Anatomy Lab week 6
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms

circular

convergent
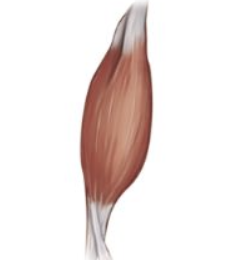
fusiform
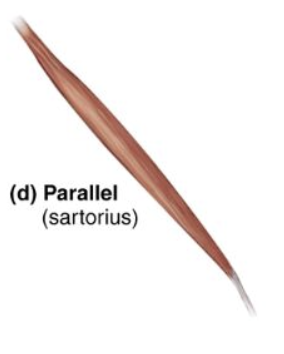
parallel

unipennate

bipennate
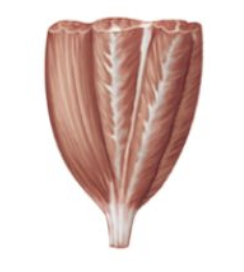
multipennate
what is an example of circular fascicle arrangement
orbicularis oculi
what is an example of convergent fascicle arrangement
pectoralis major
what is an example of fusiform fascicle arrangement
biceps brachii
what is an example of parellel fascicle arrangement
sartorius
what is an example of unipennate fascicle arrangement
extensor digitorum longus
what is an example of bipennate fascicle arrangement
rectus femoris
what is an example of multipennate fascicle arrangement
deltoid
A muscle that crosses on the anterior side of a joint produces
flexion
A muscle that crosses on the posterior side of a joint produces
extension
A muscle that crosses on the lateral side of a joint produces
abduction
A muscle that crosses on the medial side of a joint produces
adduction
origin
less moveable attachment site
insertion
more moveable attachment site
action
the motion the joint makes when the muscle contracts
innervation
the nerve that supplies the muscle (every muscle will have a nerve)
perfusion
the artery supplying the muscle
Prime mover or agonist
a muscle that has the major responsibility for producing a
specific movement
Antagonist
muscles that oppose or reverse a particular movement
synergiest
help the prime movers, either by adding a little extra force to the
movement being carried out or by reducing undesirable extra movements that the
prime mover may produce
fixator
synergists that hold a bone firmly in place, so that a prime mover has a
stable base on which to move a body part
Isometric contraction
production of muscle tension without a change in length
Isotonic contraction
consistent tension as the muscle contracts
Eccentric contraction
muscle fibers lengthen as the muscle contracts
Concentric contraction
muscle fibers shorten as the muscle contracts
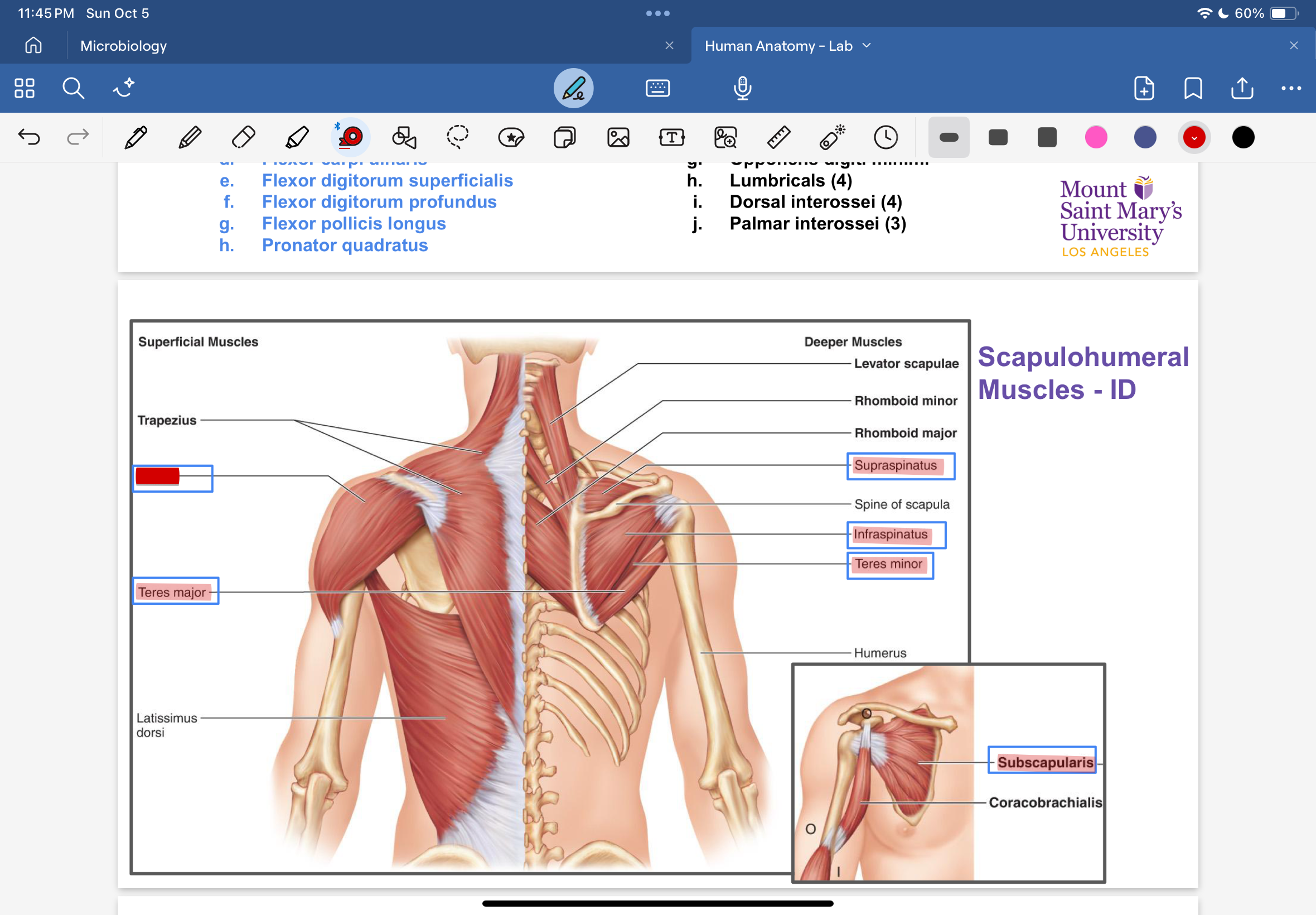
Deltoid
clavicle, scapula
humerus
arm abduction
supraspiatus
scapula
humerus
arm abduction
infraspinatus
scapula
humerus
arm lateral rotation
subscapularis
scapula
humerus
arm medial rotation
teres major
scapula
humerus
extends, medially rotates, adducts arm
teres minor
scapula
humerus
arm lateral rotation
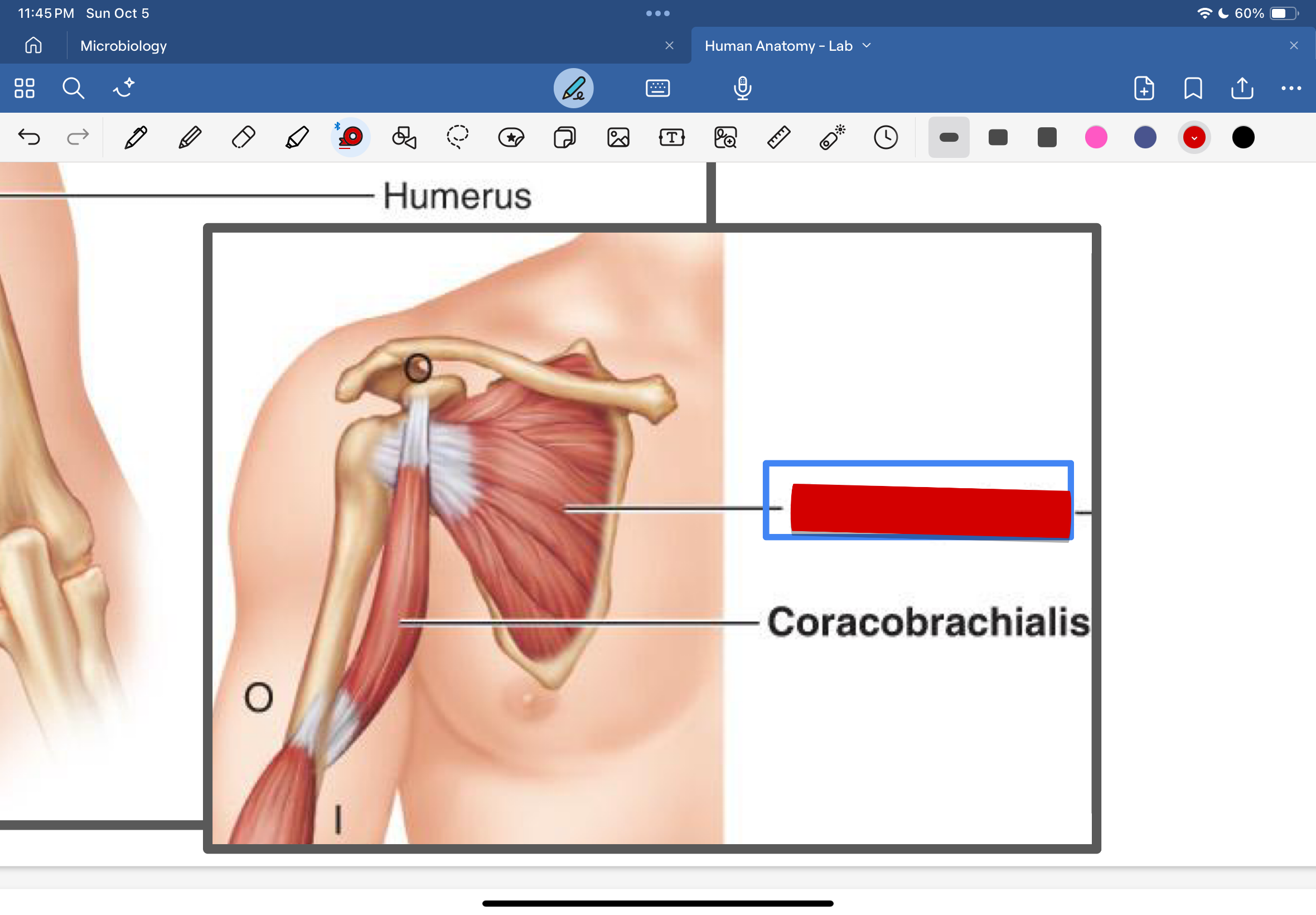
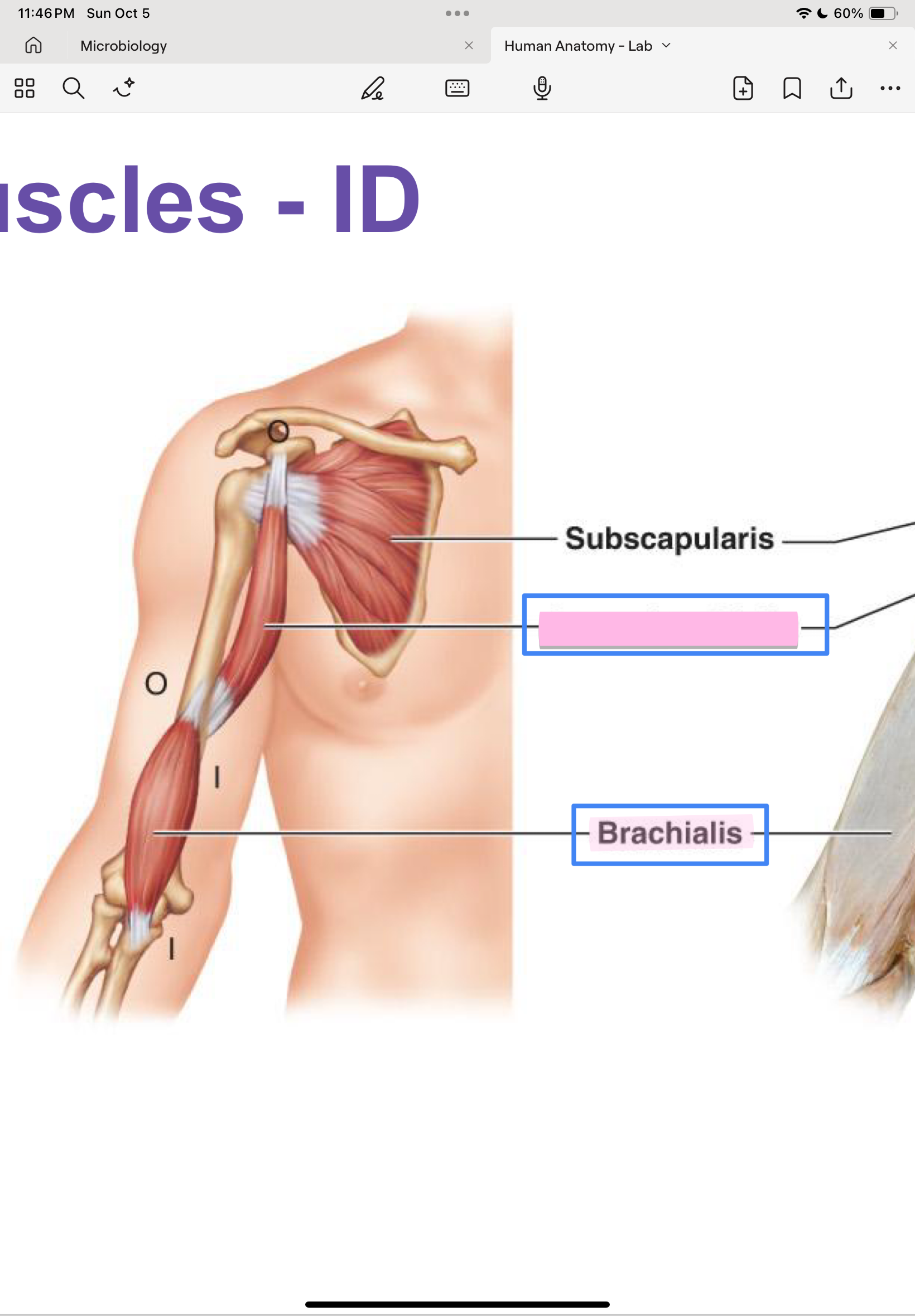
Coracobrachialis
scapula
humerus
flex and adduct arm
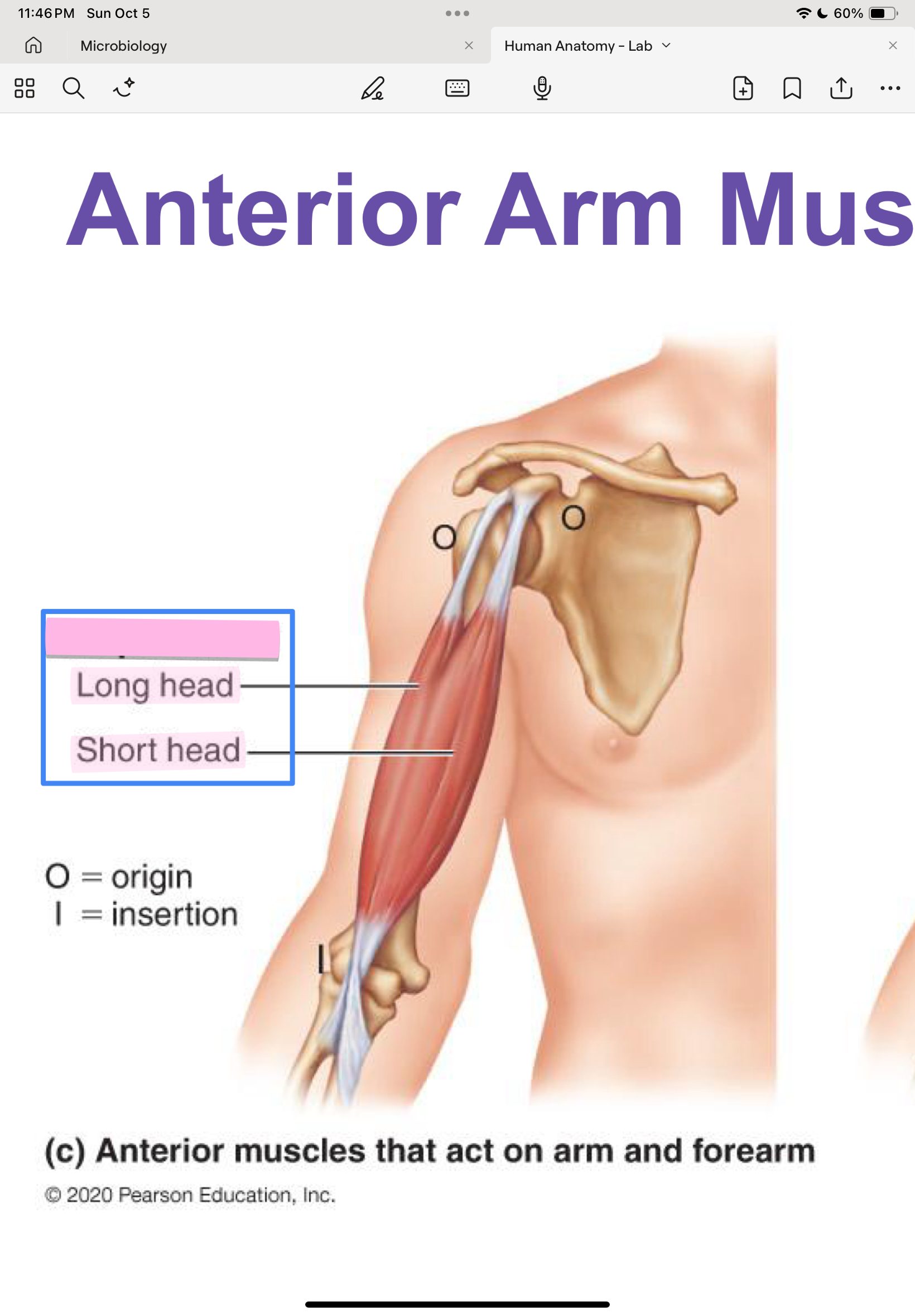
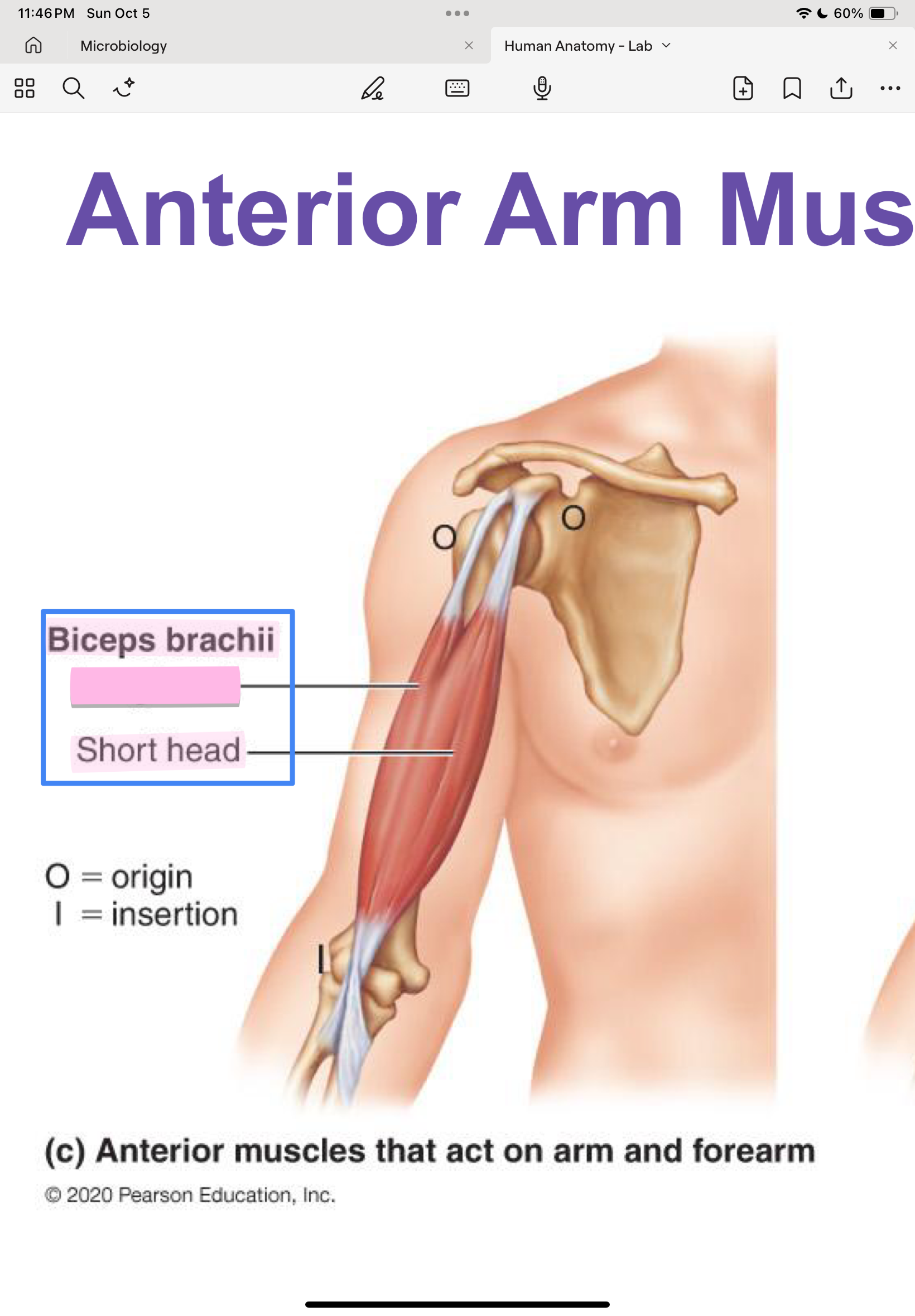
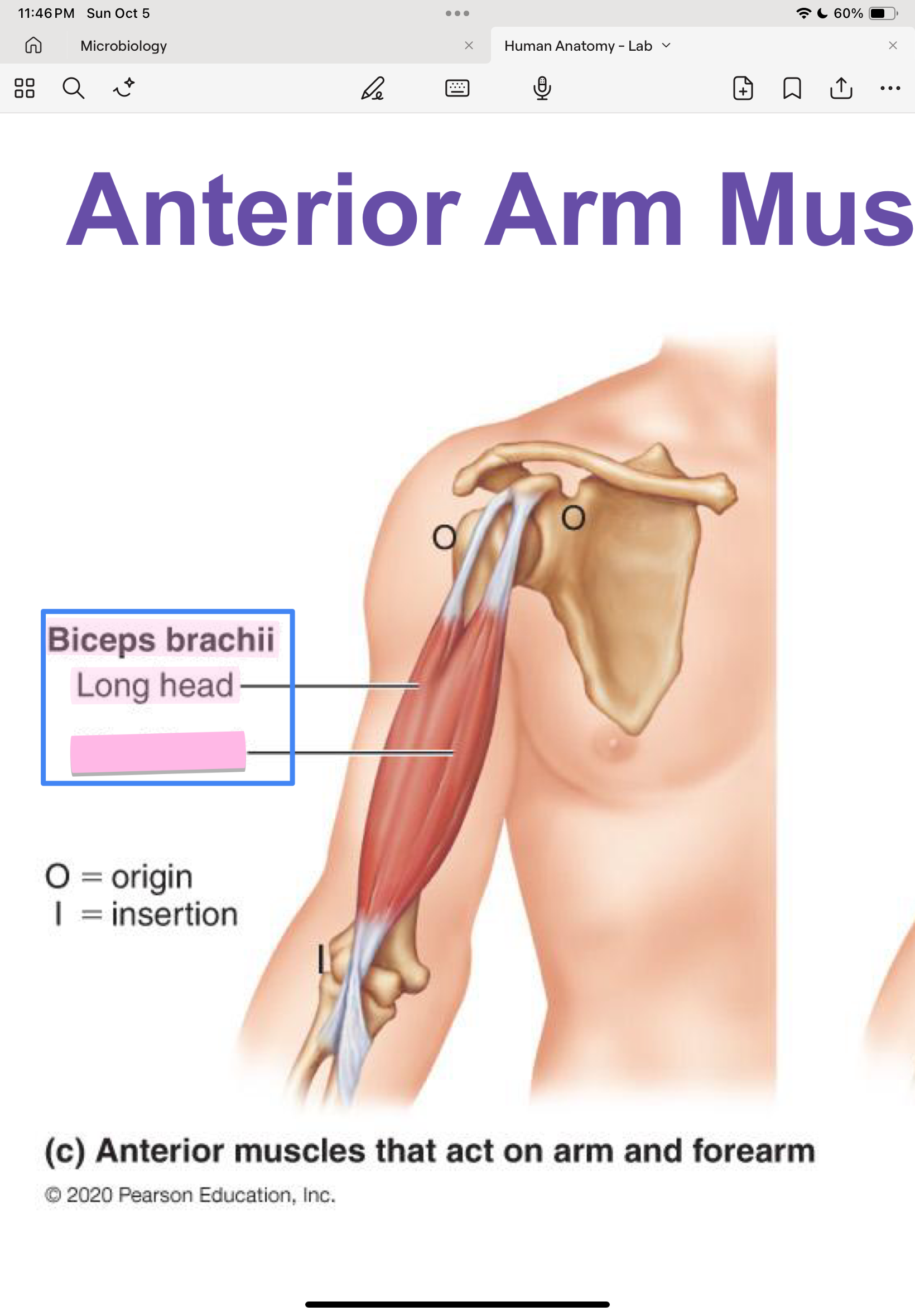
Biceps brachii (Short & long heads)
short head: scapula
long head: scapula
radius
flex and supinate forearm
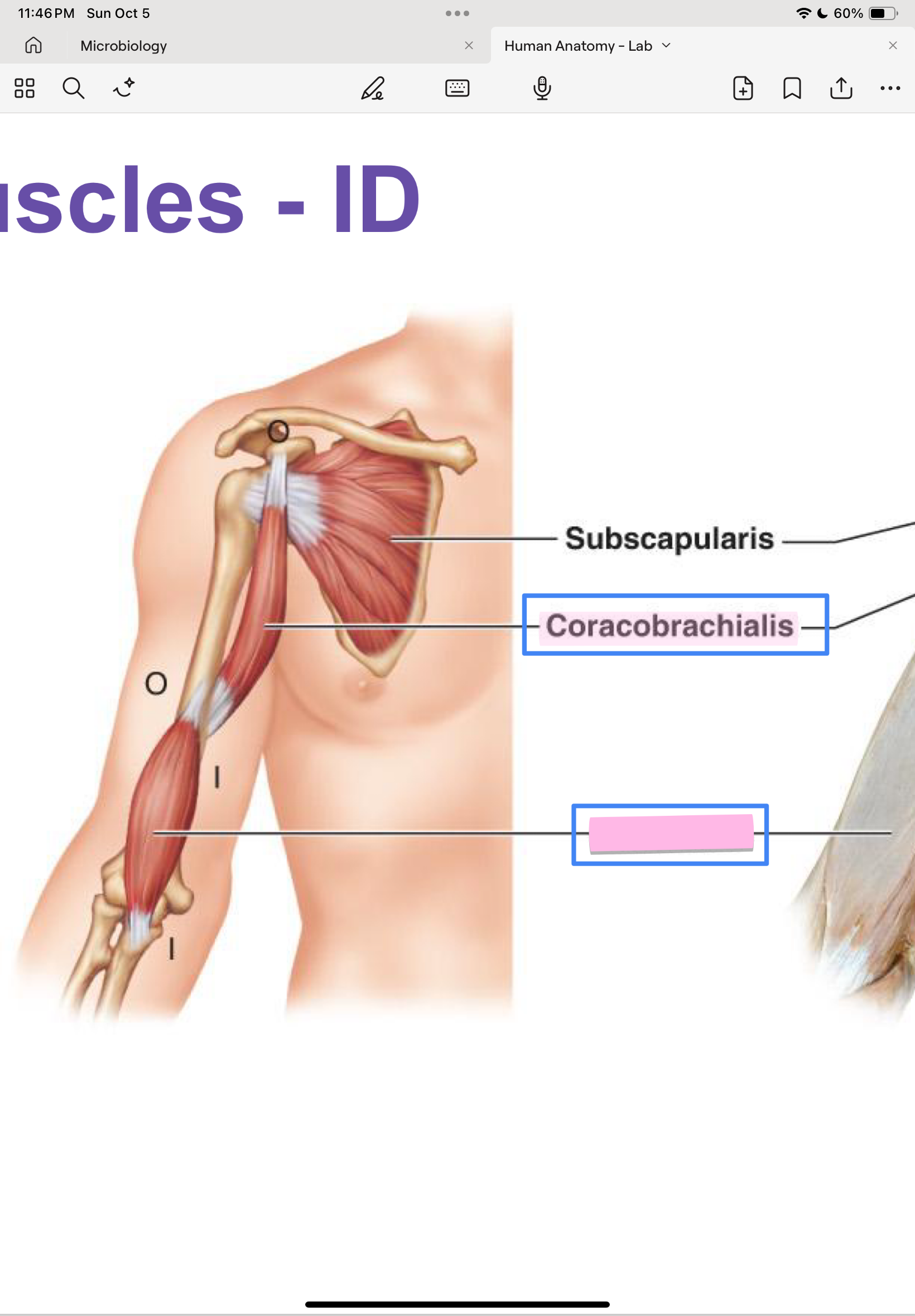
Brachialis
humerus
ulna
flex forearm
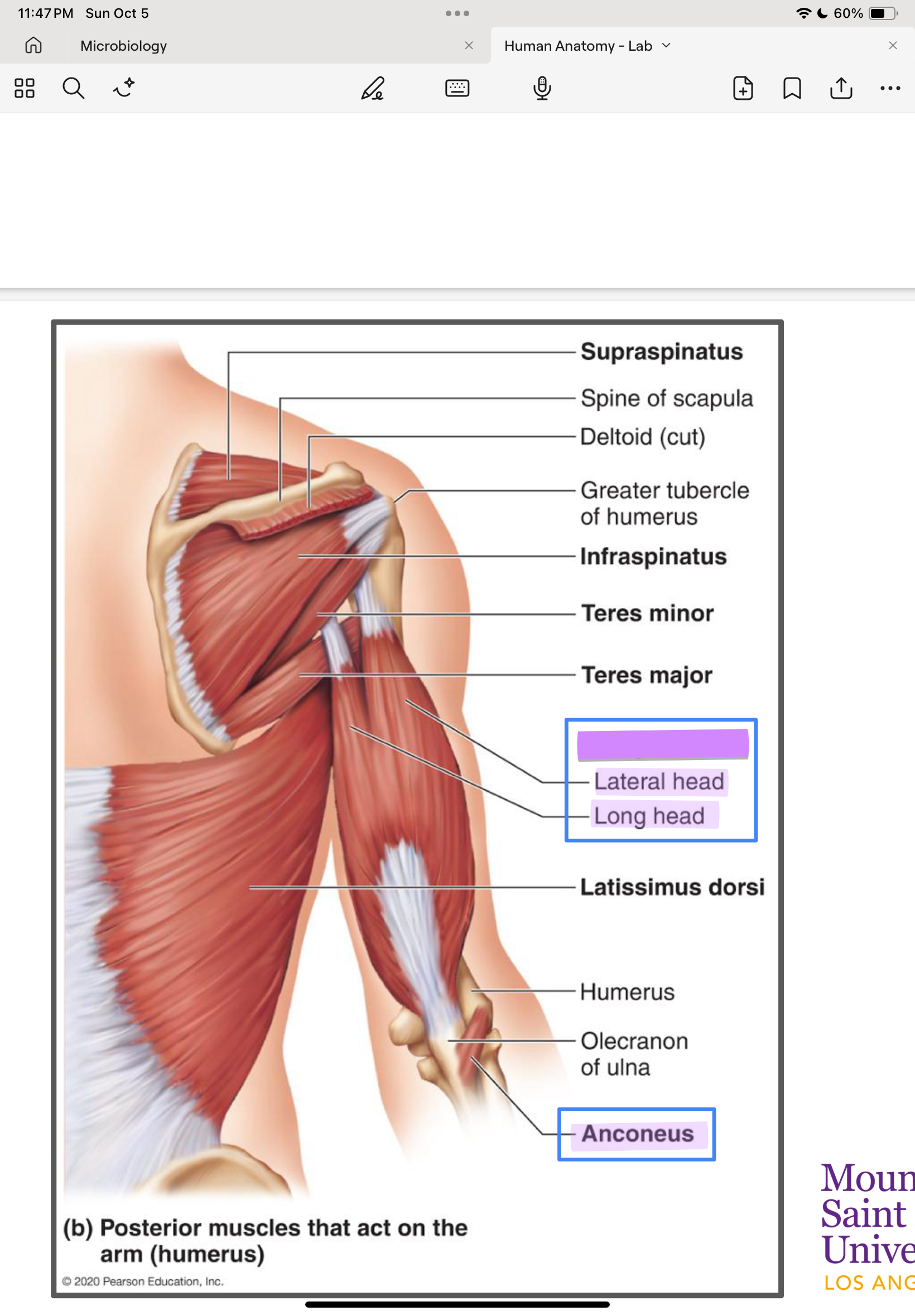
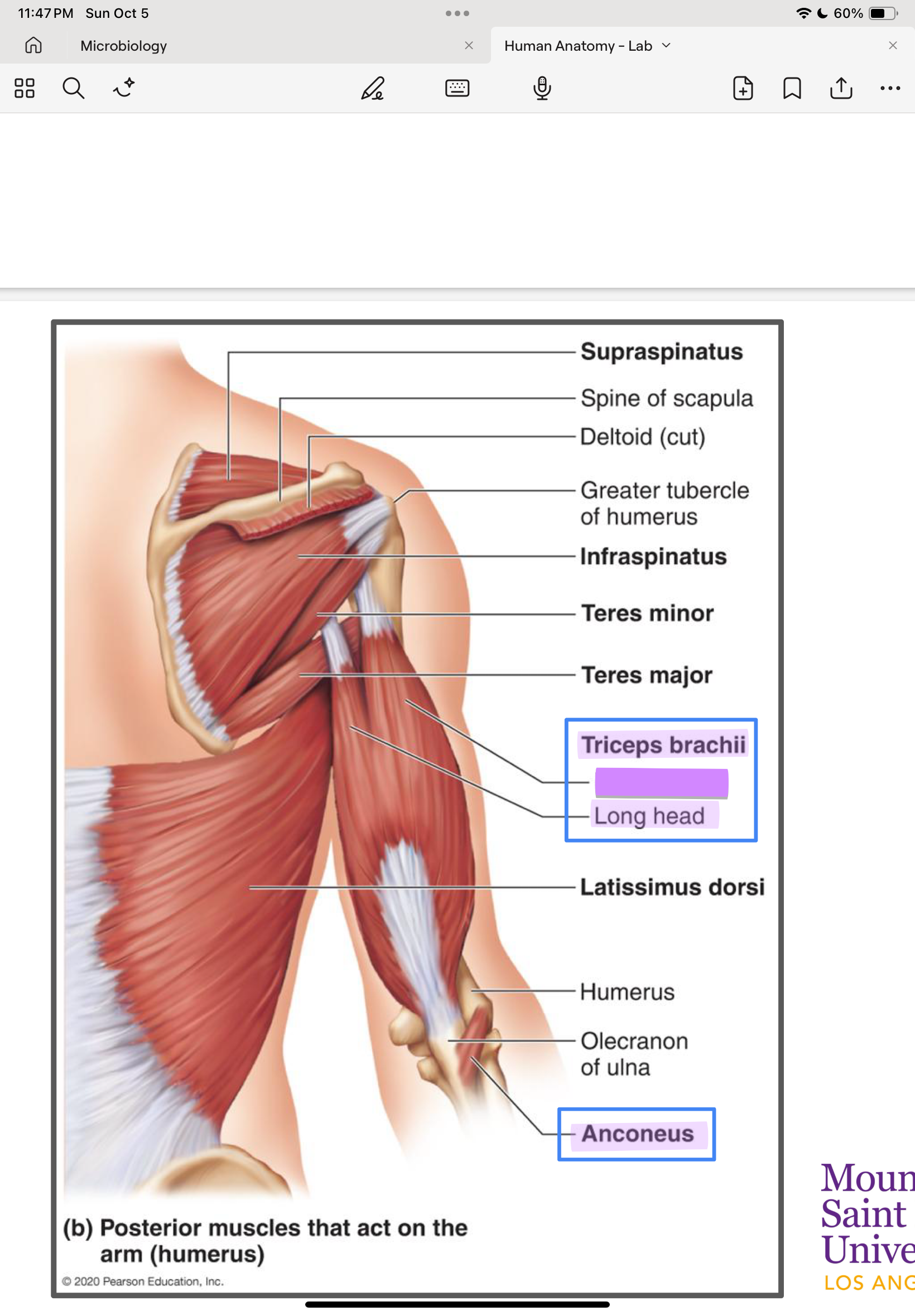
Triceps brachii (long, lateral, medial)
Long head: scapula
Lateral & medial: humerus
ulna
forearm extension
Anconeus
humerus
ulna
Synergist of triceps for forearm extension
deltoid
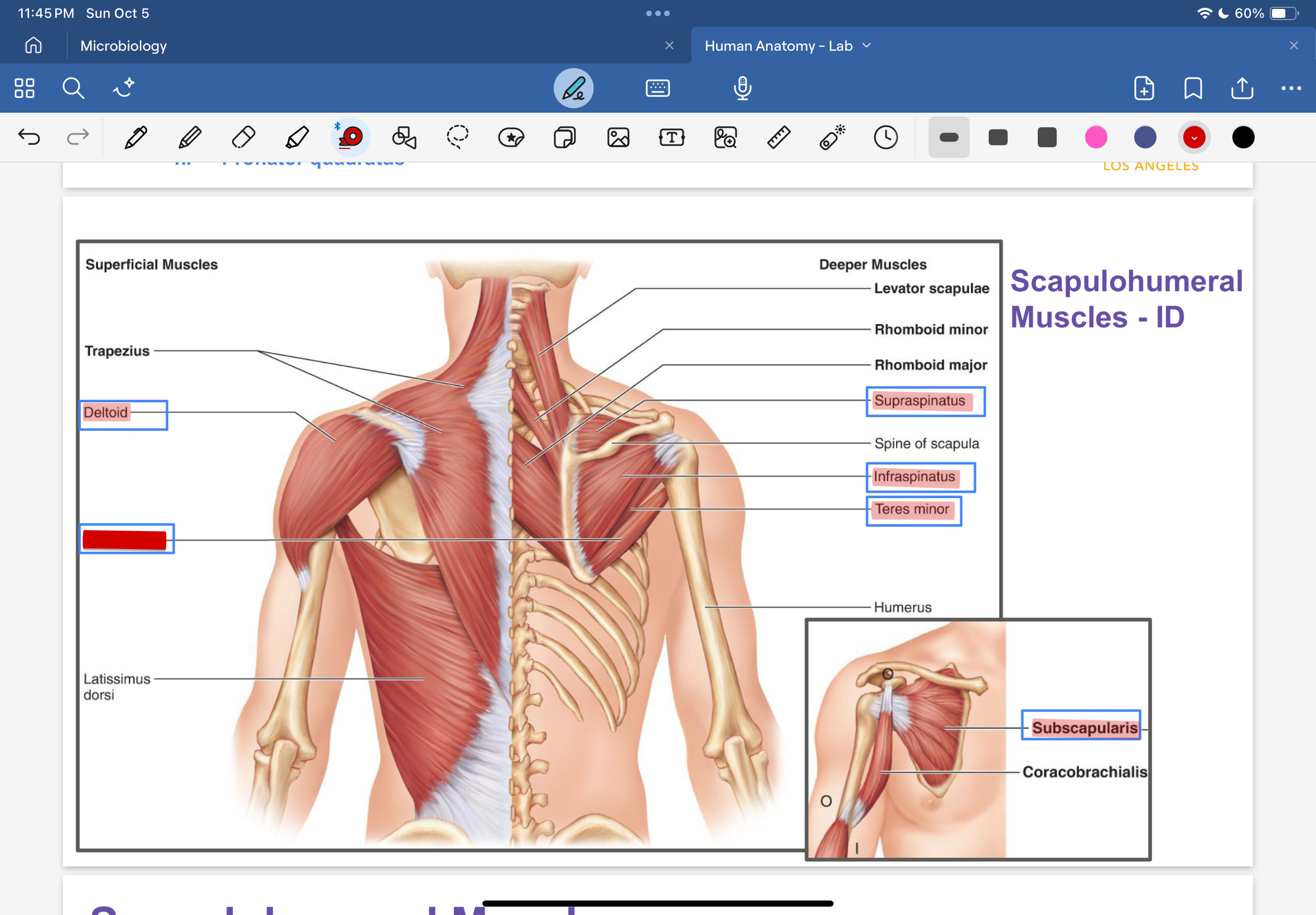
teres major
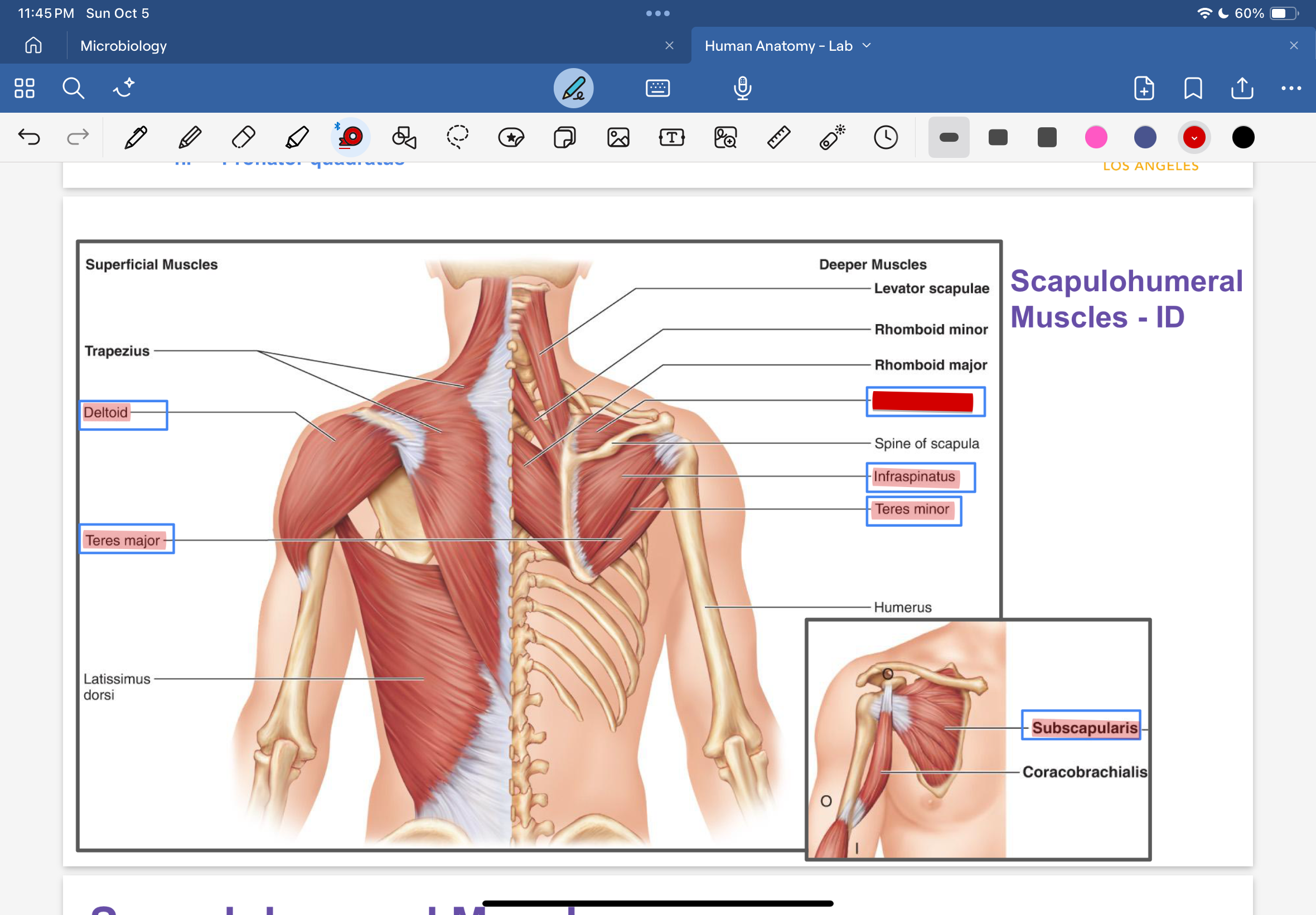
supraspinatus
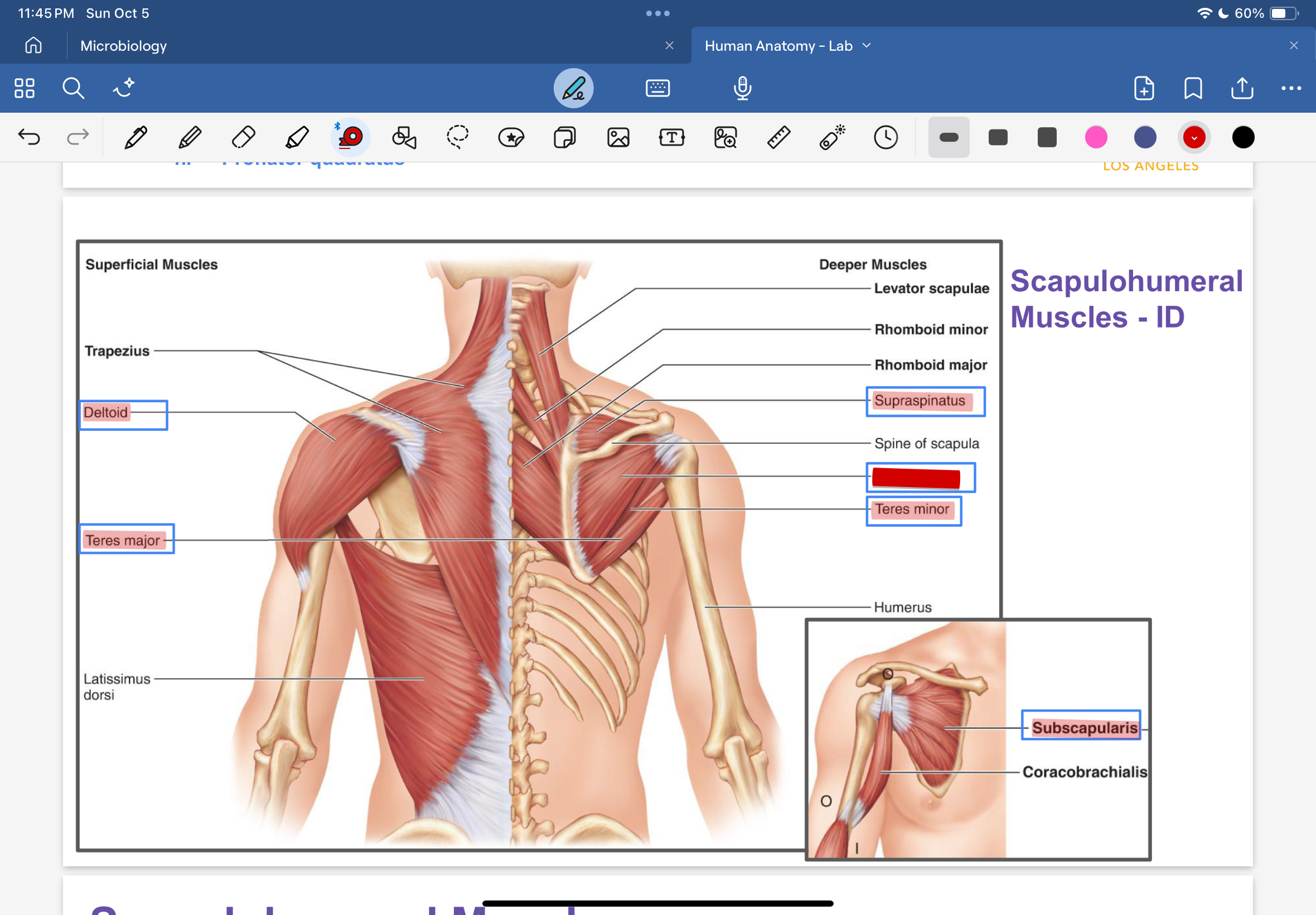
infraspinatus
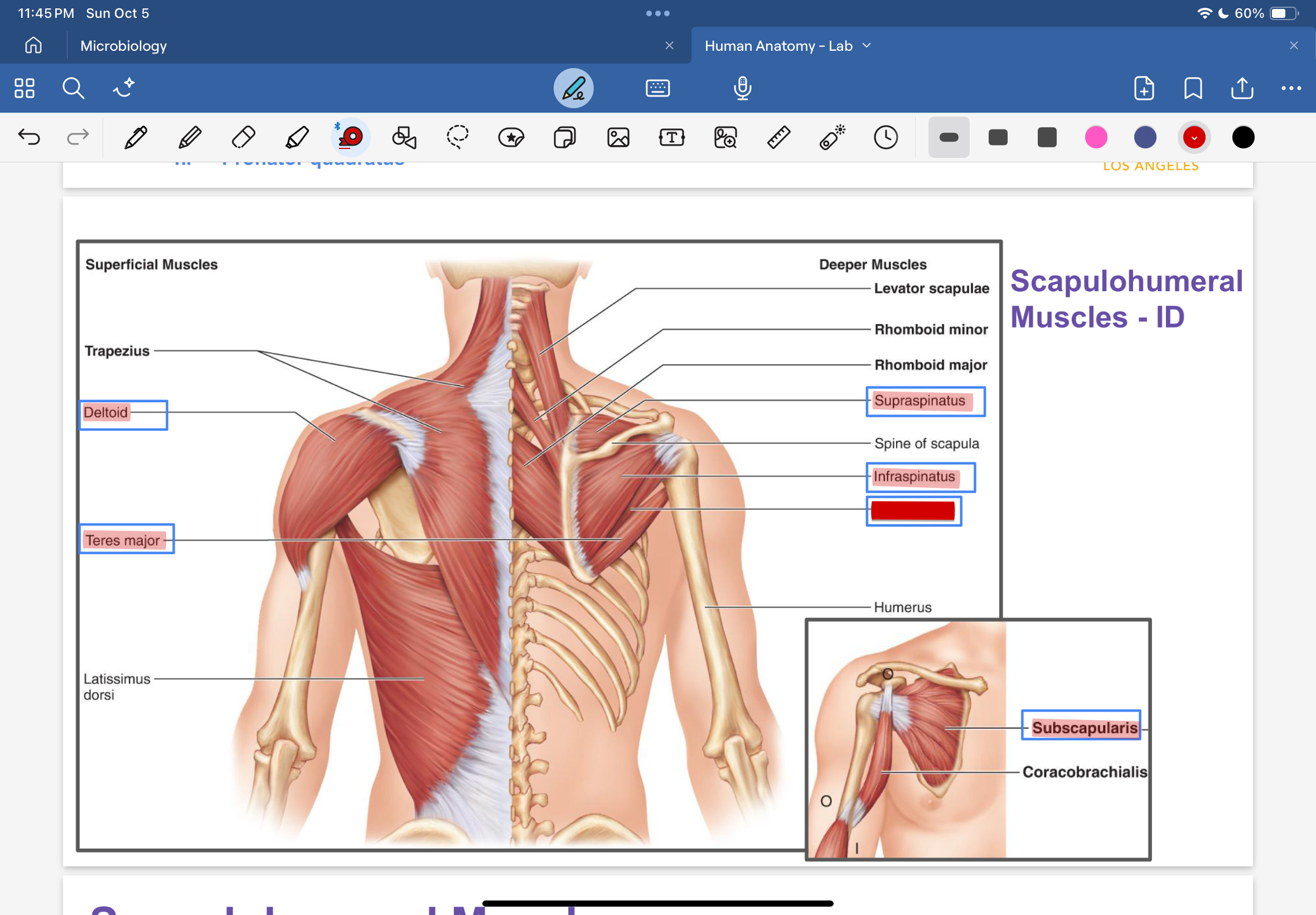
teres minor
subscapularis
biceps brachii
biceps brachii: long head
biceps brachii: short head
coracobrachialis
brachialis
triceps brachii
triceps brachii: lateral head
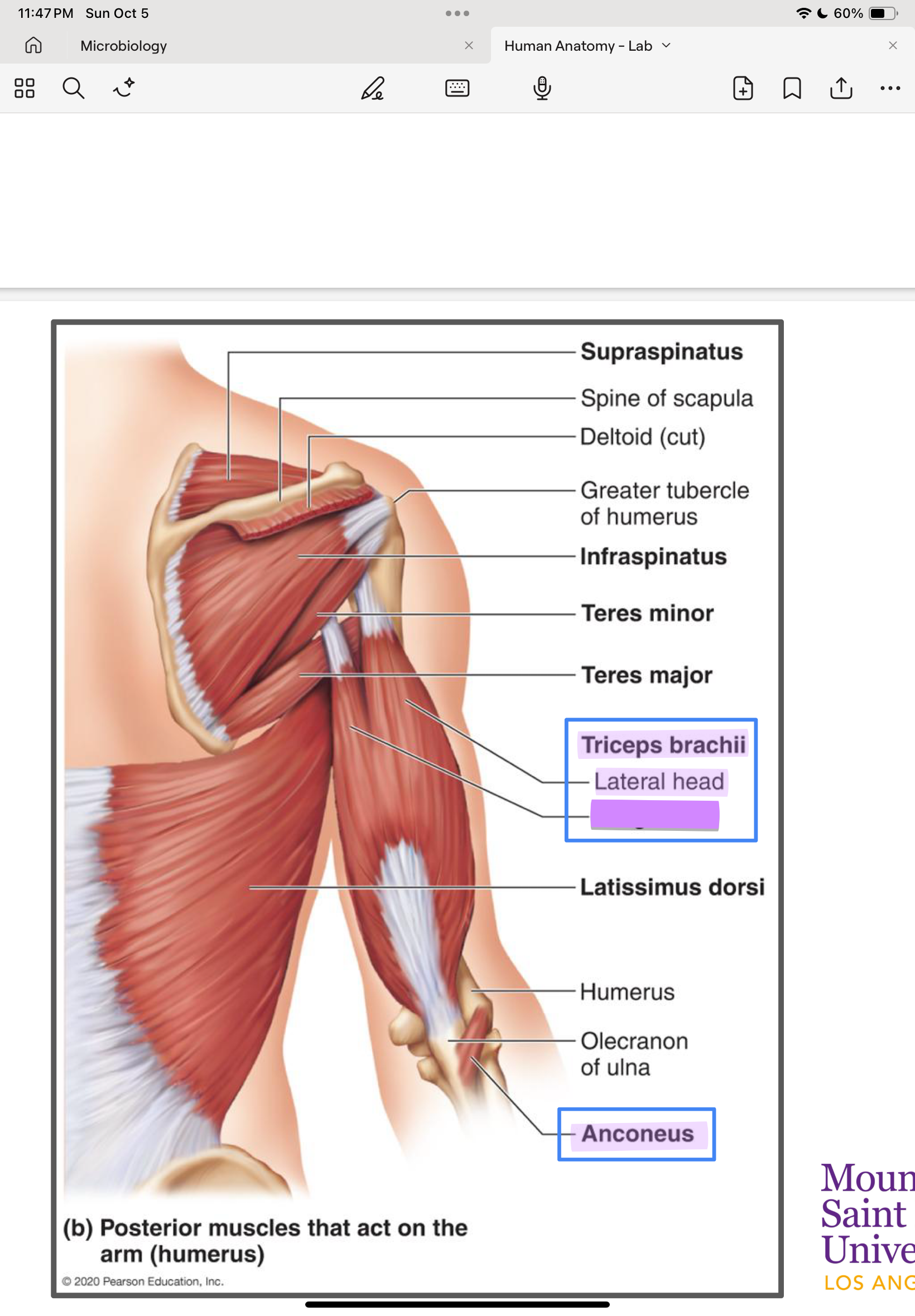
triceps brachii: long head
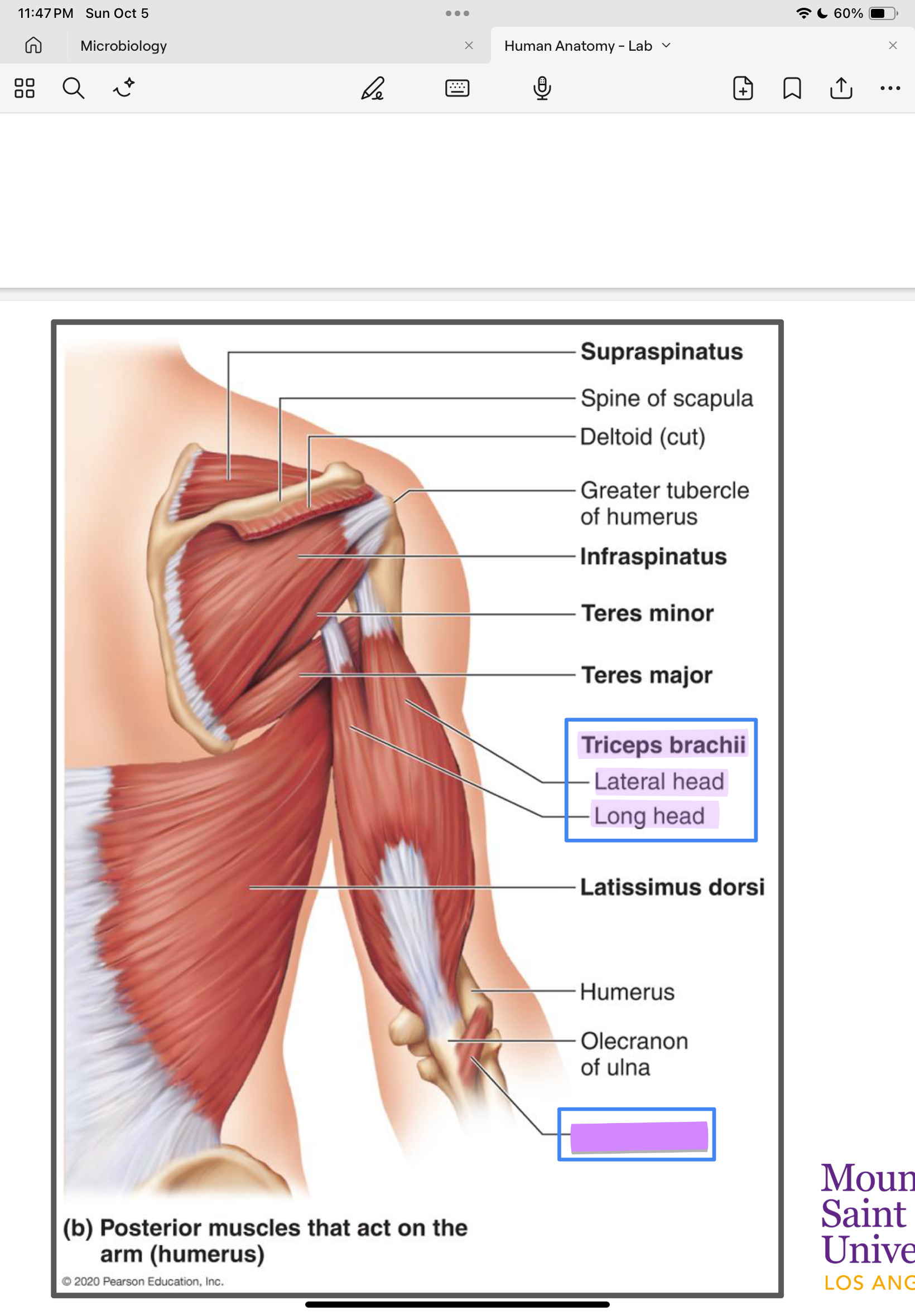
anconeus
pronator teres
humerus, ulna
radius via common tendon
pronates forearm
flexor carpi radialis
humerus
metacarpals II & III
hand flexion
palmaris longus
humerus
palmar aponeurosis
tenses skin during hand movement
flexor carpi ulnaris
humerus, ulna
pisiform, hamate, 5th metacarpal
middle phalanges of digits II-V
flexor digitorium superficialis
humerus, radius, ulna
middle phalanges of digits II-V
finger flexion
flexor digitorium profundus
ulna and interosseous membrane
distal phalanges of digits II-V
flexes distal phalanges of digits II - V
flexor pollicis longus
radius and interosseous membrane
distal phalanx of the thumb
flexes distal phalanx of thumb
pronator quadratis
ulna
radius
pronation of the forearm
brachioradialis
humerus
distal radius
flexes forearm
extensor carpi radialis
(brevis/ longus)
humerus
brevis to metacarpal II
longus to metacarpal III
extends and abducts the wrist
extensor digitorium
humerus
extensor expansion of distal phalanges II-IV
finger extension II-IV
extensor digiti minimi
humerus
extensor expansion of distal phalanx V
extends little finger
extensor carpi ulnaris
humerus, ulna
radius
asssts biceps with supination
supinator
humerus, ulna
radius
assists biceps supination
abductor pollicis longus
radius and ulna, interosseous membrane
1st metacarpal of the thumb, trapezium
abduct and extend thumb
extensor pollicis (brevis/longus)
radius and ulna, interosseous membrane
brevis to proximal phalanx of the thumb
longus to distal phalanx of the thumb
extends thumb
extensor indicis
ulna, interosseous membrane
tendons of extensor digitorum, extensor expasion of index finger
extends index finger
abductor pollicis brevis
abducts thumb
flexor pollicis brevis
flexes thumb
opponens pollicis
opposition
palmaris brevis
helps with palmar grasp
abductor digiti minimi
abducts little finger
opponens digiti minimi
helps with opposition
lumbricals
flex the fingers at the metacarpophalangeal joints while extending the interphalangeal joints.
dorsal interossei
abduct finger
palmar interossei
adduct fingers