HDFS Final Chapter 17 Physical and Cognitive Development in Late Adulthood
1/245
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
246 Terms
At what age in late adulthood do most people notice changes in their appearance and functioning?
Age 65.
A full head of silver hair, feeling out of breath after carrying groceries up a flight of stairs, and age-related ailments, such as cataracts or hearing loss, are not easily ignored.
What does the skin lose through adulthood as it becomes more dry and oil glands become less active?
Collagen and elasticity.
What makes blood vessels more visible and older adults to be more sensitive to cold?
The skin thinning and losing the layers of fat underneath it.
Changes in skin is exacerbated by exposure to
sunlight
Pigmented marks called what often appear on the hands and face?
age spots
T/F: The nose and ears grow larger and broader in older adulthood.
T
Why do men and women experience hair loss?
B/c their hair follicles die, while thin downy hair begins to grow from the scalp follicles of men with hereditary baldness.
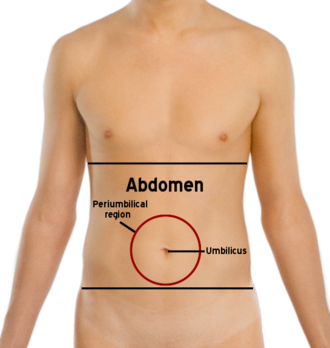
Where is fat accumulated as the body changes in older adulthood?
Fat is redistributed and accumulates in the abdomen.
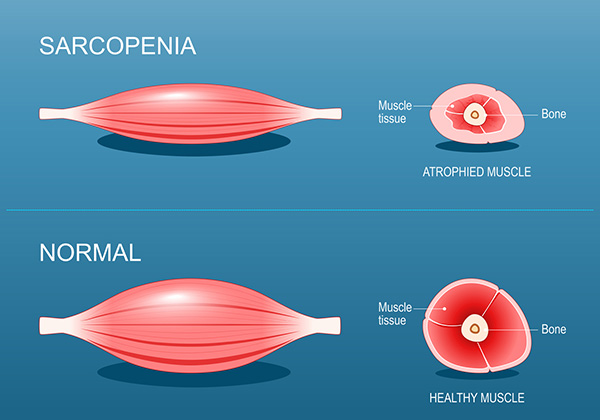
What is Sarcopenia?
The age related loss of muscle mass and strength, with averages losses of 10% to 20% by 60-70 years of age and 40% to 50% from age 70 to 80.
Similar to middle-aged adults (Chapter 15), virtually all older adults experience ____, and have difficulty seeing objects up close. In late adulthood, the lens yellows, the vitreous clouds, less light reaches the retina, and it becomes more difficult to see in dim light and to adapt to dramatic changes in light, such as those that accompany night driving
presbyopia
Many adults develop cataracts, which is?
a clouding of the lens resulting in blurred, foggy vision that makes driving hazardous and can lead to blindness
Cataracts is a combination of what two factors associated with what type of damage?
Cataracts are the result of a combination of hereditary and environmental factors associated with oxidative damage, including illnesses such as diabetes and behaviors such as smoking.
T/F: Behavior such as smoking can cause cataracts.
T
By what age do most adults have cataracts?
Age 80
How is cataracts corrected?
It can be corrected through a surgical procedure in which the lens is replaced with an artificial lens.
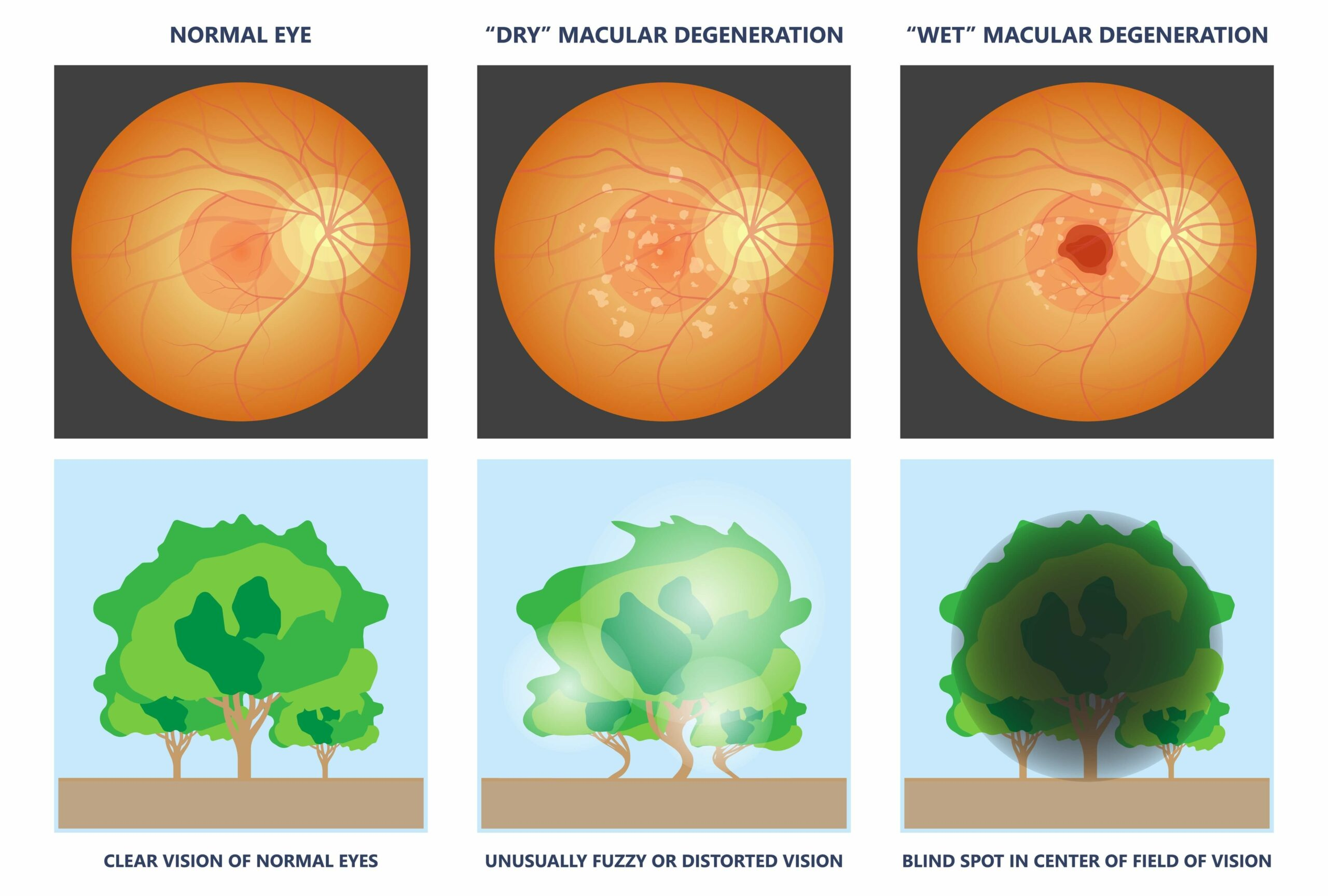
What is macular degeneration?
Some older adults experience macular degeneration, a substantial loss of cells in the center area of the retina, the macula, causing blurring and eventual loss of central vision.
What is the leading cause of blindness?
Macular degeneration
Age-related hearing loss, presbycusis, typically begins in middle adulthood. By age 70 it affects about how many adults?
it affects about two-thirds of adults as cell losses accumulate in the inner ear and cortex.
Older adults experience difficulty distinguishing high frequency sounds, soft sounds of all frequencies, and complex tone patterns and show less activation of which cortex in response to speech as compared with younger adults?
auditory cortex
Which gender tends to suffer from hearing loss earlier and to a greater extent?
Men
The inability to hear car horns and other street sounds or to hear the telephone or doorbell is a risk to not only self-esteem, but also
safety.
T/F: Difficulty hearing others’ speech can socially isolate older adults, reducing their social network, increasing feelings of loneliness and depression, and reducing life satisfaction.
T
Many older adults compensate for their hearing loss by
reducing background noise, when possible, and paying attention to nonverbal cues such as lip movements, facial expressions, and body language to optimize their ability to hear and participate in conversations.
Only % of older adults report using hearing aids.
19%
What is the avg cost for hearing aids?
$2,500, a potentially catastrophic expense for three-quarters of older adults in the United States
When hearing aids no longer provide benefit, ____ implantation is the treatment of choice, with excellent results even in octogenarians (a person who is between 80 and 89 years old)
cochlear
T/F: Sensitivity to smell declines throughout adulthood, but declines in performance are notable by age 60 in men and age 70 in women.
T
About one-third of adults experience substantial disruptions in their ability to smell by age
80
Older adults may be as able as younger adults to identify and remember unpleasant odors, but they show decline in their abilities to identify and remember ____ odors
pleasant
What do late adults produce less of that results in a dry mouth that interferes with taste?
They produce less saliva
Late adults produce less saliva with age, resulting in a dry mouth that interferes with taste, which means that most older adults may report that their food tastes ___. Also, what kind of flavors do they tend to prefer?
bland, and they tend to prefer more intense flavors, especially sweetness
What is the reason older adults may oversalt their food and cause a health risk?
Late adults produce less saliva with age, resulting in a dry mouth that interferes with taste, which means that most older adults may report that their food tastes bland.
T/F: A poor sense of taste can even be a health hazard by making it more difficult for an older adult to detect spoiled food.
T
Which impairment may be an early biomarker of pathological brain aging and is associated with increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia?
Olfactory impairment

Most adults in their 60s become aware of changes in their cardiovascular and respiratory systems, such as feeling their heart pound and taking longer to catch their breath after running to catch a train. There is a physiological reason for this, which is that?
With age, the heart experiences cell loss and becomes more rigid. The heart contains pacemaker cells that signal when to initiate a contraction; over time, these cells diminish and weaken, by nearly one-half, and the heart becomes less responsive to their signals.
The arteries stiffen, and the walls accumulate cholesterol and fat plaques, which reduce blood flow; this condition is known as atherosclerosis
The arteries stiffen, and the walls accumulate cholesterol and fat plaques, which reduce blood flow; this condition is known as ____ and is a cause of heart disease.
atherosclerosis.
Just as the heart undergoes changes with age, changes in which system also reduce the flow of oxygen to the body?
respiratory

Just as the heart undergoes changes with age, changes in the respiratory system also reduce the flow of oxygen to the body. What is happening physiologically?
The lungs gradually lose cells and elasticity over the adult years, substantially reducing the amount of oxygen that enters the system and is absorbed by the blood.
Exposure to ___ reduces immune function, and the effects increase with age: Older adults often show greater immune impairment in response to stress than younger adults
stress

Which cells of the body for older adults become less effective at protecting the body by attacking foreign substances, and the immune system becomes more likely to malfunction and display an autoimmune response by turning against body tissues?
T cells
T/F: There are large individual differences in immune function.
T. Some people retain strong immune functioning into older adulthood, but most experience at least some declines.
A lifetime of regular ____ activity predicts greater mobility in late adulthood.
physical

Interventions that encourage exercise and promote strength and balance, such as what two activities, can increase balance and strength and offset loss?
dance and yoga
age-related changes are influenced by the ability to allocate ____, and that ____ change plays a role in motor performance
attention; neurological
What type of tasks should older adults train on, such as walking and holding a tray with a ball, to improve performance and mobility?
tasks with dual demands
What is gait speed?
(the speed at which people walk
T/F: Gait speed (the speed at which people walk) naturally declines with age with reductions in muscle strength, bone density, and flexibility.
T
Many adults compensate for a slowed gait by
talking longer steps or simplifying their movements
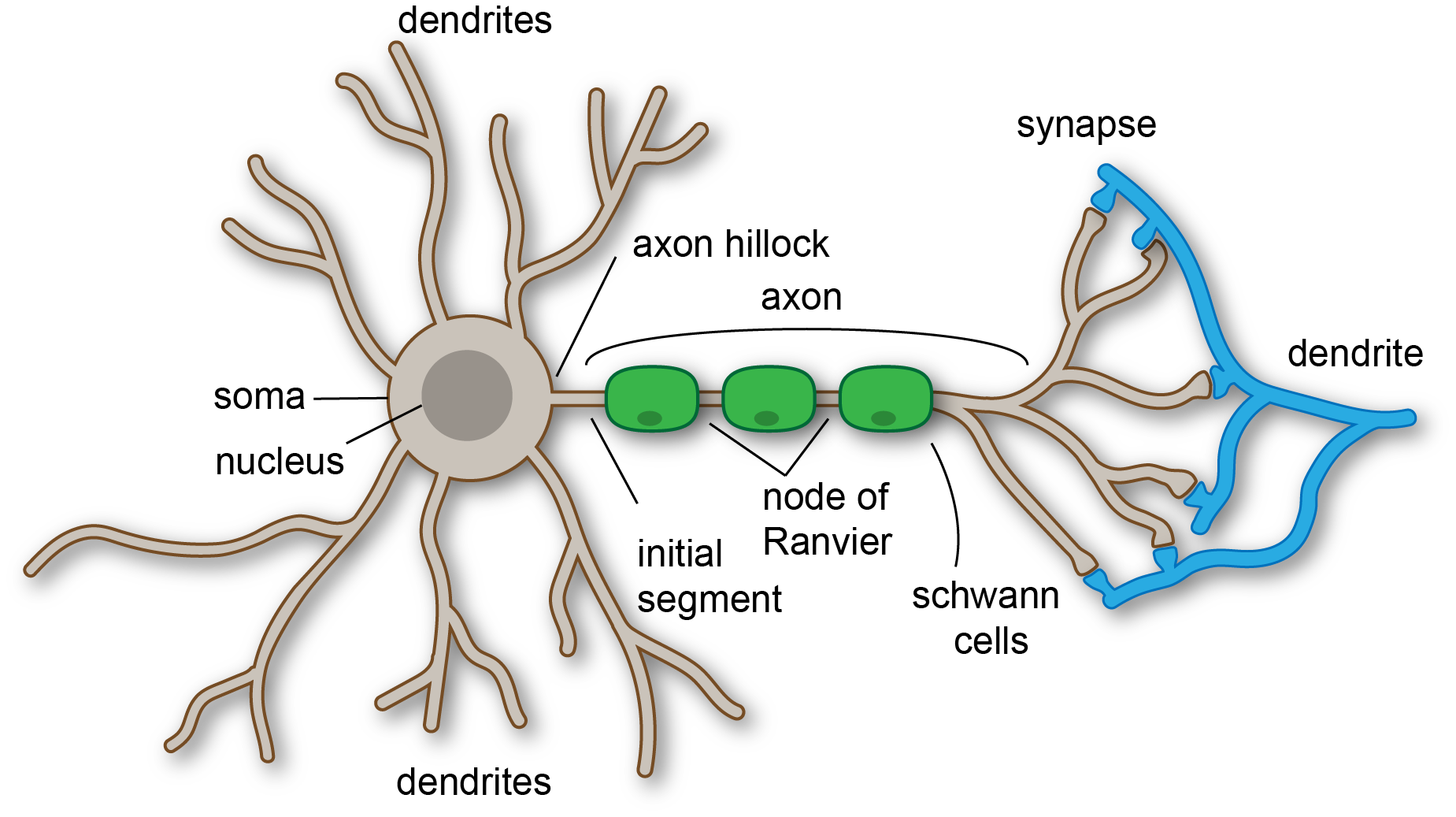
Brain volume declines with age as what parts of the neuron contract and are lost? This is also accompanied by losses in ___ and what type of cells?
dendrites; synapses and glial cells
Glial cells provide less support to neurons and many neural fibers lose their coating of __, slowing communication among neurons.
myelin
Brain related aging declines are especially marked in which cortex, responsible for executive functioning and judgment?
prefrontal
Generally speaking, the last areas of the brain to myelinate are also the first to show reductions in myelin, a pattern some experts call the ___ __ __ ___ hypothesis of brain aging. Therefore, age-related losses appear first in the prefrontal cortex, which matures in emerging adulthood.
“last-in first-out”
T/F: Following the last in first out hypothesis of brain aging, the sensory regions of the brain are among the first of the brain areas to myelinate in infancy and are the first to show loss with age.
F. In contrast, the sensory regions of the brain, including the areas responsible for vision and hearing, and the motor cortex are the first brain areas to myelinate in infancy and the last to show loss with age.
For most people, these neural changes are gradual. The reduction in brain volume is, on average, less than half of _% each year throughout adulthood
1
T/F: Older adults’ brains compensate for cognitive declines by showing more brain activity and using different brain areas in solving problems than younger adults.
T
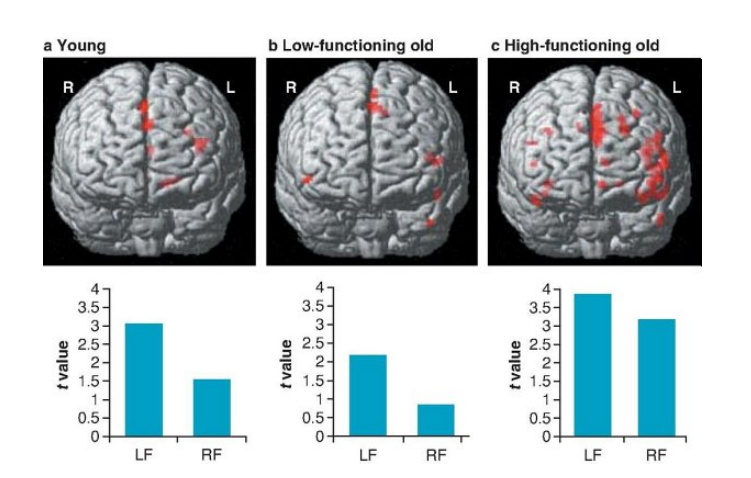
Older adults often show brain activity that is spread out over a ___ area, including both hemispheres, compensating for neural losses
larger

What is cognitive reserve?
Cognitive reserve is the ability to make flexible and efficient use of available brain resources to promote cognitive efficiency, flexibility, and adaptability.
What do adults retain to help the older adult brain compensate for loss?
Adults retain cognitive reserve, which helps the older adult brain compensate for loss. Cognitive reserve is the ability to make flexible and efficient use of available brain resources to promote cognitive efficiency, flexibility, and adaptability.
Cognitive reserve is a type of ____ cultivated throughout life from experience and environmental factors.
plasticity
What are good sources of cognitive reserve?
Educational and occupational attainment and engagement in leisure activities are sources of cognitive reserve that allow some adults to cope with age-related changes better than others and show more successful aging
T/F: Bilingualism is associated with cognitive benefits throughout life and is thought to be a marker of cognitive reserve.
T
bilingual older adults show preserved ___ matter integrity, especially in the frontal lobe, as compared with their monolingual peers
white
T/F: Overtime, neurogenesis, the creation of new neurons, dies out throughout life.
F. Neurogenesis, the creation of new neurons, continues throughout life
New neurons are created in the ___ and ___ (a subcortical part of the brain responsible for coordinating motivation with body movement) and the olfactory bulb throughout life but at a much slower rate than prenatally.
hippocampus; striatum
Research with mice suggests that intense physical activity, such as running, may promote the survival of
new neurons
T/F: Adult-born neurons play a distinct role in brain functions related to the hippocampus, such as memory encoding and mood regulation.
What % of neurons are renewed each year?
2%
In one study, greater amounts of ___ activity were associated with more gray matter volume in several areas of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, and a reduced risk for cognitive impairment over a 9-year period
physical
Some older adults experience high rates of cell death and severe brain deterioration that characterize what disease?
dementia
What is dementia?
Dementia is a term referring to the progressive loss of mental abilities due to changes in the brain that influence higher cortical functions such as thinking, memory, comprehension, and emotional control, and are reflected in impaired thought and behavior, interfering with the older adult’s capacity to engage in everyday activities
It's not a specific disease itself, but rather a collection of symptoms caused by various brain-related diseases.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) has replaced the generic term dementia with ______ disorder as a label for a set of diseases that cause brain deterioration
neurocognitive
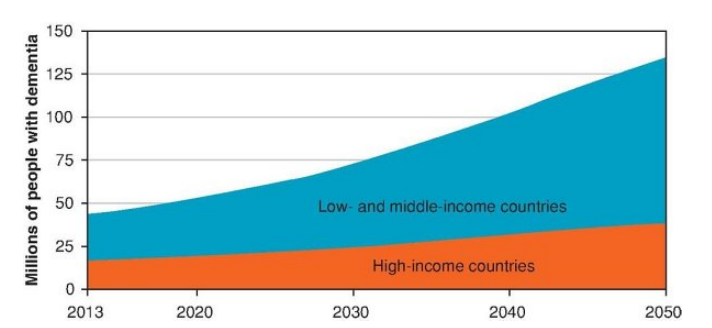
About how many people worldwide live with dementia?
50 million people, and this number may reach over 150 million in 2050. Much of the increase will be in low-income, developing countries.
T/F: adults may show different forms of dementia at once.
T
The most common cause of dementia is what, followed by what and what?
Alzheimer’s disease, followed by vascular dementia and Lewy body dementia.
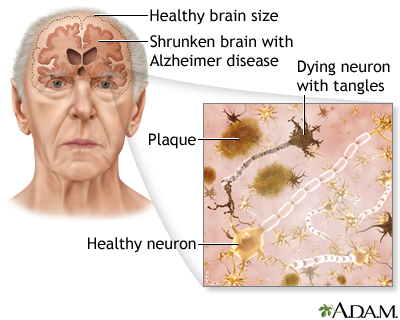
What is Alzheimer’s disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that progresses from mild to moderate cognitive declines to include personality and behavior changes, motor problems, severe dementia, and death.
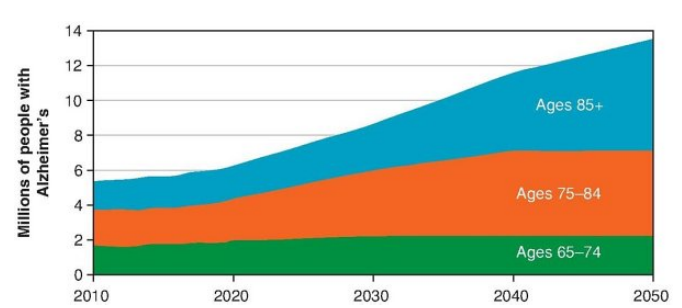
The risk of Alzheimer’s disease grows ____ with age, doubling approximately every 5 to 6 years in most Western countries.
exponentially
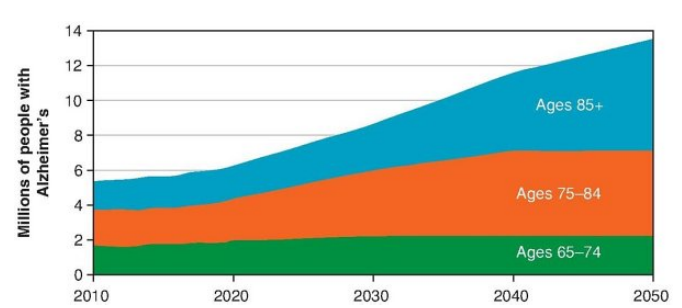
Currently 6.2 million Americans, including more than 1 in _ people over the age of 65, have Alzheimer’s disease.
9
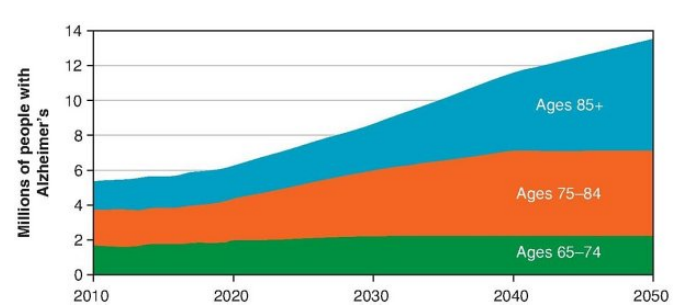
T/F: Prevalence rates increase with age: Alzheimer’s disease is diagnosed in about 5% percent of people aged 65 to 74, 14% of those 75 to 84, and 35% of those 85 or older. People younger than 65 can also develop Alzheimer's dementia, but it is uncommon.
T
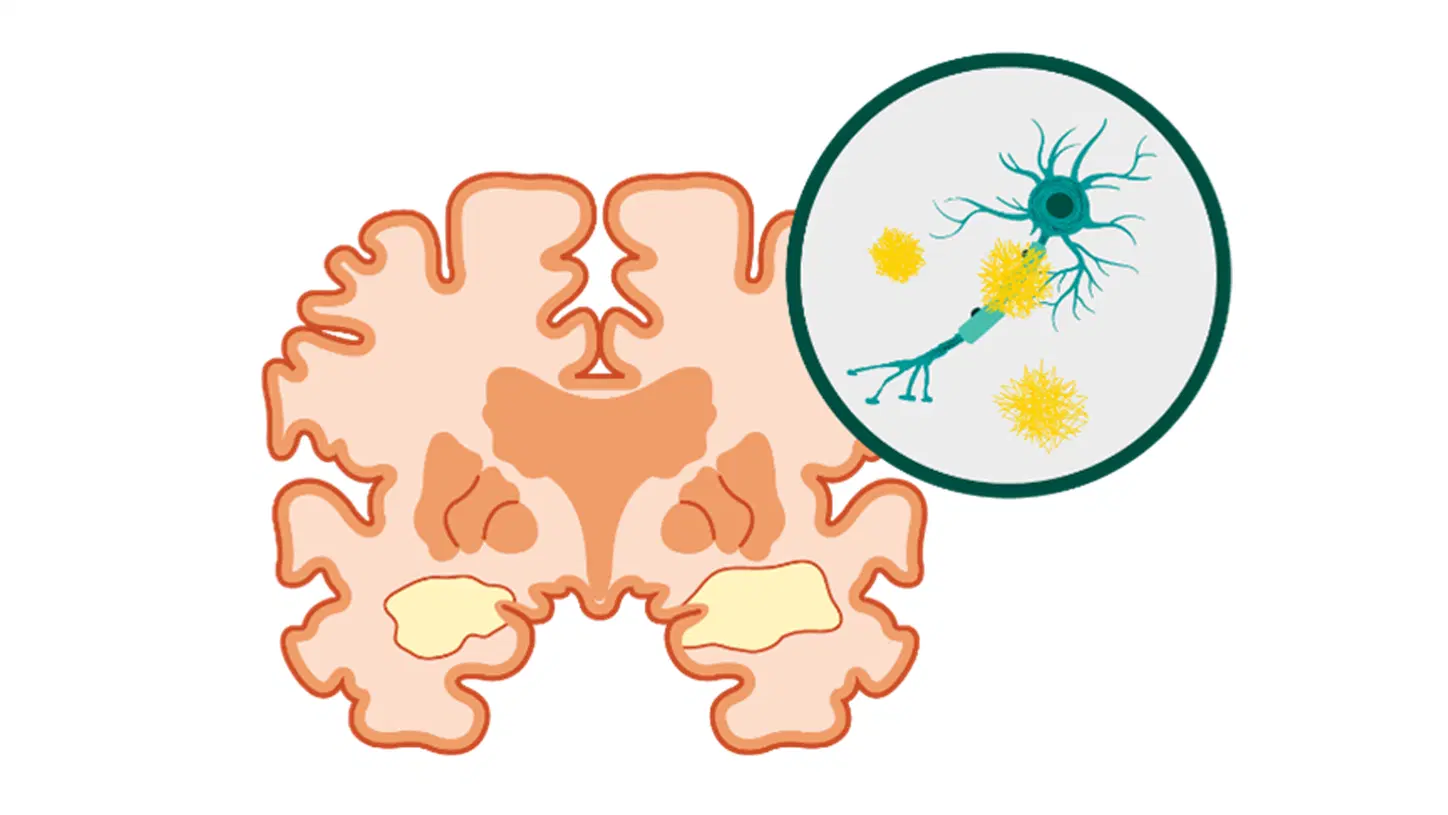
Which protein is associated with widespread brain deterioration in Alzheimer’s?
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by widespread brain deterioration associated with inflammation and accumulations of beta-amyloid, a protein present in the tissue that surrounds neurons in the healthy brain.
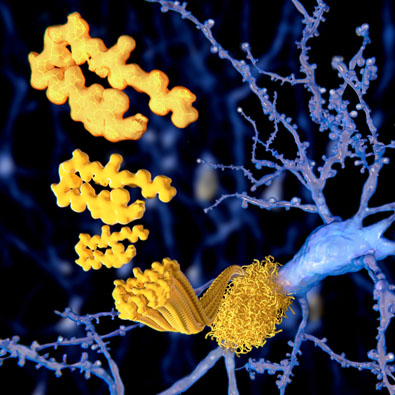
Alzheimer’s patients experience inflammation that causes the beta-amyloid to accumulate and join with clumps of dead neurons and glial cells, forming large masses called
amyloid plaques
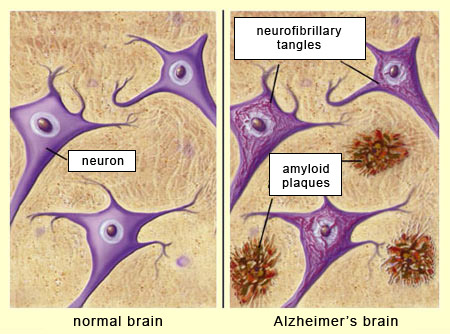
How do amyloid plaques form?
Alzheimer’s patients experience inflammation that causes the beta-amyloid to accumulate and join with clumps of dead neurons and glial cells, forming large masses called amyloid plaques.
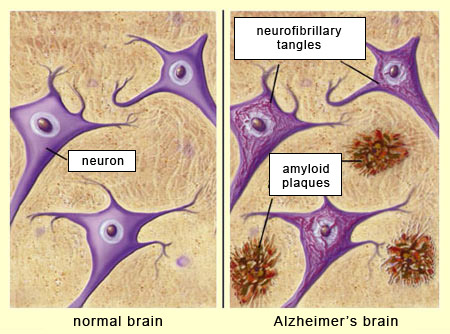
It is thought that amyloid plaques disrupt the structure and function of cell membranes and contribute to the formation of _______ ____—twisted bundles of threads of a protein called tau that occur when neurons collapse.
neurofibrillary tangles
Even healthy brains have some neurofibrillary tangles, but in cases of Alzheimer’s disease there is inflammation and a proliferation of plaques and tangles that interact, resulting in
a progressive loss of neurons that interferes with brain functioning
Alzheimer’s disease is associated with altered neurogenesis and atrophy in the hippocampus, impairing the creation and development of
new neurons
Alzheimer’s disease is generally diagnosed in living patients through ____: by ruling out all other causes of dementia
exclusion
larger than usual spaces surrounding some of the blood vessels in the brain are associated with what disease?
Alzheimer’s
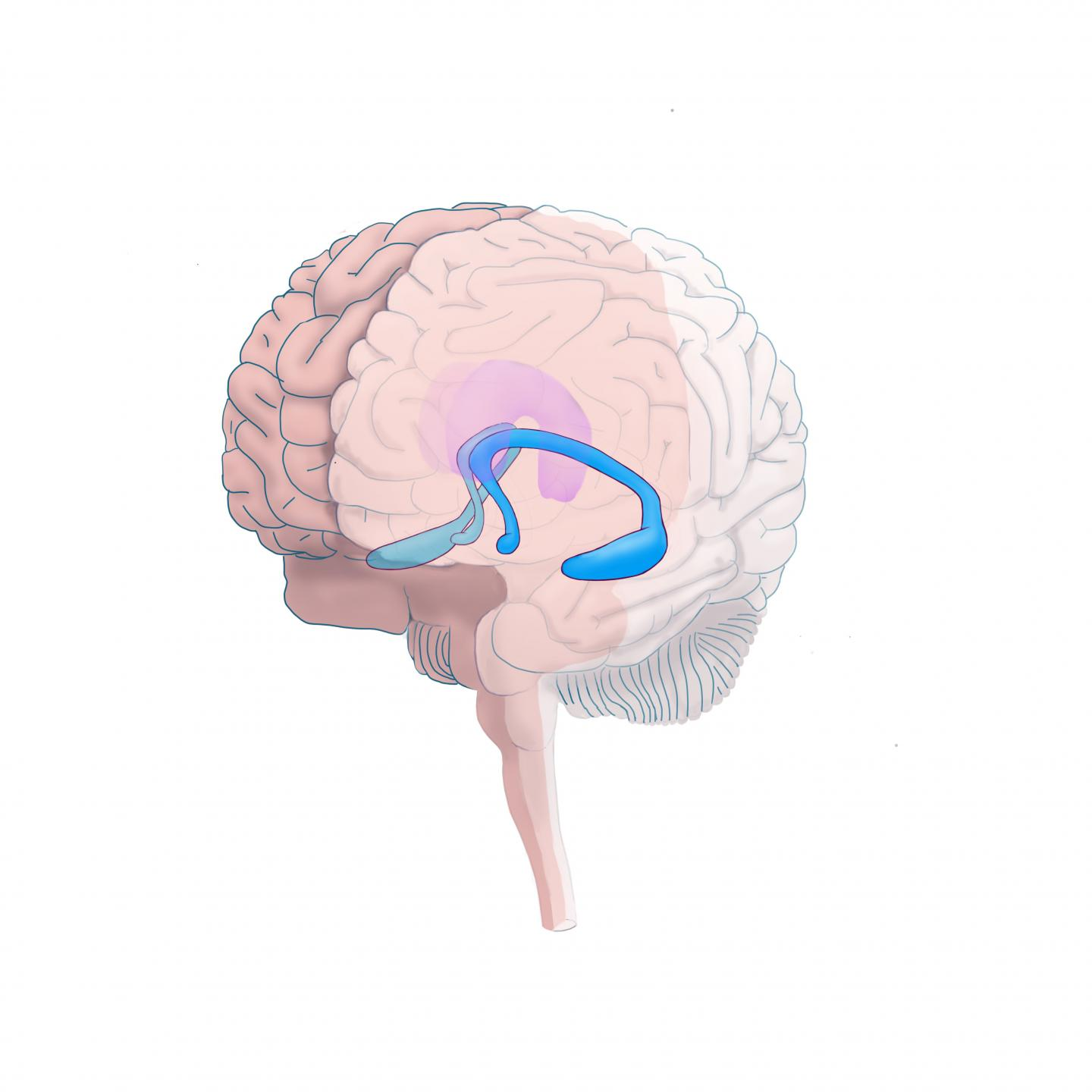
The earliest symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease are memory problems, likely because
the neurological disruptions that comprise Alzheimer’s disease usually begin in the hippocampus, which is influential in memory
First, older adults experience impairments in memory that are usually attributed to ______. They may forget the names of new people, recent events, appointments, and tasks such as turning off the iron.
absentmindedness

Up to 50% of Alzheimer’s patients experience ____ or ___ symptoms.
depression
_____ is particularly harmful to Alzheimer’s patients as it is associated with greater cognitive and behavioral impairment, disability in activities of daily living, and a faster cognitive decline.
Depression
Why is it hard to treat depression for Alzheimer’s patients?
Treating depression is difficult in Alzheimer’s patients because antidepressant medication, a mainstay of treatment for depression, appears to be ineffective on Alzheimer’s patients.
In the final stages of Alzheimer’s disease, brain deterioration interferes with the individual's ability to comprehend and produce ____, to control bodily functions, and to respond to stimuli.
speech
Eventually brain functions deteriorate to the point where organs fail and life cannot be sustained. The average patient progresses to the final stage of Alzheimer’s disease over the course of about __ years, with a typical range of 5 to 12 years
10
Does Alzheimer’s have genetic influence?
Yes, Alzheimer’s disease has genetic influences and often runs in families.
In Alzheimer’s, several chromosomes are implicated, including the 21st chromosome, which puts which individuals at risk?
Individuals with Down syndrome, trisomy 21, are at high risk to develop Alzheimer’s disease as many show plaques and tangles in their brains as early as age 40.
What is a protective factor against the brain atrophy characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease?
Cognitive reserve is a protective factor against the brain atrophy characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease.
The process of learning that accompanies higher education and occupational complexity promotes neural activity and increases connections among neurons, thickening the cortex and boosting _______ __.
cognitive reserve