Acute Coronary Syndrome
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is acute coronary syndrome, and what conditions does it include?
Acute coronary syndrome refers to any group of clinical symptoms compatible with acute myocardial ischemia - includes unstable angina, non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
Describe the pathophysiology of ACS
Acute coronary syndrome is a manifestation of coronary heart disease and usually occurs from: atherosclerosis in coronary arteries → inflammatory reaction to atherosclerosis by macrophages causes a plaque of foam cells, lipids, cellular debris and eventually calcium to build up with a fibrous cap on top → when this cap cracks (plaque rupture) the exposed plaque triggers platelet aggregation and thrombus formation → causing partial or total occlusion of the artery and cutting off blood flow to cardiac muscle → cardiac muscle cells die - myocardial infraction
How can ACS be subcategorised?
ST-elevation ACS - ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
Non-ST elevation ACS - non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) and unstable angina pectoris
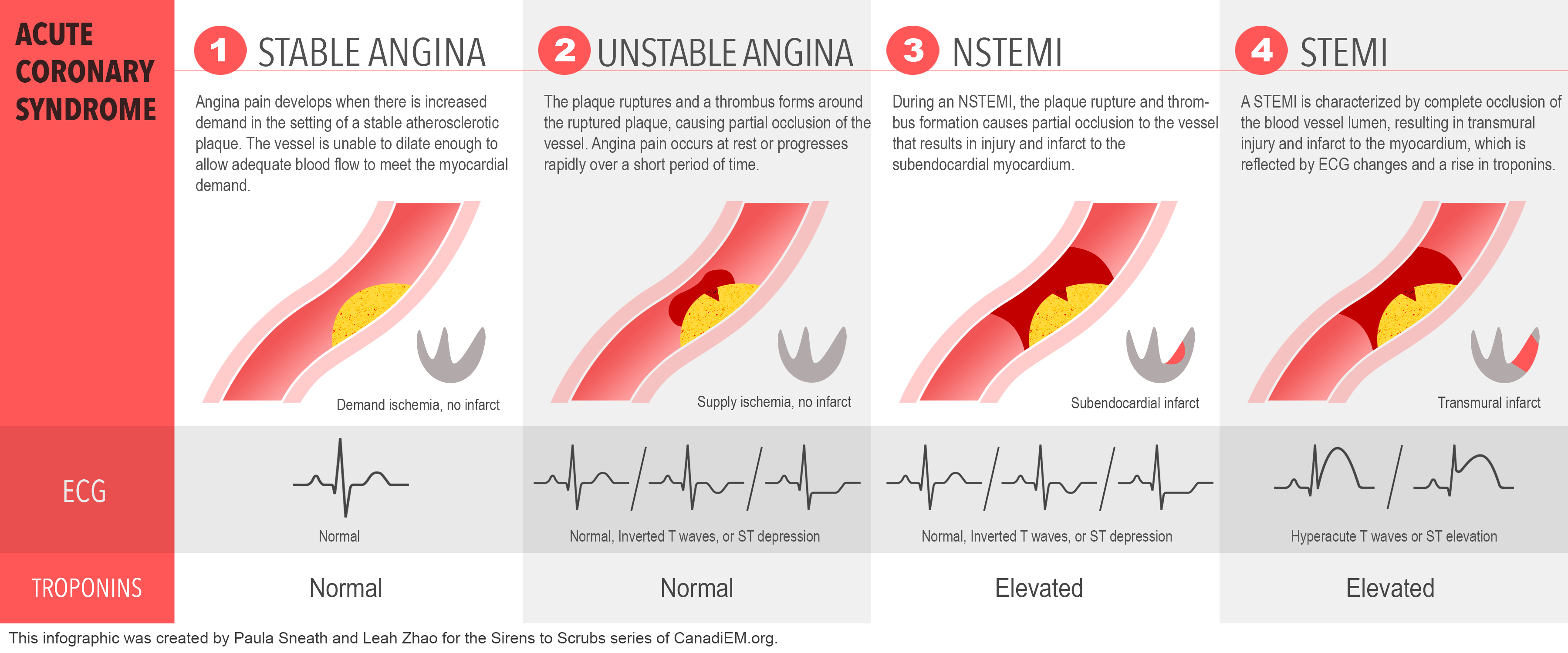
Describe the difference between unstable angina, NSTEMI, and STEMI
STEMI is characterised by transmural ischemia (lack of blood flow affecting the entire thickness of myocardium), myocardial necrosis, and release of specific chemical biomarkers, and ECG changes
In STEMI the thrombus is mostly occlusive
ST elevation is a sign of complete occlusion by thrombus causing immediate myocardial death of the area affected
NSTEMI is characterised by myocardial ischemia, myocardial necrosis, and changes of chemical biomarkers, but does not show ECG changes
In NSTEMI and UA there is partial coronary occlusion
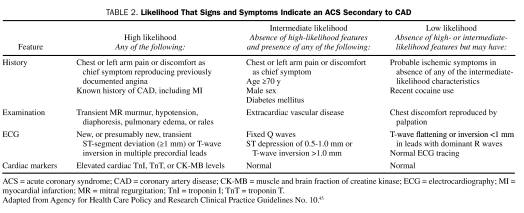
What are the signs and symptoms of ACS?
Symptoms of MI: prolonged chest/substernal pain (may radiate to left arm, jaw, back, or abdomen), nausea, shortness of breath
Symptoms of ACS:
Chest or left arm pain or discomfort as chief symptom
Transient MR murmur, hypotension, diaphoresis, pulmonary oedema, or rales
New transient ST-segment deviation or T-wave inversion
Elevated cardiac troponin 1, troponin T, or muscle and brain fraction of creatine kinase
Are there difference in symptoms between males and females?
Women are more likely to feel pain of higher intensity and to present with referred pain and symptoms other than pain - but no significant differences in the frequency or location of pain between sexes
Why is troponin raised in myocardial infarction?
Troponin is raised in myocardial infarction due to damage to the heart muscle - when the myocardium is damaged during MI the cardiomyocytes are injured and their contents leak into the blood
What are the non-ACS differential diagnoses?
Manifest with similar symptoms to ACS but is not

What are the immediate treatments for the management of ACS?
Oxygen
Nitro-glycerine
Aspirin
What is important to consider with the administration of oxygen for an ACS patient?
If patient has a normal blood oxygen saturation in blood providing oxygen raises oxygen levels (hyperoxia) can cause vasoconstriction of coronary blood vessels - further increasing ischemia
Mechanism of nitro-glycerine for the treatment of ACS? What are its side effects?
A vasodilator - causes release of NO in vascular smooth muscle causing smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation, to increase blood flow/oxygen to affected myocardium
Side effects: headache, decrease blood pressure (hypotension)
Mechanism of aspirin for the treatment of ACS? Side effects?
Is an antiplatelet agent and also have anti-inflammatory effects in ACS context
Inhibits COX-1 enzyme that converts arachidonic acid to prostaglandins - prostaglandin TXA2 increases platelet activation → inhibits TXA2-induecd platelet activation and aggregation
Side effects: asthma, salicylism (toxicity of salicylates in aspirin), peptic ulceration, intestinal bleeding, Reye's syndrome (swelling of liver and brain), idiosyncrasy, tinnitus (high doses)
What is important for the hospital management of ACS?
Increasing the time from symptom onset to reperfusion therapy increases mortality reduction %
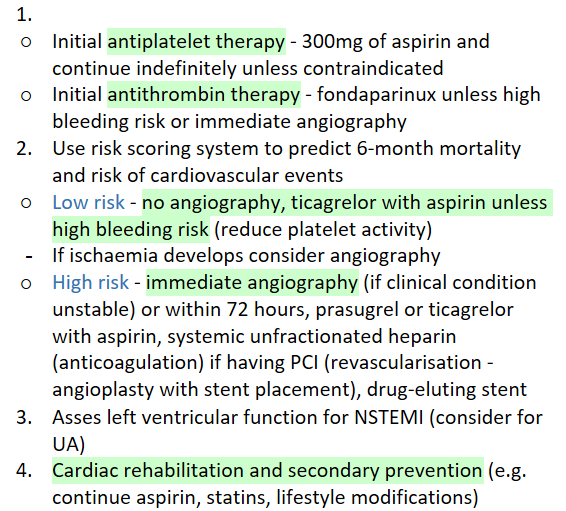
Outline the hospital management procedure for NSTEMI/unstable angina
Outline the hospital management procedure for STEMI
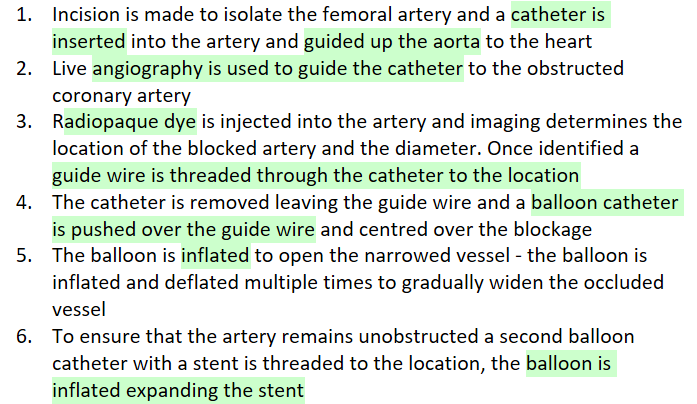
What is PCI and its method?
Percutaneous coronary intervention
What is a complication that can occur with the use of a stent, and how is it managed?
Drug eluting stents are used for some patients to decrease the chances of in stent stenosis (restenosis) - they are coated with a material that will retard new intimal hyperplasia
What are the different types of stents, and their associated advantages/disadvantages?
What is fibrinolysis, and how does it work?
Breaking down the thrombus
Use streptokinase (derived from streptococcal bacteria), alteplase (made by recombinant DNA technology)
These work by activating plasminogen which turns into plasmin - an enzyme which breaks down cross links between fibrin molecules so dissolves the clot
What is a key difference between streptokinase and alteplase?
These molecules differ in their selectivity for fibrin-bound plasminogen versus free circulating plasminogen - alteplase is more clot selective and acts to dissolve the fibrin in the thrombus, streptokinase are less clot selective and thus more likely to cause internal bleeding
What are the primary prevention methods for ACS?
What are the secondary prevention methods for ACS?
Cardiac rehabilitation
Pharmacological
What does cardiac rehabilitation involve?
Physical activity, lifestyle advice (healthy eating, alcohol use, stop smoking, reach and maintain a healthy weight), stress management, health education
What are the pharmacological secondary prevention methods for ACS?
ACE inhibitor and continue indefinitely
Dual antiplatelet therapy - aspirin plus a second antiplatelet (e.g. clopidogrel or ticagrelor)
Beta blocker
Statin
Mechanism of action of statins?
Block HMG-CoA reductase which is involved in the production of LDL, so lowers the levels of LDL