All-in-One Infection and Response
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Communicable disease
A disease caused by a pathogen which can be passed from organism to organism
Pathogen
A infectious disease-causing microorganism
How do bacteria cause disease
Once inside the body, they divide rapidly by binary fission.
They damage cells and produce harmful toxins.
How do viruses cause disease
They invade and reproduce inside host body cells.
Leads to cell bursting → making us feel ill
releases copies into bloodstream
How do protists cause disease
Parasitic, meaning they use body cells as host cells
Cause damage to body cells
How do fungi cause disease
Produce spores which can be spread to other organisms
Ways pathogens can be spread
By air → Pathogens carried in the air and breathed in: droplet infection → when sneezing, coughing or talking expels pathogens
By water - drinking or coming into contact with dirty water
By direct contact - touching contaminated surfaces: contact with bodily fluids, microorganisms, infected material
ways to reduce spread of pathogens/disease
Hygiene - handwashing, disinfectants, tissues when sneezing
Sterilising water
Barrier contraception - condoms
Reducing contact with infected individuals - quarantine.
Removing vectors - use of pesticides and insecticides, removal of habitats
Vaccination
importance of preventing viral diseases
Scientists have not yet developed cures for many viral diseases.
Dangerous pathogens: can enter all types of cells
Measles (Virus)
Symptoms: Fever, red skin rash → lung infection, brain infection, blindness
Spread by: Droplet infection: coughs, sneezes
Prevented: Vaccination for young children → reducing transmission
HIV/AIDS (Virus)
Symptoms: Initial flu-like symptoms → virus attacks immune system → AIDS
Spread by: Sexual contact, exchange of bodily fluids: e.g. blood (injections)
Prevention: Using condoms, no sharing needles, blood screening
→ Development of AIDS: antiretroviral drugs (stops virus replicating in body → must be taken for rest of life)
TMV (tobacco mosaic virus) (Virus)
Plant pathogen
Symptoms: Discolouration of leaves → leaf cannot photosynthesise properly → reduced yield
Spread by: Contact between diseased plants and healthy ones, vectors
Prevention: Field hygiene, pest control, growing TMV-resistant strains
Salmonella food poisoning (Bacteria)
Bacteria living in guts of different animals
Symptoms: Fever, stomach cramps, vomiting, diarrhoea
Spread by: uncooked/under cooked meat and eggs, unhygienic conditions
Prevention: Poultry vaccinated, separating raw and cooked food, hygiene when handling, cooking food thoroughly
Gonorrhoea (Bacteria)
Symptoms: Yellow discharge from vagina/penis, pain when urinating
Spread by: Unprotected sexual contact
Prevention: Using condoms, antibiotics (resistance strains developing)
Rose black spot (Fungi)
Symptoms: Purple/black spots on leaves → reduces area for photosynthesis → leaves turn yellow
Spread by: Spores of fungus spread in water or wind
Prevention: Fungicides, cutting off infected parts
Malaria (Protist)
Protist pathogens enter red blood cells and damage them.
Symptoms: Fevers, shaking
Spread by: Vectors (mosquitos) puncturing skin to feed on blood → protists enter bloodstream via saliva
Prevention: Insect nets when sleeping, removal of stagnant waters to prevent breeding of vectors, antimalarial drugs when travelling, insect sprays
Skin's role in pathogen prevention
Physical barrier
Produces antimicrobial secretions → kill pathogens
Respiratory system's role in pathogen prevention
Nose:
has hairs and mucus → trap pathogens → prevents from travelling to lungs
trachea and bronchi:
have mucus → traps pathogens
Ciliated cells → waft mucus upwards to be swallowed
Stomach's role in pathogen prevention
Produces hydrochloric acid → kills pathogens in mucus, food and drink
Phagocytosis
White blood cells (phagocytes) engulfs and digests pathogens so they cannot infect more cells.
→ Digest pathogens using enzymes
Antibody production (Lymphocytes)
White blood cells produce antibodies which are complementary to a specific antigen on a pathogen.
binding of antibodies to antigens → pathogens clump together → easier to destroy
In the case of a second infection:
correct antibodies can be produced at a faster rate → preventing person getting the same disease + symptoms again → immunity
Antitoxin production
Antitoxins bind to toxins released by pathogens and neutralise them.
Vaccination
Contains a dead or inactivated form of the pathogen which stimulates white blood cells to produce complementary antibodies to the pathogen.
Vaccination steps / how it works (6-Marker)
Dead/inactive/weak/ form of pathogen introduced into the body
(which) stimulates white blood cells / lymphocytes
(to) produce antibodies complementary to antigens of specific pathogen
antibodies made quickly on re-infection
(because of) memory cells that stay in bloodstream post infection
antibodies made in larger numbers and persist in bloodstream for longer
(so) pathogens rapidly killed before illness
Herd immunity
Limitation of spread of disease when a high proportion of a population is immune to a disease through vaccination.
Advantages of vaccinations
Eradicated many deadly diseases: e.g. smallpox.
Reduced occurrence of many: e.g. rubella
Epidemics can be prevented (herd immunity)
Disadvantages of vaccinations
Not guaranteed to work - might not protect against multiple strains of a pathogen
Side effects or adverse reactions: e.g. fevers
Take long time to develop
Antibiotics
Medicines that kill bacterial pathogens inside the body without damaging body cells.
Cannot kill viruses: cannot reach inside of human host cells
Antibiotics characteristics: E.g. Penicillin
Taken as a pill, syrup or injected directly
Different antibiotics are effective against different types of bacteria → receiving correct one is crucial
Use had decreased number of deaths from bacterial disease
Painkillers
Only treat symptoms of a disease, rather than the cause.
Antibiotic resistance
Occurs when mutations lead to individual bacteria being resistant to an antibiotic.
These bacteria survive
non-resistant bacteria die
resistant bacteria reproduce and pass on their gene → leading to a greater proportion of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
antibiotics no longer effective
Preventing antibiotic resistance
Avoid overuse and unnecessary use of antibiotics: e.g. use on viral infections, mild colds
→ Reduces unnecessary exposure of antibiotics to bacteria
Finish antibiotic courses - ensure all bacteria is killed
Plant digitalis is extracted from
Foxgloves.
Painkiller from willow bark
Aspirin.
Penicillin
Antibiotic discovered by Alexander Fleming
Was growing bacteria on plates
Found mould (penicillium mould) on culture plates with clear rings around mould → indicating bacteria no longer there
Found mould was producing a substance that killed bacteria (penicillin)
Three main factors tested for in drug development
Toxicity - side effects on humans
Efficacy - how efficient they are
Dose - how much of drug is needed
Through preclinical testing and clinical trials
Preclinical testing
Carried out in a laboratory - uses cells, tissues and live animals.
Clinical testing
Uses healthy volunteers and patients after preclinical testing.
Tested on healthy volunteers with low dose → for no harmful side effects
Tested on patients to find most effective dose
Patients split: one group given actual drug, one given a placebo → effect of drug observed
→ Can be single-blind - only doctor knows
→ Can be double-blind - neither patient or doctor knows → removing bias when recording results
Peer-reviewed by other scientists → check for repeatability.
Aphids
Insects / vectors that weaken a plant and can transfer pathogens from diseased plants to healthy plants.
Reducing aphids
Chemical pesticides
biological pest control - using ladybirds.
Nitrate ions: Why plants need them
convert sugars into proteins → required for the plant to grow
Nitrate deficiency
Growth of the plant will be stunted.
Magnesium ions: Why plants need them
required to synthesise chlorophyll → absorbs light energy during photosynthesis
Magnesium deficiency
Causes chlorosis (leaves appearing yellow)
Leaves cannot photosynthesise properly
Symptoms of disease in plants
Stunted growth (lack of nitrate ions)
spotted leaves (rose black spot fungus)
decay/rotting (rose black spot fungus)
abnormal growths
malformation of stems/leaves (aphid infestations)
discolouration (magnesium deficiency/TMV)
presence of pests (caterpillars)
Identifying plant disease
Reference to a gardening website or manual
laboratory testing to identify pathogen
monoclonal antibody test kits to identify pathogen
Physical defence responses in plants
Cellulose cell walls - physical barrier into entering cells
tough waxy cuticle - physical barrier into entering leaves
outside layer on stems (bark) - stops pathogens entering
leaf fall - cells fall off with pathogens
Chemical defence responses in plants
Poisons - deter herbivores
Antibacterial compounds - kill pathogens
Mechanical defence responses in plants
Thorns and hairs - deter animals
leaves that droop/curl on contact - moving away from pathogens or insects
mimicry to trick animals - droop to look unhealthy → animals avoid them
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs)
Antibodies that are clones from one parent cell, specific to one type of antigen.
ability to bind to only one protein antigen → target chemicals and cells in the body
Production of monoclonal antibodies
Specific antigen injected into an animal (e.g. mouse)
Mice lymphocytes producing complementary antibodies extracted
Lymphocytes fused with myeloma cells (tumour cells → divide rapidly) to form hybridoma cells
Hybridoma cells divide to produce clones of itself → produce same antibody
Monoclonal antibodies collected and purified.
Uses of monoclonal antibodies
Detection of pathogens
Location of cancer cells and blood clots
Used in pregnancy test kits
Myeloma cells
Type of tumour cell.
Uses of monoclonal antibodies - Pregnancy kit tests
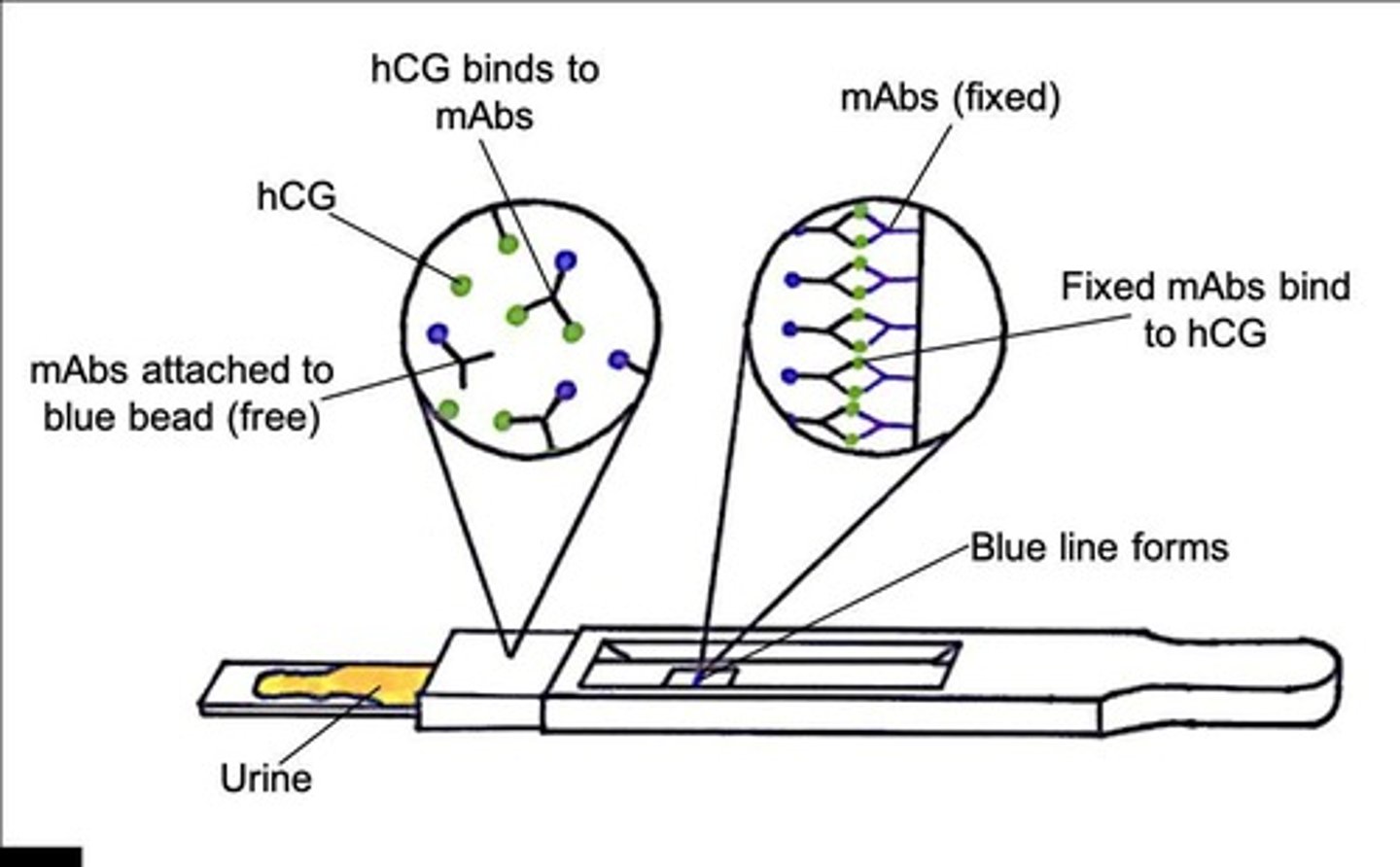
Used to detect a hormone, hCG, in the urine of pregnant women
How pregnancy test works
There are two sections of the stick:
→ first section: mobile mAbs complemetary to hCG hormone - attached to blue beads
→ second section: stationary mAbs which are stuck to the stick
Individual urinates on first section: If hCG present, it binds to mobile mAbs attached to blue beads to form hCG / antibody complexes
Carried in the flow of liquid to second section
Stationary mAbs bind to hCG / antibody complexes
As each are bound to a blue bead, results shown as blue line → indicating pregnancy
Pregnancy test results if pregnant - simple
hCG in urine binds to mAbs attached to a blue bead
mAbs with hCG diffuse up the stick
mAbs fixed to the stick bind to hCG
Blue line forms
Pregnancy test results if not pregnant
No hCG in urine so a blue line is not formed.
Uses of monoclonal antibodies - Measure and monitor
Used to measure and monitor levels of hormones or chemicals in the blood.
mAbs modified to bind to molecule wanted
mAbs bound to fluorescent dye
if molecules present, the mAbs bind to it, and dye can be observed
E.g. Blood screening for HIV infections
Uses of monoclonal antibodies - Cancer treament
Producing mAbs that bind to tumour markers to stimulate immune system to attack that cell.
Using mAbs to bind to receptor sites on cell membrane of cancer cells → growth-stimulating molecules cannot bind → stops cell divison
Using mAbs to transport toxic drugs, chemicals or radioactive substances → only damage cancer cells
Advantages of monoclonal antibodies
Specific to one particular antigen - healthy cells not affected
Can treat many different conditions
Disadvantages of mAbs
Difficult too attach mAbs to drugs
expensive to develop
produced from mice lymphocytes - trigger immune response in humans