NMSK 3 - Introduction to the Forelimb
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Identify bones forming the forelimb.
Scapula
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
Carpal bones
Metacarpal bones
Proximal, middle, and distal phalanges
Identify the bony landmarks of the forelimb.
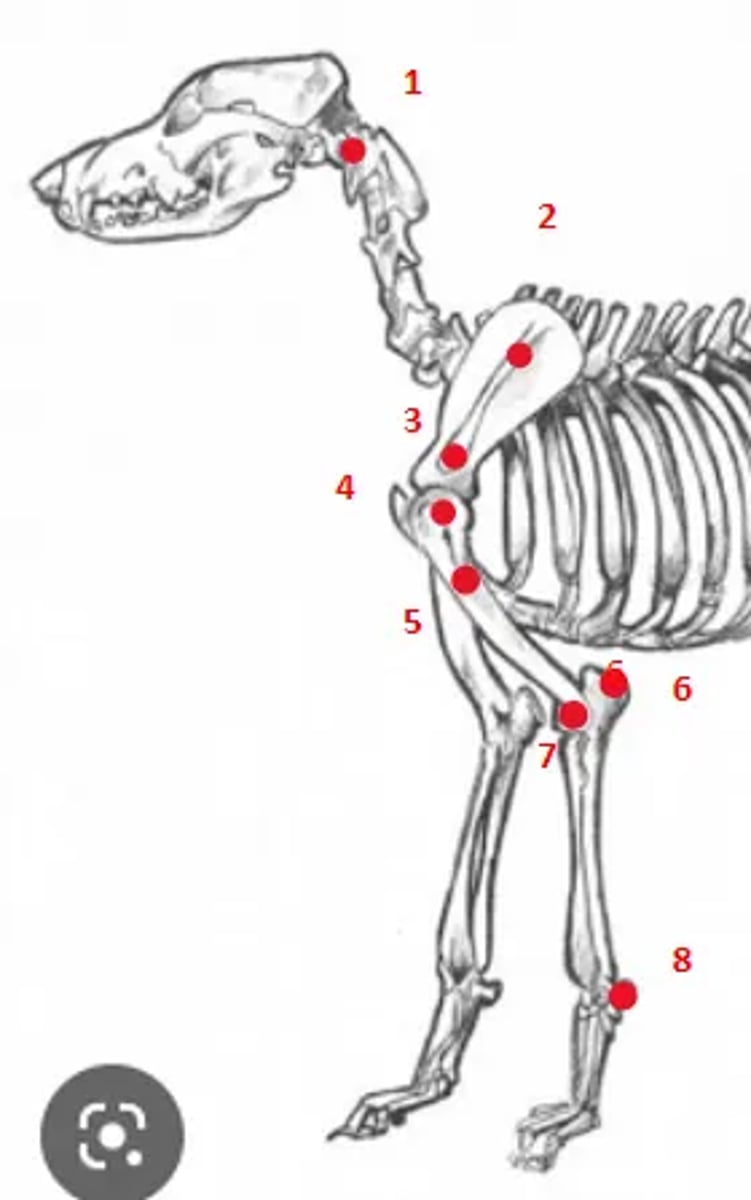
1. Wings of atlas
2. Spine of scapula
3. Acromion
4. Greater tubercle of the humerus
5. Deltoid tuberosity
6. Olecranon
7. Lateral condyle of the humerus
8. Accessory carpal bone
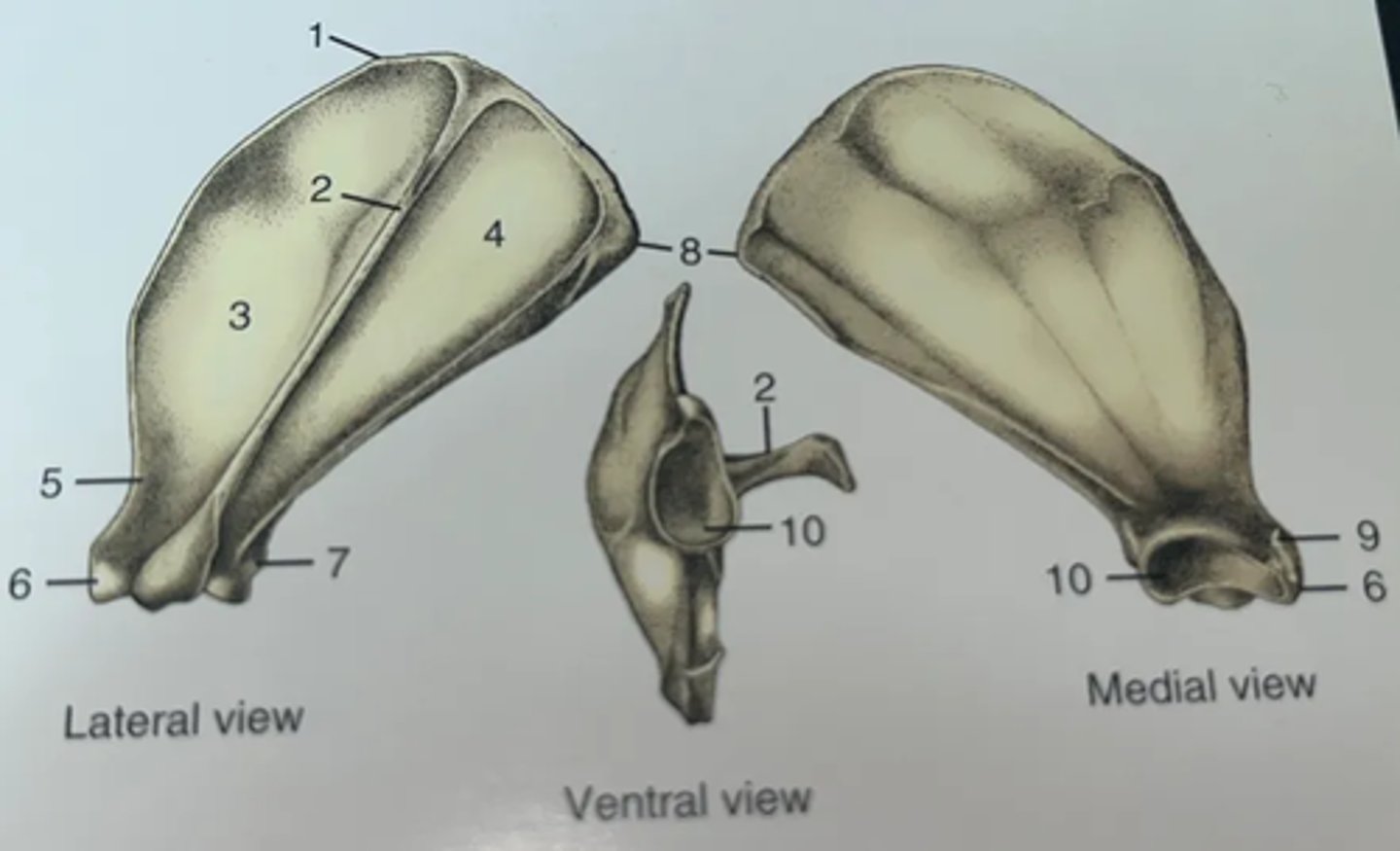
List the features of the scapula.
1. Cranial angle
2. Spine of scapula
3. Supraspinatus fossa
4. Infraspinatus fossa
5. Neck
6. Supraglenoid tubercle
7. Infraglenoid tubercle
8. Caudal angle
9. Coracoid process
10. Glenoid cavity
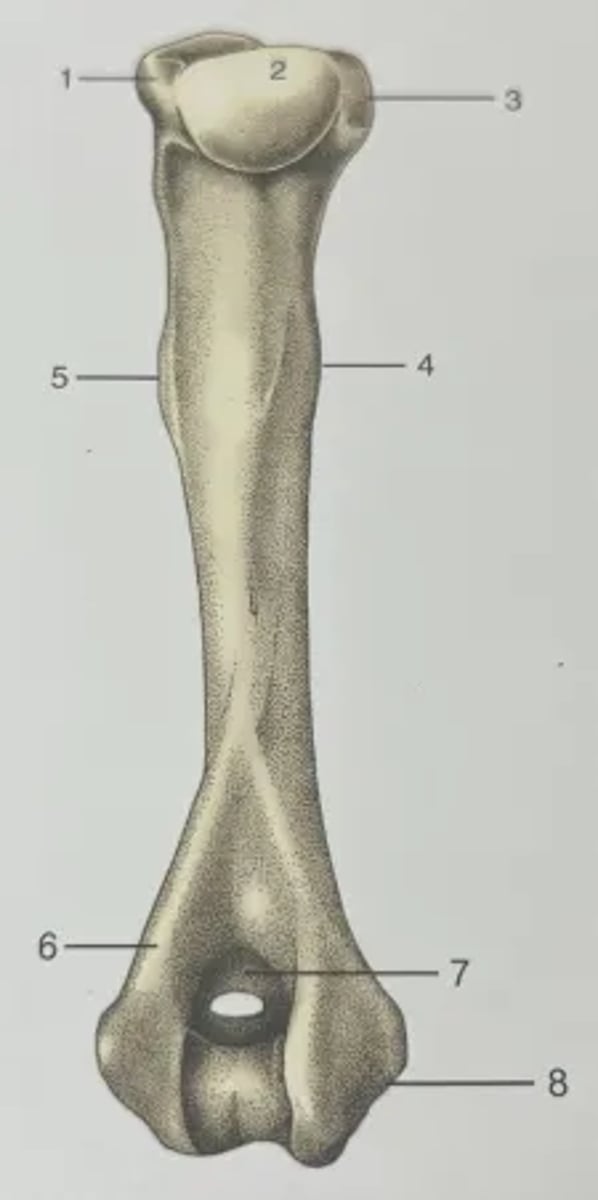
List the features of the humerus.
1. Greater tubercle
2. Head
3. Lesser tubercle
4. Teres major tubercle
5. Deltoid tuberosity
6. Lateral supracondylar crest
7. Olecranon fossa (supratrochlear foramen in dogs)
8. Medial epicondyle
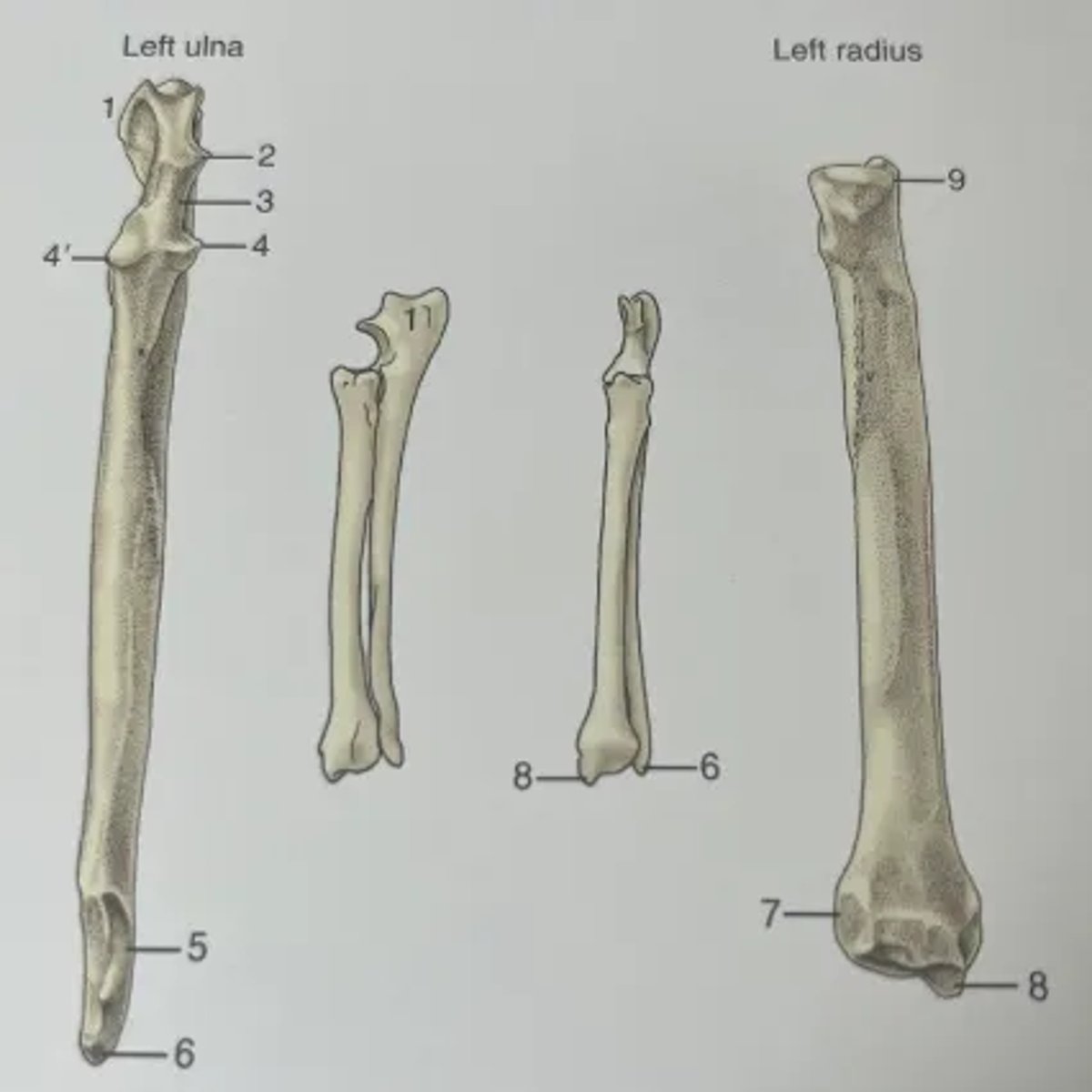
List the features of the radius and ulna.
1. Olecranon
2. Anconeal process
3. Trochlear notch
4. Lateral and medial coronoid processes
5. Distal articular facet for radius
6. Lateral styloid process
7. Articular facet for ulna
8. Medial styloid process
9. Articular circumference
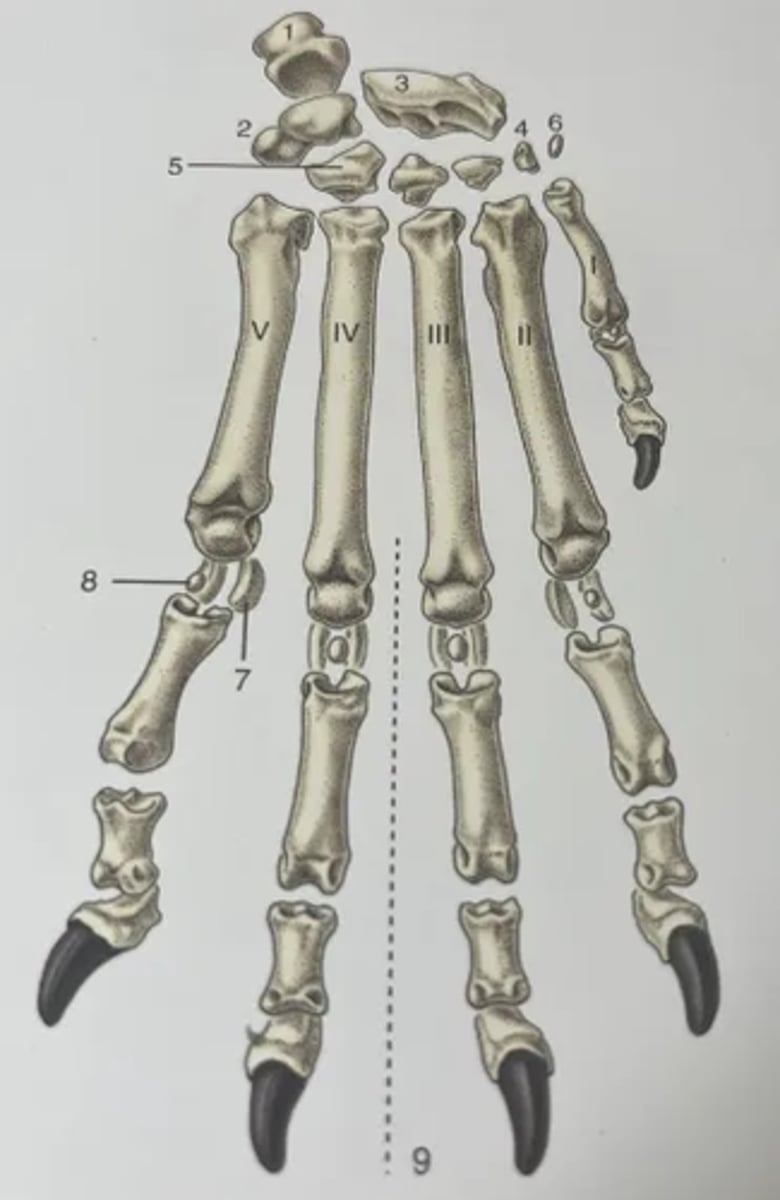
List the features of the distal limb in the dog.
1. Accessory carpal bone
2. Ulnar proximal carpal bone
3. Radial proximal carpal bone
4. 1st of the distal row of carpal bones
5. 4th of the distal row of carpal bones
6. Sesamoid bone (within tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris muscle)
7. Proximal sesamoid bones
8. Dorsal sesamoid bones
9. Axis of manus
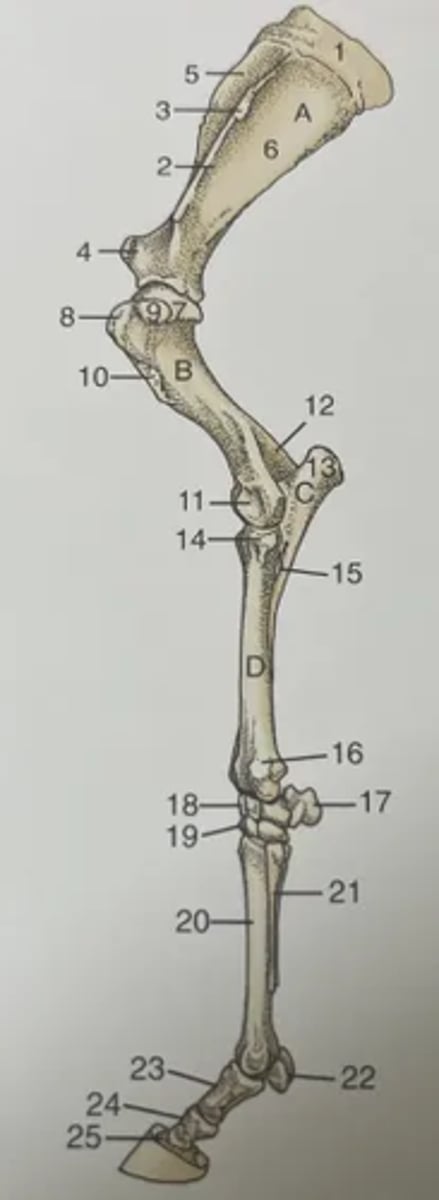
List the features of the forelimb of the horse.
A. Scapula
B. Humerus
C. Ulna
D. Radius
1. Scapula cartilage
2. Spine of scapula
3. Tuberosity of scapula spine
4. Supraglenoid tubercle
5. Supraspinous fossa
6. Infraspinous fossa
7. Head of humerus
8. Cranial part of greater tubercle of humerus
9. Caudal part of greater tubercle of humerus
10. Deltoid
11. Condyle
12. Olecranon fossa
13. Olecranon
14. Tubercle for lateral collateral ligament
15. Interosseous space
16. Lateral styloid process of radius
17. Accessory carpal bone
18. Proximal row of carpal bones
19. Distal row of carpal bones
20. Third metacarpal bone
21. Splint bone
22. Proximal sesamoid bones
23. Proximal phalanx
24. Middle phalanx
25. Distal phalanx
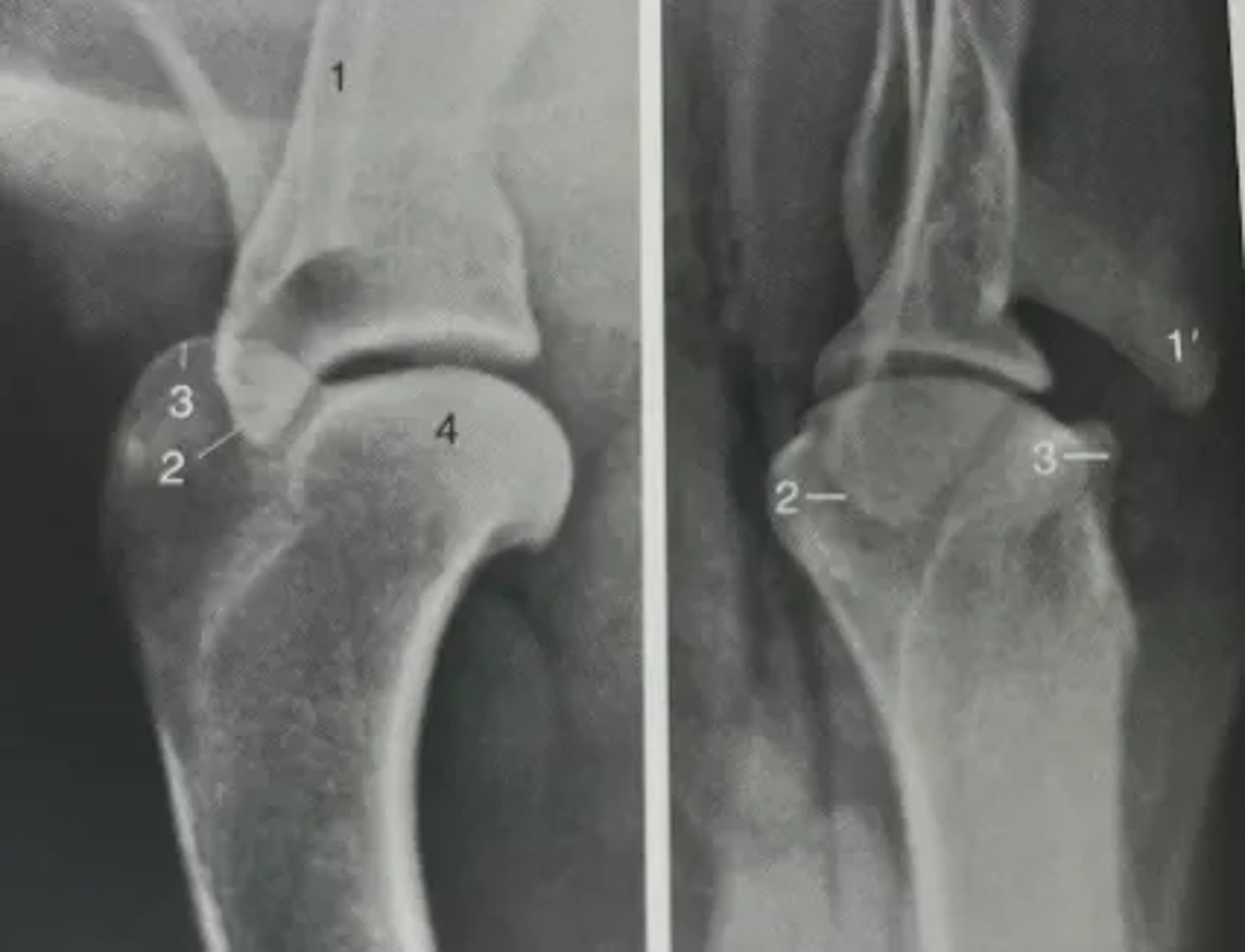
Identify features of the shoulder on a radiograph.
1. Spine of scapula
1'. Acromion
2. Supraglenoid tubercle
3. Greater tubercle of humerus
4. Head of humerus
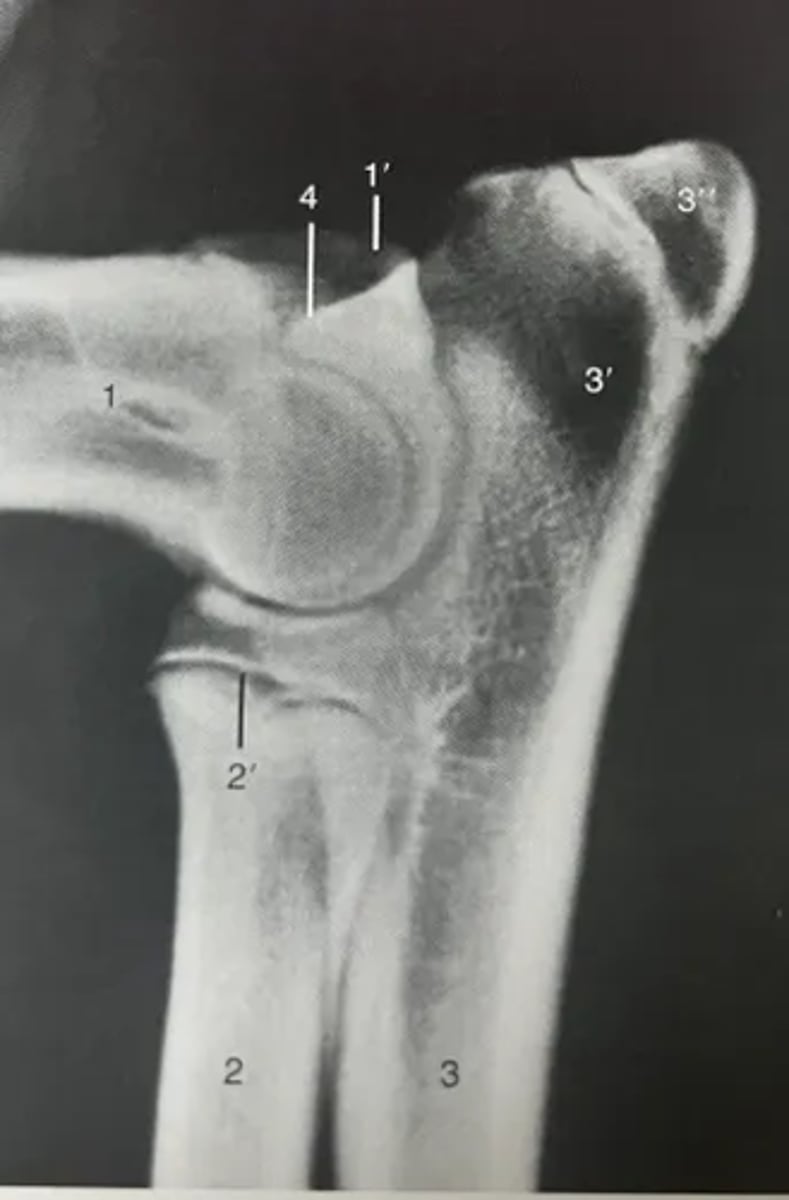
Identify features of the elbow on a radiograph.
1. Humerus
1'. Medial epicondyle
2. Radius
3. Ulna
3'. Olecranon
3''. Apophysis of tuber olecrani
4. Anconeal process
Identify the joints forming the forelimb, and their main features (bones involved, type of joint, and range of motion).
Shoulder joint between the scapula and humerus
- Synovial, ball-and-socket
- Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation
Elbow joint between the humerus, radius, and ulna
- Synovial, hinge
- Flexion and extension
- Pronation and supination
Carpal joints:
- All synovial
- Flexion, extension, and some abduction and adduction
Antebrachiocarpal joint between the radius, ulna, and proximal carpal bones
Intercarpal joint between proximal and distal carpal bones
Carpometacarpal joint between the distal carpal bones and metacarpal bones
Metacarpophalangeal joint between the metacarpal bones and proximal interphalangeal bones
- Synovial, hinge
- Flexion and extension
Proximal interphalangeal joint between the proximal and middle phalanges.
- Synovial, saddle
- Flexion and extension
Distal interphalangeal joint between the middle and distal phalanges.
- Synovial, saddle
- Flexion and extension
Describe the main muscle groups of the forelimb.
Extrinsic muscles
The forelimb is attached to the body by extrinsic muscles, which can be divided into 3 groups:
Protractor group
- Brachiocephalicus
- Omotransversarius
- Trapezius muscles
Retractor group
- Deep pectoralis
- Latissimus dorsi
Thoracic sling group (on medial side of forelimb)
- Serratus ventralis
- Deep pectorialis
- Rhomboideus
Intrinsic muscles do not hold the forelimb onto the body:
Extensors of the elbow, carpus, and digits are supplied by the radial nerve
Flexors of the carpus and digits are supplied by the medial and ulnar nerves.
Describe the extrinsic muscles of the proximal forelimb.
Brachiocephalicus
- 3 muscles:
- Action: protraction
- Innervation: accessory nerve
- Origin: back of the skull
- Insertion: medial side of humerus
Omotransversarius
- Action: protraction
- Innervation: accessory nerve
- Origin: transverse processes of atlas
- Insertion: acromion of scapula
Trapezius
- 2 parts: cervical and thoracic
- Action: protraction
- Innervation: accessory nerve
- Origin: midline
- Insertion: spine of scapula
Latissimus dorsi
- Action: retraction
- Innervation: brachial plexus
- Origin: dorsal midline
- Insertion: teres tuberosity of humerus
Deep pectoralis
- Action: retraction
- Innervation: brachial plexus
- Origin: sternum
- Insertion: medial side of humerus
Serratus ventralis
- Action: protraction and retraction
- Innervation: brachial plexus
- Origin: scapular
- Insertion: thoracic vertebrae and ribs
Rhomoideus
- Action: retraction
- Innervation: brachial plexus
- Origin: cranial thoracic vertebrae
- Insertion: dorsal scapular
Describe the intrinsic muscles of the thoracic limb acting on the shoulder joint.
Scapula muscles:
Supraspinatus
- Action: extension of shoulder joint and stability
- Innervation: suprascapular nerve
- Origin: supraspinous fossa of scapula
- Insertion: greater tuberosity of humerus
Infraspinatus
- Action: flexion of shoulder joint, and abductor of the humerus
- Innervation: suprascapular nerve
- Origin: infraspinous fossa of scapula
- Insertion: greater tubercule of humerus
Subscapularis
- Action: extension and adduction of the shoulder joint
- Innervation: subscapular nerve
- Origin: subscapular fossa
- Insertion: lesser tubercle of humerus
Shoulder muscles:
Deltoideus (draws the humerus back)
3 parts: scapular part, acromial part, and clavicular part.
Action: flexion of shoulder joint
Innervation: axillary nerve
Origin: scapular spine
Insertion: deltoid tuberosity of humerus
Teres major (draws the humerus back)
Action: flexion of shoulder joint
Innervation: axillary nerve
Origin: scapula
Insertion: teres major tuberosity
Describe the intrinsic muscles of the forelimb acting on the elbow joint.
Triceps brachii
- 3 heads, 4 in a dog
- Action: extension
- Innervation: radial nerve
- Origin: scapula and humerus
- Insertion: olecranon of the ulna.
Biceps brachii
- Action: flexion
- Innervation: musculocutaneous nerve
- Origin: supraglenoid tubercle of scapula
- Insertion: radial and ulnar tuberosity.
Brachialis
- Action: flexion
- Innervation: musculocutaneous nerve
- Origin: caudal humerus
- Insertion: medial on radius or ulna
Describe the intrinsic muscles of the forelimb acting on the carpal and digital joints.
Carpal muscles:
Flexor carpi radialis
Action: flexion of carpal joint
Innervation: medial nerve
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Action: flexion and abduction of forepaw
Innervation: ulnar nerve
Extensor carpi radialis
Action: extension of the carpal joint
Innervation: radial nerve
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Action: extension of carpal joint
Innervation: radial nerve
Digital muscles that have tendons extending to digits:
Superficial digital flexor
Action: flexion of the paw
Innervation: medial nerve
Deep digital flexor
Action: flexion of the paw
Innervation: medial nerve
Common digital extensor
Action: extension of the digits
Innervation: radial nerve
Lateral digital extensor
Action: extension of the digits
Innervation: radial nerve
List the ligaments of the forelimb.
Shoulder: poorly invested in ligaments due to its mobile nature
- Medial glenohumeral ligament
- Lateral glenohumeral ligament
Elbow: well supported by strong collateral ligaments
- Oblique ligament runs along the cranial surface of the elbow joint from the humerus, to join the medial collateral ligament.
- Medial collateral ligament
- Annular ligament holds the head of the radius against the ulna on species which can pronate/supinate
Carpal joint complex: many linking the carpal bones, distal antebrachium, and proximal metacarpus.
- Paired ligaments linkinking the accessory carpal bone to metacarpals IV and V to aid carpal flexion.
- Palmar carpal ligaments in horses, extending distally to form the carpal accessory (check) ligament which supports the DDFT.
Metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints: strong collateral ligaments to maintain joint alignment.
Describe the formation and location of the brachial plexus.
- A major network of nerves located in the region of the axilla, from which peripheral nerve trunks of the forelimb are derived.
- Formed by the ventral roots of C5/C6 to T1/T2 spinal nerves.
- Located
Describe the nerves leaving the brachial plexus, in terms of the muscles and areas of the skin that they supply.
Suprascapular nerve
Origin: cranial part of brachial plexus, C6 and C7
Route: laterally round the cranial aspect of the neck of the scapula
Motor innervation: supraspinatus and infraspinatus
Sensory innervation: none
Subscapular nerve
Origin: cranial part of brachial plexus, C6 and C7
Route: direct to muscle
Motor innervation: subscapularis
Sensory innervation: none
Musculocutaenous nerve
Origin: middle part of brachial plexus, C7 and C8
Route: medial aspect of the limb, close to medial nerve
Motor innervation: biceps brachii, brachialis, coracobrachialis
Sensory innervation: dorsomedial aspect of forelimb
Axillary nerve
Origin: middle brachial plexus, C7 and C8
Route: behind the shoulder joint
Motor innervation: shoulder flexors
Sensory innervation: dorso-lateral aspect of proximal limb
Radial nerve
Origin: caudal brachial plexus, C7 and T2
Route: through the triceps and around the humerus to the lateral aspect of the forearm
Motor innervation: extensors of the elbow, carpus, and digits
Sensory innervation: craniallateral and medial forearm in dogs, lateral forearm in horses
Median and ulnar nerves
Origin: caudal brachial plexus, C8, T1, and T2
Route: along the medial aspect of the limb
Motor innervation: flexors of the carpus and digits
Sensory innervation: caudal aspect of the limb
Identify the structures in the diagram of the cervical and thoracic muscles
1. Sternocephalicus
2. Brachiocephalicus (cleidocephalicus and cervical part)
2'. Brachiocephalicus (cleidobrachialis part)
3. Omotransversarius
4. Superficial cervical lymph node
5. Trapezius (cervical)
5'. Trapezius (thoracic)
6. Deltoideus
7. Latissimus dorsi
8. Long head of triceps brachii
8'. Lateral head of triceps brachii
9. Superficial pectorals
10. Accessory axillary lymph node
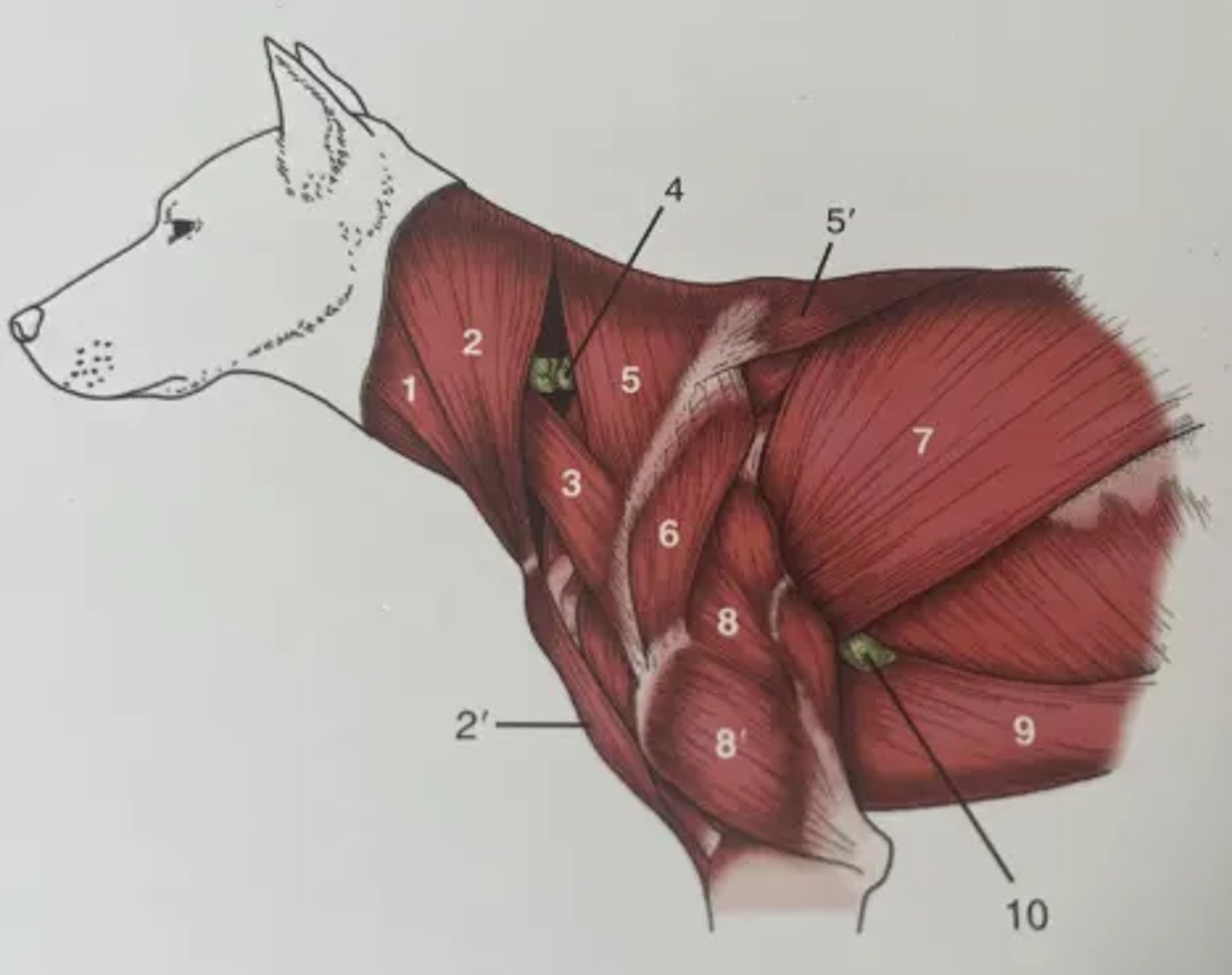
Identify the structures in the diagram of the forelimb of the muscles in the elbow joint
1. Rhomboideus
2. Teres major
3. Supraspinatus
4. Scapula part of deltoid
4'. Acromial part of deltoid
5. Latissimus dorsi
6. Long head of triceps brachii
6'. Lateral head of triceps brachii
7. Brachiocephalicus (cleidobrachialis)
8. Brachialis
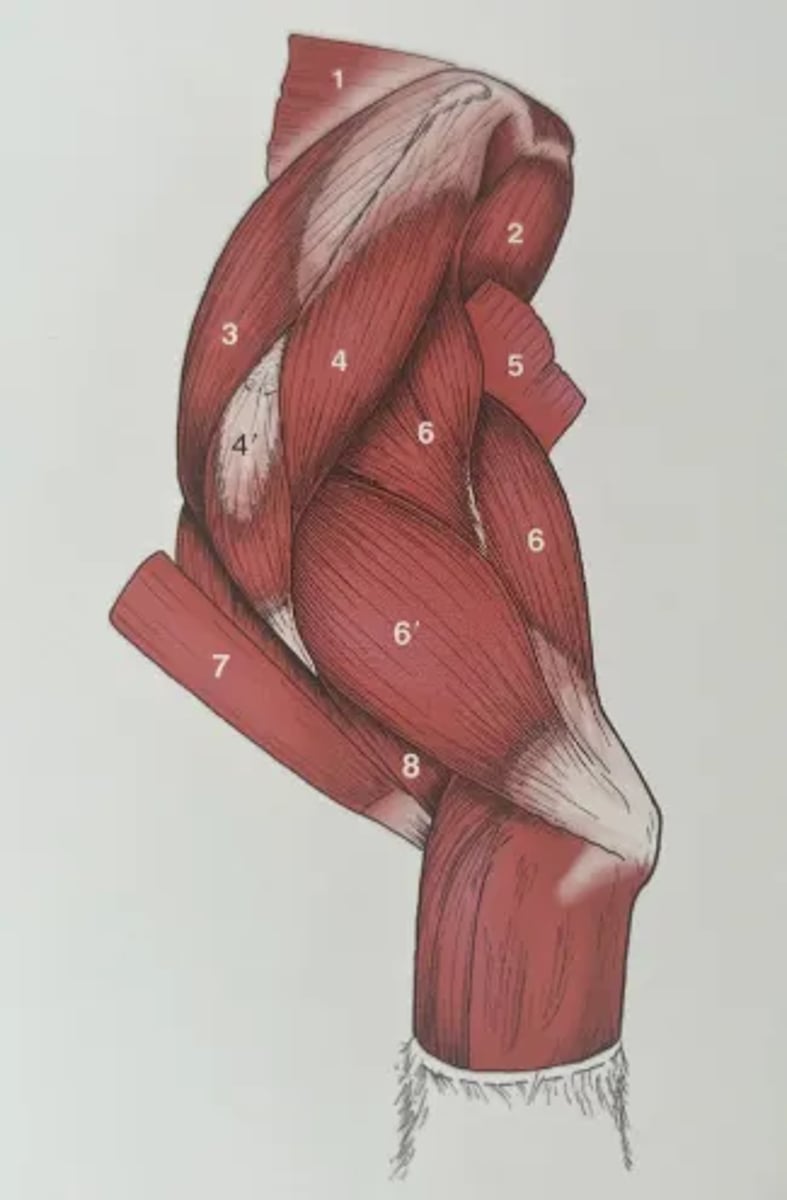
Identify the structures highlighted in the proximal forelimb
1. Trapezius
2. Latissimus dorsi
3. Omotransversarius
4. Scapula part of deltoid
4'. Acromial part of deltoid
5. Brachicephalicus (cleidocephalicus)
6. Triceps brachii
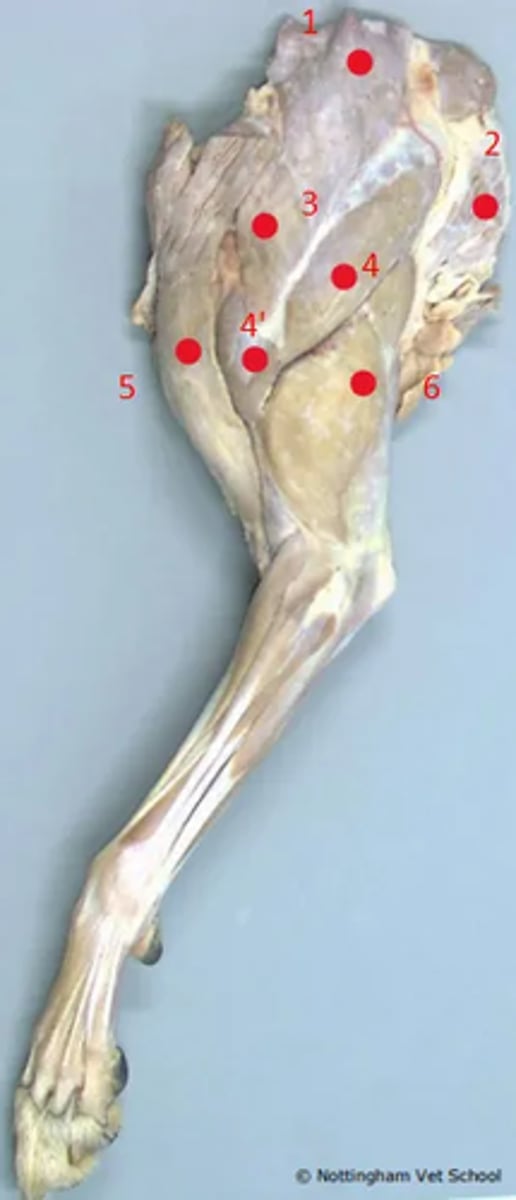
Identify the structures highlighted.
1. Latissimus dorsi
2. Teres major
3. Subscapularis
4. Supraspinatus
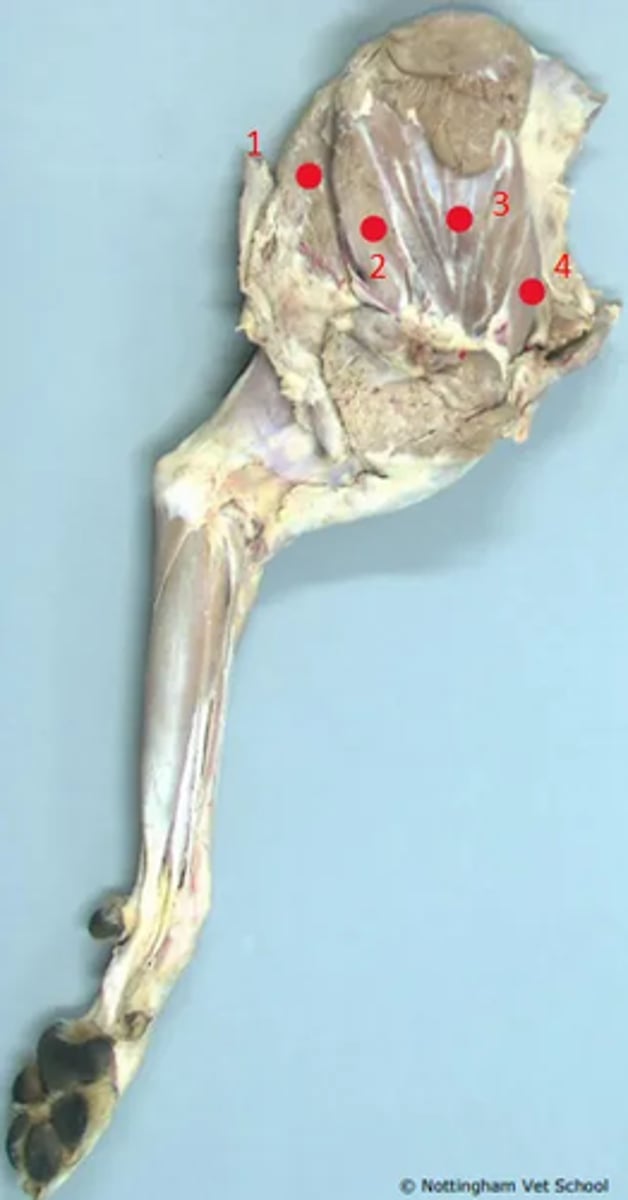
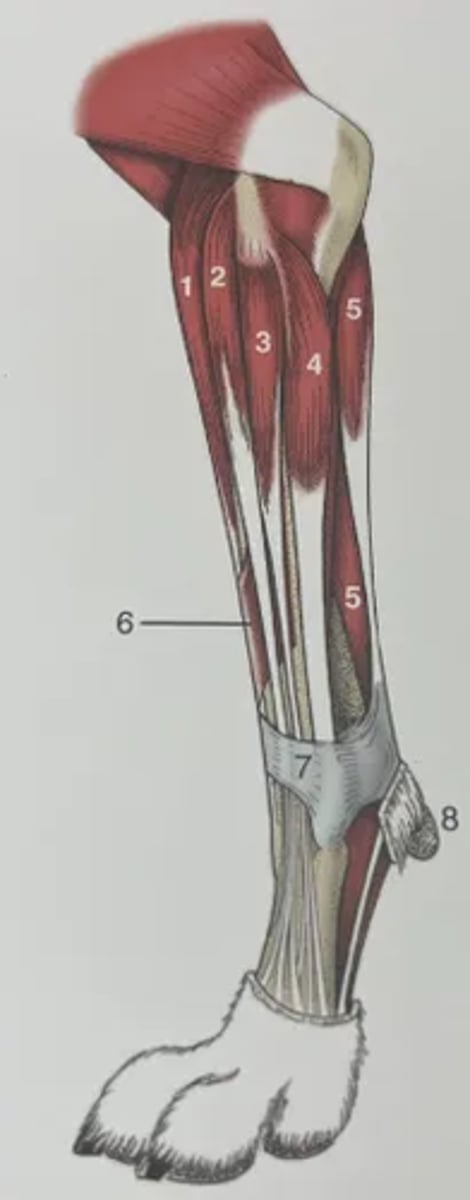
Identify the structures in the diagram of the distal limb.
1. Extensor carpi radialis
2. Common digital extensor
3. Lateral digital extensor
4. Extensor carpi ulnaris
5. Flexor carpi ulnaris
6. Long abductor muscle
7. Extensor retinaculum
8. Carpal pad
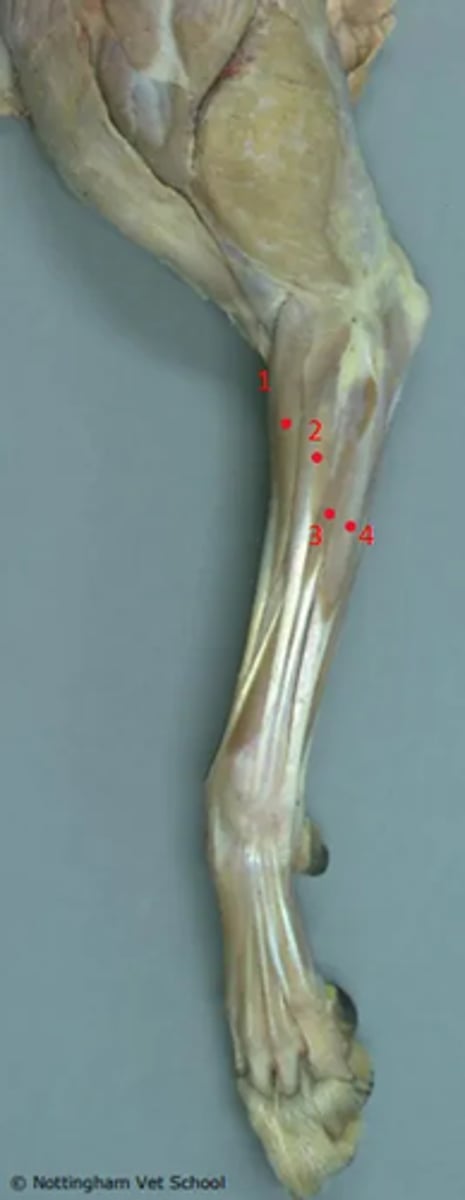
Identify the highlighted structures.
1. Extensor carpi radialis
2. Common digital extensor
3. Lateral digital extensor
4. Extensor carpi ulnaris
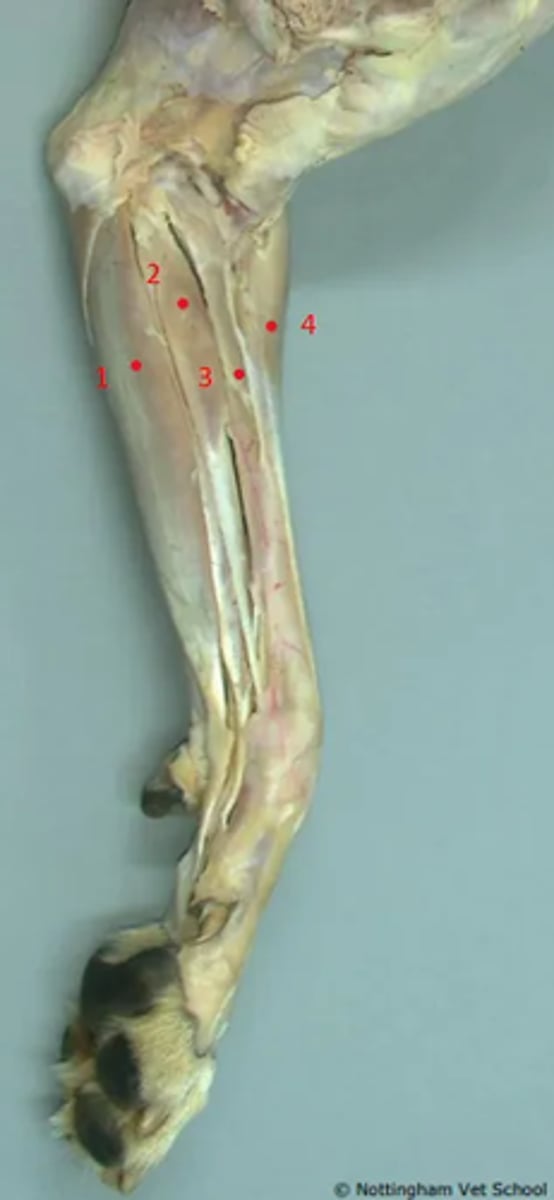
Identify the highlighted structures.
1. Superficial digital flexor
2. Flexor carpi radialis
3. Pronator teres
4. Extensor carpi radialis
List the nerves supplying the intrinsic muscles of the forelimb.
Suprascapular
- Supraspinatus
- Infraspinatus
- Subscapularis
Subscapular
- Subscapularis
Axillary
- Deltoids
- Teres major
Musculocutaneous
- Biceps brachii
- Brachialis
Radial
- Triceps brachii
- Extensor carpi radialis
- Extensor carpi ulnaris
- Lateral digital extensor
- Common digital extensor
Median
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Superficial digital flexor
- Deep digital flexor
Ulnar
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
List the nerve suppling the extrinsic muscles of the forelimb.
Accessory
- Brachiocephalicus
- Omotransversarius
- Trapezius
Brachial plexus
- Latissimus dorsi
- Deep pectorals
- Serratus ventralis
- Rhomboids
Describe the main arteries supplying the forelimb.
- The subclavian artery enters the forelimb via the axilla, where it becomes the axillary artery
- Number of branches continuing distally along the medial aspect of the limb.
- Brachial artery becomes the median artery
- Radial artery continues down into the palmar arteries.
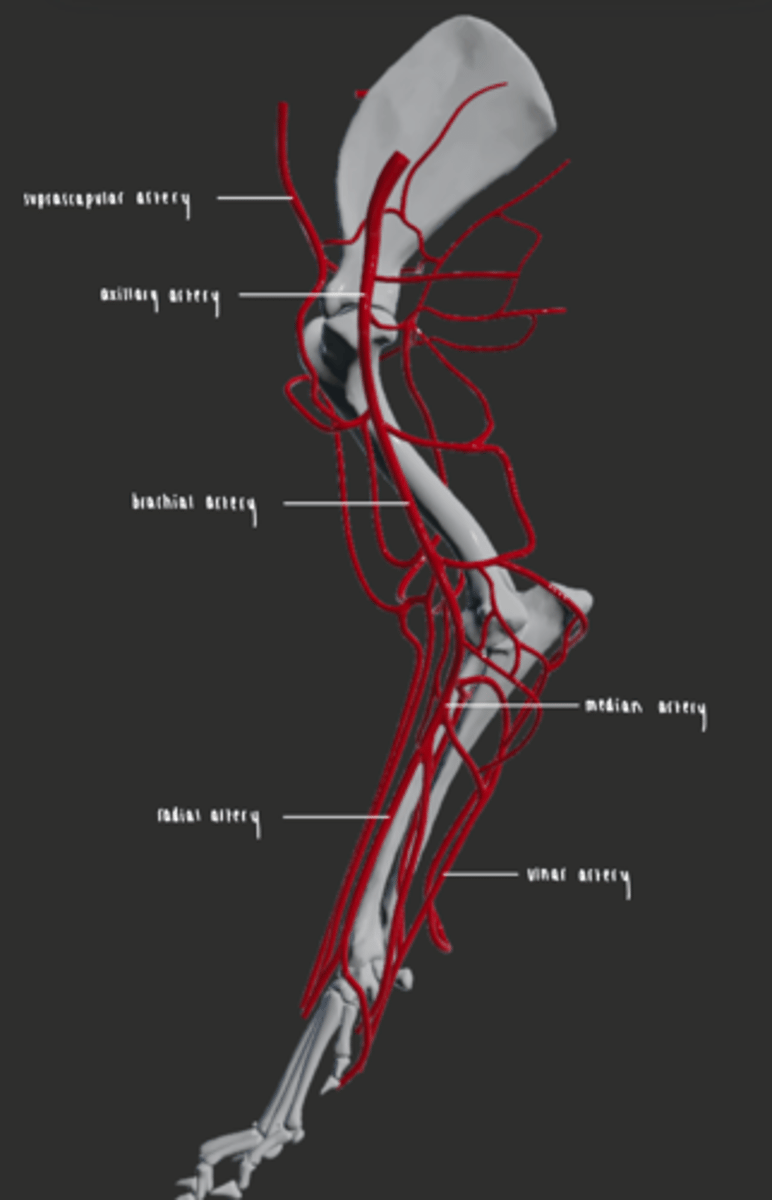
Describe the main veins supplying the forelimb.
- Cephalic vein is located on the palmer aspect of the metacarpus
- Remains on the craniomedial aspect of the limb
- Passes the shoulder joint and heads towards the midline
- Drains into the jugular vein.
- Axillary vein becomes the brachial vein, which becomes the median vein
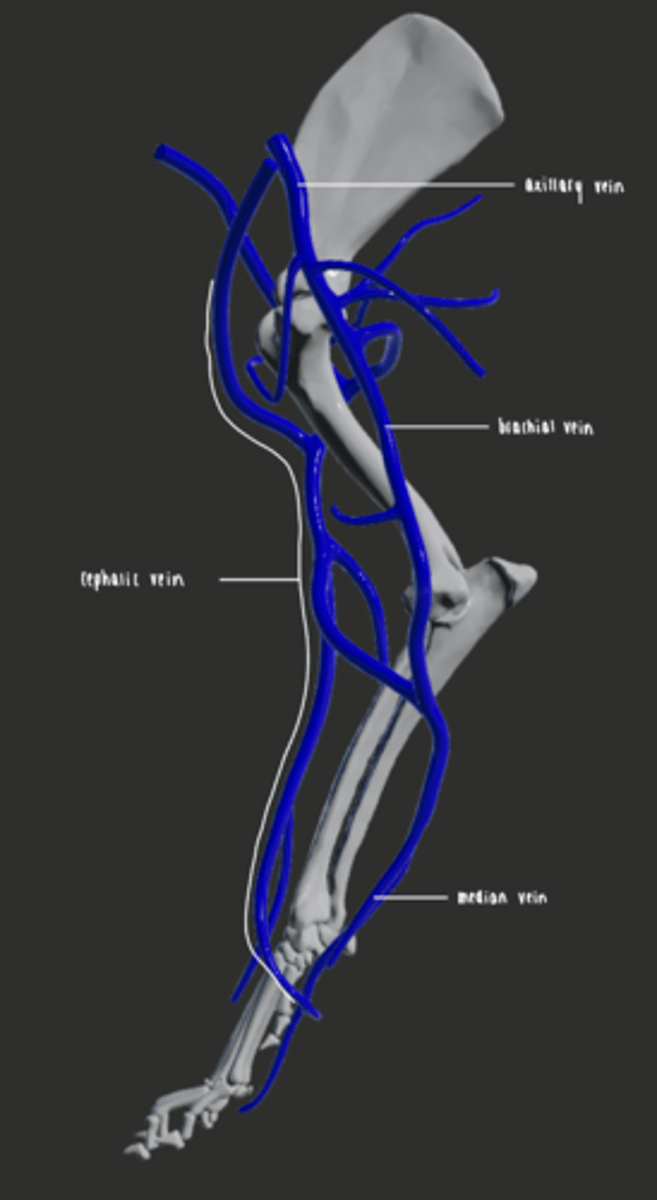
What blood vessel is used for venous access in the forelimb?
Cephalic vein
What blood vessel is used for assessing pulse in the forelimb?
Radial artery (digital artery branches)