Microbio Exam 2
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
mutualism
both organisms benefit
Which of the following substrates is an electron donor in organotrophy?
NADH
Litho-auto-trophy is a term describing microorganisms that
use inorganic minerals as electron donors to electron transport systems, and use CO2 as their carbon source.
The following are cellular processes that can be directly powered by the proton motive force (Δ p), EXCEPT
protein biosynthesis.
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
- EMP pathway—2 ATP, 2 NADH
- TCA cycle from 1 acetyl-CoA — 2 CO2, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 ATP
- Ethanolic fermentation from 2 pyruvate — 1 lactate, 1 ethanol, 1 CO2
- ED pathway—1 ATP, 1 NADH, and 1 NADPH
Ethanolic fermentation from 2 pyruvate — 1 lactate, 1 ethanol, 1 CO2
Some intestinal bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, feed on ________ from mucus secretions using the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
gluconate
Which of these pathways provides molecules for biosynthesis (e.g. ribose sugar for nucleotde biosynthesis)?
pentose phosphate shunt
Cyanobacteria and green plants have ________-based photosynthesis and their metabolism produce ________.
H2O; O2
Which of the reactions is a reduction reaction? Remember, follow the electrons.
pyruvate + 2H+ + 2e- → lactate
Electron transport systems are embedded in all of the following membrane systems EXCEPT
the eukaryotic plasma membrane.
Enzymes receiving electrons from electron donors at the start of the ETS are referred to as ________, whereas enzymes transferring electrons to the terminal electron acceptor are designated as ________.
dehydrogenases; oxidases
Which of the following is a product of microbial fermentation?
ethanol
Which of the following statements is FALSE with respect to heterotrophic organisms?
They use inorganic CO2 as their C source.
Denitrifiers are bacteria that are capable of using nitrate as their electron acceptor at the end of the ETS. They use organic electron donors to start their ETS. What kind of metabolism do denitrifiers do?
Anaerobic respiration
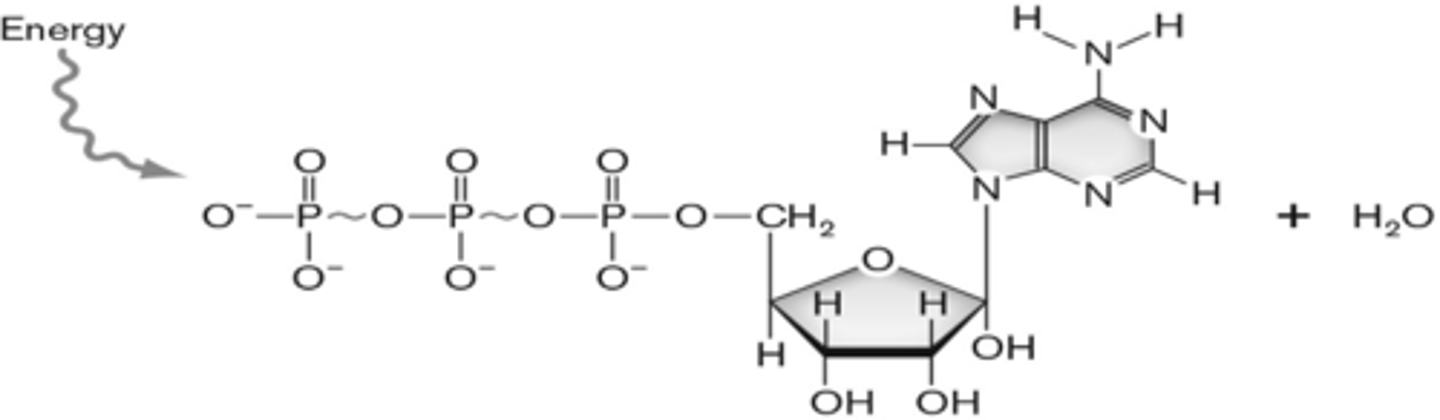
The molecule shown below carries energy in the cell in its high energy bonds shown as squiggles. It is a(n) ________ molecule.
ATP
The figure below shows a very common electron carrier that is involved in oxidation/reduction reactions in the cell. Which form (A or B) would be needed for an electron transfer reaction where the substrate will be losing electrons? In this case, after the completion of the reaction where the substrate has donated those electrons to the correct form of the electron carrier, what has happened to the substrate?
A; oxidized
Because the electron transport proteins are oxidizing one molecule and reducing the next, they are called ______.
oxidoreductases
The enzyme pyruvate kinase is part of the EMP pathway. It catalyzes the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate. During this reaction a phosphate group is transferred to ADP to make ATP. This reaction is an example of
substrate-level phosphorylation
Which of these DOES NOT pump protons during the operation of the ETS?
Mobile electron carrier (quinone)
The energy yield from fermentation is lower than from respiration because
respiration completely oxidizes glucose to CO2, resulting in greater generation of NADH and thus ATP.
Which of these are examples of lithotrophs?
Nitrifiers
Pyruvate
electron acceptor in fermentation
H2O
electron donor in photosynthesis
H2
electron donor in lithotrophy
Sulfate
electron acceptor in anaerobic respiration
All of the following are characteristics of eukaryotic organisms EXCEPT that
all types of eukaryotic cells are surrounded by a cell wall.
A trait that differentiates all Firmicutes from Actinobacteria is
GC content.
In theory, the largest reservoir for carbon is
Carbonate Rock in Earth's crust
The Haloarchaea, extreme ________, are the only form of life to grow in concentrated brine.
halophiles
Bacteria in the genera ________ produce durable endospores that remain viable for millennia.
Bacillus and Clostridium
The algal and fungal interaction within a lichen are best described as
mutualism
The following are ecological roles of fungi in nature EXCEPT
nitrogen fixation in legume nodules.
The relationship among endosymbiotic microbes in the termite gut that results in cooperation between members for the completion of their individual metabolic pathways is called
syntrophy
Thousands of species of microbes in the cow ________ ferment and break down plant material to small particles.
rumen
Which of the following is NOT a trait common to all cells on Earth?
lithotrophy and N2 fixation
Based on small subunit rRNA phylogeny studies, the current view is that there are ________ domains of life.
three
Which of the following are most likely to be found in the upper 200 m of the open ocean?
phototrophs
Which of the following major biological elements has the highest number of oxidation states?
nitrogen
symbiosis
A close relationship between two unrelated species
clade
A group of species that share a common ancestor
ED Pathway
1 ATP, 1 NADH, 1 NADPH
Fermentation- E acceptor, -e donor, complexity, efficiency,
acceptor- pyruvate
donor- nadh
complexity- simple
efficiency - low
Respiration- E acceptor, -e donor, complexity, efficiency,
acceptor- O2 (aerobic)
donor- NADH/FADH2
complexity- complex
efficiency - high
O2
electron acceptor in aerobic respiration
Synechococcus, a cyanobacterium, is a free-living marine organism that fixes CO2 into biomass while producing molecular oxygen via oxygenic photosynthesis. Which of the following is the most likely habitat of this bacterium?
the euphotic zone of the pelagic environment
The sink of an element in the ecosystem
is the reservoir to which it returns during cycling.
The process of ________ occurs only in the archaea.
methanogenesis
The loss of genes encoding unselected traits is known as
reductive evolution.
Microbes participate in which step of wastewater treatment?
secondary
Algal blooms in eutrophic lakes ultimately increases the level of ________ conditions in the water column.
anoxic
Microbes of the gut microbiome are most likely members of the ______ class of Proteobacteria
Gamma
Most forest trees require mycorrhizae for growth because
mycorrhizae significantly increase the uptake of nutrients.
Which of the following are the main decomposers in the ocean?
viruses
Which of the following is NOT a reduced form of carbon in the carbon cycle?
carbon dioxide
Which of the following decreases the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
photosynthesis
Wastewater treatment generates which of the following gases in quantities sufficient for recovery as fuel?
methane
catabolism
complex substrate into simpler molecules. ex: atp
anabolism
building simpler molecules into complex substrates
Endosymbiosis
one lives inside the body of another
assimilation
building organic molecules from inorganic one = CO2 fixation, N2 fix, photosynthesis
done by primary producer
dissimilation
process of breaking down organic nutrients to inorganic minerals= respiration, fermentation
consumers, decomposers
reservoir
part of biosphere with a significant amount of an element = atmosphere, land, ocean
what are the two heterotrophic pathways for glucose fermentation?
EMP & ED
EMP Pathway
2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH
what are the pathways for regeneration/recycling of electron carriers?
fermentation and respiration
fermentation final products
homolactic: lactic (3C)
heterolactic: lactic+ ethanol (2C)+ CO2
ethanol: ethanol +CO2
mixed acid
respiration final products
6CO2 + H2O
respiration steps:
1. PDC: 2acetyl + CoA + 2CO2 + 2NADH
2. TCA: 4CO2 + 6NADH + 2FADH2
3. ETS