Physics-Translational Motion
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
what is distance?
distance is the length of the path followed by a moving object, distance is the number of steps taken
distance is a scalar quantity
what is displacement?
displacement is the position of an object compared to an origin (often a starting point), displacement is a straight line distance in steps between where you are now and some reference point (usually where you started)
displacement is the vector counterpart of distance
distance vs displacement units
distance (the length of the path) can be described with just a number of units, like 5 meters or 4 feet, whereas displacement requires a number of units and a direction, like 5 meters North or 4 feet down
displacement is never the same thing as distance, with exception
exception is displacement equal to distance for linear motion in one direction
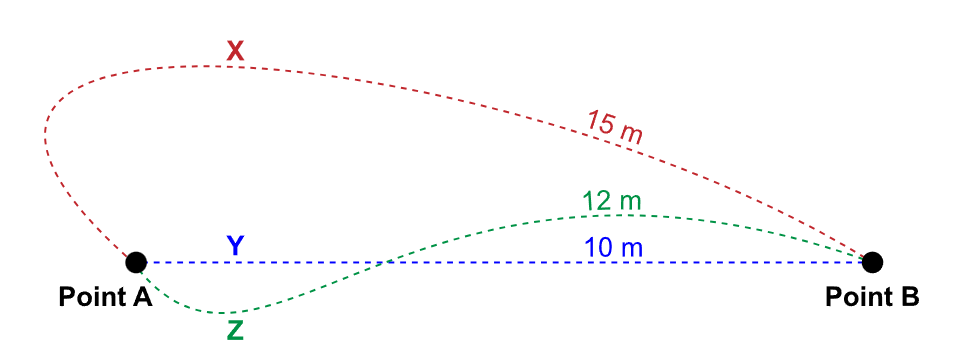
the person’s displacement
independent of path, displacement is the straight line distance and direction from point A to point B
what is speed?
speed is distance traveled divided by time traveled, speed is a scalar
what is velocity?
velocity is displacement traveled divided by time traveled
what is average velocity?
change in velocity over change in time
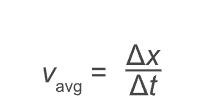
what is instantaneous velocity?
change in displacement (dx) at a given instant (dt)
the magnitude of instantaneous velocity is equal to what?
speed at that instant
if the path continuously changes, what happens to the instantaneous velocity?
the direction of the velocity is continuously changing, so the instantaneous velocity is also continuously changing
what is acceleration?
acceleration is the rate of change in velocity

what happens when acceleration points in a direction that is neither parallel nor antiparallel to velocity?
it indicates a change in direction of velocity
what is translational motion?
the movement of an object along a straight line or a curved path without rotating
what does constant acceleration mean?
the direction and magnitude of acceleration must remain constant
what is rectilinear motion?
motion along a straight line
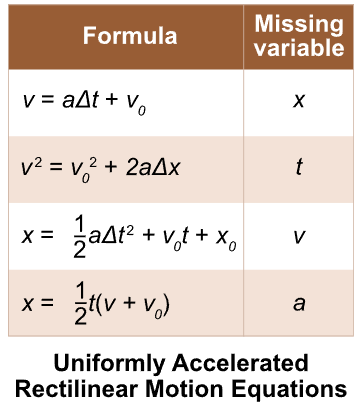
what are the uniformly rectilinear motion equations?
when appropriate, you may use delta t as an approximation for dt
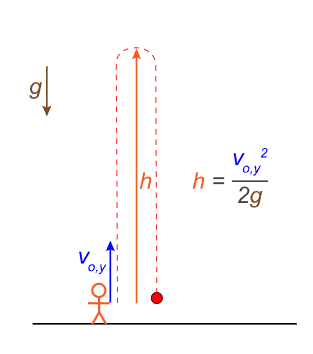
what is the projectile motion diagram?
vertical acceleration is given by gravity = 9.8 m/s²
for horizontal motion, acceleration is a constant zero
for a projectile with vertical velocity (vo) at an angle theta, the initial vertical velocity (vo,y) is equal to vosin(theta)
the horizontal velocity (vx) remains vocos(theta)
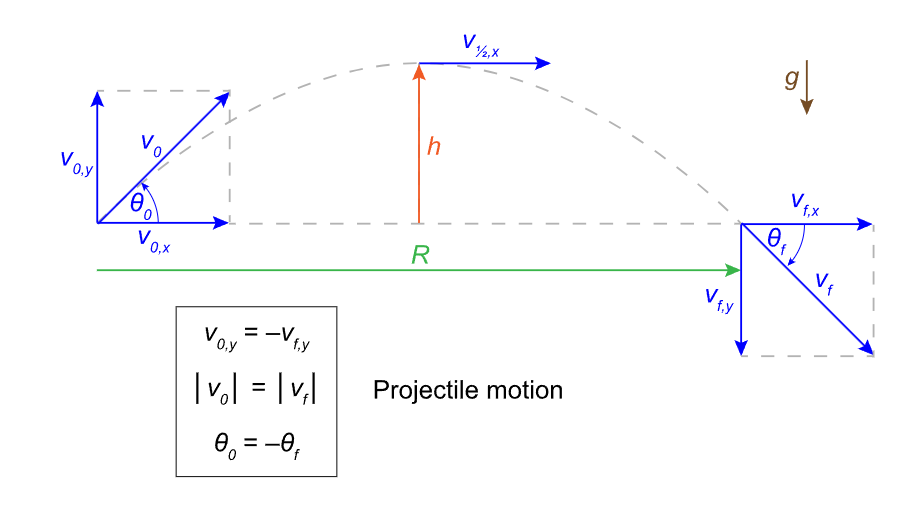
what is peak height?
at peak height, the projectile has a vertical velocity of 0 m/s, but even at this instant, is still accelerating downwards -10 m/s²