Diagnostic imaging quiz 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
The four radiology rights
Do the right exam
Do it the right way
Do it on the right person
Do it at the right time
ALARA
Radiology exams are performed based on this principle
“As low as reasonably achievable”
Radiology
The science dealing with X-rays and other high-energy radiation, especially the use of such radiation for the diagnosis and treatment of disease.
Radiologists are consult physicians.
If you are unsure of the best test to order for any given pathology, ask the radiologist.
Illuminators (view boxes)
The “old” standard
PACS
Picture archiving and communication system
Ability to store and electronically share information
Basics of image viewing
Identify:
Type of study done?
Patient name, age, DOB
Date and time of exam
Left/Right markers
Previous films?
In AP, PA, and oblique projections
Viewed as if the patient is looking at you
Exceptions:
Hands, wrist, feet: viewed as if you are looking at your own
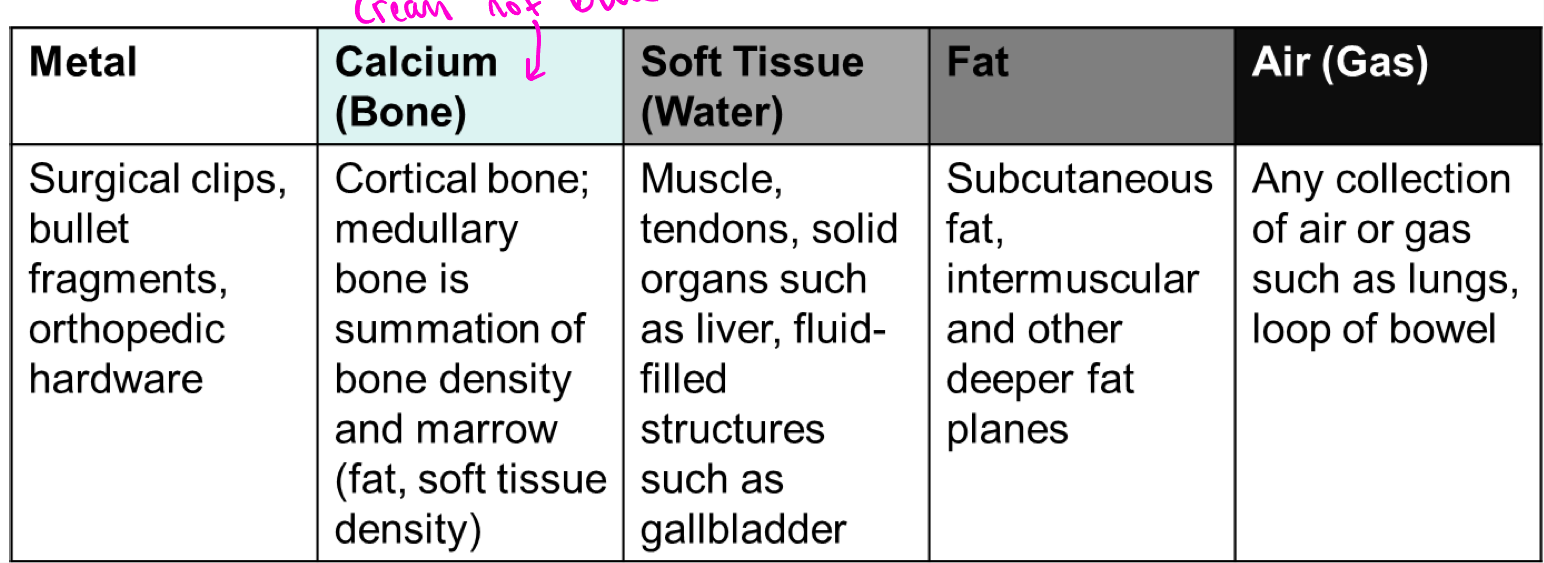
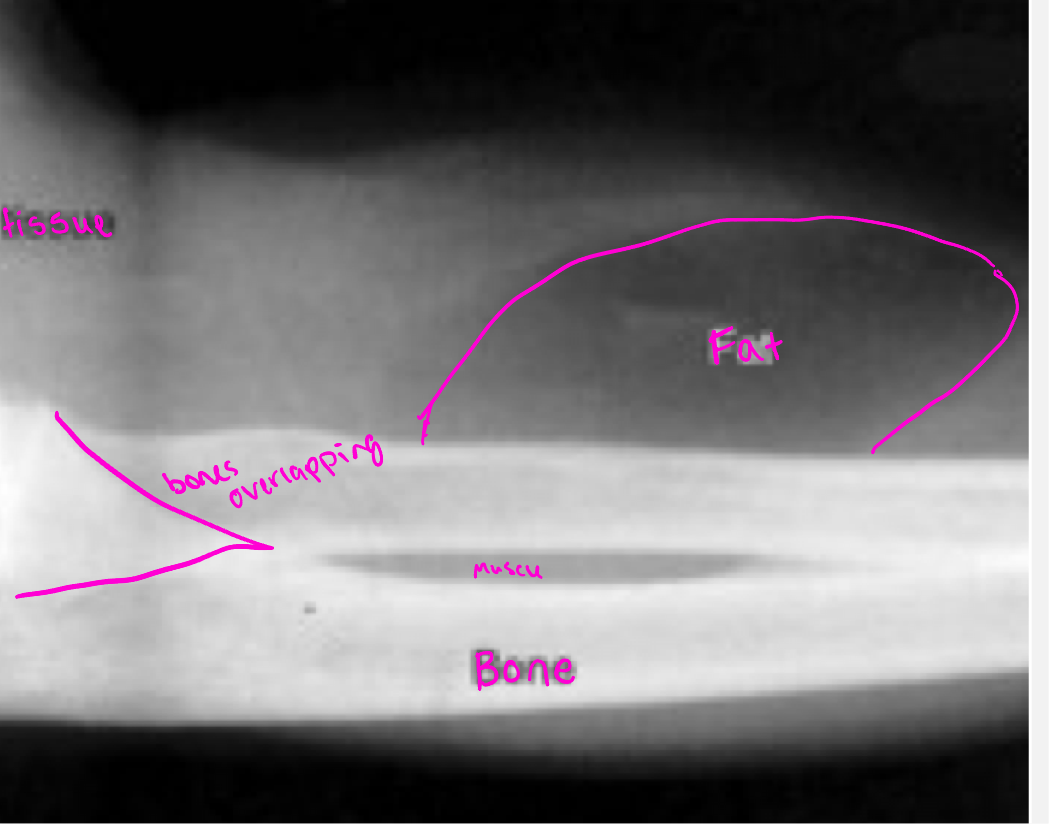
Radiographic densities
The human body is composed of four basic radiographic densities:
Air, Fat, Water (soft tissue and blood), and Bone
Summation density
reflects the density and thickness of intervening structures (two bones overlapping appear brighter than an individual bone)
Radio-opaque/hyperdense
Absorbs photons, demonstrated on images as white
Metal and bone are examples
Radiolucent/hypodense
Materials that allow x-rays to pass through with minimum absorption appear black
Fat and air are examples
Radiographic densities
Four out of 5 densities
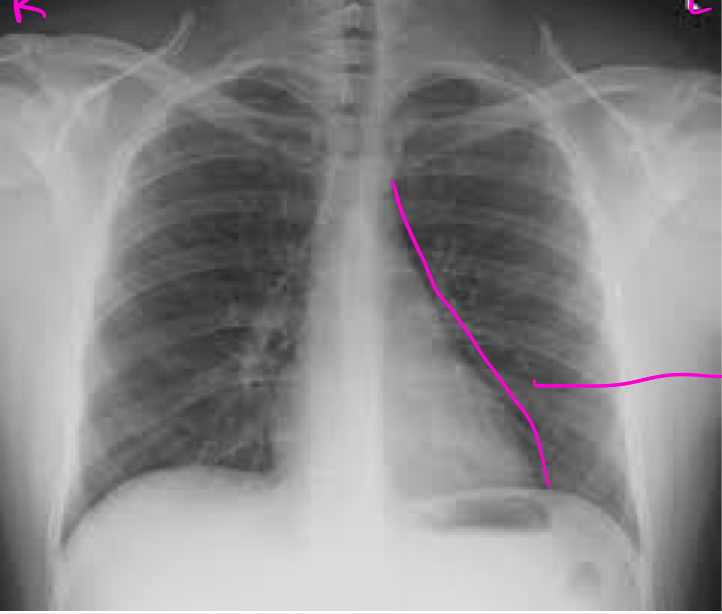
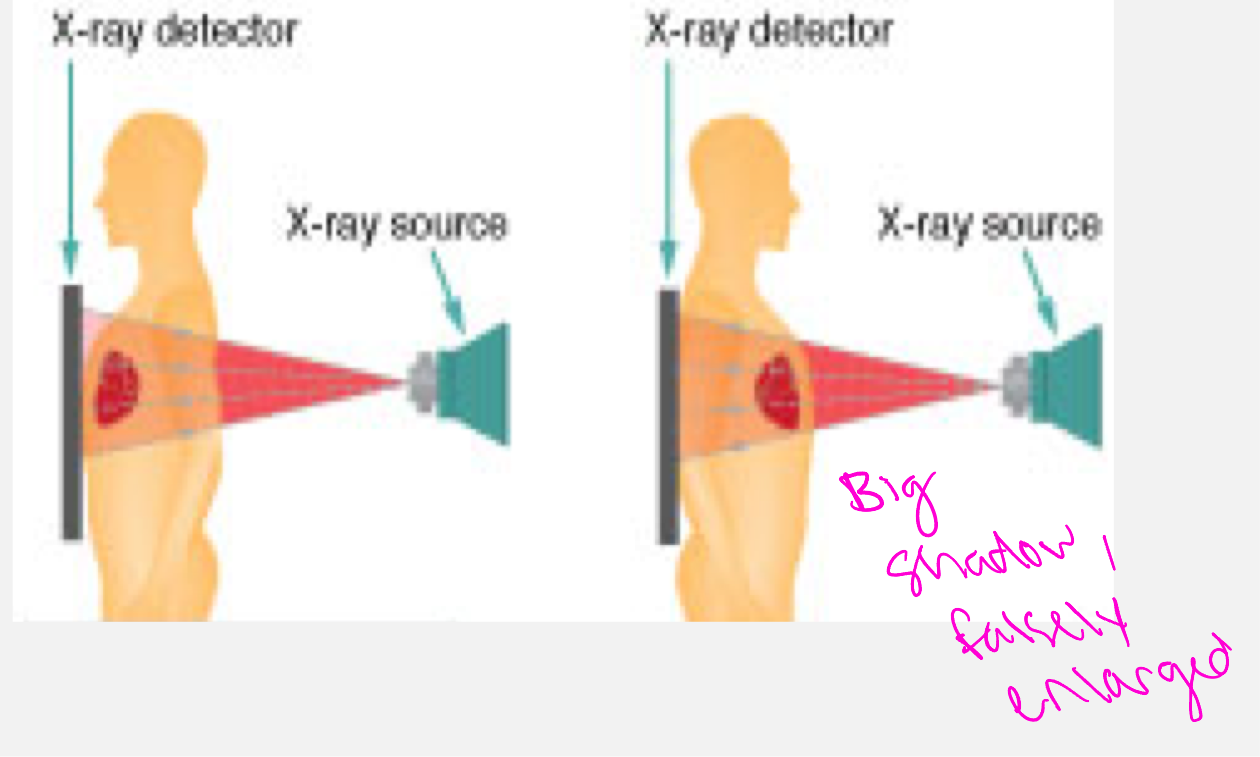
PA view
Beam goes back to front
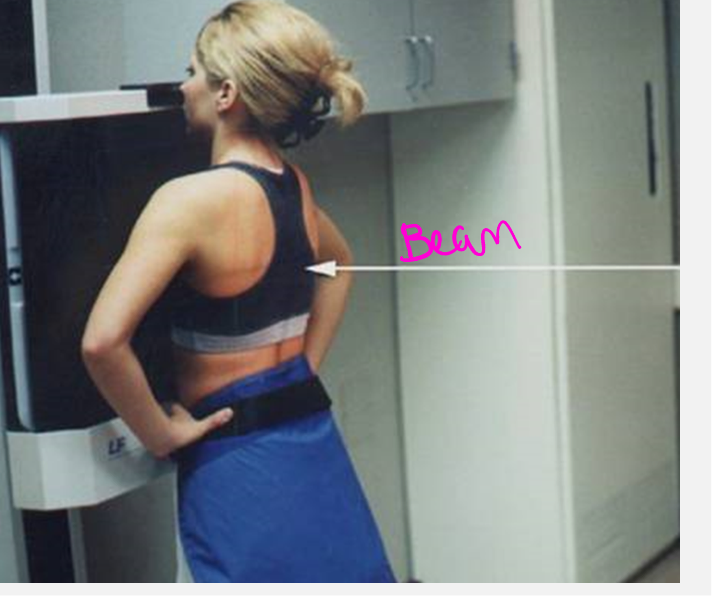

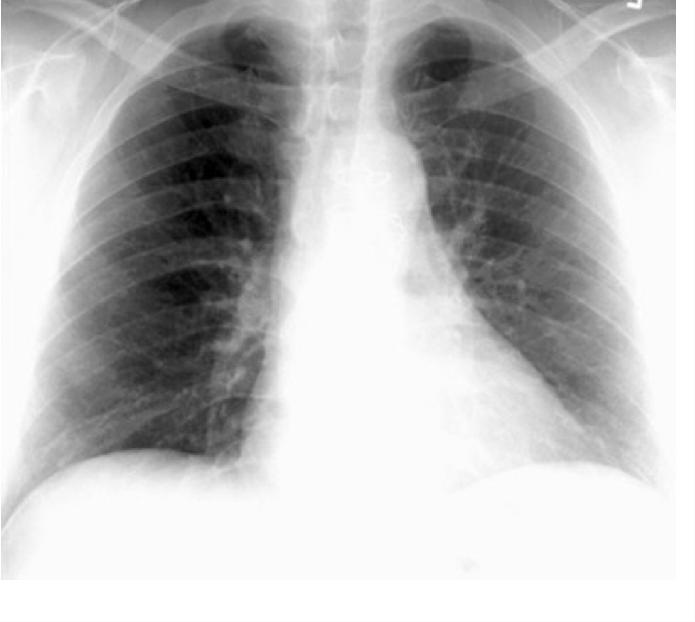
AP view
beam goes front to back
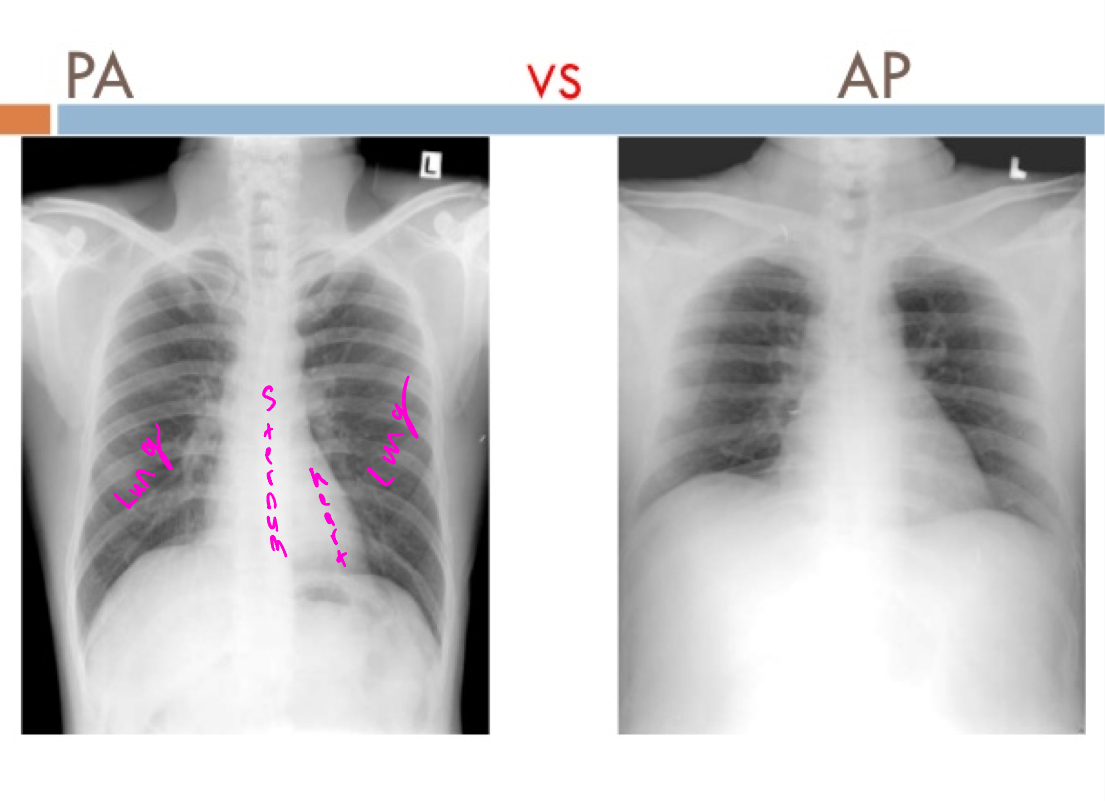
PA vs AP
X-ray comparison
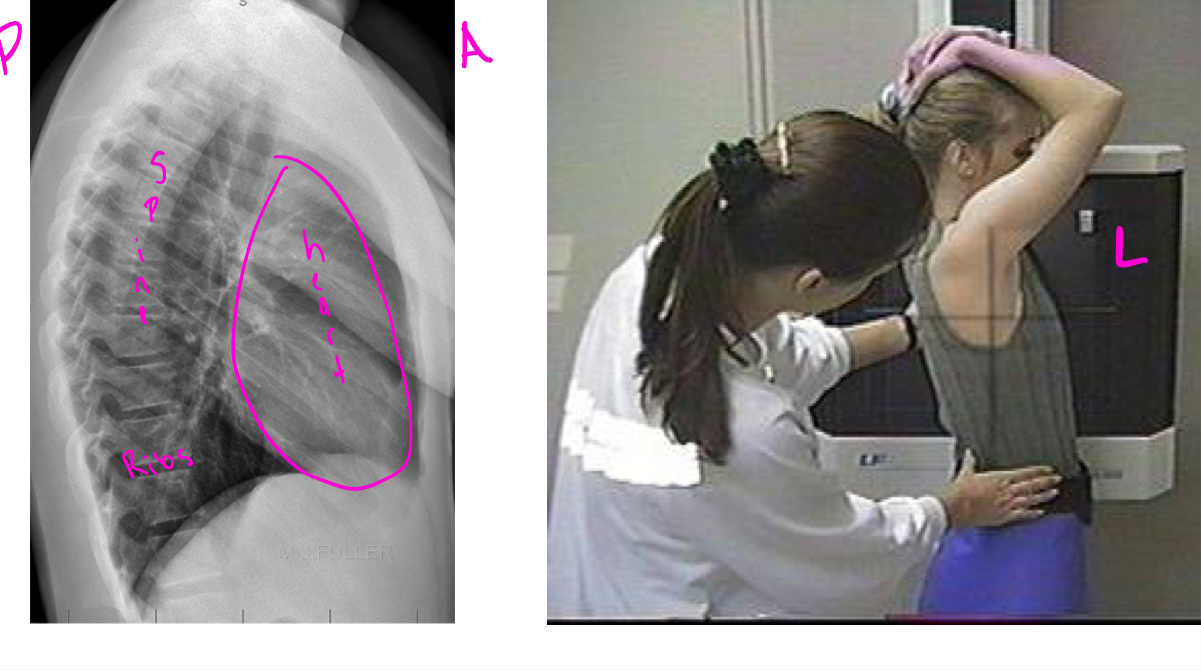
Lateral/side view
x-ray beam passes from one side of the patient or body to the other
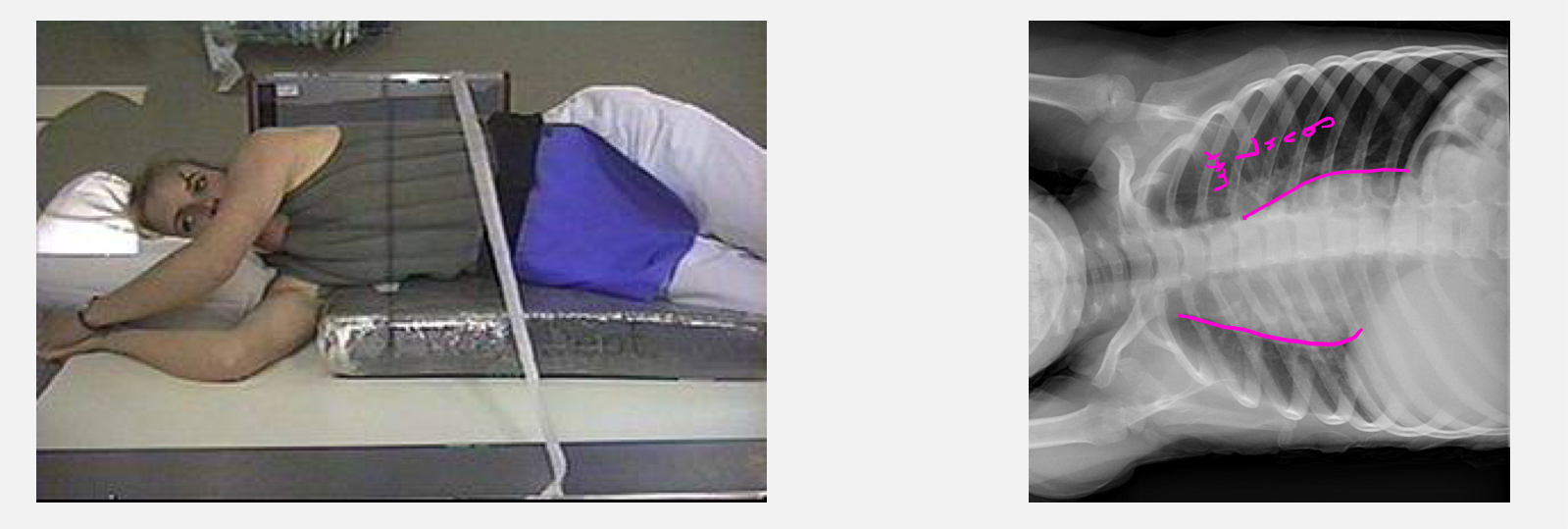
Decubitus
Patient who is lying down, with the central ray horizontal. Taken front to back. Useful when looking for abnormal fluid or air collections. Air rises, fluid falls.
Oblique
Rotated view. this is left lateral oblique. Useful for shoulder joint dislocation or fractures
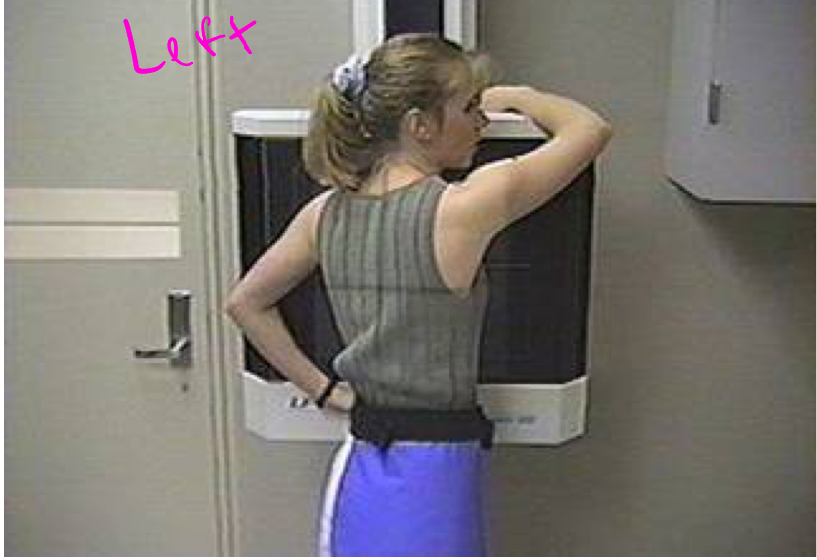
Grashey view
Oblique shoulder
Summary of positions
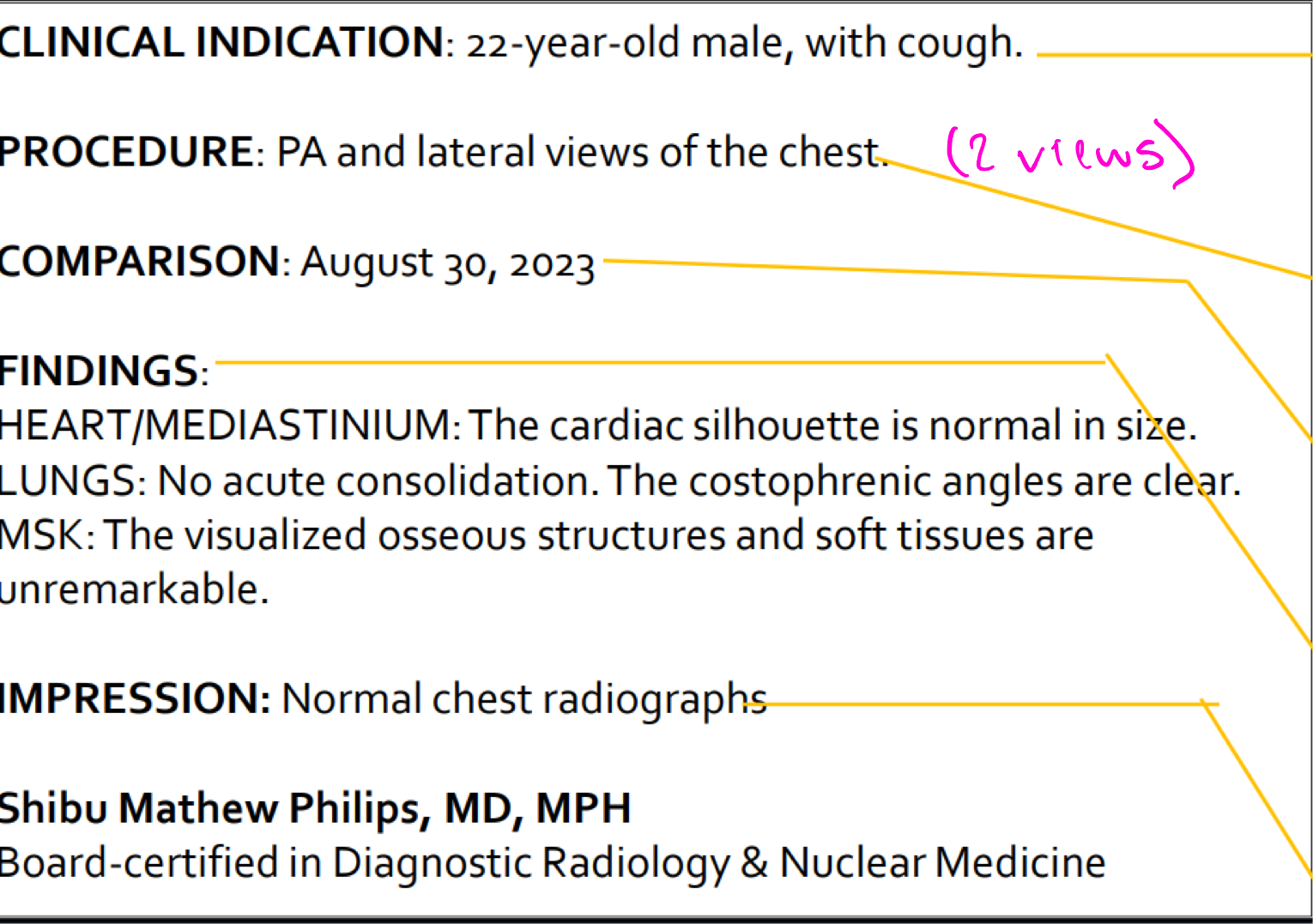
Radiology report breakdown
Indication- Why are we doing the study?
Procedure- What study is being done?
Comparison- what previous imaging do they have that we can compare?
Findings- What was evaluated on the study?
Impression- what was the outcome of the study?
Signature- Radiologist's signature with time stamp and date
Radiology modalities
X-ray/mammography
Fluoroscopy (OR)
CT scan (lot of radiation)
MRI (expensive, long, no radiation)
Nuclear medicine (invasive)
Ultrasound (miss a lot)
Radiation
Ionizing radiation in large doses is known to produce cell mutations that can lead to forms of cancer and cell anomalies.
Generally accepted principle is ONLY MEDICALLY NECESSARY diagnostic exams should be performed
Teratogens
Drugs, chemicals, infections, or other environmental factors that can cause abnormal fetal development.
Studies using x-ray should be avoided during pregnancy/teratogenic times
Radiation basics
Routine radiography (x-ray) requires two views for most diagnoses
Radiation has a cumulative effect, benefit should outweigh risk
Most radiosensitive body parts are eyes, thyroid, breasts, and gonads (lead covers)
Radiography/X-ray/Plain films
medical images that are “shadows” projected on a flat plate when x-rays are passed through the patient
x-ray/mammography compared to other modalities
Pros:
Low cost
Generally low radiation dose
Fast and available
High spatial resolution- ability to differentiate two adjacent structures as being distinct from one another
Cons:
Misleading appearance of overlapping structures
Poor soft tissue contrast resolution- ability to distinguish between differences in intensity in an image
x-ray common uses
Evaluation of bones- dense bone is surrounded by muscle and fat
Fractures, bone tumors
Initial evaluation of abdominal pain
Evaluation of solid organs in the abdomen is limited, but the bowel gas pattern can be readily seen (alterations in pattern may indicate disease)
CXR- due to different densities of internal structures
can get a detailed exam of the lung parenchyma, pulmonary blood vessels, and of the heart
Plain x-ray prep?
Non routinely needed
Patient education: tell patient x-ray will take 5-10 minutes
Mammography
x-ray of the breast
Patient ed/prep:
No powders, perfumes, lotions, or deodorant prior to exam (summation density, lump)
Fluoroscopy
Live action x-ray viewed on a closed-circuit TV
Used for GI, GU, skeletal, pulmonary system imaging and angiography/interventional procedures
To evaluate specific areas of the body, includes the bones, muscles, and joints, as well as solid organs, such as the heart, lungs, or kidneys
Fluoroscopy examples
Barium x-rays (swallowing test, contrast GI test, obstruction)
Cardiac catheterization (dilate BV, make sure no blockage)
Arthrography (leakage in joint space)
Intravenous pyelogram (kidney stones or infection)
Hysterosalpingogram (fertility test, through cervix- fallopian tubes)
Percutaneous vertebroplasty (putting vertebrae together)
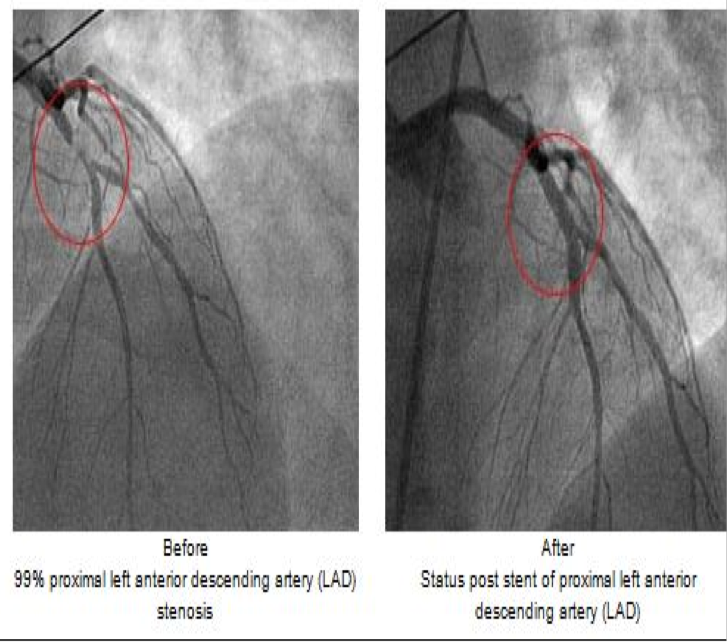
Cardiac catheterization
Fluoroscopy used as an adjunct to see the flow of blood through the coronary arteries in order to evaluate the presence of arterial blockages
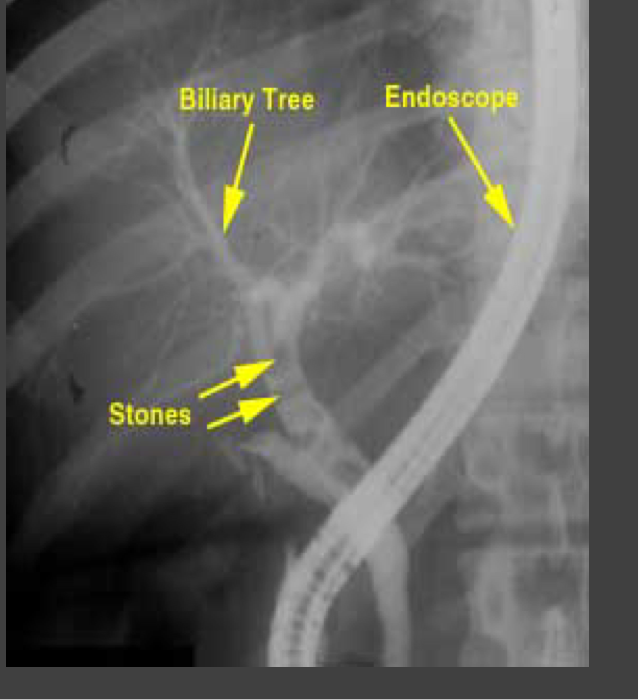
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Endoscope is passed into the duodenum and contrast is injected into the bile ducts and/or pancreatic duct
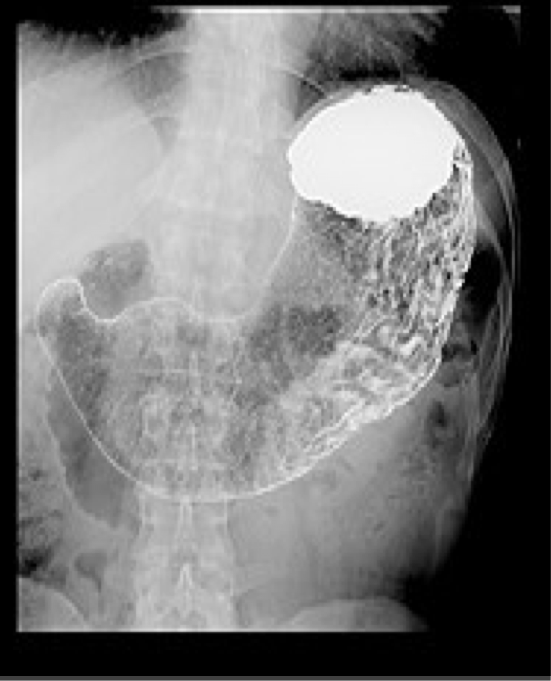
Upper GI (barium)
Evaluation of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum using oral contrast.
Detect polyps, masses, malpositioned bowel, motility problems, GE reflux, and hiatal hernia
Fluoroscopy uses
Enema exam (go up the rectum)
Evaluation of the colon using rectal contrast
Useful to detect small polyps or other precancerous lesions
Barium swallow
Evaluation of the mouth, esophagus and swallowing mechanism using oral contrast
Fluoroscopy prep/patient ed
Depends on what is being imaged
Usually, for GI studies NPO for 6 hours before study
For rectal contrast, you may need bowel prep
For spinal exams- no prep
Computed Tomography = CT scan
Combines x-ray and computer technology- digital processing is used to generate a 3D image of the inside of an object from a large series of 2D images taken
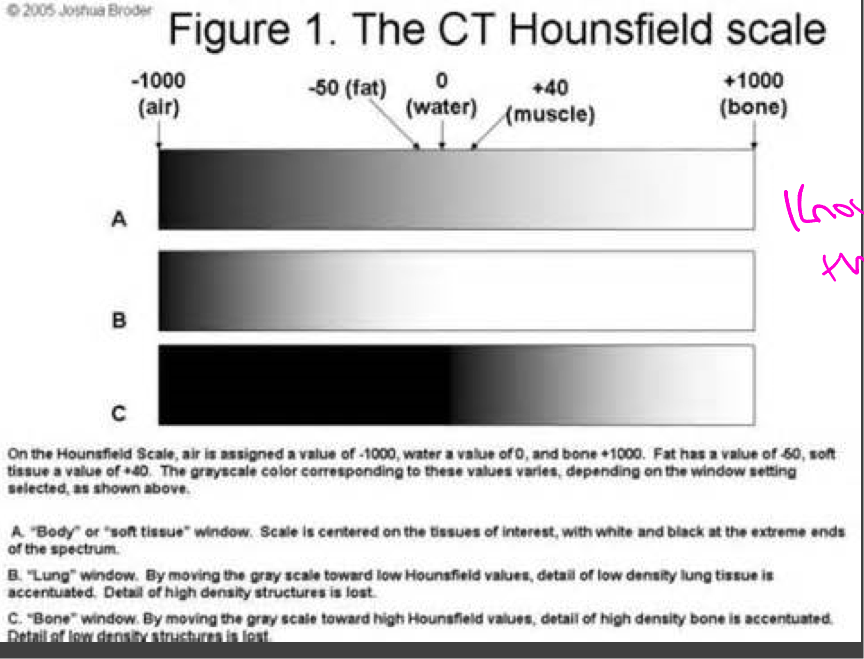
Hounsfield units
Characterizes the relative density of a substance (amount of x-ray radiation absorbed by each element in tissue)
Bone/metal: 1000 HU (brightest)
Liver: 40-60 HU
White matter: 46 HU
Grey Matter: 43 HU
Blood: 40 HU
Muscle: 10-40 HU
Kidney: 30 HU
CSF: 15 HU
Water: 0 HU
Fat: -50 to -100 HU
Air: -1000 HU (darkest)
Hounsfield scale
CT window- range of the densities that are compressed into shades of gray for viewing
Soft tissue, bone, lung window
CT imagine Pros/Cons
Intermediate cost
Much improved soft tissue evaluation compared to plain radiography
Fast and available
Higher radiation dose than plain x-ray (10-100 times more)
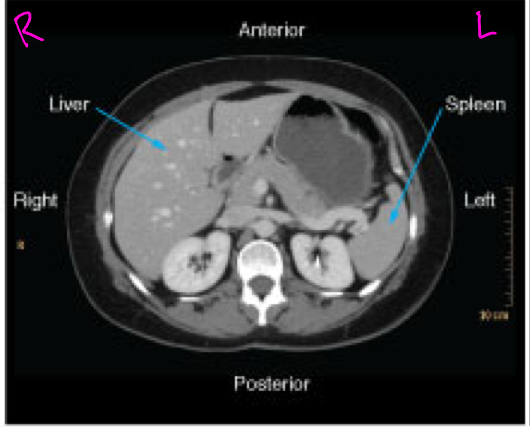
Axial CT images
Presented as if the viewer is standing at the foot of the patient’s bed; the patient’s right is to the viewer’s left; the anterior aspect of the patient is toward the top of the image
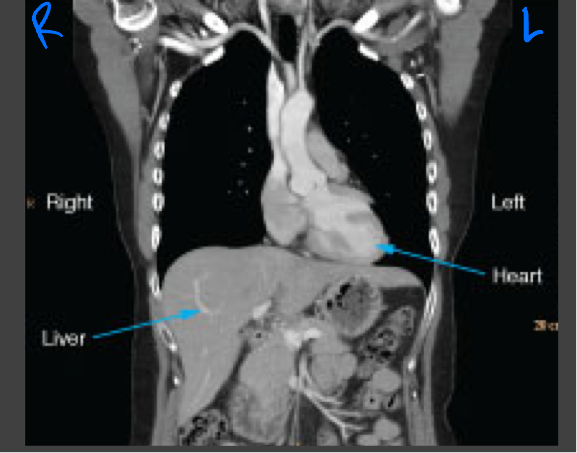
Coronal CT images
Viewed the same way that most radiographs are viewed: the images are oriented as though the patient is looking at you
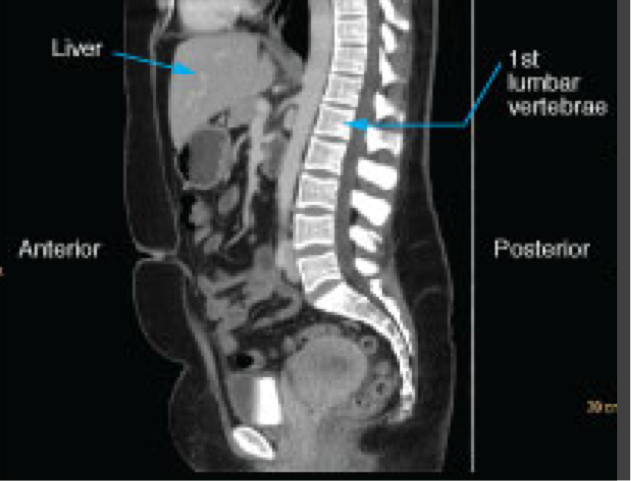
Sagittal CT images
Shown as though the patient is looking towards the viewer’s left
High resolution CT scan
Enhances resolution to show parenchymal abnormalities that may not show up on x-ray
Assesses interstitial lung disease (pulmonary fibrosis), chronic infiltrative lung disease, pneumoconiosis, bronchiectasis, and emphysema
Patient may be placed in the prone position to enhance the lung bases
Common uses for CT
Many- used extensively for chest, abdominal, neurological, and musculoskeletal disease
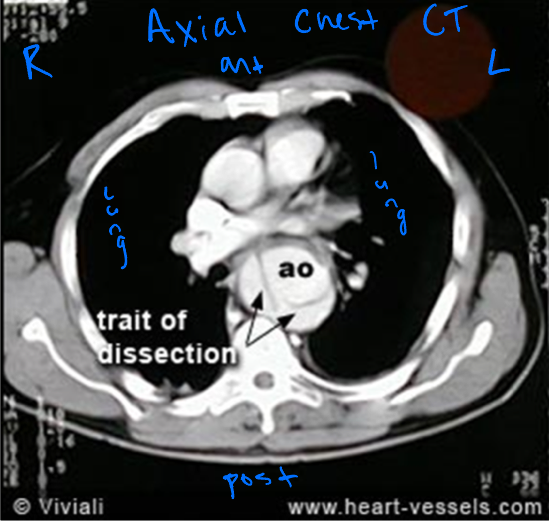
Chest CT
—for evaluation or detection of lung cancer, pathologies of the lung
—CT guided biopsies of chest lesions are also commonly performed
Abdominal and pelvic CT
Evaluating the abdominal organs for pathology such as acute abdomen or trauma
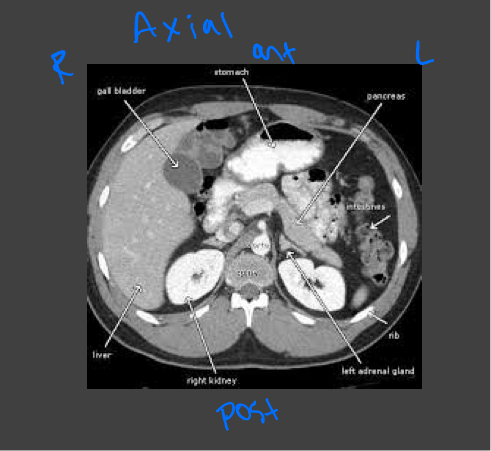
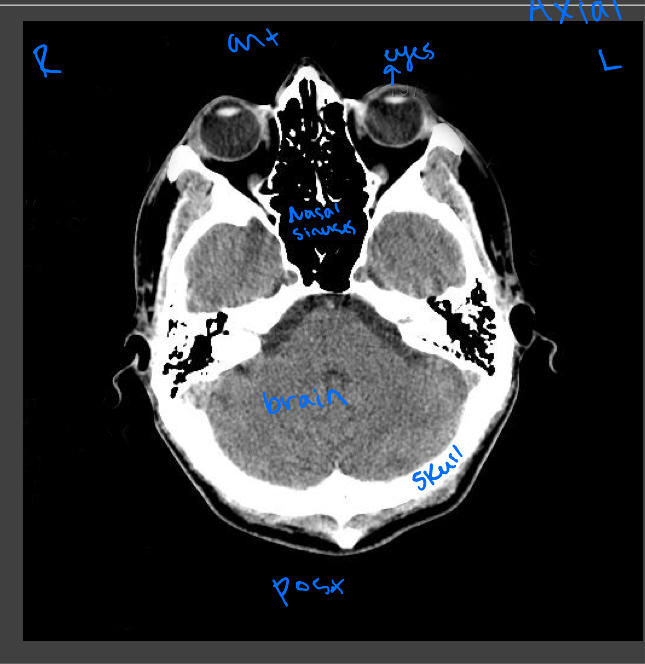
Head and neck CT
Evaluating traumatic injury or to rule out bleeding or fracture, intercranial bleeds
CT scan prep
May be performed with or without contrast (or both)
The contrast may be IV, oral, rectal, or a combo
May need to arrive 1 hour before exam
If scanning the abdomen/pelvis = NPO for 4 hours prior to the study
Fluoroscopy pros/cons
X-ray done in real-time: shows moving images of the internal structures of a patient
Similar radiation dose compared to CT
Low to intermediate cost
Operator dependent
Magnetic resonance imagine (MRI)
MRA = magnetic resonance angiography
No x-rays used
Relies on different # and behavior of hydrogen ions in diff tissues of the body to provide contrast
Uses a magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses to provide imge
Most MRI machines are 1.5T or 3T devices
MRI pros/cons
Higher cost
MRI has better soft tissue contrast resolution than CT
Long study time, very sensitive to patient motion
No exposure to ionizing radiation
MRI precautions
Remove anything potentially magnetic from the room and from the patient
May be contraindicated in patients with:
Claustrophobia
Metal clips, pacemakers, spinal cord stimulators
Cardiac defibrillators
MRI- orthopedic hardware
Should be ok with ortho hardware, prosthetic valves, titanium wires, and coronary stents
Ask patient if they have a card given to them after the implant
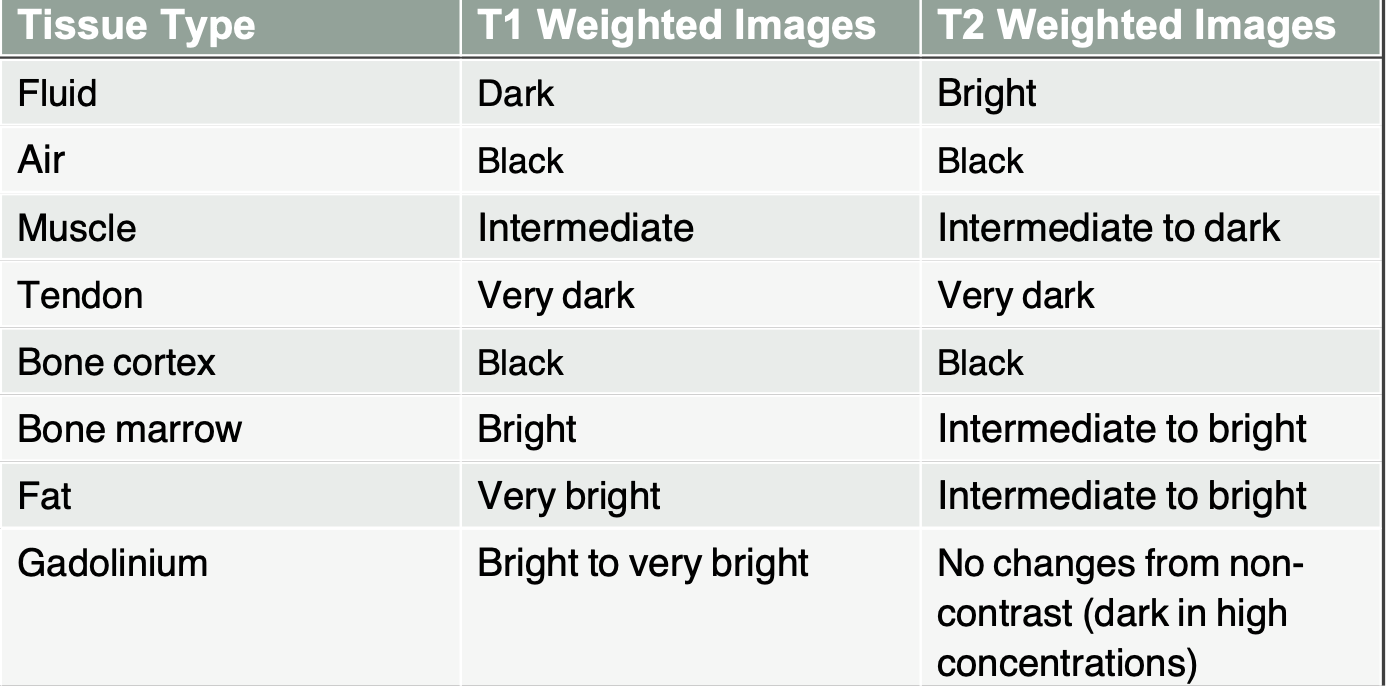
MRI: T1 weighted images
Highlights fat as bright
Muscles as intermediate
Water (blood, CSF) as dark
Brain- gray matter is darker than white matter
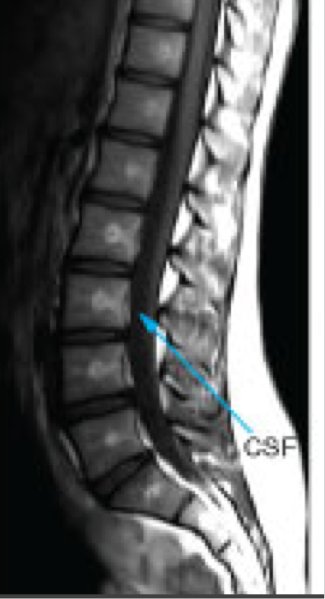
MRI: T2 weighted images
Highlights water as bright
Fat as slightly less bright
Muscle as intermediate
Brain- white matter is darker than gray matter
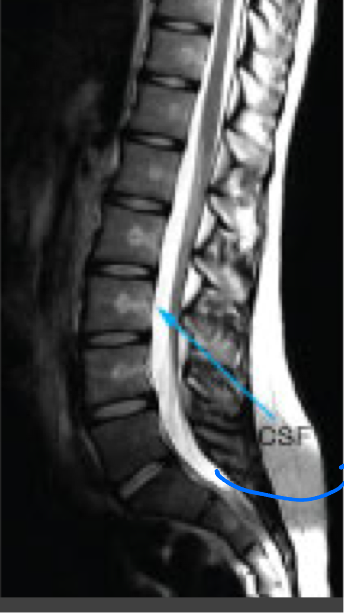
Comparison of the typical tissue appearances on T1 and T2
Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI, type of MRI)
Main use is neuroradiology, where restricted diffusion is an early sign of cerebral ischemia (stroke)
—can detect ischemic stroke as early as 30 minutes after arterial occlusion
—more sensitive to early changes after a stroke than more tradition MRI measurements such as T1 or T2 relaxation rates
DWI uses the diffusion of water molecules to generate contrast in MR images
Motion is normally restricted in tissues because of cell membranes
Disease that result in restricted diffusion of water molecules result in increased signal on DW images
Inversion recovery images
Pulse sequences are used to generate T1-, T2, or PD-weighted images while suppressing signal from specific tissues
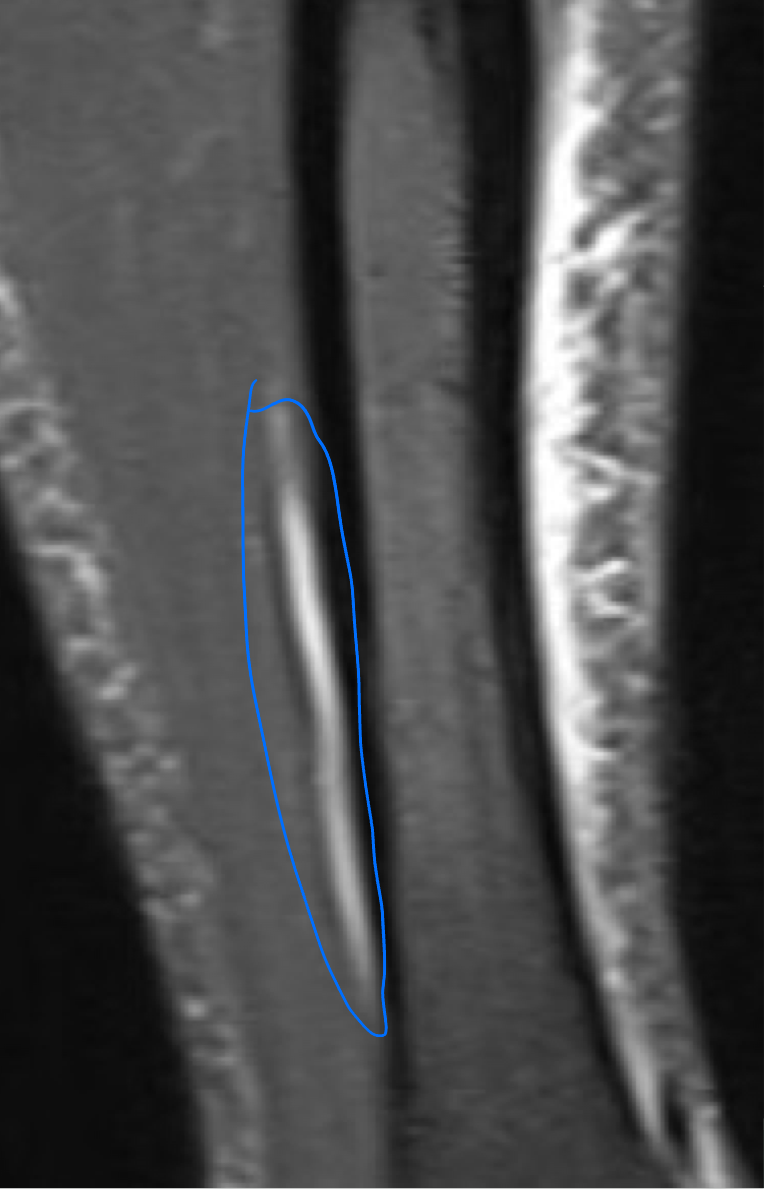
STIR (short tau inversion recovery)
—Suppresses fat will give a high signal in edema such as in more severe stress fracture
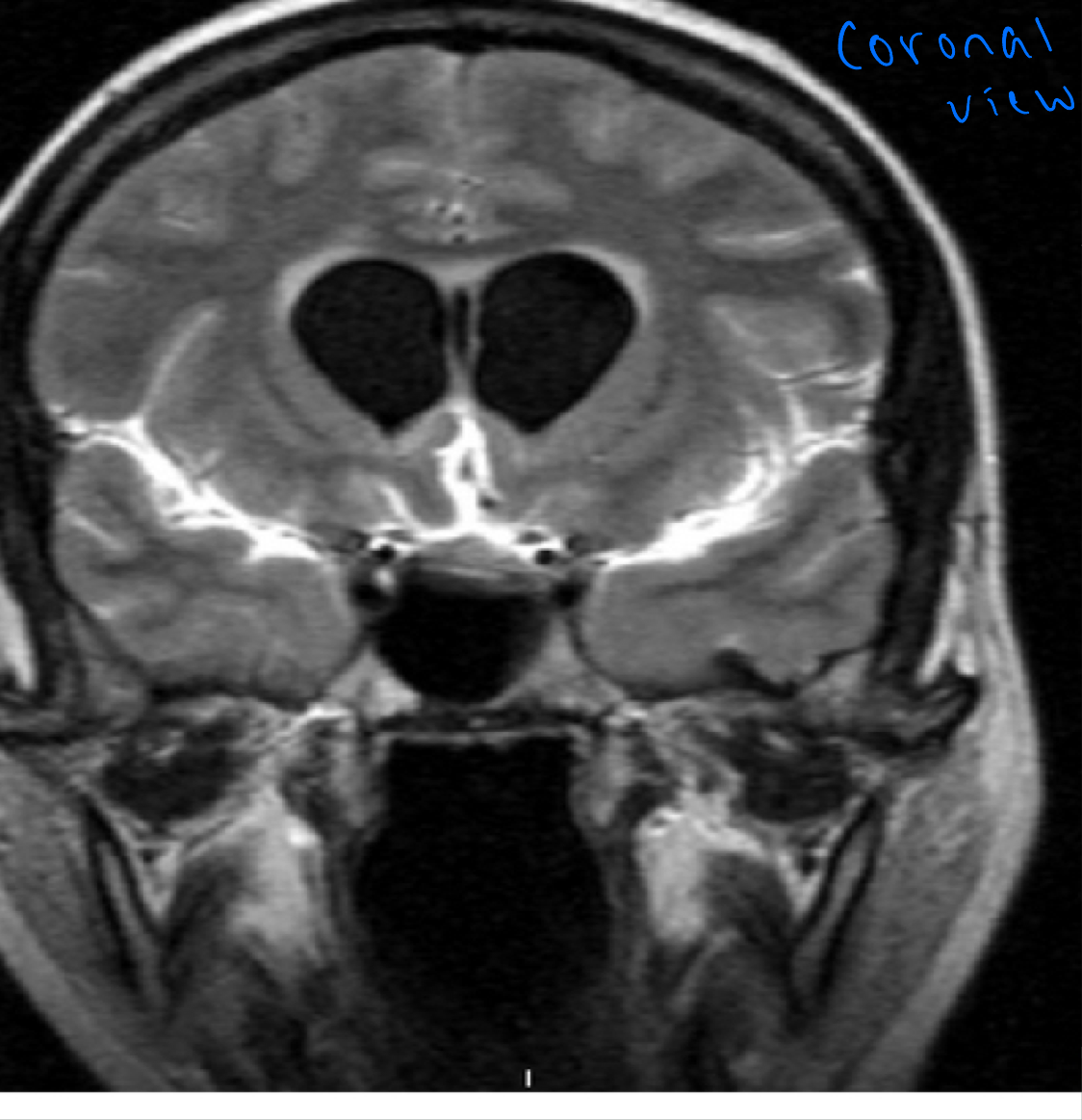
FLAIR (fluid attenuated inversion recovery)
—suppresses fluid by setting an inversion time that nulls fluids will give a high signal in lacunar infarction, MS plaques, SAH, and meningitis
STIR MRI
Coronal STIR (fat signal suppressed) MRI of a lower leg showing high signal (bright) areas around the tibia as signs of stress fracture
FLAIR MRI
Postcontrast. FLAIR MRI of a case of meningitis
Shows the enhancement of meninges at the tentorium and in the parietal region, with evidence of dilated ventricles
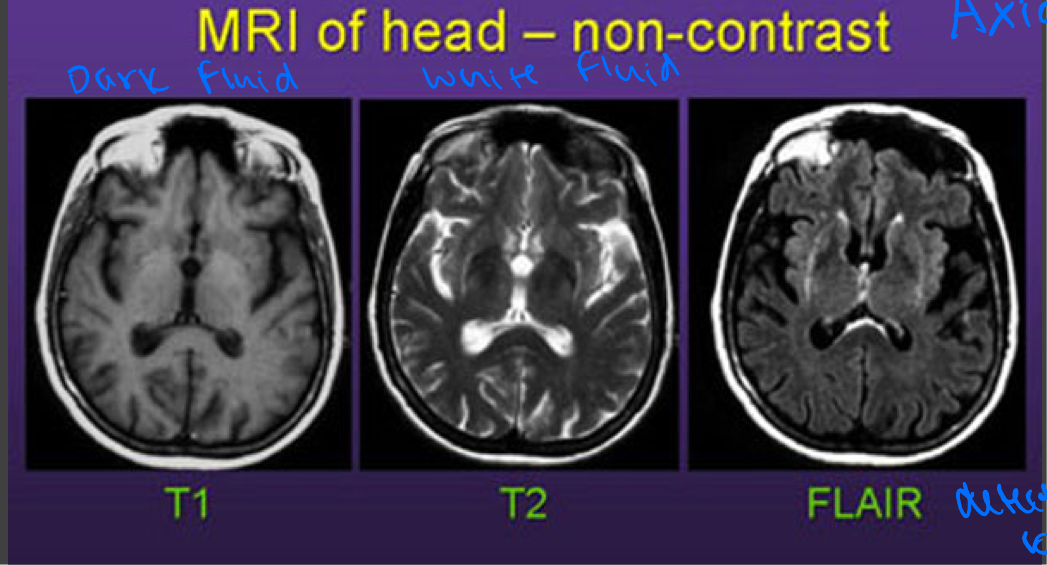
Comparison of MRI’s
Common uses for MRI
Brain, spinal cord, spine, orthopedic injury
Used in neurological and musculoskeletal imaging
Brain MRI
—used to detect and evaluate tumors, degenerative diseases and trauma
—Multiple sclerosis (MS)
Spine MRI
—evaluating soft tissues of the spine, disc herniations and spinal cord injuries, fractures are usually evaluated by CT
Body MRI
—done as a follow-up exam to further evaluate ambiguous findings on CT, such as liver or adrenal masses
Joint MRI
—evaluating soft tissues injuries, such as ACL or meniscal tears
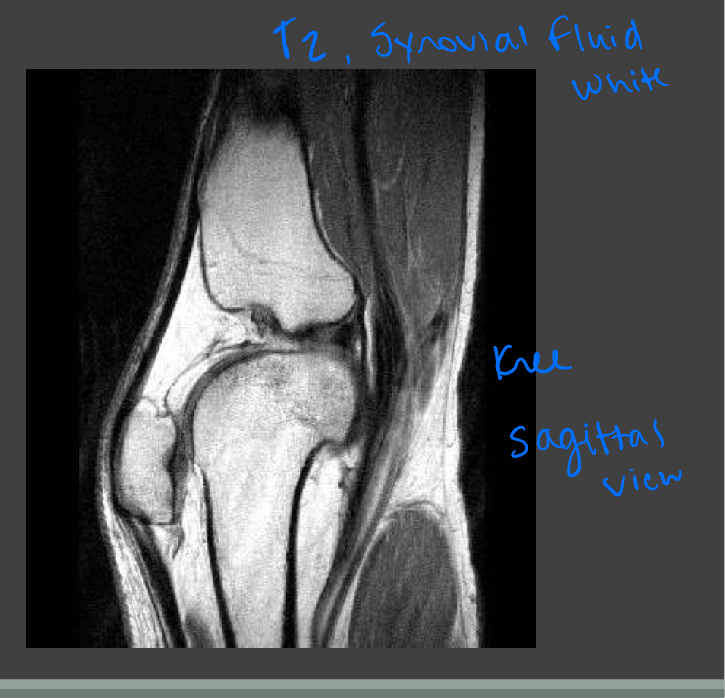
MRI/MRA prep
No special prep but remember those who may be excluded from exam
Let patients know
—need to be still
—in an enclosed space depending on body part images
—scanners are loud
What is nuclear medicine?
Ability to image the extent of a disease process in the body, based on the cellular function and physiology rather than relying on physical changes in the tissue anatomy
Uses radioactive isotopes- radioactive tracer is injected, inhaled, swallowed by patient - radioisotope targets organ of interest - then images obtained with a gamma camera
Can also be used to deliver radiation therapy to specific targets
—Thyroid mets, lymphoma
Nuclear med pros/cons
Demonstrates organ function
Reactions are rare
Relatively noninvasive
Patient ease and comfort
Intermediate to high cost
Low to intermediate radiation dose
Long exam times
NMR scan prep?
Patient prep is dependent on type of scan being done
Most don’t require fasting
—Exception: hepatobiliary scans, some GI scans
Many require initial injection, patient waits, and then repeat injection may be 1-4 hours later with scan then
Patient may need to hold meds prior (for specific organ scans)
—Bloos thinners held before cisternogram, hold thyroid I123 whole body scan
Important terms in NM
Cold
—Diminished uptake, photopenia: refer to areas of abnormally low concentration of radiopharmaceutical
Hot
—Increased uptake, increased activity: refer to areas of abnormally high concentration of radiopharmaceutical

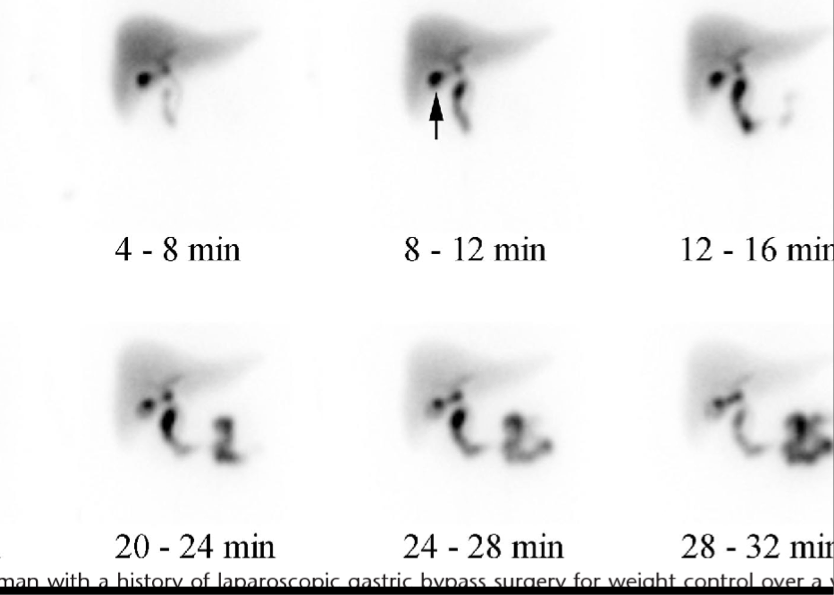
Hepatobiliary scans
HIDA- taken up by the hepatocytes and excreted like bile, used to evaluate the GB and biliary tree
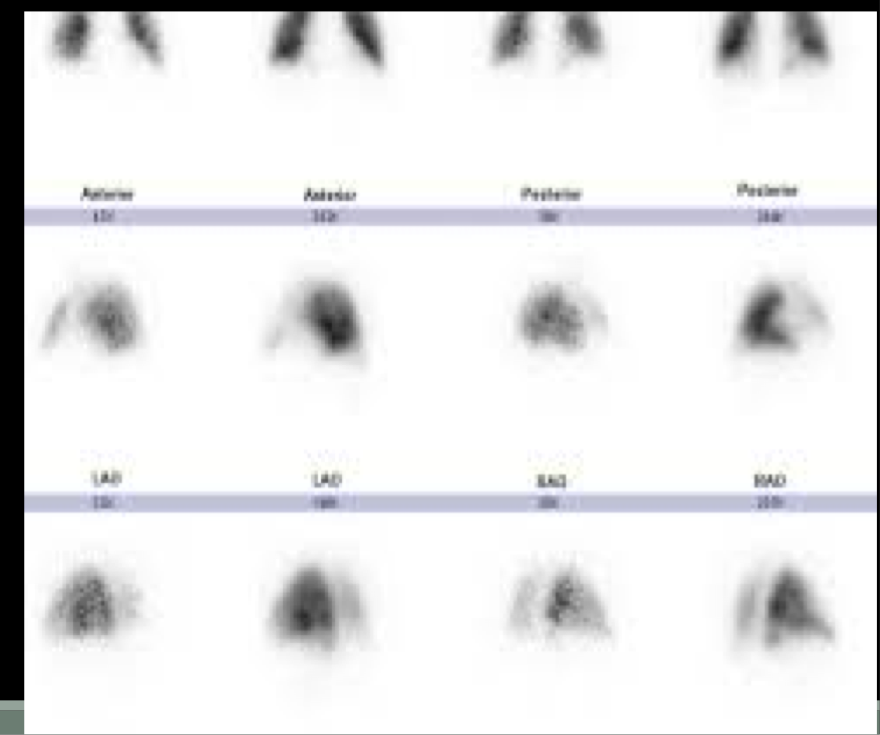
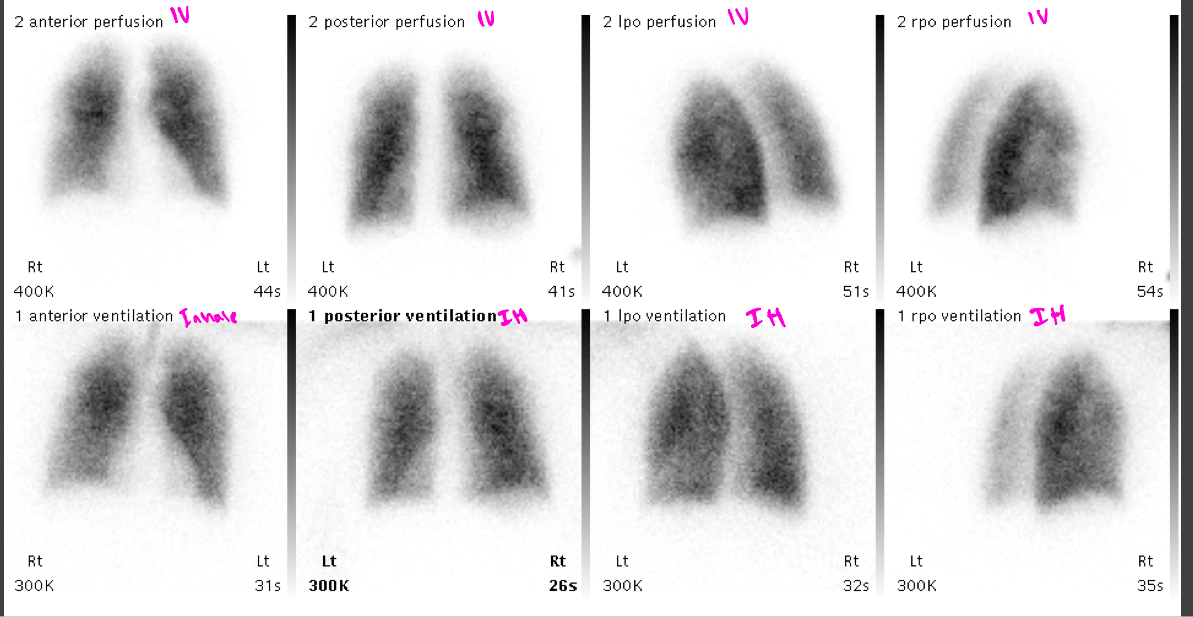
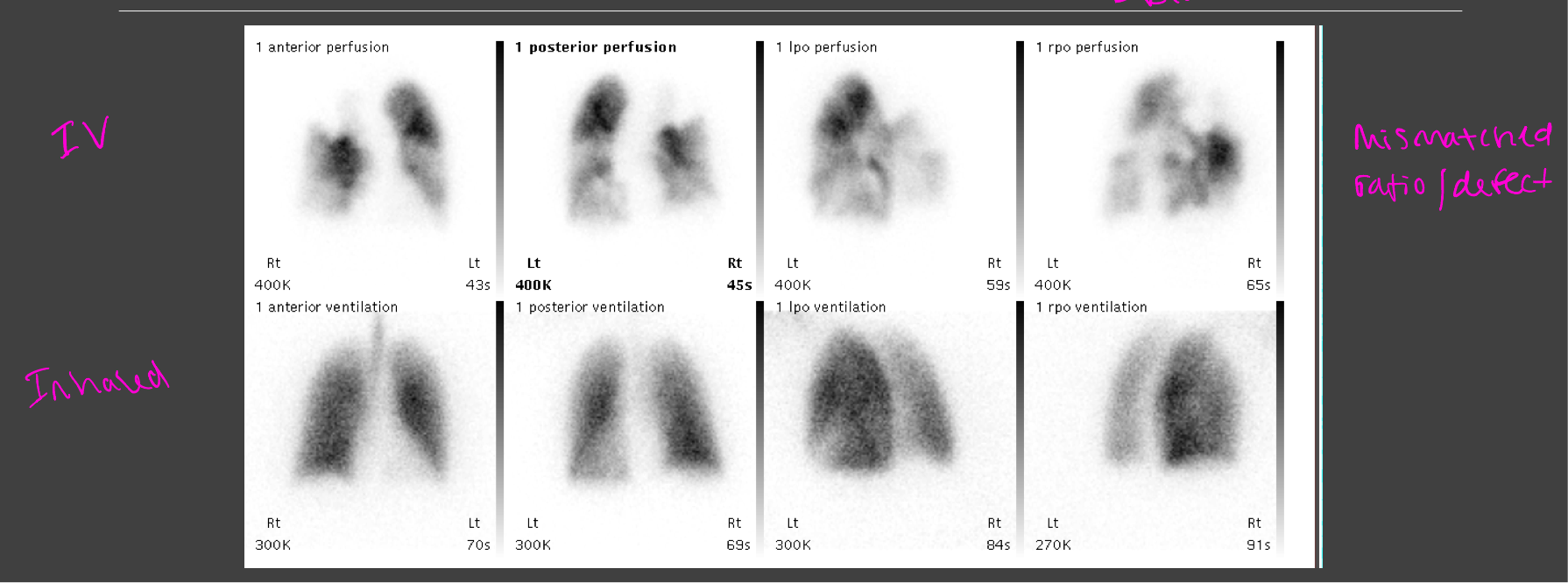
Lung-ventilation perfusion imaging
99mTc-MAA- these particles get trapped in arterioles in the lungs to show regional perfusion in the lungs
**99 = nuclear med
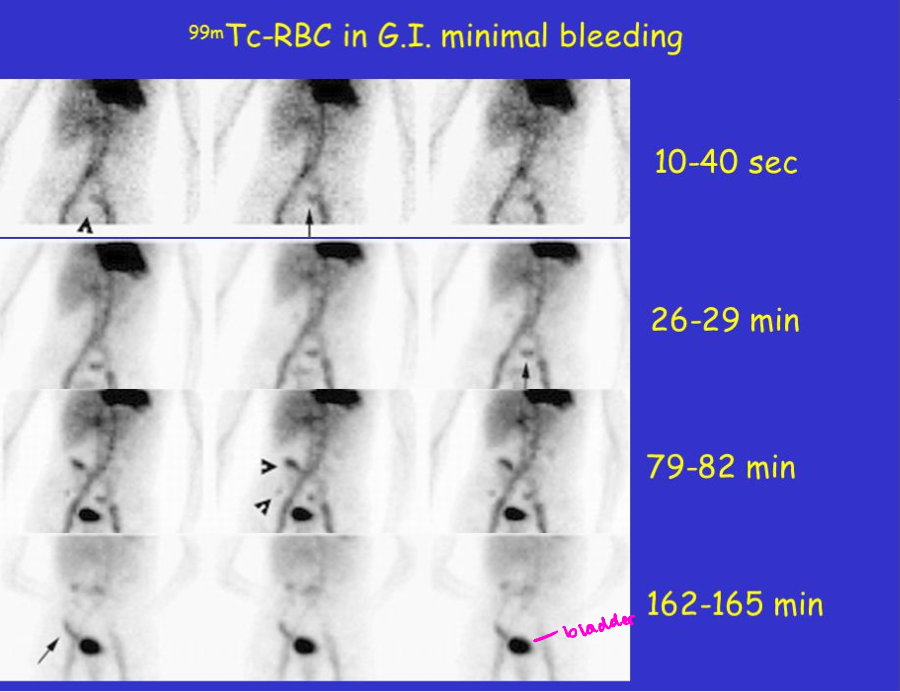
Common NM scan- GI bleeding scans
99mTc-RBC- radioactive labeled RBCs that can be used to visualize the source of a GI bleed
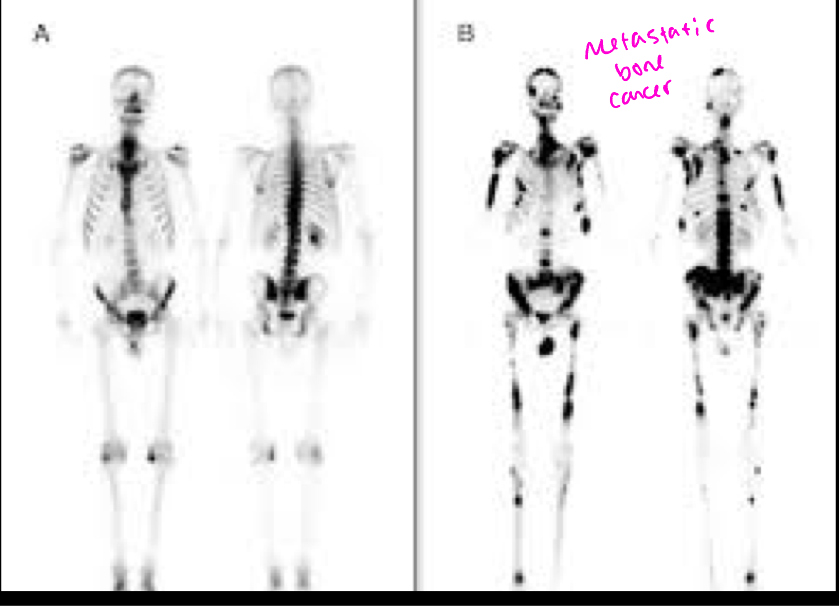
Common NM scan- Bone scans
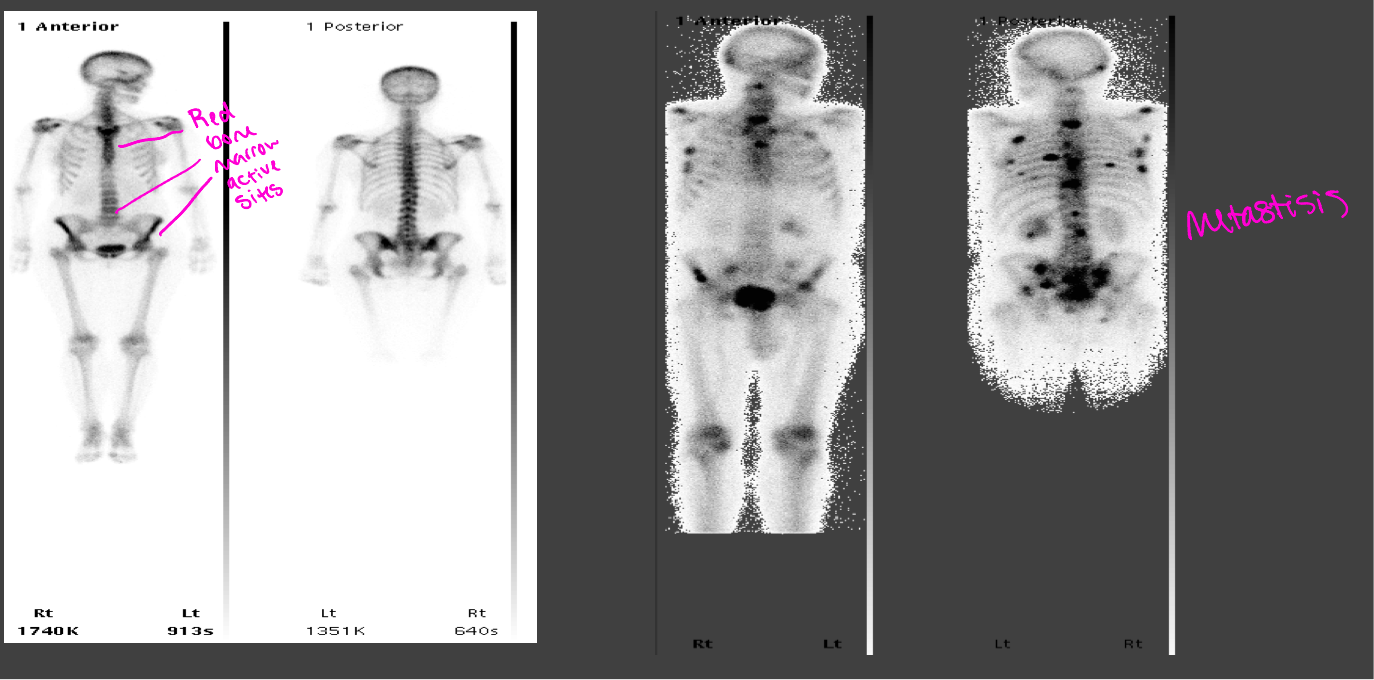
99mTc-MDP- taken up in areas of osteoblastic activity and is used to evaluate bone pathology, CANCER (blast)
Common NM scan- Thyroid imagine
NUCLEAR MED ONLY SHOWS FUNCTION-not anatomy
I-131 - take up by the thyroid tissue, used to evaluate thyroid abnormalities or to search for metastatic thyroid cancer
Normal lung (V/Q, ventilation and perfusion) scan
Abnormal lung scan= PE
Normal bone scan vs abnormal bone scan with metastisis
Positron emission tomography=PET scan
A brand of nuclear medicine that uses positron emissions to produce detailed functional images
Relatively costly
Reimbursement can be an issue
Best used for complex questions regarding tissue function
PET diagnostic uses
Detect cancer/metastasis
Follow up to see if chemo/radiation treatments are successful
Heart abnormalities (coronary artery disease and damage following an MI)
Brain abnormalities (brain tumors, memory disorders, seizures)
Other central nervous system disorders
PET prep/patient education
NPO 6 hours prior
No caffeine for 24 hours prior in heart patients
Injection, inhalation, or swallow tracer then wait for test for 30 mins-1 hour
Test may take another hour or so
Pet vs CT or MRI scan
PET scan reveals the cellular level metabolic changes occurring in an organ or tissue -thyroid, cancers, brain
PET scan can often detect very early changes whereas a CT or MRI detect changes later as the disease begins to cause changes in the structure of organs or tissues
Active bleed- CT is faster
Structure: CT
Function: NM, PET
Ultrasound (cheap and easy)
Transmission of high-frequency sound waves through tissues to provide contrast and make images from the reflected waves (Echos)
Used for peds, OB, vascular imaging, ortho, renal, scrotal, ovarian
Used for guidance of interventional procedures (biopsies, thoracentesis)- good for use in real time
Sonogram = image produced
U/S pros and cons
Low cost
No radiation
Operator dependent
Good soft tissue evaluation in specific clinical scenarios (cyst vs mass)
Fast and readily available
Echogenicity
Level of gray or brightness on an ultrasound image
Described in relation to surrounding tissues
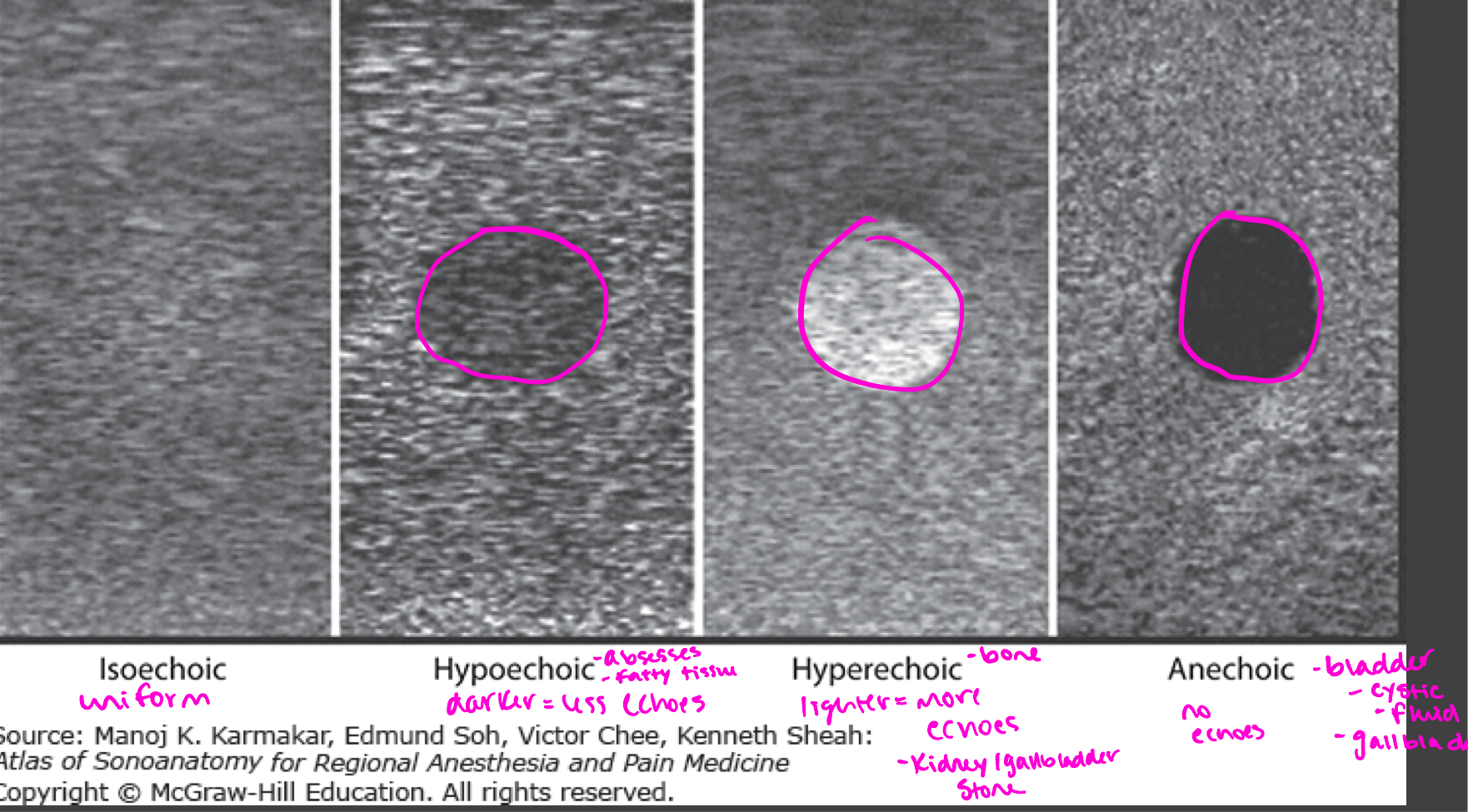
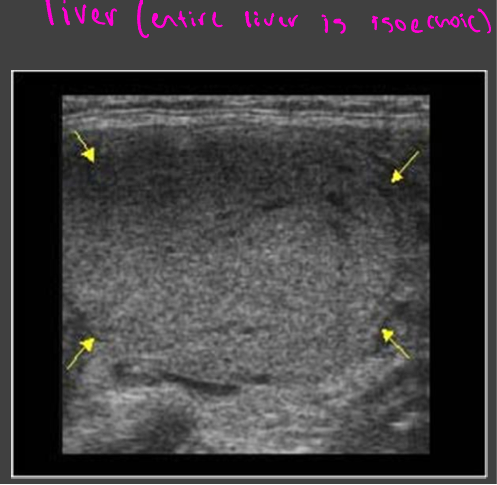
Isoechoic
Uniform in color
Liver
Hypoechoic
abscesses, fatty tissue
Darker = less echoes
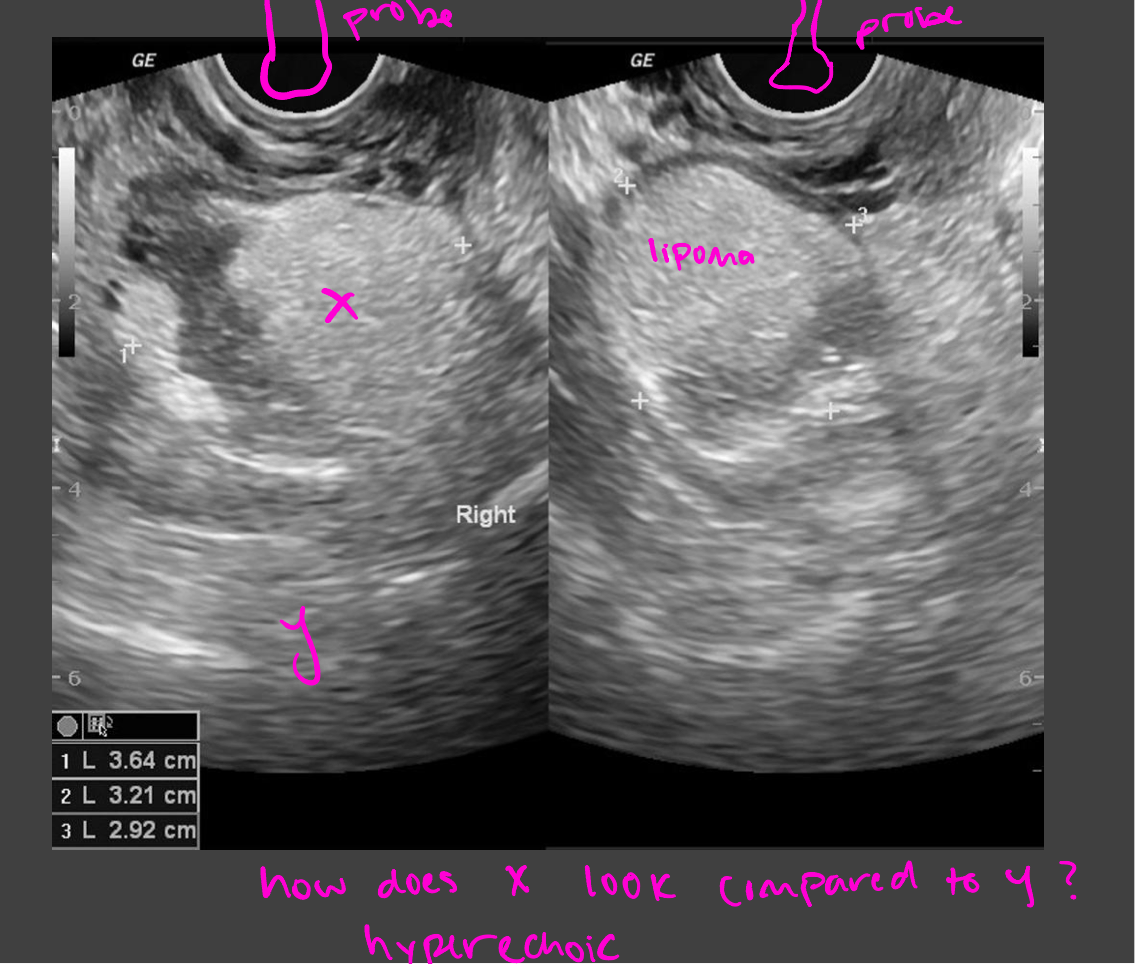
Hyperechoic
Bone, kidney/gallbladder stone
lighter = more echoes
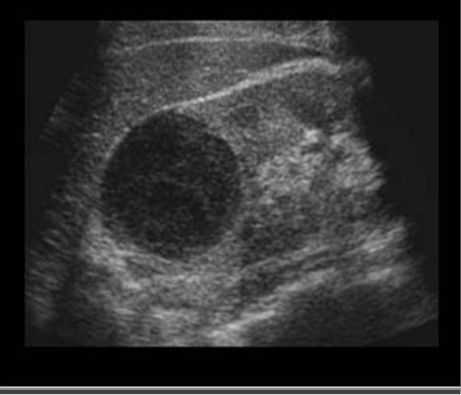
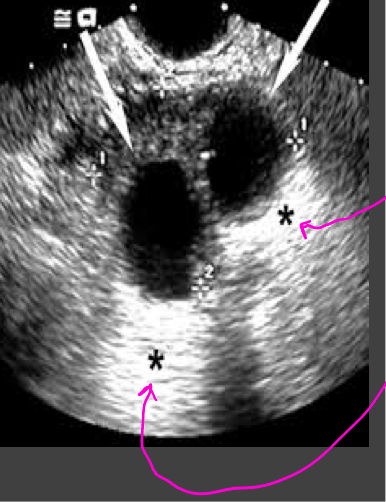
Anechoic
no echos
Bladder, cystic fluid, gallbladder
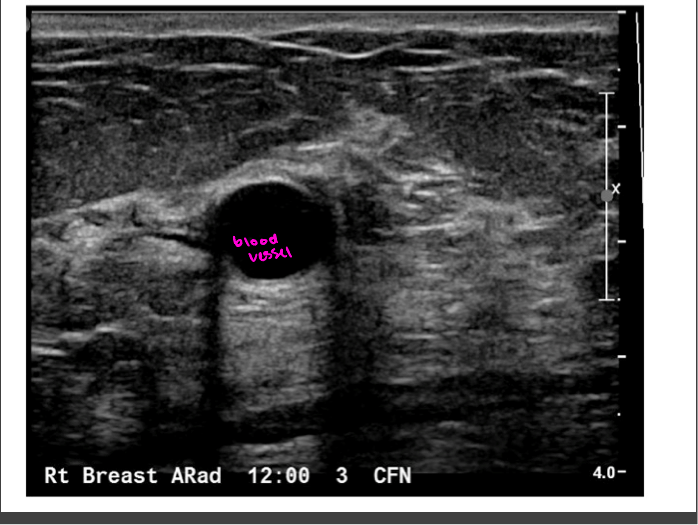
Artifacts-enhancement
Acoustic enhancement- sound travels through fluid uninterrupted, so the echoes deep to a fluid collection are brighter than the adjacent tissue
In poorly attenuating objects such as a cyst, the echoes returning from regions deep to the object are of higher amplitude
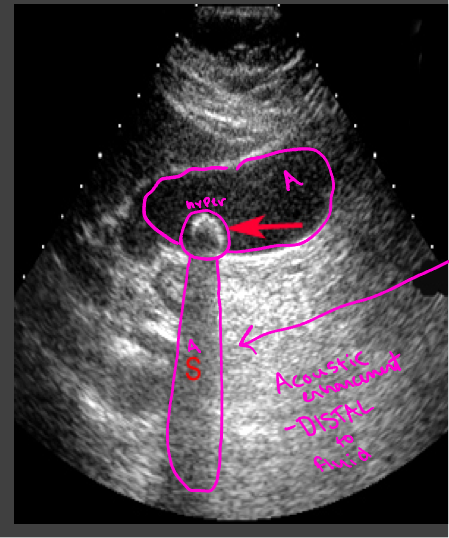
Artifacts- shadowing
A structure that blocks the sound wave causes acoustic shadowing (gallstones)
Strongly attenuating or highly reflective surface, the returning echoes posterior to the structure are decreased in amplitude
U/S prep
Vascular studies = no prep
Abdominal = NPO for 6 hours prior
Trans-abdominal pelvic= drink 32 oz of water a half hour prior (requires a full bladder)
Fetal U/S
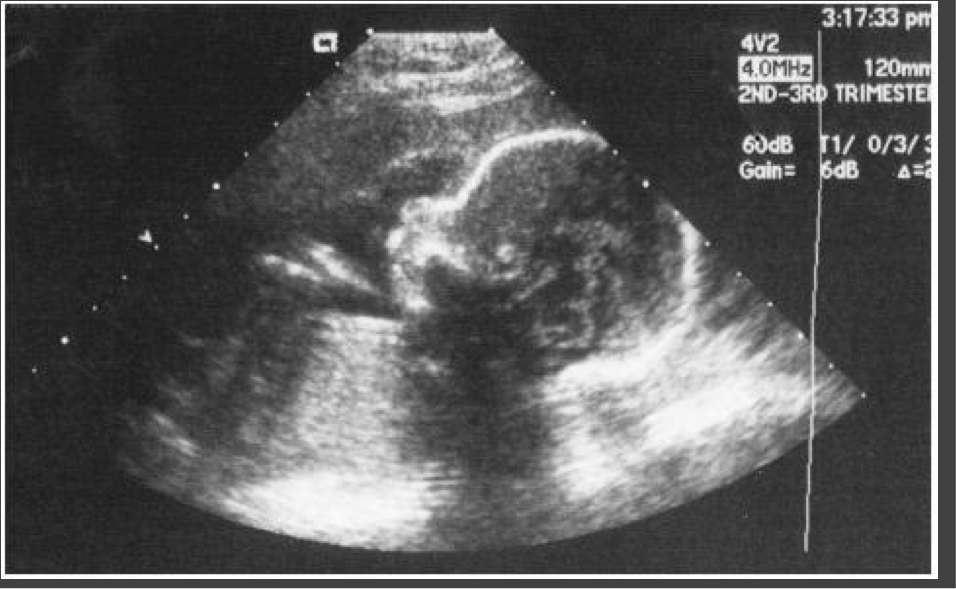
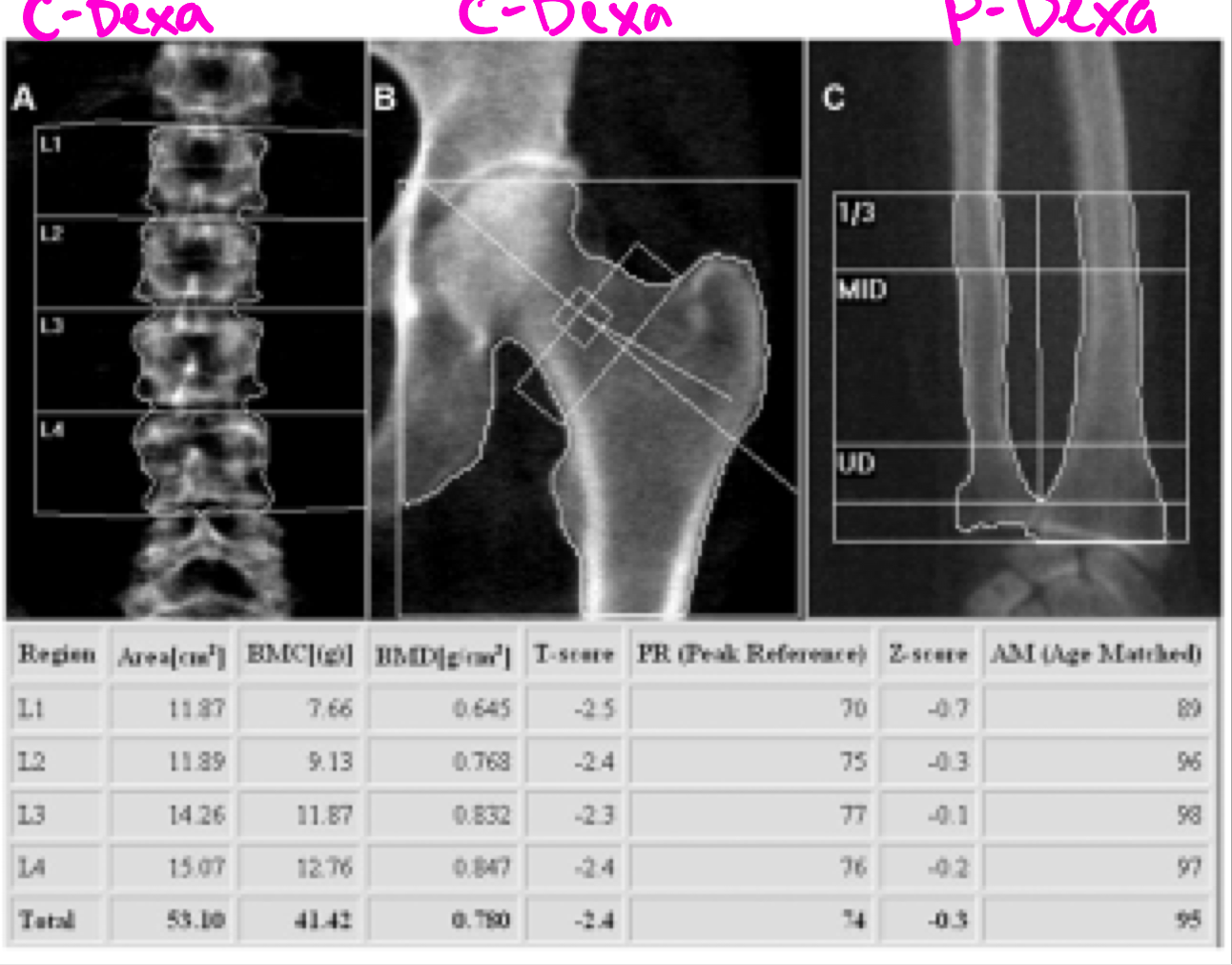
DEXA scan
DEXA or DXA scan = bone densiometry = dual x-ray energy absorptiometry
Type of x-ray: measuring bone mineral content and density (BMD) od specific skeletal sites
Used to diagnose osteoporosis and assess fracture risk
Relatively inexpensive
simple for patient and operator
Used for planning and follow up of treatment
DEXA prep
No calcium supplements for 24 hrs prior
Scan only takes 10-15 minutes
Peripheral or p-DEXA
Scan measures bones on the body’s periphery- such as the heel, wrist, or finger
Should not be used for diagnosis or tracking progress from year to year (IS A SCREENING TEST)
Central DEXA
Bone mineral density score in lumbar spine and femoral neck
Provide an accurate diagnosis and method of tracking progress in bone growth or loss from year to year
T-SCORE
Indicated patients BMD in standard deviations above or below that of mean for young adult women
For each 1 SD in T score, fracture risk nearly doubles
Osteoporosis: below -2.5
Osteopenia: between -1 and -2.5
Normal score>-1
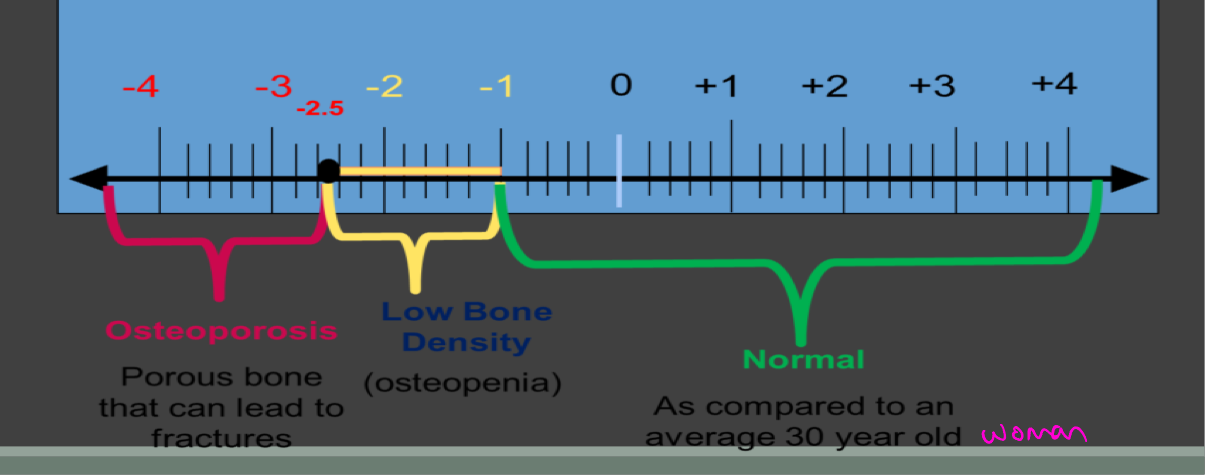
Z SCORE
Used for children, young adults, men, pre-menopausal women
Compares your bone density to the average bone density of people your own age and gender
Ex. If you are a 50 year old male, a Z score compares your bone density to the average bone density of other 50 year old males
DEXA scan example
Measurements of the lumbar spine demonstrate a total T-score in the range of osteopenia