A&P I Chapter 15 Reading
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
In glaucoma, damage occurs primarily to the ______.
ganglion cells in the retina
In theory, cataracts could be prevented by invention of a treatment that would ______.
increase diffusion rates within the lenses
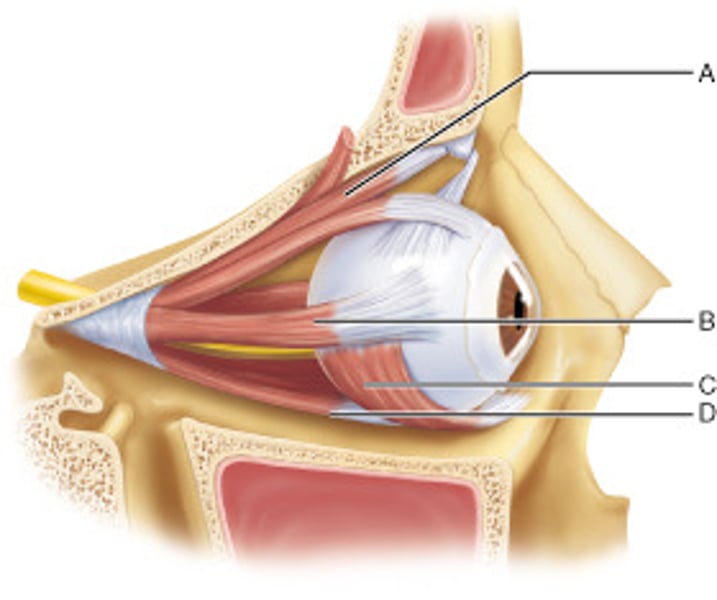
Identify the muscle that is controlled by the abducens nerve (CN VI).
B
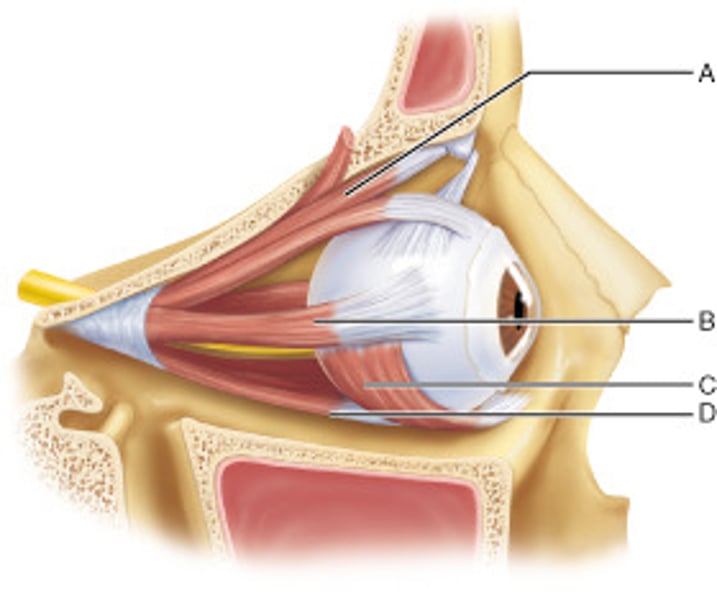
Identify the muscle responsible for depressing the eye and turning it laterally.
A
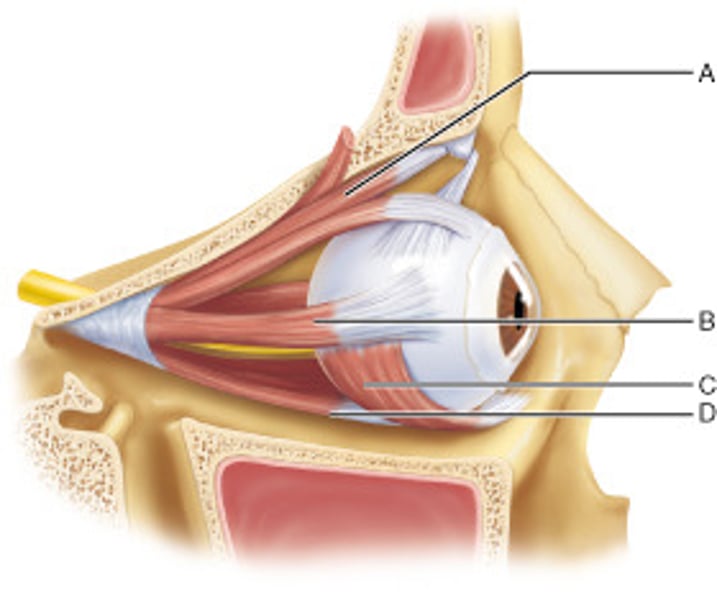
Name the muscle at D.
inferior rectus
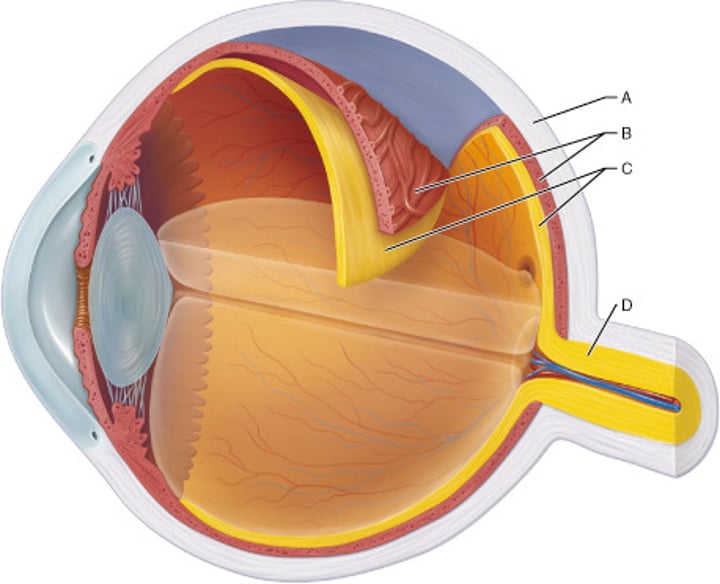
Which layer of the eye is indicated by letter A?
fibrous
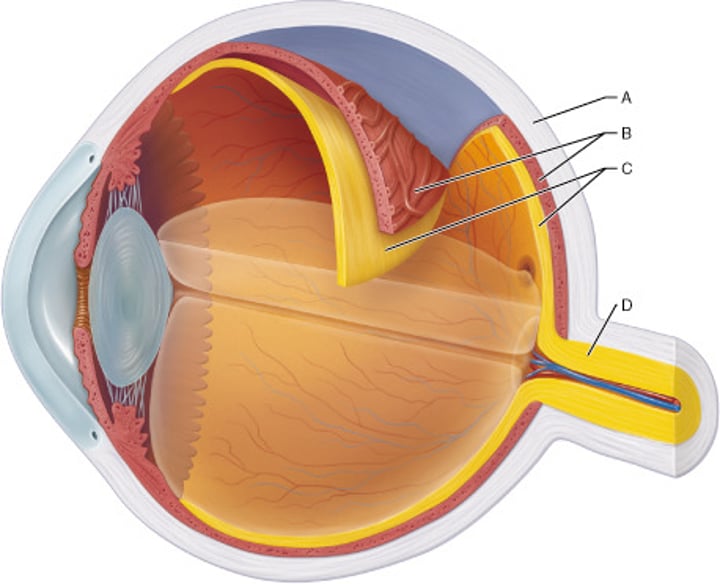
Identify the choroid.
B
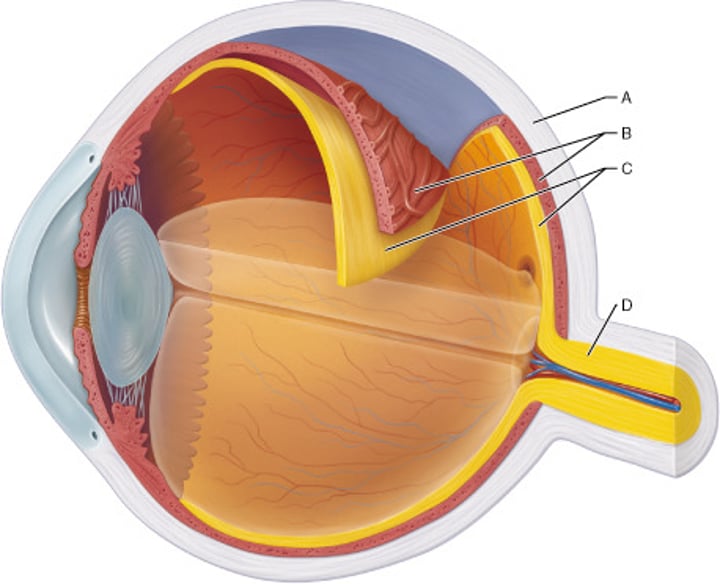
Identify the layer that contains both a single-celled pigmented layer and a neural layer.
C
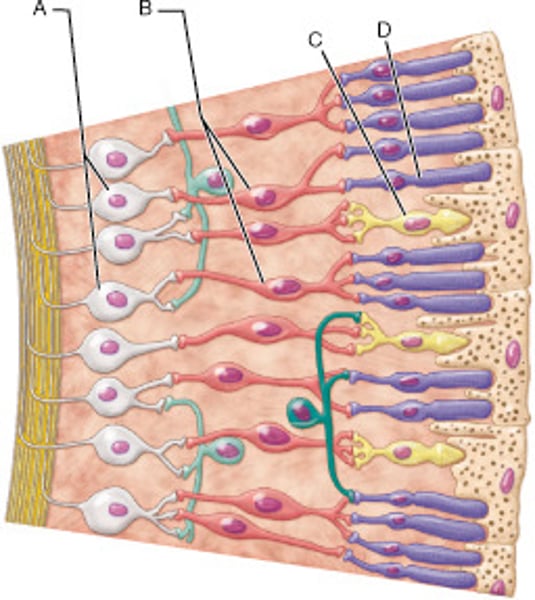
Identify the type of neuronal cell that detects bright light and provides high-resolution color vision.
C
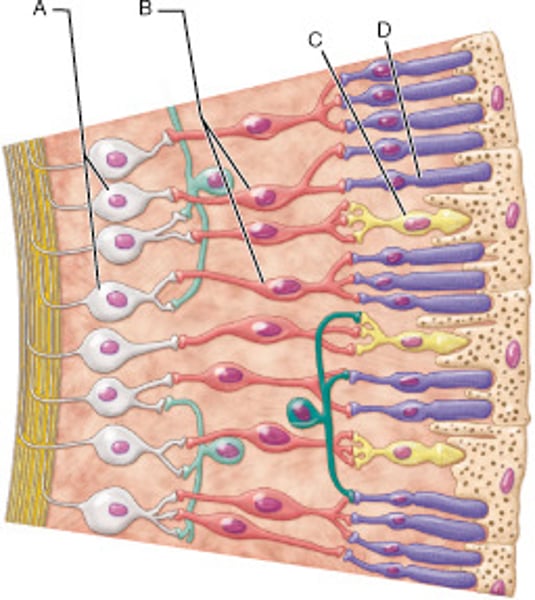
Identify the type of neuron that would be secreting neurotransmitter in the light.
A and B
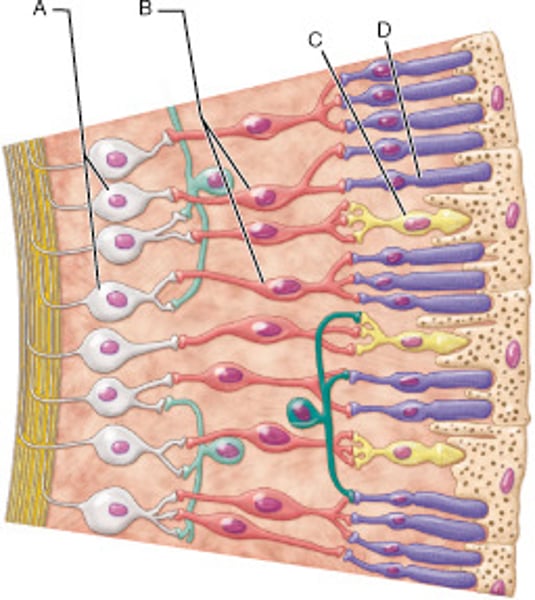
Identify the neuron that is last in the transmission pathway of light information, given the cells shown in this image.
A
Which accessory eye structure is NOT correctly matched with its function?
tarsal glands: produce tears
Which structure provides the vascular support for the eye?
the choroid
What structure in the eye creates a visual blind spot?
optic disc
Which of the following is a characteristic of the lens?
The lens focuses light on the retina.
Which structure is NOT matched with its function?
ciliary body: focus the pupil
You want to look up and to your right. Which extrinsic eye muscles would be the most active in each eye?
right eye: inferior oblique left eye: superior rectus
Aqueous humor forms during capillary filtration in the __________?
ciliary body
What is the portion of the eye that allows light to pass into the posterior chamber?
iris
Which of the following statements is true?
Contraction of the ciliary muscles is required for hyperopic individuals to clearly see distant objects.
Atropine eye drops are used to temporarily paralyze the accommodation reflex and as a long-lasting pupil dilating agent, or mydriatic. What action causes the dilation effect?
blocked contraction of sphincter pupillae muscle
What term refers to the eye's moving medially to track items close at hand?
convergence
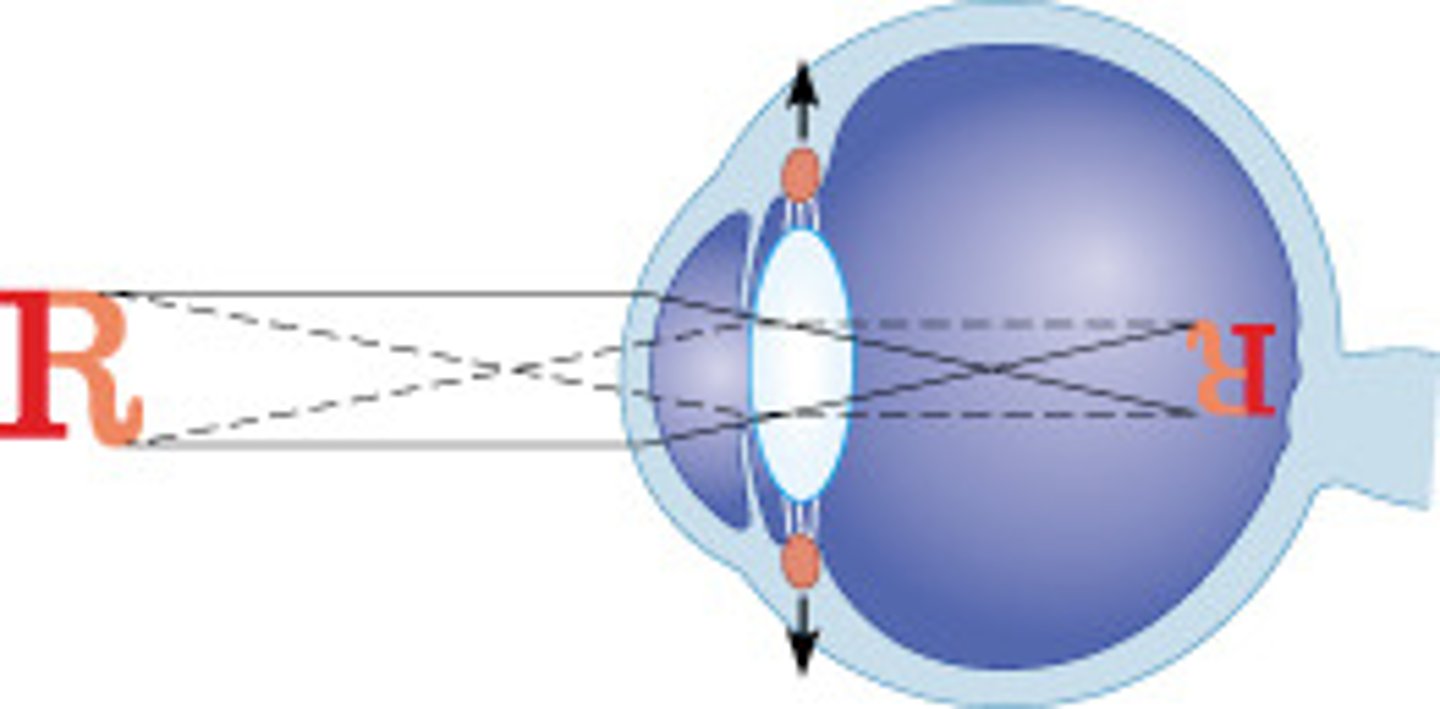
During close vision, what actions must the eye take to bring an object into focus?
contract the ciliary body
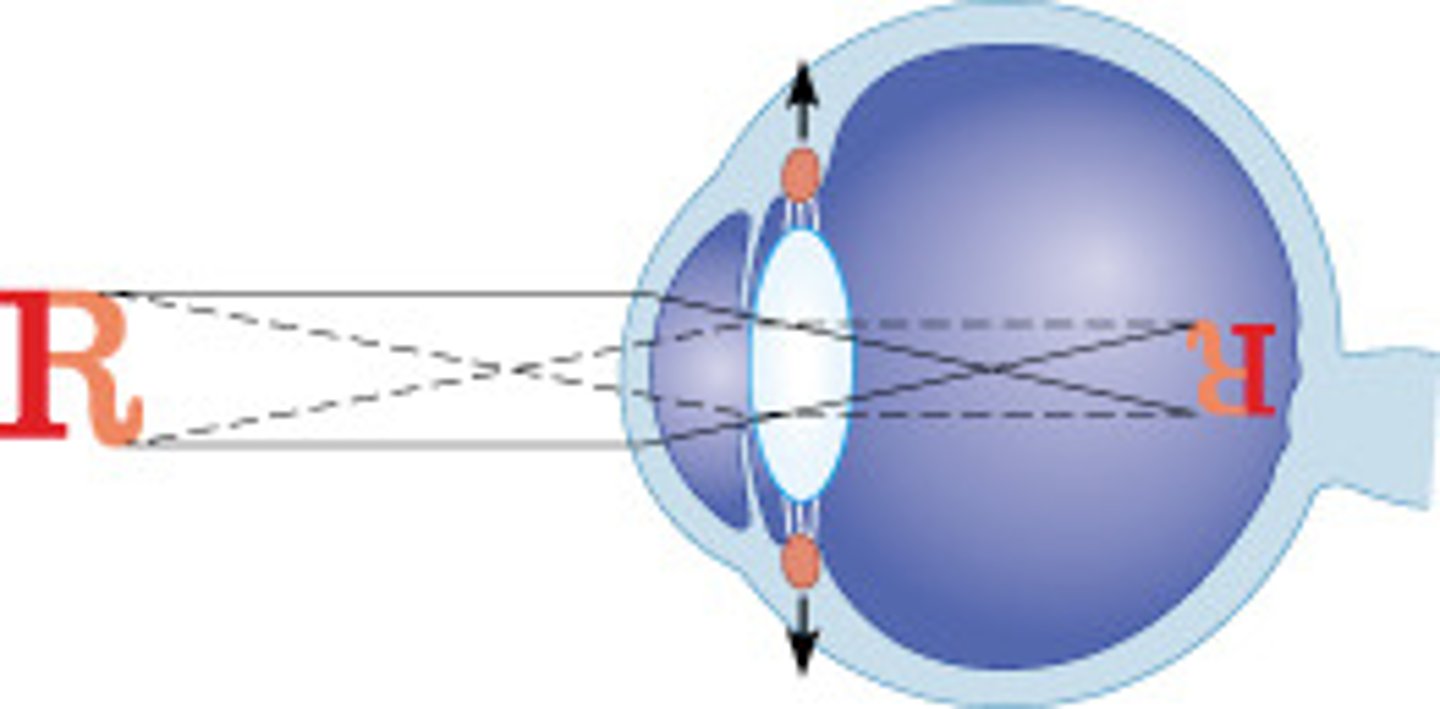
This image best illustrates an eyeball that is __________.
emmetropic
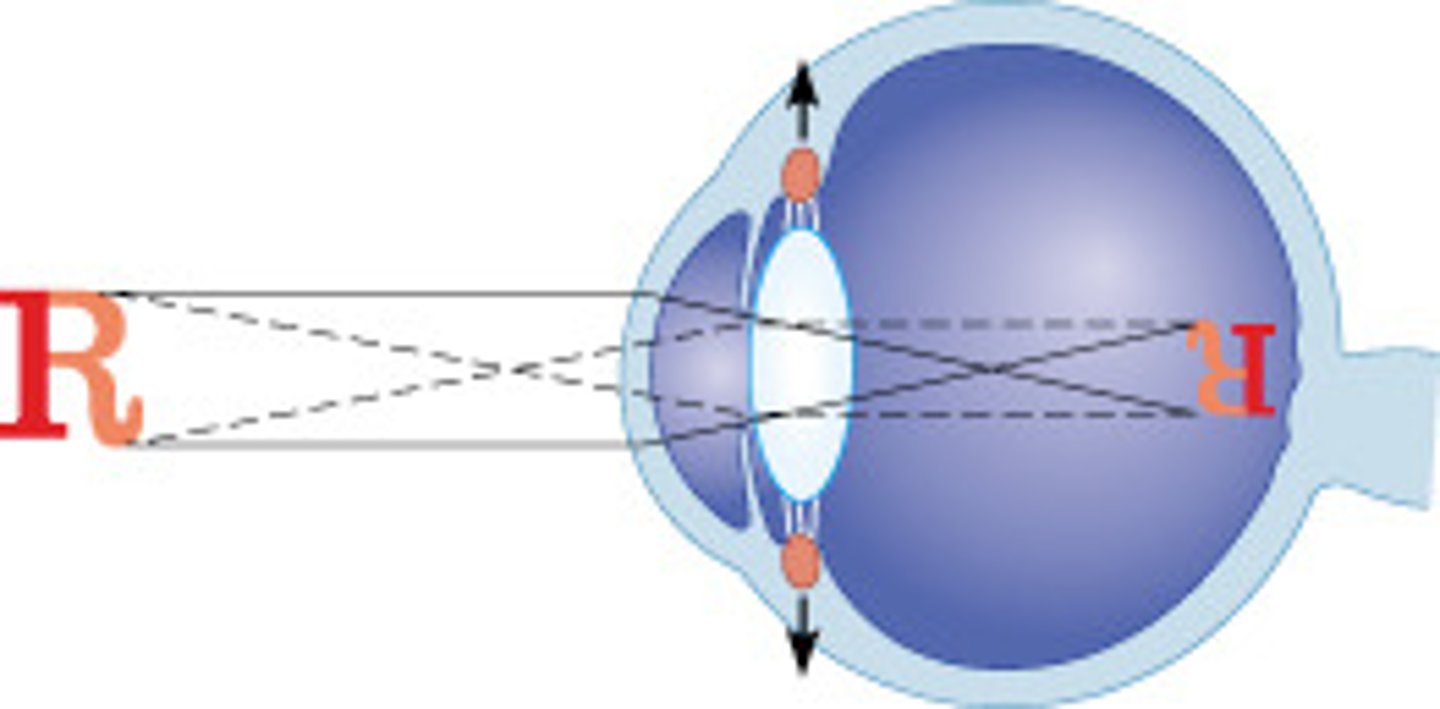
As the ciliary muscle relaxes, the suspensory ligaments tighten and stretch the lens, allowing for distance vision.
True
Choose the correctly paired terms.
nyctalopia: night blindness
In a 30 year old man who has red-green color blindness, light having a wavelength of 530 nm is perceived as being green. This man ______.
perceives that red light has a green color
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
Nyctalopia affects vision in the fovea centralis, resulting in impaired vision.
Which photoreceptors respond to very dim light?
rods
As light hits the retina, the first structure the light encounters is a rod or a cone.
False
If the optic chiasma is destroyed but the rest of the visual pathway to the brain is not damaged, the result would be ______.
loss of peripheral vision on both the far right and far left sides of the visual field
Which part of the visual pathway is responsible for our daily biorhythms?
suprachiasmatic nucleus
Damage to the medial portion of the optic chiasm, cause by a pituitary tumor, would lead to __________.
loss of peripheral vision
During otitis media, large amounts of fluid or pus may accumulate in the tympanic cavity; the fluid is primarily ______.
interstitial fluid
Identify the structure that forms cranial nerve I.
C
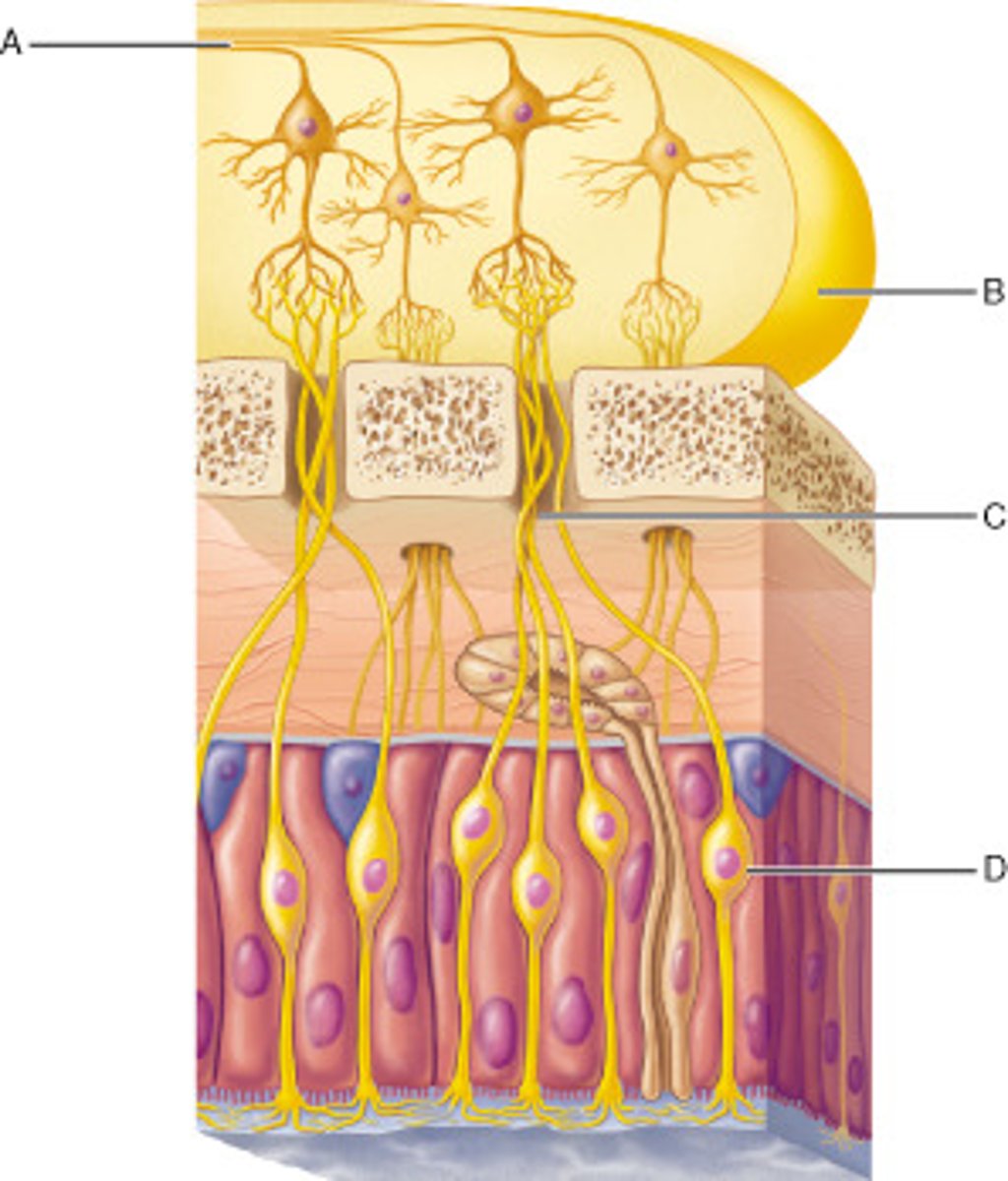
Which cells in this pathway are ciliated?
D
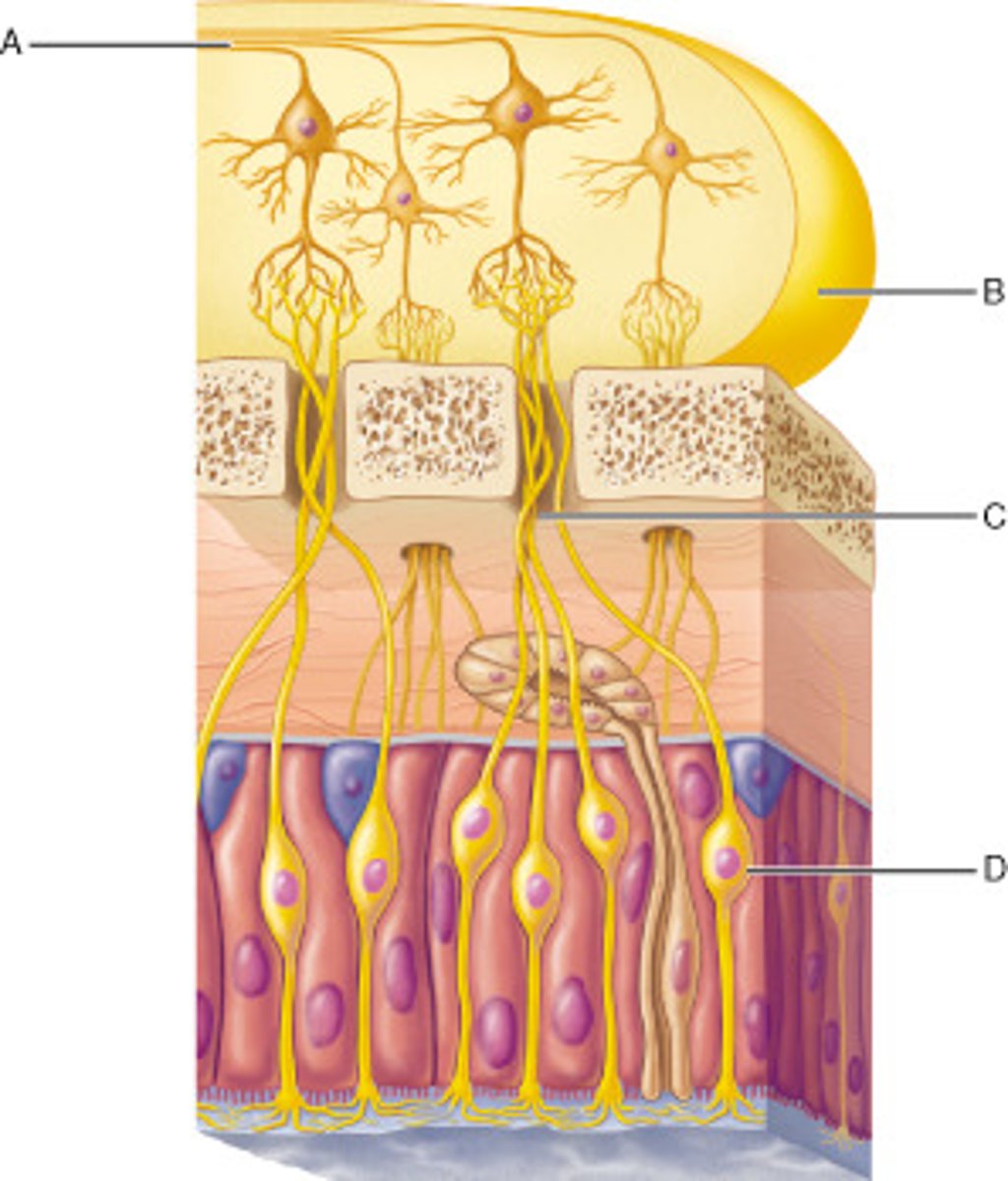
Which of these is NOT found in the olfactory epithelium?
olfactory tracts
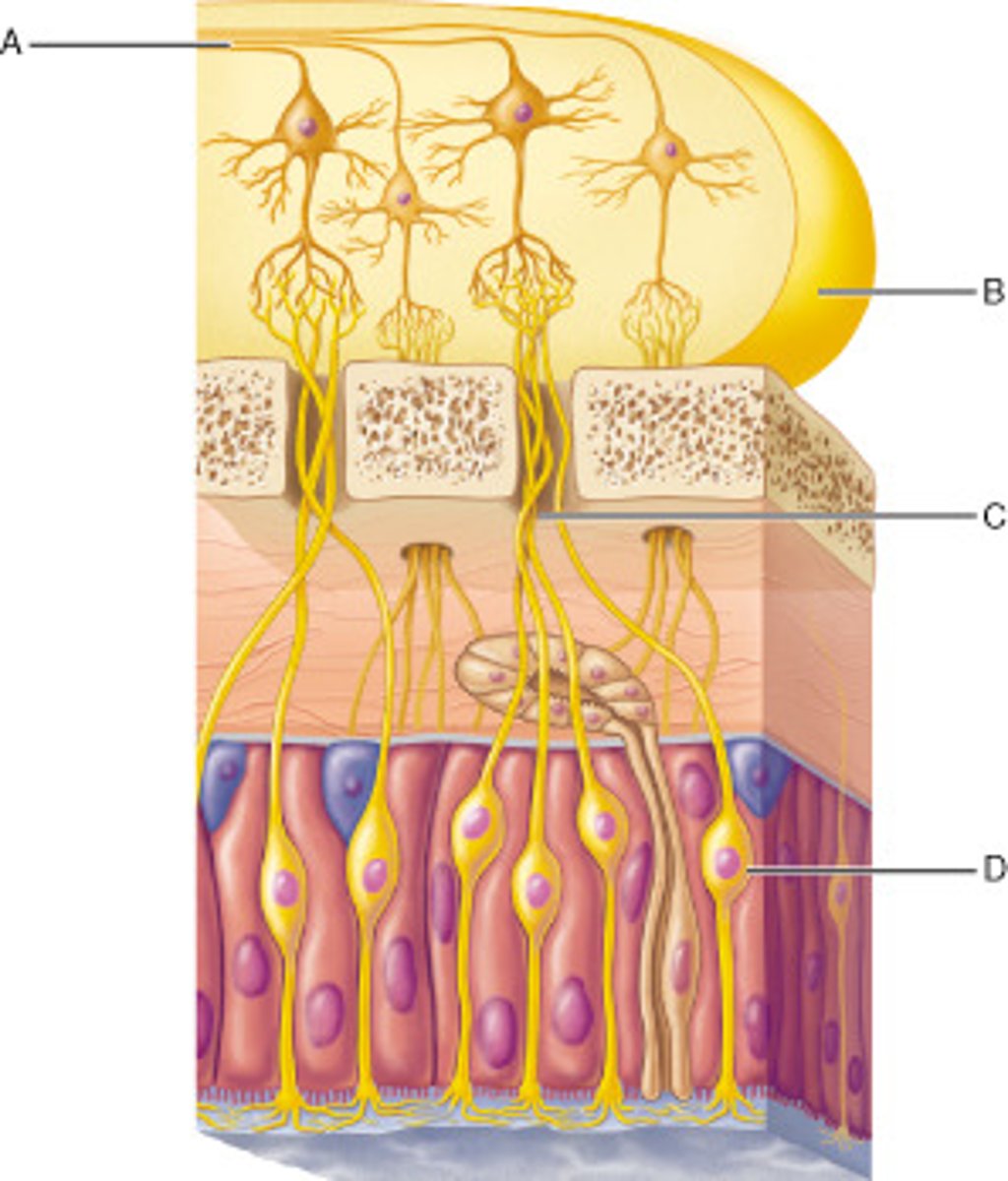
How are the olfactory receptors activated?
Odorants dissolve in the mucus and bind to receptors.
Choose the FALSE statement about the olfactory epithelium.
It is made of simple squamous epithelium.
Which of the following would be the LEAST likely to be associated with the development of motion sickness?
having a non-functional vestibular apparatus
Which of these lettered structures serve as the taste cells?
C
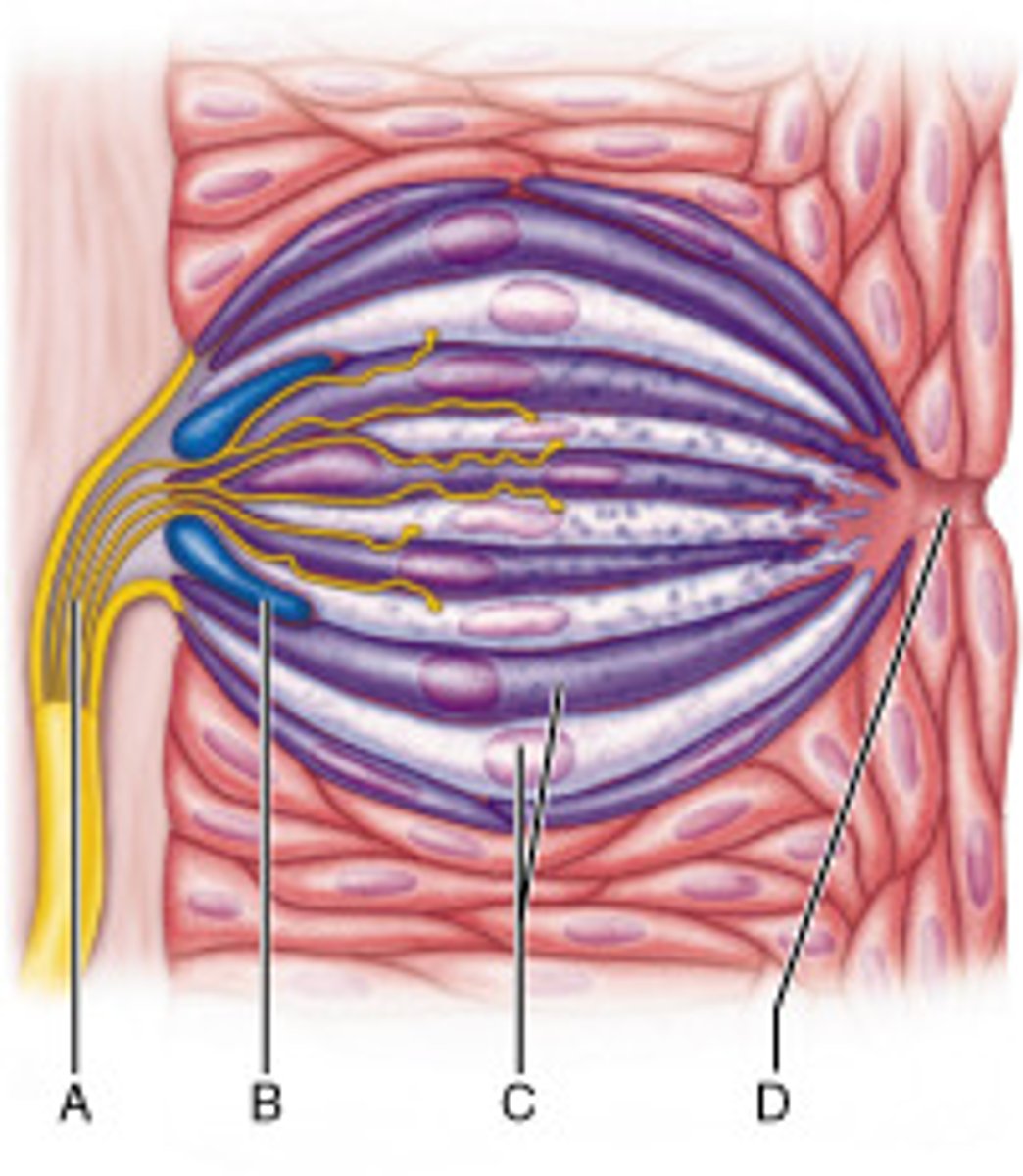
Name the types of papillae that contain taste buds.
fungiform, foliate, and vallate
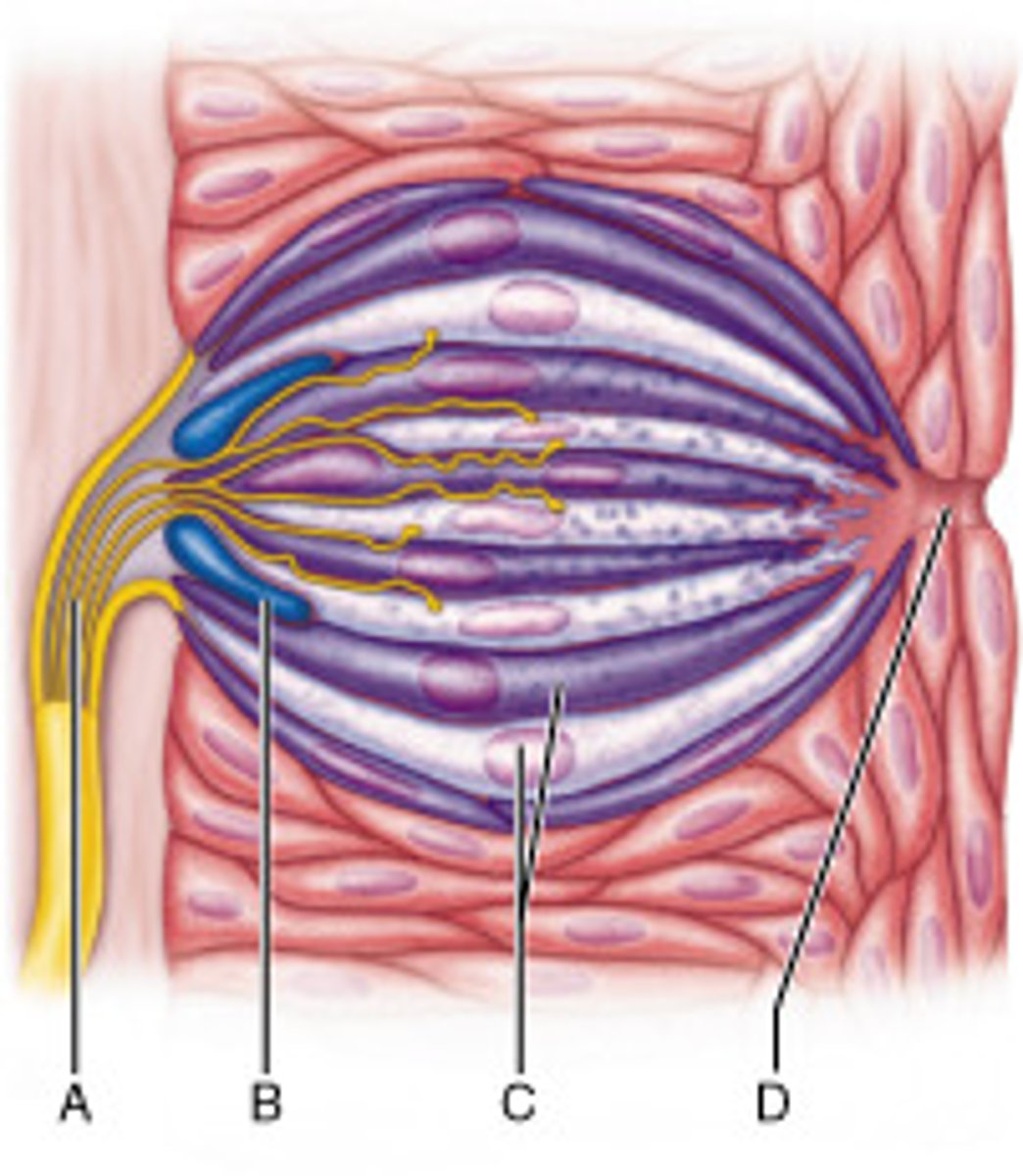
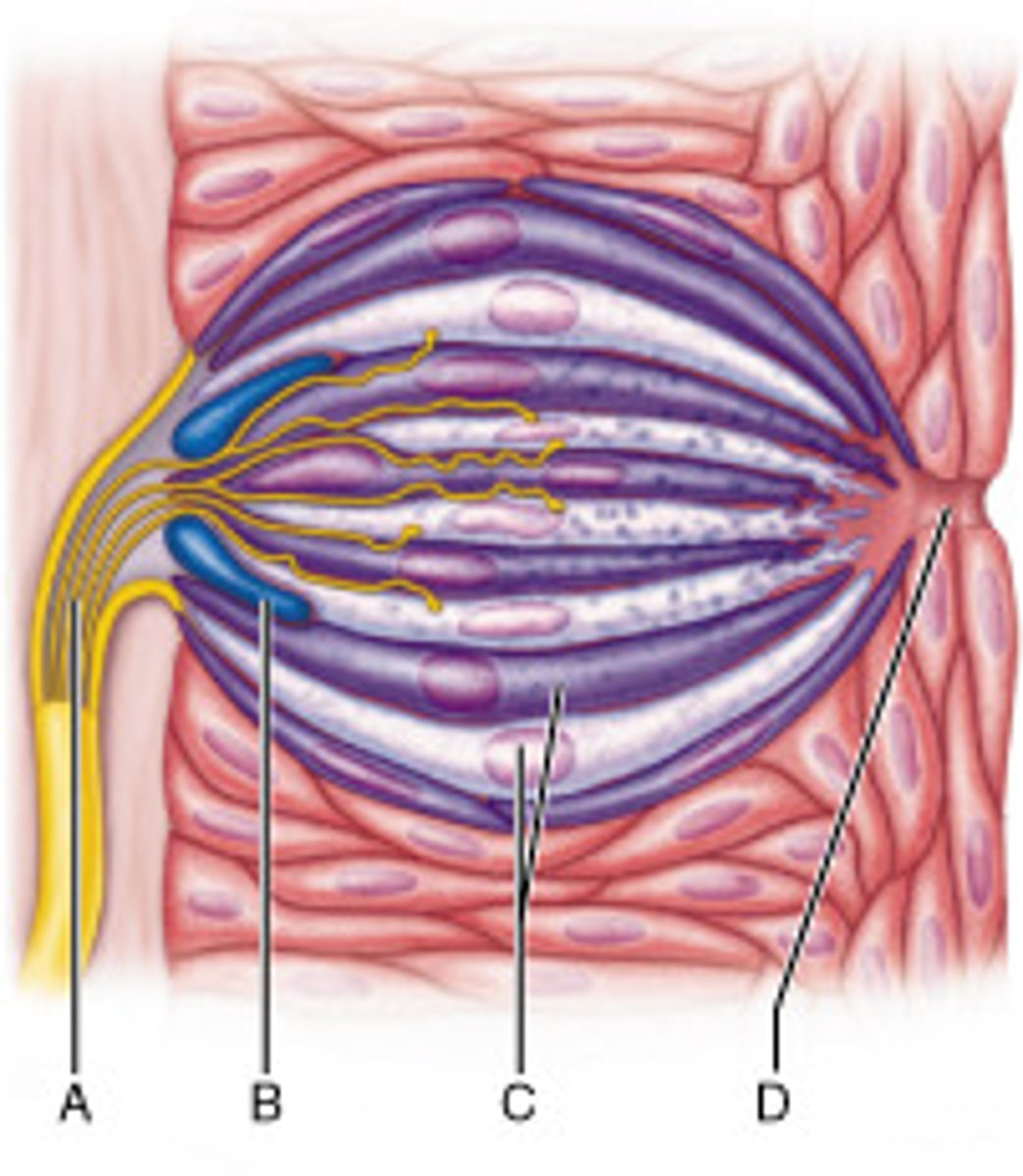
What is the purpose of the cell at letter B?
to replace gustatory cells that are damaged
Which of the following is the basic taste quality responsible for the amino acid flavor of steak?
umami
Most taste buds are located __________.
on the top surface of the fungiform papillae
Which of the following is NOT a requirement for something to be tasted?
The tastant must contact the basal epithelial cells of the taste buds.
Rubella infection during early pregnancy may cause damage to the embryo's ______.
All of the listed responses are correct.
Which region of the ear houses perilymph and endolymph?
C
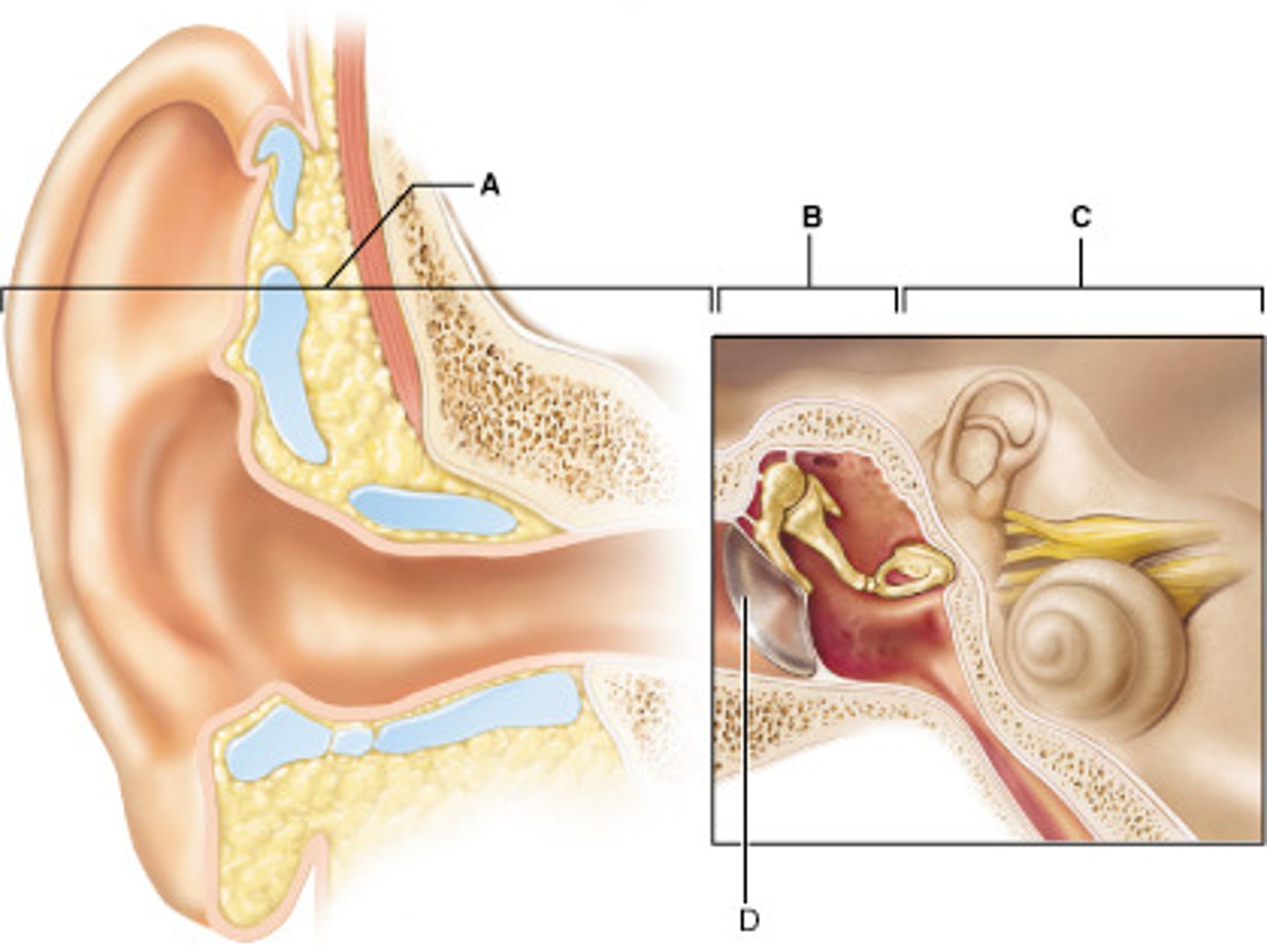
Which letter indicates structures involved in detection of BOTH hearing and equilibrium?
C
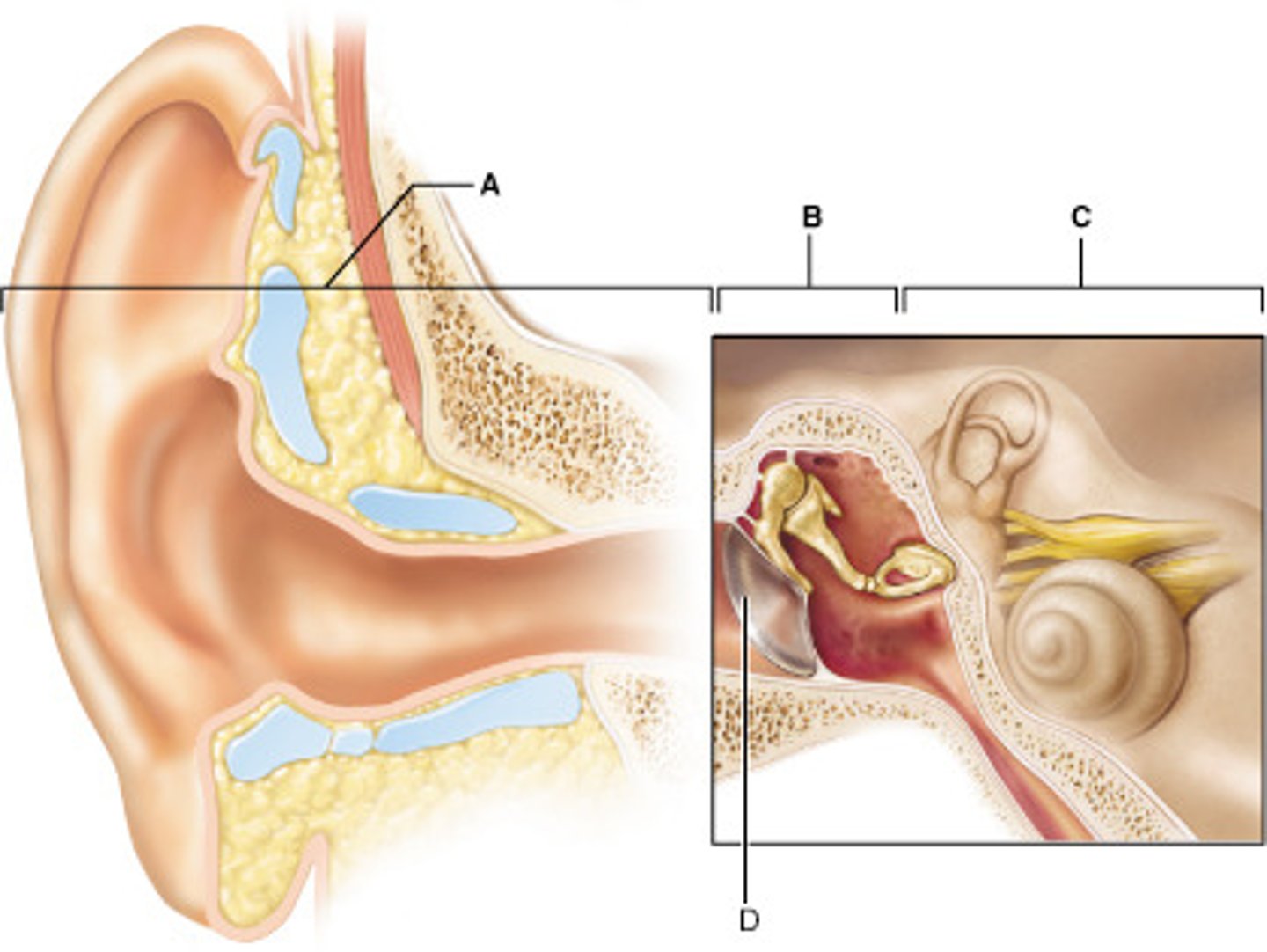
A middle ear infection (otitis media) would be located in which region?
B
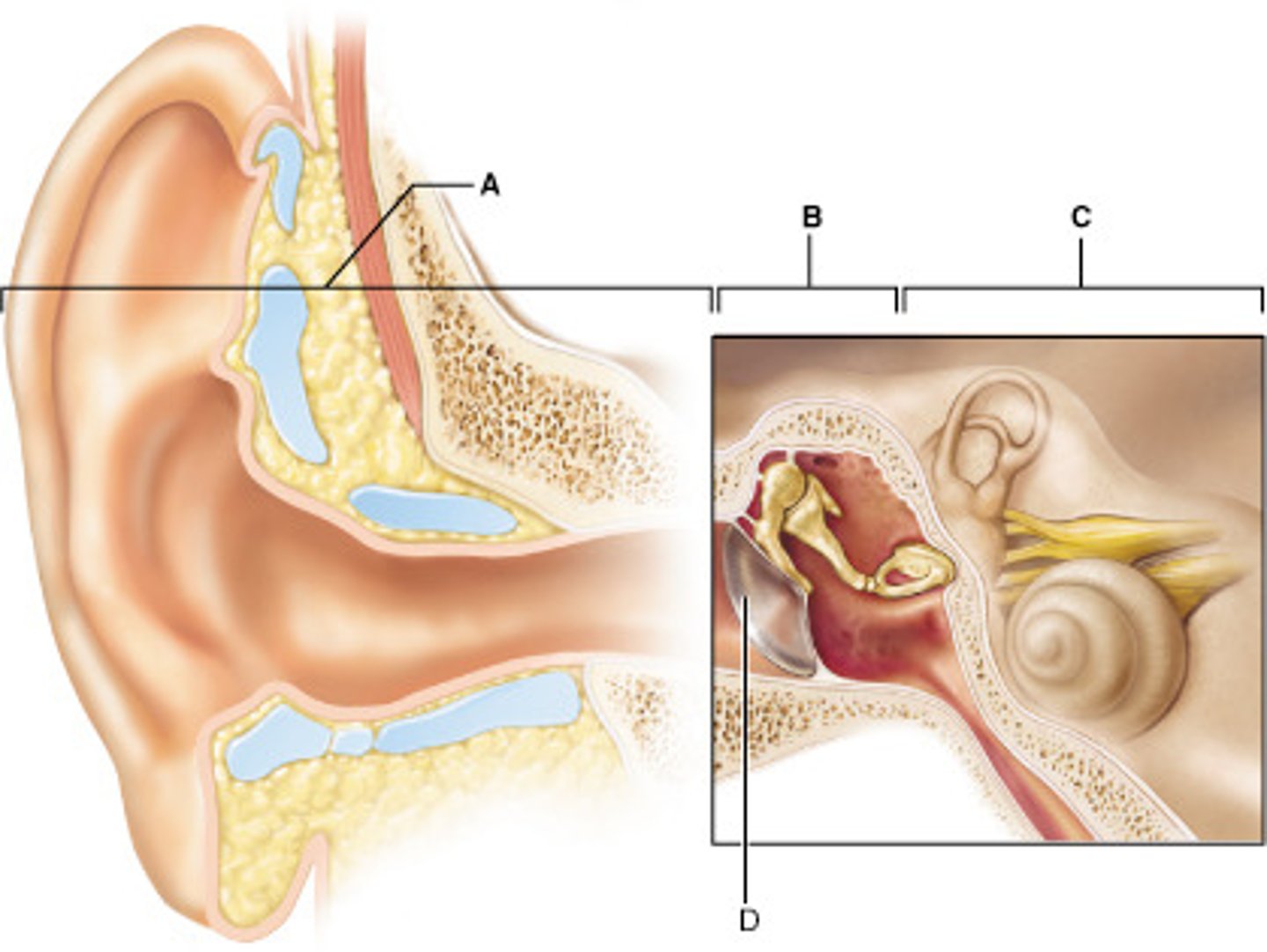
Damage to which of these structures can result in sensorineural deafness?
D
Otosclerosis, which can result in conduction deafness, affects which of these structures?
A
What are the names of the bones at A, in order from left to right?
malleus, incus, stapes
What part of the inner ear houses the receptor organ of hearing, the spiral organ (organ of Corti)?
D
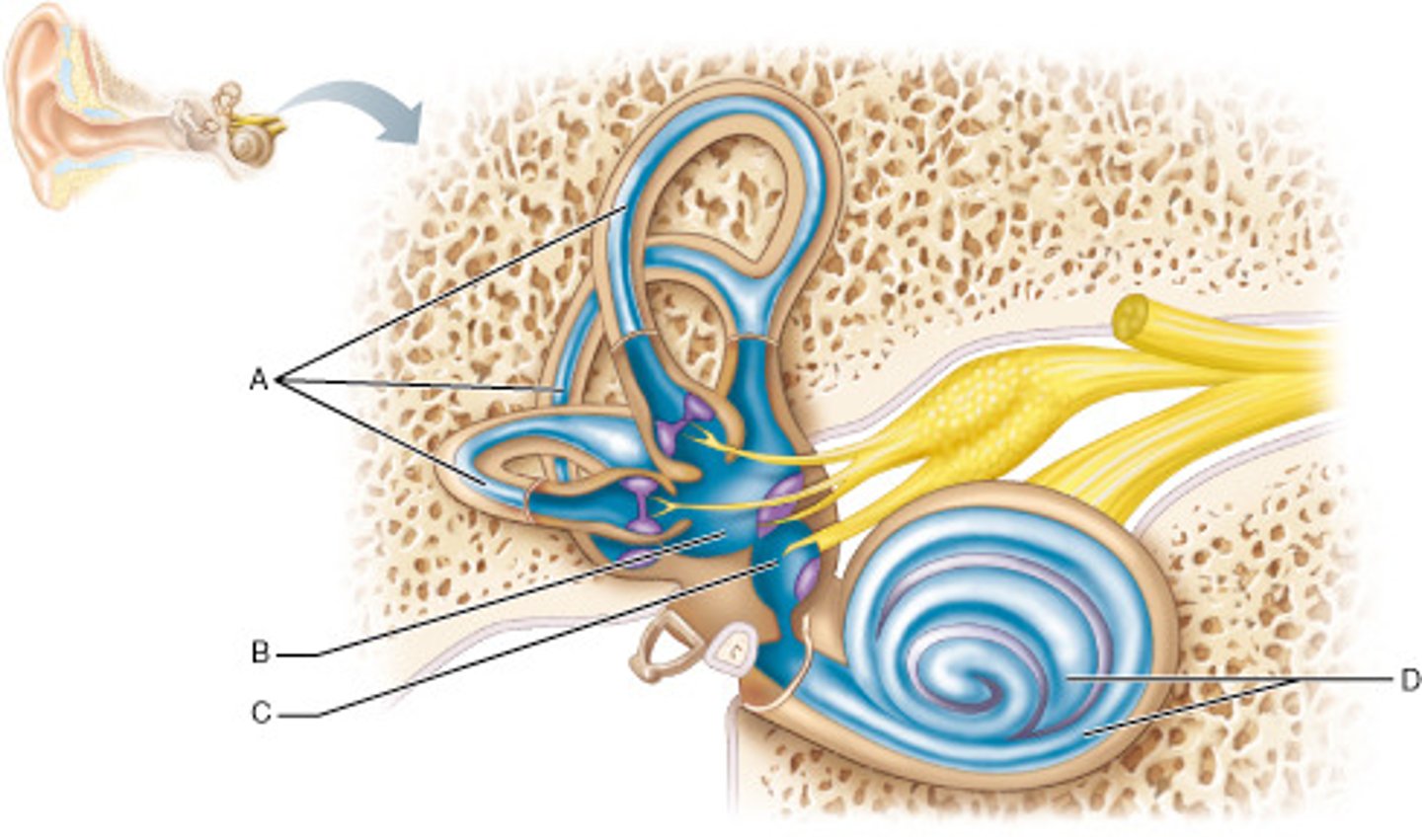
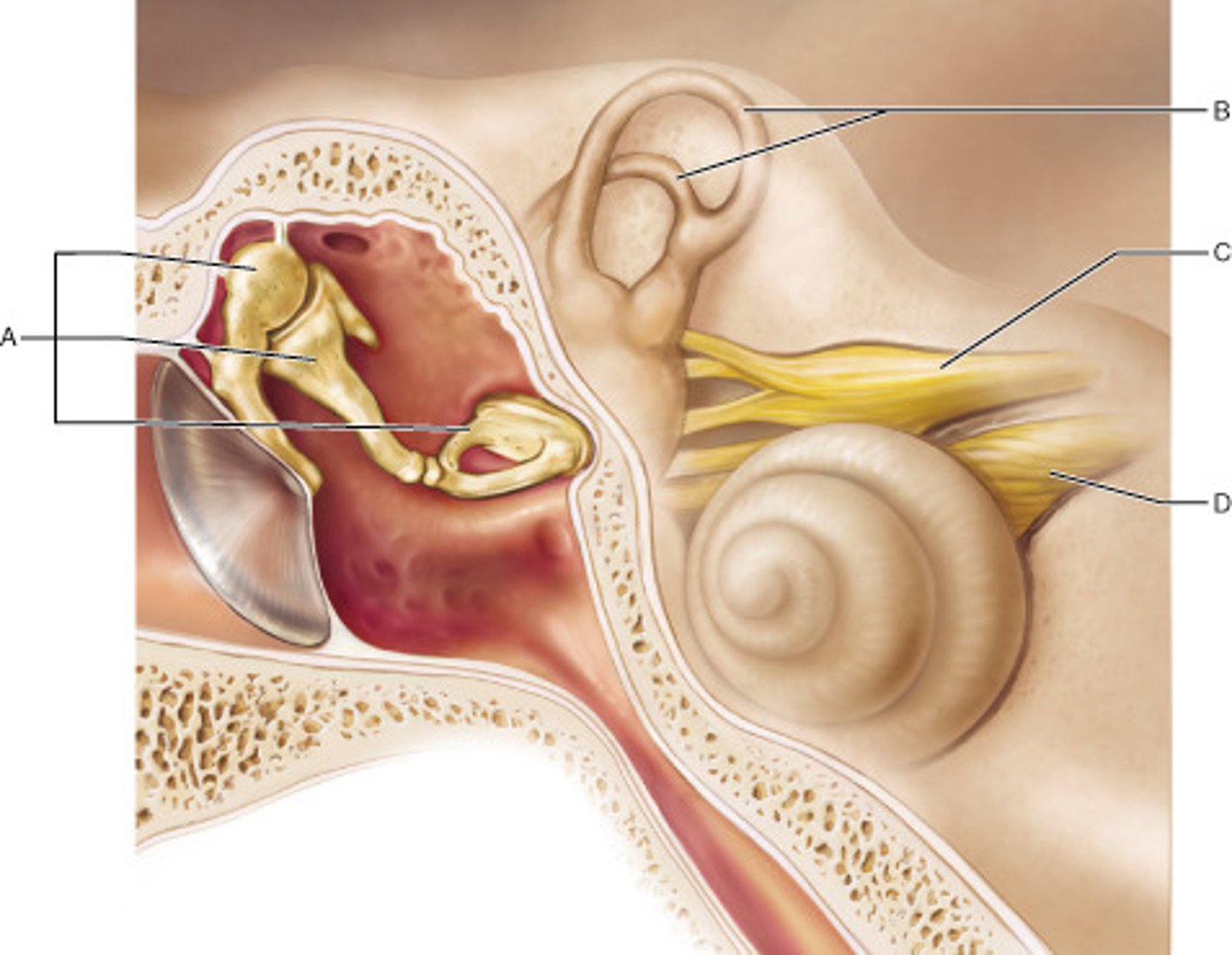
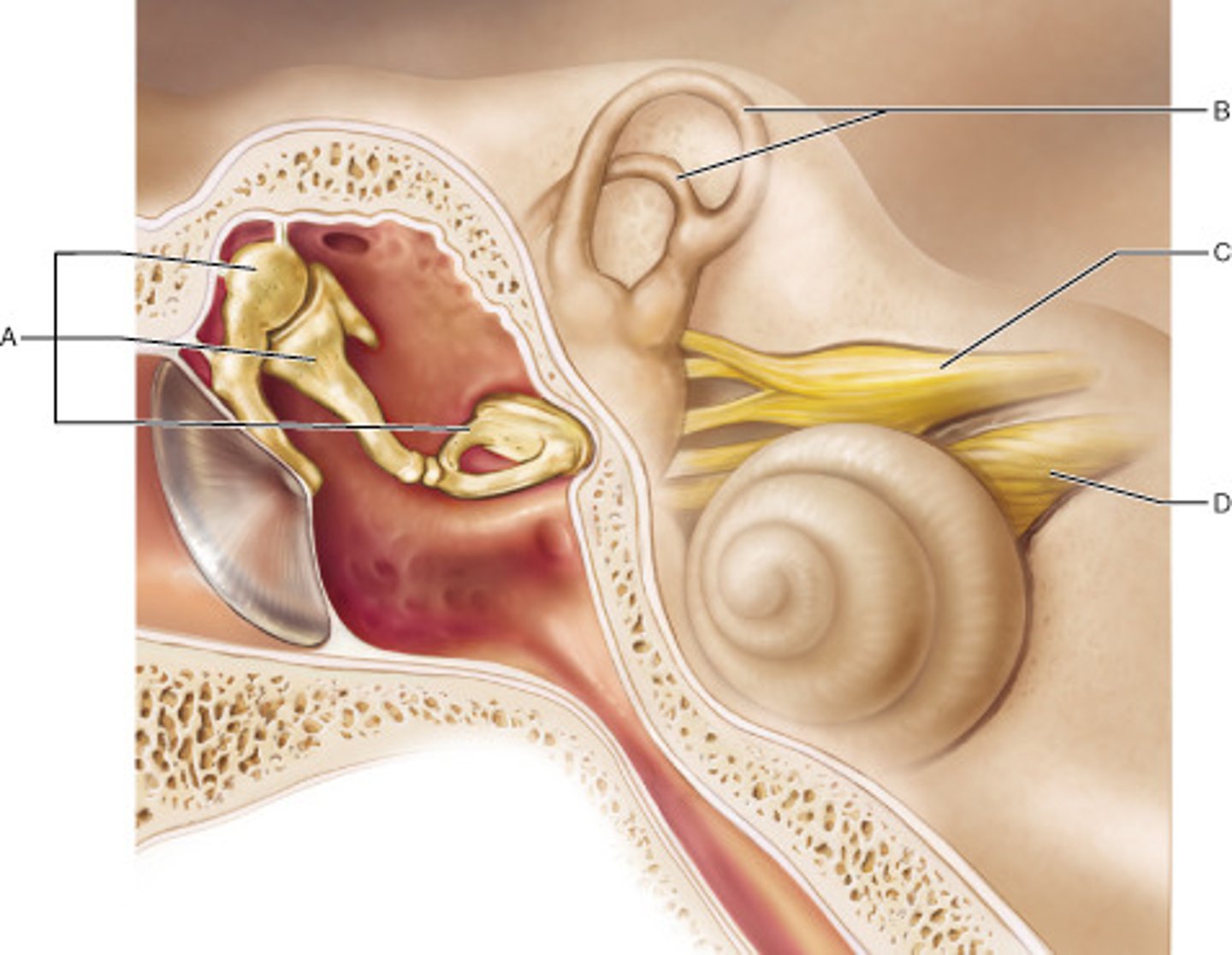
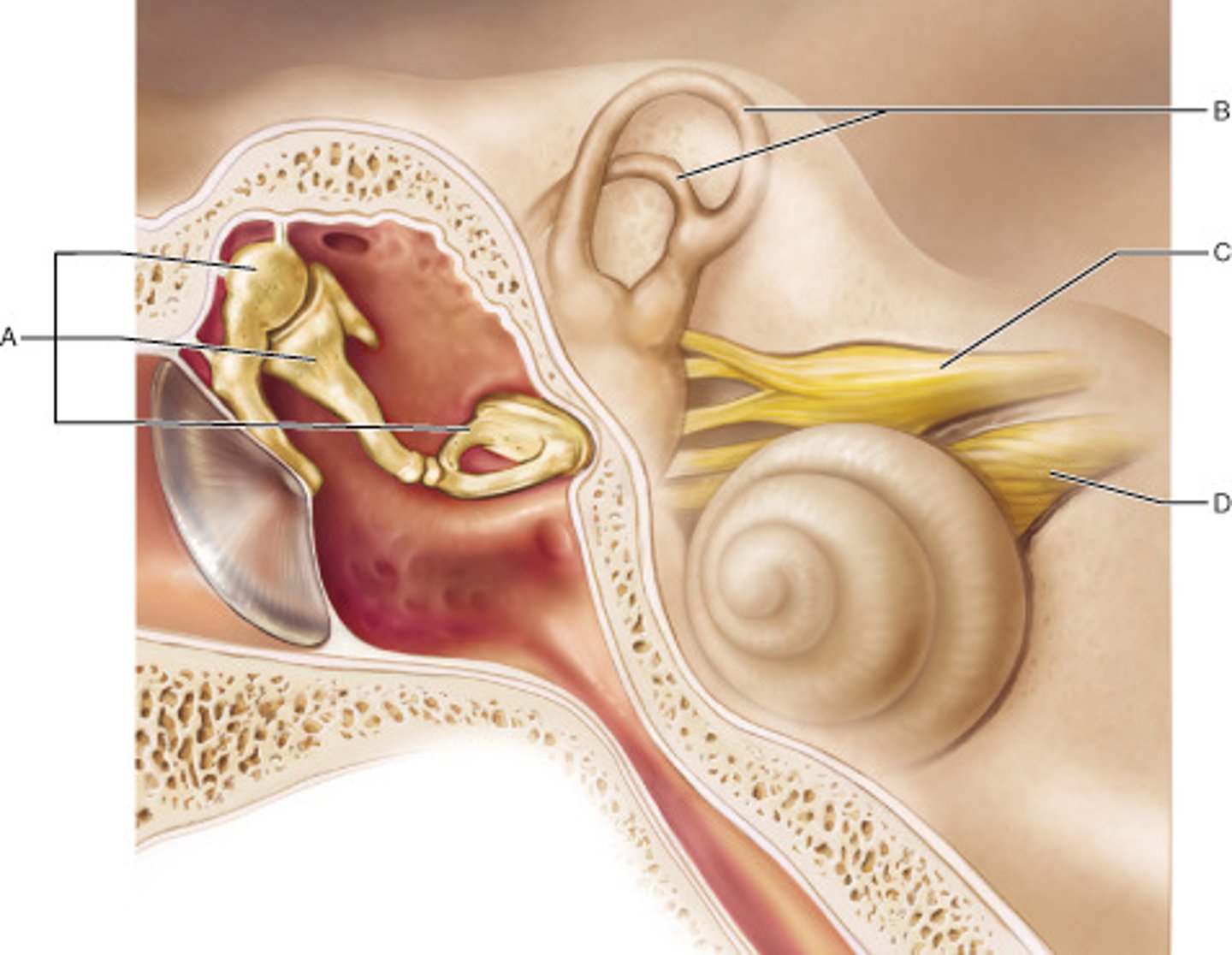
Which part of the inner ear houses receptors for rotational (angular) movement of the head?
A
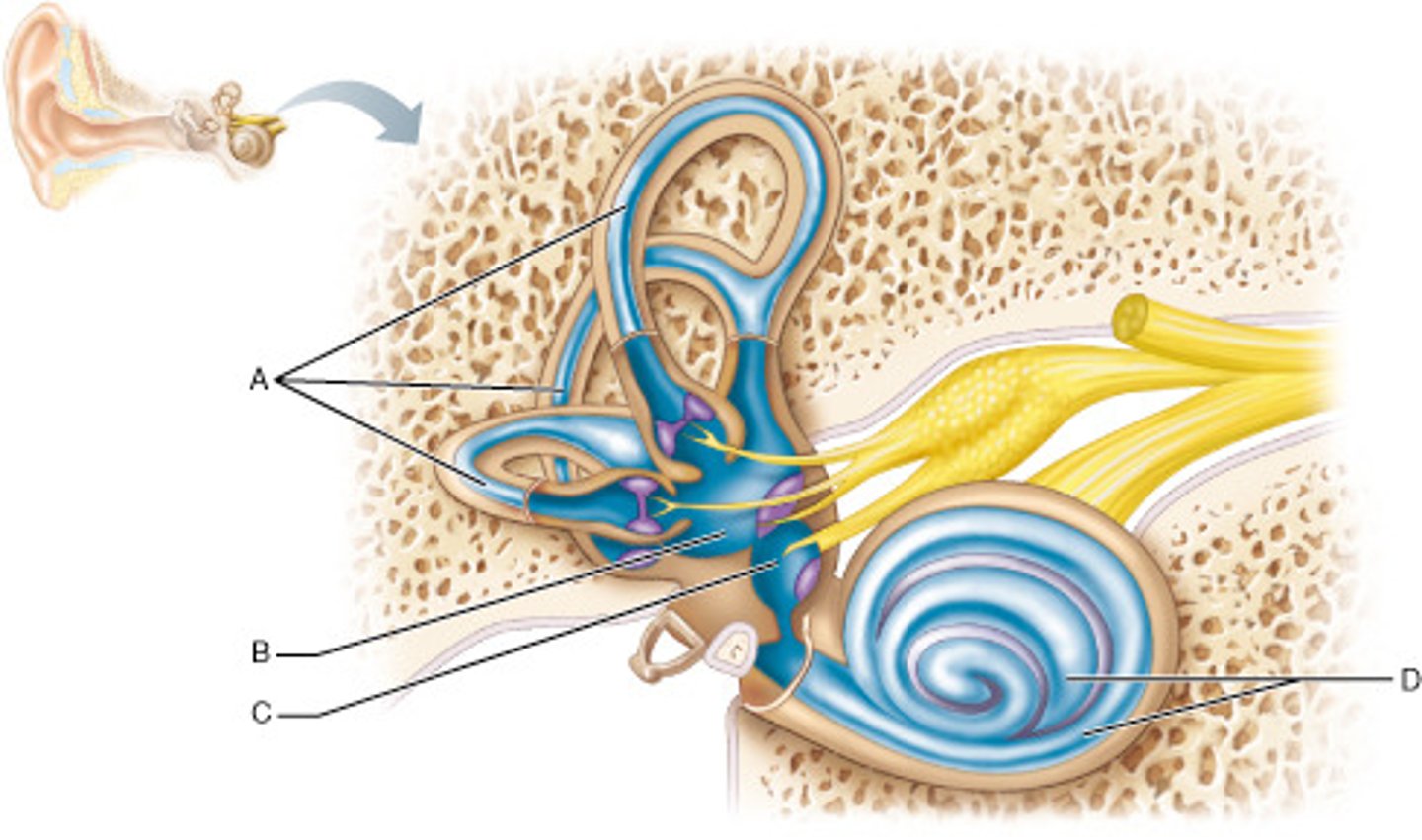
Name the enlarged swelling at the end of A that is a sensory structure.
ampulla
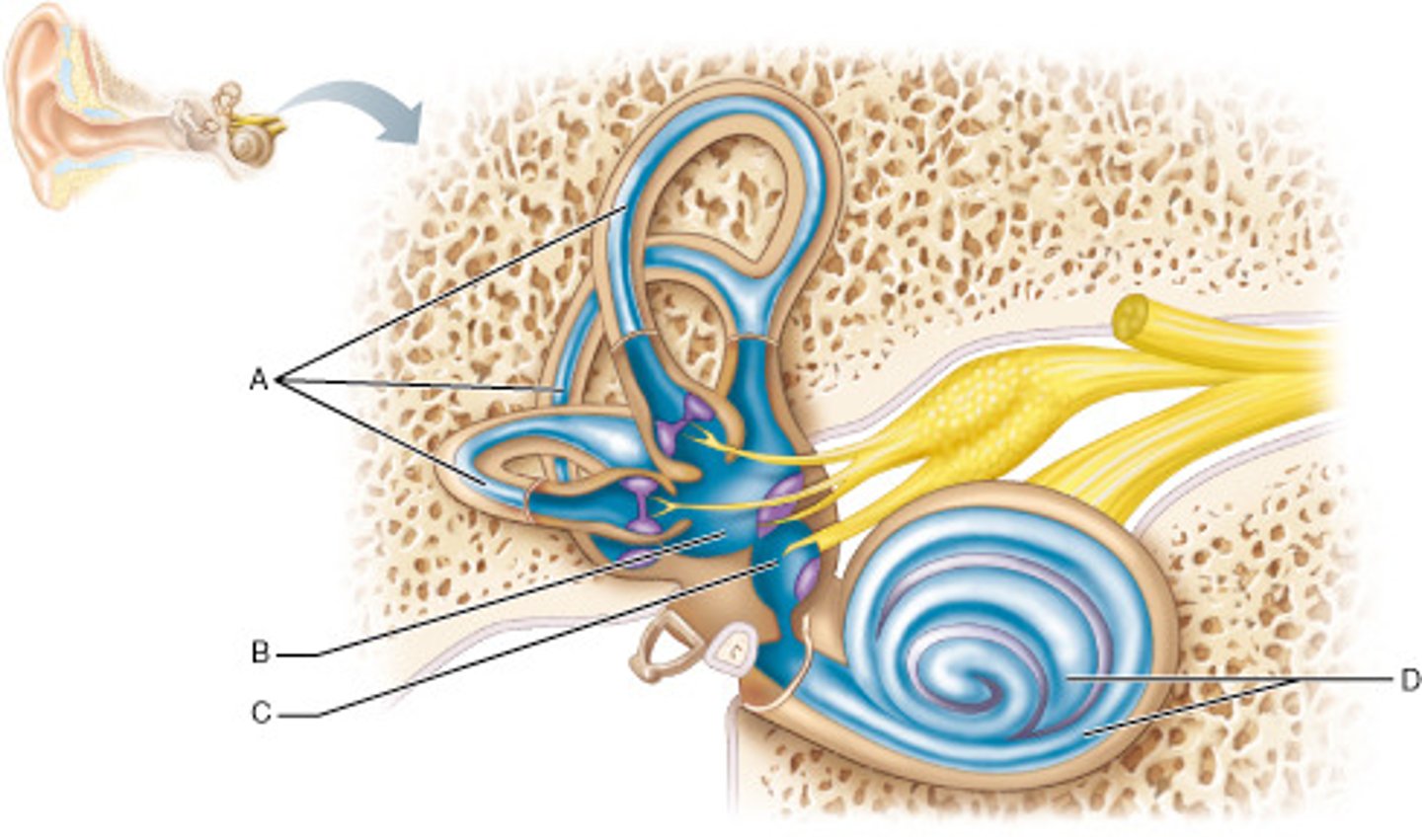
Which middle ear ossicle is attached to, and transmits vibratory motion to, the oval window?
stapes
Which portion of the ear is responsible for sound transduction?
the cochlea
How many ossicles are found in the ear?
three
What type of channel is responsible for the initial changes in the membrane potential of the hair cells, which ultimately determines the cochlear nerve response to sound?
mechanically gated
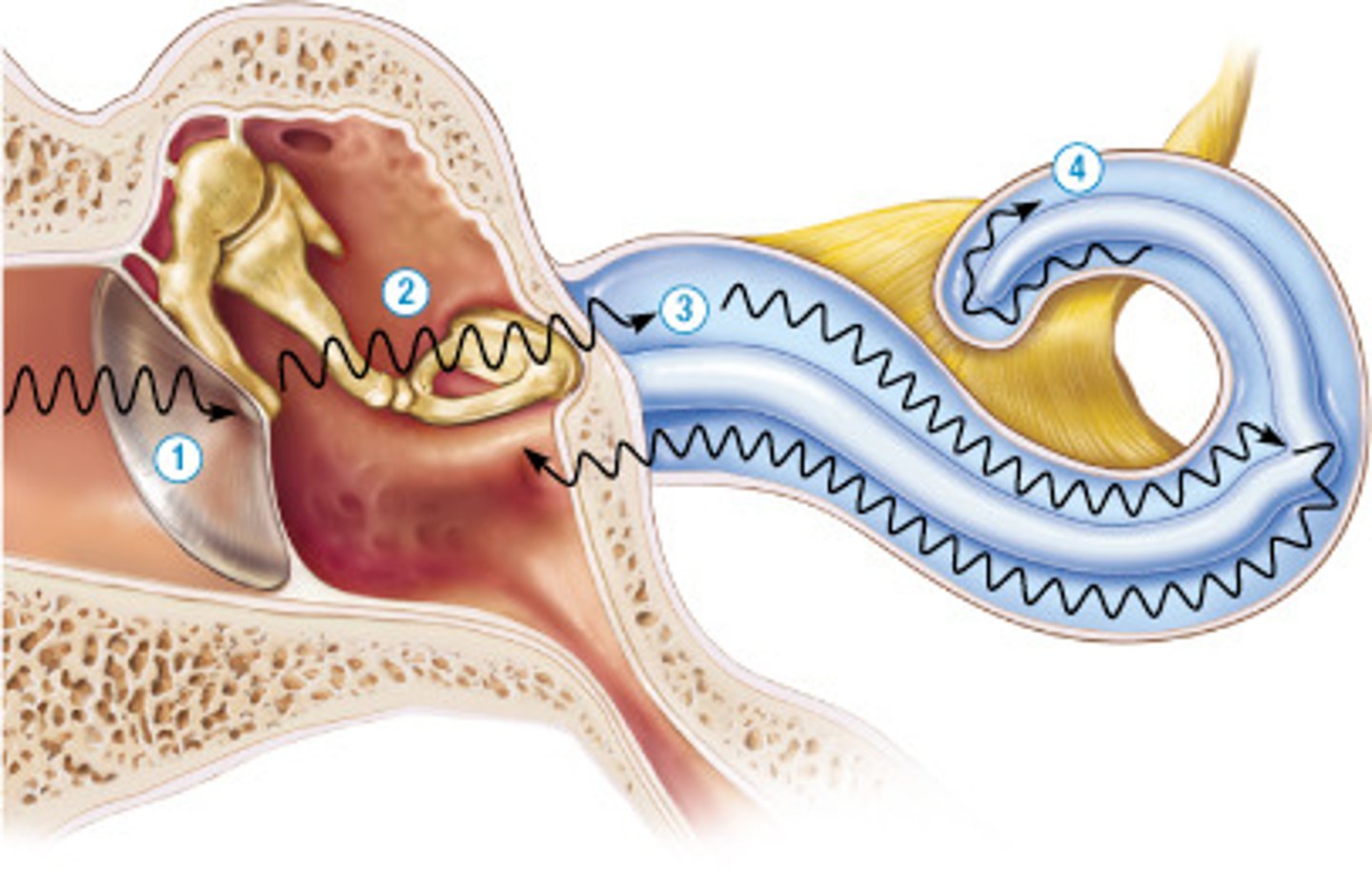
Name the structure represented by (1).
tympanic membrane
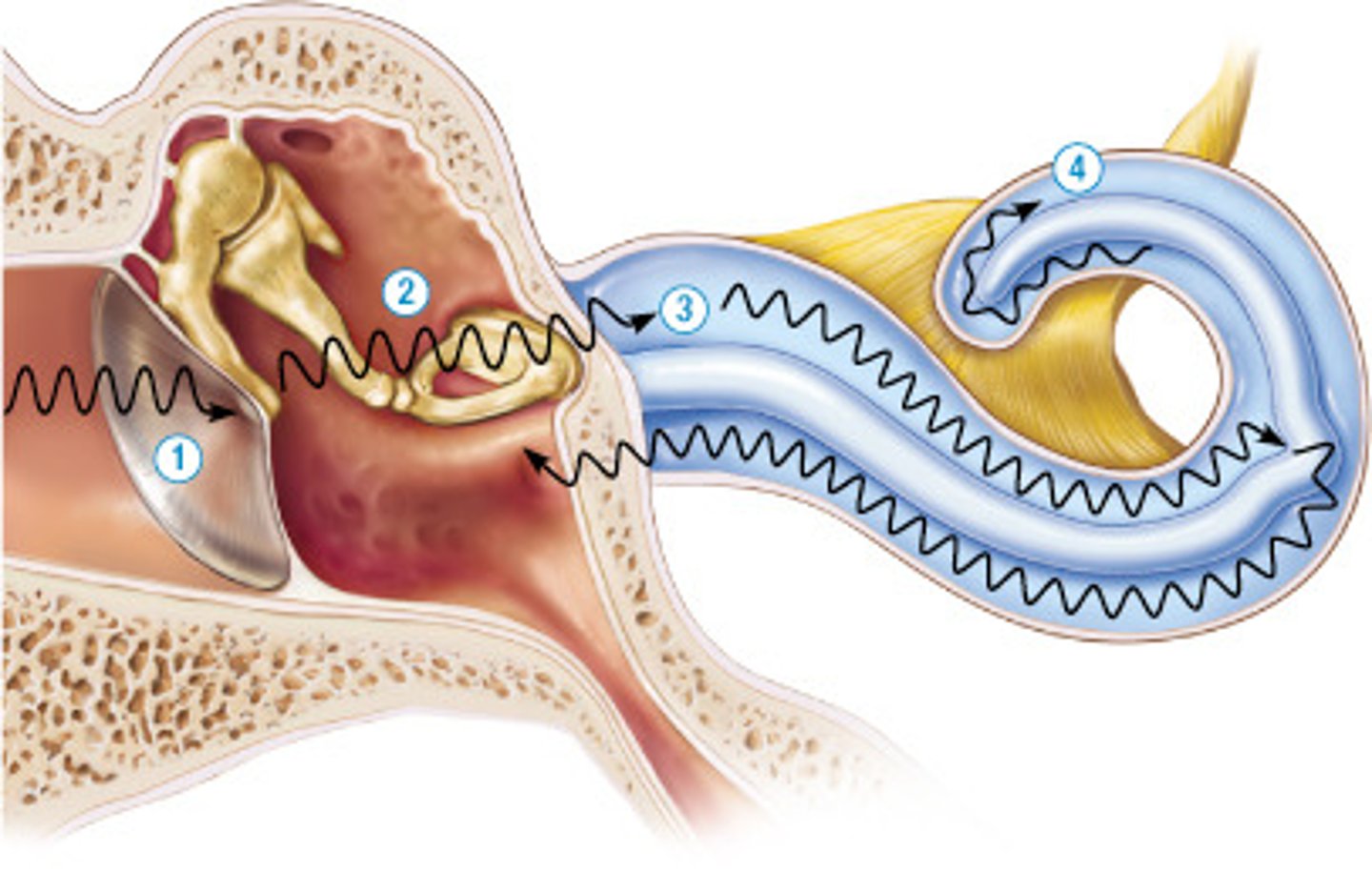
Identify the function of (2) in this image.
They conduct sound waves and amplify the vibrations within the middle ear.
Transduction of lower frequency sound waves occurs at the __________ of the cochlea.
apex
At rest, when no sound is entering the cochlea, the hair cells send no signal.
False
Height of a wave is called the __________.
amplitude
What structure helps us localize sound?
the superior olivary nucleus
Congenital sensorineural deafness most commonly involves damage to ______.
the cochlear hair cells
Which of the following are the receptors for static equilibrium?
hair cells
What does the vestibular apparatus detect?
head position in space
Which of the following correctly matches the equilibrium receptor organs to the type of equilibrium it monitors?
maculae/static equilibrium
Where are equilibrium receptors located?
in the semicircular canals and in the vestibule of the ear
The semicircular canals are adapted to detect static equilibrium.
False
Which of the following is true of receptors for dynamic equilibrium?
The receptors for dynamic equilibrium respond to rotational forces.
Information from balance (equilibrium) receptors is processed in __________.
the brain stem