Materials Science And Engineering
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
Six Property classifications of materials
Mechanical, Electrical, Thermal, Magnetic, Optical, Deteriorative
Material Structure
How internal components of the materials is arranged
4 Elements of materials to consider
Processing, structure, properties, and performance
3 Important Criteria for materials selection
In-service conditions, deterioration of material properties, and cost of material
4 classifications of materials
metals, ceramics, polymers, composites
Advanced Materials
Semiconductors, biomaterials, smart materials, nanomaterials
atomic number (Z)
number of protons
isotope
Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons
atomic weight
Average of the mass numbers of all isotopes
4 Dimensions of structural elements
Subatomic, atomic, microscopic, and macroscopic
atomic mass unit (amu)
used to compute atomic weight
1 mole
6.02 x 10^23
quantum mechanics
Study of physics at the atomic level where energy is quantized in discrete, rather than continuous, levels.
Bohr atomic model
Atoms described as electrons orbiting the nucleus in well defined paths.
wave-mechanical model
the current model of the atom that deals with the wave-particle duality of nature.
quantum number
a number that specifies the properties of electrons
electron state
values of energy that are permitted for electrons
Pauli exclusion principle
An atomic orbital may describe at most two electrons, each with opposite spin direction
ground state
The lowest energy state of an atom
electron configuration
the arrangement of electrons in an atom
valence electron
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom
electropositive
When something is not at all electronegative, i. e. most metals
electronegative
Capable of receiving electrons, i. e. most non-metals
Force-potential energy relationship for two atoms
E=Integral (F dr)
bonding energy
energy required to separate two atoms to an infinite separation
primary bond
ionic, covalent, and metallic
ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
coulombic force
A force between charged particles such as ions
Attractive energy-interatomic separation relationship
Ea=-(A/r)
Repulsive energy-interatomic separation relationship
Er=(B/r^n)
covalent bonding
A bond formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
metallic bonding
the chemical bonding that results from the attraction between metal atoms and the surrounding sea of electrons
secondary bond
Weak bonds, such as Van der Waals bonds, that typically join molecules to one another.
van der Waals bond
A type of secondary bond in which a temporary dipole induces another dipole in an adjacent atom
dipole
created by equal but opposite charges that are separated by a short distance
hydrogen bonding
secondary bond that exists between molecules that contain hydrogen
polar molecule
A molecule that has electrically charged areas.
crystalline
A solid that is made up of crystals in which particles are arranged in a regular, repeating pattern.
crystal structure
the arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a regular way to form a crystal
lattice
The three-dimensional arrangement of atoms or ions in a crystal.
unit cell
the smallest group of particles within a crystal that retains the geometric shape of the crystal
face-centered cubic (FCC)
A unit cell of cubic geometry with atoms located at each of the corners and the centers of the faces
Unit cell edge length for FCC
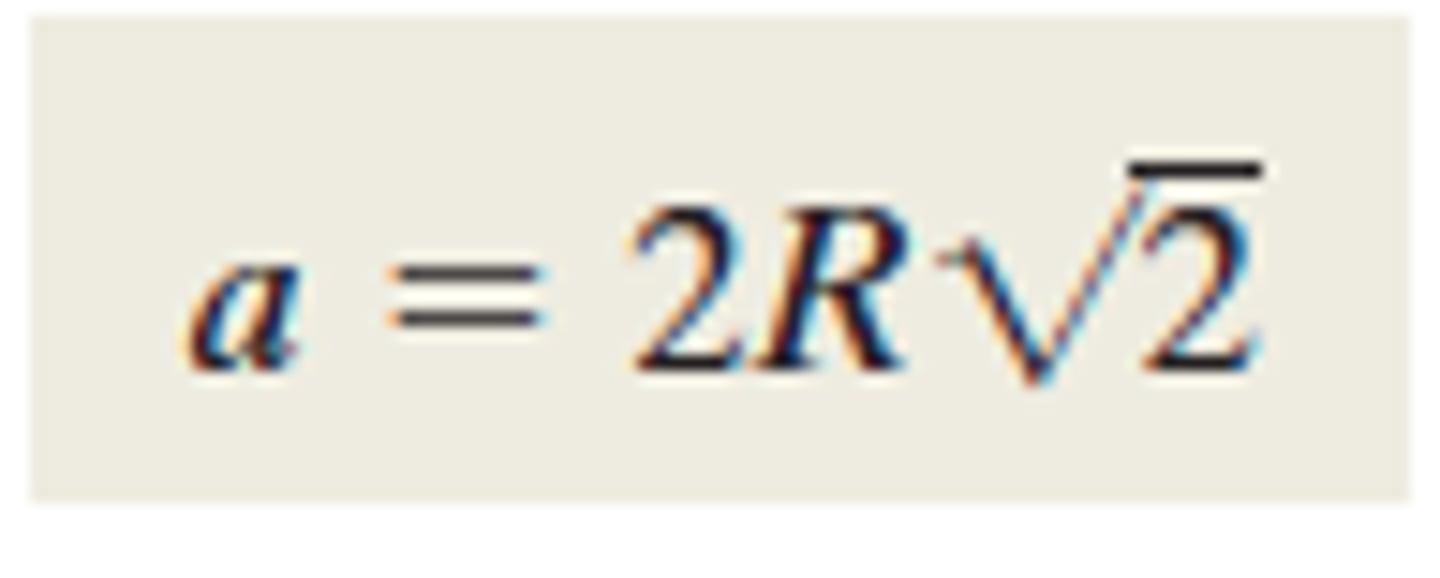
coordination number
number of nearest neighbor or touching atoms
atomic packing factor (APF)
The volume of atoms in a selected unit cell divided by the volume of the unit cell.

body-centered cubic (BCC)
cubic unit cell with atoms located at all eight corners and a single atom at the cube center
Unit cell edge length for body-centered cubic
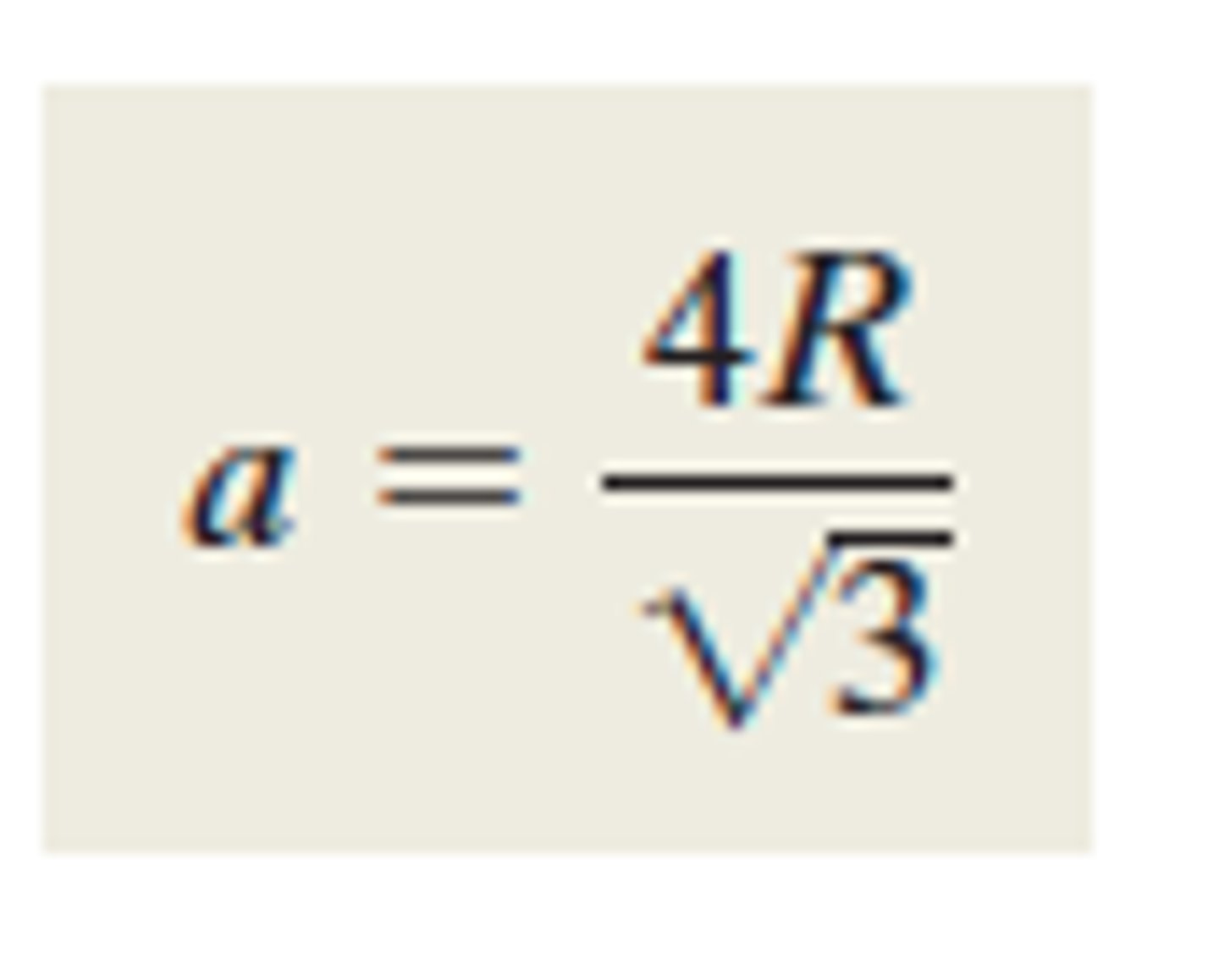
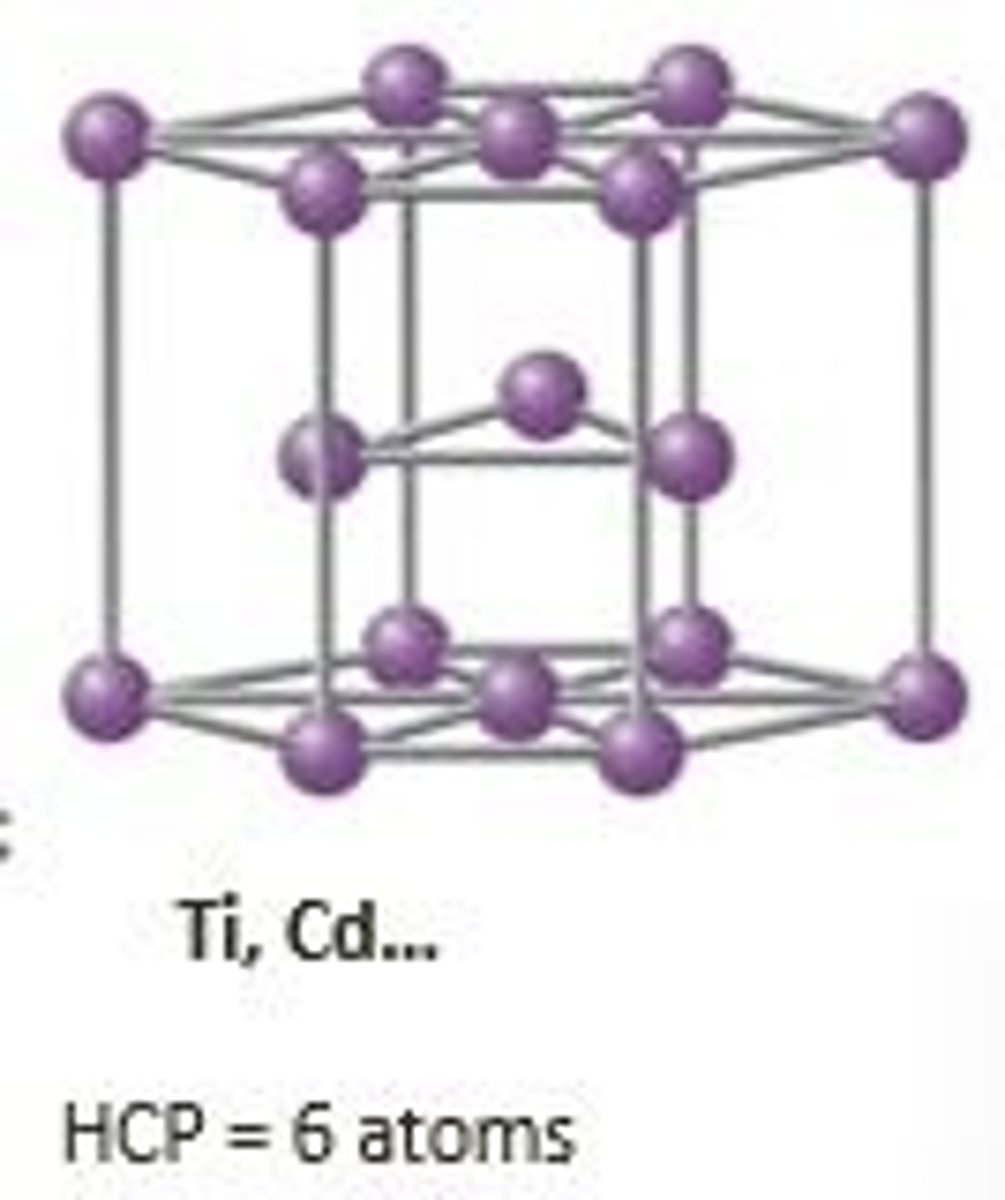
hexagonal closed-packed (HCP)
Theoretical density for metals
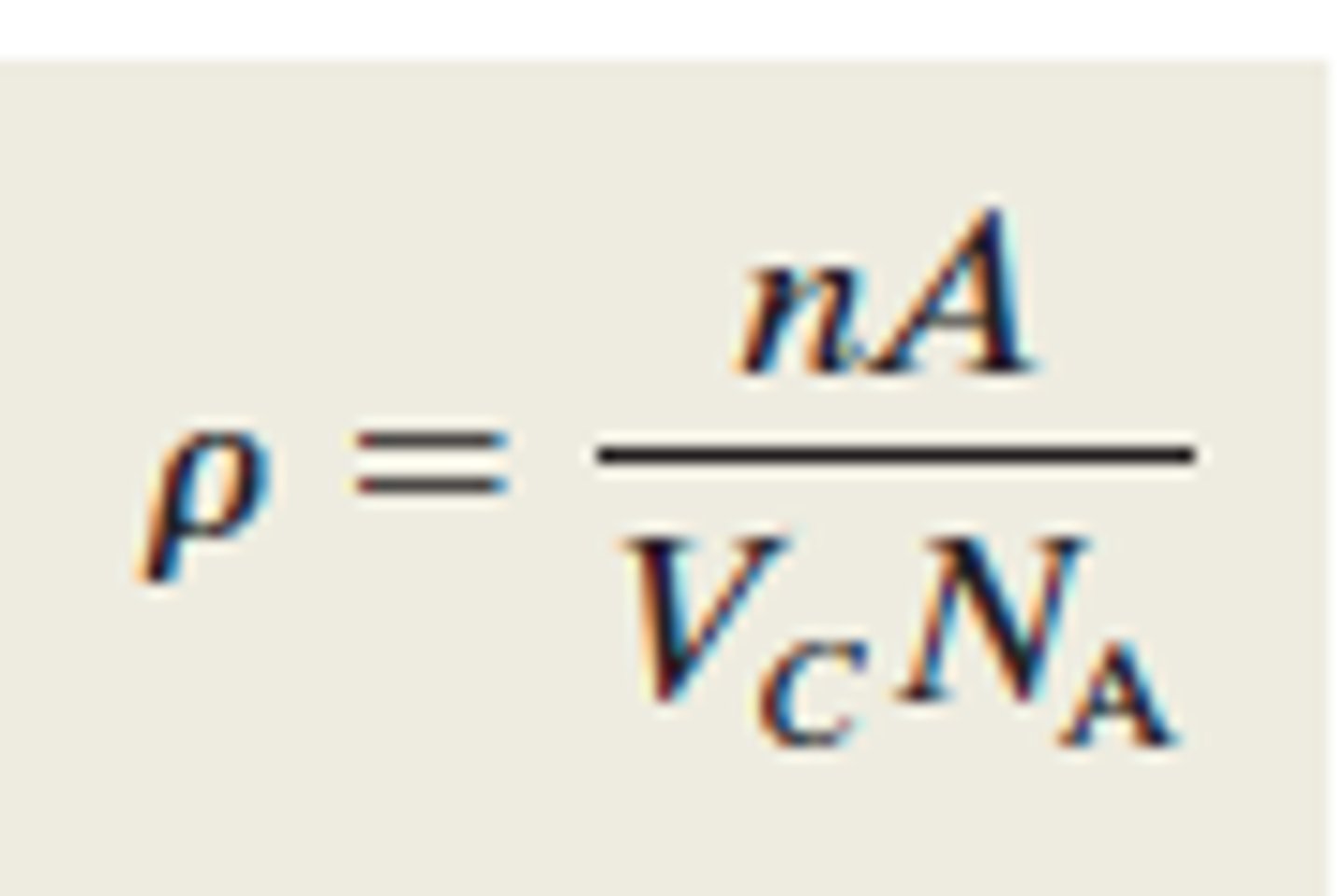
polymorphism
The ability of a solid material to exist in more than one form or crystal structure
allotropy
when polymorphism is found in elemental solids
lattice parameters
The combination of unit cell edge lengths and interaxial angles that defines the unit cell geometry.
crystal system
A way in which the structures are classified. (BCC, FCC ...)
Miller indices
A shorthand for expressing directions and planes in crystals
Linear Density
The number of atoms centered on a crystallographic direction per unit length.
planar density
The number of atoms or ions centered on a crystallographic plane per unit area of the plane.
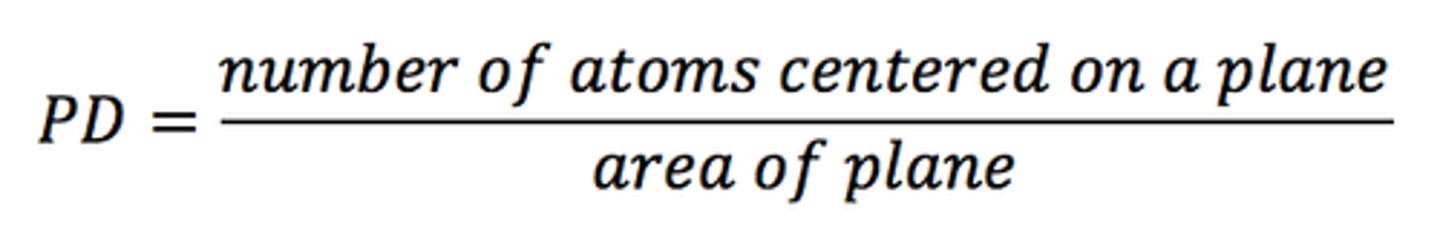
single crystal
A crystalline solid for which the periodic and repeated atomic pattern extends throughout its entirety without interruption
grain
a small crystal that composes most crystalline solids
polycrystalline
Describing a solid, usually isotropic, of joined crystals or grains.
grain boundary
region of mismatch between two adjacent grains in a polycrystalline microstructure
isotropic
properties of a material are independent of directions
diffraction
Occurs when an object causes a wave to change direction and bend around it
Bragg's law
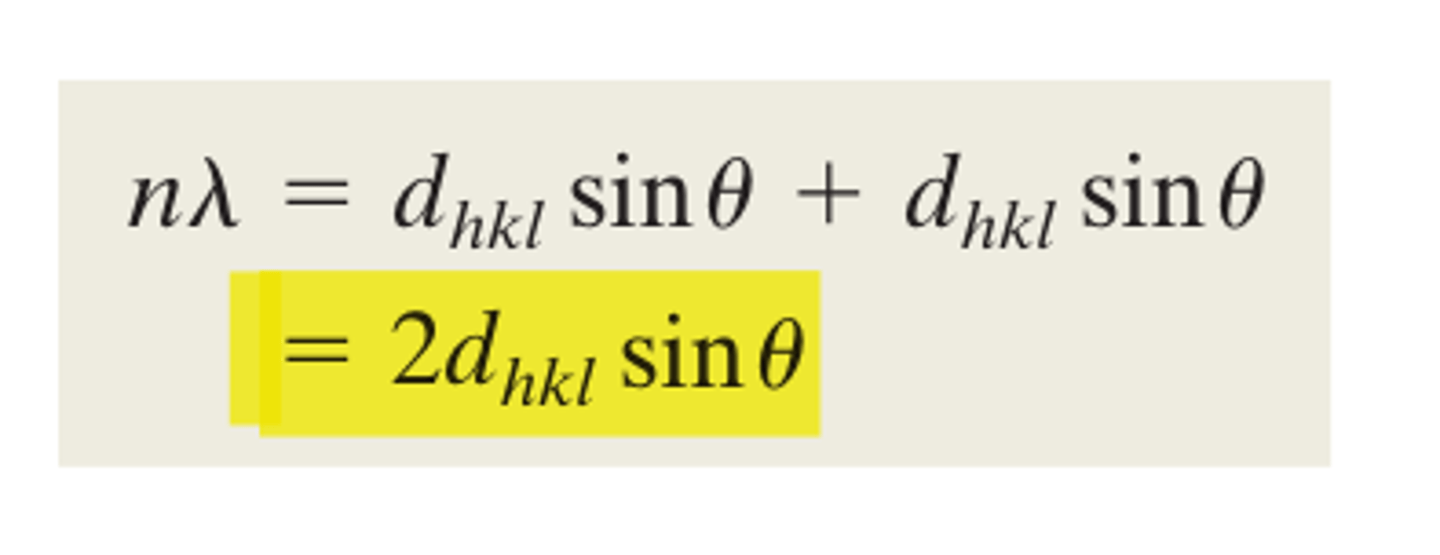
Interplanar spacing for a plane having indices h, k, and l
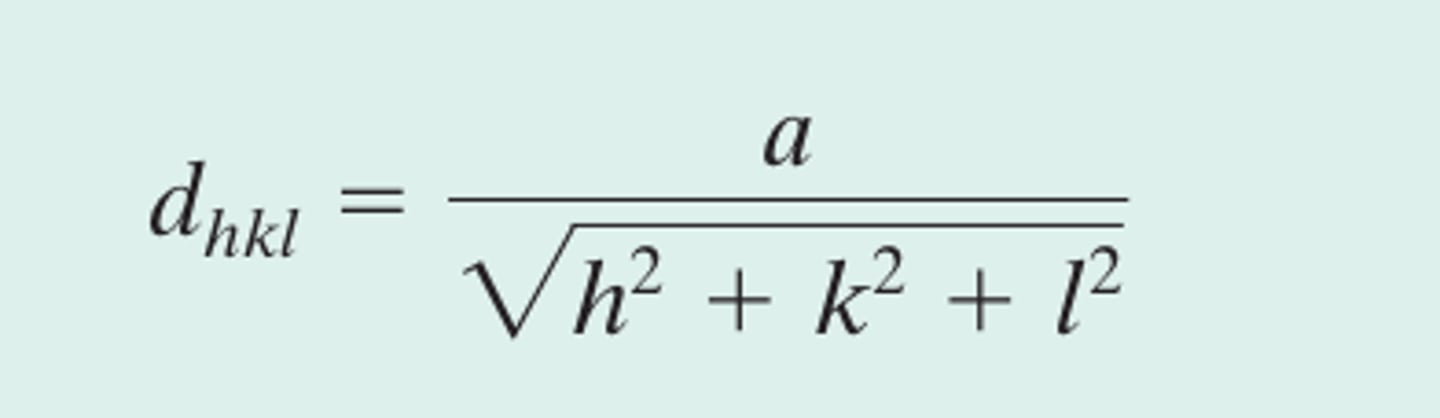
noncrystalline
molecules do not arrange into repeating patterns
amorphous
Without definite form
imperfection
a type of defect in the perfect order of a crystalline material
point defect
A crystalline defect associated with one or, at most, several atomic sites
vacancy
A missing atom or ion at a lattice site that would normally be occupied
temperature dependence of the equilibrium number of vacancies
Nv=N^(-(Qv/k*T)
Boltzmann's constant
Kb=1.38 x 10^-23 K/K
self-interstitial
A host atom or ion positioned on an interstitial lattice site.
alloy
A mixture of two or more metals
solid solution
An alloy of two or more metals or a metal(s) and a nonmetal(s) which is a single-phase atomic mixture
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
substitutional solid solution
A solution formed by substituting species B directly for species A on the lattice sites normally occupied by A.
interstitial solid solution
A solid solution in which atoms or ions of a foreign species are located in the interstitial positions.
composition
the nature of something's constituents
weight percent
A concentration specification on the basis of weight (or mass) of a particular relative to the total alloy weight (or mass)
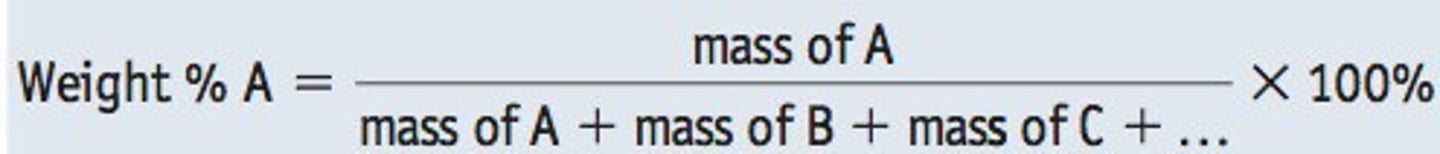
atom percent
A concentration specification on the basis of the number of moles (or atoms) or a particular element relative to the total number of moles (or atoms) of all elements within an alloy
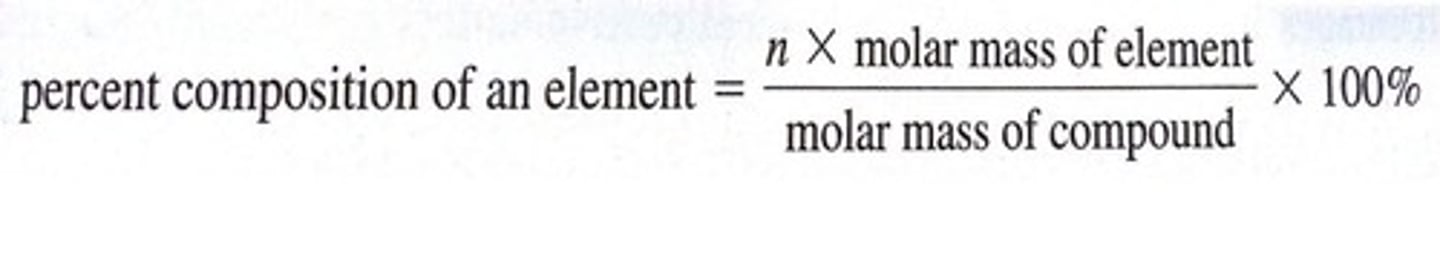
edge dislocation
an extra "half plane" of atoms inserted into a crystal
dislocation line
The line that extends along the end of the extra half-plane of atoms for an edge dislocation and along the center of the spiral of a screw dislocation
screw dislocation
result of shear forces on part of material that caused displacement of a portion of crystal
mixed dislocation
A dislocation that has both edge and screw components
Burgers vector
a vector that denotes the magnitude and direction of lattice distortion associated with a dislocation.
atomic vibration
The vibration of an atom about its normal position in a substance
microstructure
The structural features of an alloy subject to observation under a microscope
microscopy
investigation of minute objects through a microscope
photomicrograph
Photograph of an image produced by a microscope.
transmission electron microscope (TEM)
microscope where image is derived from electrons that have passed through it
scanning electron microscope (SEM)
An instrument that bounces electrons off objects to create a three-dimensional image that is more highly magnified than possible through a light microscope.
scanning probe microscope (SPM)
Microscope with a very sharp tip that is scanned over a surface to measure some property.
grain size
The average grain diameter as determined from a random cross section
relationship between ASTM grain size number and number of grains per square inch
n=2^(G-1)
diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
interdiffusion
atoms of one metal diffuse in another metal; in an alloy, atoms migrate from high to low concentration
impurity diffusion
when diffusion occurs by the movement of solute atoms in a dilute solution
self-diffusion
The mechanism by which a species diffuses in itself
vacancy diffusion
the diffusion mechanism in which net atomic migration is from a lattice site to an adjacent vacancy