NCLEX 3
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
The nurse is caring for a group of clients. It is a priority to follow up on which client situation? A client
A. admitted with an asthma exacerbation that is wheezing while receiving albuterol via nebulizer.
B. admitted with pulmonary emphysema who puts on their nasal cannula oxygen before eating.
C. with pneumonia is ambulating around the nursing unit while wearing a surgical mask.
D. receiving oxygen via nonrebreather and has an oxygen saturation of 92%.
D- a nonrebreather administers approximately 80-95% FiO2 so if the highest they can go is 92% then they might need more aggressive measures to improve oxygenation
Electrolyte abnormality associated with subarachnoid hemorrhage
hyponatremia (after experiencing a subarachnoid hemorrhage the client is at risk for SIADH and in turn hyponatremia)
Action necessary for nurse to take when caring for Native American
avoid excessive direct eye contact
What does administration of fresh frozen plasma do?
provide clotting factors
What complications should you assess for during TPN therapy?
-hyperglycemia
-infection
-air embolism
-dehydration
Renal diet
low potassium, phosphorus, protein, and sodium
What do you monitor during continuous infusion of norepinephrine?
-blood pressure
-IV site
-UO
-blood glucose
AE of motelukast
hallucinations
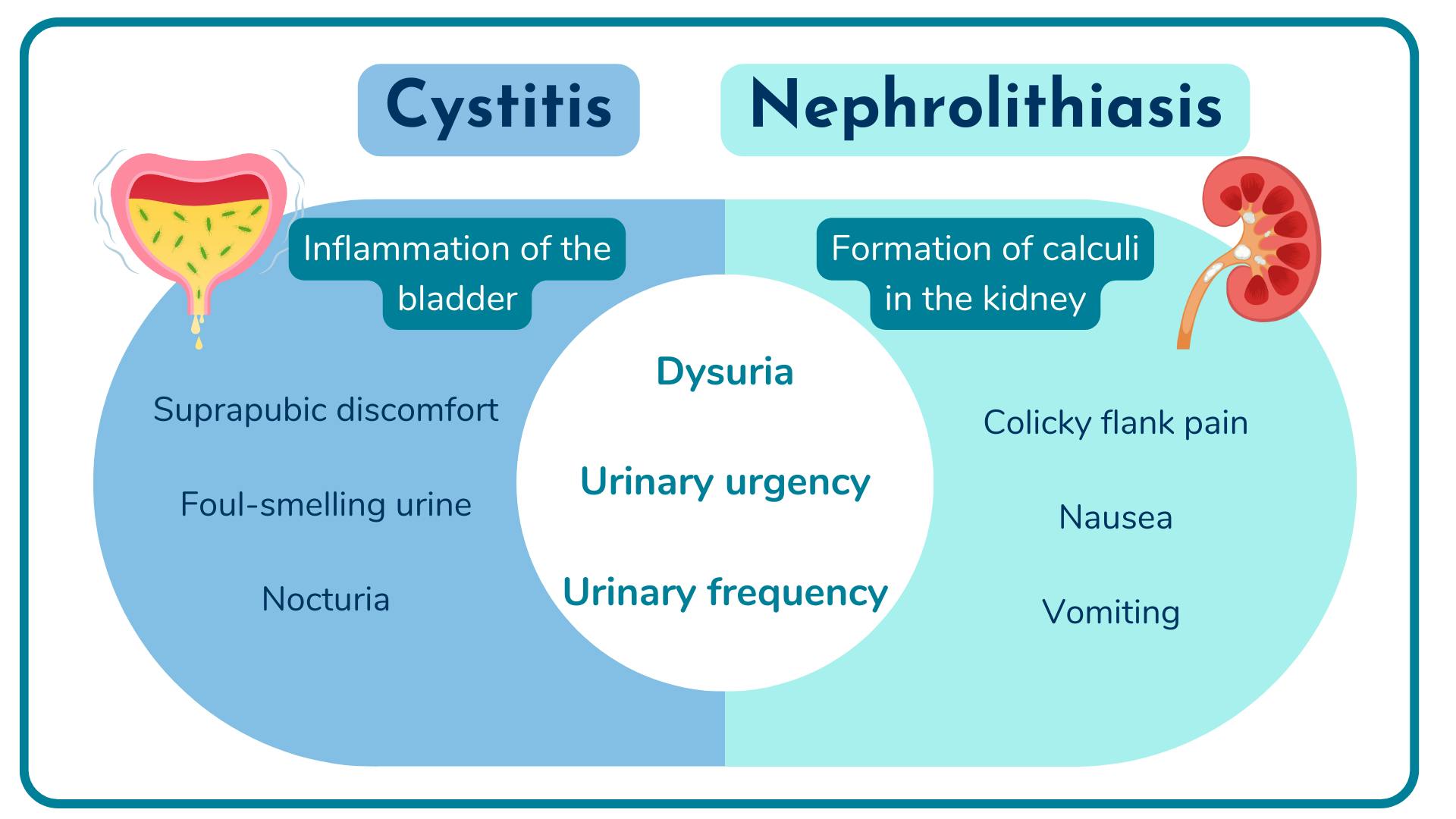
Cystitis vs Nephrolithiasis
Client Finding | Cystitis | Nephrolithiasis |
|---|---|---|
Dysuria | x | x |
Flank pain | x | |
Increased urinary frequency | x | x |
Nausea and vomiting | x |
Hemothorax vs asthma exacerbation
client findings | hemothorax | asthma exacerbation |
|---|---|---|
tachypnea | x | x |
reduced (or absent) breath sounds of the affected side | x | |
labored breathing | x | x |
percussion on the involved side produces a dull sound | x | |
chest wall tenderness | x | |
use of accessory muscles to breathe | x | x |
Isolation for infectious mononucleosis
standard precautions
Isolation for HIV
standard precautions
Foods high in magnesium
-spinach (green leafy veggies)
-salmon
-bananas
-dairy products
What fetal risk factor is commonly associated with shoulder dystocia?
macrosomia
What is essential for a client with a suspected ruptured AAA?
tight blood pressure control
What does aortic regurgitation do?
-increases preload in the left ventricle
-causes decreased cardiac output
-increases left ventricle end diastolic pressure
What kind of foods should be limited when taking an ACE-I?
potassium rich foods
What elements should be met in a negligence lawsuit?
-duty owed
-breach of duty owed
-causation
-harm or damages
What is acamprosate?
used to support alcohol abstinence
What kind of disturbances are expected for a client with a stroke affecting the occipital lobe?
visual disturbances
What kind of disturbances are expected for a client with a stroke affecting the parietal lobe?
disturbances in sensory input, proprioception, and taste
AE of aspirin
black tarry stools
What is hydralazine?
a vasodilator used to treat hypertension
Reversal agent for apixaban
andexanet
S/s of phenylketonuria (PKU)
-Children with phenylketonuria commonly have a musty odor to their urine.
-Hypopigmentation of the hair, skin, and irises is a prominent sign of the disorder.
-Common manifestations of PKU include lethargy, poor feeding, vomiting, diarrhea, hypoglycemia, and metabolic acidosis.
What meds can be used to treat opioid use disorder?
-naltrexone
-methadone
-buprenorphine
Hypothyroidism has intolerance to heat or cold?
cold
Cystitis vs Nephrlithiasis
AE of montelukast
hallucinations
LSHF vs RSHF
Clinical Finding | Left-sided Heart Failure | Right-sided Heart Failure | Both |
|---|---|---|---|
Crackles auscultated bilaterally | x | ||
Bilateral lower extremity edema | x | ||
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea | x | ||
Fatigue | x | ||
Weight gain of 4 pounds | x | ||
Accessory muscle use | x | ||
Juglar vein distension | x |
What is spironolactone?
-mineralcorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA)
-blocks aldosterone effects
What is sacubitril/valsartan?
-angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNI)
-blocks RAAS and neprilysin
What is dapaglifozin?
-Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2)
-causes osmotic diuresis
If the client has primary hypothyroidism, the client’s thyroid panel will have high _____ and low _____.
high TSH; low T4
The nurse is assessing a group of clients prescribed lithium. The client at most significant risk for lithium toxicity is a client with
A. asthma taking both long- and short-acting bronchodilators.
B. chronic migraine headaches and was newly prescribed naproxen.
C. hypertension newly prescribed clonidine transdermal patch.
D. hypothyroidism and was recently prescribed levothyroxine.
B. chronic migraine headaches and was newly prescribed naproxen.
-NSAIDS, ACE-I, and diuretics should be avoided while a patient is taking lithium
Lithium requires a consistent intale of _____ rich foods.
sodium rich
What kind of laboratory monitoring should a client on lithium include?
thyroid panel
What kind of vital sign will be seen in a client with Wilms tumor?
hypertension
What reflexes will not be present in a 7 month old infant?
-rooting (disappears by 3-4 months)
-moro (disappears by 3-4 months)
-palmar (disappears by 5-6 months)
-tonic neck (disappears by 4 months)
When would you give a client albumin?
treatment of thermal burns or third spacing
When would you give a client platelets?
severe thrombocytopenia
What should you monitor for when you administer cefriaxone?
skin reactions
What meds increase the risk for falls?
-alprazolam (benzos)
-bumetanide (diuretics)
-verapamil (CCB)
What is mutual pretense at the end of life?
allows the client to preserve a degree of dignity and privacy at the end of life
Preeclampsia vs Severe preeclampsia vs Eclampsia
Assessment findings | Preeclampsia | Severe preeclampsia | Eclampsia |
|---|---|---|---|
blood pressure 143/91 mm Hg | x | ||
proteinuria | x | x | x |
no abdominal pain | x | ||
facial edema | x | x | x |
frontal headache | x | x | x |
photophobia | x | x |
AE of sitagliptin
abdominal pain
Foods high in phosphorus
-garlic
-nuts
-turkey
Normal age related skin changes
-decreased dermal blood flow
-development of actinic lentigo
-degeneration of elastic fibers
-loss of subcutaneous fat
What are kosher meals?
Animals that have split hooves and chew the cud, such as cows, bulls, sheep, lambs, and goats, are allowed. Pig (pork) is forbidden. Certain poultry is allowed, such as chicken, goose, duck, and turkey, but all others are forbidden.
Acute pancreatitis vs Cholecystitis
Assessment Findings | Acute Pancreatitis | Cholecystitis |
|---|---|---|
Severe epigastric pain | x | |
Gray-blue discoloration of the flanks | x | |
Nausea and vomiting | x | x |
Leukocytosis | x | x |
Elevated lipase and amylase | x | |
Hypocalcemia | x |
The nurse is planning care for a client following bilateral adrenalectomy. The nurse should anticipate a prescription for which postoperative medication?
A. Pantoprazole
B. Propylthiouracil (PTU)
C. Propranolol
D. Hydrocortisone
D. hydrocortisone
-they are at risk for adrenal crisis post op
What is scleroderma?
medical condition that causes fibrosis to the connective tissue
-mans: skin thickening and hardening, vasospasms of the fingers, arthritis, muscle stiffness, fatigue, dysphagia, esophageal reflux, insult to kidneys that can lead to renal failure
Positioning for hypertensive crisis
semi fowlers
Conditions that may cause a client to manifest hyperglycemia
-pheochromocytoma (a tumor sitting on the adrenal medulla, leading to an excessive discharge of catecholamines, causing an individual to develop hyperglycemia, headaches, and high blood pressure)
-hyperpituitarism (excessive release of growth hormones, causing hyperglycemia)
-pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas, leading to the impairment of the beta-cells from secreting insulin)
The nurse is assessing a client with leukemia. Which of the following assessment findings would be expected?
A. Dyspnea, malaise, and hypotension
B. Bruising, fatigue, and bone pain
C. Bradycardia, hypotension, and palpitations
D. Paresthesia, facial rash, and abdominal pain
Bruising, fatigue, and bone pain
-Because the bone marrow is not making enough red blood cells and platelets, the patient will experience fatigue due to anemia and bruising due to decreased platelets. The stretching of the periosteum causes bone pain because of the excessive white blood cells. The CBC may show increased blasts or immature white blood cells, crowding out the healthy RBCs and platelets.
The nurse is conducting a community health fair. Which of the following clients is at the greatest risk of developing osteoporosis?
A. 27-year-old woman who jogs three times a week and drinks red wine daily
B. 60-year-old woman who smokes cigarettes and just recently stopped drinking alcohol
C. 51-year-old man who suffers from alcoholism and recently stopped smoking
D. 25-year-old man with asthma who takes inhaled corticosteroids
B. 60-year-old woman who smokes cigarettes and just recently stopped drinking alcohol
-post menopausal status and smoking cigarettes
Med for viral croup syndrome (laryngotracheobronchitis)
dexamethasone
-in viral croup, the upper airway becomes inflammed leading to airway narrowing and dexamethasone will reduce the edema
Unstable vs Stable angina
Assessment findings | Unstable angina | Stable angina |
|---|---|---|
Location of pain | chest | chest |
Onset of pain | abrupt, unpredictable, rest | predictable, triggered by activity |
ECG findings | ST changes | no changes |
Pain intensity | severe, crushing, prolonged | moderate chest pain |
Duration of pain | persists for more than 5 minutes, unrelieved w/ nitro | subsides within 5 minutes, relieved w/ nitro |
Early sign of retinal detachment
seeing bright flashes of light
SE of dexamthylphenidate
appetite suppression
Most common complications with a regular insulin infusion
-hypoglycemia
-hypokalemia
-blurred vision
Fetal heart rate pattern for a prolapsed umbilical cord
variable deceleration
Embolic stroke vs Hemorrhagic stroke
Findings | Embolic Stroke | Hemorrhagic Stroke |
|---|---|---|
Abrupt unilateral weakness | x | x |
Intense headache that begins suddenly | x | |
Remains alert during initial symptoms | x | |
Vomiting or convulsions early in symptom presentation | x | |
Trouble forming words or speaking clearly | x | x |
Prevention for tumor lysis sundrome (TLS)
IV hydration
AE of risperidone
gynecomastia (d/t increasing prolactin levels)
What do you do if an over-the-counter nasal decongestant drop results in unrelieved and worsening nasal congestion?
discontinue the medication for several days
-a side effect associated is rebound congestion
Precaution for urticaria
standard (hives)
What does tranexamic acid do?
causes inhibition of fibrinolysis (reduces blood loss)
Position post surgical repair of cleft lip
on the opposite side of the repair
Why is dizziness after hemodialysis bad?
indicated hypotension or fluid volume depletion
Rheumatoid Arthritis vs Osteoarthritis vs Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Client Finding | Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) | Osteoarthritis | Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) |
|---|---|---|---|
Fatigue | x | ||
No Heberden's nodes | x | x | |
Low-grade fever | x | ||
Pain relieved with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | x | x | x |
Pain relieved with splinting | x | x | x |
Morning stiffness | x | x |
Med used for urinary bladder urgency and incontinence
oxybutynin
How do you administer ceftriaxone?
in the ventrogluteal to avoid nerve damage
Pink frothy sputum indicates
pulmonary edema