Anatomy and Physiology Skeletal System and Articulations Lecture Notes
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What are the functions of bone?
support
protection
movement
mineral storage
hematopoiesis (forming blood cells)
What is the axial skeleton and what part of the body are included?
It is the vertical body axis which includes the skull, vertebral column and thoracic cage (ribs and sternum)
What is the appendicular skeleton and what part of the body are included?
This skeleton is made of up limb bones and their connection to the axial skeleton
What are the other names for spongy bone?
cancellous and trabecular skeleton
What is another name for compact bone?
dense bone
define: tendon
muscle to bone connection
define: ligament
bone to bone connection
What are the classes of bone?
long bones
short bones
flat bones
irregular bone
sesamoid bone
What are long bones and where are they found?
Long bones have a length that is greater than the width. An example of this would be arm or leg bones.
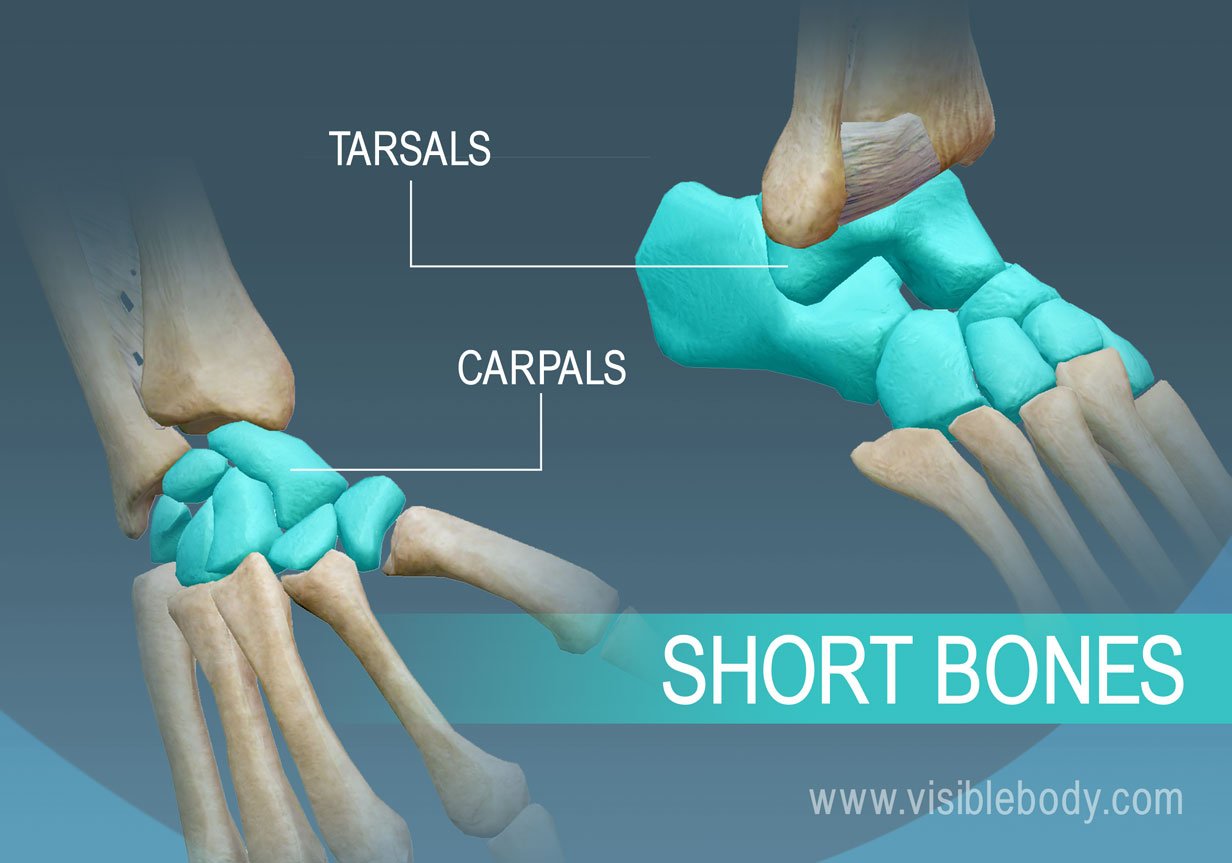
what are short bones and where are they found?
short bones have a length that is about equal to the width so they are circular-ish. They are generally in the wrists and ankles
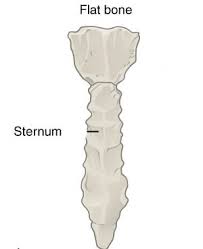
what are flat bones and where are they found?
They have a very thin surface and the bones can be curved. This most prominent of these bones is the skull, and the sternum
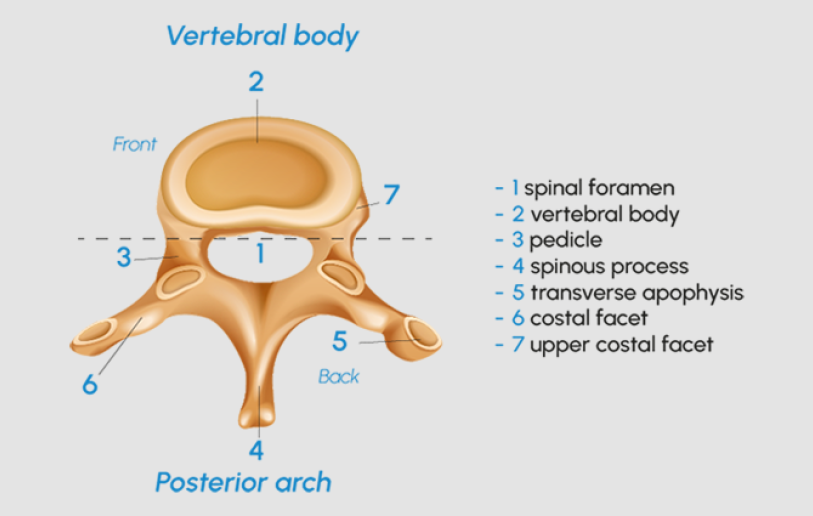
what are irregular bones and where are they found?
these are the bones that are irregular shapes, like vertebral bones
What are sesamoid bones and where are they found?
Sesamoid bones are little bony nodules that are suspended in a joint (floating bones). The biggest sesamoid bone is the knee cap
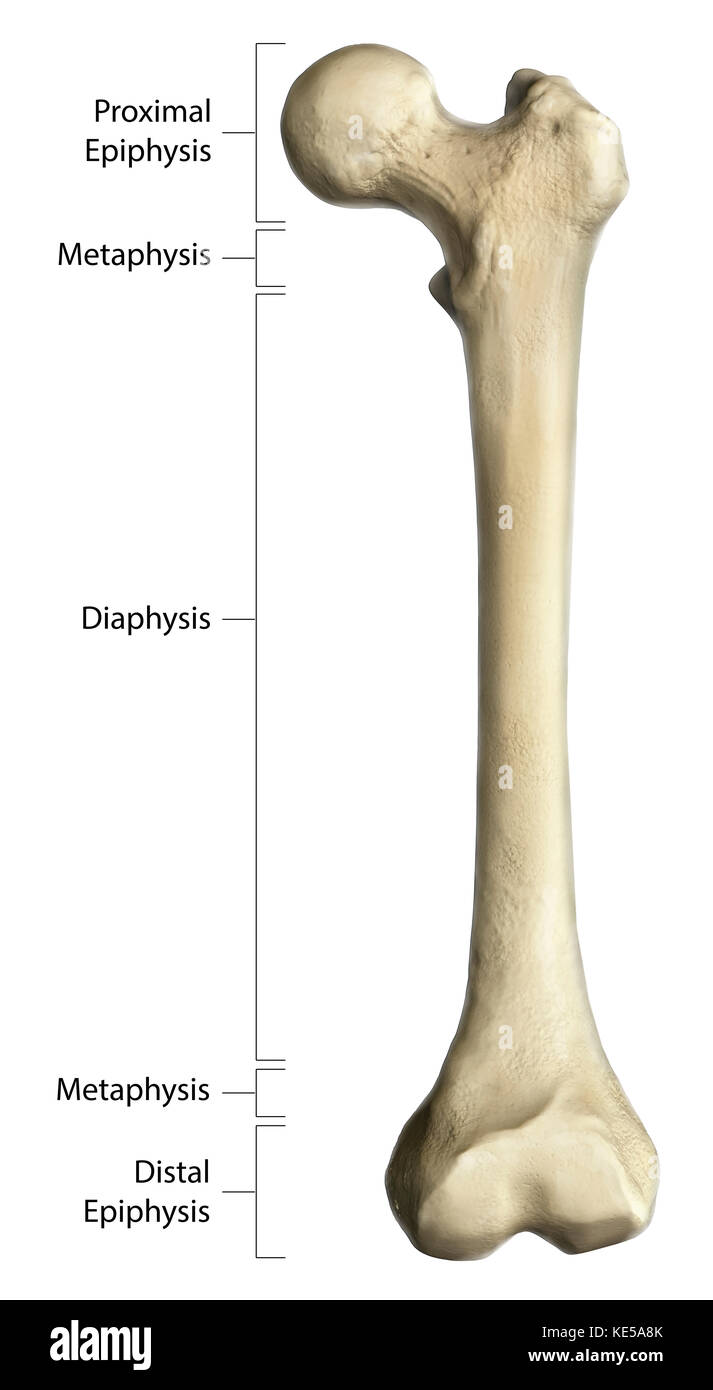
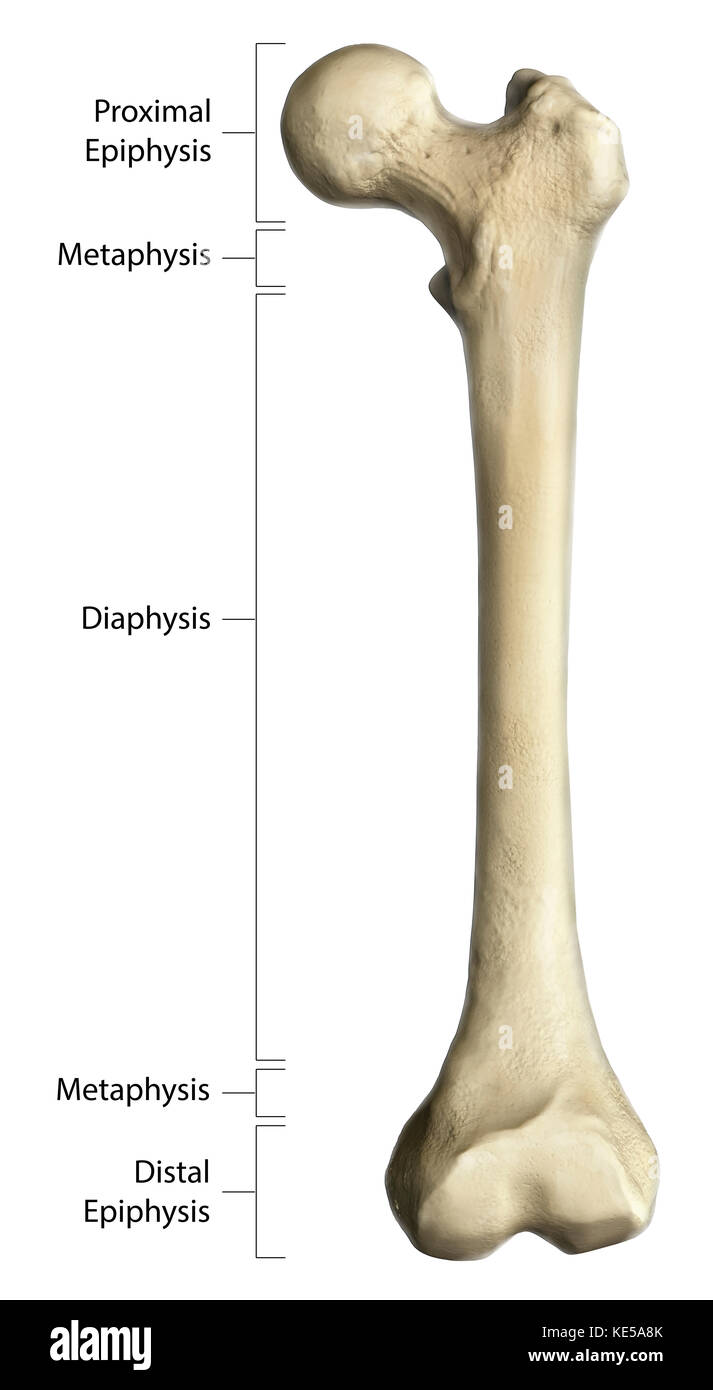
What are the regions of a long bone?
diaphysis
epiphysis
metaphysis
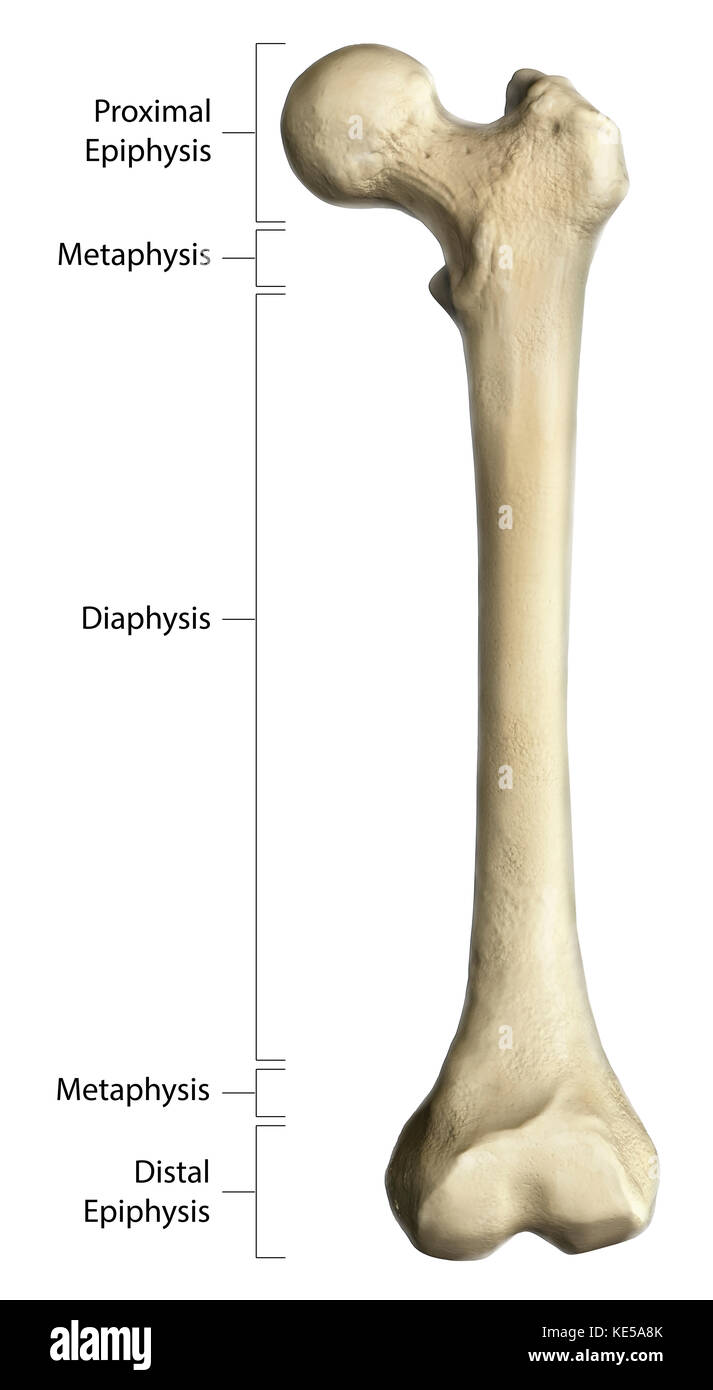
What is the diaphysis region of a long bone?
middle region
has medullary cavity (hollow portion for bone marrow)
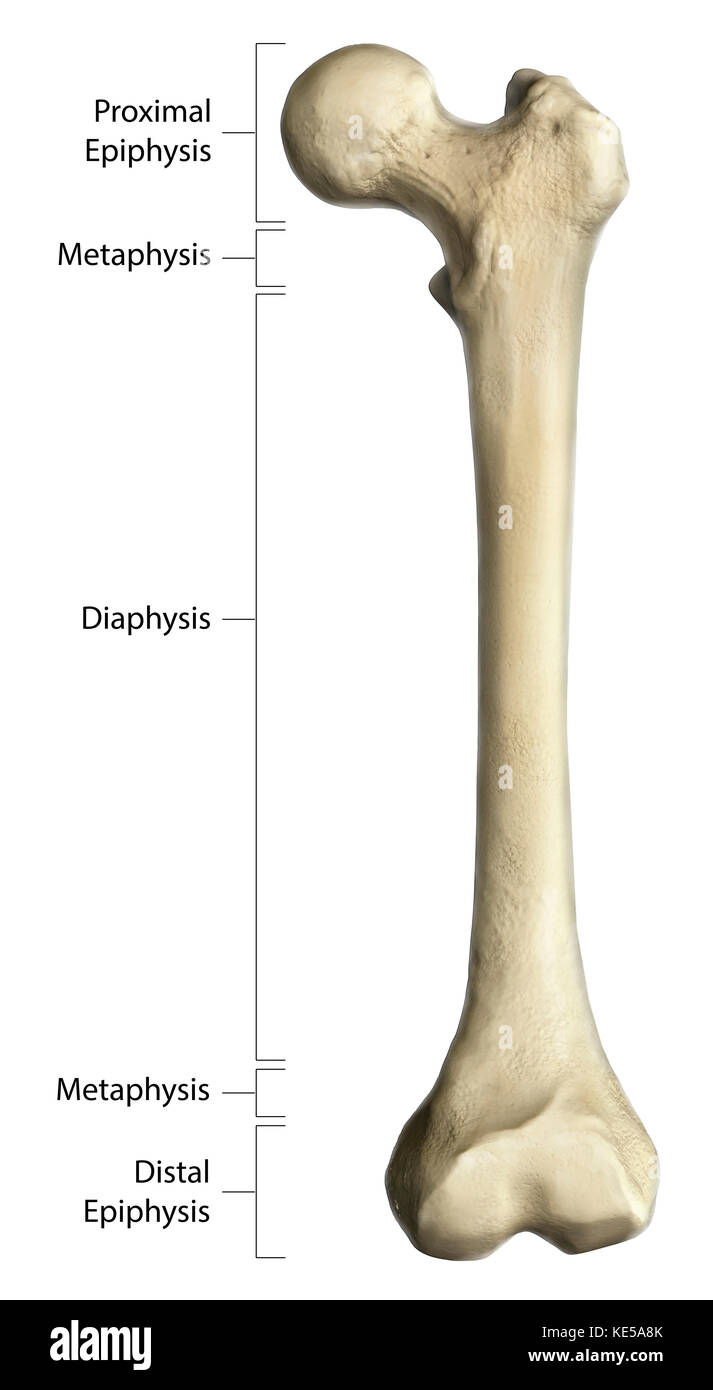
What is the epiphysis region of a long bone?
end bit of a bone
covered by hyaline cartilage
epiphyseal line: in adults, fusion line between epiphysis and metaphysis (growth plate)
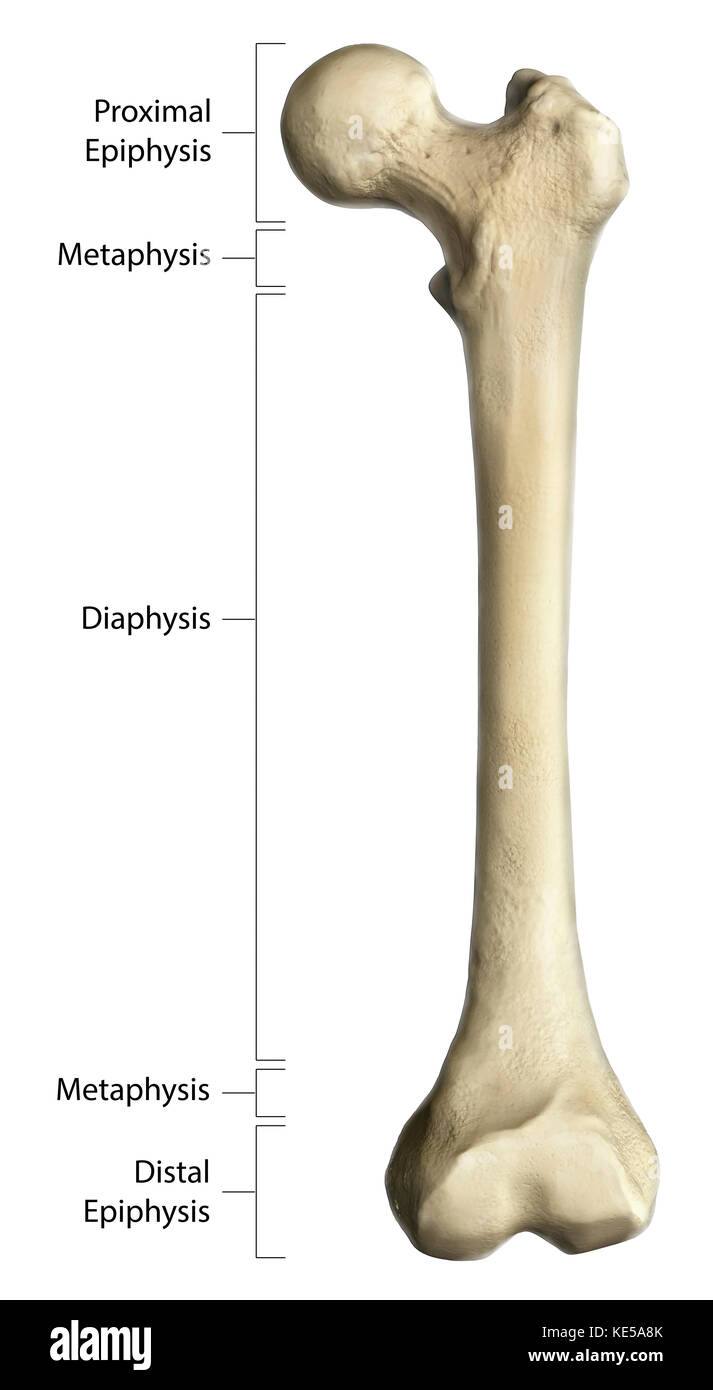
What is the metaphysis region of a long bone?
the space between the diaphysis and epiphysis
What are the types of bone lining?
periosteum
endosteum
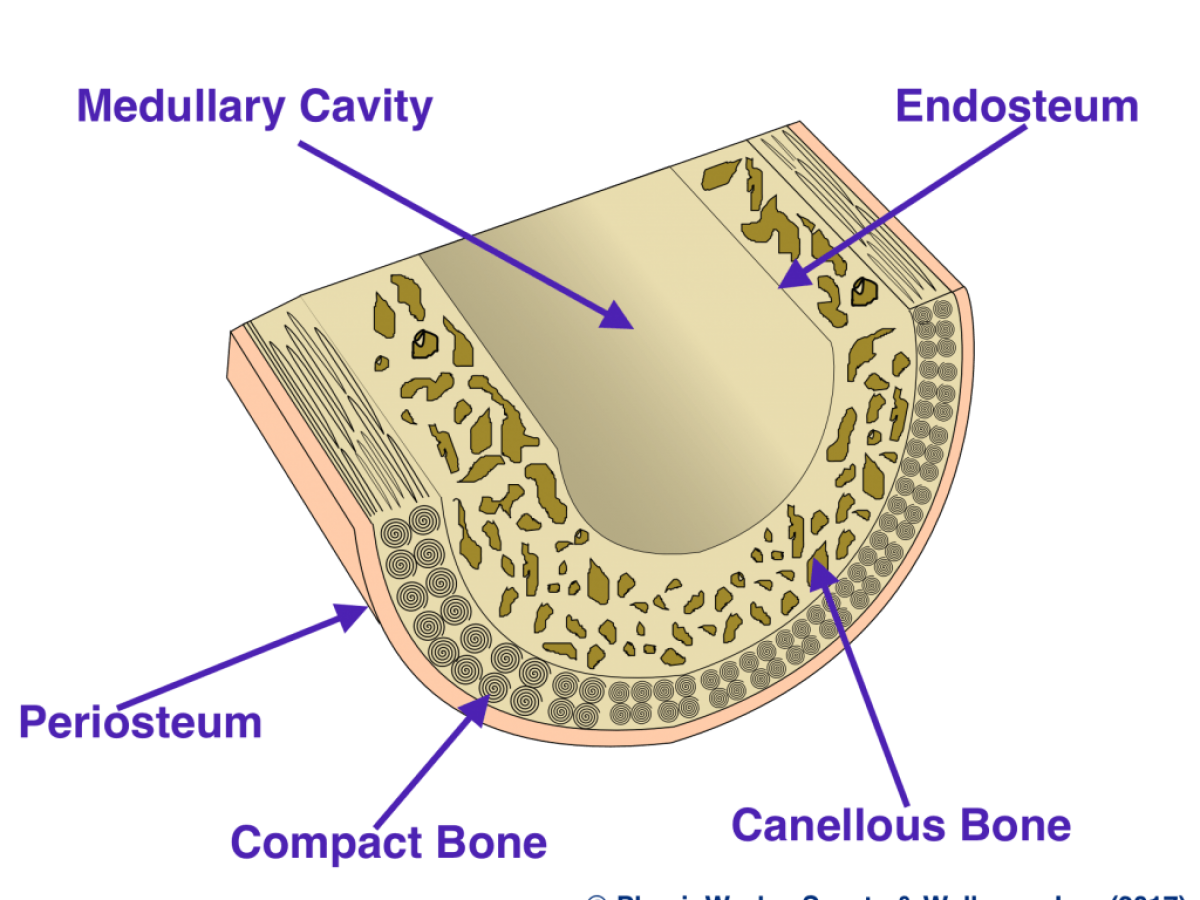
Where is the periosteum found?
layer that covers the OUTER surface of bone
Where is the endosteum found?
a very thin layer that covers internal surface and medullary cavity
active during bone growth
What are the types of bone marrow?
red bone marrow
yellow bone marrow
What is the function of red bone marrow and where is it found?
hematopoiesis (blood cell formation)
more widespread in children
eventually gets replaced with yellow marrow
in adults, in the axial skeleton and the ends of the humerus and femur
What is the function of yellow bone marrow, and where is it found?
it’s adipose tissue
stores triglycerides for energy
replaced red marrow as children get older
Anemia and red/yellow bone marrow?
Anemia is a lack of red blood cells. When the body senses a decrease in RBC, the yellow marrow converts to red marrow to create more RBC (negative feed back look. When there isn’t enough RBCs, there is a decrease in oxygen in the blood.
What are the types of bone cells?
osteoprogenitor cells
osteoblasts
osteocytes
osteoclasts
What are the functions of osteoprogenitor cells?
they are stem cells found in the periosteum and endosteum
highly mitotic/high replication rate
matures into osteoblasts
what are the functions of osteoblasts?
synthesis and secretion of osteoid (semi-solid matrix of calcium and collagen)
makes new bone during development and remodeling
some mature to osteocytes
What are the functions of osteocytes?
maintain bone matrix
triggers bone formation (signals osteoblasts)
don’t replicate
What are the functions of osteoclasts?
reabsorb bone
found on bone surface
they are big phagocytic cells
osteoclasts and osteoblasts work together to break down old bone and replace it with stronger, newer bone
What are the organic components of bone matrix?
osteoid
collagen, proteoglycans, glycoproteins
What are the inorganic components of bone matrix?
salt crystals
What are the types of osteogenesis/ossification?
intramembranous ossification
endochondral ossification
What are the steps to intramembrane ossification?
1) ossification centers (clusters of osteoblasts) form in thickened regions of mesenchyme
2) osteoblasts make unmineralized “soup” (osteoid) that calcified
3) spongy bone and periosteum form
4) compact bone develops around spongy bone
Why does the skull rarely break?
it has a oreo-like sandwhich of compact bone and spongy bone. There is one layer of spongy bone sandwhiched between two layers of compact bone which gives it extra strength
What are the steps of endochondral ossification?
1.) fetal hyaline cartilage model of bone forms
2.) primary ossification center forms in diaphysis
3.) vascular invasion of primary center
4.) bone replaces most cartilage (officiation happens throughout childhood and into late 20s)
5.) epiphyseal plate ossifies by mid-late 20s
What is endochondral/ interstitial growth?
lengthening bone/ growing taller
happens at epiphyseal plate
there is an increase in the # of chondrocytes before ossification happens
5 zones of ossification (Do I need to know this??)
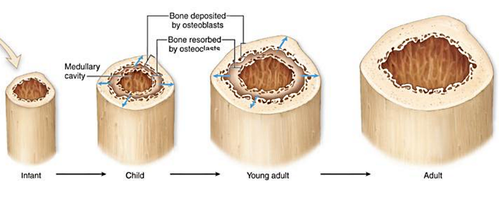
What is appositional growth?
increase in bone width
in periosteum
increase in width of medullary cavity when osteoclasts reabsorb some bone matrix after compact bone has been laid down
What is bone remodeling?
bone gets worn out with age and with use, so osteoclasts eat away the worn-out bone, while osteoblasts replace it with fresh, stronger bone.
What is parathyroid hormone (PTH) and how is it used?
PTH increases the number and activity of osteoclasts (breakdown of bone) if there is an increase in stress on the bones. Bone acts as calcium storage, so when the bone gets broken down, calcium and phosphates are released. This is used in conjunction with calcitonin in a negative feedback mechanism.
What is calcitonin and how is it used?
Calcitonin increases the number of osteoblasts (making bone) and decreases the number of osteoclasts (bone breakdown). When the body detects that there is an increase in calcium levels, calcitonin is used to decrease this by making new bone. It stops osteoclast activity and stimulates the kidneys to release the excess calcium in pee. This is used in conjunction with PTH in a negative feedback mechanism
What is calcitriol and how is it used?
Calcitriol increases the absorbance of calcium and used in conjunction with calcitonin. It increases the amount of calcium in the body.