Bug Parade: Gram-Positives
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
staphylococcus aureus reservoir
anterior nares, skin, axillae. intestine, throat, perineum
staphylococcus aureus virulence
adhesins
small colony variants (don't get detected on plate)
antimicrobial resistance (MRSA)
toxins (toxic shock syndrome, food poisoning, scalded skin syndrome)
staphylococcus aureus diseases
skin and soft tissue: impetigo, folliculitis, furuncle, carbuncle, pyoderma, abscess, cellulitis
organ and systemic: bacteremia, osteomyelitis, empyema, arthritis, endocarditis, pneumonia
Foreign body-related infections: stick to plastics or prosthetics
staphylococcus aureus growth/screens
-beta hemolytic
-white, goldish pigment
-mid-large colony
-cocci in clusters
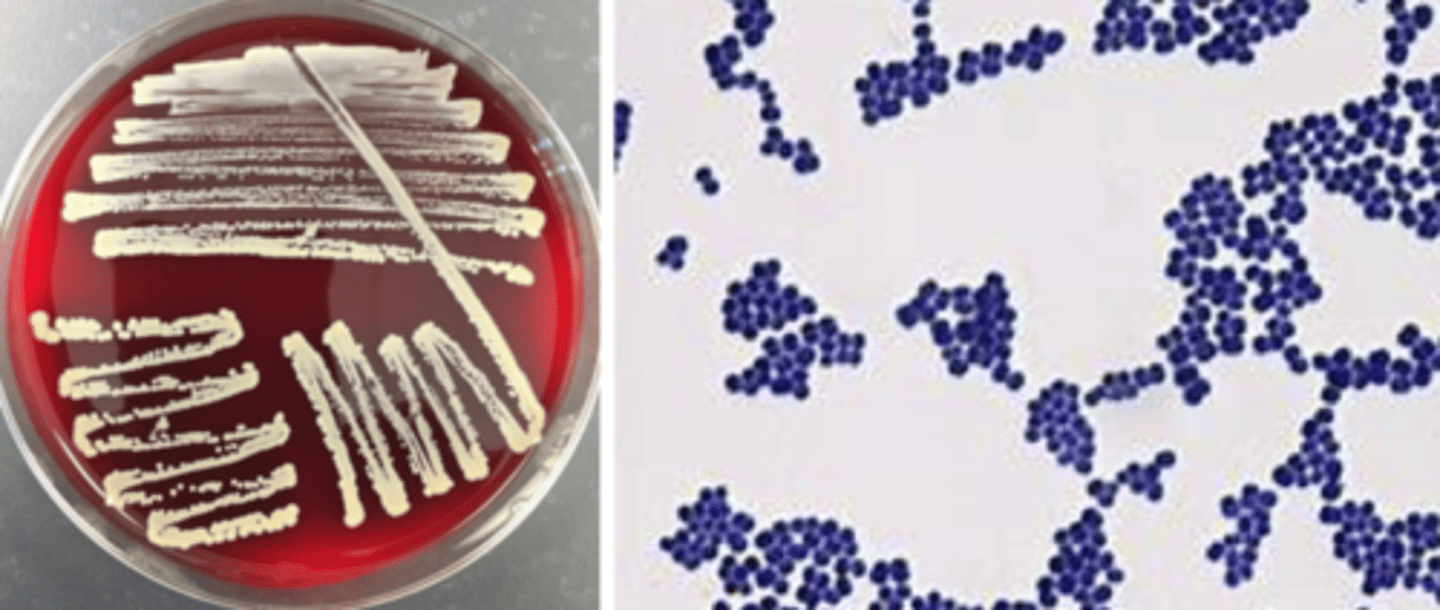
staphylococcus aureus identification
-catalase positive
-coagulase positive
-latex agglutination
coagulase-negative staphylococci
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus lugdunensis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Staphylococcus hominis
Staphylococcus warneri
Staphylococcus haemolyticus
coagulase-negative staphylococcus reservoir
skin, axillae, inguinal, perineal, nares
S. saprophyticus (coagulase-negative staphylococcus) reservoir
rectum, genitourinary tract
coagulase-negative staphylococcus virulence
urease
glycocalyx (biofilm): decreases opsonization, antibiotic penetration, phagocytosis, and lymphocyte proliferation
coagulase-negative staphylococcus disease
catheter - UTI
device infection - prosthetic valve endocarditis, right-sided endocarditis
coagulase-negative staphylococcus growth/screens
-non-hemolytic
-white pigment (S. lugdunensis is "yellow")
-mid-large colony
-cocci in clusters
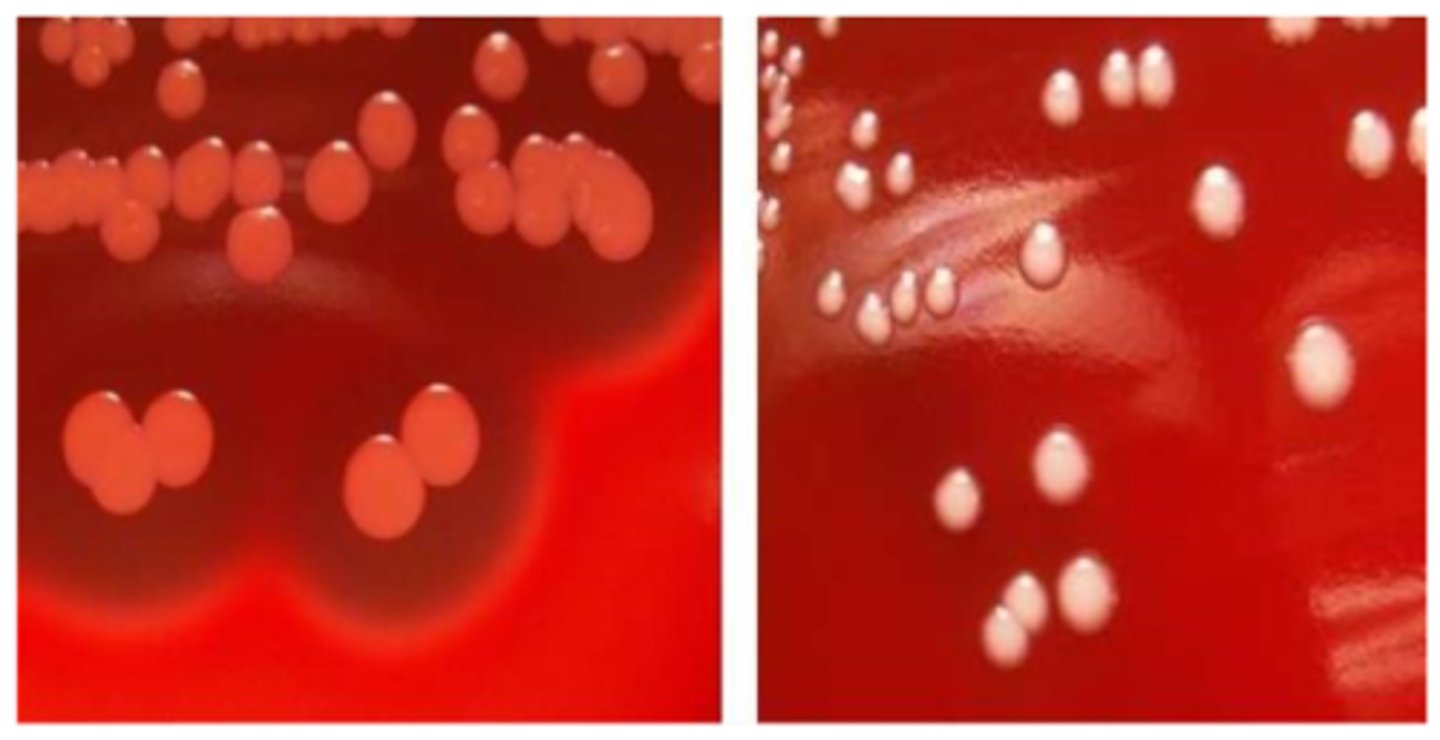
coagulase-negative staphylococcus identification
-catalase-positive
-coagulase-negative
-S. lugdunensis: pan-susceptible
-S. saprophyticus: resistant to novobiocin
Streptococcus pneumoniae reservoir
upper respiratory tract, particularly sinus and oropharynx
more colonization in young kids (30-70% rate)
household transmission between kids and adults
Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence
antiphagocytic capsule
Streptococcus pneumoniae diseases
30% of community-acquired pneumonia (bacteremia)
meningitis (sequelae)
#1 in otitis media
sinusitis, peritonitis, rare endocarditis
Streptococcus pneumoniae growth/screen
alpha-hemolytic
mucoid or cheerio/checker colony
lancet-shaped gram-positive diplococci
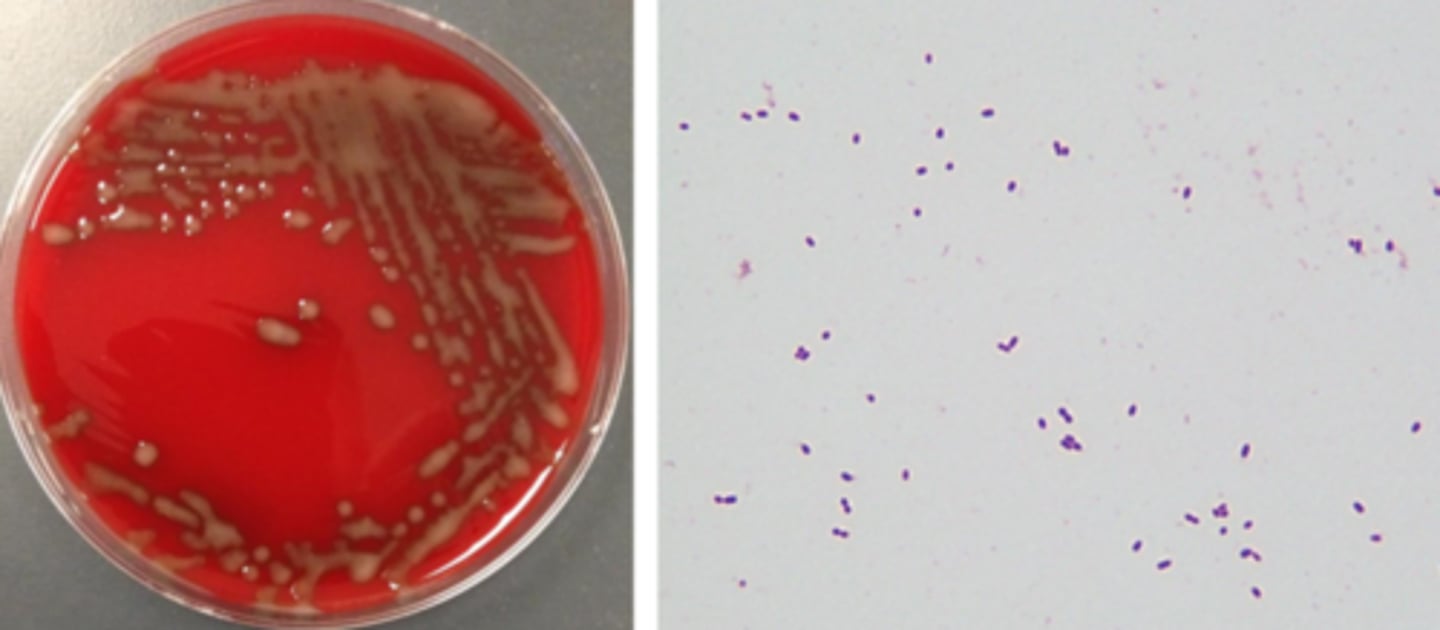
Streptococcus pneumoniae identification
alpha hemolysis (leaves green remnant)
catalase-negative
bile solubility-positive
susceptible to optochin
viridans group streptococcus reservoir
oral cavity, lower GI tract, skin, female genital tract
viridans group streptococcus virulence
none - part of normal flora
can be virulent if immunocompromised
viridans group streptococcus diseases
#1 in native valve endocarditis
#1 infectious disease worldwide = cavities
bacteremia (can also be a blood culture contaminant)
viridans group streptococcus groth/screens
alpha-hemolytic
cocci in chains
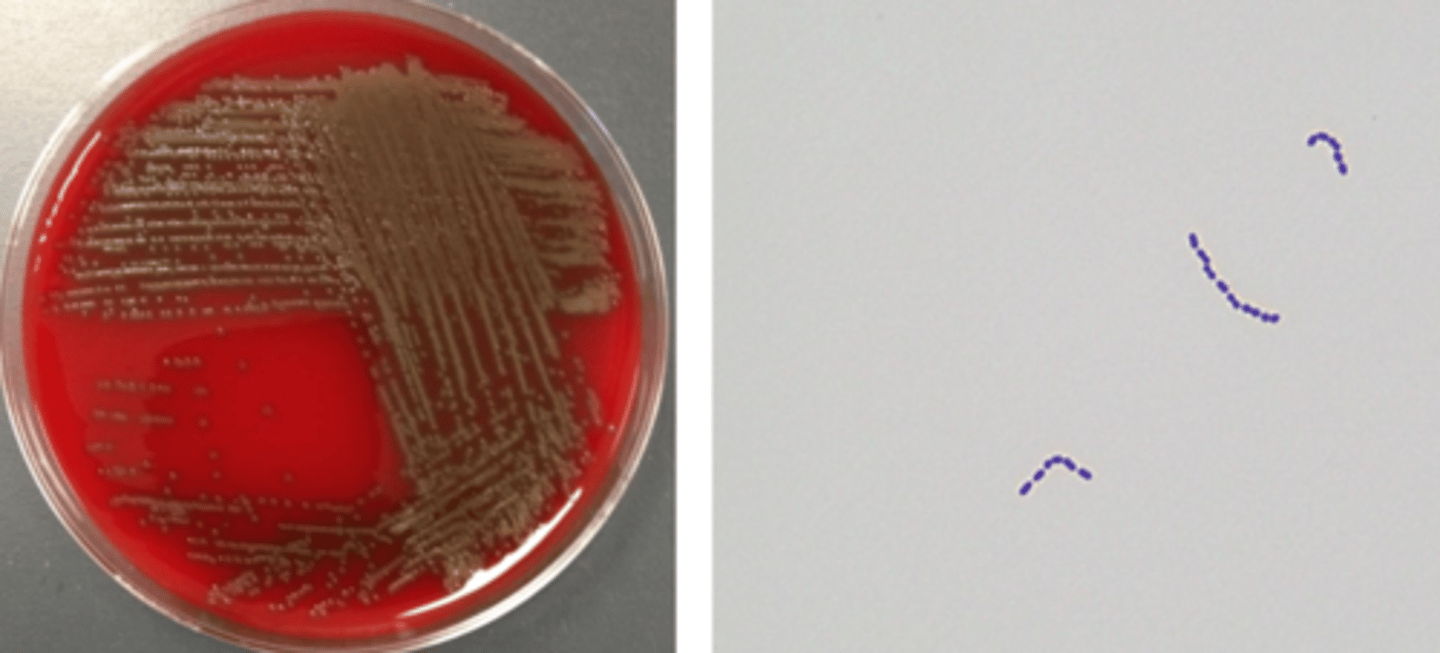
viridans group streptococcus identification
alpha hemolysis
bile solubility-negative
resistant to optochin
streptococcus pyogenes reservoir
throat, skin
streptococcus pyogenes virulence
M protein: resistant to phagocytosis
erythrogenic exotoxin: scarlet fever
immune-mediated superantigen: toxic shock syndrome
streptococcus pyogenes diseases
#1 in bacterial pharyngitis
#1 in impetigo
deep soft tissue infections (erysipelas, cellulitis, flesh-eating virus)
non-suppurative sequelae: glomerulonephritis, acute rheumatic fever
streptococcus pyogenes growth/screens
beta hemolytic (large zone)
grey pigment
small colony
cocci in chains
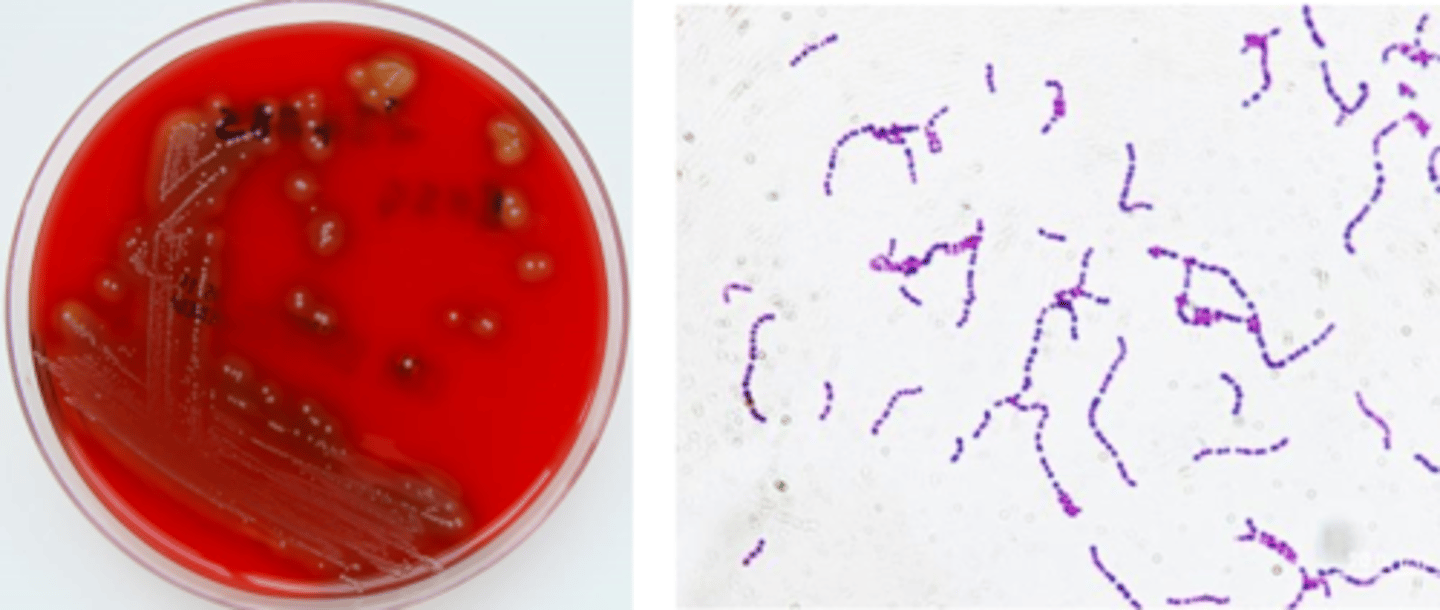
streptococcus pyogenes identification
catalase-negative
Lancefield group A
PYR-positive
streptococcus agalactiae reservoir
lower GI tract, urogenital tract (especially female)
streptococcus agalactiae virulence
lack of antibody developed versus capsular antigens
sialic acid: inhibits activation of alternative complement cascade and prevents phagocytosis
streptococcus agalactiae diseases
early-onset neonatal disease (sepsis, pneumonia 7 days)
late-onset neonatal disease (sepsis, meningitis 3 months)
adult (invasive, SST, pneumonia, bacteremia, UTI)
streptococcus agalactiae growth/screens
beta hemolytic (small zone)
grey pigment
smallish colony
cocci in pairs
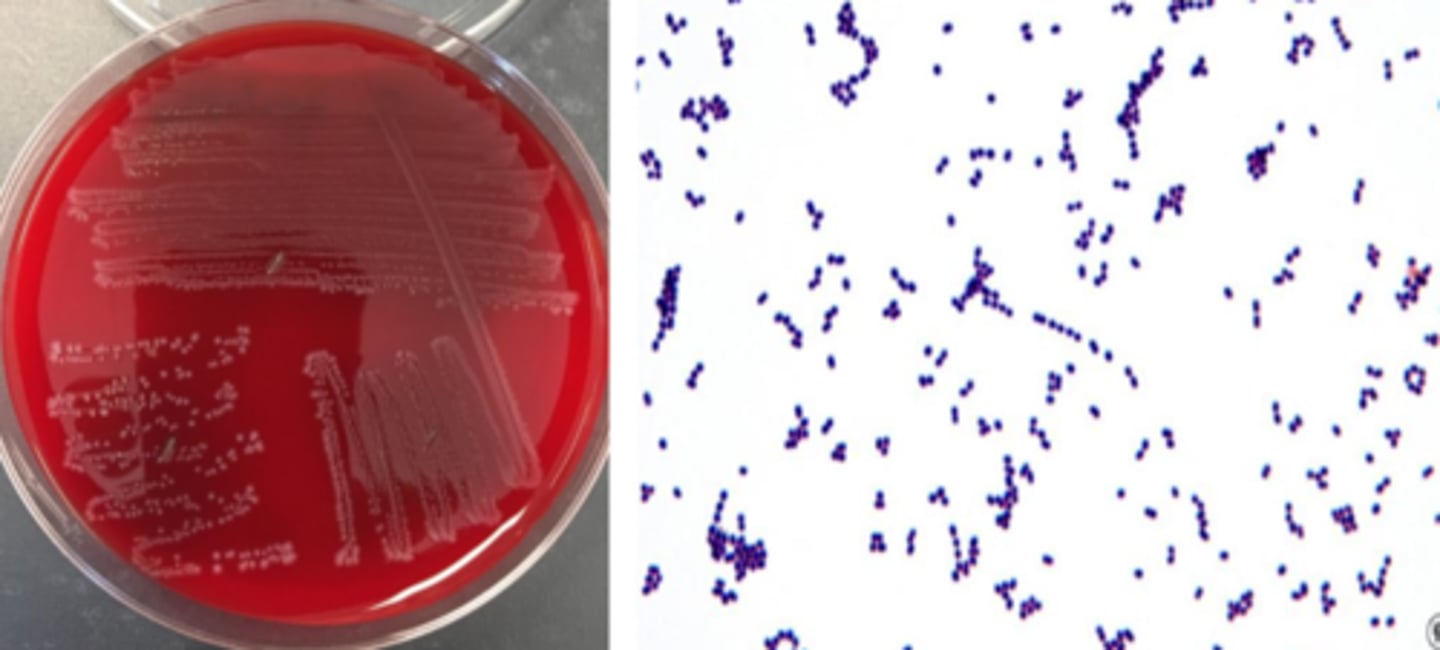
streptococcus agalactiae identification
catalase negative
Lancefield group B
hippurate hydrolysis-positive
Streptococcus groups C, F, and G
can also cause pharyngitis but do not cause sequelling or glomerular nephritis
Milleri-group streptococci
identified by the scent of butterscotch
enterococcus reservoir
lower gastrointestinal tract, less common genitourinary tract, oral, cavity, skin (perineal)
enterococcus virulence
wimpy pathogen
biofilm
antibiotic resistance
aggregation substance
enterococcus diseases
10% of UTIs
bloodstream infection
endocarditis (20% of native valve, 5% of prosthetic valve)
surgical site infection (especially abdominal)
device infection
trend toward nosocomial infection
enterococcus growth/screens
non-hemolytic
VRE often alpha-hemolytic
grey pigment
smallish colony
cocci in pairs
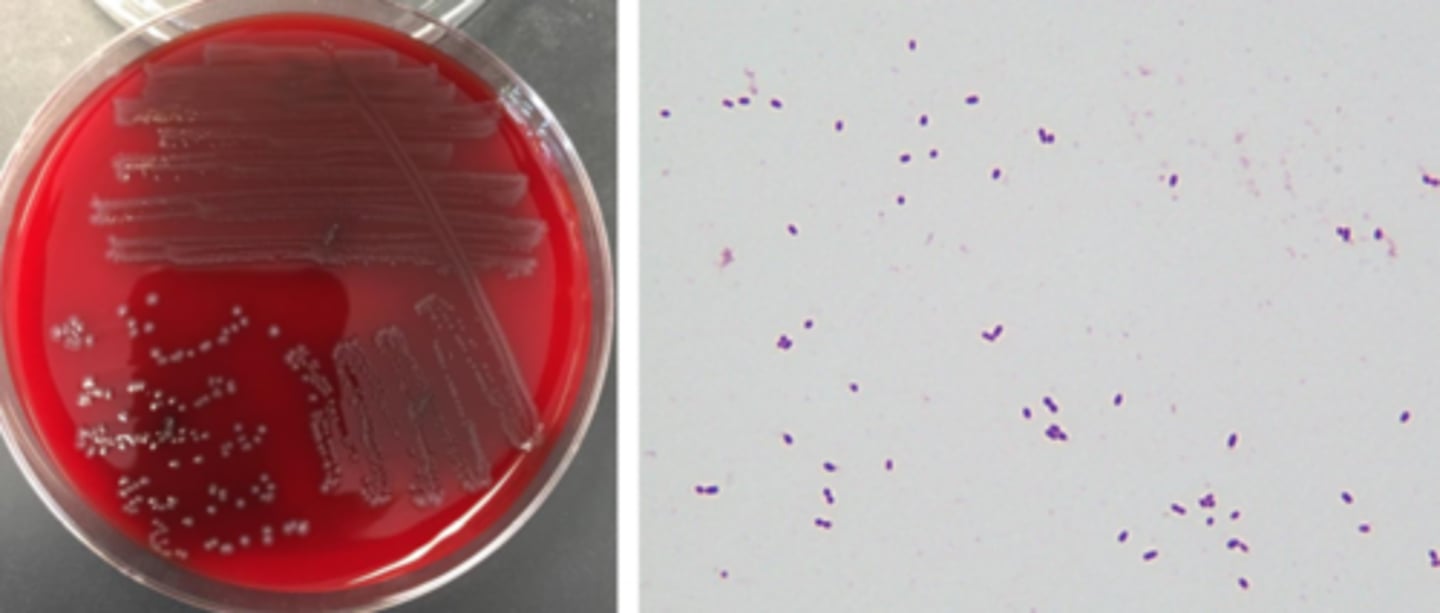
enterococcus identification
catalase negative
esculin positive
PYR positive
growth in 6.5% NaCl
streptococcus bovis group growth/screens
non-hemolytic
grey, small colonies
group D streptococcus, not enterococcus
"D not E"
streptococcus bovis group identification
catalase negative
esculin positive
PYR-negative
no growth in 6.5% NaCl
listeria monocytogenes reservoir
typically environmental, some animals
several opportunities to enter food production (poultry, meat, veggies, raw milk, soft cheese)
listeria monocytogenes virulence
persistence in macrophages (intracellular)
Escape host vacuole
Internalin has tropism for fetal trophoblasts
listeria monocytogenes diseases
adult sepsis, CNS disease (CLL, cancer, transplant, EtOH, age >60)
pregnancy: milkd, self-limiting, influenza-like; transplacental
listeria monocytogenes growth/screens
beta hemolytic (small zone)
grey pigment
smallish colony, bacilli in stacks
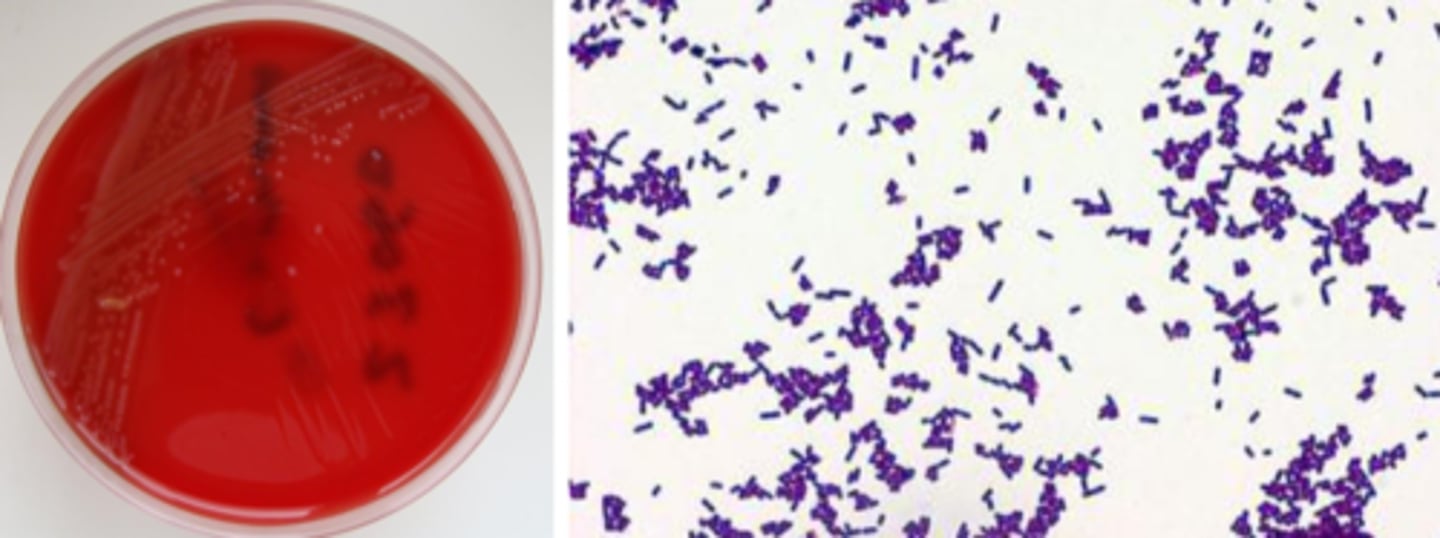
listeria monocytogenes identification
catalase positive
umbrella-like motility
esculin hydrolysis-positive
hippurate hydrolysis-positive
Bacillus reservoir
ubiquitous
spore-producer - can survive anywhere
opportunities to enter food supply
Bacillus virulence
emetic toxin
enterotoxin
bacillus diseases
anthrax (B. anthracis; cutaneous, ingestion, inhalation injection)
food-borne illness (B. cereus)
right-sided endocarditis (IVDA; can be non-cereus, non-anthracis,)
covert bioterrorism agent
bacillus growth/screens
beta hemolytic and motile is ok!
non beta hemolytic and nonmotile should be watched out for
spreading colony
spore-forming bacilli
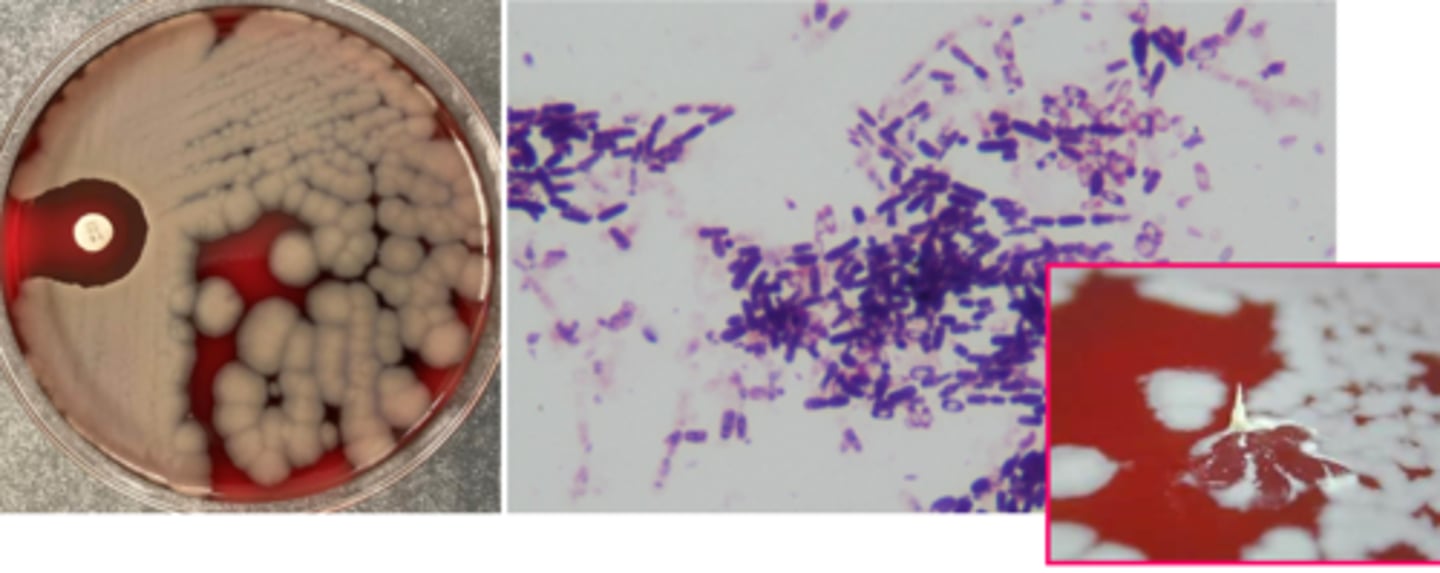
bacillus identification
catalase positive
colony morphology helpful; B. anthracis can be tenacious
if cannot rule out B. anthracis, send to public health lab
corynebacterium reservoir
largely skin and mucous membrane
some environmental
often "along for the ride"
corynebacterium virulence
exotoxin
nasopharyngeal-adherent membrane may cause obstruction
corynebacterium diseases
diphtheria (C. diphtheriae - can also be cutaneous; vaccine-preventable)
UTI (C. urealyticum)
nosocomial, antibiotic resistant (C. jeikeium)
corynebacterium growth/screens
non-hemolytic
club, palisading bacilli (Chinese letters)
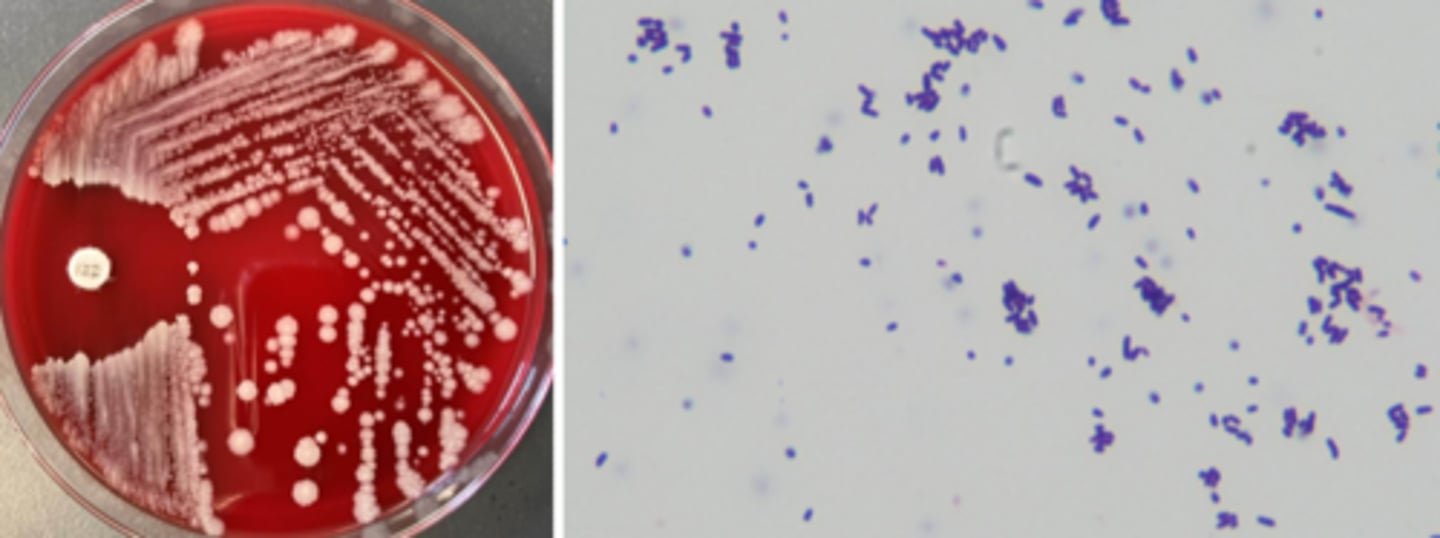
corynebacterium identification
catalase positive
often identified to genus level (catalase and gram stain)
C. diphtheriae ID at reference laboratory; + toxin testing