Plant Anatomy
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Adaptions of Leaves
Large SA to absorb more sunlight, thin so gases reach cells easily.
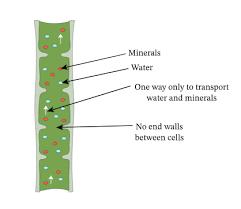
Xylem: What does it Transport? What is it Composed of? What is it’s direction?
Water and mineral ions, hollow dead cells with walls of lignin, transports its substances in one direction (up).
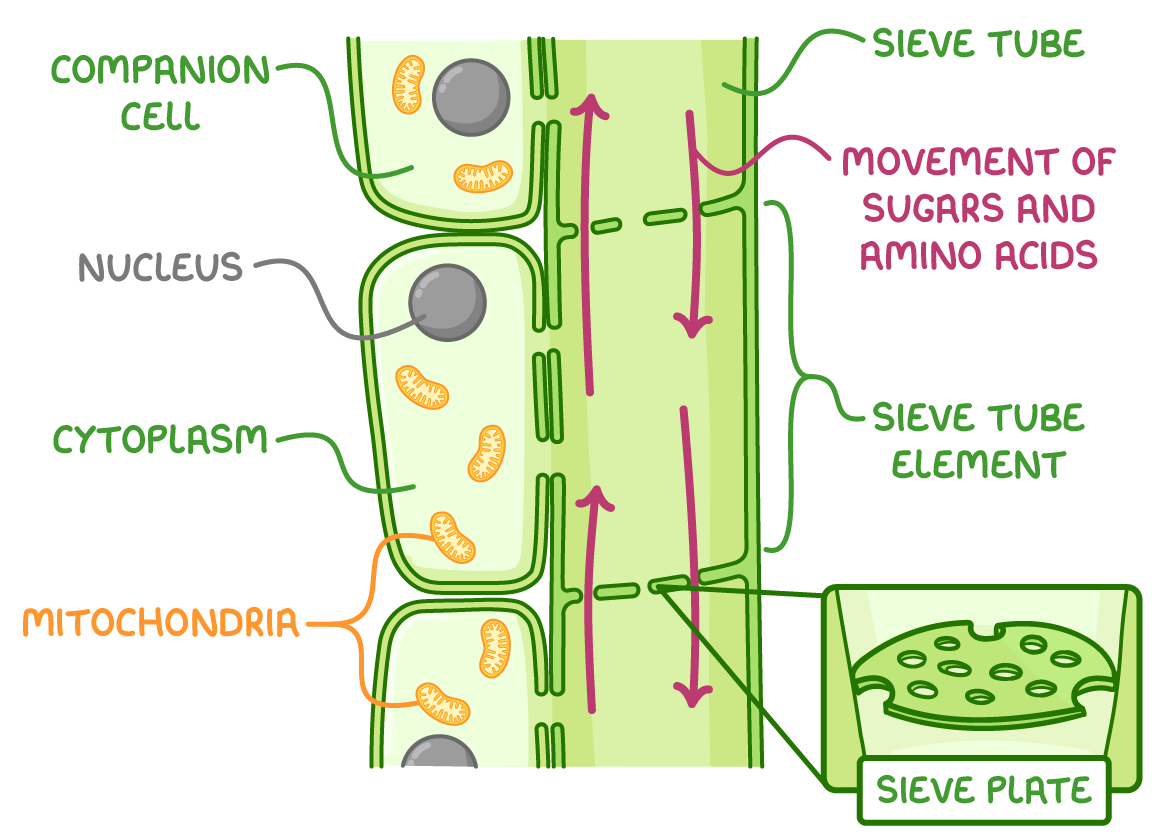
Phloem: What does it transport? What is it composed of? Direction?
Sugars and amino acids (any nutrients/food), living cells with walls made out of cellulose, both directions.
What is stomata and what is used for?
These holes are found on the underside of a leaf, and can be open and closed by their surrounding guard cells. They are used to control gas exchange and water loss in plants, allowing carbon dioxide in for photosynthesis and oxygen out.
What is transpiration?
Transpiration is the process by which water vapor is released from plant leaves into the atmosphere, primarily through stomata. It helps in cooling the plant and facilitates the uptake of minerals and nutrients from the soil.
How does light affect rate of transpiration?
light opens the stomata, allowing more carbon dioxide in. this increases rates of photosynthesis, but also loss of water vapour. (graph plateaus)
How does temperature affect transpiration?
Increasing temperature gives the molecules more kinetic energy, leading to water evaporating quicker increased concentration gradient and thus transpiration. (plateau graph)
How does wind affect transpiration?
Increases the evaporation of water from stomata. (inclined graph)
How does humidity affect transpiration?
Decreases evaporation from stomata. (declining graph)