Foundations of PMHN Theorists/Neurobiology and Philosophical Underpinnings of Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Psychosocial Theories
Theoretical models to explain and/or predict patient responses exist in each of these domains (physiological, psychological, sociocultural, developmental, and spiritual needs of patients)
Psychoanalytical and Neo-Freudian Theorists (5)
Freud: Psychoanalytical
Alfred Adler: Individual psychology
Carl Jung: analytical psychology
Karen Horney: feminine psychology
Harry Stack Sullivan: interpersonal forces
Freud: Psychoanalytical
Unconscious could be accessed through dreams and free association
Id, ego, superego; defense mechanisms;transference and counter transference
Alfred Adler: Individual psychology
Motivating force in life: intolerable sense of inferiority
Principles of mutual respect, choice, responsibility
Carl Jung: Analytical psychology
Extroverted vs. introverted personalities
Harry Stack Sullivan: Interpersonal forces
Importance of human relationships (instinct & drives less important)
Interpersonal relations as the basis for human development & behavior
Humanistic Theorists (3)
Carl Rogers: Client-centered therapy
Frederick S. (Fritz) Perls: Gestalt therapy
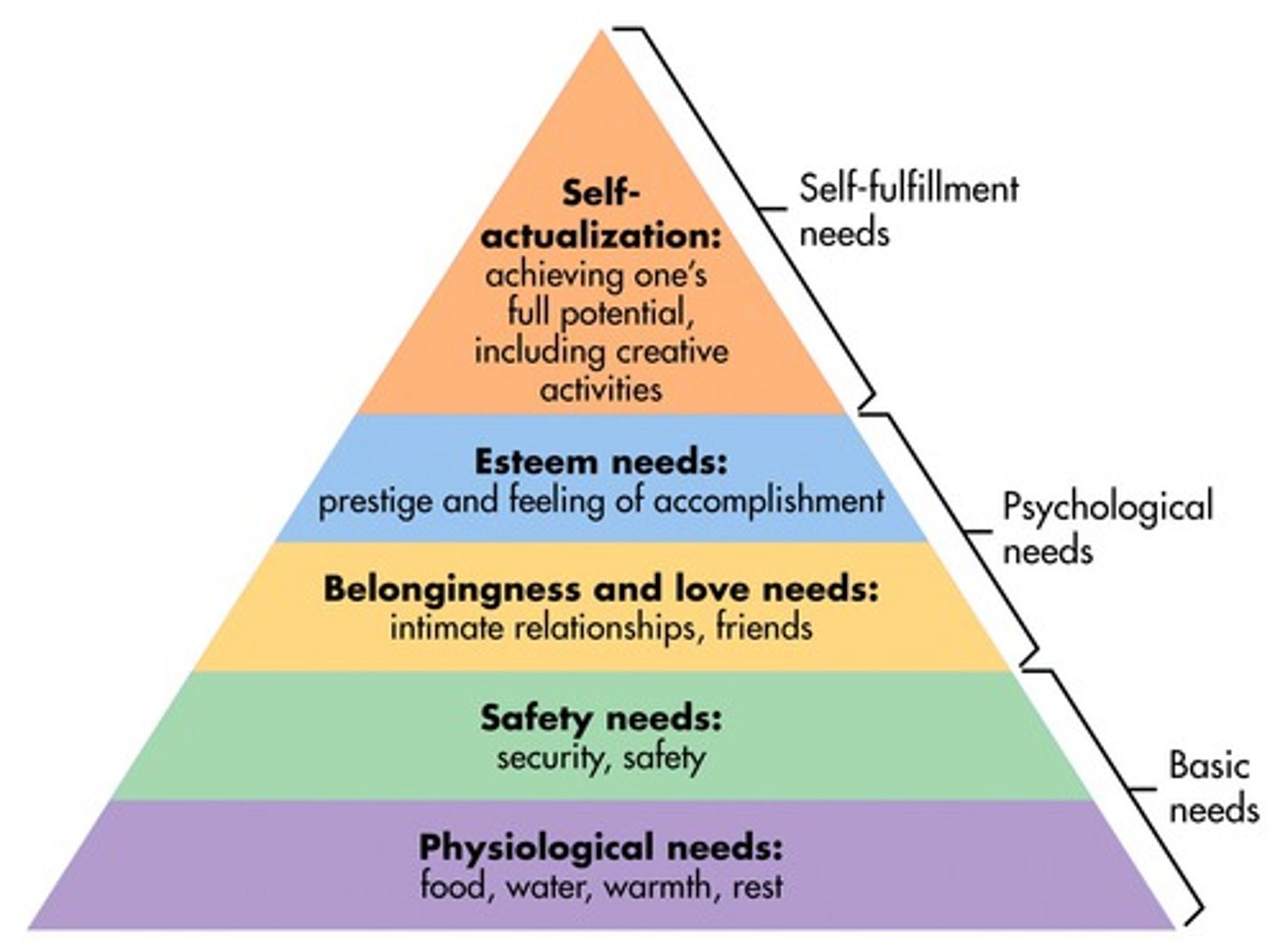
Abraham Maslow: Hierarchy of needs
Carl Rogers: Client-centered therapy
Unconditional positive regard (responding positively but truthfully to whatever pt has to say)
Empathy and genuineness
Frederick S. (Fritz) Perls: Gestalt therapy
Anxiety resulting from inability to express natural biologic and psychological desires; repression --> anxiety
Abraham Maslow: Hierarchy of needs
Physiological
Safety
Belongingness/Love
Esteem
Self-actualization
Cognitive Behavioral Theories
Stimulus-Response Theories
Reinforcement Theories
Cognitive Theories
Stimulus-Response Theories (Who and What)
Pavlovian theory: classical conditioning
John B. Watson: behaviorism
Reinforcement Theories (Who and What)
Link between behavior and consequences
Edward L. Thorndike: "stamping in" (reinforcement of positive behavior)
B. F. Skinner: operant conditioning
Cognitive Theories (Who and What)
Theories that emphasize mental processes in development, such as logic and memory
Albert Bandura: social cognitive theory; self-efficacy
Aaron Beck: thinking and feeling; cognitions
Hans Selye Stress Theory
Initial description of the stress response: General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
3 Stages of General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
1. Alarm: Body reacts to stress (SNS activates)
2. Resistance: Adaption to stress (Flight or flight)
3. Exhaustion: Body resources have been depleted
Social Determinates of Mental Health
Level concerns of poverty, violence, crime, abuse of civil and political rights and freedoms
Threats to personal safety
Economic uncertainty
Health & Social Policy
Access to safe, effective, quality care at all levels
Hildegarde Peplau
Expanded role of psych nurse- outlined the scope of practice, interpersonal relations in nursing- first systematic theoretical framework for psych nursing
Established the first nursing graduate program (Psychiatric Clinical Nurse Specialist) at Columbia University in 1956
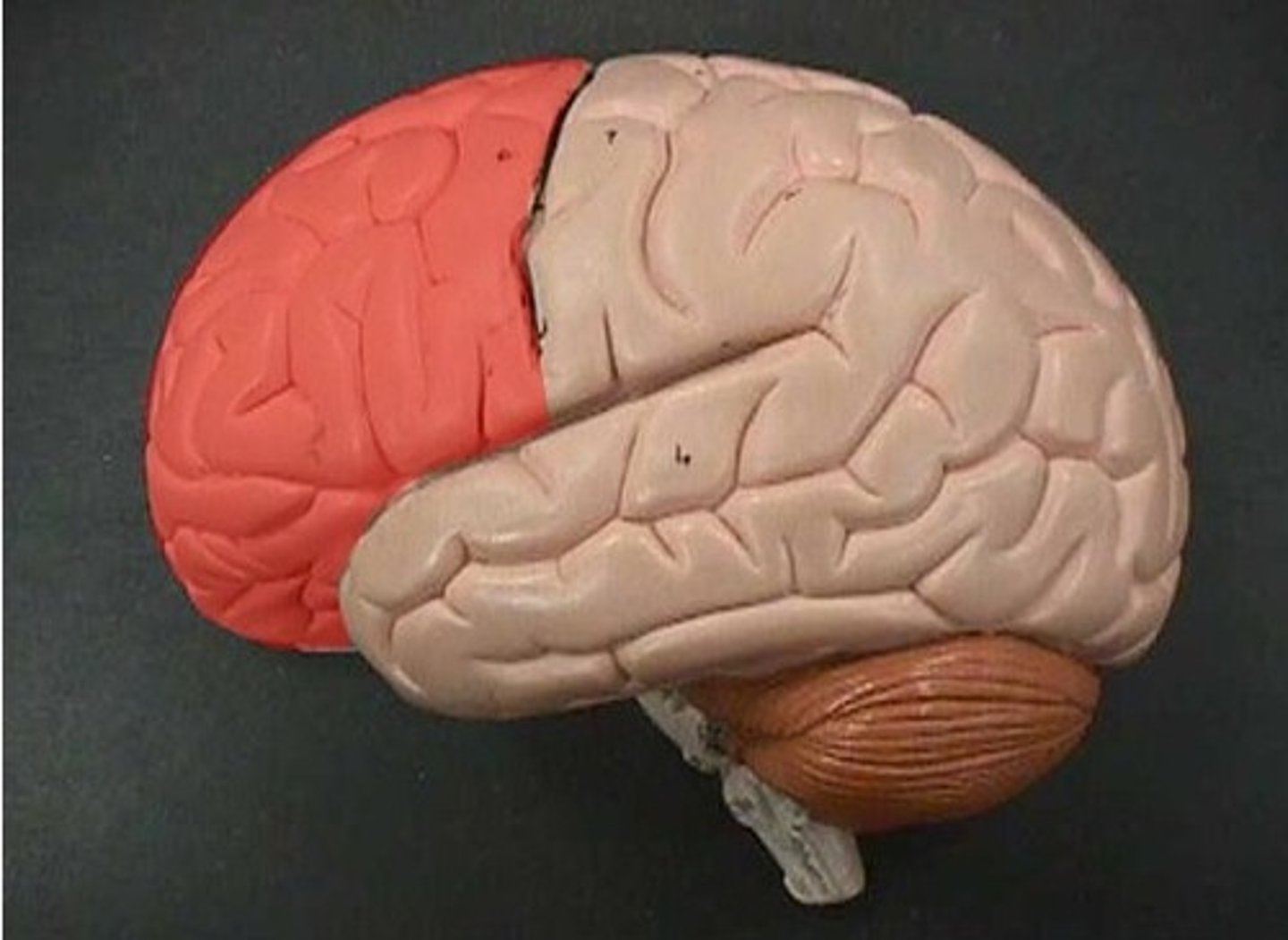
Frontal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
Decreased executive functioning→ poor modulation of impulses→ mood and personality changes
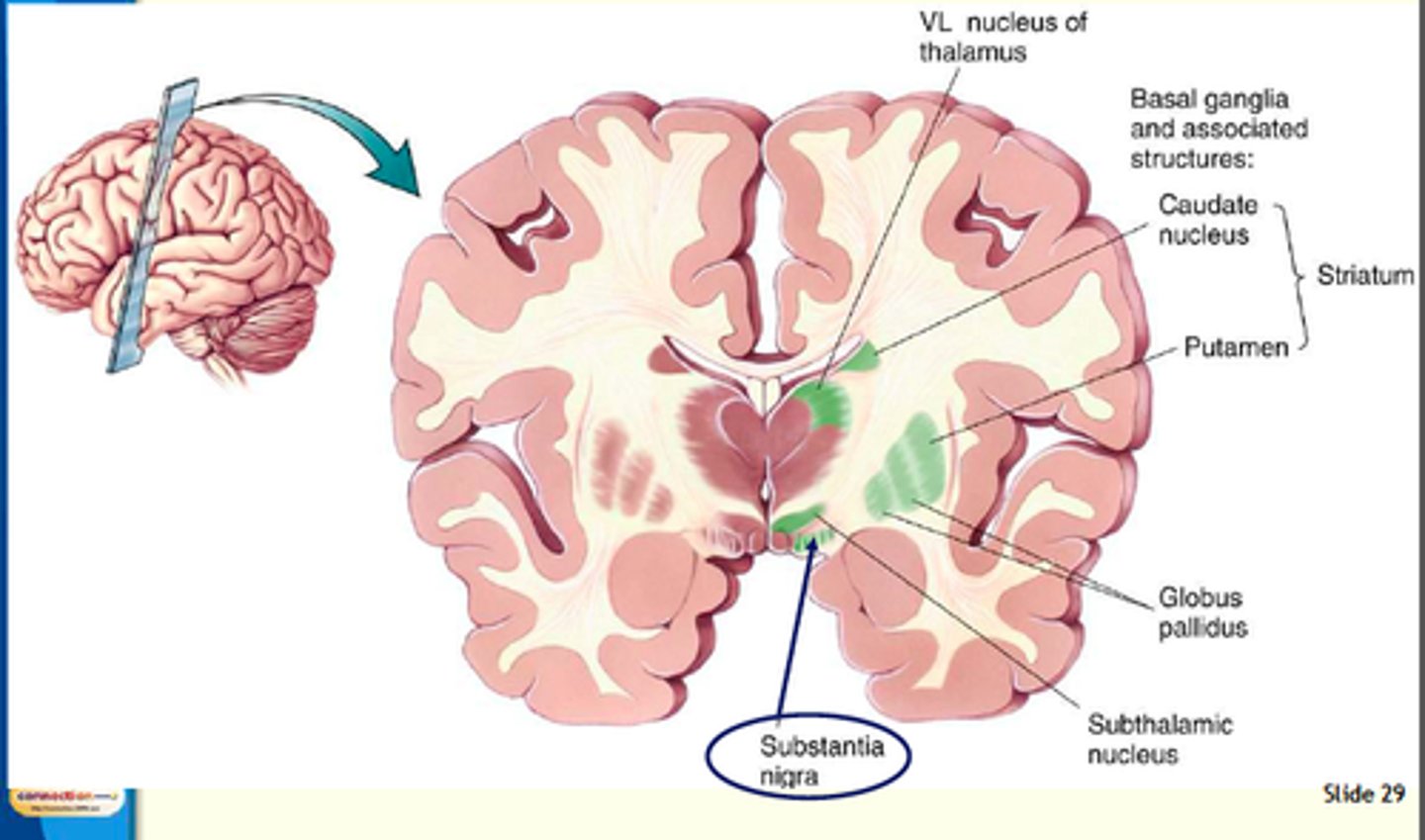
Basil Ganglia
Structures in the forebrain that help to control movement
Defects cause abnormal movement disorders, tremors, twitches
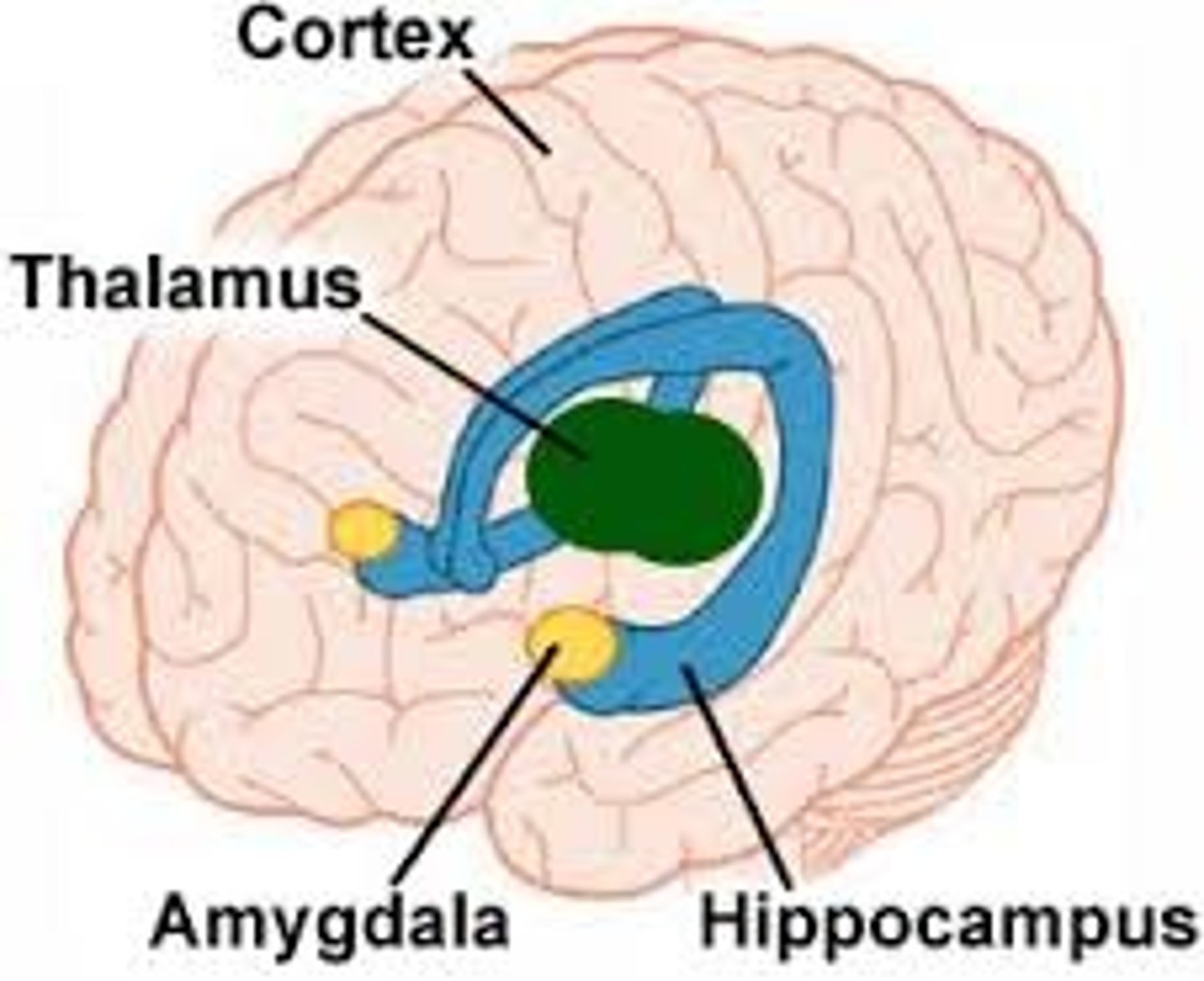
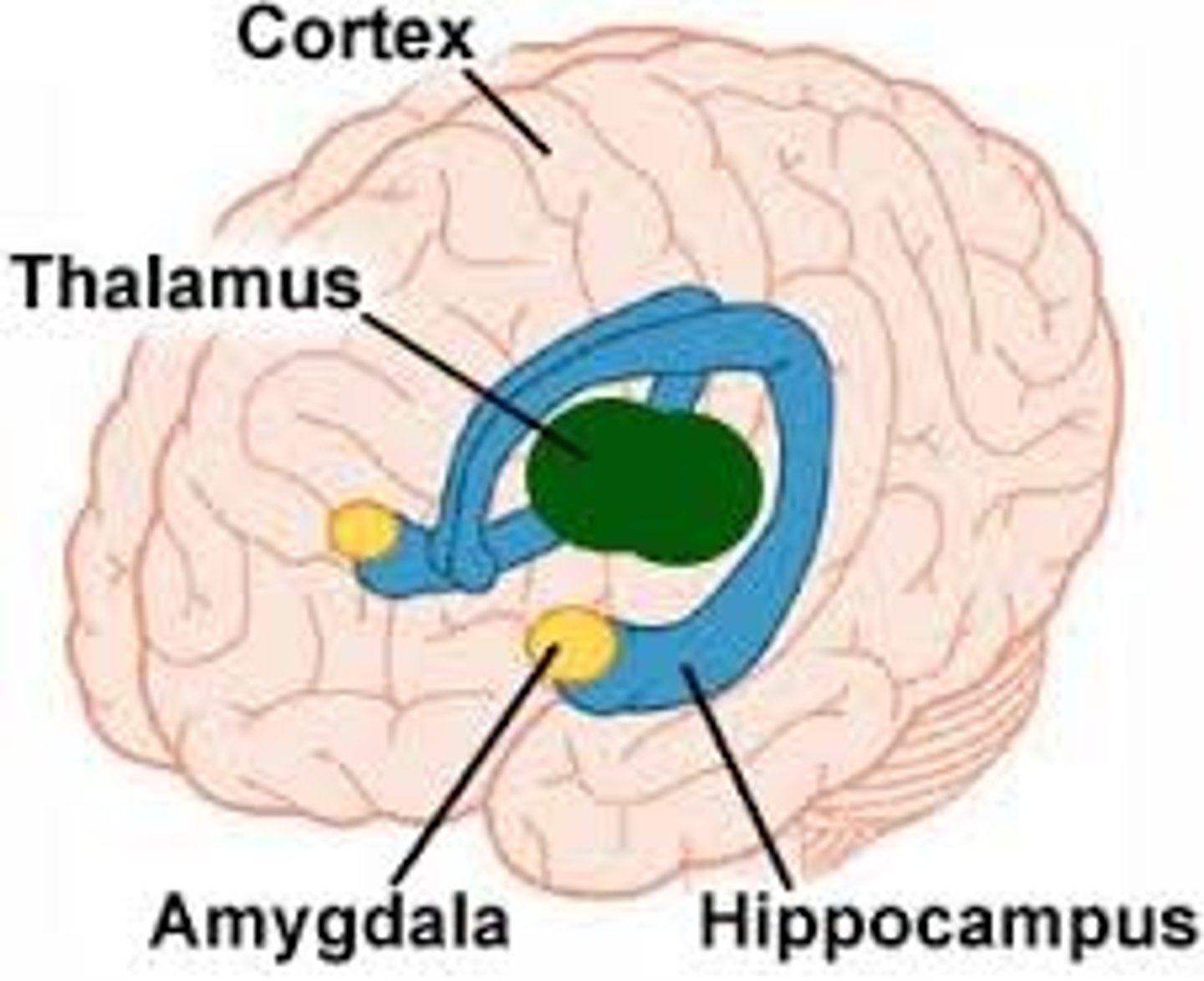
Limbic System
Neural system (including the hippocampus, amygdala, thalamus, and hypothalamus) located below the cerebral hemispheres
Associated with basic emotions, needs, drives, and instincts
Hippocampus
Neural center located in the limbic system; helps storing memories, especially emotional memories
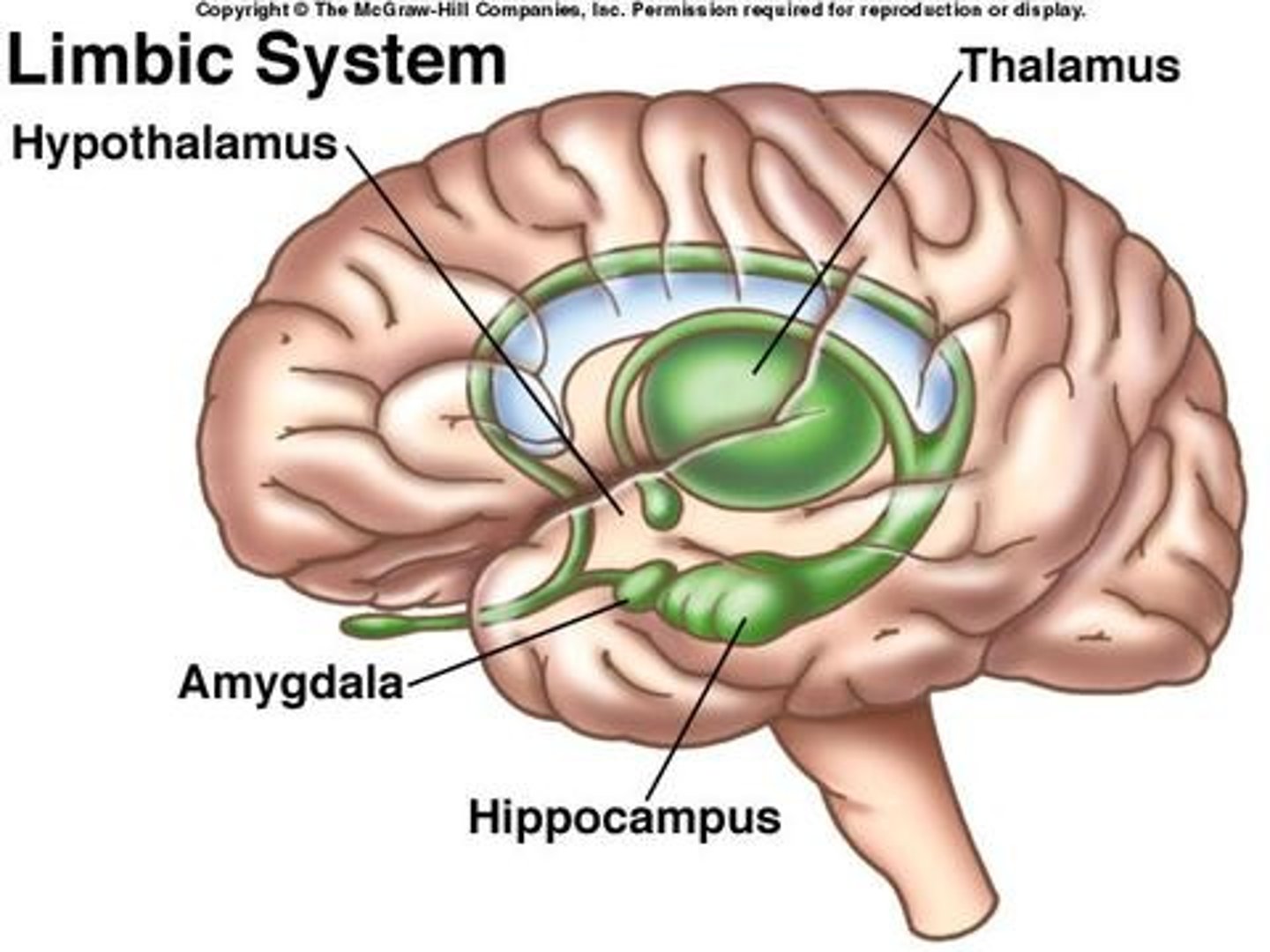
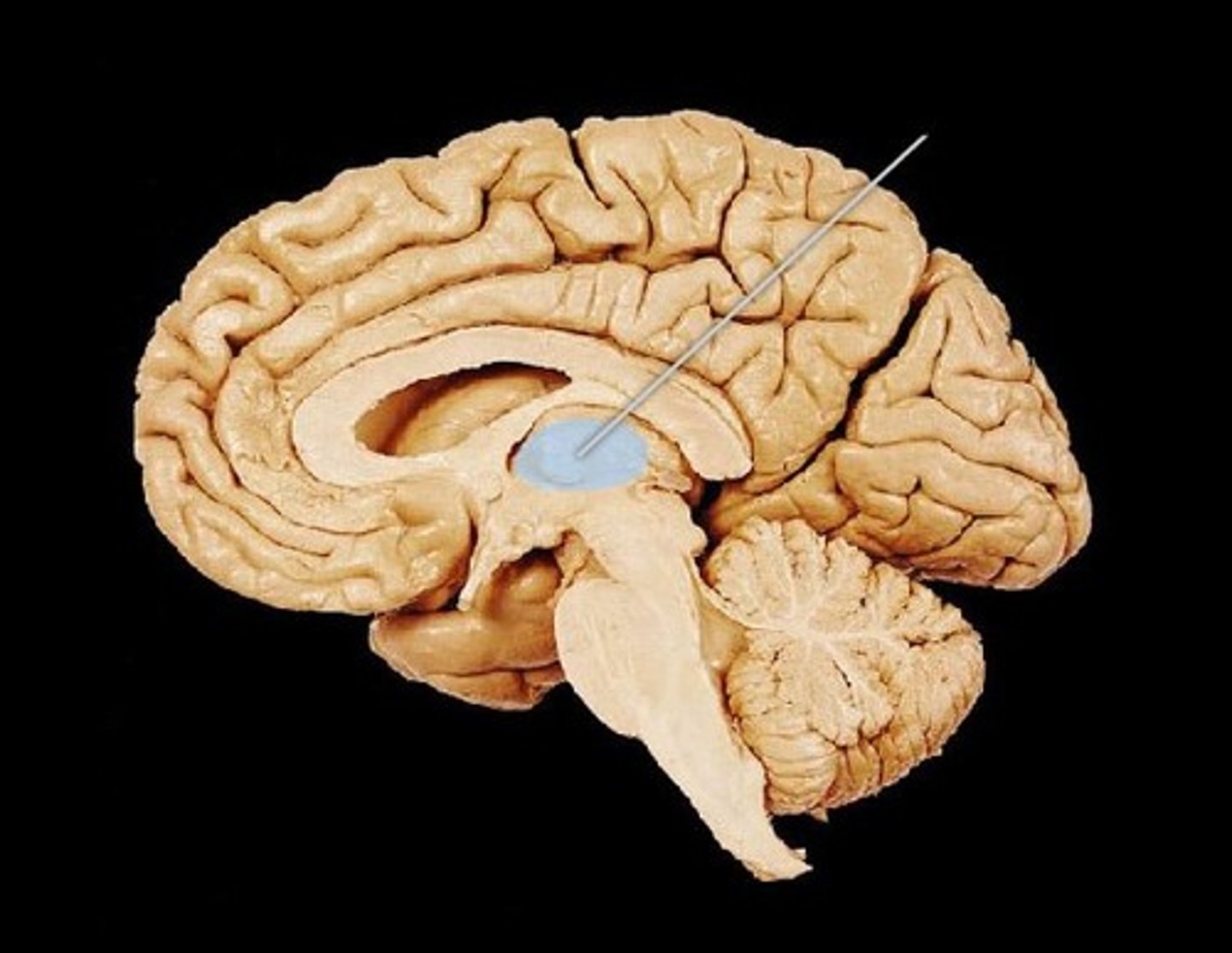
Thalamus
The brain's sensory switchboard for all senses but smell, located on top of the brainstem
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs basic human activities: sleep-rest, body temperature and physical drives (hunger, sex); with pituitary gland controls most hormone function
Amygdala
A limbic system structure which is the emotional component to the brain attached to memory; aggression, impulse control
Limbic Midbrain Nuclei
Pleasure center or reward center, chemically reinforces certain behaviors; plays role in biologic basis of addiction
Pineal Gland
Secretes melatonin (sleep) and immune systems responses
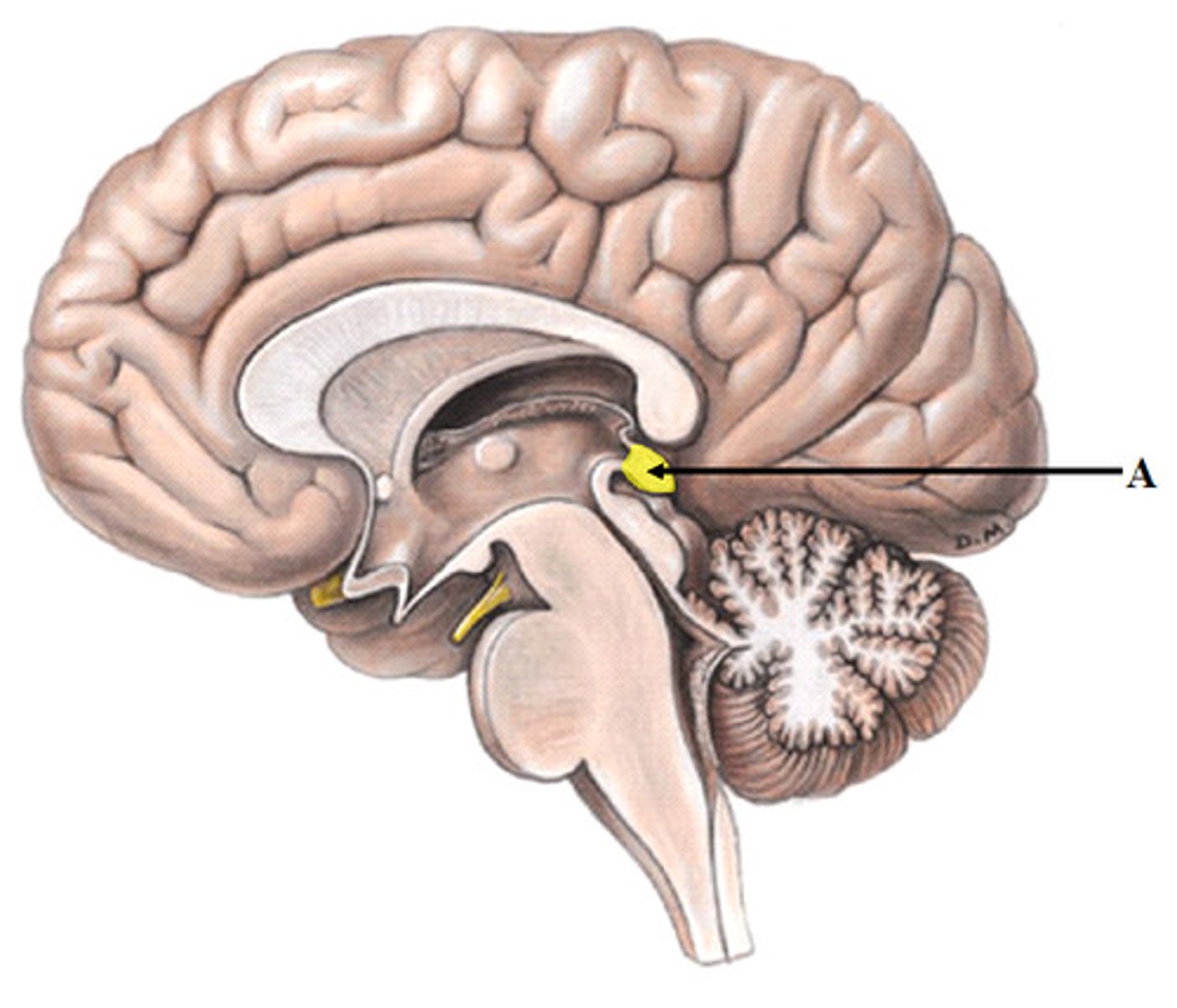
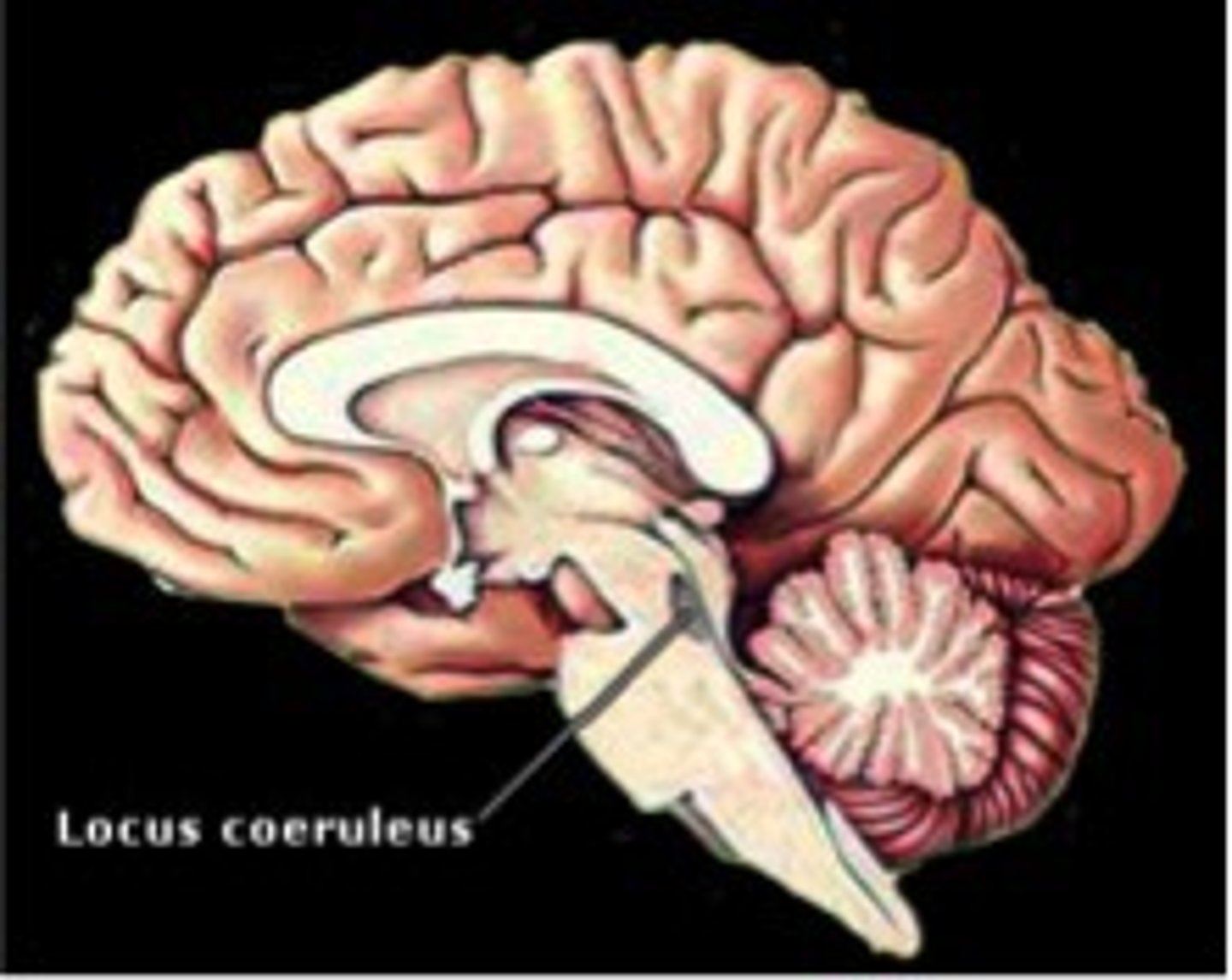
Locus Coeruleus
Area of the brainstem that pertains to attention, focus, arousal (excitement), learning
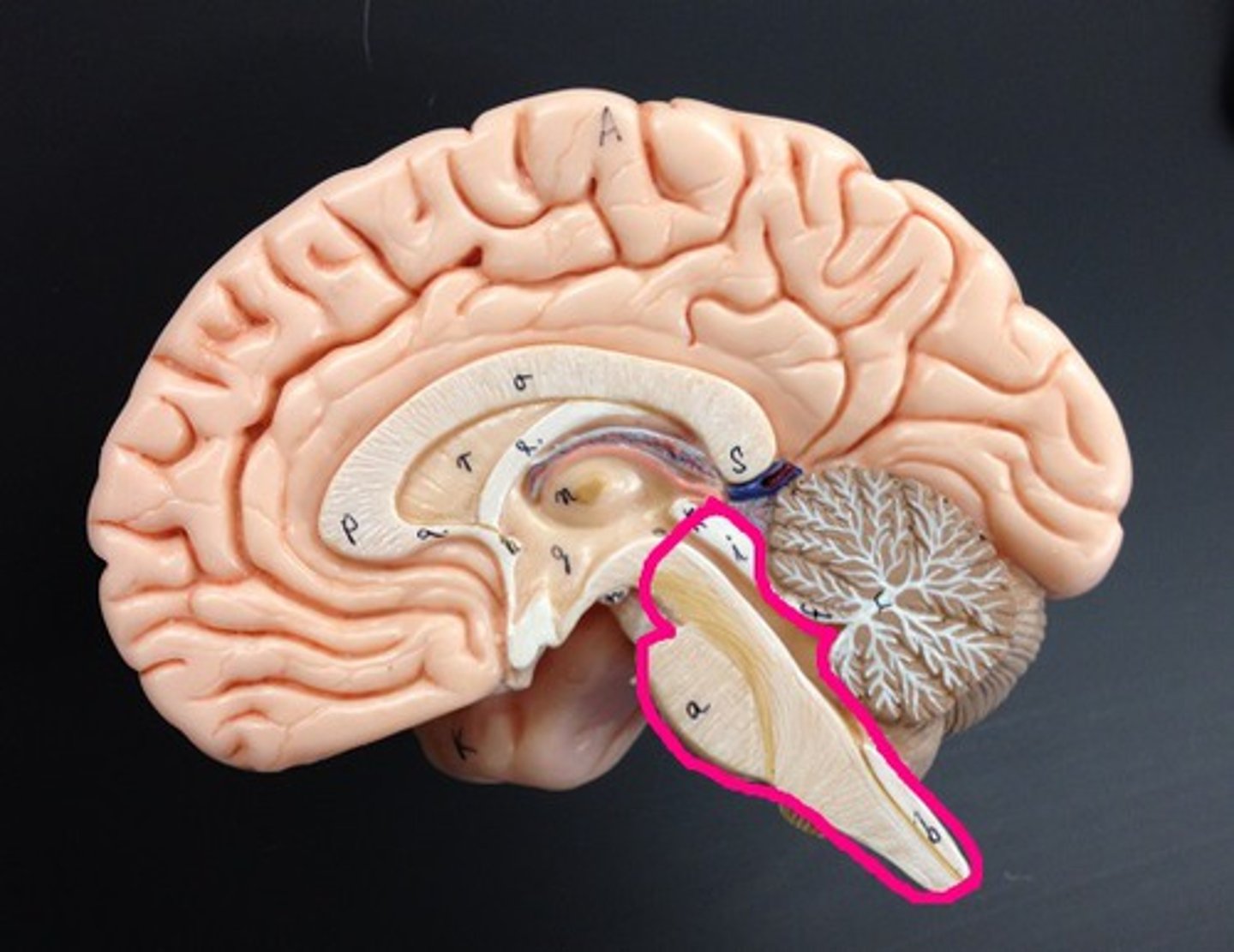
Brain Stem
Responsible for life-sustaining functions
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
A set of nerves that carries involuntary and automatic commands that control blood vessels, body organs, and glands
Parasympathetic and Sympathetic
Parasympathetic vs Sympathetic
Parasympathetic (Rest and digest)
Sympathetic (Fight or flight)
Neuroplasticity
The ability within the brain to constantly change both the structure and function of many cells in response to experience or trauma
Neurotransmitters
Small molecules that directly and indirectly control the opening or closingof ion channels
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Enables muscle action, learning, and memory.
In Alzheimer's disease, ACh-producing neurons deteriorate
Dopamine
Influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
Oversupply linked to schizophrenia
Undersupply linked to tremors and decreases mvmt in Parkinson's
When you hear schizophrenia, think what neurotransmitter?
Dopamine (Too much)
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
Undersupply linked to depression
Some antidepressants increase serotonin levels
Norepinephrine
Helps control alertness and arousal
Undersupply can depress mood
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter
Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia
Glutamate
A major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved in memory
Oversupply can overstimulate the brain (Migraines/seizures)
Immunology Implications for Psychiatric Illness
Decreased immunity has been associated with grief, bereavement, and depression
Immunological abnormalities have also been associated with alcoholism, autism, and dementia
Mental Health
Emotional and psychological balance in the pursuit of wellness and a meaningful quality of life
What is mental wellness
Purposeful process of individual growth
Integration of experience
Meaningful connection with others, reflecting personally valued goals and strengths that results in being well and living values
Factors that can affect Mental Wellbeing
Poverty, unemployment, underemployment
Trauma
ACEs (Adverse Childhood Experiences)
Lack of education
Stressor
A biological, psychological, social, or chemical factor that causes physical or emotional tension
Psychological adaptation to stress is explained in what two terms?
Anxiety: Associated with feelings of uncertainty and helplessness
Grief: Subjective state of emotional, physical, and social responses to the loss of a valued entity
Adaptive Responses to Stress
Behavior that maintains the integrity of the individual
Viewed as positive and is correlated with a healthy response
Maladaptive Responses to Stress
When behavior disrupts the integrity of the individual
Considered to be negative or unhealthy
Mental Disorders
Health conditions characterized by alterations in thinking, mood, or behavior associated with distress and/or impaired functioning
A mental illness or mental disorder is a syndrome, what is a syndrome?
A set of symptoms that cluster together that may have multiple causes and may represent several different disease states
Public Stigma of Mental Illness
Stereotypes leading to prejudice and discrimination
"Dangerous, unpredictable, unable to function independently, weak."
Recovery from Mental Illness
A process of change through which individuals improve their health and wellness, live a self-directed life, and strive to reach their full potential
Continuum of Care for Mental Illness
Consists of an integrated system of settings, services, healthcare clinicians, and care levels, spanning illness-to-wellness states
Primary goal is to provide treatment that supports recovery in the LEAST RESTRICTIVE ENVIRONMENT