BIOL-N251 Exam 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What microorganisms are
-Range in size (smallest virus to the largest parasites and fungi)
What are different type of microorganisms
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
difference between prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic: "pre-nucleus" No membrane bound organelles, example: bacteria
Eukaryotic: "true-nucleus", possess membrane bound organelles; parasites, amoeba, paramecium, man
Microorganism also include the viruses
only consist of proteins and nucleic acid.
viroids and prions
smaller and less complex infectious particles than viruses
-Viroids are only genetic material they have no protein
-Prion don't have a genetic material
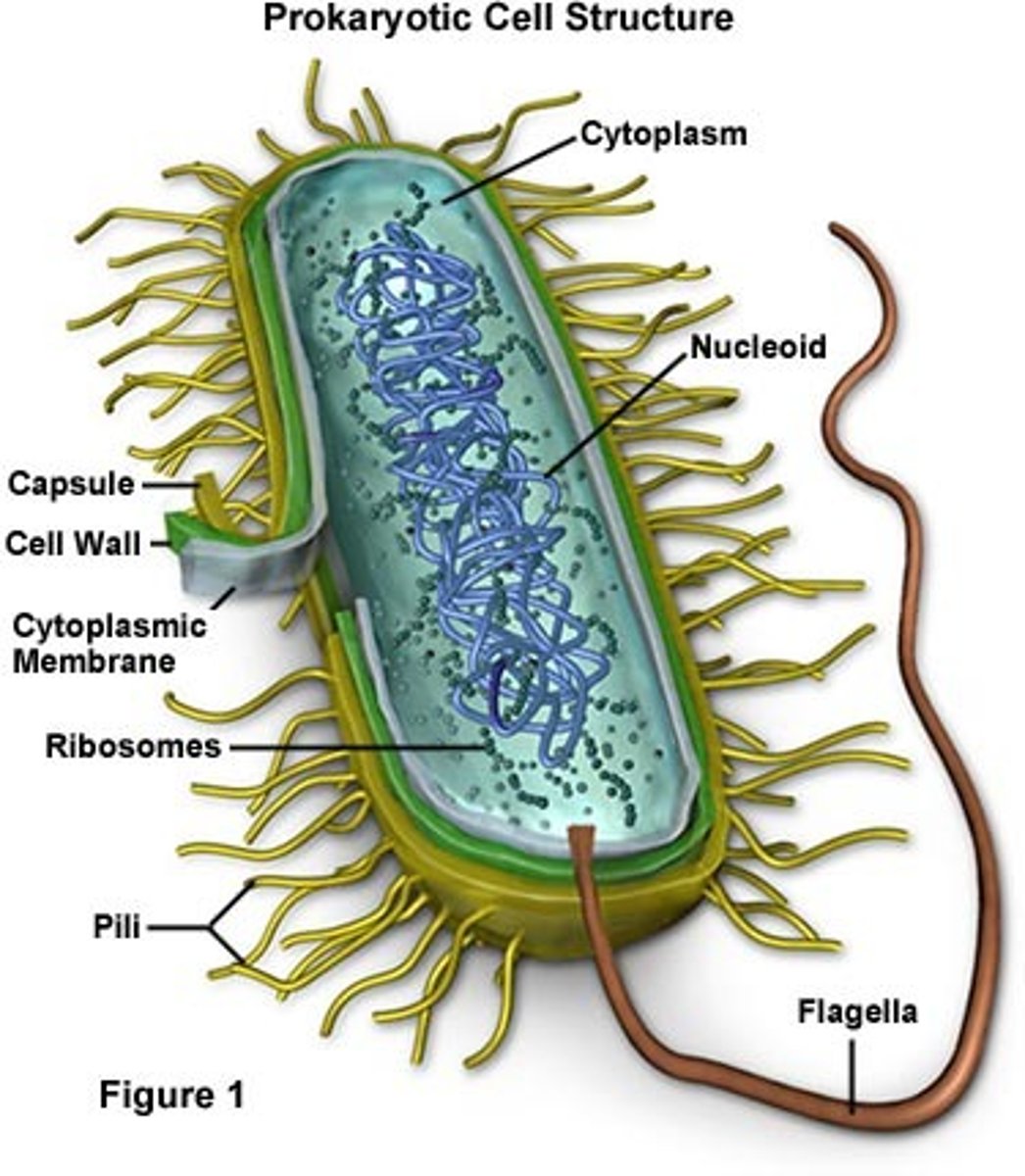
Prokaryotic cell
-Plasma membrane: genetic material, pass genetic
-Fimbriae: let them stay in place
Eukaryotic cell

Structure of bacterial cell
Flagellum, Fimbria, Pillus, Cell envelope. Glycocalyx, Coating.
Flagellum
provide motility, allow prokaryotic to move around
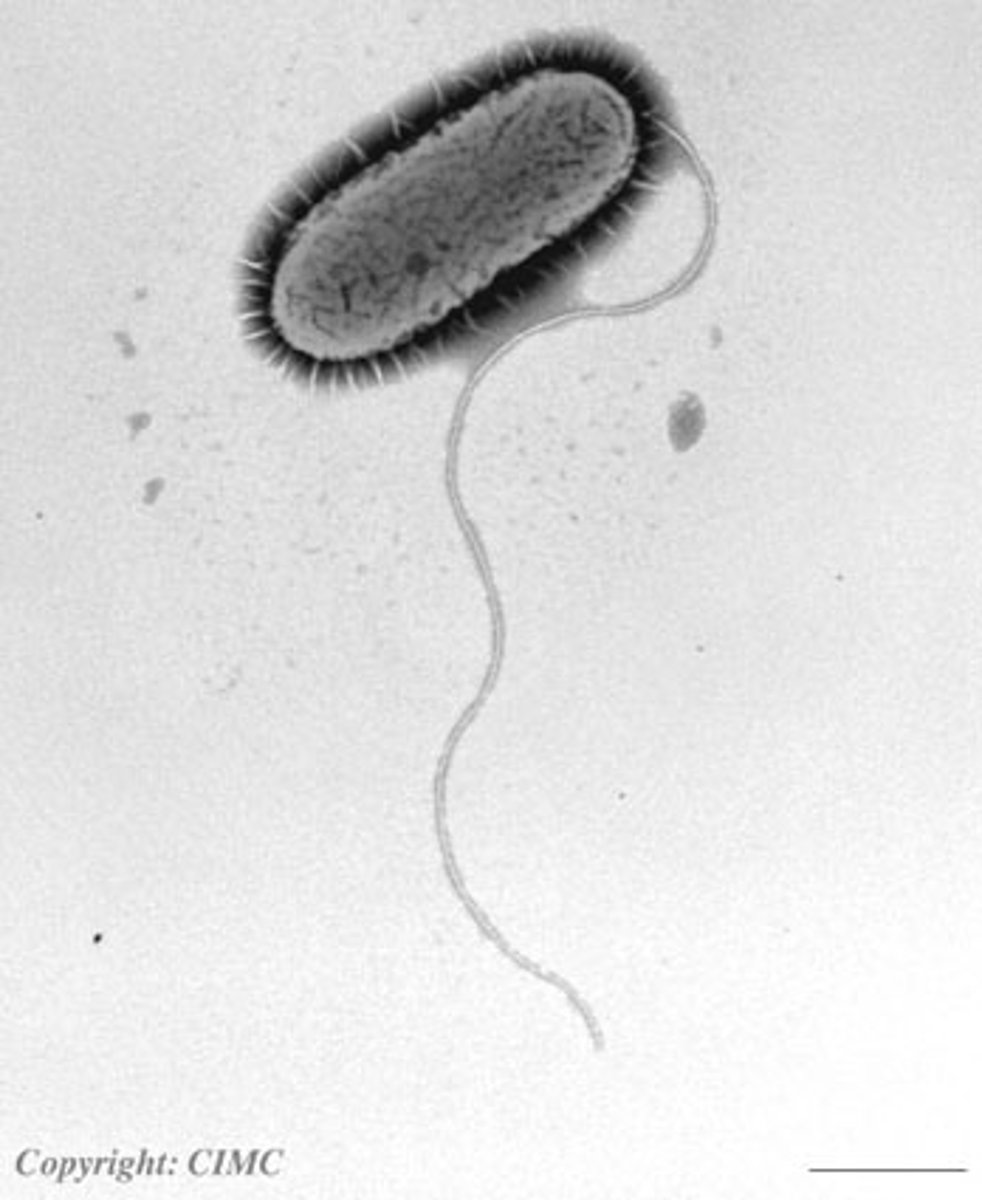
Fimbria
-small blister like fibers on surface
-helps bacteria stick to each other and surfaces
Pillus (pilli)
-Elongated, rigid tubular structure
-sexual reproduction: conjugation
- Transfer DNA from one cell to another
-Bacteria become resistant to drugs
genetic material is pilus
is responsible for bacteria being antibiotic resistant
Cell Envelope
-Composed of the glycocalyx (outter one), Cell wall (Middle), and cell membrane.
-Protects the cell
Cell membrane
-closest to the cell
-Flexible thin skin that encloses the cells interior
-controls in/out transport of substances (via proteins in membrane)
Cell wall
-Middle Part
-Provide rigidity, strength, and protection
-Different Structure from Gram+ and Gram- bacteria
-Cell wall-deficient. bacteria:cause chronic diseases (ex: lyme)
Glycocalyx
-External Layer
-Slime Layer: loose, soluble polysaccharide; not bound to the cell; aids bacteria in colonizing surfaces slide along solid surfaces
Glycocalyx function
coating of macromolecules: protect the cell, helps cell adhere to its environment
Coating :Capsule
-Bound to the cell
-Thick gummy consistency
-gives colonies a sticky, mucoid characteristics
-Makes bacteria more virulent: protect bacteria from some phagocytosis by the cells of the host
-prevents drying out of bacteria
-Aids in attachment to surfaces for colonization
Phagocytosis
Engulf and destroy microorganisms
Chemitaxis
Chemical attraction of phagocyte to bacterium. Chemical attractants are microbial products, components of damaged tissue, and products of complement system
Adherence
Attachment of phagocyte plasma membrane to microorganisms
Ingestion
-Plasma membrane of phagocyte extends out projections called pseudopods that surround the microbe.
-Forms a sac called phagosome
Digestion
-Phagosome comes into contact and fuses with lysosomes that contain digestive enzyme and bactericidal substances
-Forms a larger vacuole called the phagolysosome
-Phagolysosome moves to cell membrane
Excretion/Exocytosis
elimination of digested contents (waste)
Cell Wall Importance
Made up of subunits found nowhere else in nature
In many species causes symptoms of disease
Site of action of some of the most effective antibiotics
Differences in chemical composition determines the gram
staining properties of the cell
Cell wall function
Protects the cell and gives it shape
Outer membrane function
Protect the cell against some antibiotics (only present in gram -)
cell membrane function
regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell; contains enzymes important to cellular respiration
Plasmid
circular piece of DNA that contains some genes obtained through genetic recombination
Capsule & Slime layer
protect the cell and assist in attaching the cell to other surfaces
cell wall strong structural support
prevents the cell from bursting or collapsing due to changes in the environment
Bacterial Environment
usually consist of some water with small amounts of salts and other molecule
Bacterial cytoplasm
Is concentrated solution of salts and molecules
Water will tend to flow into the cell to
equalize the concentration of molecules
cell wall resist the force
preventing the cell from bursting
Cell wall chemical structure
Composed of peptidoglycan
Only found in bacteria
Similar to chitin found on lobster, insects, and cutin of plants
cell membrane
1-regulate entry and departure of the cell
2-typical structure: phospholipids with proteins
3- some areas of the membrane fold inward forming mesosomes
-increases the internal surface area for membrane function
-Most enzymes needed for biochemical reactions are located on the membrane
Protoplasm
site of biochemical and synthetic activity
contains 70-80% water, sugars, amino acids, salts, enzymes, chromatin body, ribosomes, mesosomes, granules
chromatin body
Bacterial chromosome; DNA aggregates in dense area called the nucleoid
Plasmid
circular piece of DNA: extrachromosomal strand
Protective function: provides resistance to drugs
Advantage to man: use this in genetic engineering techniques
Ribosomes
used in protein synthesis, inside prokaryotic cells
inclusion granules
concentrate nutrients inside the cell, storage & are not permanent
Gram positive cell wall
-thick layer of peptidoglycan associated with teichoic acid
-Retain Crystal violet stain
Mordant joins with crystal violet forming large molecules
gram negative cell wall
thin layer of peptidoglycan
Outer membrane and periplasmic space
Crystal violet-mordant molecule can escape when decolorized
gram stain reagents
Crystal violet - primary stain
Gram's iodine - mordent
Acetone alcohol - decolorizer
Safranin - counter stain
Gran staining procedure
-apply primary stain ( stains all the the bacteria)
- Apply mordant, binds with the stain inside the cell wall making a larger molecule
-decolorize with acetone/alcohol: this causes the stain to escape some bacterial cell walls rendering them unstained.
-add a counterstain: this adds color to the cells that were decolorized
Differences between gram positive and gram negative
Gram positive: one layer, thick, no outermembrane, periplasmic space present in some, chemical composition: petidoglycan, Teichoic Acid and lipotechoic acid. Porin protein absent. Less lipid. More Peptidoglycan. More penetrable. Less resistance to molecules.
Gram negative: two layers, thin, outermembrane is present. periplasmic space present in all. Chemical composition: lipopolysaccharide, lipoporteins and peptodoglycan. Porins protein present. Lipid More. Peptidoglycan Less. Less penetrable of molecules. More resistance to molecules.
Bacterial shapes
coccus, streptococcus, staphylococcus, diplococcus, tetrad, Sacrina, Bacillus, Diplobacillus, streptobacillus, coryneform bacillus, spirillum, vibrio and spirochete
Effect of penicillin on the cell wall
-effectiveness depend on the composition of the cell wall.
-toxic to bacteria because it inhibits the synthesis of peptidoglycan layer
-more effective against gram positive cells than gram negative bc outer membrane for gram negative prevents penicillin from reaching peptidoglycan layer
transmissible
An infectious disease agent that is transmitted from either a reservoir or a portal of exit to
another host's portal of entry. The disease is transmitted in one of three modes: 1-contact transmission 2- vehicle transmission 3-vector transmission
contact transmission
Direct: person to person (kissing, touching, sexual)
Indirect: one host to another by fomites, needles, toothbrushes, drinking glasses
Droplet: droplets of mucus that exit mouth/nares during exhaling, coughing, and sneezing
vehicle transmission
spread of pathogens via air, drinking water, and food, as well as bodily fluids being handled outside the body. Airborne, waterborne, foodborne, blood and body fluid
vector transmission
animals that transmit diseases from one host to another
Biological: vectors affecting humans are bitting arthropods mosquitoes, ticks, lice, fleas, mites
Mechanical: vectors passively carry pathogens to new hosts on their feet or other body parts. Houseflies , cockroaches
epidemic
Appearance of infectious disease or condition which attacks many people at the same time in same geographical location flu, food poison
Pandemic
Epidemic that occurs simultaneously on more than one continent Aids, Covid, flu
endemic
A disease peculiar to and recurring continuously in a particular locality or population. (Ex: histoplasmosis- Ohio Valley)
contagious
A communicable disease that is easily transmitted from a reservoir or person. ( ex:common cold, legionnaires disease)
Epidemiology
The study of the occurrence, distribution, and spread of disease in humans. (Ex: tracking SARS, Bird Flu, seasonal flu)
Incidence: the number of new cases of a disease in a given area or population during a given period of time
Prevalence: the total number of cases, new and existing in a given area or population during a given period of time
Microorganisms as our Foe: 750 million infectious diseases a year worldwide
>200,000 deaths annually in the US
Tens of billions of dollars in health care
Leading cause of illness and death: respiratory, diarrheal disease
food borne outbreak common ones
Salmonella, shigella, E. Coli, Staph, Bacillus Cereus, clostridium, listeria, noro virus
Ways Microorganisms help us ( how are microorganisms our friends?)
-breakdown food in the gut
- produce foods: yogurt, cheese, wine, bread
-used to make vitamins, insulin, drugs
- Decompose waste
- Recycle nutrients back into the earth
- used as a food source for other organisms
-make chemical products: acetone, glycerine, organic acids, enzymes, alcohols
-Agriculture
Broth
a liquid medium that contains various nutrients and is used to culture bacteria and other microorganisms in culture
Agar
A gelatinous material derived from algae, specifically used as a culture medium of bacteria and other cells for diagnostic or laboratory experiments purposes. Agar melts at 85 C, solidifies at 32-40 C. This property known as hysteresis
Deep
Used for a culture where you need a deep inoculation into a solid medium that is used especially for the growth of anaerobic bacteria
Slants
a culture made on the slanting surface of a solidified medium in a test tube that has been tilted to provide a greater area for growth. slanr, Butt-
Plates
A petri dish that contains a solid growth medium, typically agar plus nutrients used to culture small organisms such as microorganisms
incubation
Act of maintaining controlled environmental conditions for the purpose of favoring growth or development of microbial cultures
colony
A visible mass of microorganisms all originating from a single mother cell, therefore a colony constitutes a clone of bacteria all genetically alike
picking colonies
selecting a colony from a plate and transferring it to another media or a slide
Loop
A simple tool used mainly by microbiologist to retrieve an inoculum from a culture of microorganisms. The loop is used in the cultivation of microbes on plates by transferring inoculum for streaking
Needles
Used in the field of microbiology to transfer and inoculate living microorganisms. It is one of the most commonly implicated biological laboratory tools and can be disposable or re-usable
Cross contamination
the spreading of pathogens from one food to another
Anaerobic tests
No oxygen
Aerobic
Oxygen
Metabolism
General term used for all of the reaction occurring in cells
Types of reactions
catabolic and anabolic
catabolic reaction
The metabolic breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, often resulting in a release of energy
Anabolic reaction
The phase of metabolism in which simple substances are built into the complex materials of living tissue
anabolic pathways
Small molecules are assembled into large ones. Energy is required
Catabolic pathways
Large molecules are broken down into small ones. Energy is released.
catabolism
energy is released and stored in cells as ATP
breakdown of large molecules by catabolic process results in production of smaller molecules
Anabolism
-opposite of catabolism by synthesizing larger molecules into cellular structures.
-Building requires more energy which comes from ATP molecules produced during catabolism
Reactants
A starting material in a chemical reaction
products
The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction.
relationship between catabolism and anabolism
Catabolism provides energy for anabolism
Enzymes characteristics
-Protein molecules that act as catalyst: increase the rate of a reaction that would normally occur at a slow rate.
-An enzyme works on a specific type of substrate: substrate fits into the enzymes active site.
Lock and key fit: lock is enzyme, key is substrate
Active site
The part of an enzyme or antibody where the chemical reaction occurs.
An enzyme
not permanently changed nor becomes part of the product of the reaction
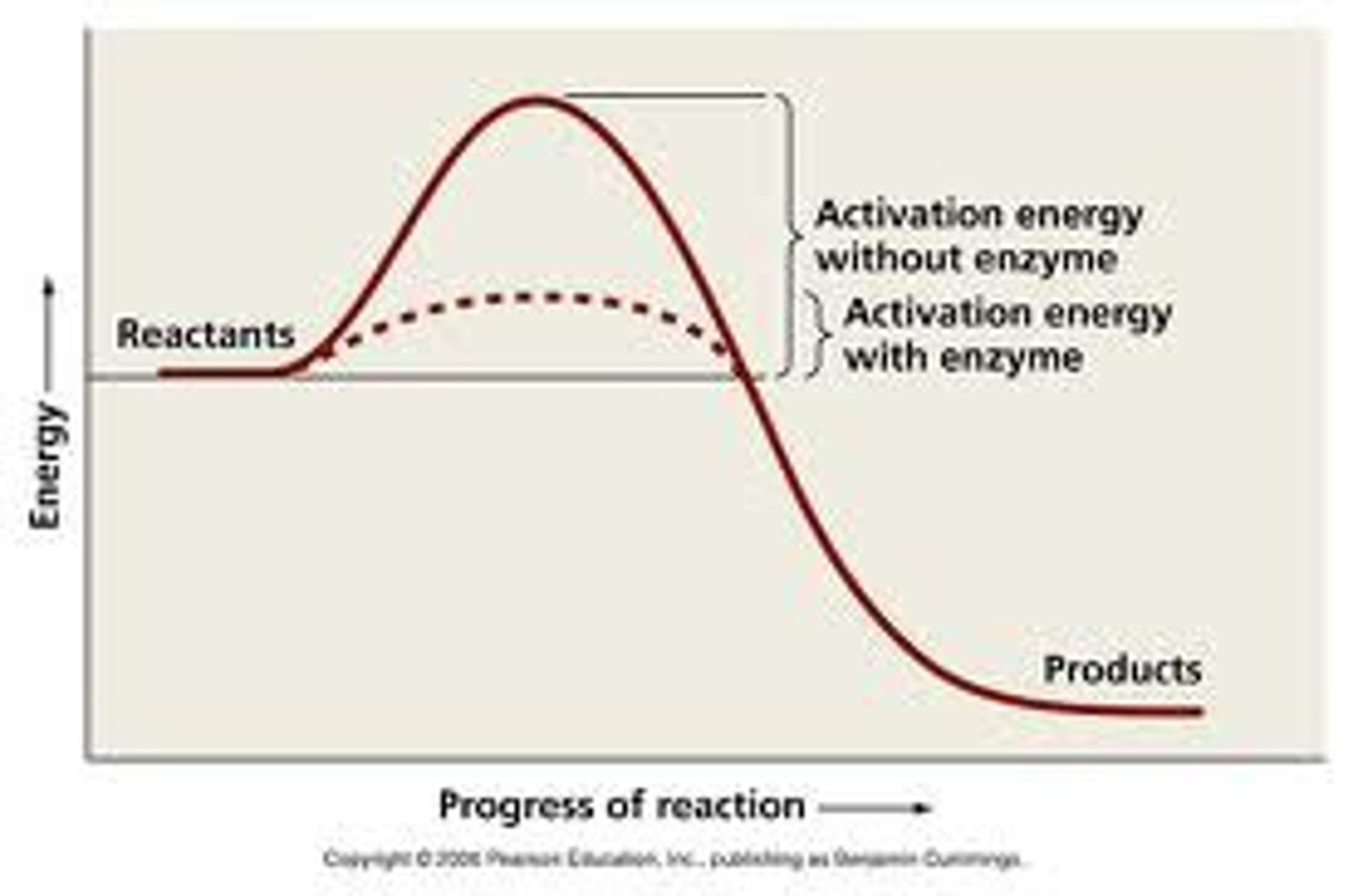
activation energy
the amount of energy needed to trigger a chemical reaction
Enzyme lowers activation energy
makes reaction go faster
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
substrate
A specific reactant acted upon by an enzyme
Naming enzymes
named after the substrate or the kind of reaction they catalyze.
End with the suffix "ase"
Some enzyme still go by their old name
Two main methods used for production energy from nutrient
1- Fermentation
2-Respiration
Fermentation (Reduction)
-The final acceptor in the pathway is an organic molecule, pyruvic acid
-Made in the pathway itself so no externally supplied acceptor is needed, thus oxygen not required
-The pyruvic acid is further reduced to lactic acid and ethanol, called end products, depending on the species of bacteria.
-Produces less energy from glucose
Respiration (Oxidation)
-Final acceptor is an inorganic molecule, usually CO2 and H2O
-O2 must be supplied by the environment
-Produces more energy from glucose
Describe three characteristics of enzymes
1-Protein molecules that act as catalyst: increase the rate of a reaction that would normally occur at a slow rate.
2-An enzyme works on a specific type of substrate
3-Enzyme lower activation energy
given a substrate, name the enzyme
Lipid-Lipase
Maltose-Maltase
Sucrose-Sucrase
Protein-Protease
Amylose-Amylase
Lactose-Lactase
Given a graph representing activation energy, identify the reaction curve with and without enzyme
Aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration
2 types of cellular respiration