Methods and measurement in pharmacology
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
what is molecular target selection in the drug discovery phase?
Functional proteins (e.g. receptors, enzymes, transport proteins)
Disciplines such as genomics, bioinformatics, proteomics and systems analysis
what is lead finding in the drug discovery phase?
Involves cloning and expression of the target protein
Assay system→ cell-free enzyme assay, a membrane-based binding assay or a
cellular response assay
what is lead optimisation in the drug discovery phase?
Increase the potency of the compound on its target
Identify one or more drug candidates suitable for further development
what are analytical techniques and examples?
To determine the identification and concentration of unknown chemical substance.
Simple weighing
Titration - Use of coloured complex to indicate end point
Chromatographic - Separate two or more analytes
Spectroscopic - Absorption and emission of light or other radiation by matter
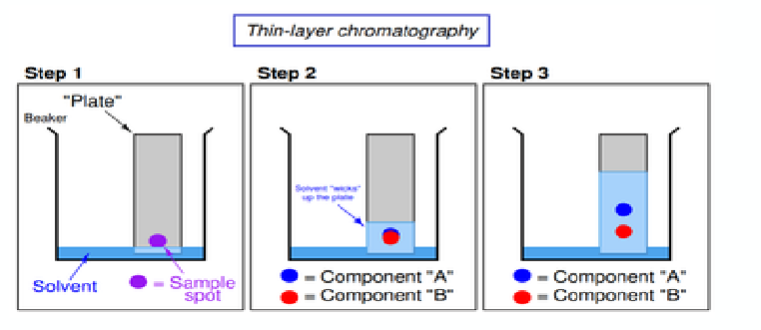
what is chromatography?
Most powerful and widely used of analytical method(s) for separation and determination of chemical components in a complex mixture.
Broadly defined as a separating system consisting of two phases – Mobile and Stationary.
what are chromatography methods categorised into?
The nature of the mobile phase
How the stationary phase is supported
what are the 4 major types of chromatography?
Paper Chromatography - Cellulose filter paper contains water in it pore
Thin layer chromatography - Glass plate is coated with stationary phase
Gas chromatography - Gas as a mobile phase
Liquid chromatography - Liquid as a mobile phase
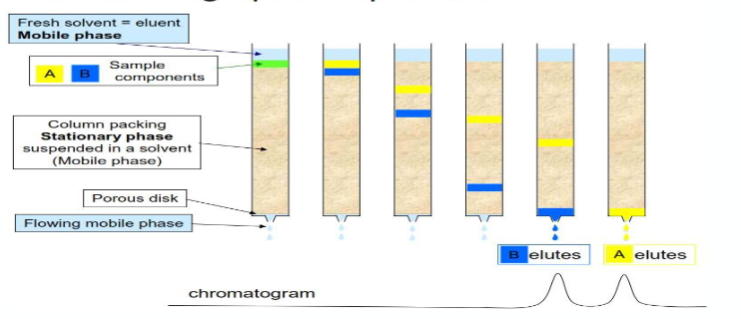
what is chromatographic separation?
what are the two principles for gas chromatography?
Sample must either be a gas or be in a form easily converted to a gas
Only works for compounds that are volatile or semi-volatile or that may be converted into volatiles (derivatisation)
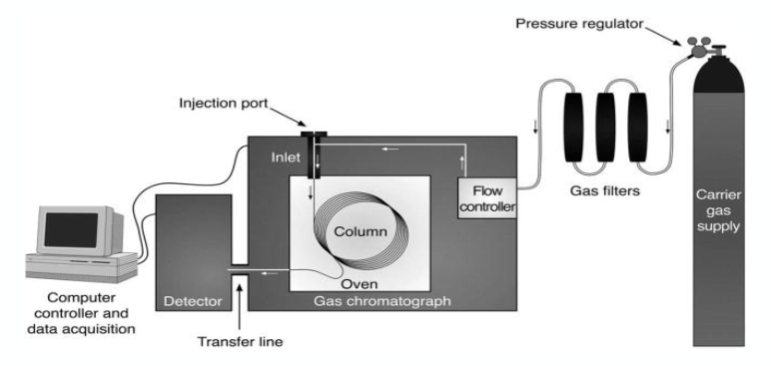
what is the mobile phase in gas chromatography?
An inert gas referred to as the carrier gas.
Does not interact with molecules of analyte - it merely transports the analyte through the column.
what are the two mechanisms of separation on a gas chromatography column?
Boiling point – the higher the boiling point of compound the longer it takes to elute
Retention by stationary phase – depends upon stationary Phase type (e.g. polar stationary phase retains polar compounds
what are the applications of chromatography in pharmacology?
Quantification of drug substances - Concentration of active pharmaceutical ingredients, Purity of drugs
Compliance with regulatory standards - Quality control, Stability testing
Measurement of drug concentration - Quantification in biological fluids, ADME studies
Determination of pharmacokinetic parameters - Half-life & clearance rate etc, optimising drug dosage and drug behaviour
Forensic toxicology - Abuse of drugs, Drug related offenses
Research studies - Development of new drugs
what is liquid chromatography?
Separation of components in a liquid sample based on their differential interactions with a stationary phase and a mobile phase
what are the components of liquid chromatography?
Stationary Phase: Solid or liquid material where separation occurs.
Mobile Phase: Liquid solvent that carries the sample through the stationary phase.
what are the types of liquid chromatography?
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): High-resolution technique
Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC): Separates molecules based on size.
Ion-Exchange Chromatography (IEC): Separates ions based on charge.
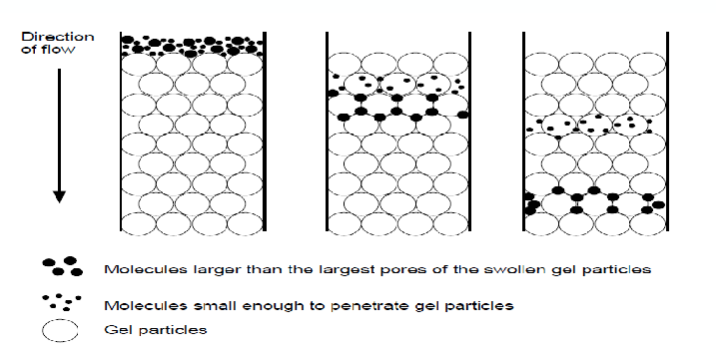
what is size exclusion chromatography?
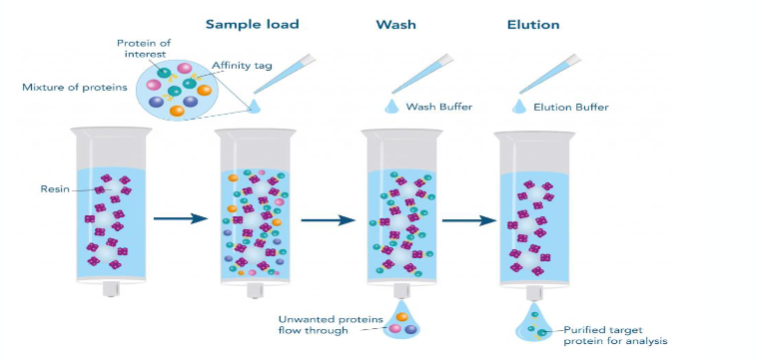
what is affinity chromatography?
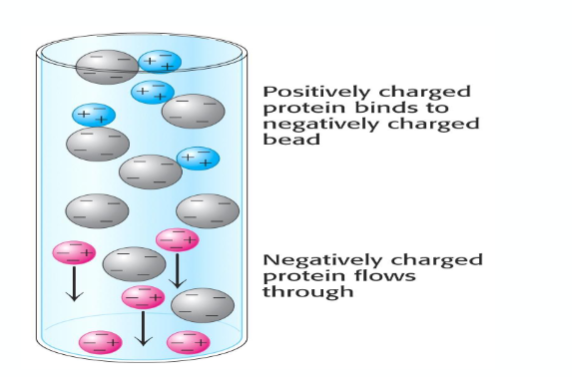
what is ion exchange chromatography?
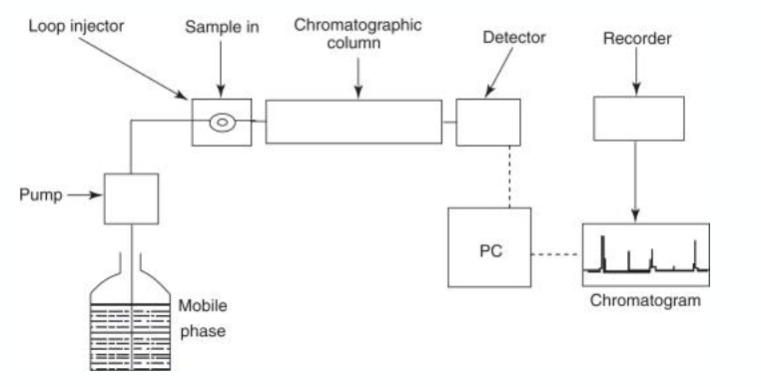
what is high pressure liquid chromatography?
what are the advantages of liquid chromatography in the pharmaceutical industry?
Very Efficient separation technique
Quantification of drug substances and impurities in pharmaceutical formulations.
Identification of metabolites and degradation products.
Assessment of drug stability and shelf-life.
Measurement of drug concentrations in biological fluids
Determination of pharmacokinetic parameters
Evaluation of drug purity and potency.
what is the difference between chromatography and mass spectrometry?
Chromatography is a separation technique while mass spectrometry is an identification technique
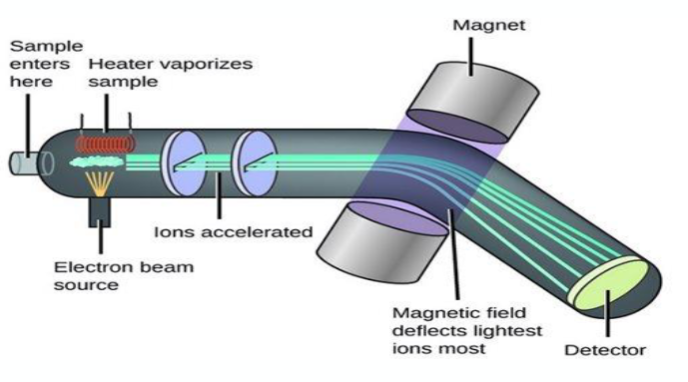
what are the 3 main events of mass spectrometry?
Ionisation - Sample is ionised to produce charged particles
Acceleration of ions - Ions are accelerated through and electric field
Separation of ions - Ions are separated on the base of mass/charge ratio