phospholipid membranes
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
biology ocr
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
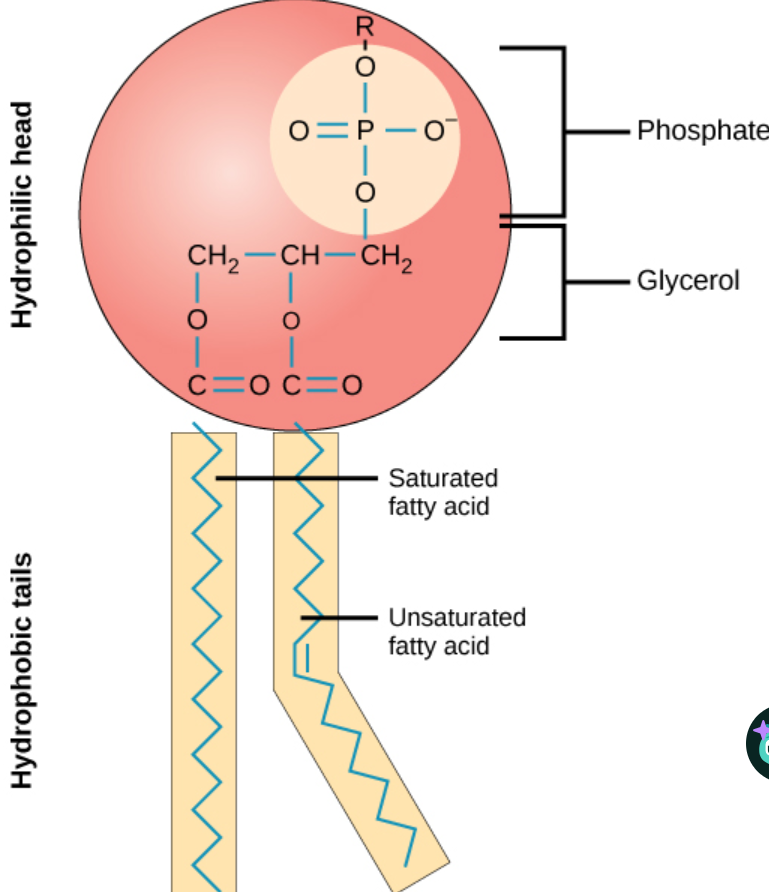
what is the structure of a phospholipid
Made up of a phosphate group, glycerol unit and two fatty acid tails
Formation of a membrane
Negatively charged (polar) phosphate head is hydrophilic
The fatty acid tails are non-polar, they are hydrophobic
If phospholipids are completely surrounded by water they form a phospholipid bilayer
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid: phospholipid bilayer in which individual phospholipids can move so membrane is flexible. proteins can move freely through the bilayer.
Mosaic: Extrinsic and intrinsic proteins are randomly arranged
Movement of fat soluble molecules and polar molecules through bilayer
Fat soluble organic molecules:
diffuse through the bilayer
Polar molecules:
require proteins
why can’t ions enter the cells
phospholipid bilayer acts as a barrier
Two types of proteins in bilayer
intrinsic proteins
extrinsic proteins
Intrinsic proteins
completely span phospholipid bilayer
main transport system
can form channels, carrier proteins or active pumps
Extrinsic proteins
on surface of bilayer or partially embedded in it
provide mechanical support
act as cell receptors
Types of intrinsic proteins
Channel proteins
Carrier proteins
Channel proteins
Pores in the membrane that let ions diffuse through
Carrier proteins
Change shape to let specific molecules through
Glycoproteins
Protein with a carbohydrate molecule attached
can allows cells to attach to each other (cell adhesion)
acts as receptors for hormones and neurotransmitters
cell signalling
act as antigens
recognition of cells
Glycolipids
Carbohydrates attached to phospholipid molecules
act as cell markers or antigens
cell signalling
cell recognition
cell adhesion
Purpose of cholesterol in cell membranes
Stabilises the membrane
regulates its fluidity
Prevent phospholipids from packaging too closely together and connects them
how do proteins move through lipid bilayer
-proteins move freely but this ease is dependent on the number of phospholipids with unsaturated fatty acids in the bilayer
what is the 3 roles of a membrane in a cell
partially permeable barriers between the cell and its environment, between organelles and the cytoplasm and within organelles- act as barrier
compartmentalisation
sites of cell communication (cell signalling)
controls what enters and leaves
creates concentration gradients