Nursing Care of the Hospitalized Child
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is the age of an infant
●Infant (0-1 years)
infant- dependent care- rely on someone else
What is the age of a toddler
(1-3 years)
toddler- want independence at that age, have seperation anxiety , think that procedures are punishment, might be fearful, can demonstarte a teddy bear to show what you do
What is the age of a preschooler
(3-5 years)
Preschoo- think procedures punishment. Demonstarte. fear of mutlilation with body- fear of worst case sceneraio- magical thinking. fear unkown. May see regression - ex. potty trained byt in hospital peeing self. normal if under stressful situation
What is the school age
●(5-12 years)
schol age- fear pain and procedures. want to be around children their own age, dont want to feel diff with ilness, explain everything, show and demonstrate w equippent
What is the adolescent age
●(13-18 years)
teen- orivacy, appearance, peers are important. school age- teenage- let them pick/ include them in care. go thrpigh phases where they feel the only control they have is saying no.
What are Stressors of Hospitalization
Separation Anxiety
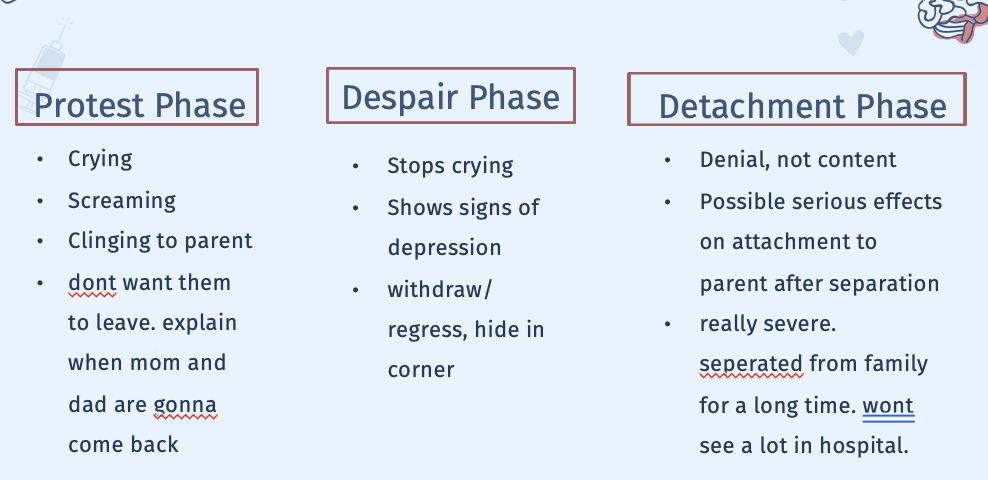
What are the Effects of Hospitalization
●Before admission, hospitalization, or after discharge
●Child’s concept of illness more important than intellectual maturity in predicting anxiety
●May be affected by previous
●Individual Risk Factors harder time in hospital:
○“difficult” temperament
○Age, especially 6 months- 5 years
○Males
○Below average intelligence
○Frequent hospitalizations. Could be benefit or negative
What are the good and bad outcomes of a kid being in the hospital
Beneficial Outcomes
○Recover from illness
○Competence in coping ability
○Master stress
○New socialization when they can see other kids
Adverse Outcomes
Typically children under 7
○Regression
○Separation anxiety
○Apathy- Apathy is a state of emotional indifference and lack of interest or motivatio
○Fears
○Sleeping disturbances - try to mimick routine as much as we can.
What are the parent and sibiling rx
Parent Reactions
○Feel Helpless
○Question staff and skills
○Accept reality of hospitalization
○Dealing with fear and uncertainty- take out their fear and anger out on you
○Want reassurance- educate and include kid in their own care , provide resources
Siblings Reactions
○Many changes, may not understand
○Cared for by others- other family members
○Receiving too little info about sibling tend to think worst case scenario- want the truth
○May think treated differently- like put on back burner
How do we prepare a child for admission and what assessment do we do
●ADL’s
●Medications
●Physical Assessment-
●Ask open ended questions - can you tell me about their day, what time take med – want to try to mimick routine
●*** provide support, and resources
Prepare child for admission
●Decreases negative feelings & fear
●Prehospital counseling- or tour the facility
●Room assignments- shared rooms
What interventions do we do
●Prevent & minimize separation- can help w anxiety. Set up facetime, pictures, leave familiar item, toys
●Minimize loss of control- give them choices to have freedom.
●Prevent & minimize fear of injury
●Provide developmentally appropriate activities- school work can help if in school age. May have low energy- simple non-complex- puzzle, reading book, educational
●Provide opportunities for play
●Child Life Specialists- great resource. Help explain and describe procedures. Can throw bean bags or mash if angry. ART in the form of aggressive play to express how they feel in a safe manner
●Prepare for procedures- let kids perform surgery on teddy bears
●Perform procedures safely but quickly and may need help
Praise and encourgage them
How do we care for the family
●Support Family Members- cultural differences, status can effect how families perceive care
●Provide accurate and honest information
●Encourage parent participation- education may start day 1.
●Prepare for discharge & home care- what to expect . Ex. Bulding a ramp for wheelchair
○Follow up care
○Begin discharge teaching early
Incorporate their learning level- ex. If they can’t read do pictures
WHat are the Potential Benefits of Hospital
●Fosters parent-child relationship- helps parent see they are capable, helps kid becoming more competent on how they care for themselves
●Provides educational opportunities
●Promotes self-mastery
○Stress, coping successfully, maturing
●Provides socialization- ex. Prom nights, parents get to talk to each other
What are Special Hospital Situations
●Ambulatory- out pt. ex. Day surgery- educate and teach. Quick procedures or Outpatient Clinic
●Isolation- PPE, explain when you walk in w gown, do they have family visiting
●Emergency Admission- most traumatic. Little time for preparation, prepare child and family.
●Intensive Care Unit- stressful to child and family. Need honest information, orient them. Show how to hold them while still being connected to tubes. Try to accomadate needs of family.
●4yrs old scheduled day surgery, child asks when dad will rertun, what is the best response
●Best response- your dad will be back after you wake up.
●Not back at 11 am or within 2 hrs bc they wont understand
●Development- preschool. Think pain or preduced ounishment, magical thinking
What do we do for surgeries, pre and post op
●Informed Consent
○Must be able to give consent, usually by age
○Must act voluntarily, need to reveice info to make a decision
●Prepare for Procedures
○Education and developmentally appropriate
○Establish trust, encourage family support- keep parents w child as much as you can, distraction
●Surgical Procedures
○Pre-op, stressors, goals and outcomes. Keep family w them preop. Ex. Sedate them then IV. Save painful or significant interventions until maybe they’re under. Pre op med- versed, laughing gas calm them, decrease anxiety, decrease secretions during surgery.
●Postoperative Care
○Vitals, assess, pain control, education, side effects of medication, encourgage child did good, reunite w family as soon as you can. Worried about respiratory system. To expand lungs- blow bubbles. Areate lungs important. Infection important.
Don’t think about very specififics
Situations- emancipated minors- minor but married, miltitray, court – can make own informed consent
TX without parent consesnt- emergency or if parents refuse but minor might say yes - certain cultures. Maintain hippa.
There are emancipitaed conditions where they can give consent to w out permission for ex. if need tx for STI, mental health, Alchol and drug dependency, pregnancy, abortion, contraception
Assent- ethical choice where child has allowed to that tx as well. Not required by law. Ex, 10 yr old w ADHD- parent wants them to be in a study for new med. Child agrees to it and has been informed to tx.
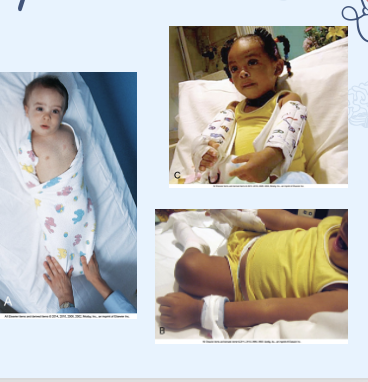
How do we keep kids safe
●Environmental Factors
oSafety, side rails, doors locked Fall risk- see where equipment is, swaddle to keep save like NGT tube , elbow immobilizers, keep them from bedning so they don’t feel tubes/ lines.
●Infection Control
oPPE, wearing appropriate PPE
●Transportation
oMedical equipment, ex wheelchair make sure they’re buckled in. NICU- make sure its flat not raised up
●Restraints & Therapeutic Holds- just know assess frequently
How do we collect specimens
●Fundamental Steps
●Urine
oClean catch- need to be able to hold cup and catch it in there
o24-Hour- pee urine bag kind of looks like purewick bag
oCatheterization- in and out.
Stool Specimen- saran wrap
●Blood Specimen
●Respiratory Secretions
○Cough and expel mucous
○Nasal swab- saline and swab nose. Always have someone safely hold their head.
Bandaids
Get all supplies, do procedure on right pt
How do we adminster meds for kids
●Safety
●Liver and kidneys not fully developed- use smallest syringes so we give most accurate dose
●Always Weight based- double check any med and dose.
●Accurate measuring devices
●Nursing judgement
●Developmental considerations
oOral meds: put in pockets of cheeks , aspiration
oInjection sites: choose appropriately.
Vastus lateralis- be more painful. infants- 0.5ml , cjildren 2.0ml 22-25 g 5/8-1 inch
ventrogluteal- 0.5ml , cjildren 2.0ml, less painful vastus lateralis 22-25 1/2-1 inch
Deltoids- 22-25 1/2-1 inch faster abdorption than other ones, easily accessible, less painful and less local side effects. (0.5-1 ml)
D2l test taking skills- practice questions math

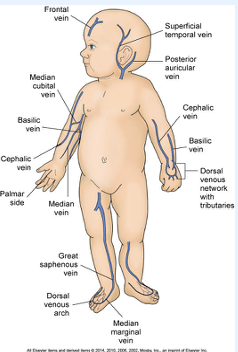
What is Parenteral Fluid Therapy
•Site- if walking don’t want to start on feet than adults,
•Infusion Pumps- 1-2 hrs max for volume to be infused, dont infuse entire bag of fluid
•Securing Lines- armboard & Equipment. Clear dressing to assess site.
•Removing Lines- aseptic technique
•Complications
oInfection
oInfiltration- Can infiltrate faster than adults because they are very tiny and they have subcut fat- IV needle or catheter has accidentally moved out of the vein and into the surrounding tissues
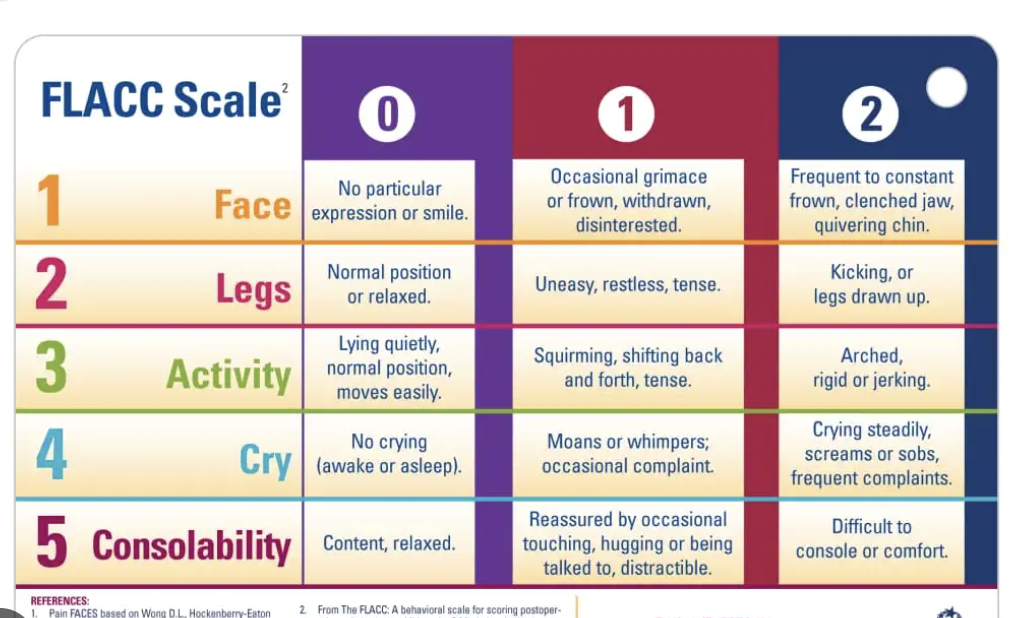
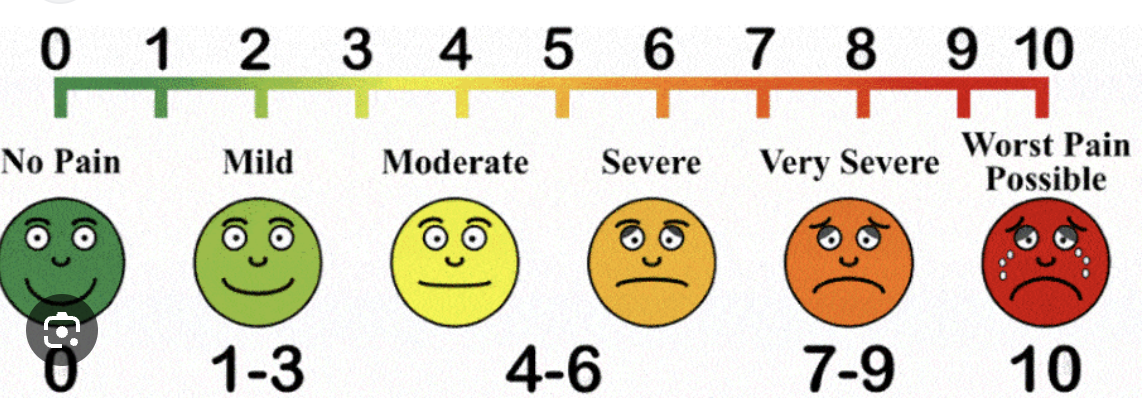
What are the different scales for pain assessment
●Behavioral Pain Scale
○FLACC- Face, Legs, Activity, cry, consolibitlity . Under 4 non verable . More reliable when measure short term pain
●Self Reporting Scales
○FACES, NRS- numeric reporting scale over 8 yrs old. Not under 4
●Adolescent Pediatric Pain Tool
○Color areas of pain and shade based on intesnity
●Chronic Pain
○Diary- log and interventions may or may not help
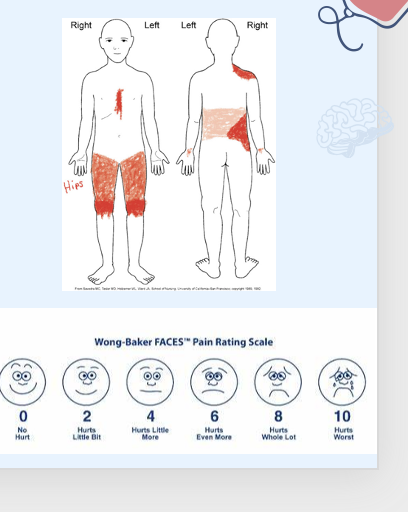
Pain Assessment in Specific Populations
●Children with communication & cognitive impairment
○Parents and caregivers important- familiar with child to know when they have pain.
oNoncommunicating Children’s pain checklist- questionnaire
oPain indicators for impaired children
●Cultural differences
○Inadequate pain assessment w diff backgrounds. Ex. Some cultures may not admit to being in pain.
●Chronic illness & complex pain
WHat are Nonpharmacologic Pain Management
●Distraction, relaxation
●Guided imagery ex. imagine on a beach
●Swaddling, can parents hold them
●Nonnutritive sucking- dip pacifier in sugar?
●Behavioral contracts
Tokens, stickers, etc.
What Pharmacologic Pain Management do we do
●Acetaminophen, NSAIDs- ex. tylenol, ibuprofen mild pain 1-5
●Opioids moder to severe 6-10
●Co-analgesia- not specifically for pain ex. Benadryly , antiaxiety meds, antimetics or adjuvant analgesia
●Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA)- need to understand how to push button.
●Transdermal analgesia- lidocaine or topicals takes 30-60 min
●Side effects
●Non opioids act on peripheral
●opiodes- act on central . Monitor for resp depression and constipation . Weaning schedule and monitor for adverse se
Can metabolize drugs wuicker- may be giving them more quickly
What are consequences of untreated pain
●Infant pain often inadequately managed
○due to misconception regarding pain effects
●Chemical and hormonal responses
Greater morbidity in NICU
If baby is left in pain reactiosn will occur and can lead to death.
If they can stay on top of pain- better, decreases how long in hospital

●Parents concerned about 3 week old pain which response therapeutic
●It is import to monitor for sitress behaviors such as crying
●We will reasss pain frequently to see if interventions are successful
●Use flacc scale.
●Think are you being honest, still validating feelings, answer question
WHat is Cognitive Impairment
●“Cognitive Impairment” (CI): encompasses any type of mental difficulty or deficiency
●Used synonymously with “intellectual disability”
●Diagnosis
●Classified as mild, moderate, severe, or profound
○determined by IQ
WHat are Causes of Cognitive Impairment
●Intrauterine infection/intoxication
●Trauma
●Metabolic or endocrine disorders
●Inadequate nutrition
●Postnatal brain disease
●Unknown prenatal influences
●Chromosomal anomalies
●Prematurity, low birth weight, post maturity
●Psychiatric disorders with onset in childhood
●Environmental influences
What care do we do for Impaired Cognitive Function
●Educate child and family
○Early intervention
●Teach self-care skills
●Promote optimal development- educated on social norms, how to dress appropriately, ecnourgae them to reach their full potential
●Encourage play and exercise
●Assess that childs specific deficines
●Demonstration is preffered to verbal . Don’t explain why as much , short clear, to point
●May have short term memory
Motivation enhances learning
●Provide means of communication. If delayed in speech- see how they communicate, can they hear well.
●Establish discipline- teach limitations and boundaries early, and have clear simple language
●Encourage socialization
●Provide information on sexuality- straightforward, teach anatomy
●Help families adjust to future care
●Care for the child during hospitalization- can alter how care looks like , ask open ended questions , let parents explain routines
What do we do for hearing impairment
●Promote Communication
●Reassess understanding of instructions
●Supplement with visual & tactile aids
●Provide communication devices
○Picture boards
○Speech, child life therapy
Additional aids
Can be a choking hazard, make sure they acknowledge you before you touch them.
Make sure healthcare team is aware theyre hearing impaired
What care do we do for visual impairment
●Provide safe environment
●Reassurance during treatments
●Orient child to surroundings- don’t try to move stuff around
●Encourage independence
Consistent team members
Chronic illness, Disability, End of life Care
●Increased viability in preterm infants- improved medical care
●Life-sustaining technology
●Life-extending treatments
●Rise in number of children with complex & chronic diseases
What are the Effects of chronic illness or disability
●Parents
○Parent roles- can grieve sense of normalcy
○Differences
○Single-parent families- can be arder
●Siblings
○Limitations
○Need honest information
○May have psychosocial problems
○Siblings may feel different
Include family as much as we can

How do we help families cope
●Families have stress of care in addition to regular stress
●Approach- family is like this is my new normal- movinf towards acceptance versus Avoidance behaviors- not realtic goals- maladaptive coping to what has happened
●Parent Empowerment
oRecognize, promote, enhance competence
●Help manage feelings
oShock, denial, - allow them to work through emtoions at first adjustment- starts to follow. Might be angry , reintegration- come up w realatic goals acknowledgement
What care do we do for the kid and family
●Assessment
●Provide support at diagnosis- how do they perceive it
●Support family’s coping methods
●Educate about disorder and care- do they need another car seat-
●Promote normal development
●Establish realistic future goals
Ex- ●Mom of NG tube refues learn care and assists toddler doesn’t need tube -
●Malaptive – avoidance
What options are there for end of life care
●Palliative care
○Pain management
●Decision making at end of life
○Ethical considerations
○Physicians + healthcare team
○Parents- very overwhelmed – support them.
○The dying child
○Need very honest and accurate
○Open communication
●Treatment options for terminally ill
○Hospital- make as home like as they can.
○Home care
○Hospice- specialized in comfort and end of life care.
What care do we do for end of life
●Child and family usually have fear
○Pain and suffering: Pain management important
○Fear of dying alone (child)- help w rotation of parents to come or not being there when it happens (parent)
○Fear of death
○Maximize time for them to stay- adovate as much as we can.
Give meds- breathing

Organ-Tissue Donation & Autopsy
●Meaningful act to benefit another human
●Sensitive approach
○Staff determines and come in and talk to the family
●Organ donation: legislated in many states
●Childrens organs are hard to find.
●Common questions by families-
●Unexplained, violent death, suspected suicide
○Autopsy may be required by state law
How do we helo w grief and mourning
●Grief is a process, not event
●Highly individualized
●Anticipatory guidance- helpful, reassure reactions are normal and expected. Can hear persons voice as they pass. Reassure that did everything you could.
●Mourning process
●Complicated or abnormal grief- last longer than year, lonliness, sleep distrubatnce, maladaptive
●Parent and sibling grief- not as much- most profound loss.
●Nurse’s reaction- same reactions family feels, support yourself