Changing landscapes of the UK: rivers
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is deposition
This is when a river loses energy and it drops off the material it is carrying
What are the factors leading to deposition
shallow water
At the end of the rivers journey
When the volume of water decreases
What is drainage basin
This is an area of land around the river that is drained by the river and its tributaries
What is a watershed
This is an area of high land forming the edge of a river basin
What is the source of a tuber
This is where the river begins
What is the mouth of a river
This is where the river ends and meets the sea
What is a confluence
This is a point where two rivers meet
What is a tributary
This is a small river that joins a larger river
What is a river channel
This is where the river flows
What is the long profile of a river
This is a line representing a river from its source to its mouth
What is the upper course of a river
This is where the river starts and is usually an upland area. The river channel is narrow and shallow here and the load here is large because it hasn’t been broken down by erosion
What is the mid course of a river
This is where the gradient becomes less steep and the river channel gets deeper and wider as the bed and banks are deeper
What is the lower course of a river
This is the final course of the river where the land is a lot flatter. The rivers load is fine sediment as erosion has broken down the rocks
Describe erosion at the upper course of river
As the river flows downhill there is increase in vertical erosion. The channel is shallow and narrow because there isn’t a lot of water here
Describe erosion in the middle course of a river
As the river flows into the middle course there is some vertical erosion but more lateral erosion this makes the channel wider and deeper
Describe erosion in the Lower course of a river
This is a lot less erosion only some lateral erosion. The river is at its widest and deepest
What is a waterfall
This is a sudden drop along the river course. It forms when there are horizontal bands of hard rock over soft rock
Describe the formation of a waterfall
the soft rock is eroded quicker than the hard rock and thus creates a step
As erosion continues the hard rock is undercut forming an under hang
The action of abrasion and hydraulic action creates a plunge pool
The plunge pool gets bigger increasing the size of the overhang until the hard rock is no longer supported and it collapses
This process continues and the waterfall retreats upstream
A steep sided valley is left where the waterfall once was this is called a gorge
What is a meander
This is a curve or bend in a rivers course
Describe the formation of meanders
meanders are formed by erosion and deposition
The force of the faster flowing water erodes the outside bend undercutting thee bank and forming a steep river cliff
The water is shallower and flows more slowly on the inside bend
Sand and gravel are deposited on the inside bend to form a slip off slope
Deposition takes place here because the river has less energy
As meander erodes the outside bend the bends get wider
Lateral erosion widens valley floor
What is an oxbow lake
U-shaped body of water that forms when a river's meander, or bend, is cut off from the rest of the river
How are oxbow lakes formed
erosion makes the neck of a meander narrow
The meanders move closer together
When there is a flood the river cuts across the neck taking a new shorter route
Deposition will cut off the original meander leaving a horseshoe shaped oxbow lake
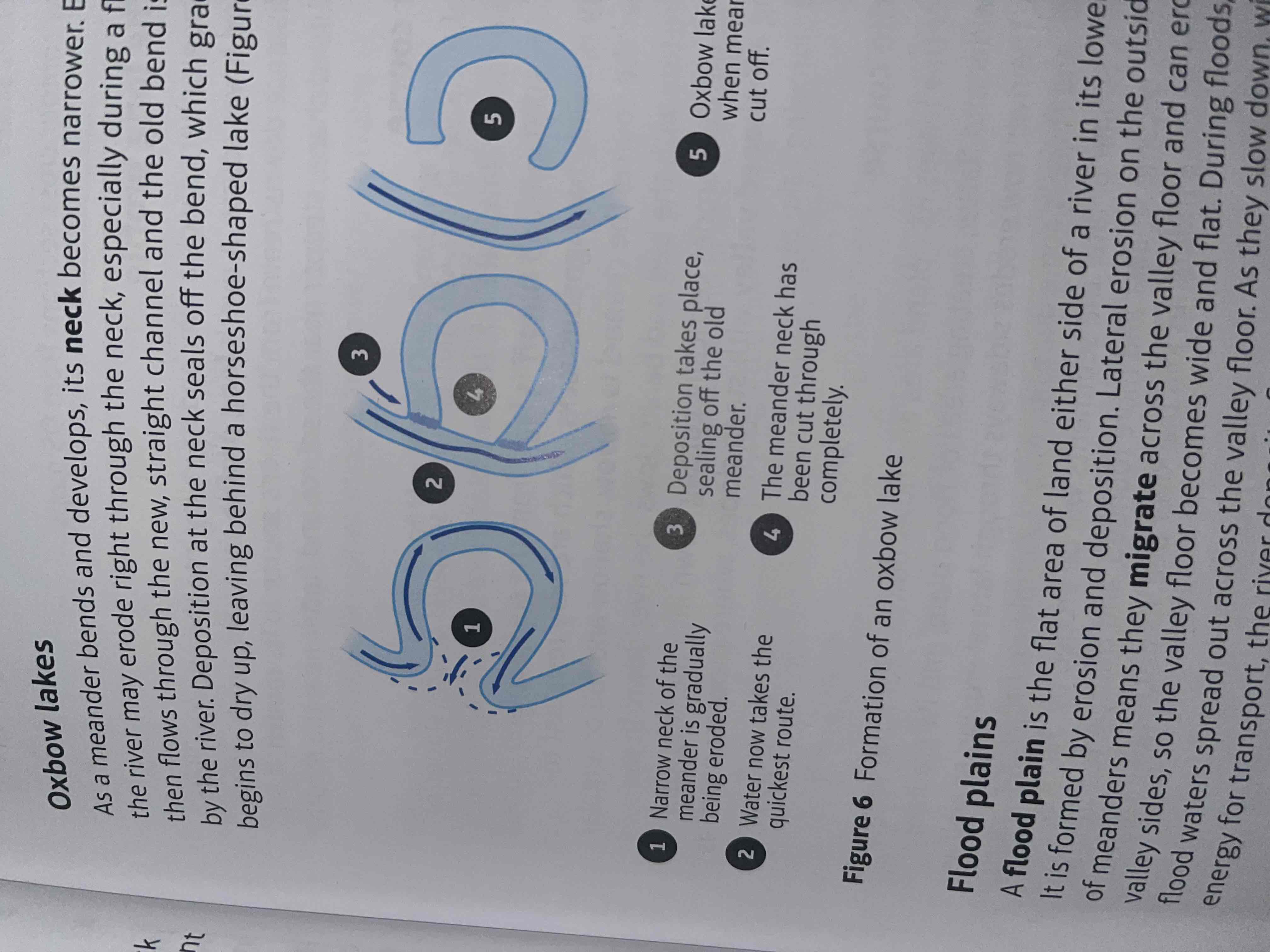
What is a floodplain
This is an area of land which is covered in water when the river bursts its banks
How are floodplains formed
they are formed due to erosion and deposition
Erosion removes any interlocking spurs creating a wide flat area on either side of the river
During a flood material carried by the river is deposited
Over time the height of the floodplain increases as material is deposited on either side of the river
What are levees
These are naturally raised river banks found on the side of a river and are prone to flooding
How are levees formed
levees occur in the lower course of a river when there is an increase in the volume of water flowing downstream and flooding occurs
how do levees affect rivers
sediment that has been eroded further upstream is transported downstream
When a flood occurs the river loses energy. Yhe largest material is deposited first at the side of the river banks and smaller material further away
After many floods the sediment builds up to increase the height of the river banks meaning that the channel can carry more water and flooding is less likely to occur
What is an estuary
This is where the river meets the sea
What is flooding
Flooding occurs when a river breaks its banks and overflows the surrounding land
What are the causes of flooding
prolonged rainfall
Heavy rainfall
Relief: steep valley is more likely to flood than a flatter valley cause the rainfall will run off into the river more quickly
Geology: permeable rocks allow water to pass through pores
Vegetation: trees and plants absorb water known as interception
What is an hydrograph
This shows how a river responds to a period of rainfall
What is peak discharge
Maximum amount of water held in a river channel
What is peak rainfall
Maximum amount of rainfall
What is lag time
This is the time between peak discharge and peak rainfall
What is the rising limb
This shows the increase in discharge on an hydrograph
What is the falling limb
This shows the return of discharge to base flow on an hydrograph
What is base flow
The normal discharge of a river
What factors affect lag time
geology: if the rock are impermeable the lag time is shorter
Soil type: clay soils do not drain easily so they increase lag time
Slope: steeper slopes lead to rapid water transfer and shorter lag times
Vegetation: no vegetation means the water runs off quicker therefore it would have a short lag time
Antecedent conditions: wet conditions before a storm cause the ground to be saturated which speeds up over land flow and shortens lag times
What are hard engineering strategies for flood
damns
River straightening and dredging
Embankments
Describe dams
can be used to produce electricity by passing water through a turbine
They can attract tourists
Very expensive to build
Habitats are flooded leading to rotting vegetation
Describe river straightening and dredging
river straightening speeds up the water so high volumes of water can pass through
Dredging makes the river deeper so it can hold more water
More water can be held in the channel
Dredging needs to be done frequently
Speeding up the river leads to floods downstream
Describe embankments
this involves raising the banks of rivers so it can hold more water
Cheap with one off cost
Allow for flood water to be held in a river
Looks unnatural
Can increase flood risk downstream
what are soft engineering strategies for floods
flood warnings
Floodplain planing
Describe floods warning
People have time to try and protect their property
People have time to evacuate areas
Flash floods may happen too quickly for any warning to be effective
They do not stop flooding
describe floodplain planing
More expensive buildings are further away from the river
Less damage is caused leading to fewer insurance claims
Not always possible to change existing land users
Why does river discharge change along the course of a river
Why does river velocity increase downstream
tributaries join the main channel so there’s more water in the river
Channel becomes a more efficient shape so there’s less friction