Ch. 22 Substance-Related and Addictive Disorders💗
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Objectives
. Differentiate between various substance abuse disorders (e.g., alcohol, stimulants, sedatives, hallucinogens). Based on clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria, and potential complications.
2. Develop individualized evidenced based nursing care plan for patients with substance-based use disorders incorporating physical, psychological, and social needs.
3. Implement therapeutic nursing interventions such as motivational interviewing, harm reduction strategies, and relapse prevention strategies for clients with substance use disorders.
4. Describe therapeutic interventions for patients with substance abuse disorders.
5. Describe appropriate pharmacologic treatments used in the management of substance use disorders, including medications for withdrawal, maintenance, maintenance, and relapse prevention (e.g., methadone, buprenorphine, naltrexone, disulfiram).
Substance Use Disorders
Pathological use of a substance that leads to a disorder of use.
Symptom fall into 4 major groups:
uImpaired control
uSocial impairment
uRisky use
uPhysical effects (i.e., intoxication, tolerance, and withdrawal)
need more and more bc of tolerance level
benzo- give narcan reversal
antebuse
if pt unstable- you have to act
if stable- assess
dont tell pt what to do
watch for headaches in them- bc higher risk for head bleeding.
Substances That Lead to
Use Disorders
AlcoholCaffeineCannabisHallucinogenInhalant- like spray canOpioid- dilodid, morphine, tramidolSedative-hypnoticStimulantTobacco
Other:
In addition to substances behaviors can also be addictive. Process addictions—Gambling, shopping, sex, social media etc.
What are Concepts Central to Addictive Use Disorders
Addiction
uchronic medical condition
Intoxication
uin the process of using a substance to excess
Tolerance
utakes a higher dose to achieve the initial level of response.
Withdrawal
usymptoms that occur when a person stops using a substance, can be mild or life threatening
How many people are addicted to substances
Alcohol
u15 million people addicted
Other substances
uAbout 8 million people addicted
uMarijuana: 4.5 million
Opioids: 2.0 million
Comorbidity
Psychiatric comorbidity
uAny combination of two or more substance use disorders and mental disorders
What are the risk factors
uGenetic factors- parents
uNeurobiological factors
Environmental factors- poor , bad neighborhoods, increased stress, anxiety-, depression.
What is caffeine use disorder
Caffeine
Most widely used psychoactive substance in the world. Its not an official use disorder.
Can result in intoxication, overdose, and withdrawal
Excessive use is associated w bipolar, eating and sleep disorders.
Effects can happen 15 min after drinking and can last 6 hrs.
What are the s/s of caffiene intoxication
Intoxication- more than 250 mg.
S/S- restless, nervousness, excitement, agitation, rambling speech, inexhaustibility,
Flushed face, diuresis ( increased urine), muscle twitching, tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias.
What are the s/s of caffine overdose and how do we tx it
Overdose and tx
Fever, tachycardia or bradycardia, hypertension at first and then hypotension.
Extremely high doses can cause seizures, respiratory failure, even death.
Common- Mydriasis ( pupils dilate) , hyperreflexia, N/V.
Disorganized thinking, agitation, delusions, hallucinations and seizures dt ischemia from vasoconstriction.
Tx- Hydration oral or IV, gastric lavage to remove excess caffeine or activated charcoal, Beta blockers for +HR, Vasopressors to maintain BP.
What are the s/s of caffiene withdraw
Withdraw
Headache, drowsy, irritability, poor concentration, Flu like symptoms like N/V, muscle aches. Symptoms happen in 12-24 hrs after the last dose, peak in a day or two and resolve in a week
What is cannibis disorder
Cannibis (Marijuana)
Third most commonly used psychoactive drug in the United States after alcohol, and illicit drugs. can have auditory, hallucinations, visual tactlie- thing something crawling on them. When stop- anxiety
Hyperemsis canaboid disorder- N/V
What are the s/s of cannabis intoxication
Heightens sensations, experience brighter colors, see new details in common stimuli, time goes more slowly, in higher doses can experience depersonalization and derealization.
S/S required for a diagnosis- Two or more symptoms- conjunctival infection- eyes red, increased appetitie, dry mouth, tachycardia.
Hallucinations w intact reality testing, auditory, visual, and tactile illusions in the absense of delirium
What are the s/s of cannibis withdraw
Withdraw
happen within 1 wk of stopping. Irratable, anger, agression, anxiety, restless, depressed mood.
Insomnia, distrubing dreams, decreased appetitie- can cause weight loss.
Physical symptoms include at least one of the following- abdominal pain, shakiness, sweating, fever, chills, or headache.
What tx do we do for cannabis abuse
Tx- Abstinence and support. Therapy- either one. Antianxiety meds for short term relief, if they have underlying anxiety and depression - can do antidepressants.
What are Hallucinogens
Hallucinogens
Cause a profound disturbance in reality,
They cause flashbacks, panic attacks, psychosis, delirum, mood and anxiety disorders
Ex. Classic- LSD, Dissociative drugs- Ketamine, Phencyclidine PCP
In a 12 month period they can have intense cravings, difficulty w role obligations, and impairment/ tolerance
What are the s/s of halluciongen intoxication
Paranoia, impaired judgment, intensified perceptions, depersonalization, derealization.
Illusions, hallucinations, synesthesia ( hearing colors or seeing sounds),
Dilation of pupils, tachycardia, sweating, palpitations, blurred vision, tremors, incoordination.
What tx do we do for hallucinogen intoxication
Talk the pt down, reassure that symptoms are caused by the drug, and they will go away.
Physical restraints,
Severe cases- haloperdiol- antipsychotic
benzodiazepine like diazepam in short term.
What is Phencyclidine intoxication
Medical emergency that can cause violent side effects.
They can be belligerent- hostile and aggressive, assultaive, impulsive and unpredictable.
S/S
Nyastagmus ( eye movement), hypertension, tachycardia, diminished reponse to pain,
ataxia ( loss of muscle control),
dysarthria ( unclear speech),
muscle rigidity, seizures, coma,
hyperacusis ( sensitive to sound)
Hyperthermia and seizure activity
TX
Cant be talked down- may require a restraint.
Calming med like benzodiazepine IM or IV
Mechanical cooling for hyperthermia
What are the s/s of hallucinogen withdraw
red eyes, increase appetitie, dry mouth, hallucination, very irritable when wean them off
What is inhalant use disorder
Inhalants
Solvents for glues and adhesives
Propellants
Thinners
Fuels
paint sprays, gas, propane
Toxic gases inhaled- Can cause death bc it goes into blood stream
What are the s/s of inhalant intoxication
Small doses= Disinhibition and feel euphroria, auditory, impaired d
High doses= fearfulness, illusions, aduitory and visual hallucinations, distorted body image. Apathy( loss of interest) , diminished social and occupational fx, impaired judgment, impulsive and agressive.
Nystagmas, diplopia, nausea, anorexia, depressed reflexes,
High doses- stupor, unconscious, amnesia, delirium, psychosis, dementia
What is the tx for inhalant use
Tx- end up in coma, arrhythmias, bronchospasm,
WIll get haldol for agitation
What is opiod use disorder
Heroin and prescription drugs
Opioid intoxication
uCravings result in larger amounts, longer periods of use, increasing tolerance to its effects
uResults in significant impairment in life roles, interpersonal conflict, and puts a person in physically hazardous situations
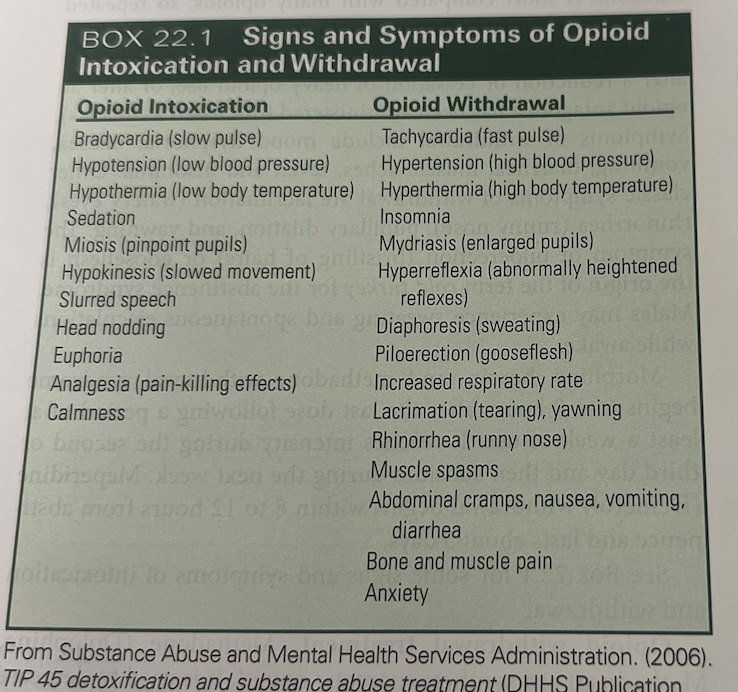
What are the s/s of opioid intoxication
Psychomotor retardation- slowing down, drowsiness, slurred speech, altered mood ( withdrawn to elated), impaired memory and attention,
myosis- pinpoint pupils ( red flag), decrease bowel sounds. RR and BP low, HR low to normal
track marks or fresh injection sites
What are the s/s of opiod overdose
Opioid overdose
Death usually due to respiratory arrest
S/S
unresposive, slow RR, coma, hypothermia, hypotension, bradycardia,
the big 3 symptoms tells you its an overdose- pinpoint pupils, coma, respiratory depression
What is the tx for opiod overdose
Treatment:
promote breathing; aspirate secretions, insert airway, mechanical ventilation.
nalaxone IN, IM,sub q, IV- increased rr and dilated pupils should happen quickly. Repeat if needed. Too much naloxone can cause withdraw symptoms
What are the s/s of opioid withdraw
Mood dysphoria ( persistent low mood), N/V, diarrhea, muscle aches, fever, insomnia,
Lacrimation ( watery eyes)
Rhinorrhea ( runny nose)
pupils dilate, yawning
piloerection ( hairs stand up or goosebumps)
Males- sweating and spontaneous ejaculations while awake.
What are the meds given to tx opidod withdraw
Opioid withdrawal
methadone, clonidine, buprenorphine, lofexidine
these meds help with pain but wont make you overdose. Wont put you in resp distress, or kill you.
Pts can wean off opiods witht these meds- will control the pain.
Opioid maintenance
uPharmacological
uPsychotherapies
always call poison control center
What are the s/s of methadone
Methadone- used to decrease painful symptoms of opiod withdraw. It blocks the euphoric effects of drugs such as heroin, morphine, codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone. if have these s/s need to seek medical care- difficulty breathing, light headed, fast herat beat, chest pain, anaphylaxis, hallucinations or confusion should re reported to provider.
What is clonidine
clonidine- eases sweating, hot flashes, watery eyes, and restlessnes,, decreases anxiety,
What are the s/s of buprenorphine/naloxone
buprenorphine/naloxone- used to help people reduce or quit opiates. Opioid partial agonist. Like opiods it produces euphoria or resp depression but these effects are weaker compared to heroin or methadone.
S/S- N/V, constipation, muscle aches and cramps, insomnia, irratble, fever. used only after 12-24hrs after withdrawal.
It can bring on acute withdraw for pts who arent in the early stages of withdrawl and who have other opioids in their system. Its a long acting drug, once pt is stablized they can switch to having it alternating oral tansmucosal instead of every day dosing.
What is Lofexidine
Lofexidine- can help people at home in a few days rather than a week.
What meds are given for opioid maintenance therapy
This is once sober we want to contiune abstinence.
Buprenorphine/ nalaxone and methadone reduce carvings.
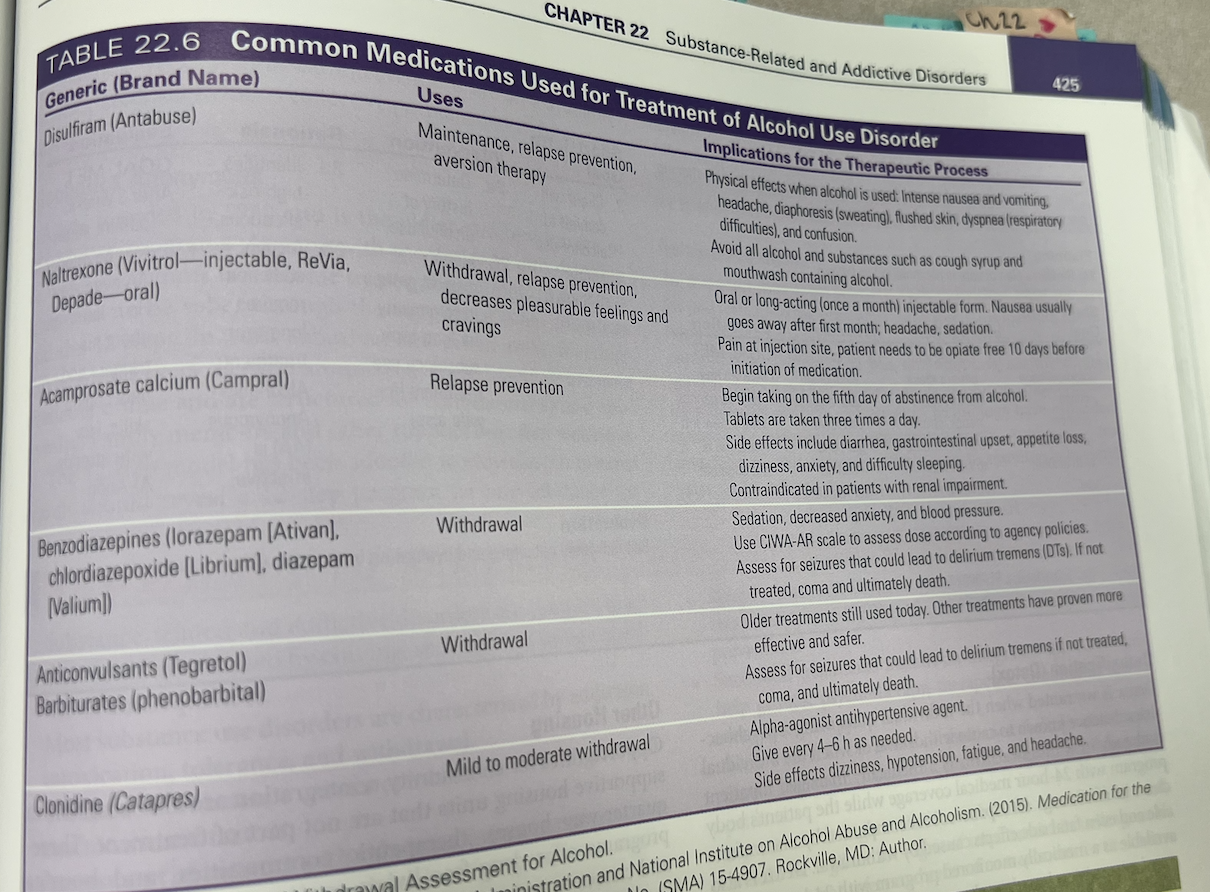
Naltrexone- opioid antagonist that prevents intoxication. Blocks the activation of opiod receptors and the feeling of euphoria. 1x a day dosing.
Can also give injectable form naltrexone callled vivitrol- given 1 a month IM . good for pts struggle w nonadherance and problems w access to healthcare.
Naltrexone S/S- Gi distress, muscle cramps, dizzy, sedation, appetitie disturbances. Feel pain, sweeling brusing if injection site rx. Complications- cellulitis, induration- hardening or thickening of tissue, rarely- necrosis, abcesses.
What psycholigical tx do we do for opioid abuse
All types of therapy- indvidual, behavioral, cognitive, family therapy,
social skills training
support groups like narcotics anonymous- 12 step program
Residental tx and theraputic communities- more structure is provided. They work best w highly motivated individuals. Confronation in the group enviornment and isolation from the outside word are empahsized in these settings.
What is Sedative, Hypnotic, and Antianxiety Medication Use Disorder
Problematic Substances
uBenzodiazepines- cant mix w alchohol
uBenzodiazepine-like drugs. Ex. zolpidem and zaleplon
uCarbamates
uBarbiturates- Ex. Secobarbital
uBarbiturate-like hypnotics ex. mathaqualone
This class includes all prescription medications and antianxiety meds.
Craving is a typical feature
What are the s/s of Sedative, Hypnotic, and Antianxiety Medication Use Disorder
This is a group of depressants- think calms you down
Slurred speech, incordination, unsteady gait, nystagmus, impaired thinking. Coma
Inappropriate agression and sexual behavior, mood flucation, imapired judgment
What tx do you do for overdose of Sedative, Hypnotic, and Antianxiety Medication Use Disorder
sent to ICU with withdraw and overdose symptoms. Have to be intubated bc have respiratory depression
Overdose: gastric lavage, activated charcoal, VS, if they’re awake after overdosing then they should be kept awake to prevent loss of consciousness. if uncosious- Iv fluid line, ETT for airway, mechanical ventilation.
What are the s/s of Sedative, Hypnotic, and Antianxiety Medication Use withdraw
Withdrawal:
We can have rebound hyperactivity where body has depressed CNS and then it tried to return to homeostasis.
S/S
Autonomic hyperactivity, tremors, insomnia, psychomotor agitation, anxiety, grand mal seizures
Tx
gradual reduction of benzodiazepines to prevent seizures and other symptoms. Barbituate withdraw can be aided by using long acting barbituate like phenobabital.
What is Stimulant Use Disorder
Clinical Picture
uAmphetamine-type, cocaine, or other stimulant drugs.
uSecond only to cannabis as the most widely used illicit substances in the United States
Truckers, athletes, studying exams
disordered pattern can occur in as little as 1 wk
Euphoria, high energy
what are the s/s of stimulant intoxication
feel superhuman
euphoric, socialable, elated, hypervigilant, sensitive, anxious, angry, tense agitated
2 or more of the following- , chest pain, arrythmias. high or low bp and hr, resp depression, dilated pupils, diaphoretic- perspiration,chills, N/V, weight loss, psychomotor agitation or retardation, weakness, confusions, seizures, coma

What are the s/s of stimulant withdraw
can happen within few hrs or several days. Tired, vivid nightmares, increased apeitite, insomnia or hypersomnia, psychomotor agitation or retardation. Function is impaired
depression and suicidal thoughts
What withdraw do we do for stimulate use disorder
Withdrawal treatment
Amphetamines- inpatient setting is necessary.
Group/ family and individual therapy
Antipyschotics for a few days
If there is no pyschosis- Possible diazepam for agitation
1 to 2 weeks’ cocaine withdrawal requires no inpatient care; no drugs reduce symptoms such as fatigue, mood changes, disturbed sleep.
Depression treatment once withdrawal is complete (e.g., bupropion)
Intense cravings for cocaine- might hospitalized.
unscheduled urine drug tests
What are other disorders
Tobacco
Withdrawal is distressing- have these patterns around cigarette and its so addicting.
Withdraw s/s- irritability, anxiety, depression, difficulty concentrating, restlessness, insomnia. Within days of them quiting smoking their HR decrease by 5-12 beats/ min. Within a year they increase their weight by 4-7 lbs.
Withdrawal treatment: behavioral therapy- to teach them how to recognize their cravings. hypnosis, nicotine replacement therapies- ex. gum, patches. ; antidepressant- bupropion or varenicline- mimics the effects of nicotine- nicotine receptor antagonist - partially blocks the receptor and blunts the effect of nicotine if they resume smoking.
Gambling disorder
Lie to conceal gambling, it can be regular or episodic. Heavy gambling may be interspersed with abstinence. Stress and depression increase this behavior.
Tx-
Gamblers Anonymous (GA)- 12 step program kind of like AA- publicly confess, peer pressure, peer counselors who used to gamble and are now reformed.
Hospitalization can remove them from a gambling environment. Individual, group and family therapy.
Possible treatment with SSRIs, bupropion- antidepressant (Wellbutrin), mood stabilizers- lithium , and anticonvulsants like topiramate.
what is Alcohol Use Disorder
uSedative with initial euphoria
Severity based on number of DSM-V symptoms
uMild: 2–3 symptoms
uModerate: 4–5 symptoms
uSevere: 5 or more symptoms
uExtensive List in DSM-V box


What other disorders do people with Alcohol Use Disorder have
Epidemiology
uAlmost twice the prevalence among adult men than adult women- runs in family
uAmerican Indians/Alaska Natives (12.1%) have the highest rates; disproportionately affected by alcohol problems.
Comorbidity
uBipolar disorders, schizophrenia, antisocial personality disorder, major depressive disorder
What are the risk factors of alcohol use disorder
Risk Factors
uGenetics
uNeurobiological
uSocial
uCultural
Types of Problematic Drinking
uBinge Drinking
uHeavy Drinking
What is alcohol withdraw s/s
Alcohol intoxication
uLegal definition of intoxication in most states: blood concentration of 80 or 100 mg ethanol per deciliter of blood (mg/dL).
uOften expressed as 0.08 to 0.10 g/dL.
uAlcohol withdrawal
s/s
Tremulosness aka shakes or jitters- classic sign happens 6-8 hr after withdrawl.
Agitation, lack of appetitie, N/V, insomnia, impaired cognition, mild perceptual changes- they can have delusions and hallucinations if they have delirium.
BP, HR, temp increase
Chlodiazepoxide can be used for tremulousness and mild to moderate agitation.
if psychotic and perceptual symptoms- medical emergency bc of risk of unconscious, seizures, delirium. Give lorazepam and Chlodiazepoxide PO or IM
Withdraw seizures- generalized tonic clonic - Diazepam IV
Alchohol withdraw delirium- aka delireum tremens - medical emergency that can result in death. can happen anytime within the first 72 hrs. Autonomic hyperacitvity- + HR, diaphoresis, fever, anxiety, insomnia, hypertension, delusions and visual and tactile hallucinations are common. -Give oral diazepam for acute symptoms, Chlodiazepoxide to keep them out of danger, once delirium disappears lorazepam IV for severe symptoms. Seclusion, correct dehydration dt sweating or fever w oral or iv fluids.
What is Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
Cognitive disturbances people w heavy alcohol use may suffer from short term memory disturbances.
encephalopathy, dont absorb nutrients, become malnourished rather drink than eat. Can get cognitively impaired, confusion,- decrease in thiamine
eye. abnormalities. tremors
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome-
Wernickle enecepalopthay- acute and reversable.
S/S- Altered gait, vestibular dysfunction, confused, eye problems ex. horizontal nystagmus, lateral orbital palsy, gaze palsy. Eyes not symetrical. sluggish rx to light, anasocria- uneven pupil size
Korsakoff- chronic condition that can kill you.
medical emergency. mimick stroke symptoms. Have to get IV vitamins ( banana bag) and nutritional support
both are tx w thiamine
Fetal alcohol syndrome- teach them to not drink alchohol at all
What are the effects of Alcohol Use Disorder
Systemic effects
uPeripheral neuropathy- nerve damage - presethesia like numbness, pain, muscle weakness, sensitvity to touch, burning. gait issues, thymine/ folic acid replacement. discontinuing alchohol will prevent further deteroriation.
uAlcoholic myopathy- muscle weakness and myonecrosis- muscle damage. signifant reduction in muscle mass
Alchoholic cardiomyopathy- weakens and thins the muscle of heart. Leads to enlargment and HF. fatigue, sob, edmea
uEsophagitis, gastritis, and pancreatitis-
gastritis- alchohol irriate lining of stomach and can cause ulcers. also have n/v, loss apetite, belching, and bloating.
if pancrease dies- get diabetes, vomit, nausea, have bad abdominal pain, increase amylase, lipase, gonna be IV fluids, NPO, monitor shock. Chronic pancreatitis- malnutriton, weight loss, diabetes mellitus.
vommiting and damage to esophagus- burns tissue and can get worn down. this can cause esophageal varacies
uAlcoholic hepatitis- diseased and inflamed liver. appetite changes, dry mouth, weight loss, N/V, pain, swelling in abdomen, jaundice, fever, confusion, fatigue.
uCirrhosis of the liver- makes clotting factors. AST. ALT, increase PT and INR, blood thin not clotting. Need vit K but they’re not absorbing that. S/S- bleeding and bruising, pruritus, jaundice, ascites, leg edema, weight loss, confusion, spider like vessels, petechiae, Tx- transplant , low Na diet
uLeukopenia- bone marrow not working, doesnt make WBC so risk infection. Low WBC dt vitamin deficiencies and low protein.
uThrombocytopenia- Low plts- bleeding.
Cancer (especially head and neck)-
cant fx until get drink- have tolerance as well.
rapid hr, sweating, delusion, hallucinations- psychosis delirium. cant miss a pt whos an alcoholic
screen everyone
What are screening tools
SBIRT: Screening, brief intervention, and referral to treatment
AUDIT: Alcohol use disorders identification test
CAGE: 4 questions to identify alcohol abuse- have you felt the need to cut down on your drinking. Are you annoyed by your drinking. Have you felt guilty about your drinking. Have you ever had a drink in the morning ( eye opener) . Score of 2 or more is signifcant.
CAGE-AID: Same questions as CAGE but adds drug use to alcohol. Adapted to Include Drugs
T-ACE: Tolerance, Annoyance, Cut down, Eye-opener
good response- your answers help us figure out how to tx you. What concerns you.
What drugs do we give
Pharmacotherapy
uDisulfiram- antebuse, tachycradia, sweating, blurry vision, resp distress, teach not to drink alchohol, contraindicated in pregnancy. Inform the patient that ingesting alcohol while taking this medication produces a toxic reaction that causes intense nausea and vomiting, headache, sweating, flushed skin, respiratory difficulties, and confusion. Avoid all alcohol and substances like cough syrup and mouthwash that contain alcohol.
Disulfiram must be taken consistently to maintain the aversion to alcohol.
uNaltrexone- used for withdraw and relapse prevention
uBenzodiazepines- LAM/PAMS
WHat do we assess, and plan
Assessment
uFamily assessment (codependence)- doing things for others when they are capable of doing it themselves. Their self worth is dependent on caring for others at the expense of their own needs. Enabling- calls in for spouse, covering for them, bail out of jail.
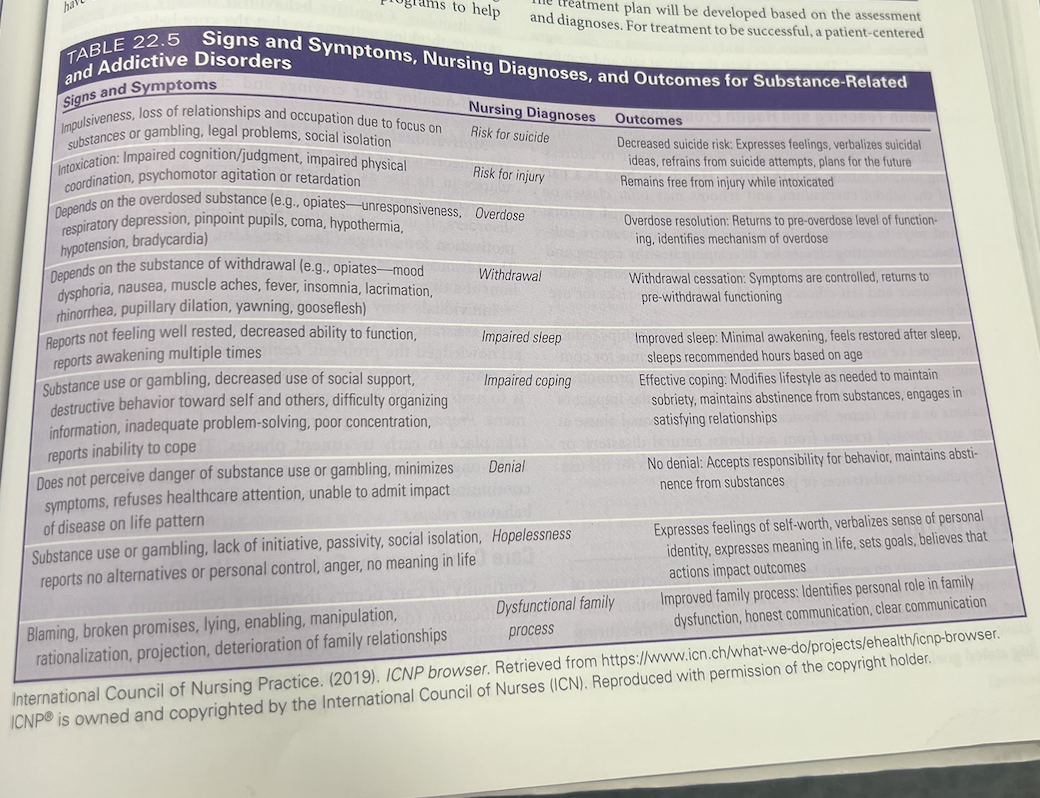
Planning
uIdentifying problem
uSetting a goal
uDetermining the interventions that will accomplish the goal
Care Continuum for Substance Use Disorders
uDetoxification (detox)- 24 hr medical coverage while they detox.
uRehabilitation- short term rehab offers rehabilitation ( learning a lost skill) long term rehab offers habilitation ( learning a new skill).
uHalfway houses- focus on extending the period of sobriety. Get case management involved in addressing educational, economic, and social needs.
uOther housing- not part of treatment. Ex. therapeutic communities, housing programs that offer a drug free environment and classes to remediate the skills needed for daily living. They attend outpatient substance use treatment.
uPartial hospitalization program- Ex. 5 days a wk for 6 hrs a day. Can live in supportive housing or an independent home. Dont need 24hr residential tx.
uIntensive outpatient programs- 3 days a wk for 3 hrs a day. Not a residential program. Highly structured w scheduled tx groups and at least 1 individual session.
uOutpatient treatment- Mix of individual and psychotherapy groups. Structured, drug free, non residential. No more than 5 contact hrs a week, web- where its is self paced and anonymous.
uAlcoholics Anonymous (AA)- can also include friends and family
Relapse prevention- pts learning health coping skills, stress management. learning skills to continue not drinking if relapse occurs.
Psychotherapy
Motivational interviewing- strengthens motivation for change. Ex.

WHat implementation do we do
Implementation
uPromoting safety and sleep: first-line interventions
uReintroduce good nutrition and hydration
uSupport for self-care (hygiene)
uExploring harmful thoughts and spiritual distress
Health teaching and health promotion
uPrevention against genetic vulnerability
uPublic classes
Give thymine before glucose
benzoz and alchohol withdraw can kill
complications. MI, stroke, hyperthermia
DKA- IV insulin.
Know how to give thymine.