Chapter 10 - Product/brand Management - BUAD301
1/29
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Product life cycle
Course that a product’s sales and profits take over its lifetime. The product life cycle have five distinct stages (product development, introduction, growth, maturity, decline)
Introduction (product life style)
Low sales
High cost per customer
Negative profits
Few competitors
Growth (product life cycle)
Rapidly rising sales
Average cost per customer
Rising profits
Growing number of competitors
Maturity (product life cycle)
Peak sales, sales increase at a decreasing rate
Low cost per consumer (most consumers are repeat buyers or have tried the product once and abandoned it)
High profits
Stable number of competitors
Decline (product life cycle)
Declining sales
Low cost per customer
Declining profits
Declining number of competitors
Alternative product life cycles
Depending on the type of product, the life cycle can be a little bit different
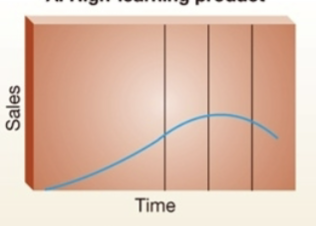
High learning product (Alternative product life cycles)
Need learning to use the product, introduction stage takes much longer (Microsoft office)
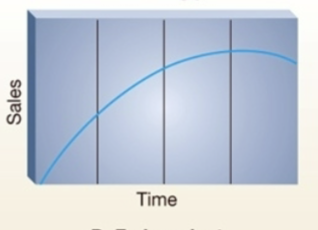
Low-learning product (alternative product life cycles)
If the product does not require learning the introduction stage is much shorter (drink)
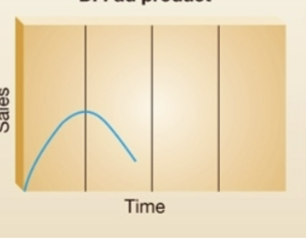
Fad product (alternative product life cycles)
a product that has a very short life cycle, comes in and out of relevancy very fast (ex. kids toys, yoyo, slime)
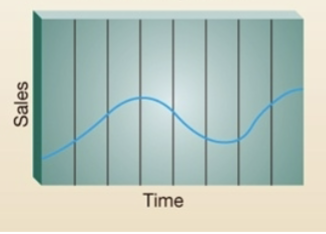
Fashion product (alternative product life cycles)
Fashion trends come in and out all the time, meaning that the product life cycle goes up and down all the time (ex. flare pants)
Multiproduct branding (corporate branding)
Use one name for all of its products in a product class
Line extension (multi-product branding)
Offering additional items in the same product line under the same successful brand name (new colors, flavors etc)
(Coke → Diet Coke → Diet Coke with lime)
Subbranding (Line extension)
Combine a corporate brand with a new brand
(Porsche → Porsche carrera (high end), Porsche Boxster (low end))
Brand extension (Multiproduct branding)
Using successful existing brand name to launch a new product line
(Virgin (radio shop) → Virgin casino, Virgin radio)
Line extension advantages
Takes advantage of the value of the original brand, saves in advertising
Line extension disadvantages
Cannibalization - A situation where a company’s new product or service negatively impacts the sales of its existing products or services
Brand extension advantages
Instant recognition and earlier acceptance of the extended brand
Substantial savings in marketing costs
Brand extension disadvantages
Brand Dilution: A mismatch between a original brand and a new product can damage the original brand.
Multi-Branding (individual branding)
Use distinct name for each product
(P&G - Oral B and Pringles)
(Toyota - Lexus)
Multi-branding advantages
Low brand dilution risk
Differentiation of each brand (target different markets, positioning different images etc)
Multi branding disadvantages
High promotion costs
Private branding
Use the brand name of a wholesaler or retailer
(Target smartly, Heyday, Wild fable)
Mixed branding
A compromise between a manufacturer and private branding.
Sometimes putting your brand name on product, but when it’s sold in different stores they use that stores brand name.
(Apple and Mastercards Apple Pay OR A pet food is sold under its actual brand name online but in Costco it is sold under Costcos brand)
Brand Equity
Added value a given brand name gives to a product beyond the functional benefits provided
(emotionally attached to brand, having a tattoo of the apple logo)
PLC and Consumers
Consumers differ in their tendencies to adopt a new product, and this difference can be used as a market segment factor
PLC marketing strategy - Introduction
Gain awareness of your product by informing and educating the public about your product
PLC Marketing strategy: Growth
Maximize market share by differentiation (make yourself seem different from other products on the market)
Product proliferation occurs
PLC marketing strategy - Maturity
Maximize profit while defending market shares, maintain brand loyalty
Diversify brand and Models
PLC marketing strategy - Decline
Reduce expenditures and milk the brand
Limitations of PLC
Managers often have trouble identifying what stage of PLC they (brands) are in
By pushing products (brands) through the PLC managers may miss an opportunity to rescue products (brands) foundering in the maturity phase.