AP BIO TEST 2
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What does cholesterol do?
maintains temperature stability in the cell membrane
What is compartmentalization?
the fact that the cell is separated into distinct compartments, like organelles.
What is exocytosis?
molecules taken out of the cepl
What is endocytosis?
molecules taken in the cell
What is passive transport?
things are able to pass straight through the membrane
What is active transport?
What does amphipathic mean?
has a hydrophobic and hydrophilic region
What are integral proteins?
proteins that goes through the entire cell membrane
What are peripheral proteins?
proteins found on the side of the cell membrane
What is diffusion?
movement of particles so they can spread into available space
What is tonicity
the ability of a surrounding solution to gain/lose water
What is hypertonic?
cell looses water or “shrinks”
What is hypotonic?
cell swells with water
What is facilitated diffusion?
diffusion with the help of a transport protein
what are transport proteins?
moves solutes up and transports them
where does active transport get its energy?
ATP hydrolysis
What is cotransport?
membrane traffic, where a transport protein can couple the diffusion, or the transport of a second substance against its own concentration gradient
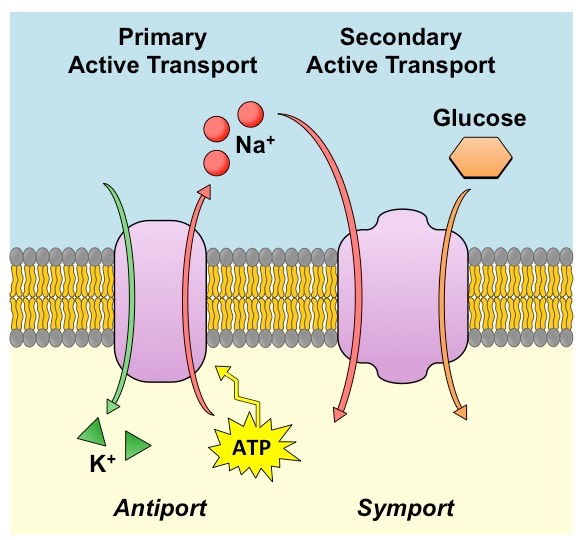
What is phagocytosis?
cellular eating of solids
What is pinocytosis?
cellular drinking of liquids
What organelle is responsible for removing water and protists?
contractile vacuole
what area in the nucleus where ribosomes are made in the DNA?
nucleolus
What holds the starch and is usually the largest structure in a plant cell?
vacuole
where does the synthesis of proteins that are made to be exported from the occur?
rough endoplasmic reticulum
where is the site for ATP synthesis?
mitochondria
what organelle produces hydrogen peroxide?
peroxisomes
where are macro molecules, hydrolyzed or digestion occurs in some processes?
lysosomes
primarily involved in the synthesis of oil, phospholipids and steroids, and in the liver is responsible for detoxification of many poisons and drugs…
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
what is the most likely pathway taken by a newly synthesized protein that will be secreted by a cell?
ER > Golgi > vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane
In a plant cell, where is DNA found?
nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplast
what does the endosymbiot theory suggest the eukaryotic cell came from?
endosymbiosis of an aerobic bacterium in a larger host cell- the endosymbiont evolved into a mitochondria