Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A collection of vocabulary flashcards covering key concepts in chemical bonding and molecular geometry.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Octet Rule
The principle that atoms tend to bond in such a way that they have eight electrons in their valence shell.
Lone Pair
A pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom.
Formal Charge
A hypothetical charge an atom would have if all bonding electrons were shared equally.
Resonance
The phenomenon where multiple valid Lewis structures can represent a molecule, indicating that the real structure is an average of these
Bond Energy
The energy required to break a specific covalent bond in one mole of gaseous molecules.
VSEPR (Valance shell electron pair repulsion) Theory
A theory that predicts the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs surrounding their central atoms.
exception when drawing lewis structures
Free radicals: odd # of valance
Electron deficient Molecules: there isn’t enough for 8
Hypervalent molecules: period 3 or higher can have more than 8
Formal charge rules
0 is preferable
fewest not 0’s
adjacent charges are 0 or opposing signs
neg. formal charges on more EN atoms
Bond strength trends
increases with # of electrons shared
decreases with increasing bond strength (1 A = 0.1 nm)
Between 1 and group elements, decreases down a group
lattice energy
strength of attraction between ions in ionic compounds
endothermic
C (crystal), R (distance), Z (charge)
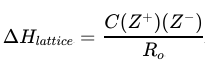
bond angle
the angle between two bonds in a molecule, influenced by molecular geometry.
bond distance
distance between two nuclei
strength varies as:
lone pair - lone pair > lone - bonding pair > bonding pair - bonding pair
for a molecule to be polar
must have at least 1 polar covalent bond AND have a molecule structure that the dipole moments do not cancel out each other