A&P 10
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Two main parts of the nervous system
Central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What does the central nervous system consist of?
The brain and spinal cord
How many neurons are approximately found in the human brain?
About 86 billion neurons
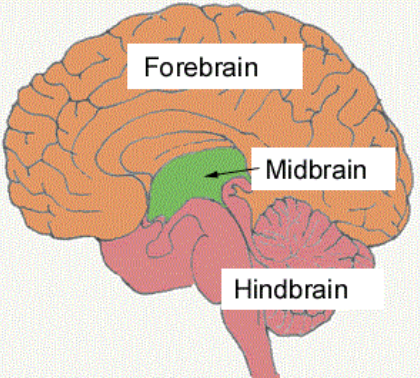
Three major regions of the brain
Forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain
Two components of the forebrain
Diencephalon and telencephalon
Structures in the diencephalon
Thalamus, hypothalamus, and pineal gland
Function of the thalamus
Serves as a major relay station for almost all sensory information, directing it to cerebral cortex
Role of the hypothalamus
Controls hunger, thirst, body temperature, sleep/wake cycles, and regulates hormone release through pituitary gland
What hormone does the pineal gland secrete, and what is its primary function?
Melatonin; it regulates the sleep-wake cycle
Largest and most complex part of the brain
Telencephalon (cerebrum)
Parts of the telencephalon
Basal ganglia, olfactory bulbs, and cerebrum
Basal ganglia
Control and coordinate voluntary movements. Also help in learning and memory, decision-making, planning and goal-directed behavior, and habit formation.
Olfactory bulbs
First to process sense of smell
Cerebrum
Two hemispheres, covered by layer of gray matter called cerebral cortex. Initiates and coordinates voluntary movements and is responsible for higher-order cognitive processes.
Four lobes of the cerebrum
Frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes
Frontal lobe
Controls voluntary movement, executive functions, personality, and speech. Contains Broca's area.
Parietal lobe
Processes sensory information like touch, temperature, and pain. Also plays a role in spatial awareness and language.
Temporal lobe
Processes auditory information, stores memories, and helps understand language. Contains Wernicke's area.
Occipital lobe
Processes visual information
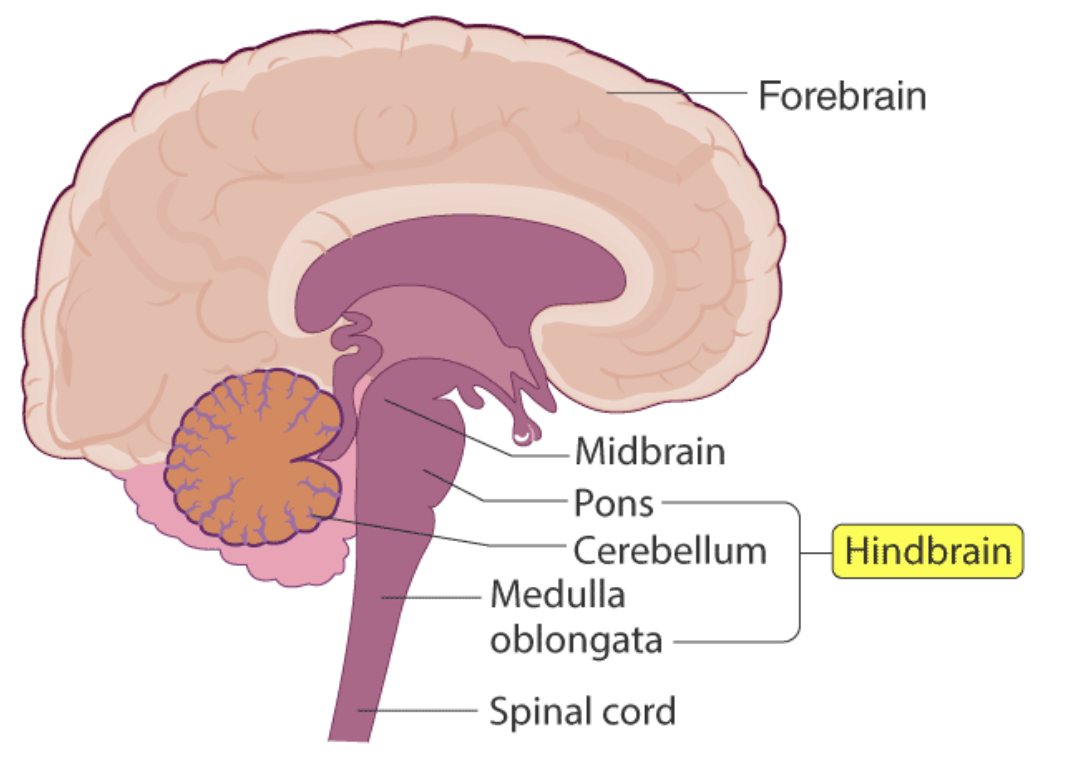
Structures of hindbrain
Cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata
Cerebellum
Coordinates voluntary movements, maintains balance and posture, and contributes to motor learning
Pons
Regulates breathing and bladder function (micturition).
Medulla oblongata
Regulates heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing
Difference in cerebrum and cerebellum
The cerebrum initiates voluntary movement; the cerebellum fine-tunes and coordinates it
Midbrain
Controls eye movements, pupillary reflexes, and processes auditory information
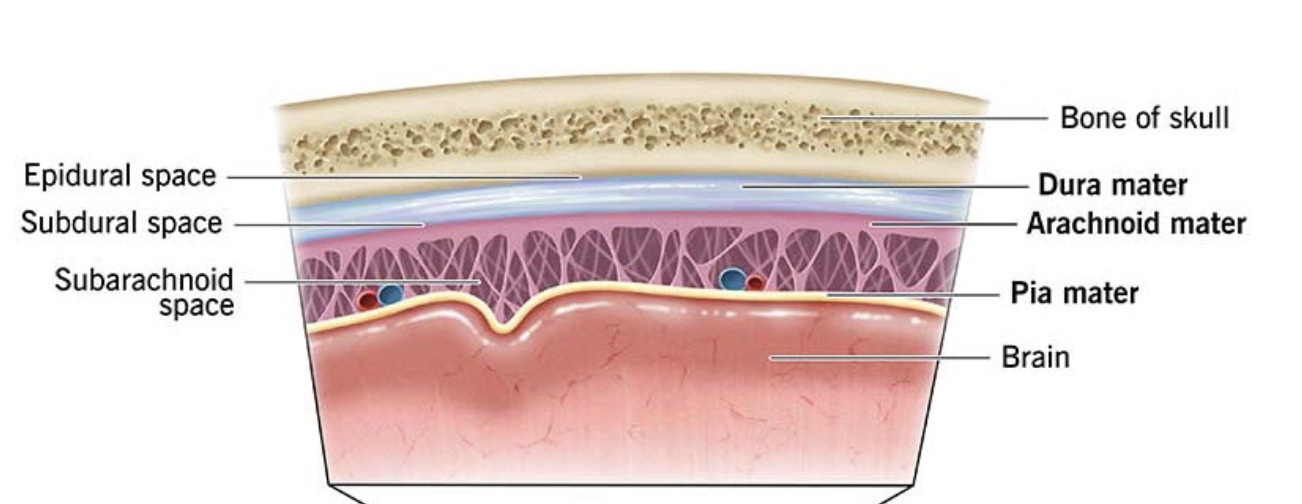
Types of meninges
Dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
Spaces between meninges
Epidural space, subdural space, subarachnoid space
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Cushions the brain and spinal cord, providing buoyancy, nourishment, and protection. Subarachnoid space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Length of the spinal cord in adults
About 45 cm (18 inches)
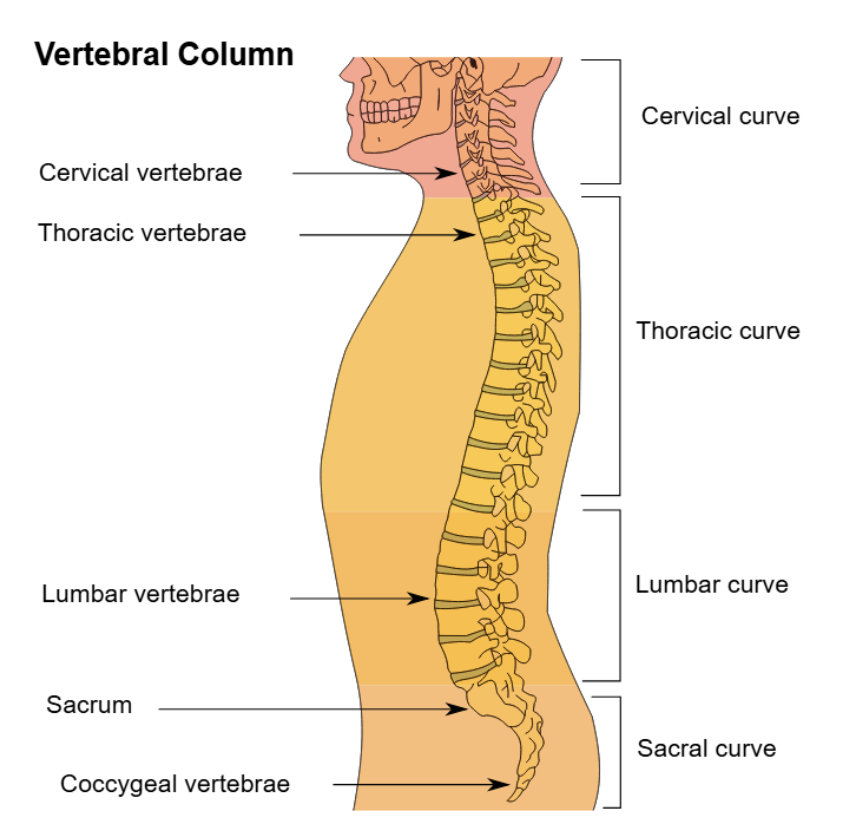
Five regions of the spinal cord
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions
Functions of the spinal cord
Sensory function, motor function, reflex control, and autonomic function
Sensory function of spinal cord
Receiving sensory information and transmitting it to the brain for processing
Motor function of spinal cord
Sends motor commands from the brain to muscles throughout the body
Reflex control in spinal cord
Mediates simple reflexes without involving the brain for rapid responses
Autonomic function in spinal cord
Controls involuntary bodily functions and maintains homeostasis