Patho Exam 4
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Neuro Digestive Hematology Musculoskeletal Endocrine & Hormonal
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Papilledema (edema of the ____ ____) is ____ of the optic disc due to increased ____ ____.
optic nerve, swelling, intracranial pressure
The swelling of papilledema is a reaction to a buildup of ____ or ____ in or around the ____.
pressure, fluid, brain
The ____ ____ (optic nerve head) is the location where ____ ____ ____ exit the eye to form the optic ____.
optic disc, ganglion cell axons, nerve
The _____ is the pigmented part of the retina located in the very center of the _____.
macula, retina
In the center of the macula is the _____.
fovea
The ____ is the area that allows for the sharpest visual acuity. It contains a large amount of ____; nerve cells that are photoreceptors with high acuity.
fovea, cones
Sensorineural hearing loss means there is a problem occurring in either _____ _____ or the _____ _____, which delivers sound to the brain.
inner ear, auditory nerve
Conductive hearing loss is usually due to an _____ or _____.
Assessment is with the _____- _____ test.
obstruction, trauma
Weber- Rinne
_____ conduction is greater with conductive hearing loss.
bone
_____ conduction is greater than ____ conduction.
air, bone
Increased cranial pressure is caused by an increase in _____ _____, _____ _____, excessive _____, or _____.
intracranial content, cerebral edema, CSF, hemorrhage
Pulse pressure = ____-____.
Normal is between __-__.
>60 is risk factor for _____ _____.
systolic pressure - diastolic pressure
40-60mmHg
cardiac disease
_____ injuries are brain contusions occurring at the point of _____.
coup, impact
_____ injuries result when the brain impacts the side the skull _____ the point of impact.
countercoup, opposite
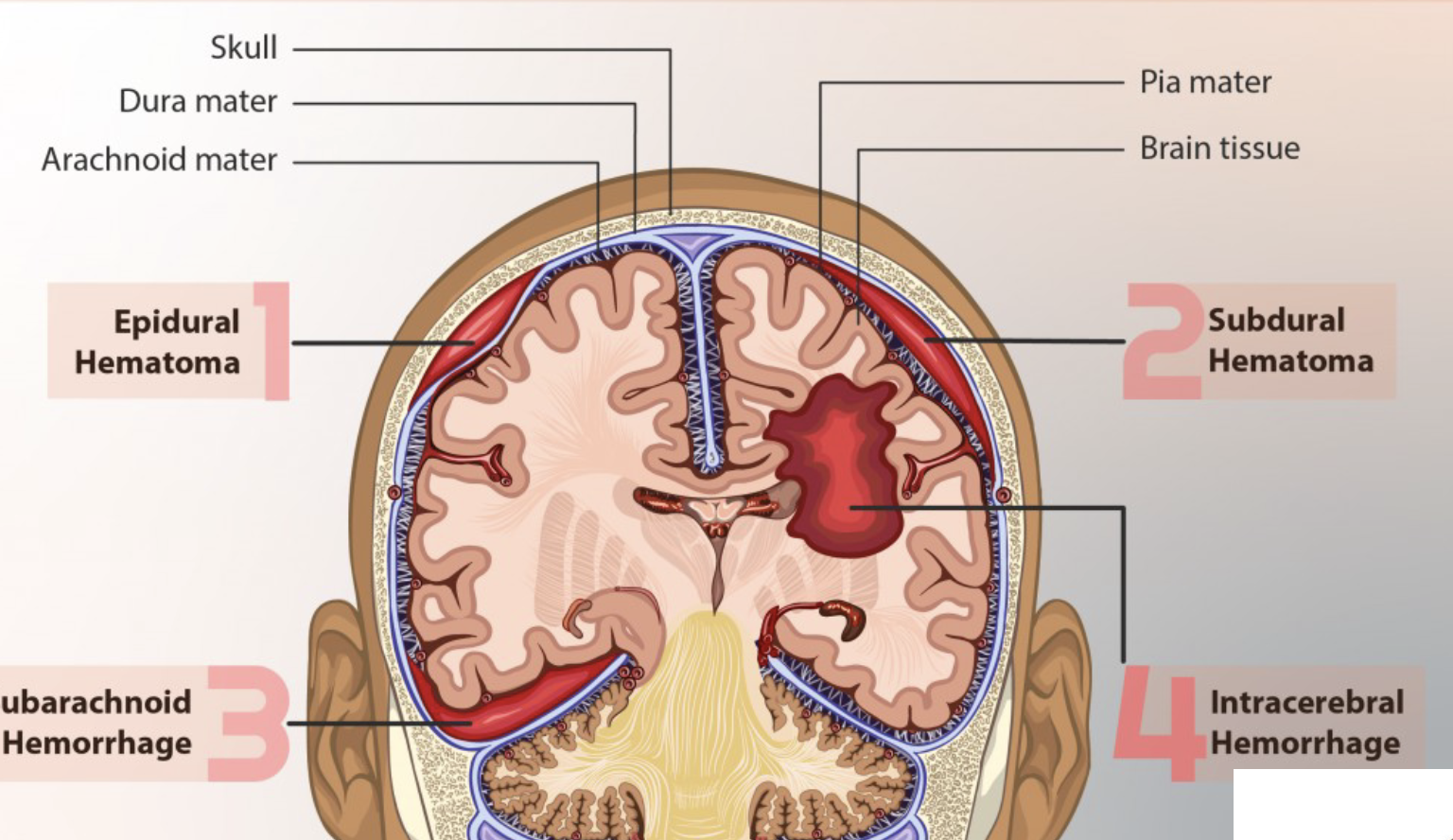
A(n) _____ hematoma is bleeding between the dura mater and the skull.
epidural
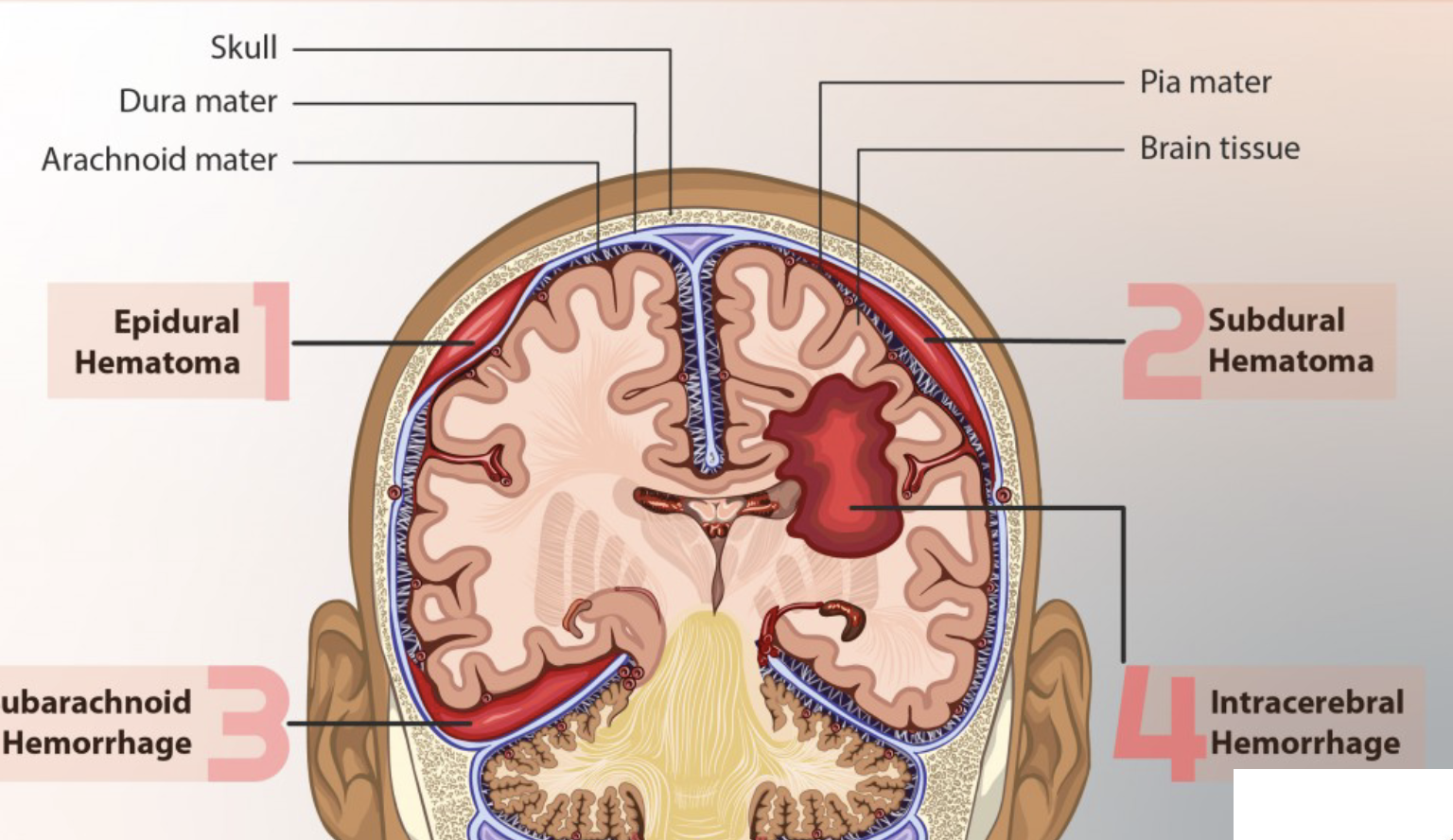
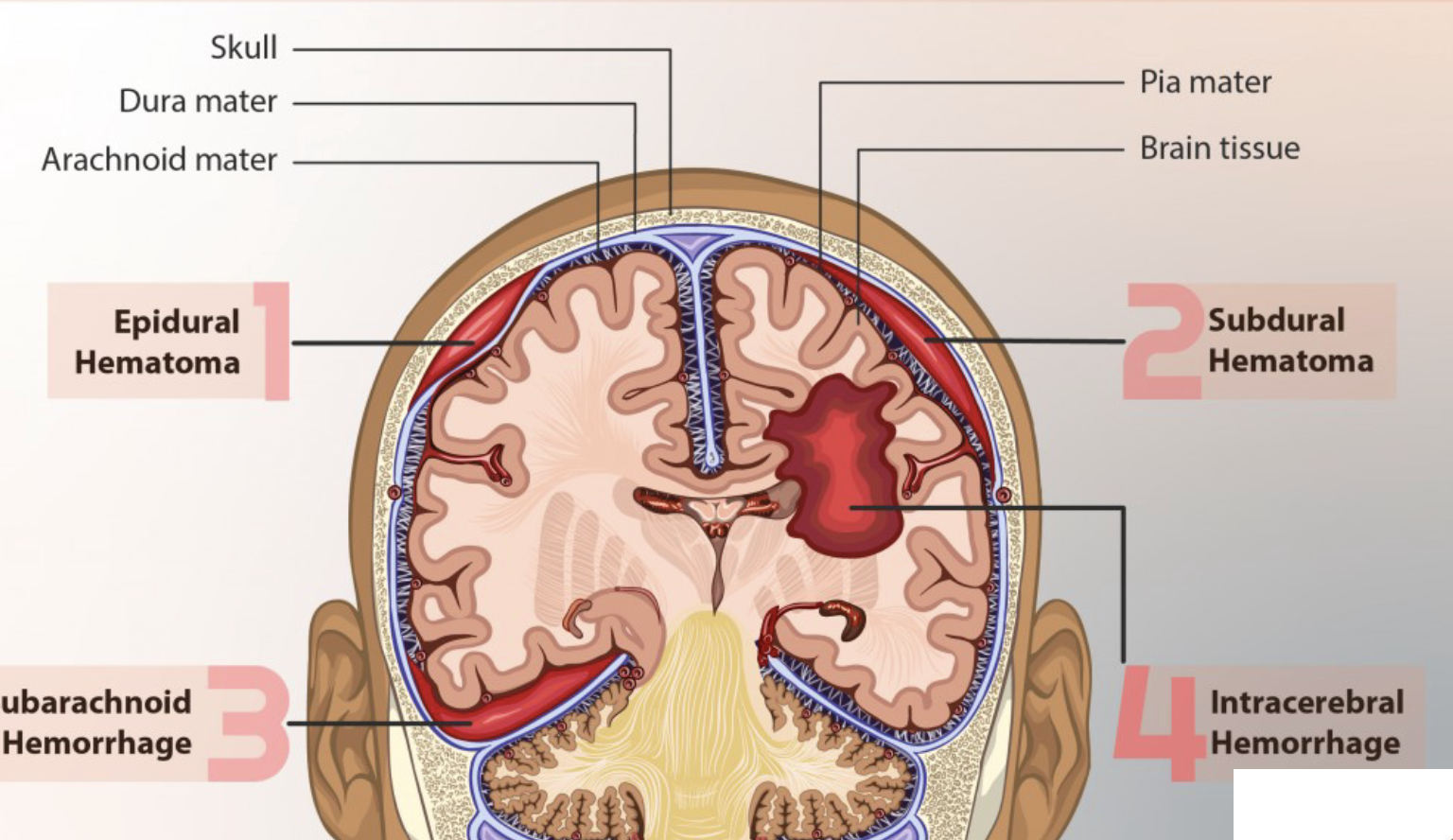
A subdural hematoma is bleeding between the _____ _____ and _____ _____ covering the brain is caused by tearing of _____.
dura mater, subarachnoid membrane, veins
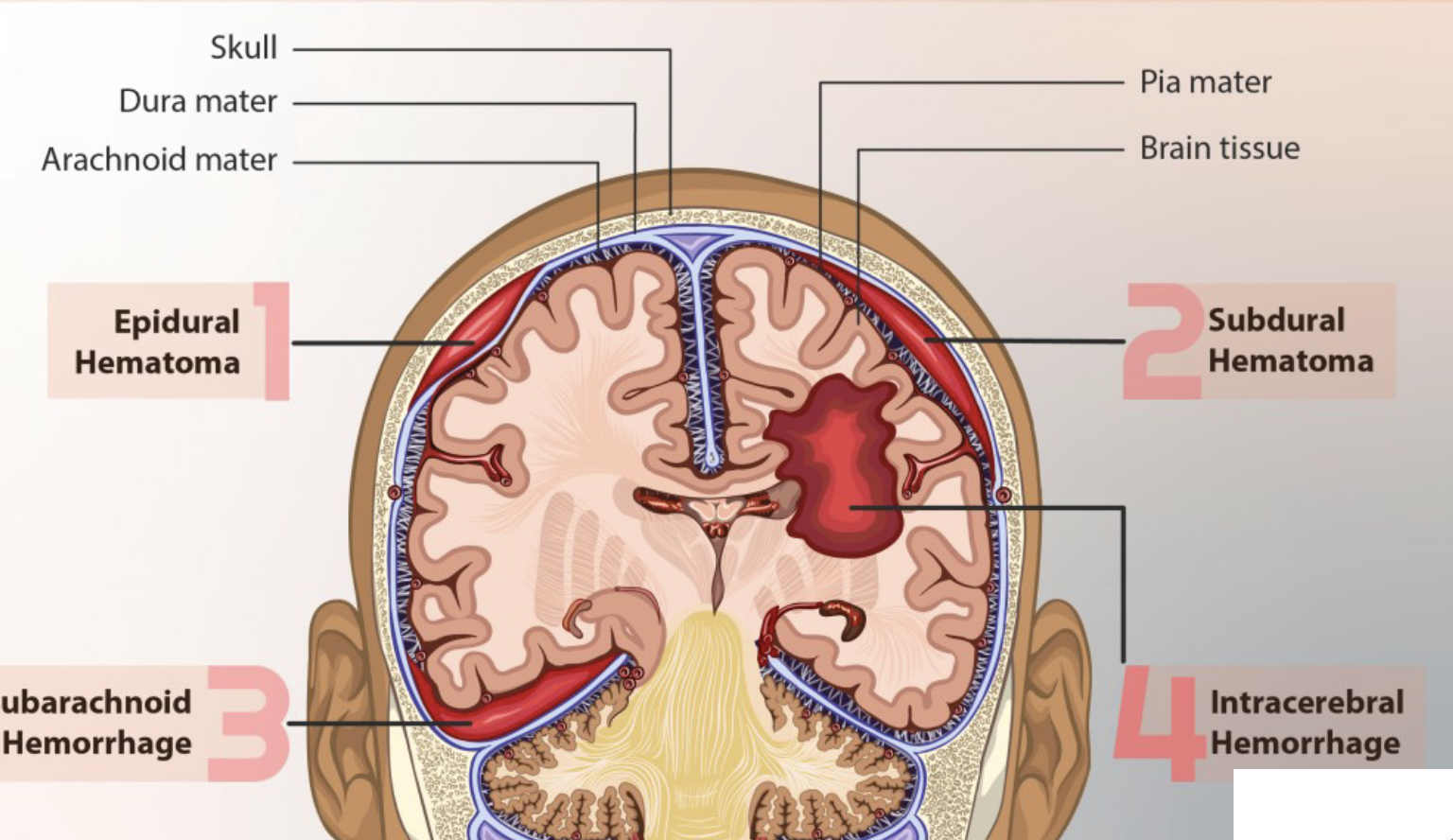
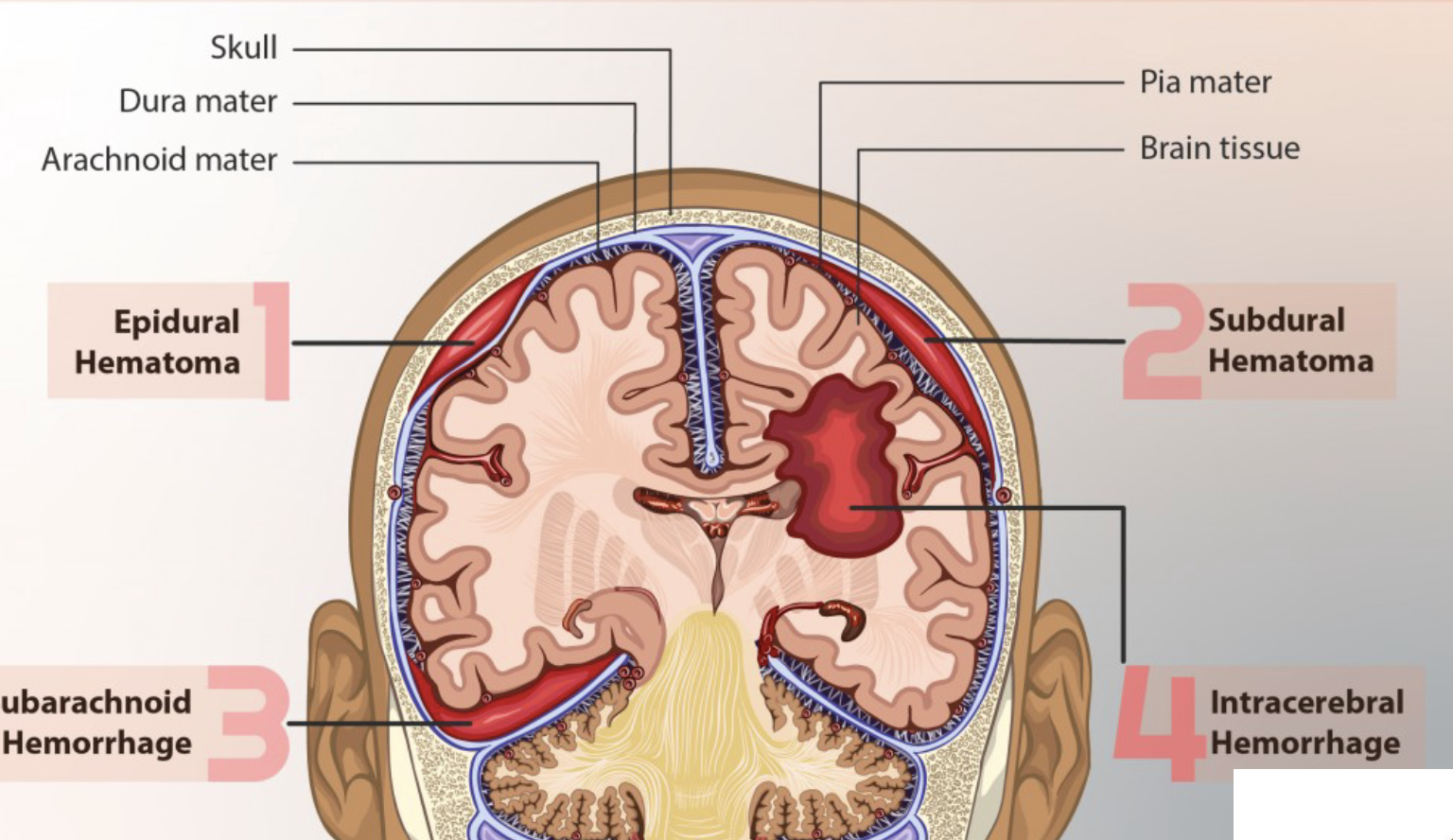
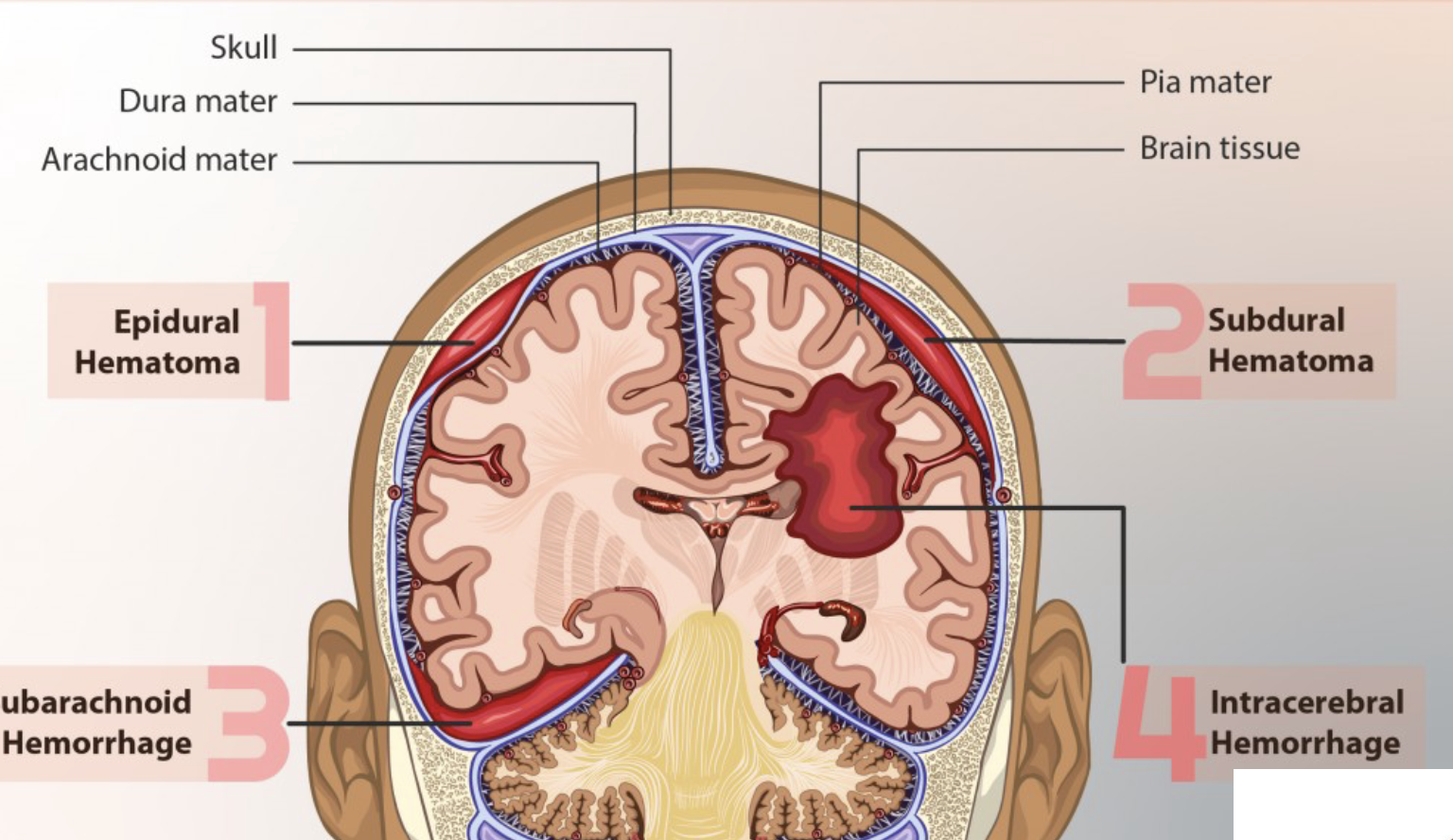
_____ hematomas (bleeding within the brain) are most commonly located in the _____ and _____ lobes, but may occur in the hemispheric deep white matter.
intracerebal, frontal, temporal
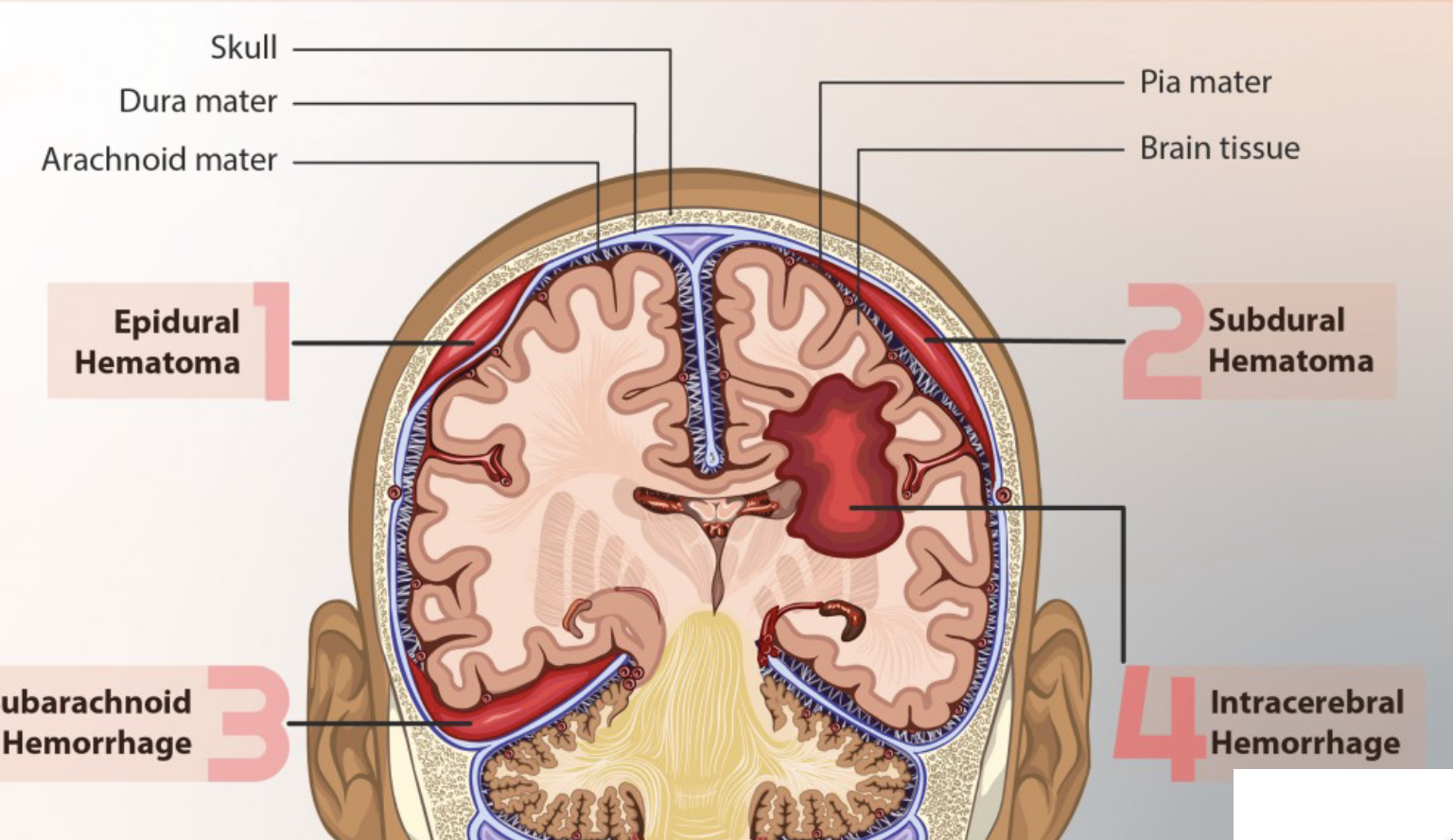
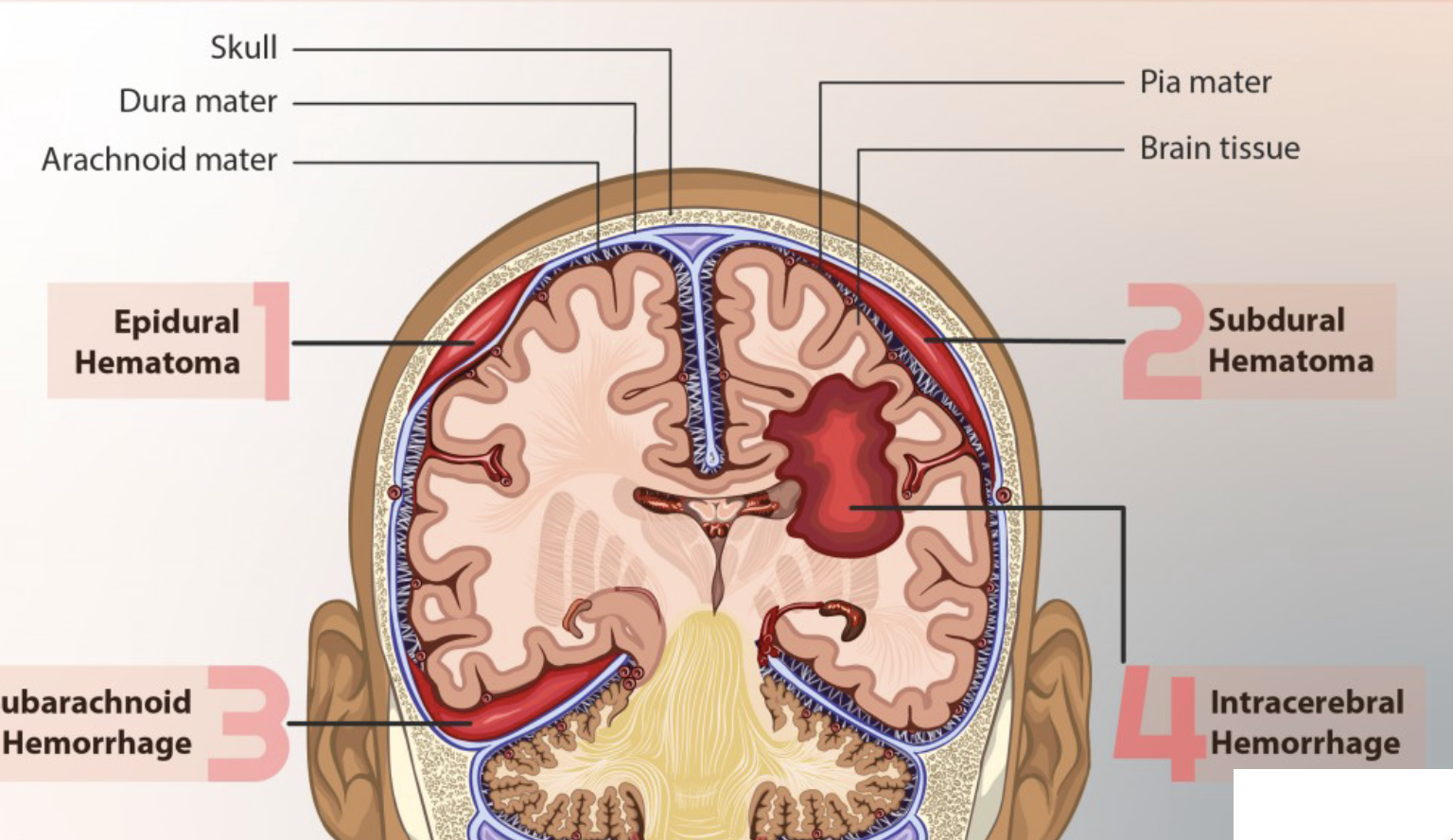
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (hematoma) is associated with _____ _____, _____ malformations or _____ _____.
ruptured aneurysms, arteriovenous, brain trauma
Neurogenic shock occurs with injury above __.
T6
_____ _____ (_____) is a sudden, massive reflex sympathetic discharge because descending inhibition is blocked.
Stimulation of the _____ _____ below the level of the cord lesion.
autonomic hyperreflexia (dysreflexia)
sensory receptors
Autonomic hyper/dysreflexia is caused by _____ _____, _____ _____, and _____.
urinary retention, bladder distention, constipation
Signs and symptoms of autonomic hyper/dysreflexia are BP __-__mmHg above normal, _____, _____ _____, _____ skin, _____ chest and _____ nose, and _____ vision.
20-30, sweating, pounding headache, flushed, tight, stuffy, blurred
With chronic progressive immune mediated inflammatory disease; _____ _____ (MS), the immune system attacks the protective sheath (_____) that covers nerve fibers, and causes _____ problems between the brain and the rest of the body.
multiple sclerosis, myelin, communication
MS can cause _____, _____, impaired _____, _____ disturbances, or _____ incontinence.
paresthesia, weakness, gait, visual, urinary
_____ _____ is a chronic autoimmune, neuromuscular disease that causes weakness in the skeletal muscles that worsens after periods of _____ and improves after periods of _____.
myasthenia gravis, activity, rest
In myasthenia gravis, _____ block, alter, or destroy the receptor for _____ at the neuromuscular junction, which prevents the _____ from _____.
antibodies, acetylcholine, muscles, contracting
With myasthenia gravis, an ____ antibody is produced against ______ receptors.
IgG, acetylcholine
With a Greenstick bone fracture, the _____ is _____ and the _____ bone is _____.
cortex, perforated, spongy, splintered
____ regulates aldosterone secretions.
RAAS
Patients should consume _____ for thyroid hormone synthesis.
iodine
Posterior pituitary secretes _____ and _____.
ADH, oxytocin
An example of a direct effect of hormone release (obvious change in cell function) is _____ binding to _____ _____, increasing _____ uptake by the _____ cell.
insulin, muscle receptors, glucose, muscle
Hormones have specific _____ and _____ feedback mechanisms, most levels are regulated by _____ feedback.
negative, positive, negative
_____ _____ hormones _____ freely across the plasma and nuclear membranes.
lipid soluble, diffuse
_____ _____ hormones cannot diffuse across plasma membrane.
water soluble
_____ stimulates contractions during birth.
oxytocin
Manifestations of prolactinoma (hypersecretion of prolactin) in females are _____, _____, _____ (milky nipple discharge unrelated to normal milk production), _____, excessive _____ and _____.
Suspect a pituitary _____.
amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, galactorrhea, hirsutism, excitability, osteopenia
adenoma
The manifestations of prolactinoma in males are _____, _____, and _____ dysfunction.
gynecomastia, hypogonadism, erectile
Clinical manifestations of ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ (SIADH- hypersecretion of ADH) are related to ____ and are determined by severity.
syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion, hyponatremia
Neurogenic form of diabetes insipidus is an inadequate response to ____.
Side effect of some ____ agents.
ADH
anesthetic
Graves disease is an autoimmune disease, _____ condition caused by stimulation of the _____ by _____ against _____ receptor.
hyperthyroid, thyroid, antibodies, TSH
Type __ diabetes mellitus is the most common _____ chronic disease and is immunologically mediated _____ cell destruction and _____ (immune destruction of the _____).
I, pediatric, beta, apoptosis, pancreas
_____ is reduced oxygen- carrying capacity, and is a physiologic symptom of _____.
hypoxemia, anemia
_____ (neutrophilia) is an increase in granulocytes.
granulocytosis
The most common cause of infectious mononucleosis is ___.
Recovery time is ____ ____.
EBV: Epstein- Barr virus
a few weeks
Physical findings of Hodgkins lymphoma are enlarged painless ____ ____ in ____, ____ mass, and ____.
lymph node, neck, mediastinal, splenomegaly
Symptoms of Hodgkins lymphoma are ____, unintentional _____ _____, regular ____ ____, and ____ (itching).
fever, weight loss, night sweats, pruritis
______ is an error in lab test giving a false reading for thrombocytopenia (platelet count <____)
pseudothromocytopenia, 150,000/mm3
____ is a ligament tear.
sprain
____ tear is called is strain.
tendon
General anesthesia causes ____ ____ ____.
nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
_____ _____ tests for long term diabetes control.
hemoglobin A1C
____ ____ ____ causes immune destruction of the pancreas.
type I diabetes
____ is characterized by uric acid levels.
gout
Functions of the GI tract; ____ and ____ breakdown of food, ____ of digested food, and secretion of ____.
mechanical, chemical, absorption, mucous
____ is vomiting blood.
hematemesis
____ (reflux) is regurgitation of ____ from the stomach into the esophagus d/t loss of ____ ____ at the lower ____ sphincter.
GERD, chyme, muscle tone, esophageal
Clinical manifestations of GERD are ____, chronic ____, ____, and ____ regurgitation.
heartburn, cough, dysphagia, acid
NSAIDs (ex. ibuprofen) and H. pylori cause ____ ____.
duodenal ulcers
Symptoms of ulcerative colitis are ____ (10-20x/day), ____, ____ stools, and ____.
The patient will be very ____ and lacking ____.
diarrhea, urgency, bloody, cramping
dehydrated, nutrients
Patients of Crohn’s disease present ____.
malnourished
Appendicitis causes ____ or ____ pain, rebound tenderness to ____, and ____ ____ fever.
epigastric, periumbilical, RLQ, low grade
Hepatitis B and D have an incubation period of up to ___ days.
_____ (cholelithiasis) have a high concentration of _____.
gallstones, cholesterol
_____ pain is pain originating in organs.
visceral
Food moves down the esophagus by ____.
peristalsis
___ is found in normal saliva.
IgA
Multiple myeloma pain is d/t destruction of ____ ____/ ____.
bone marrow/ tissue
Saliva contains ____ ____ (ptyalin) which initiates ____ digestion.
salivary amylase, carbohydrate