06.3B3 U6P1 (PART B) Microscopic Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
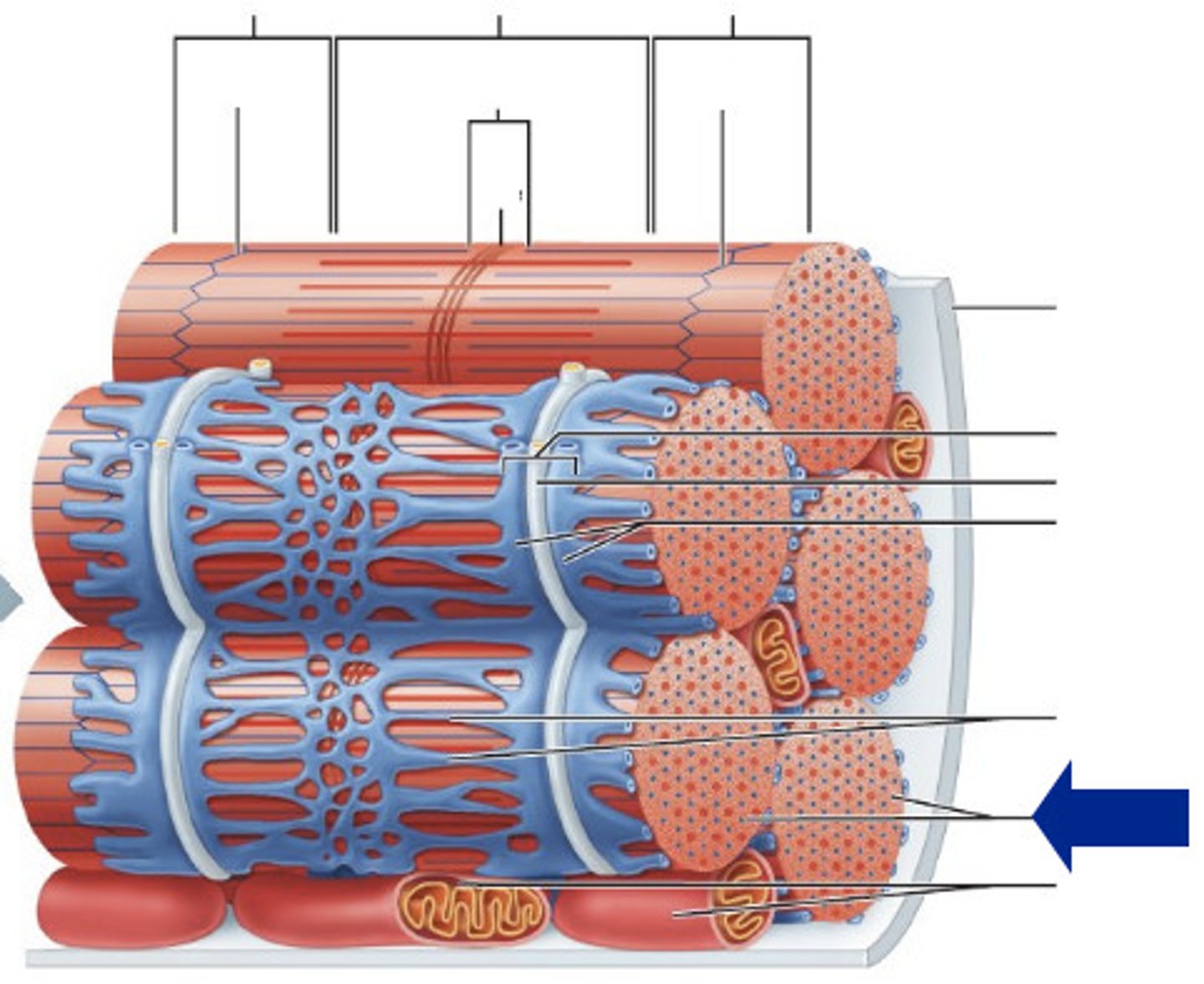
Fascicle
A bundle of muscle fibers
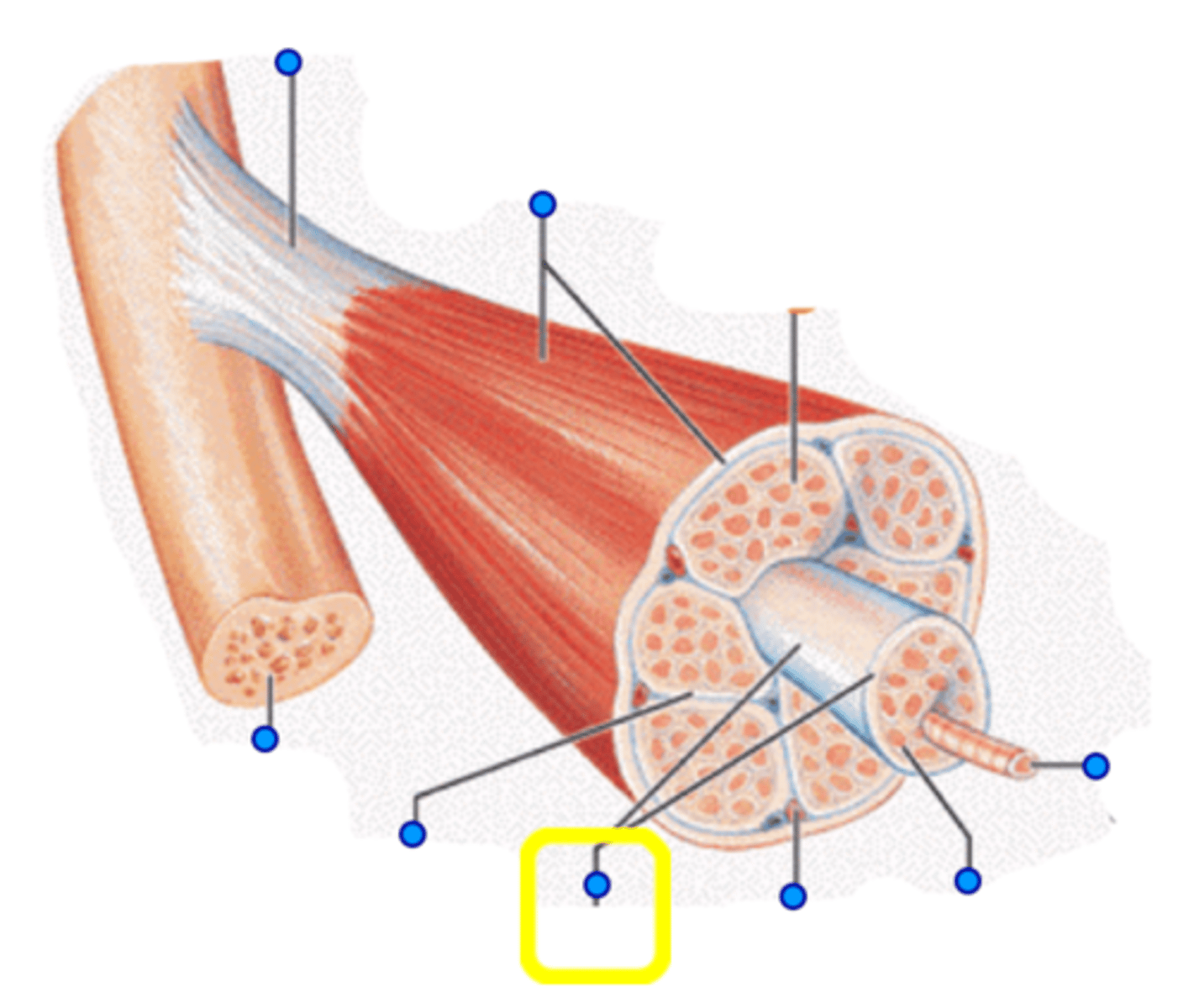
Muscle fiber (Muscle cell)
A long cylindrical multinucleate cell; nuclei are just beneath the sarcolemma; sarcolemma is a specialized plasma membrane; many mitochondria provide energy for muscle contraction; contain sarcoplasmic reticulum, T tubules, and myofibrils
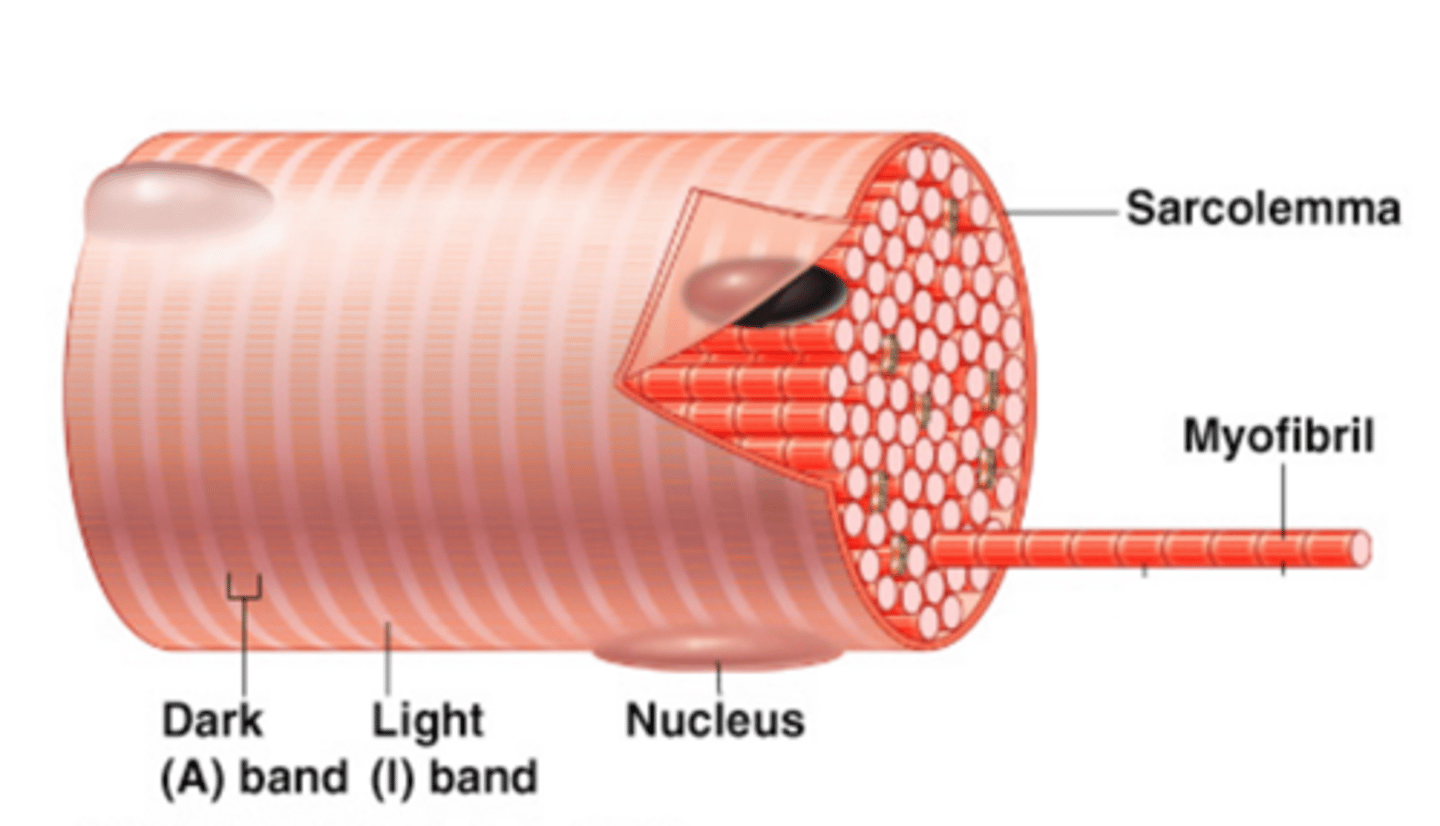
Sarcolemma
A specialized plasma membrane that surrounds muscle fibers that can conduct an electrical impulse
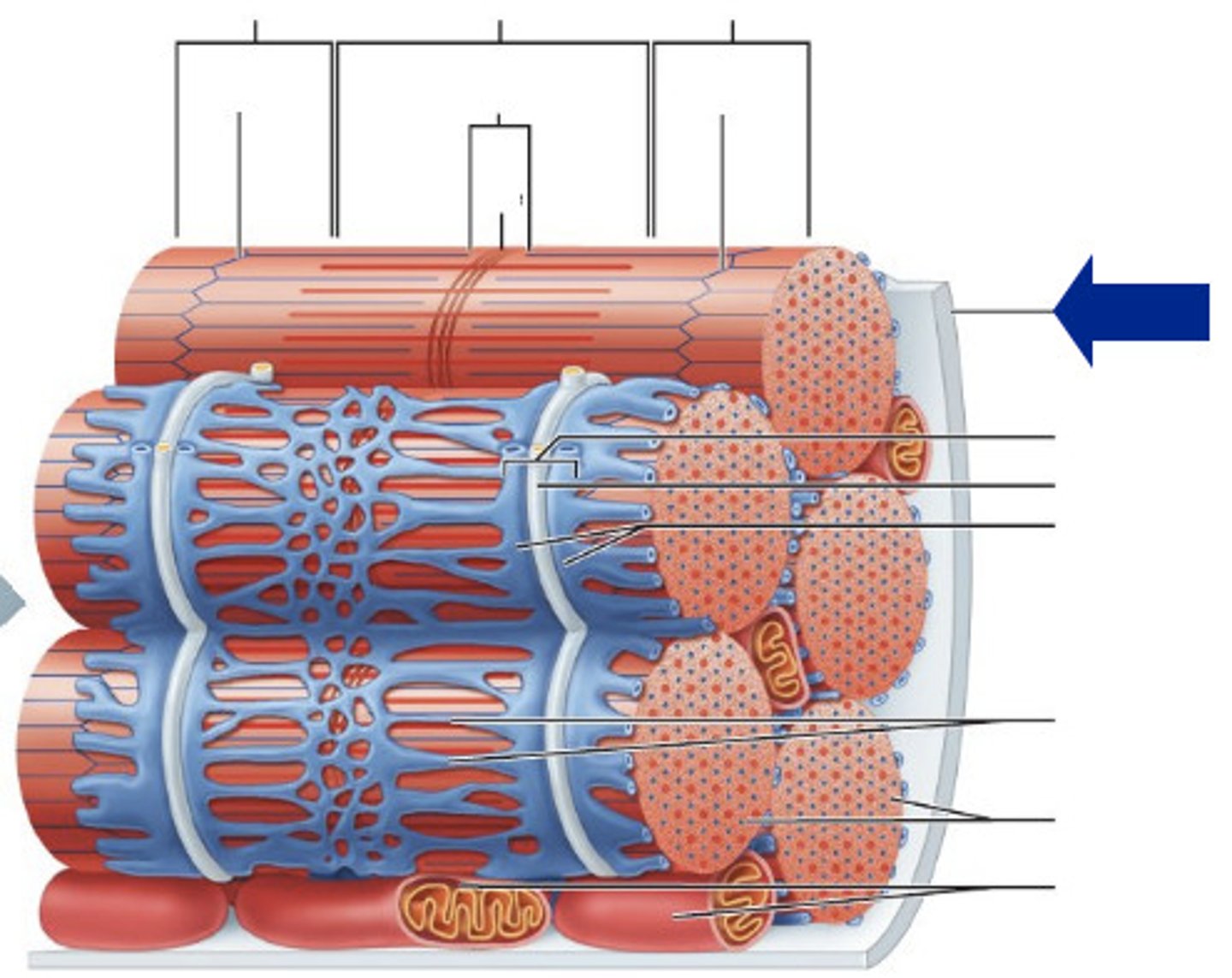
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
The specialized endoplasmic reticulum of the muscle cell that surrounds each myofibril and stores calcium ions
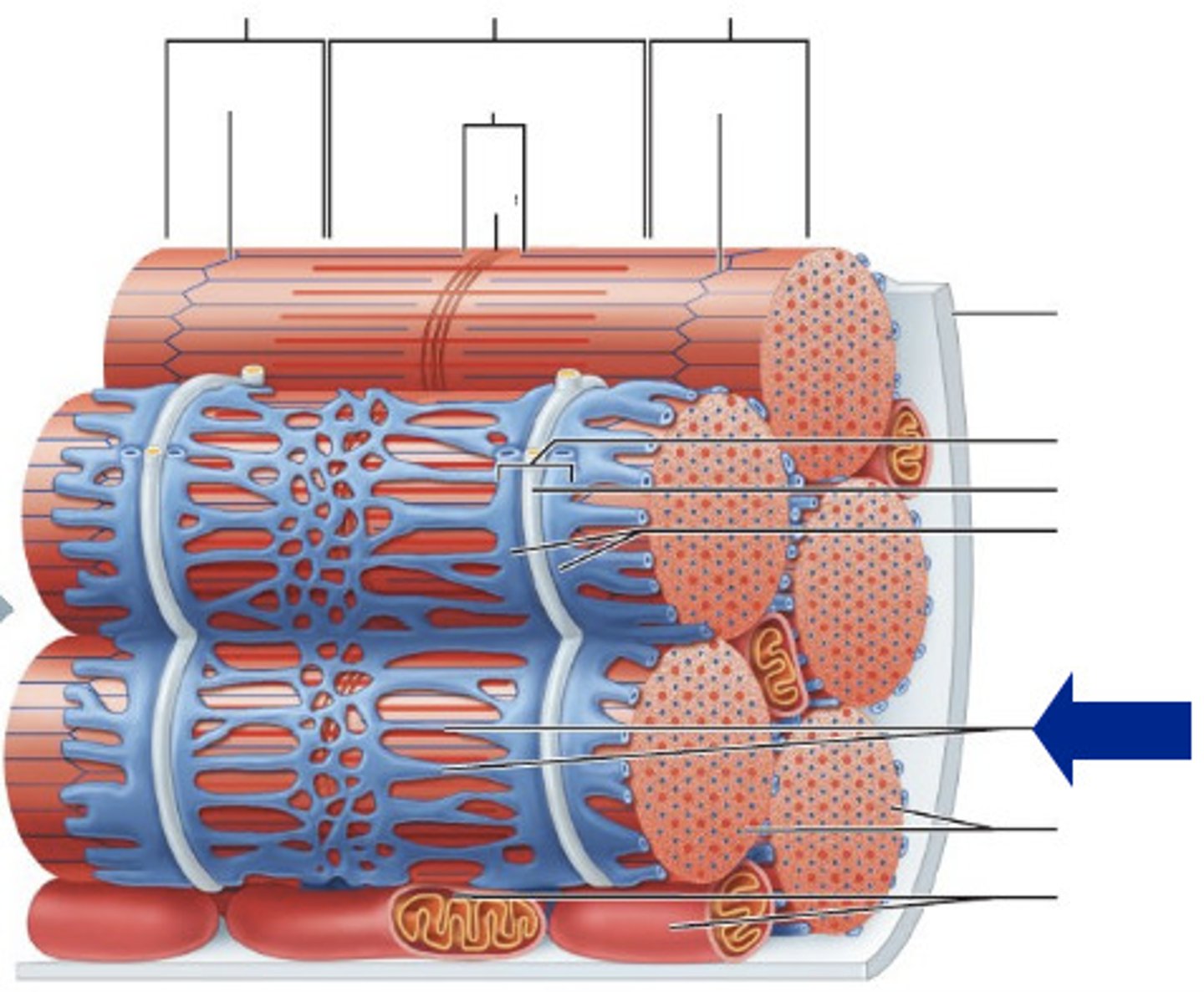
T-tubules
Small channels in the sarcolemma (muscle cell membrane) that allow for uniform muscle contraction because action potential spreads more quickly
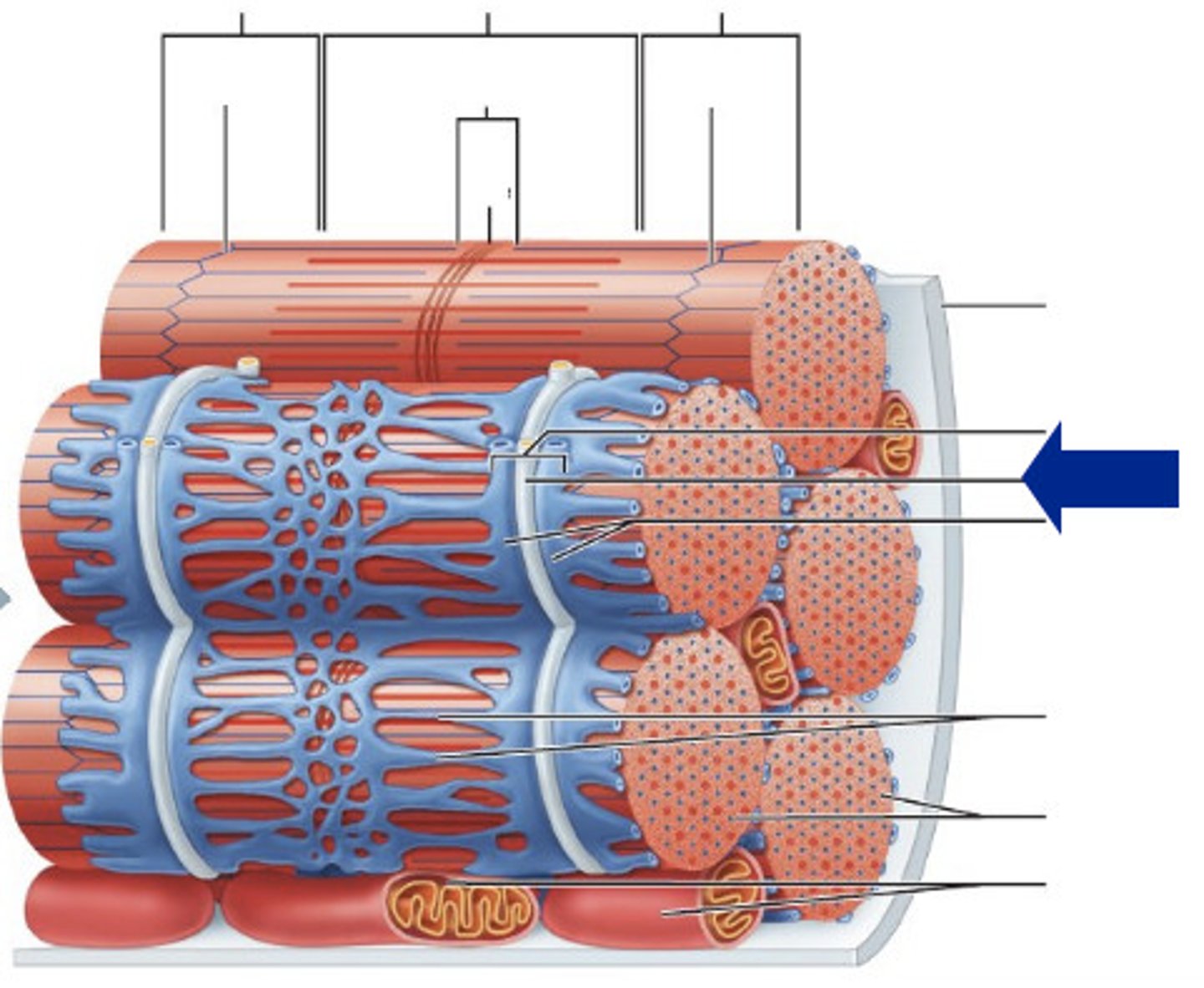
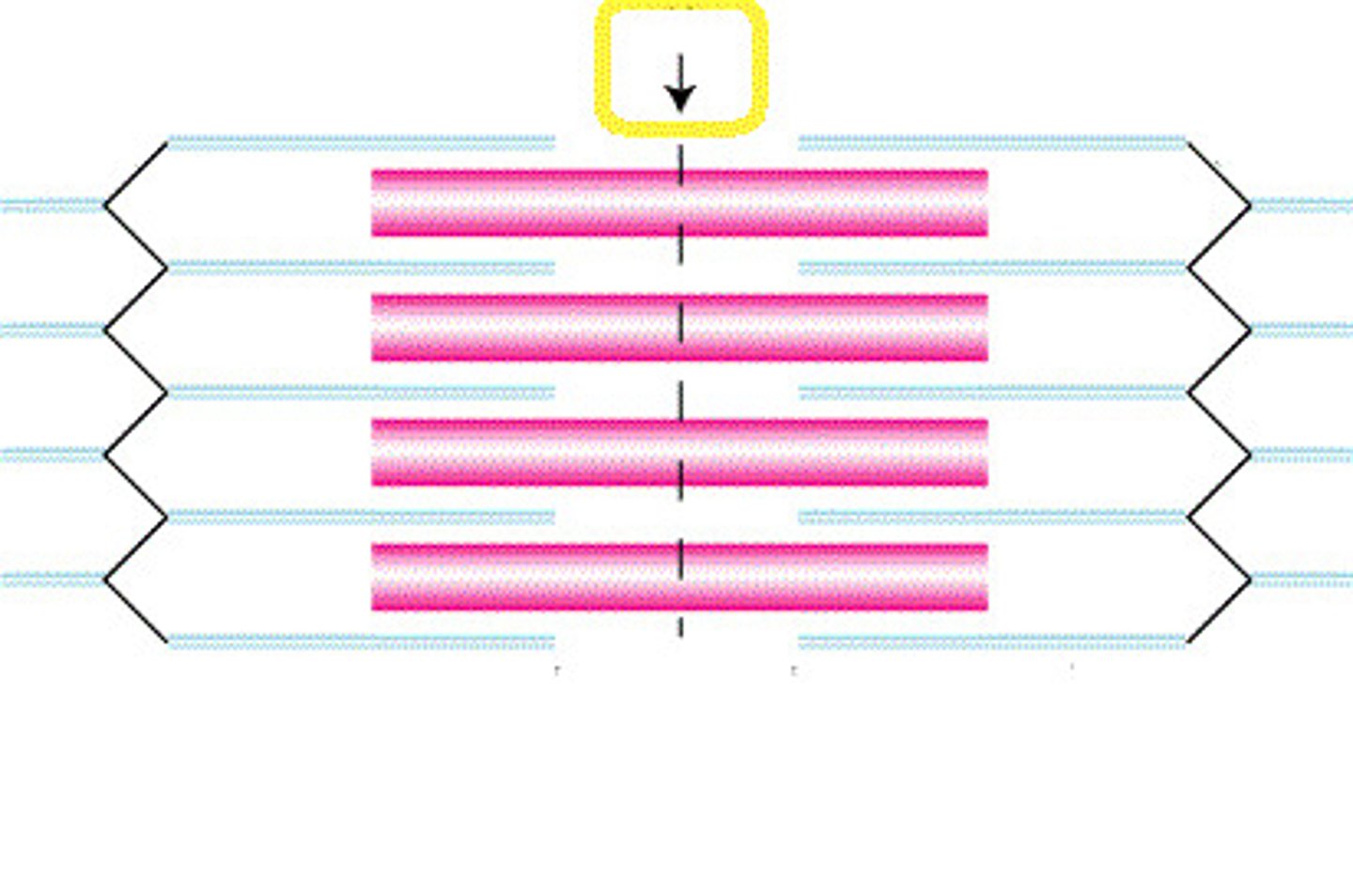
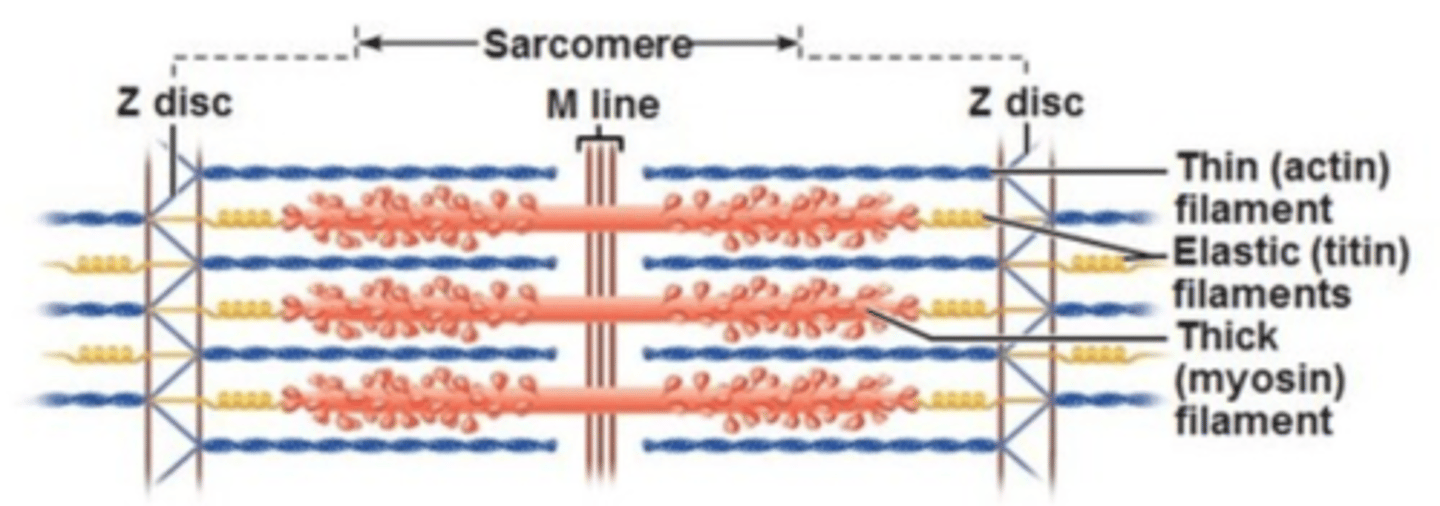
Sarcomere
The functional unit of muscle that produces muscular contraction and consists of repeating sections of actin and myosin.
Myofibrils
The contractile organelles of a skeletal muscle fiber that contain actin and myosin
Myofilaments
The contractile proteins, actin and myosin, of muscle cells
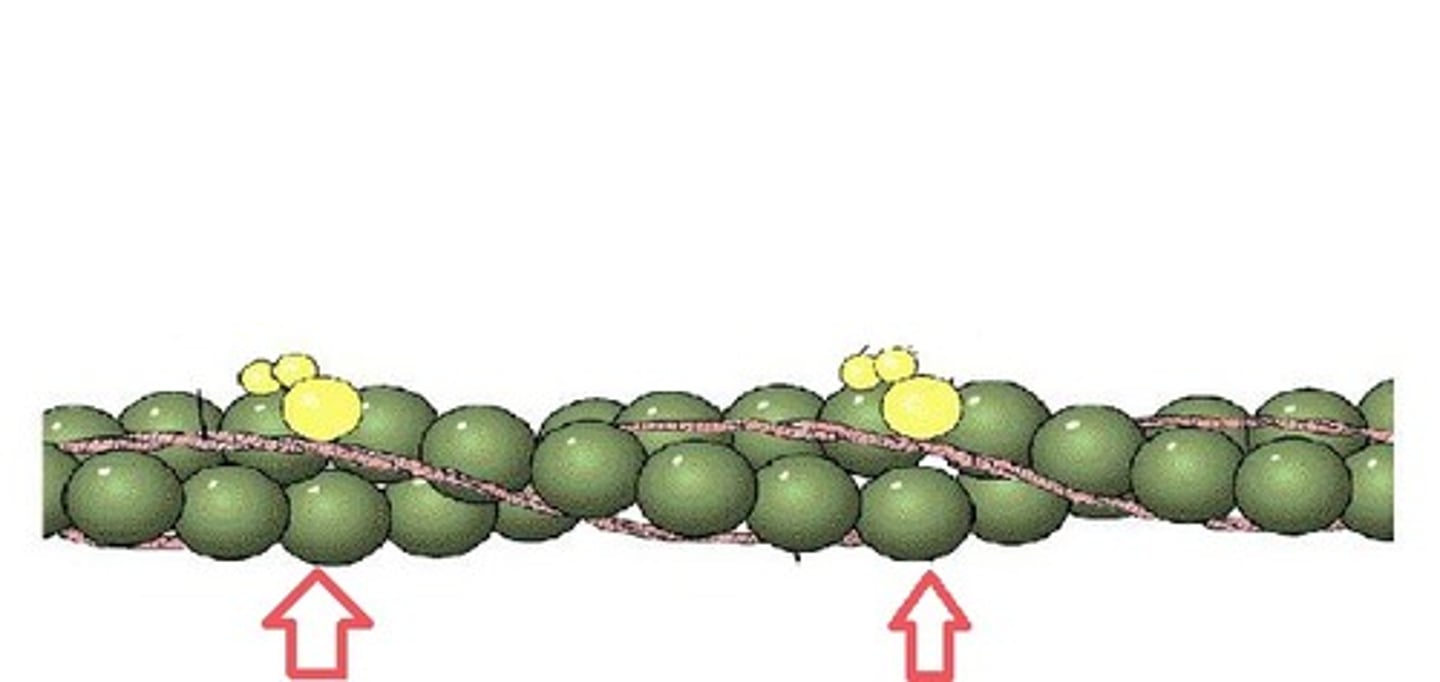
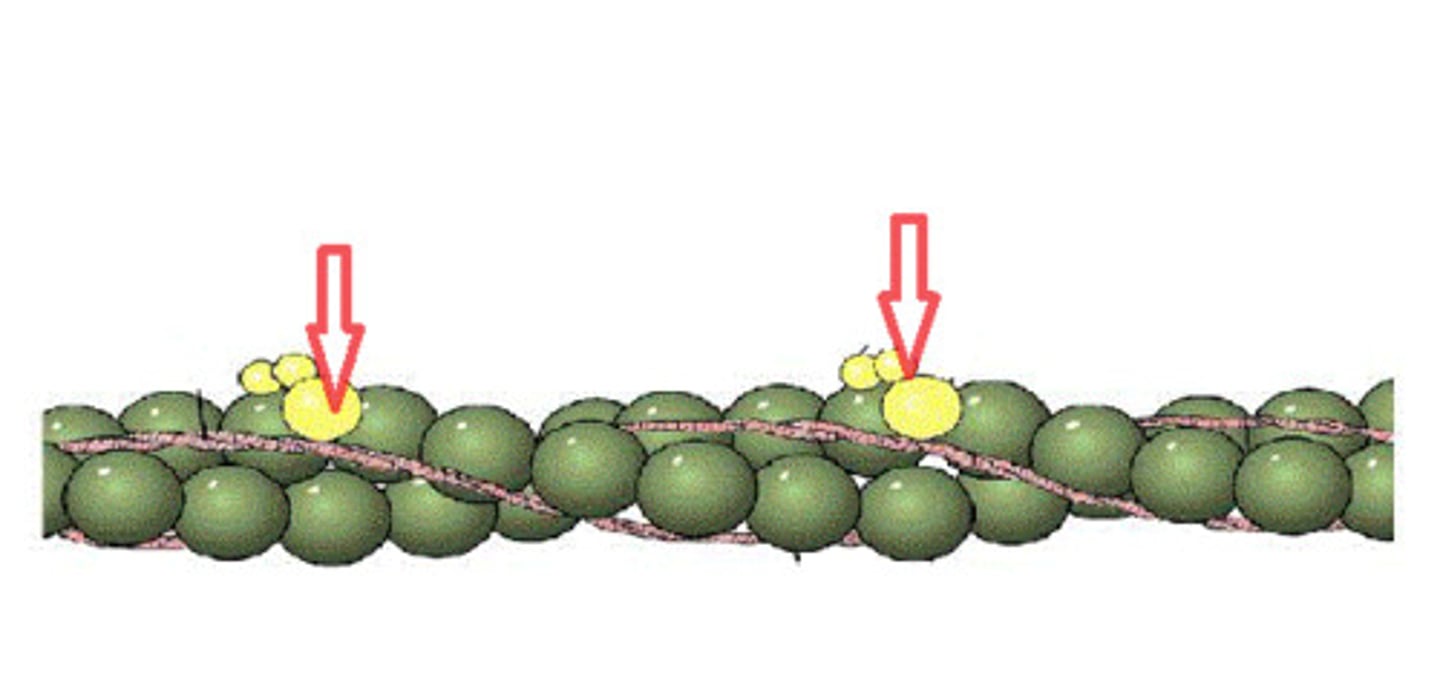
Actin
A thin contractile protein found in muscles that forms two long chains that wrap around each other; looks like a double strand of pearls
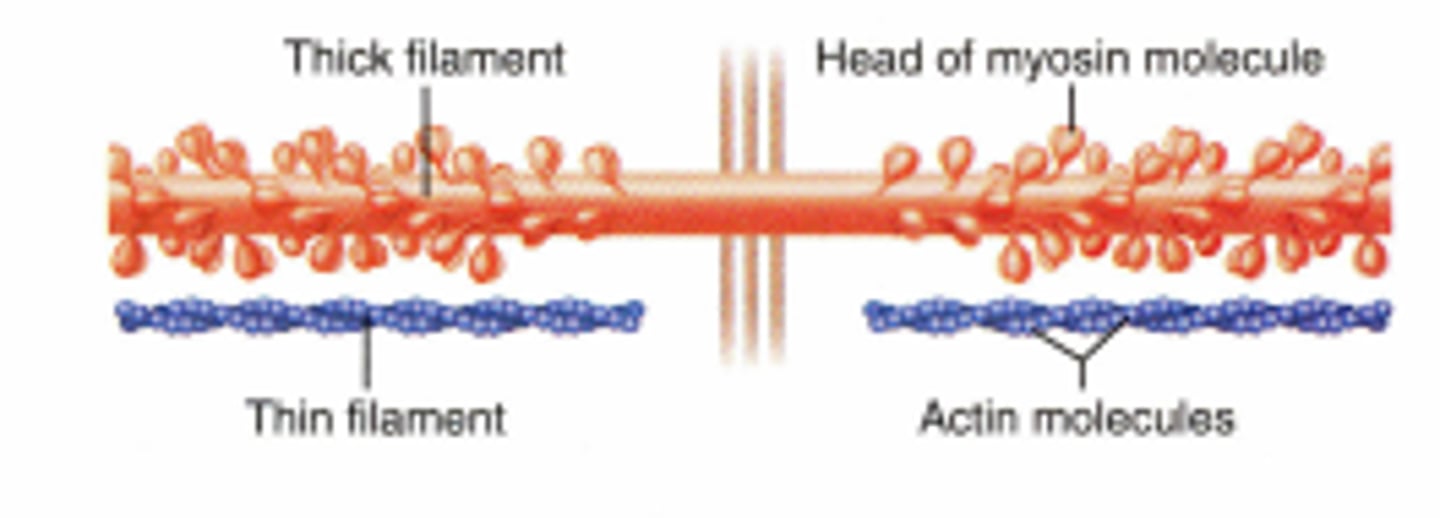
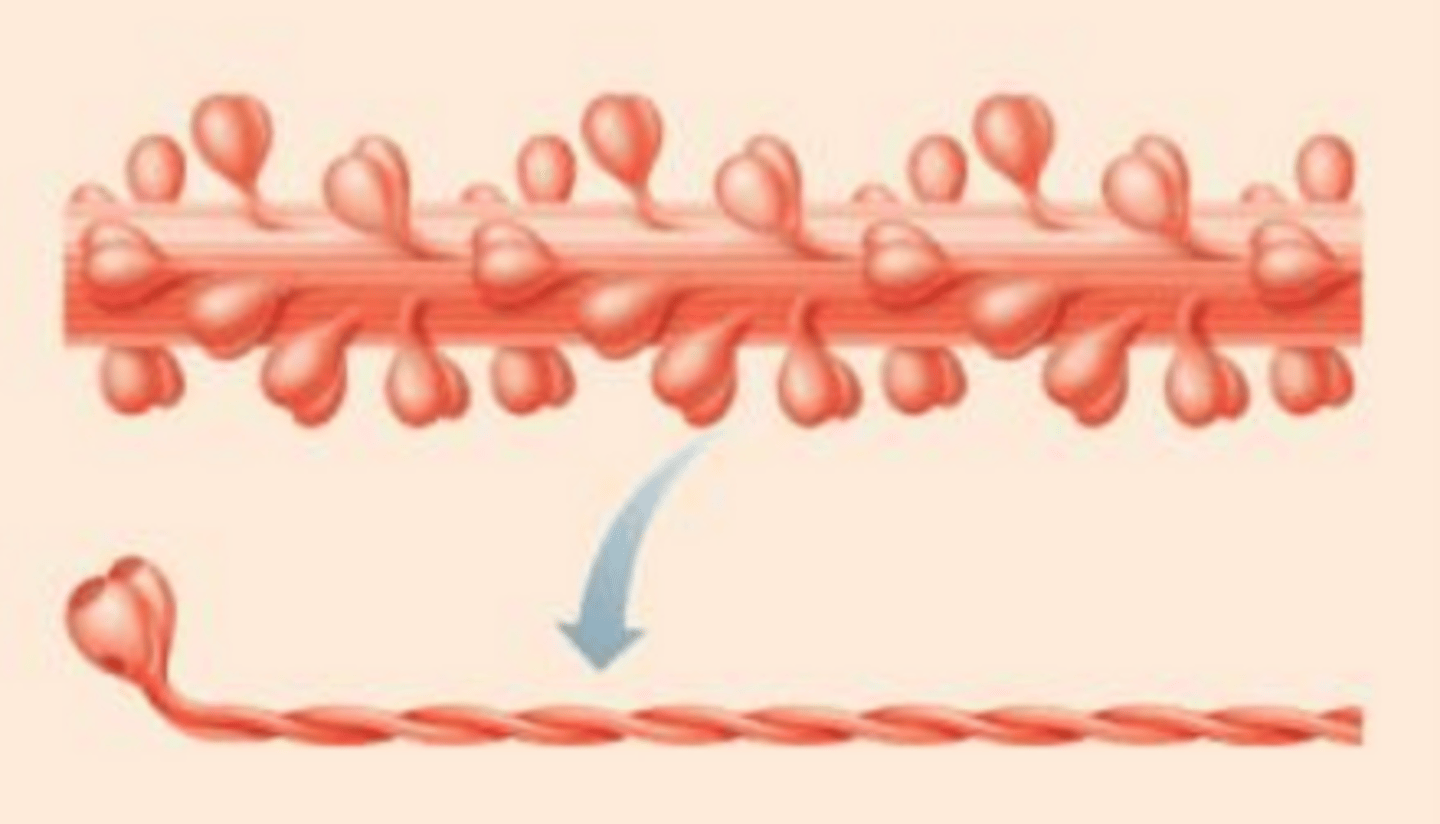
Myosin
A thick contractile protein found in muscles that interacts with actin to produce muscle movement
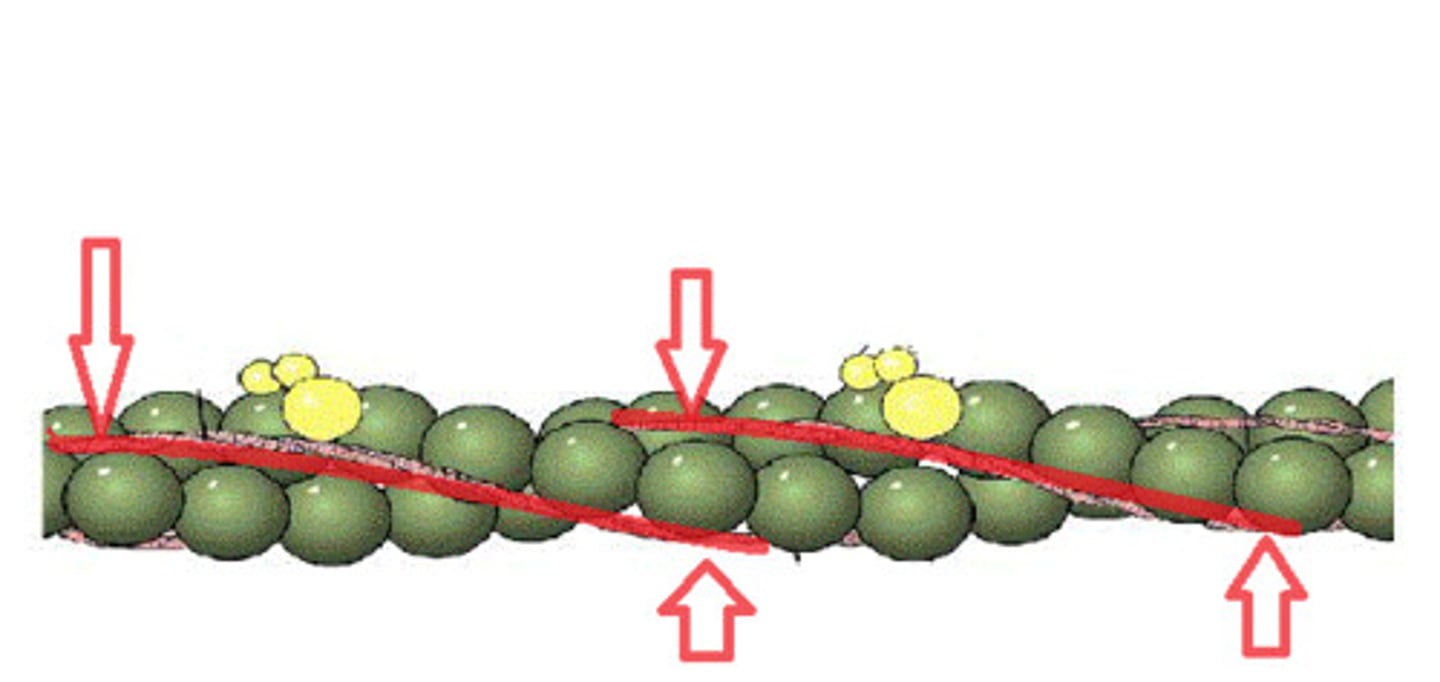
Tropomyosin
A rod-like regulatory protein that, on a resting muscle fiber, covers myosin binding sites along the thin filament, preventing actin and myosin from interacting
Troponin
A protein of muscle that together with tropomyosin forms a regulatory protein complex controlling the interaction of actin and myosin and that when combined with calcium ions permits muscular contraction
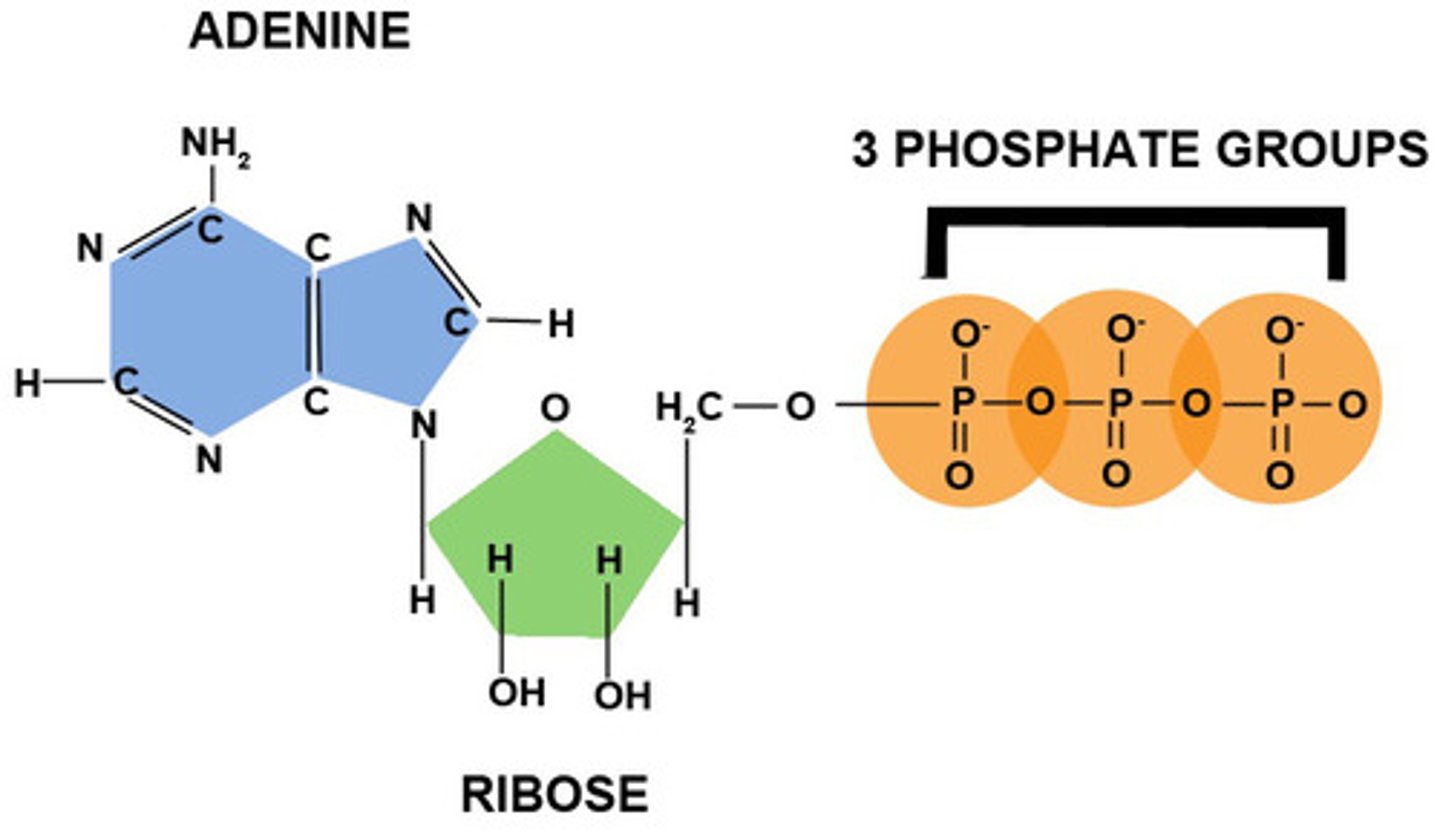
ATP
A compound composed of adenosine and three phosphate groups that supplies energy for many biochemical cellular processes like muscle contraction by undergoing enzymatic hydrolysis.
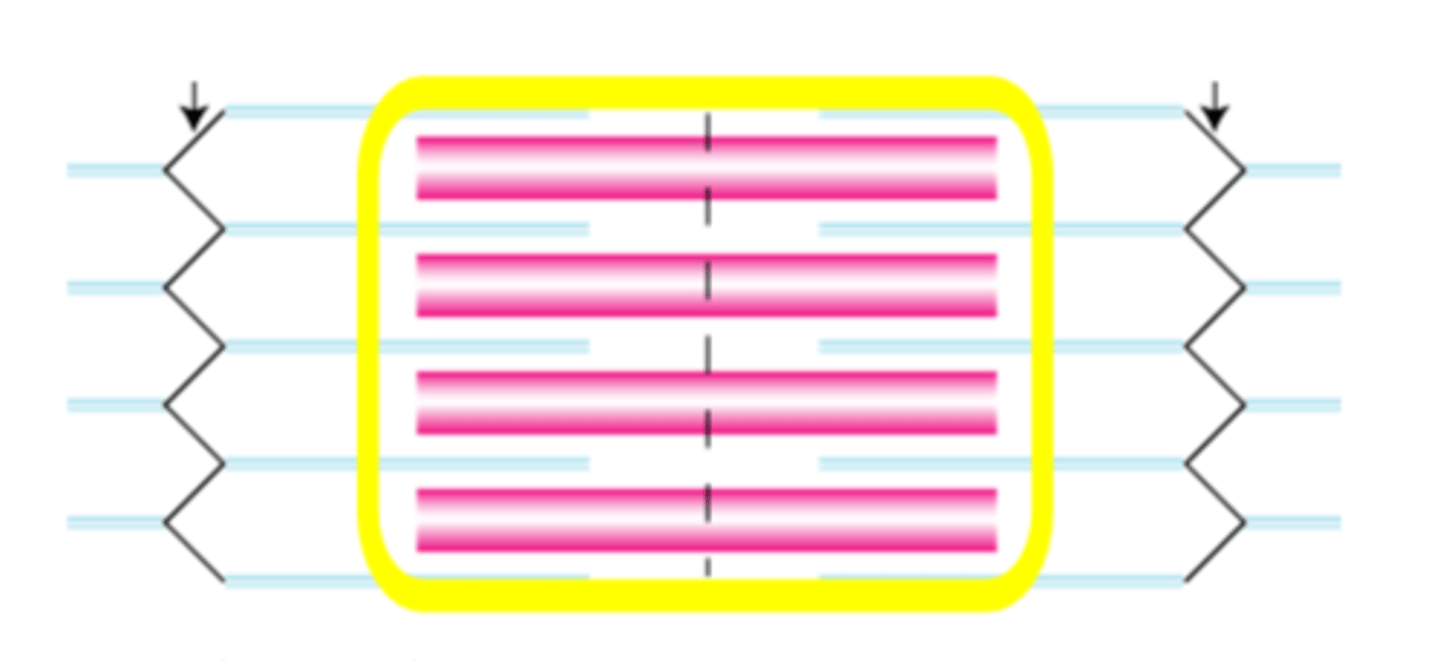
A band
The band of the sarcomere that extends the full length of the thick filament and includes regions of thick and thin filament overlap, as well as a region of thick filament only. These bands alternate with I bands to give skeletal and cardiac muscle a striated appearance and does not shorten during muscle contraction.
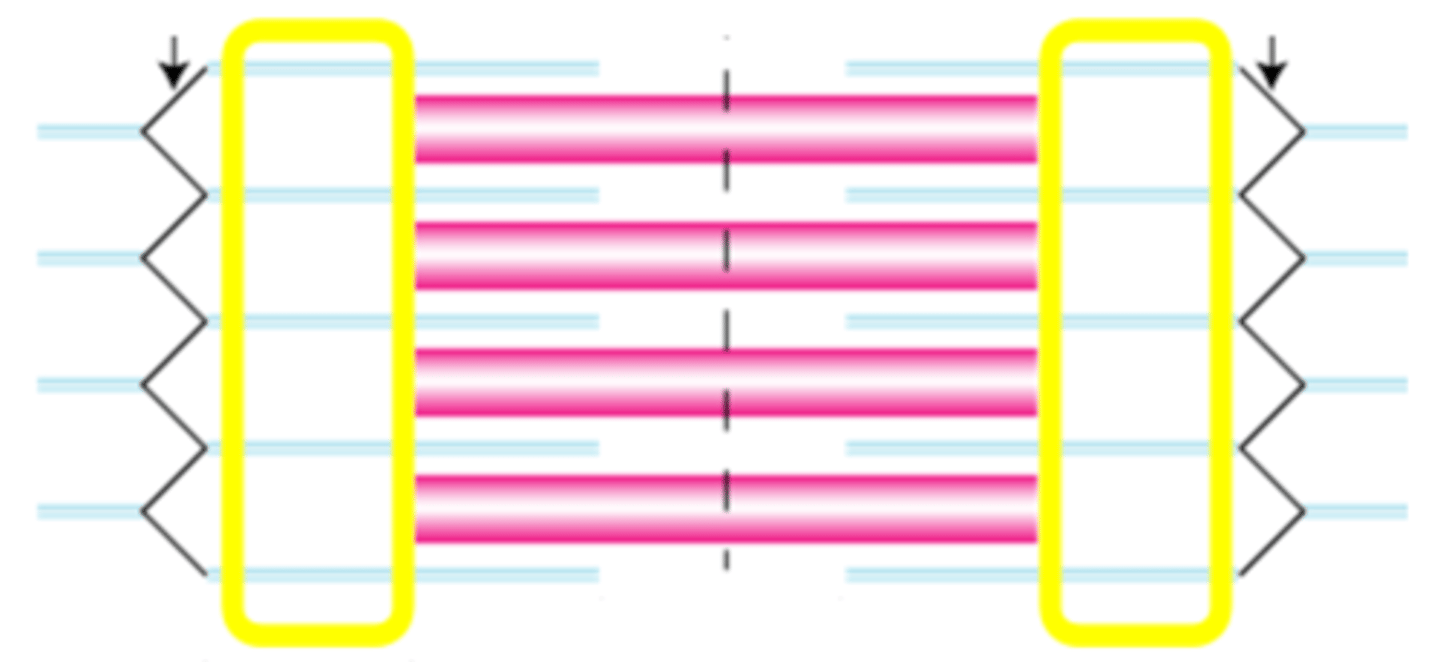
I band
The region of the sarcomere made up only of thin filaments. These bands alternate with A bands to give skeletal and cardiac muscle a striated appearance and get shorter (and may disappear completely) during muscle contraction.
Z-disc
Sheet of proteins that anchor thin filaments, connect the myofibrils to one another and define the boundaries of the sarcomere
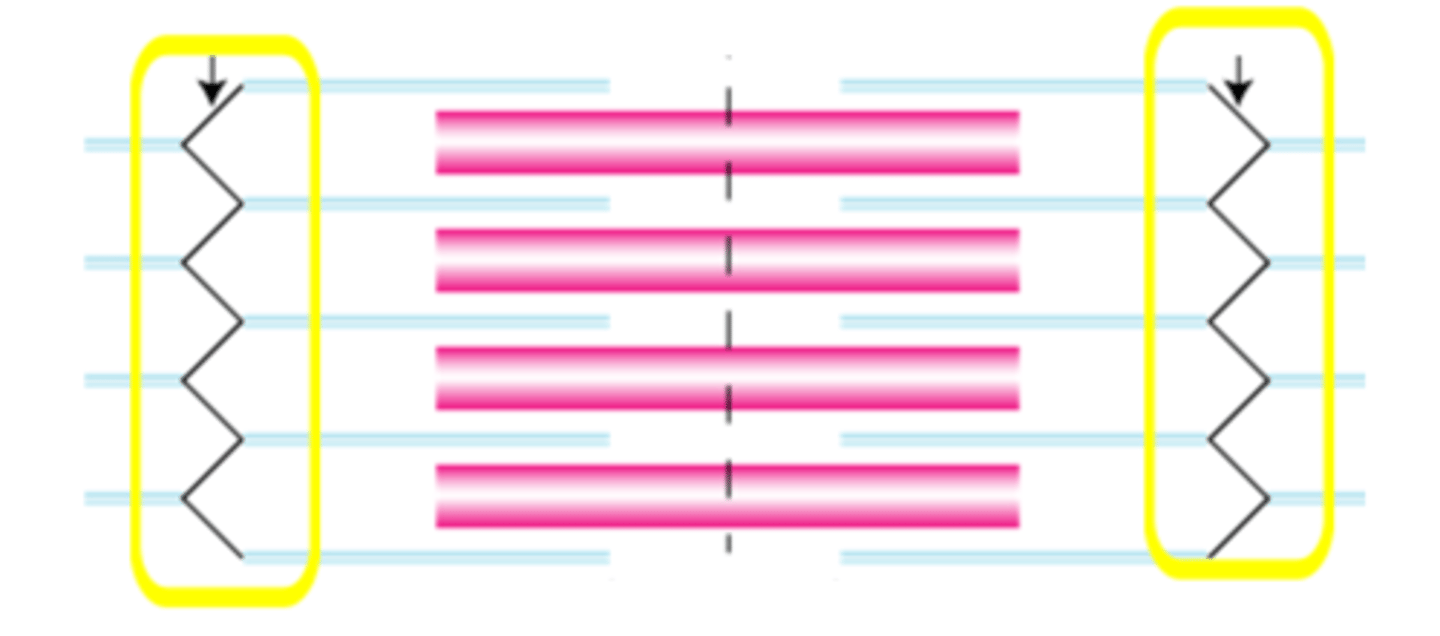
H zone
The region at the center of an A band of a sarcomere that is made up of myosin only; this zone gets shorter and may disappear during muscle contraction.
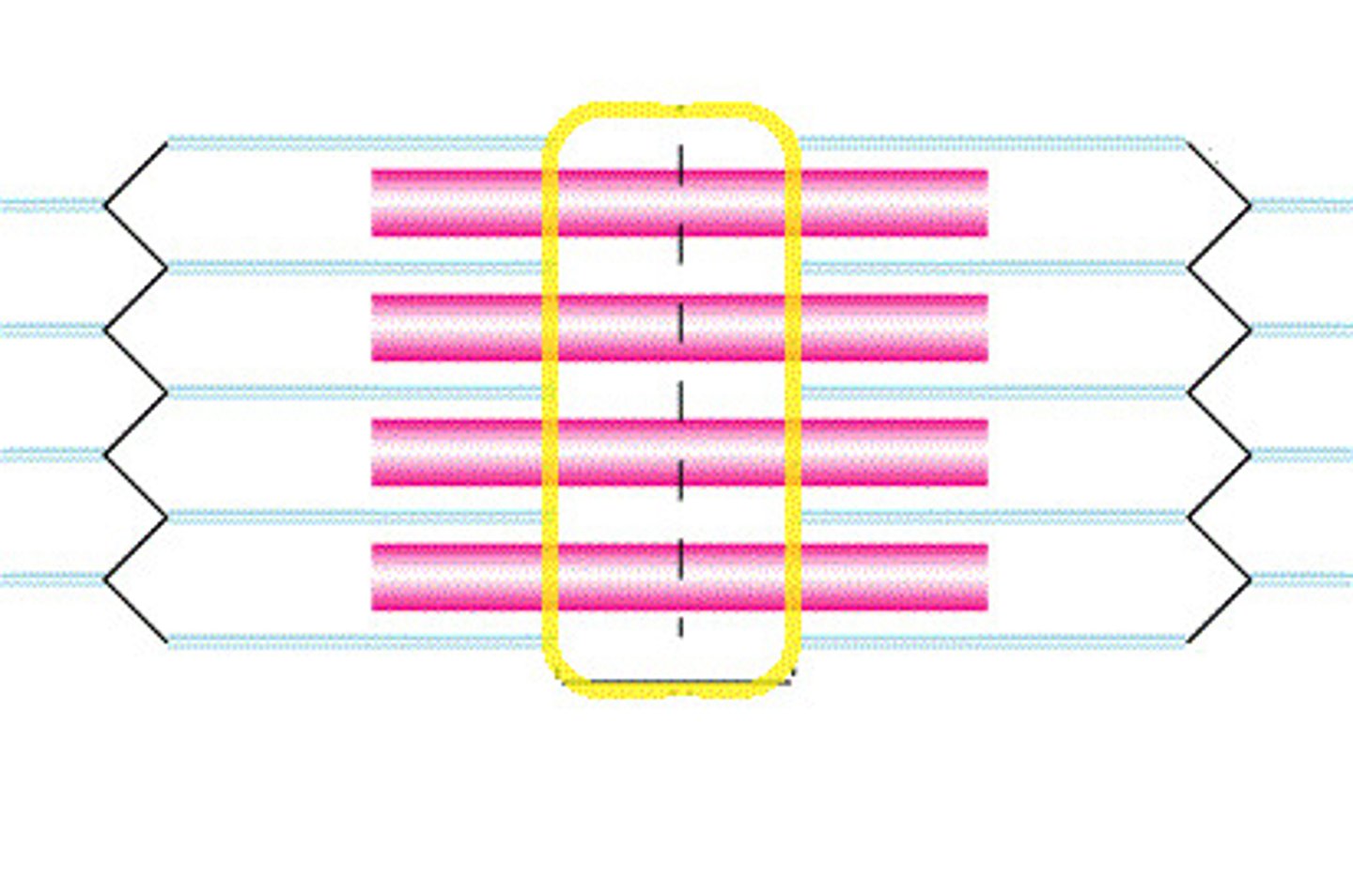
M line
Supporting proteins that hold the thick filaments together in the H zone