Membrane Potential
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
dendrites
input
cell body of a neuron contains its
nucleus
the axon hillock is where
an Ap starts
the axon of a neuron
carries AP out
a neurons terminals
contact next cell’s dendrites, often multiple cells at once
K+ concentration is high
inside the cell
K+ concentration is low
outside of the cell
chemical potential
energy generated by an ion moving with its concentration gradient
electrical potential
energy generated by an ion moving with its electrical gradient
electrochemical gradient
combination of electric and chemical gradient
Nernst equation
equilibrium potential
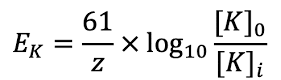
Na+ concentration is low
in the cell
Na+ concentration is high
outside of the cell
Vm represents
potential difference between inside and outside of cell, with outside being set to 0
Goldman equation
membrane potential

Vrest is
membrane potential with no AP
leak channels
channels open at rest
Pion is determined by
number of open leak channels
at rest, there are more channels open of which ion, K or Na
K, meaning Pk>PNa
Vrest is approximately
-70 mV
Vm=Eion when
only one ion is able to cross the membrane
to depolarize means to
increase Vm, flip charges so that the outside is now more negative than the inside of a cell
to repolarize means to
decrease Vm back towards Vrest, where inside of the cell is more negative than the outside
to hyperpolarize means to
overshoot Vrest, where inside of cell is more negative than usual
Ionic current, Iion
number of ions crossing a membrane
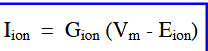
Force, F ion
force driving ion movement
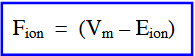
conductance, Gion
similar to permeability
according to the Fion equation, when Vm is far from Eion
there is a large force on the ion
according to the Fion equation, when Vm=Eion
the same amount of ion enters the cell that leaves, so there is no net ion movement, hence no force on ion
when a cation leaves the cell, I (current) is
positive
when a cation enters the cell, I (current) is
negative
when an anion enters the cell, I (current) is
positive
when an anion leaves the cell, I (current) is
negative
when deciding whether ionic current is negative or positive
outside of cell is used as reference, keep in mind whether it is an anion or a cation
What are two ways to depolarize a cell
increase Na ionic current, decrease K ionic current
how can Na ionic current be increased
increase Na conductance (most common) or increase force on Na by increasing ENa
how can K ionic current be decreased
decrease K conductance (most common) or decrease force on K by increasing EK
V-I plots
plot I against Vm, slope is conductance
what is steady state for a neuron
when Vm is stable, cations going into cell=cations going out of cell, IK=-INa
how is Vrest maintained
active transport
how much Na+ is pumped out for how much K+ pumped in?
3Na+ out for 2 K+ in
Can pumps create a rapid repolarization?
No, they are too slow