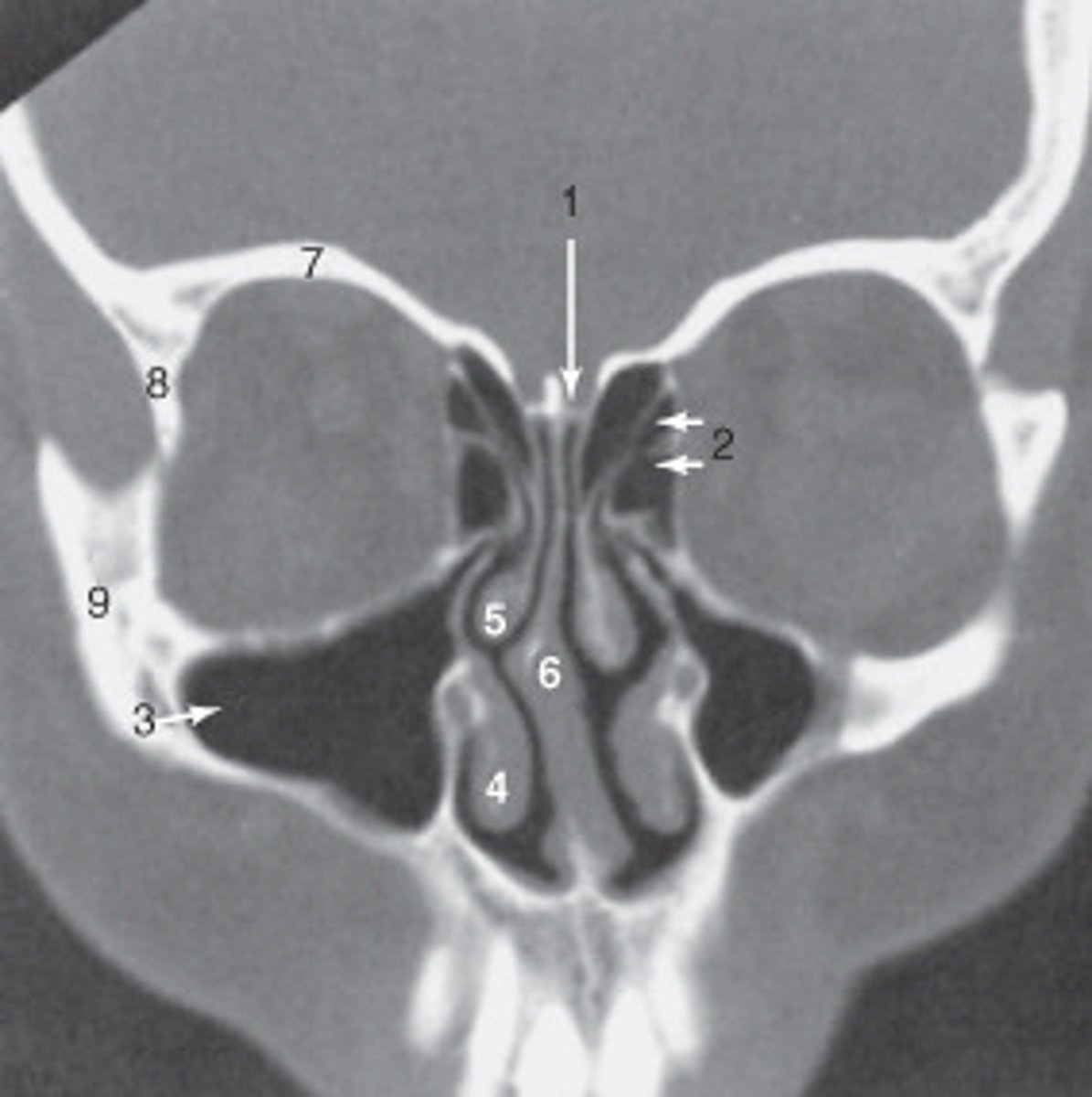
roof of the orbit
the structure labeled 7 is the:
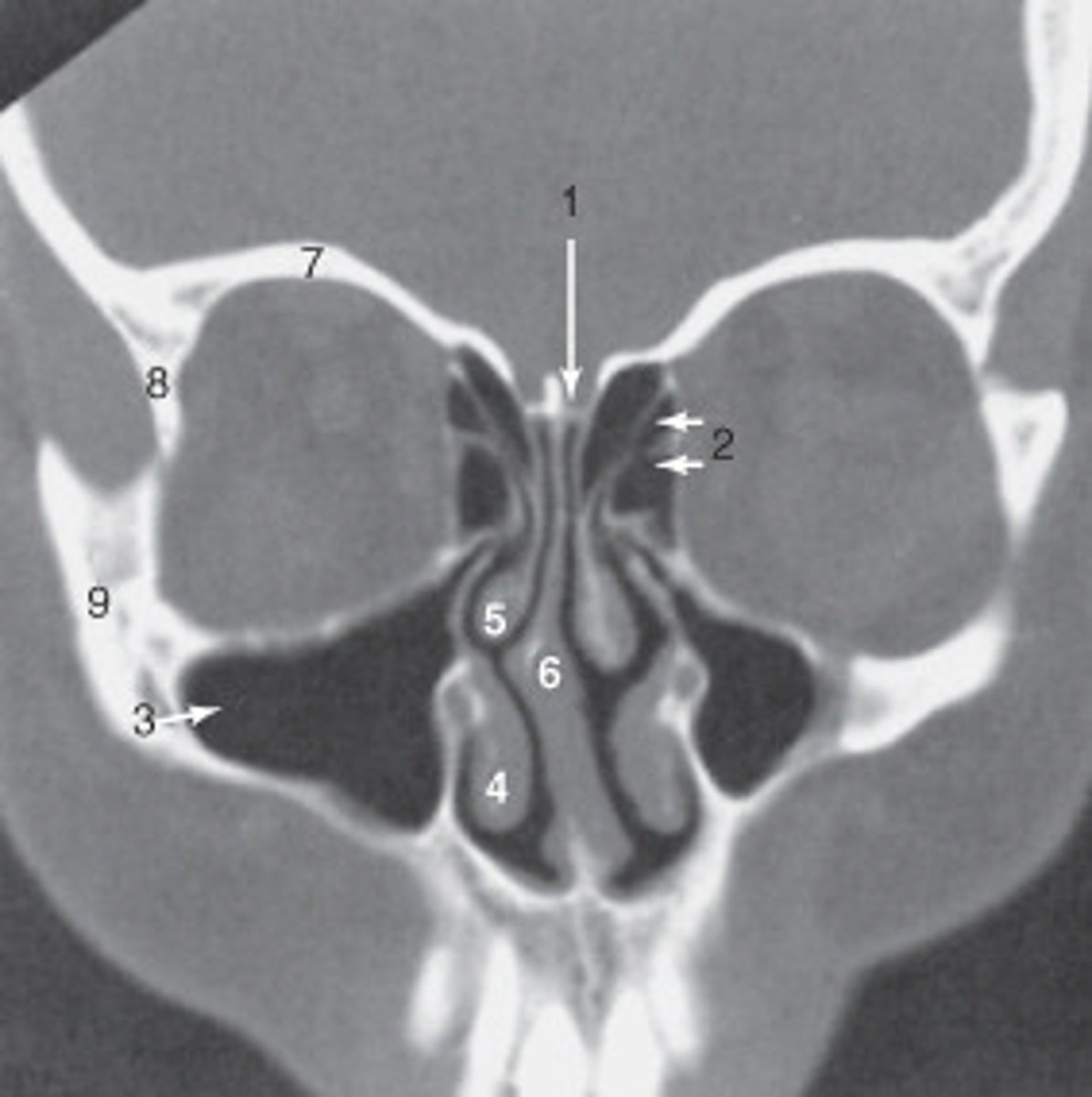
8
The anterior (frontal) horn of the lateral ventricle is labeled as:
1
The sphenoid sinus is labeled:
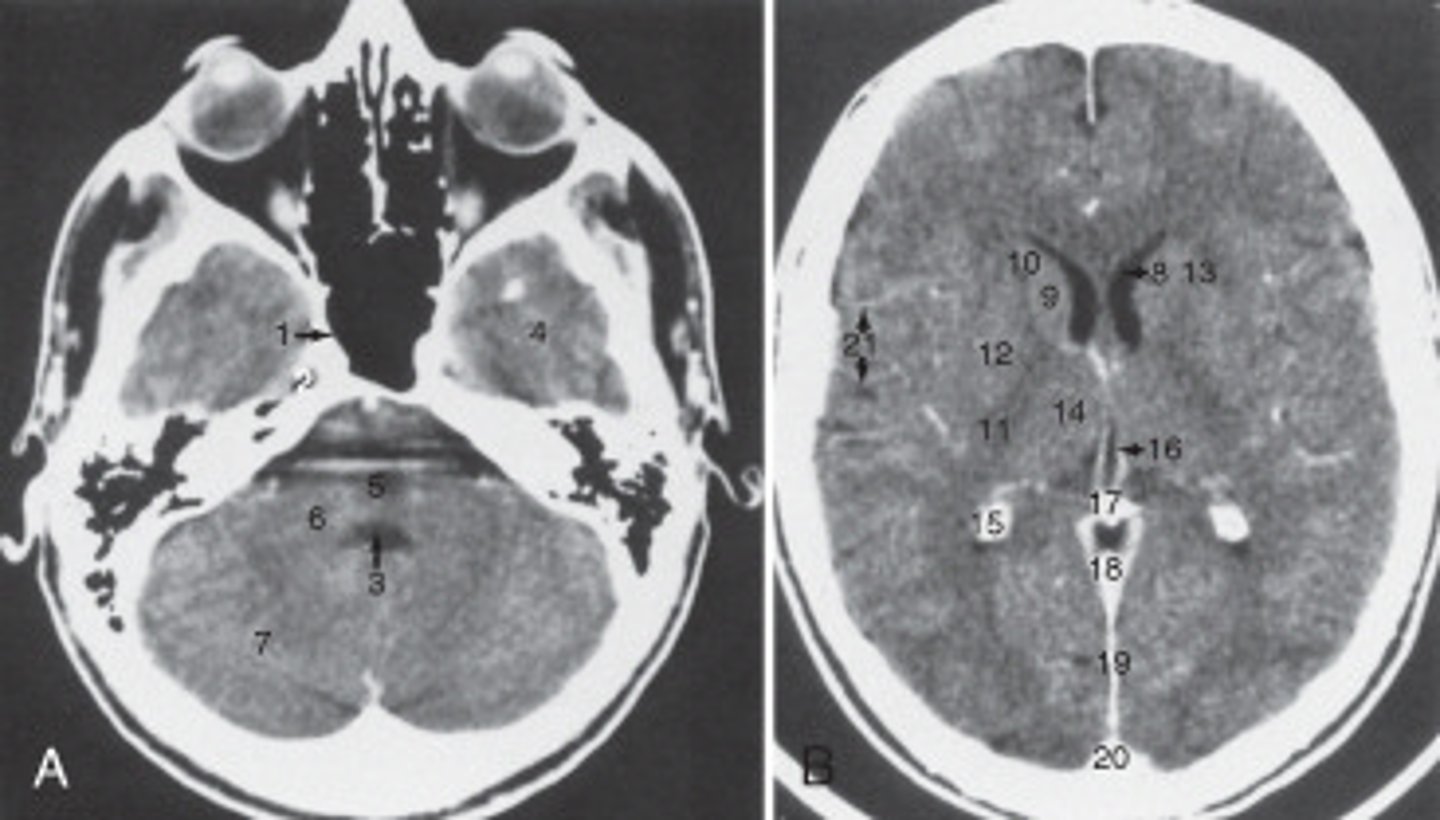
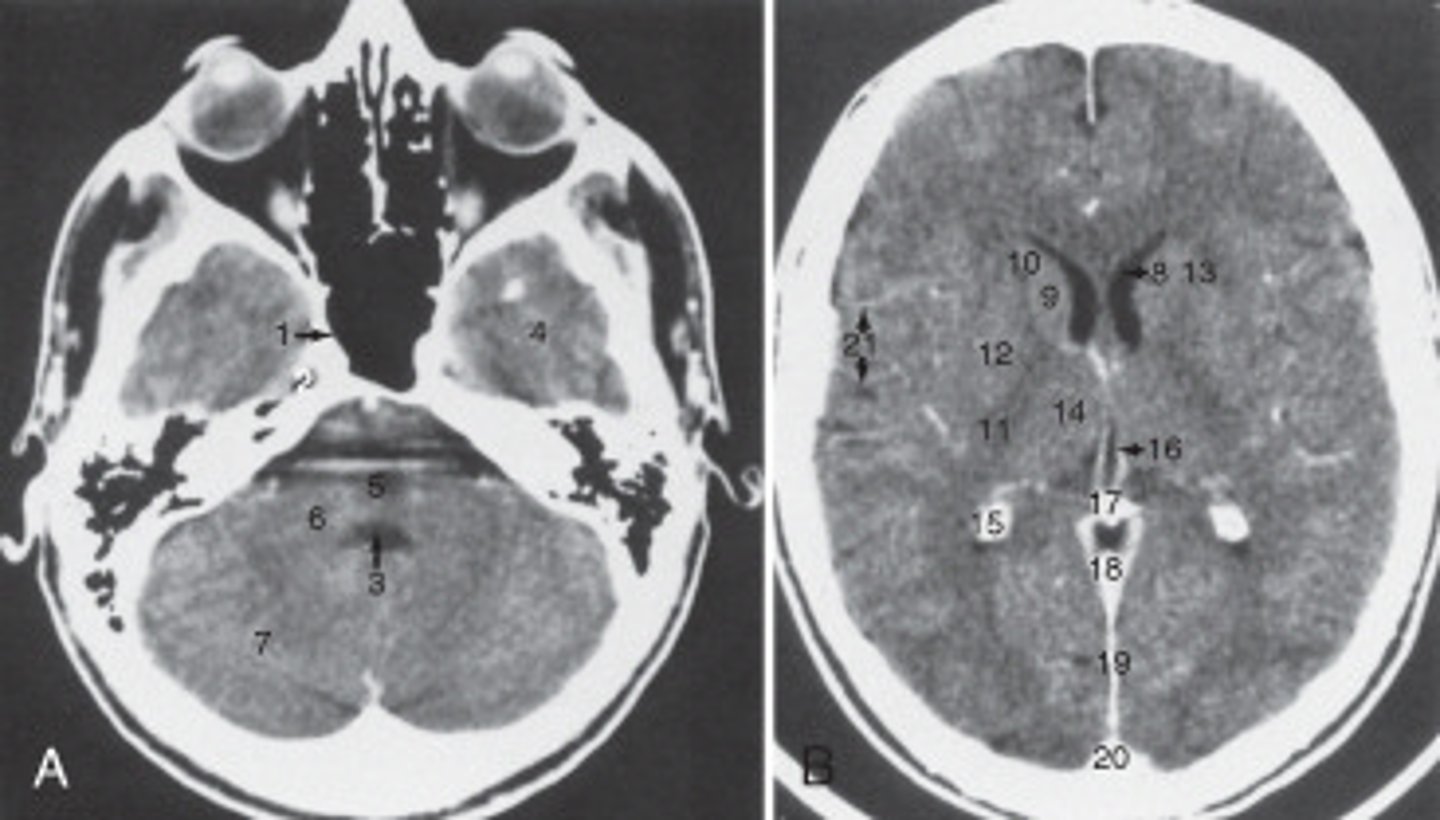
14
The thalamus is labeled:
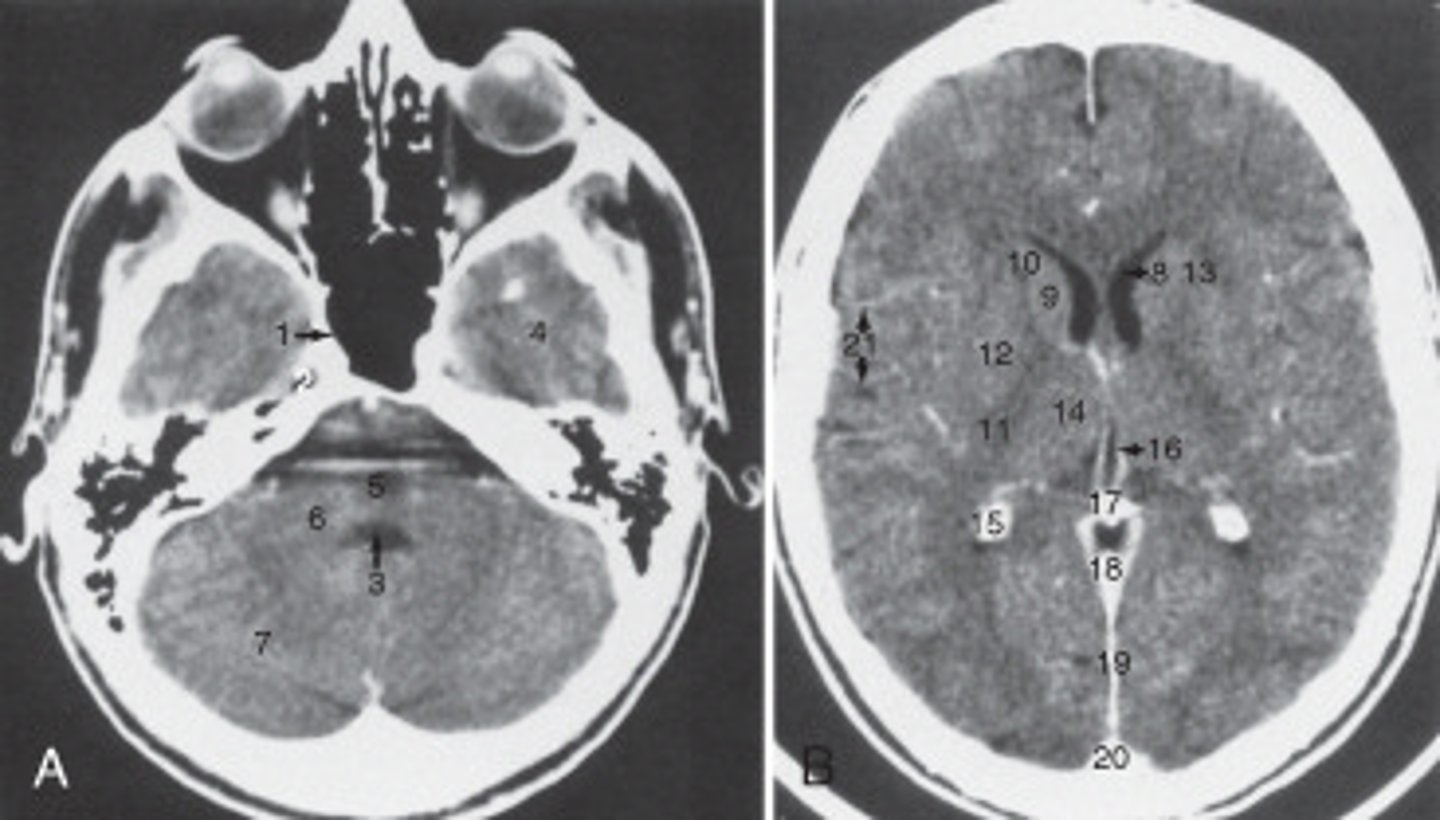
19
the fall cerebri is labeled:
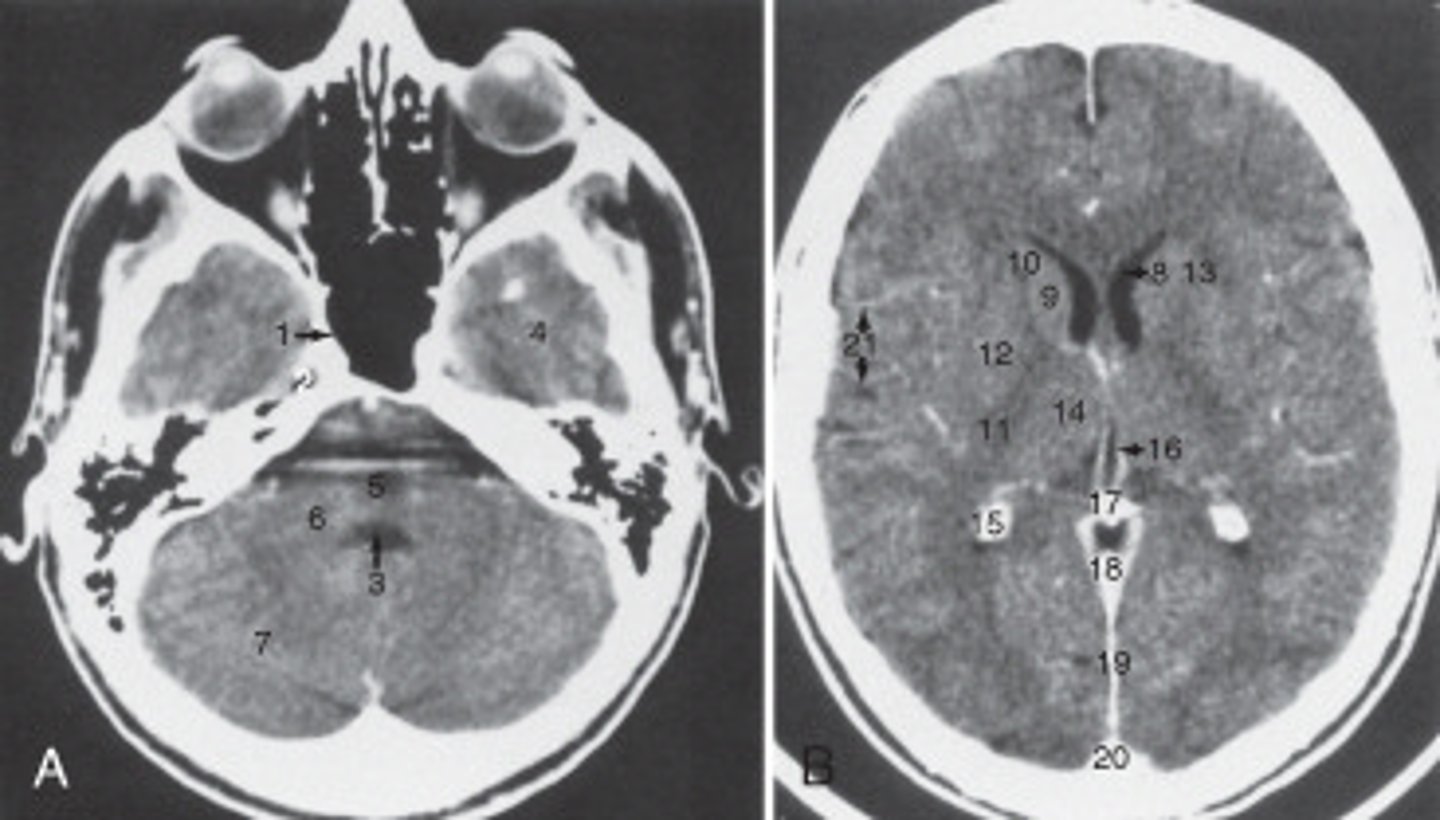
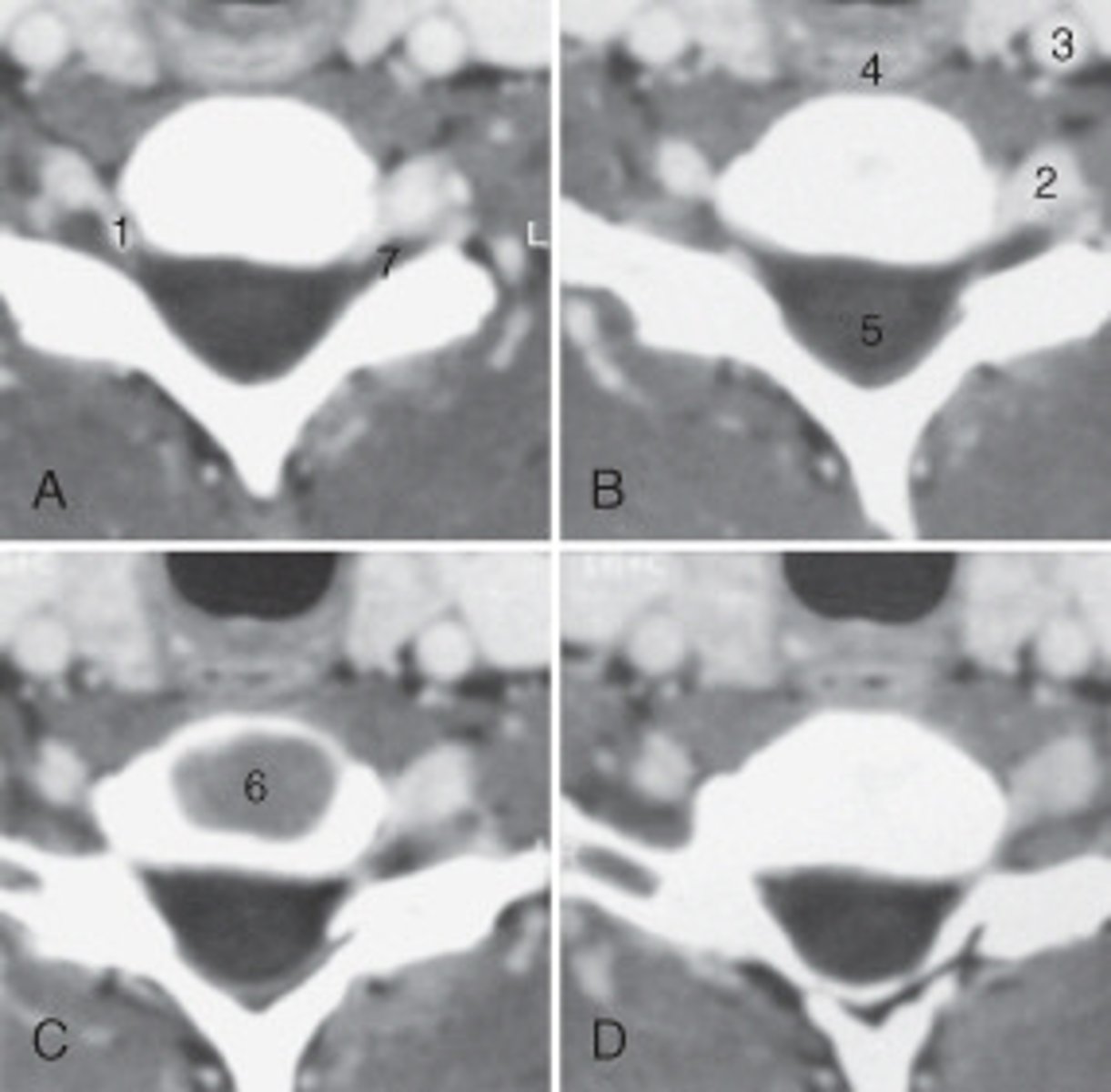
calcified choroid plexus
The structure labeled 15 is the:
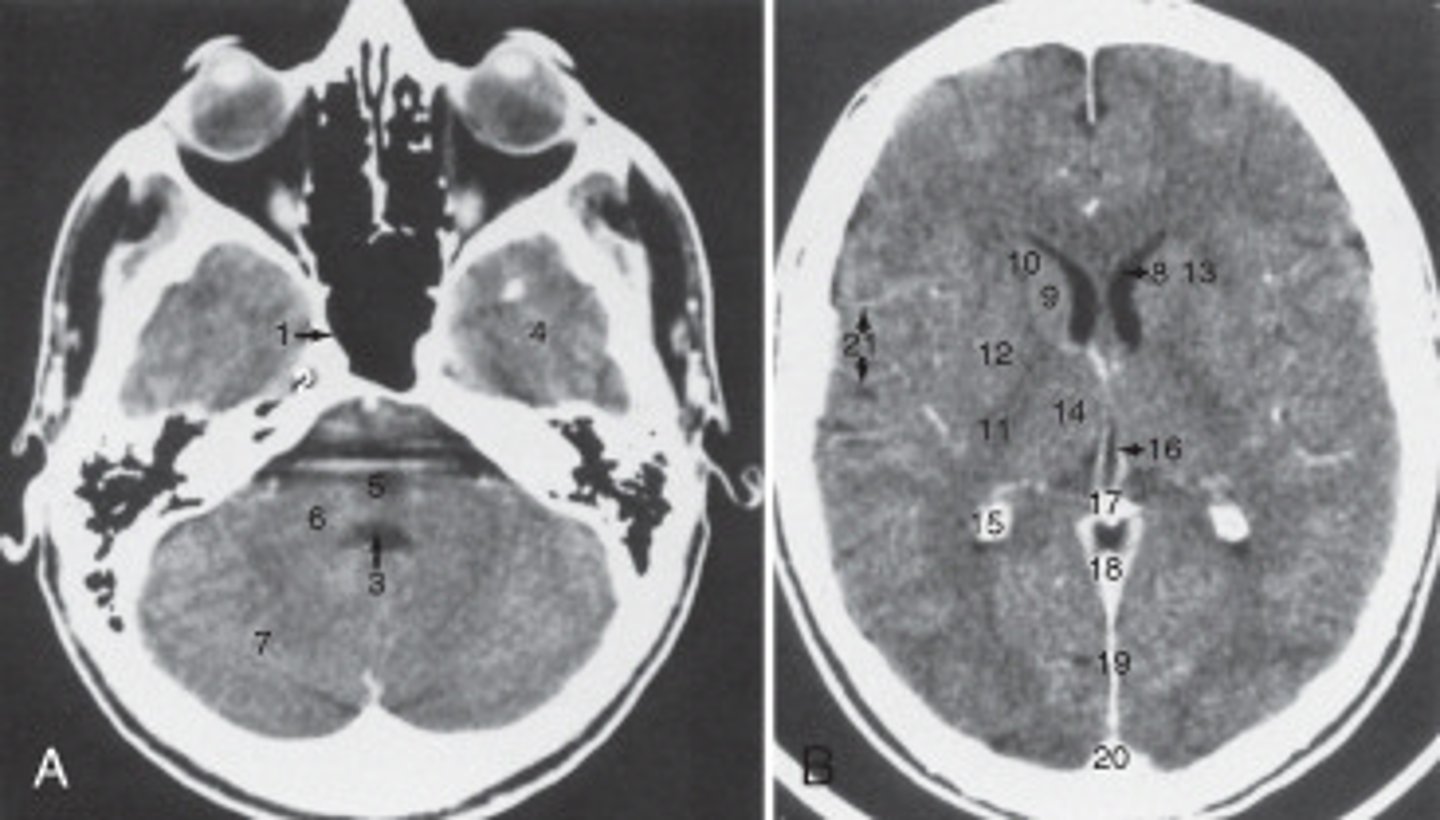
fourth ventricle
The structure labeled 3 is the:
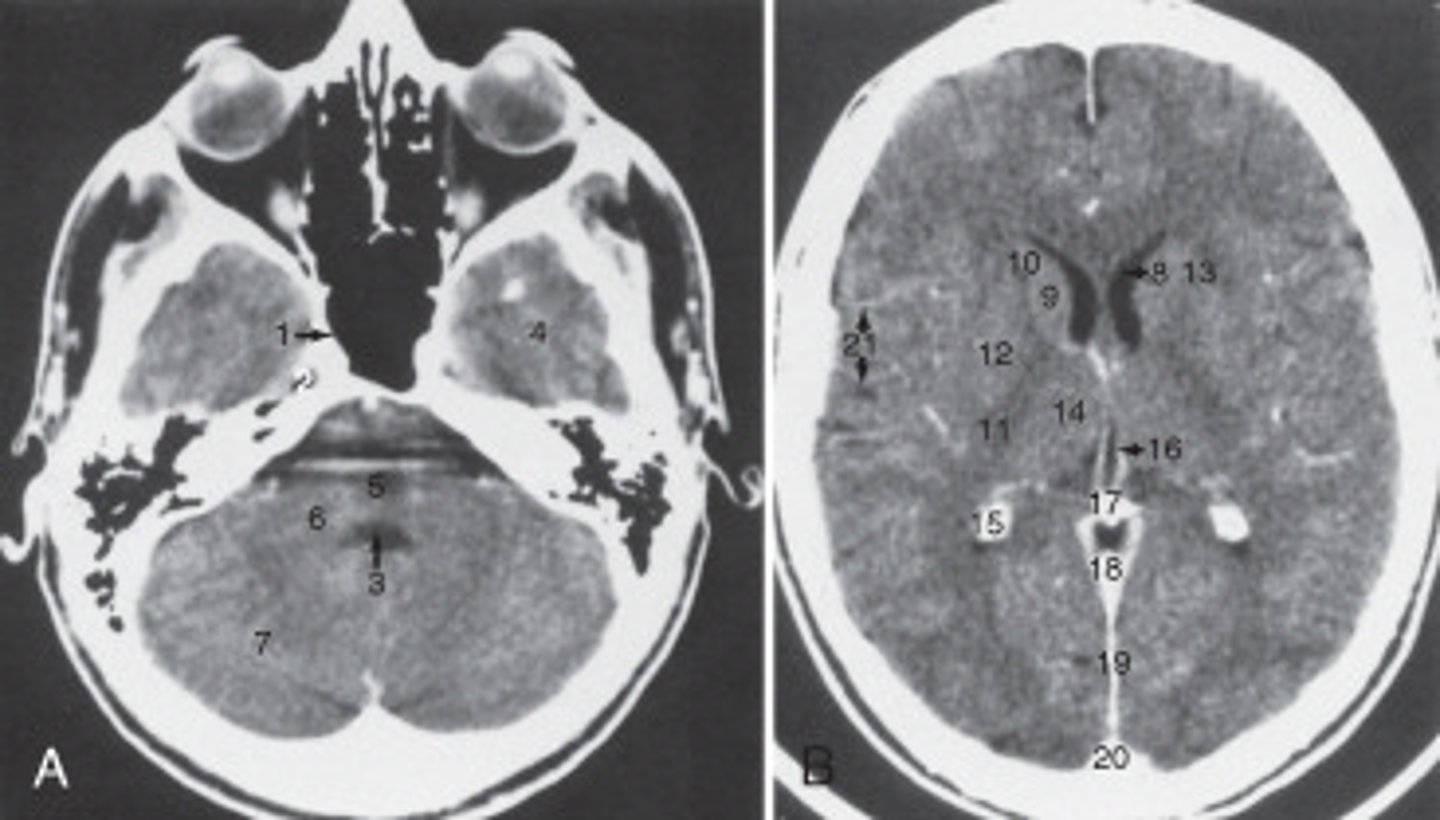
cerebellar hemisphere
The structure labeled as 7 is the:
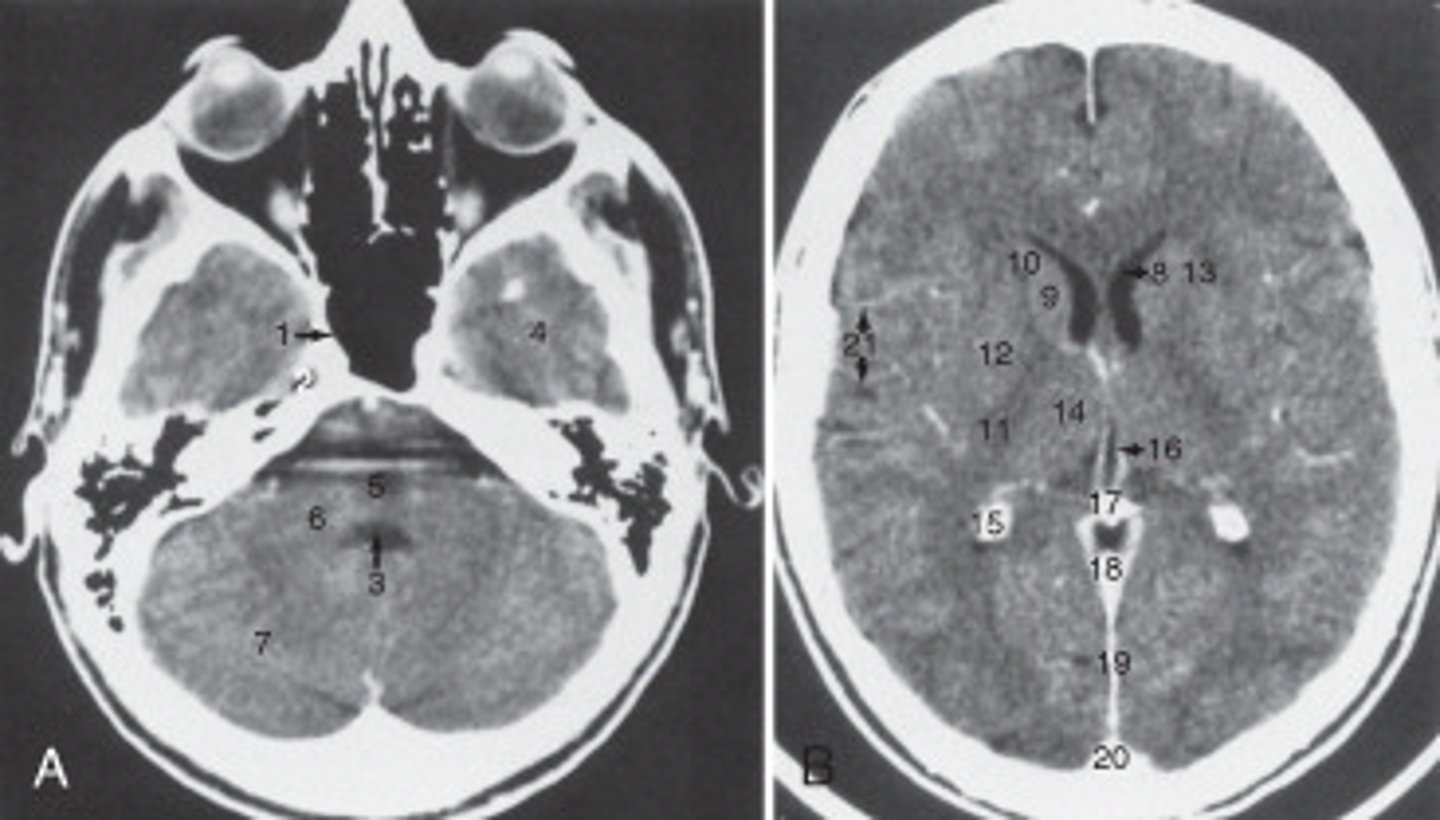
7
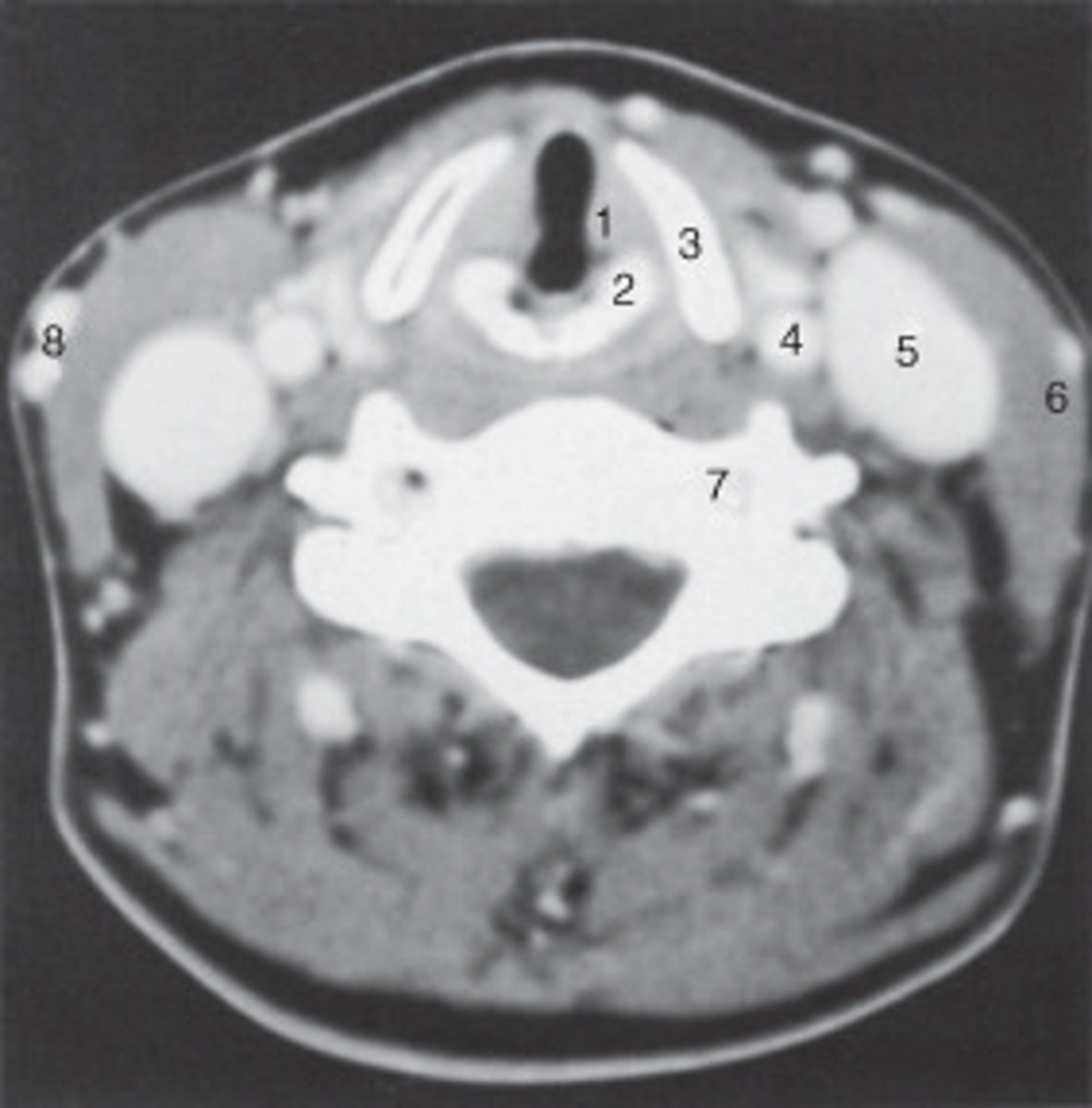
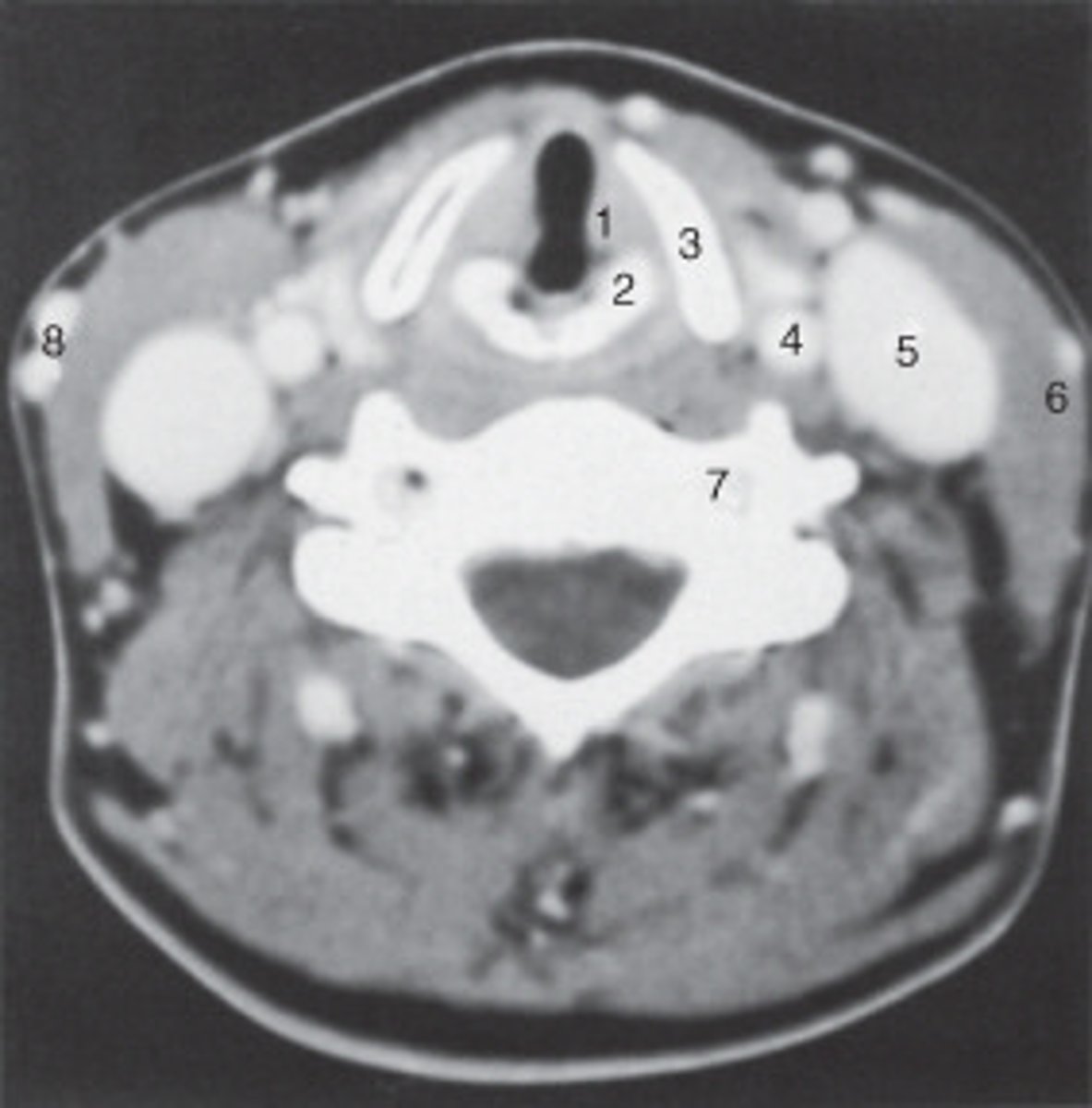
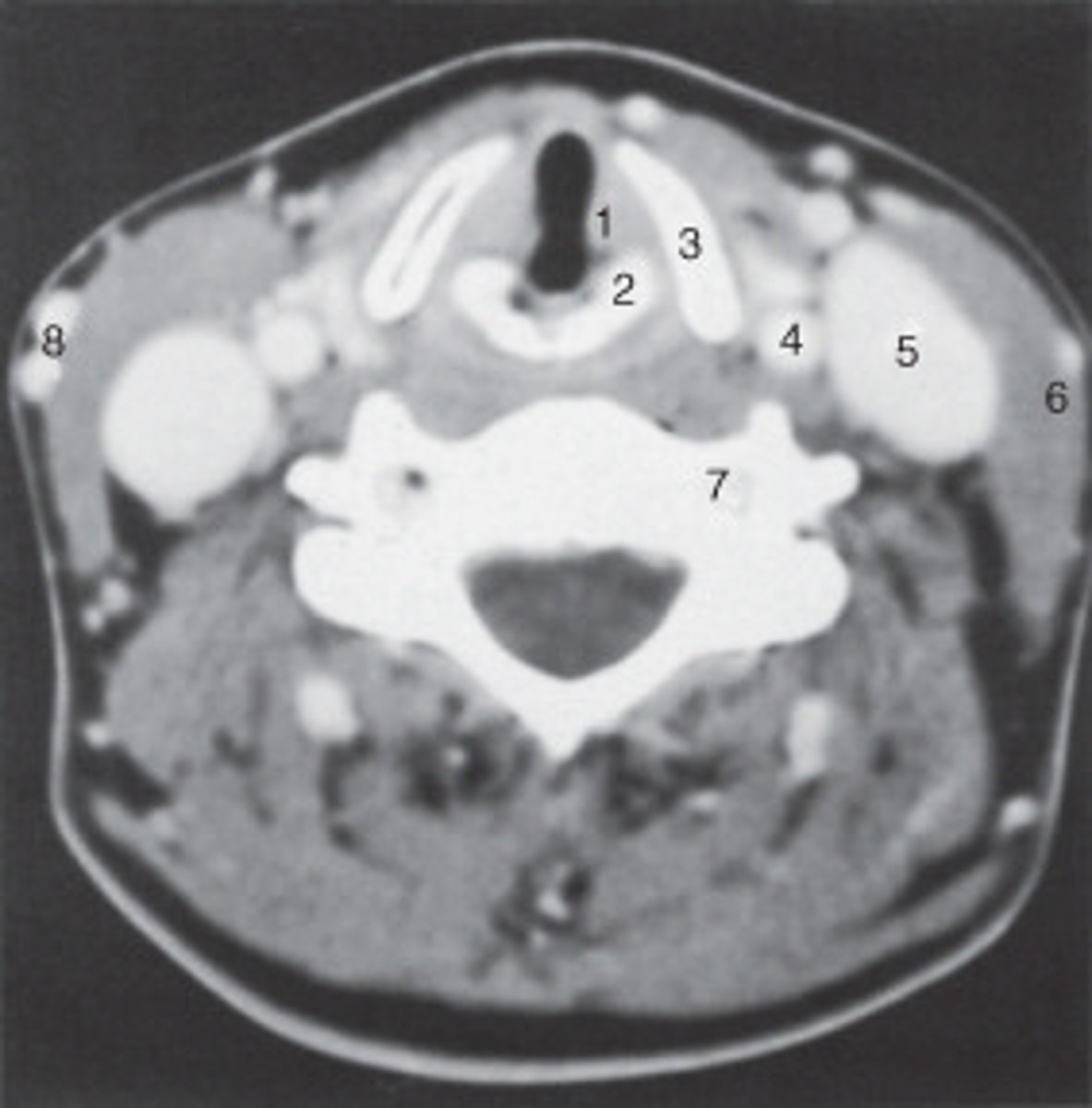
The internal jugular vein is labeled:
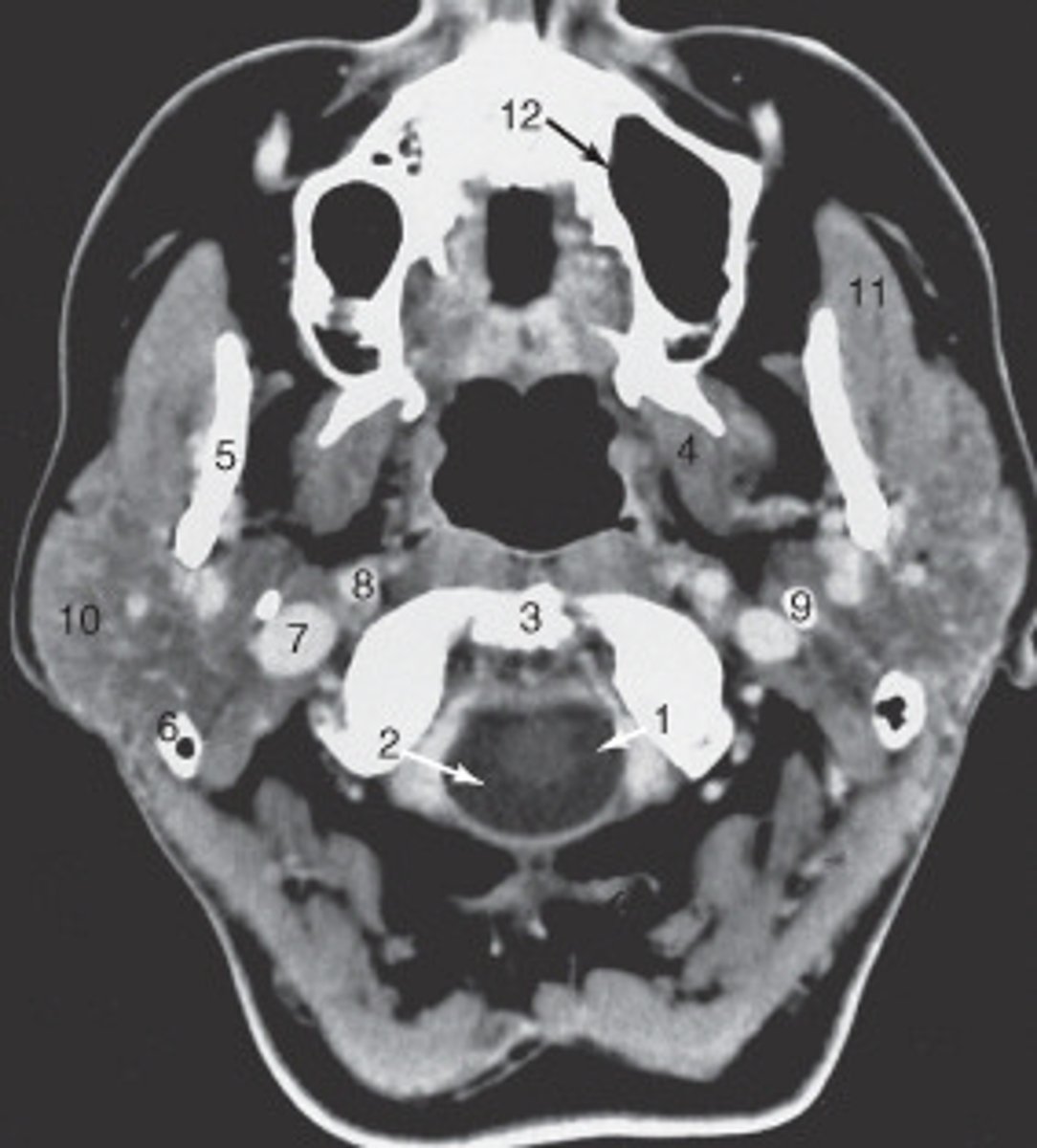
10
the parotid gland is labeled:
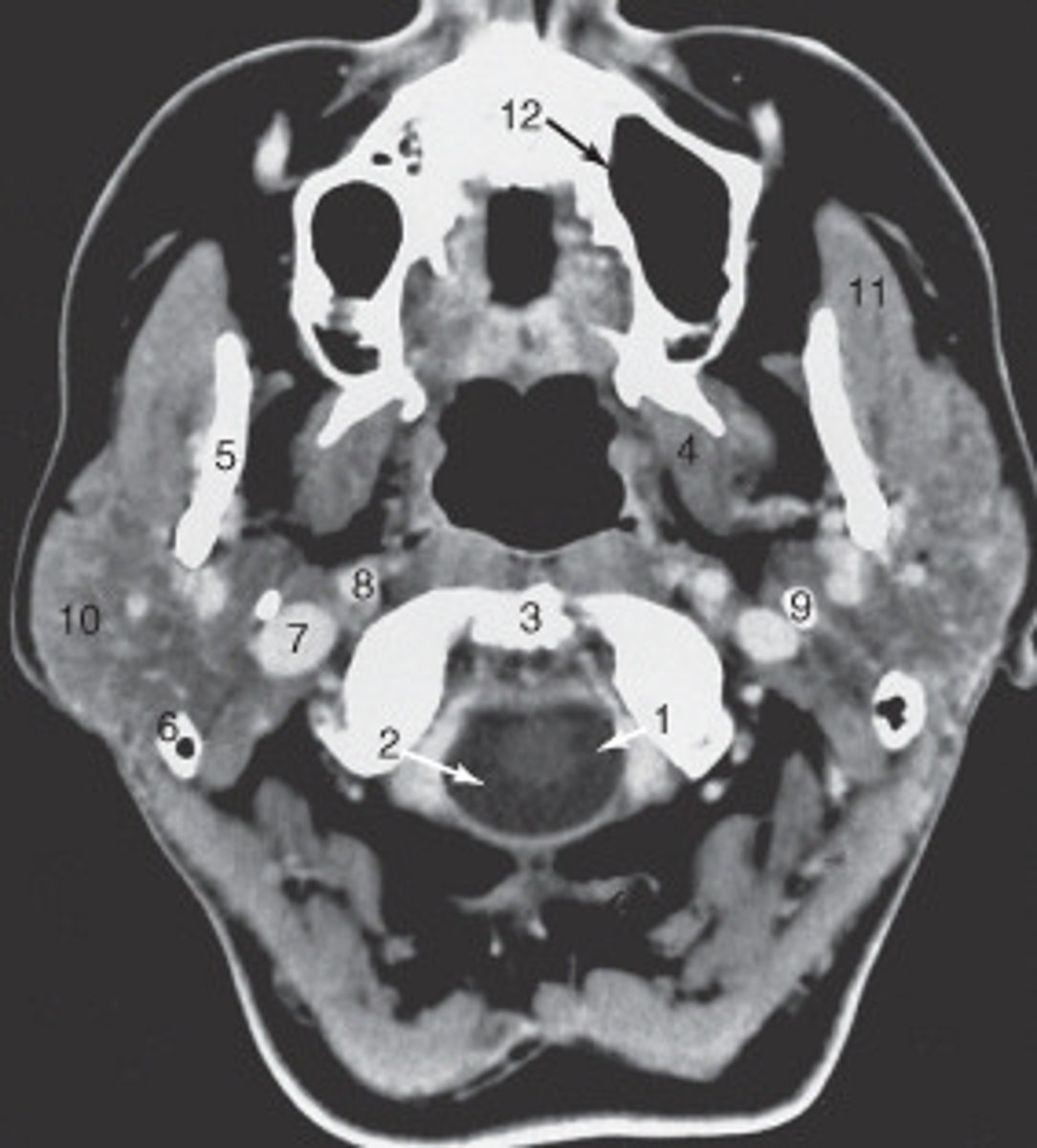
internal carotid artery
the structure labeled as 8 is the:
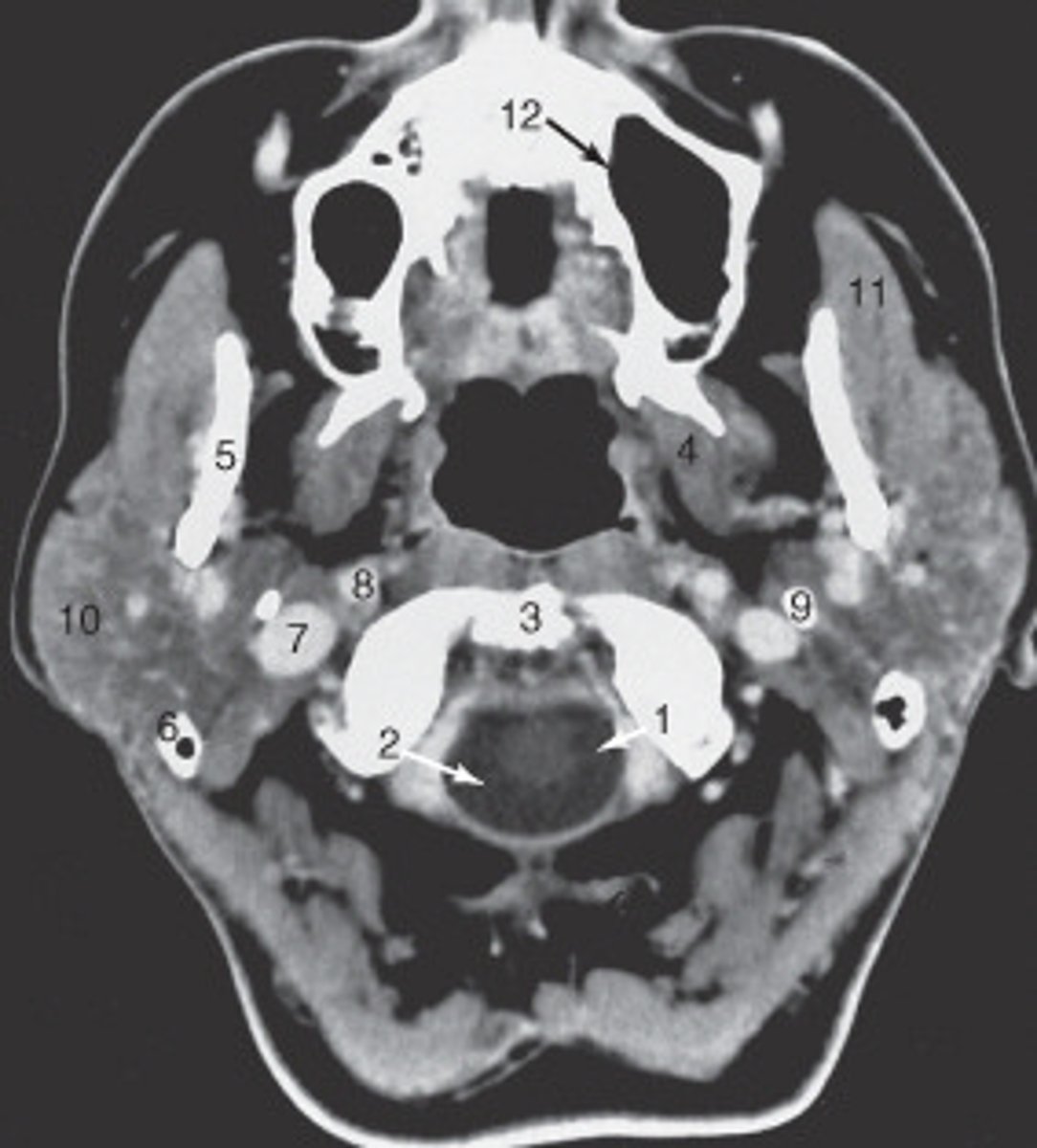
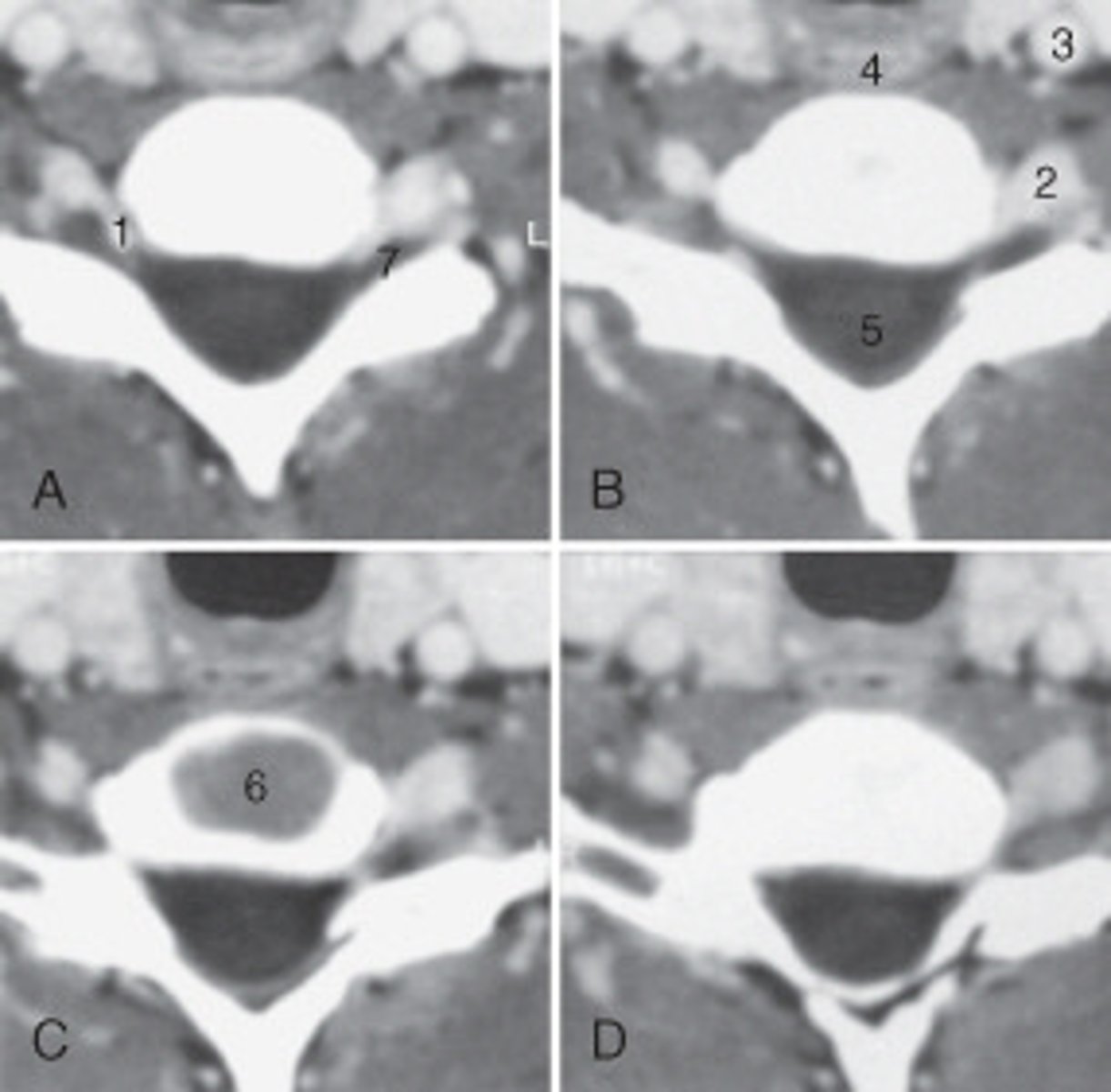
spinal cord
The structure labeled as 1 is the:
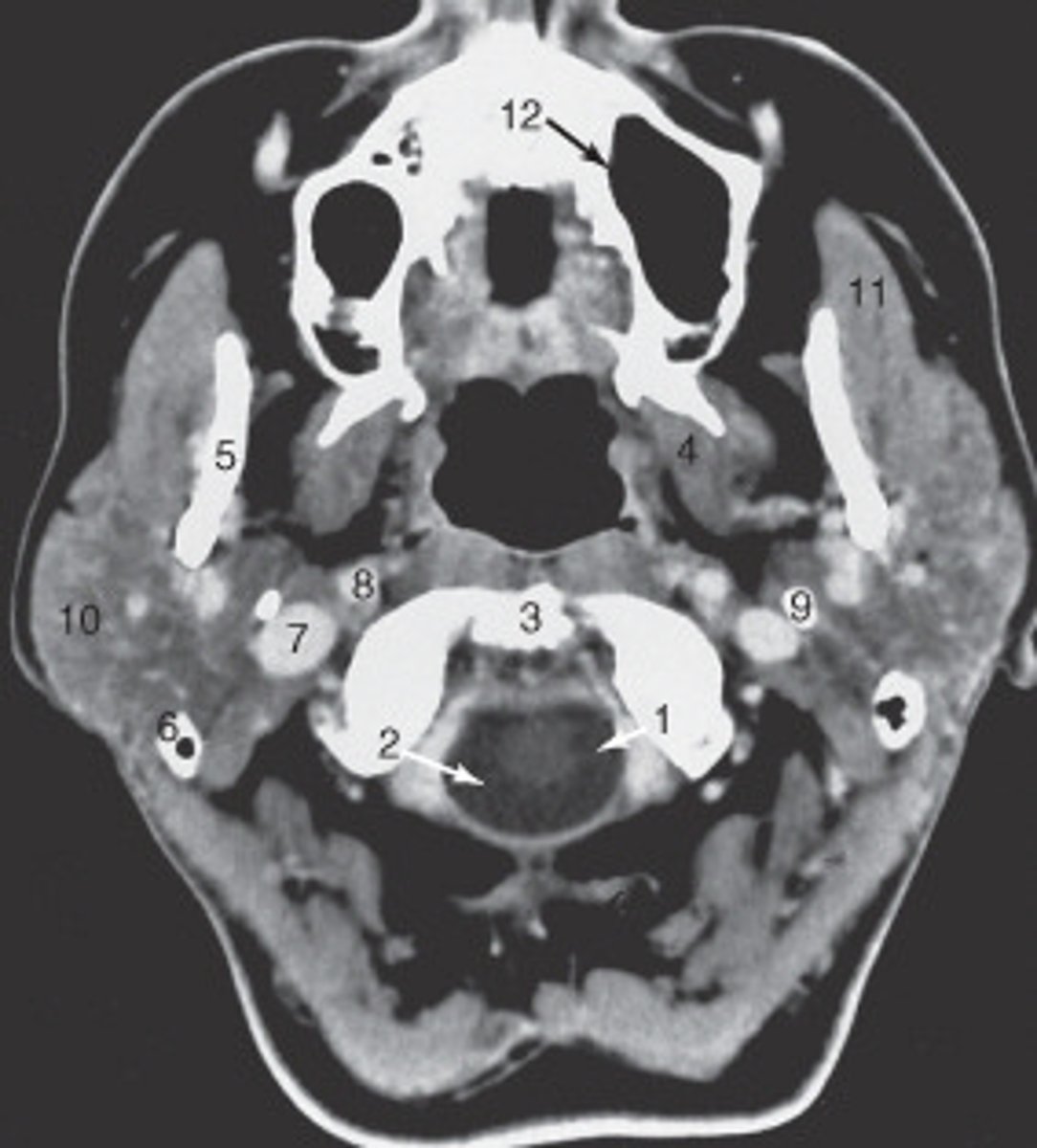
3
The thyroid cartilage is labeled:
4
The common carotid artery is labeled:
internal jugular vein
The structure labeled as 5 is the:
6
the intervertebral disk is labeled:
esophagus
The structure labeled as 4 is the:
false
true/false: Sinus disease is not well demonstrated by CT.
true
true/false: CT has largely replaced plain films of the cervical spine in cases of trauma.
true
true/false: As with plain radiographs, transverse images and coronal reformatted images are viewed as if facing the individual.
false
true/false: Sagittal images of the temporal bone can highlight the relationships of the ossicles and the structures along the medial wall of the middle ear.
true
true/false: Sagittal sections are helpful in evaluating midline structures.
true
true/false: In children, a steeply angled plane is used to scan the brain to avoid radiating the ocular lens.
false
true/false: Contrast enhancement is well visualized on bone algorithm or bone windows.
true
true/false: A standard dose of contrast is administered for each type of examination on the basis of the patient's weight, up to a maximum.
true
true/false:A CT venogram (CTV) visualizes the jugular veins and dural sinuses for sites of possible thrombosis.
false
true/false: Contrast-induced nephropathy indicates a deteriorated liver function as a result of iodine-based contrast.