Bio Lab 3 Post-Quiz: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Define an anabolic reaction.
Anabolic reactions involve building up large molecules
Define a catabolic reaction.
Catabolic reactions involve breaking down large molecules.
What is the primary site of photosynthesis in a plant?
Leaves are the primary site of photosynthesis.
Name the three ways leaves facilitate photosynthesis.
Leaves facilitate photosynthesis through
light absorption
water and nutrient transport
gas exchange (through stomata).
Where are stomata primarily found, and what structures are associated with them?
Stomata are primarily found on the underside of plant leaves. They are associated with Guard cells.
What is the function of guard cells and stomata?
Guard cells regulate gas exchange. Stomata are crucial for photosynthesis and water regulation.
Where do the Light Reactions take place, and what environmental requirement do they have?
Location: thylakoid membranes. Requirement: Requires sunlight.
What molecules are converted in the Light Reactions regarding water and oxygen?
Water converts to Oxygen.
Name the two energy/electron-carrying molecules produced by the Light Reactions, and describe their function.
ATP (produced via Photophosphorylation) is a short-term energy storage molecule.
NADPH is an electron carrier.
Where does the Calvin cycle (Dark Reaction) take place?
stroma
What molecule is required for the Calvin cycle to run?
ATP is required.
What conversion occurs in the Calvin cycle, and what is this process called?
CO2 converts to Sugar. This process is called Carbon fixation. This process produces sugar for long-term energy storage.
Define plant pigments.
Plant pigments are Molecules capable of absorbing light energy.
Which specific pigment is the only one that converts light energy into chemical energy?
Chlorophyll a.
What function do Carotenoids serve in the fall?
Carotenoids give the leaves yellow and orange color in the fall.
Based on its absorption spectrum, which colors of light does Chlorophyll a absorb and reflect?
Chlorophyll a Absorbs red and blue light and Reflects green light.
Provide the formula used to calculate the Rf value in Chromatography.
Rf = (Distance traveled by pigment) / (Distance traveled by solvent front).
What liquids did we use in the lab?
Bromothymol blue and Chromatography solvent.
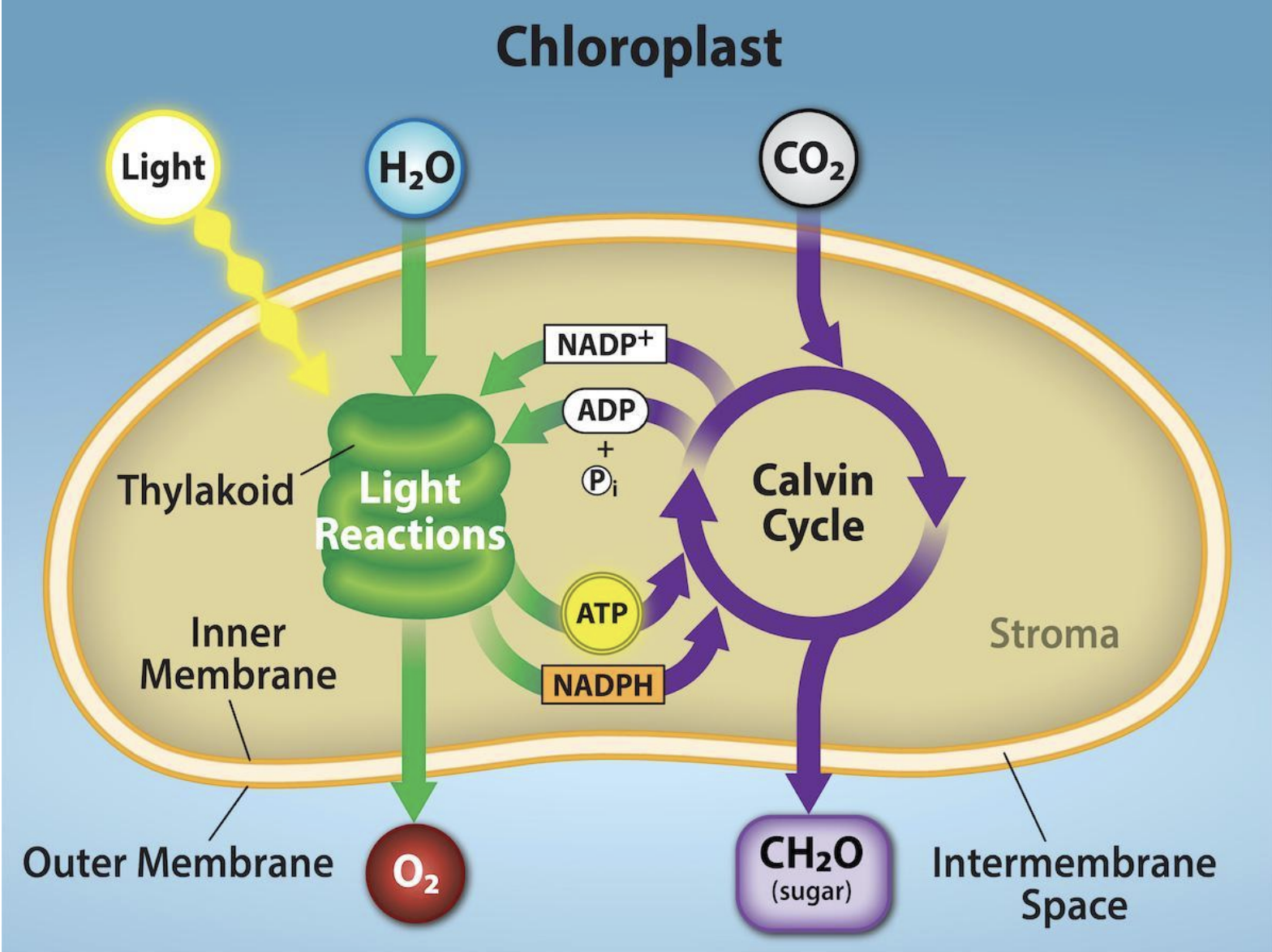
Light reactions
Location: thylakoid membranes
Requires sunlight
Water → Oxygen
Produce ATP: Photophosphorylation
ATP: short-term energy storage molecule
NADPH: electron carrier
Calvin cycle (Dark Reaction)
Location: stroma
Requires ATP
CO2 → Sugar: Carbon fixation
Produce sugar for long-term energy storage