Lungs Pt 2 (E1)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Bronchiectasis = walls of bronchi thickened by inflammation or infection., may be diffuse or focal
**The CXR in affected individuals is often normal or shows non specific findings
What is bronchiectasis?
The CXR in affected individuals is often normal or shows non specific findings
Later: “tram-tracking” and honeycomb type infiltrates on medial aspects of lower lobes.
oEasily seen on CT scan.
What does in x-ray in those with bronchiectasis show? (early vs late)
oTypical organisms include Klebsiella species, Staphylococcus aureus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, nontuberculous mycobacteria, Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex, measles, pertussis, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus, herpes simplex virus, and certain types of adenovirus
What are typical organisms causing bronchiectasis (idk if this will actually be on exam but it's bolded and red)
Bronchiectasis
-tram lines
Dx. What is this finding?
bronchiectasis
Dx
o Both terms refer to lung tissue with air space but no alveoli – (non-functioning).
o Bleb = less than 1 cm diameter
o Bullae = greater than 1 cm but often much larger
o Walls of lesion are very thin (often invisible)
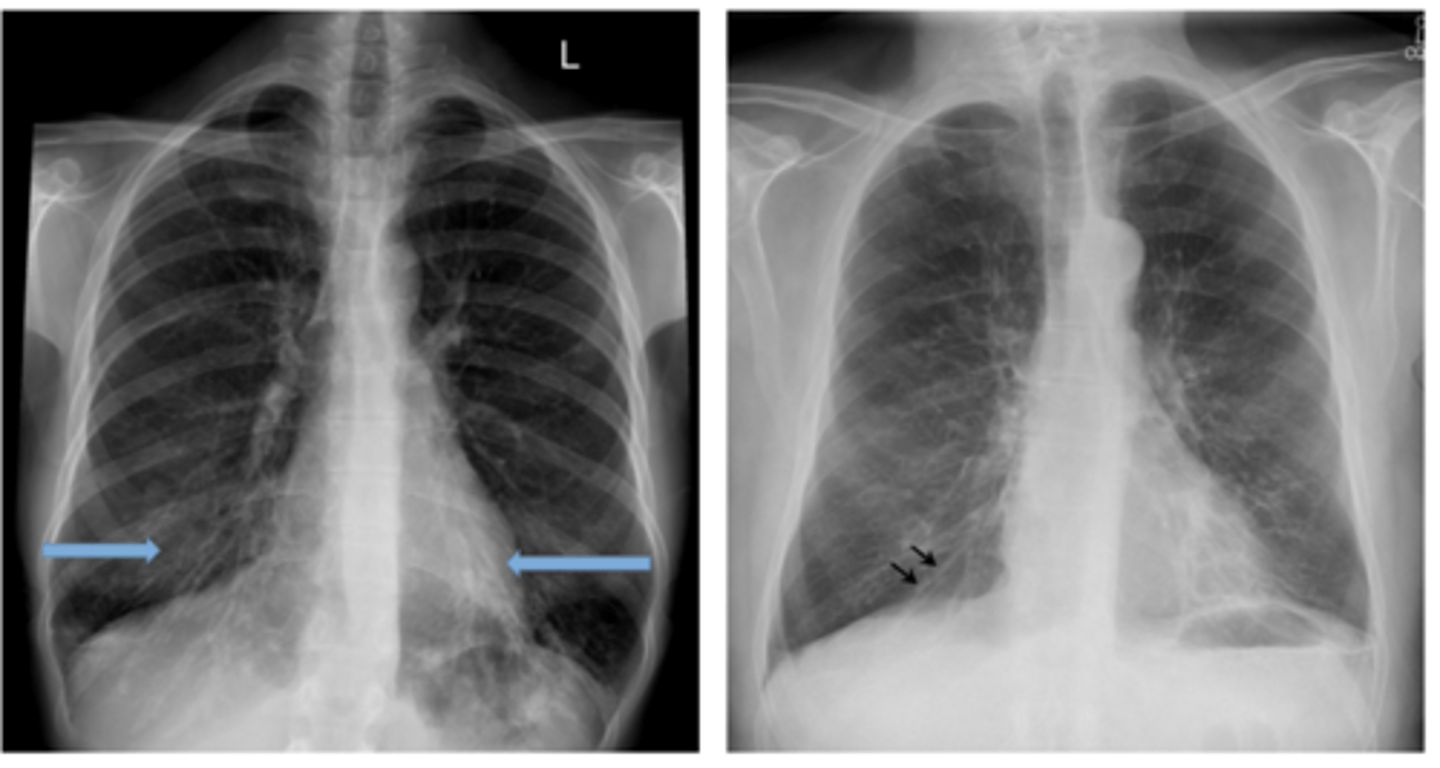
o Difficult to see on CXR – can be seen as absence of pulmonary markings.
o Easy to see on CT scan.
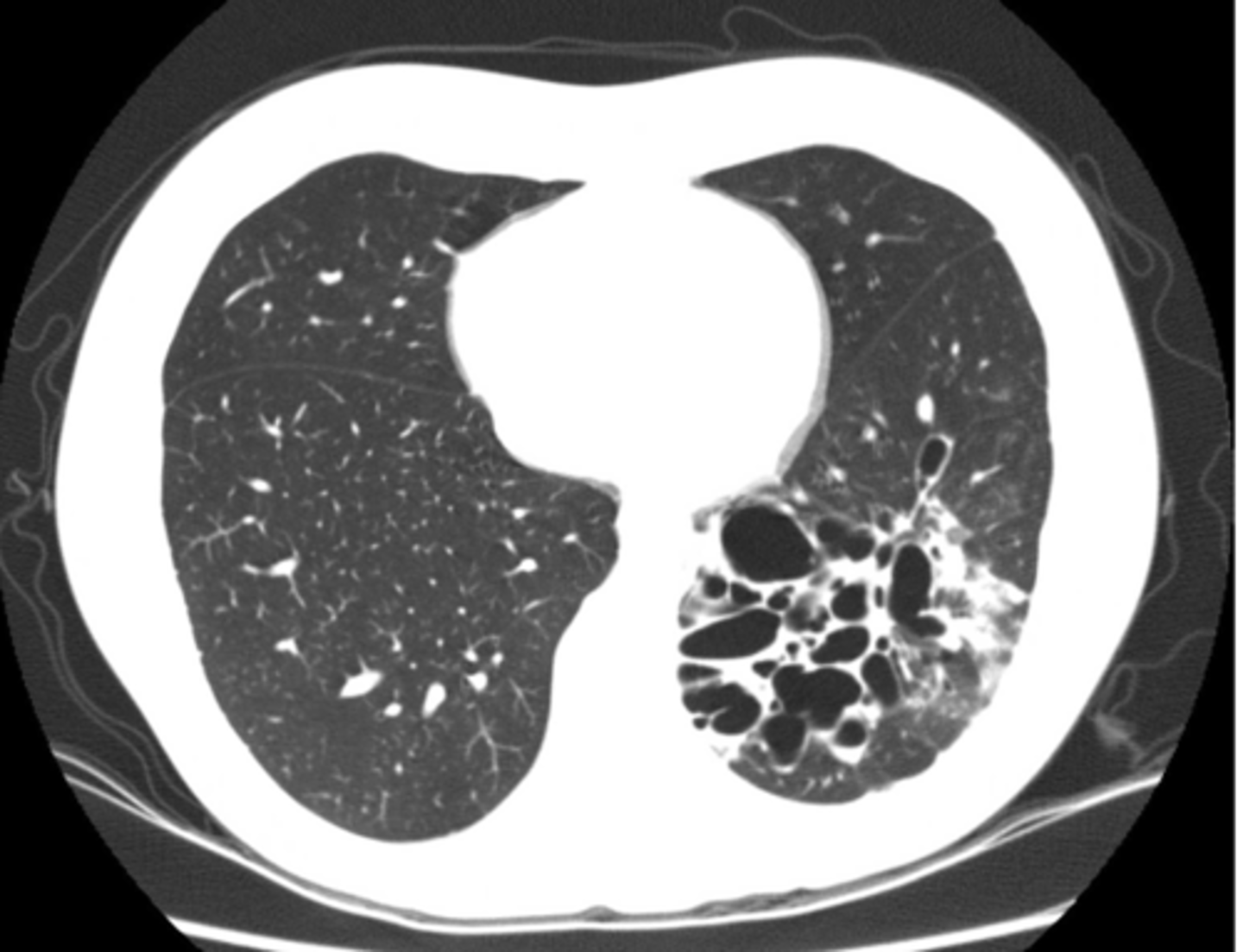
What are blebs and bullae - what findings would you find on xray?
Often associated with COPD or emphysema but bullae can be present in normal asymptomatic patients. (this pt has emphysema)
What dz are blebs and bullae associated with?
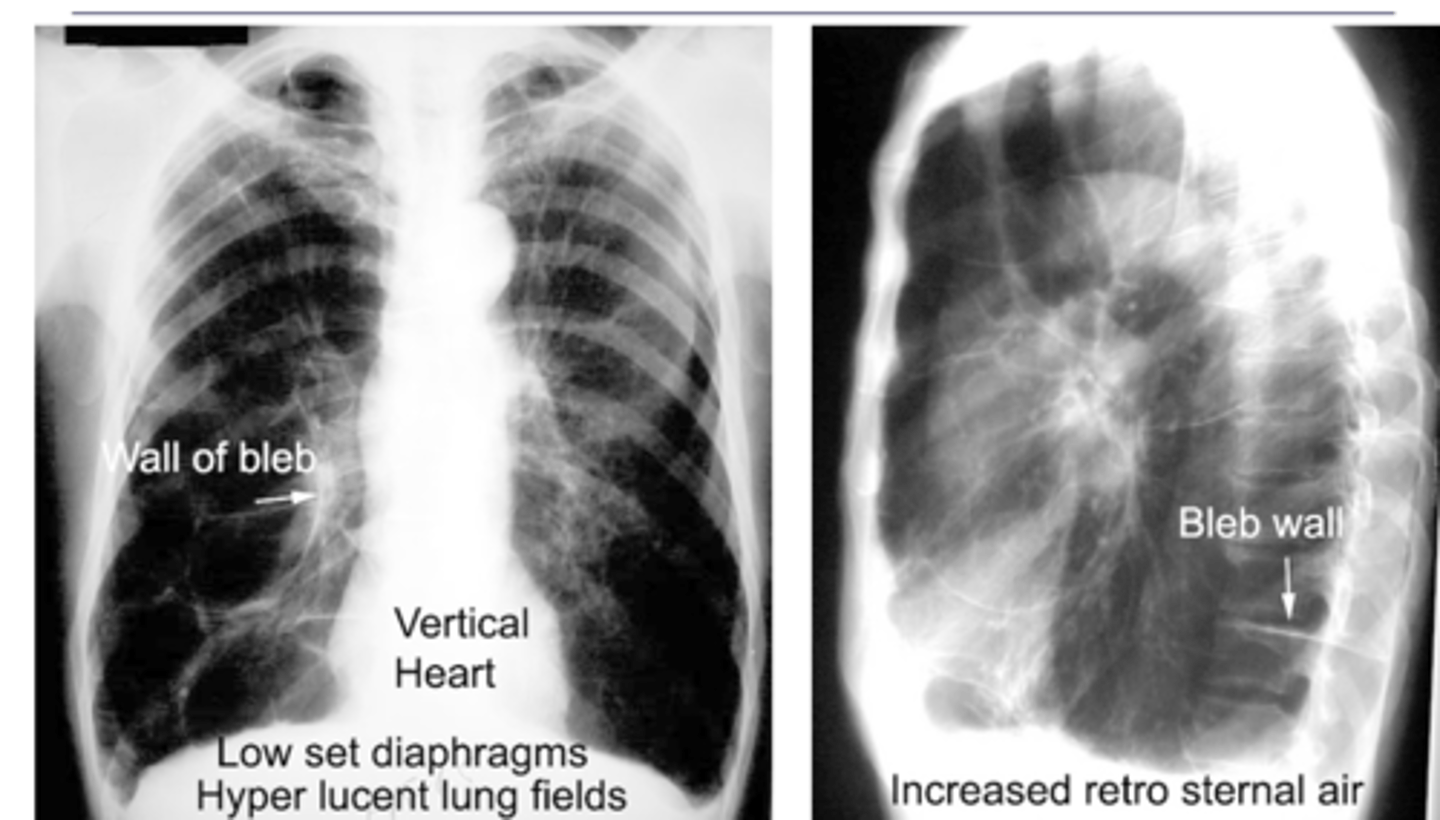
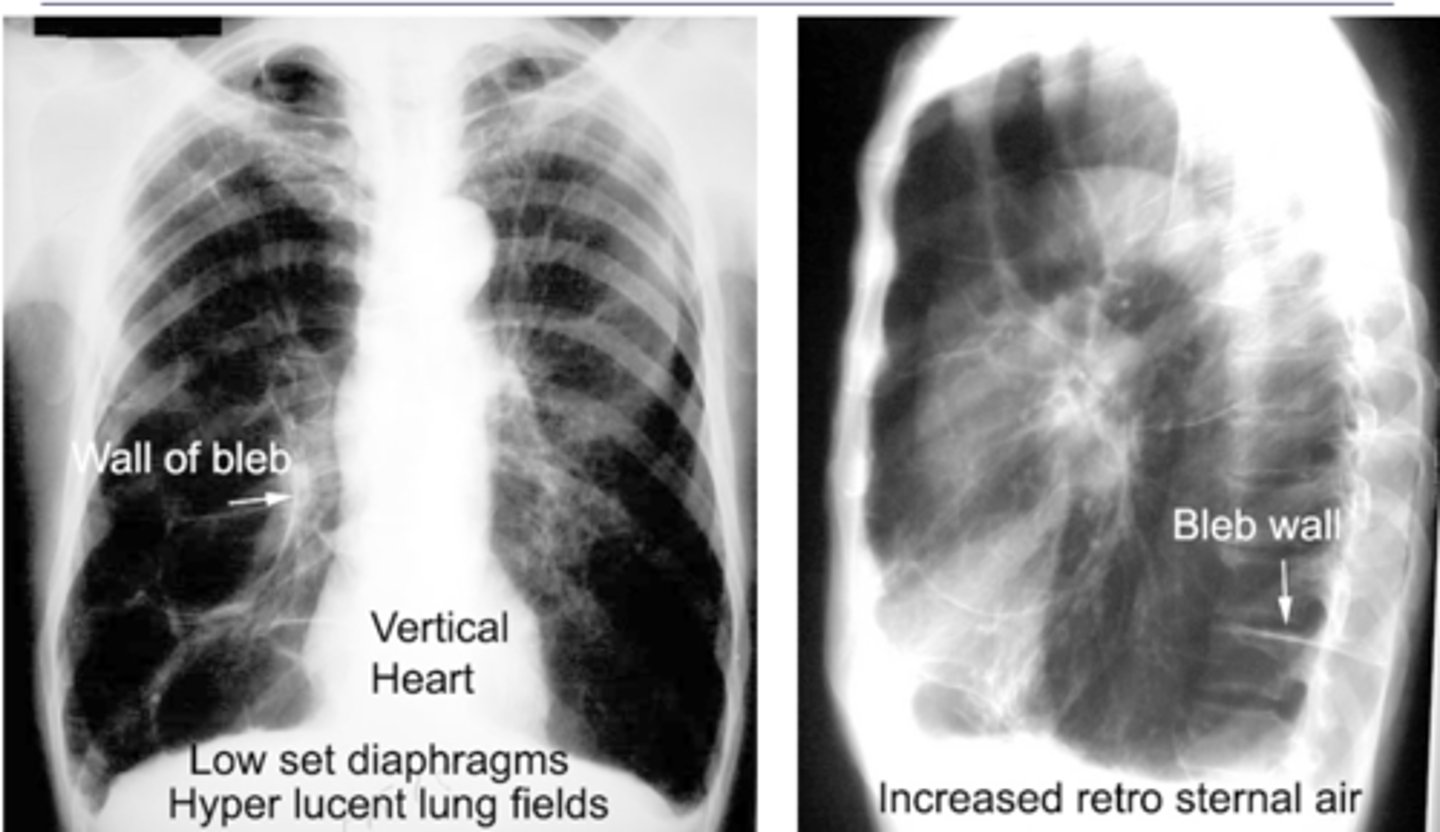
-Flattening of hemidiaphragms with blunting of costophrenic angles.
-Increased AP diameter of chest on lateral view (barrel chest)
-Presence of bullae or large air cavities
What x-ray findings are found in advanced stages of COPD/emphysema?
Flattened diaphragms, ant mediastinal space increased --> COPD/emphysema
Dx and ID radiological findings
complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or area (lobe) of the lung. It occurs when the tiny air sacs (alveoli) within the lung become deflated or possibly filled with alveolar fluid
What is atelectasis?
in patients who have difficulty taking a deep breath as with rib fractures or post operatively
What pts is atelectasis commonly seen in?
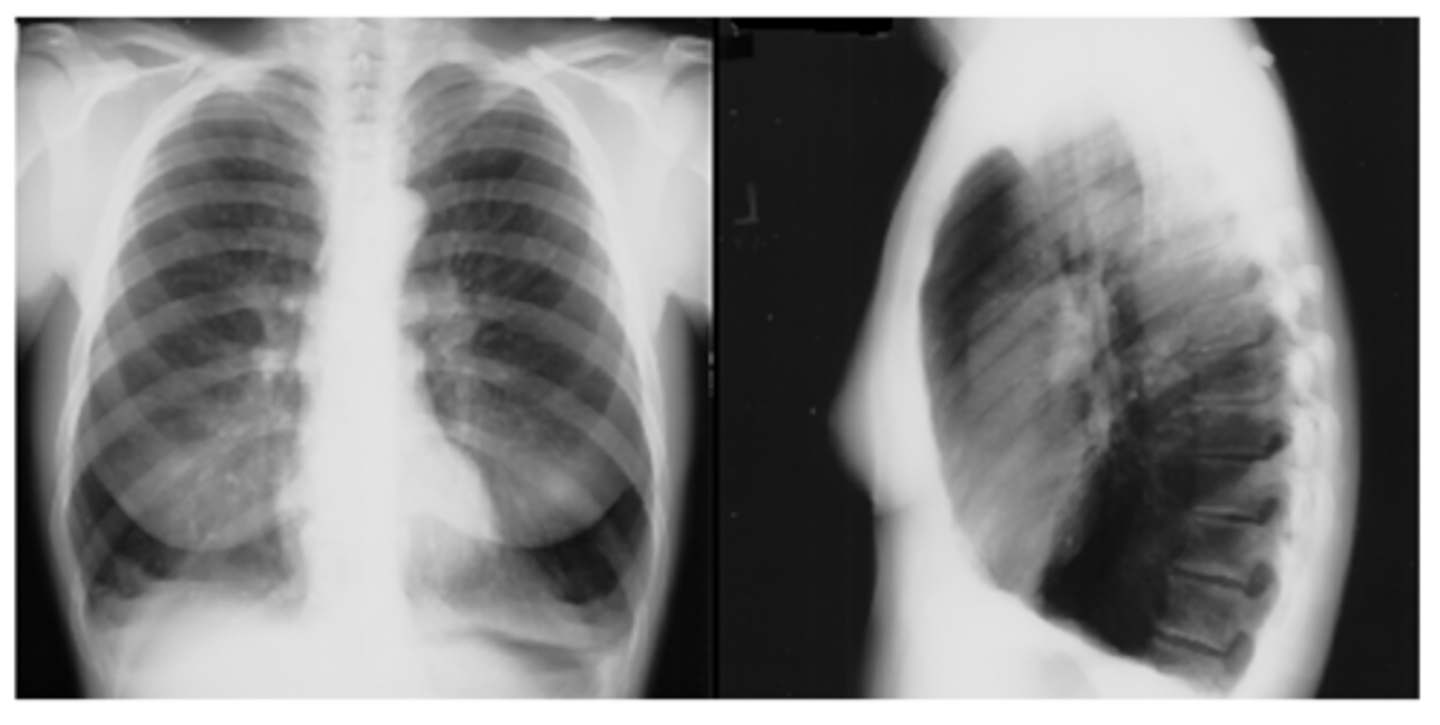
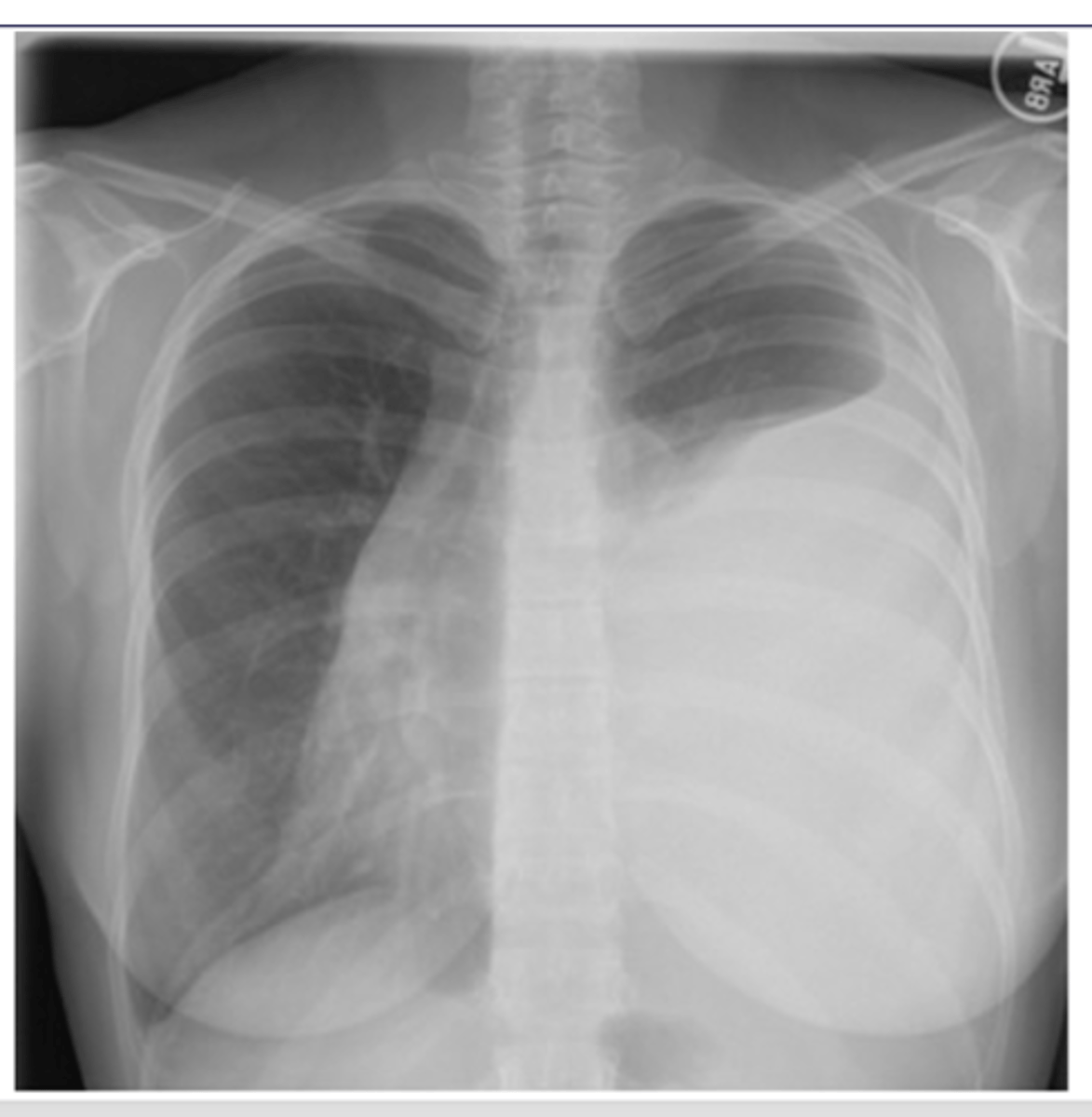
atelectasis - R lung collapse
--note: collpased lung pulling mediastinum towards R
Dx
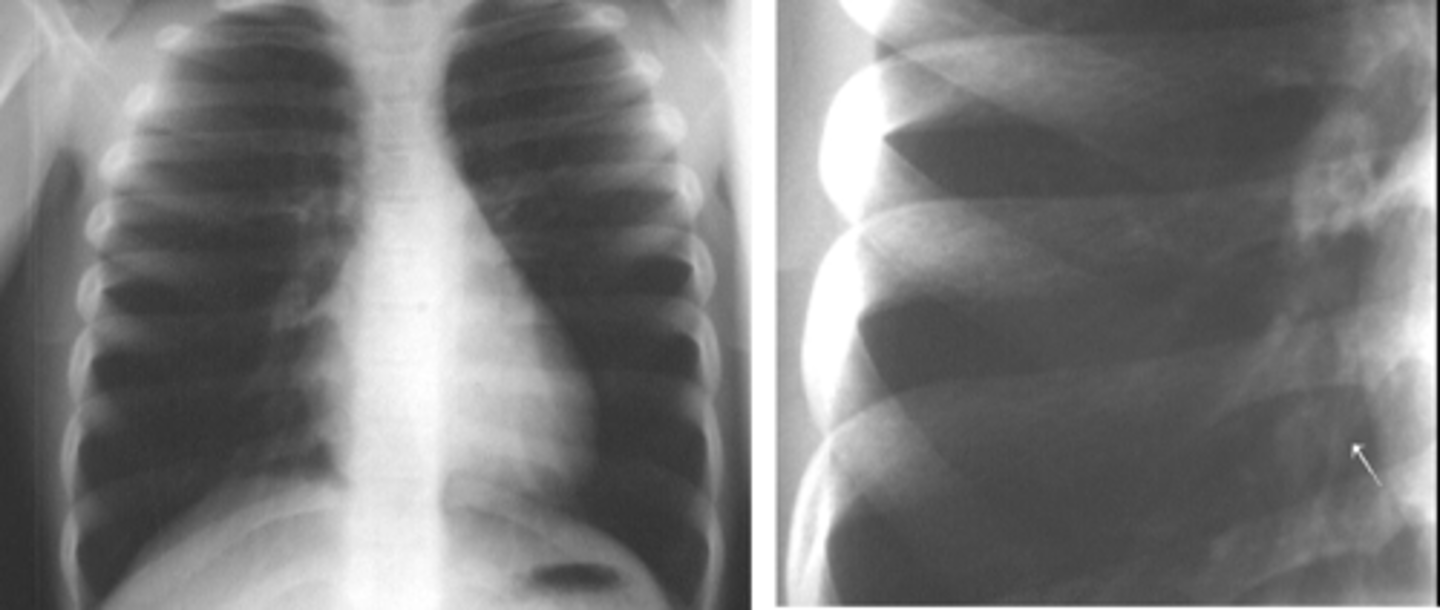
oLinear (discoid or plate-like) atelectasis.
oOften seen in post-op patients who fail to take a deep breath due to pain.
Dx
F
T/F, CXR is indicated for an acute asthma exacerbation?
radiologic signs that are usually accompanied by pulmonary edema in cases of congestive heart failure and bronchiectasis
What are tram lines/tracks? What dz states might they indicate?
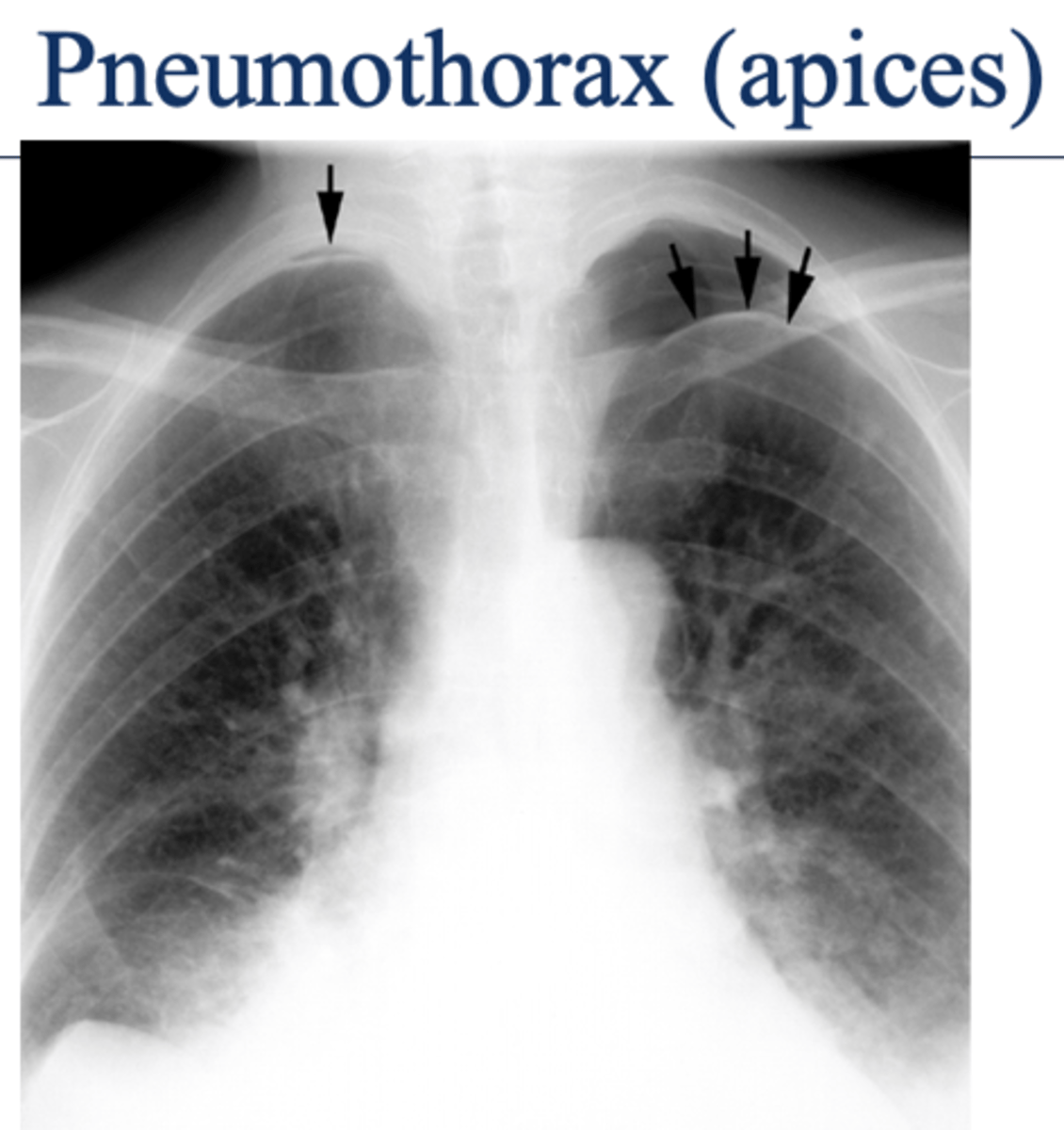
oAir in the pleural space (pneumothorax) is usually seen in the apices if the patient is upright.
Seen as an area of no vascularity and a thin white line representing the visceral pleura
**air has no density (so air will show up as darker)
What will pneumothorax look like on imaging? What area of the lungs does pneumothorax affect?
Shift of mediastinum
-if you're able to see t-spine in view, heart is not in the right place, likely laterally shifted
-hemidiaphragm
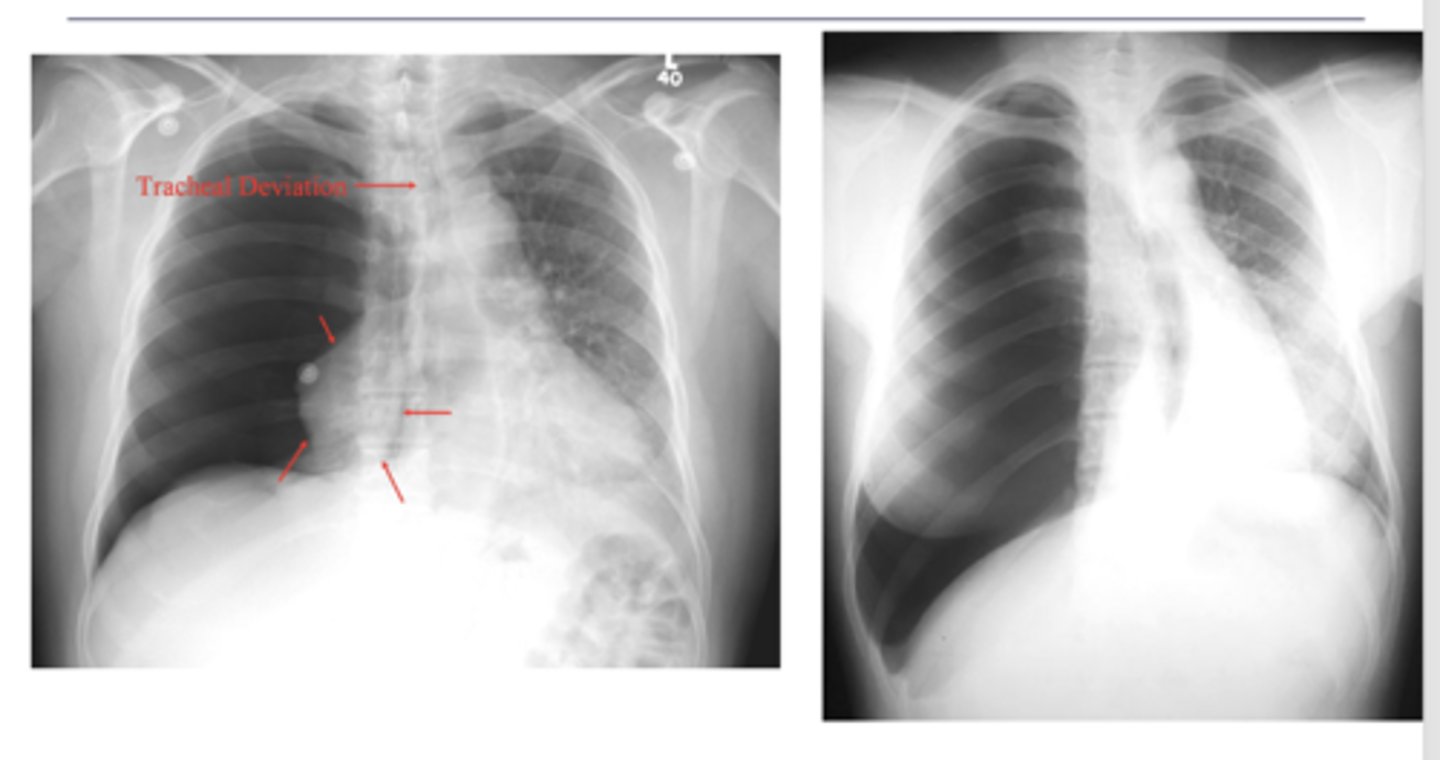
What is the main radiologic finding that differentiates tension and non-tension pneumothorax?
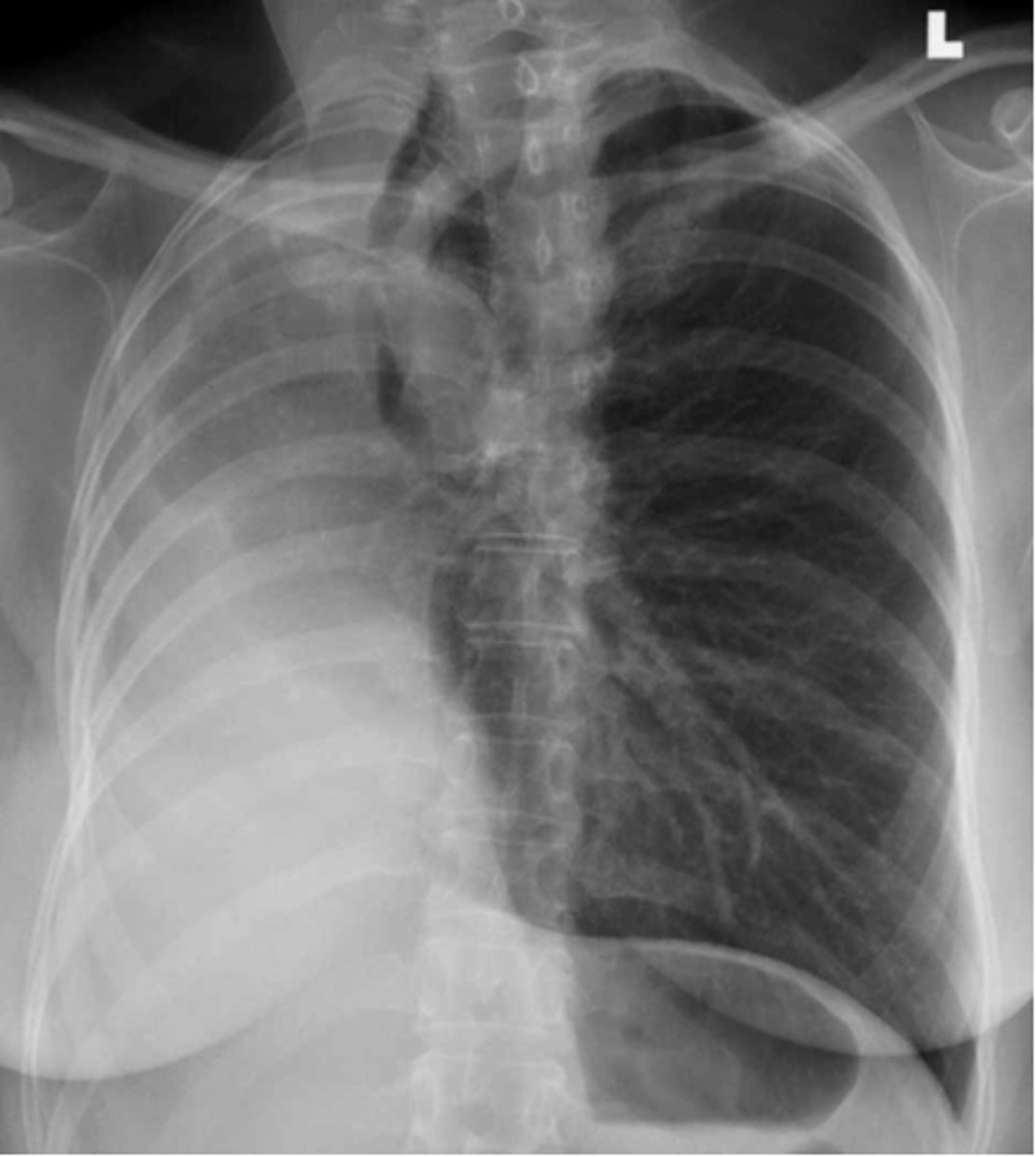
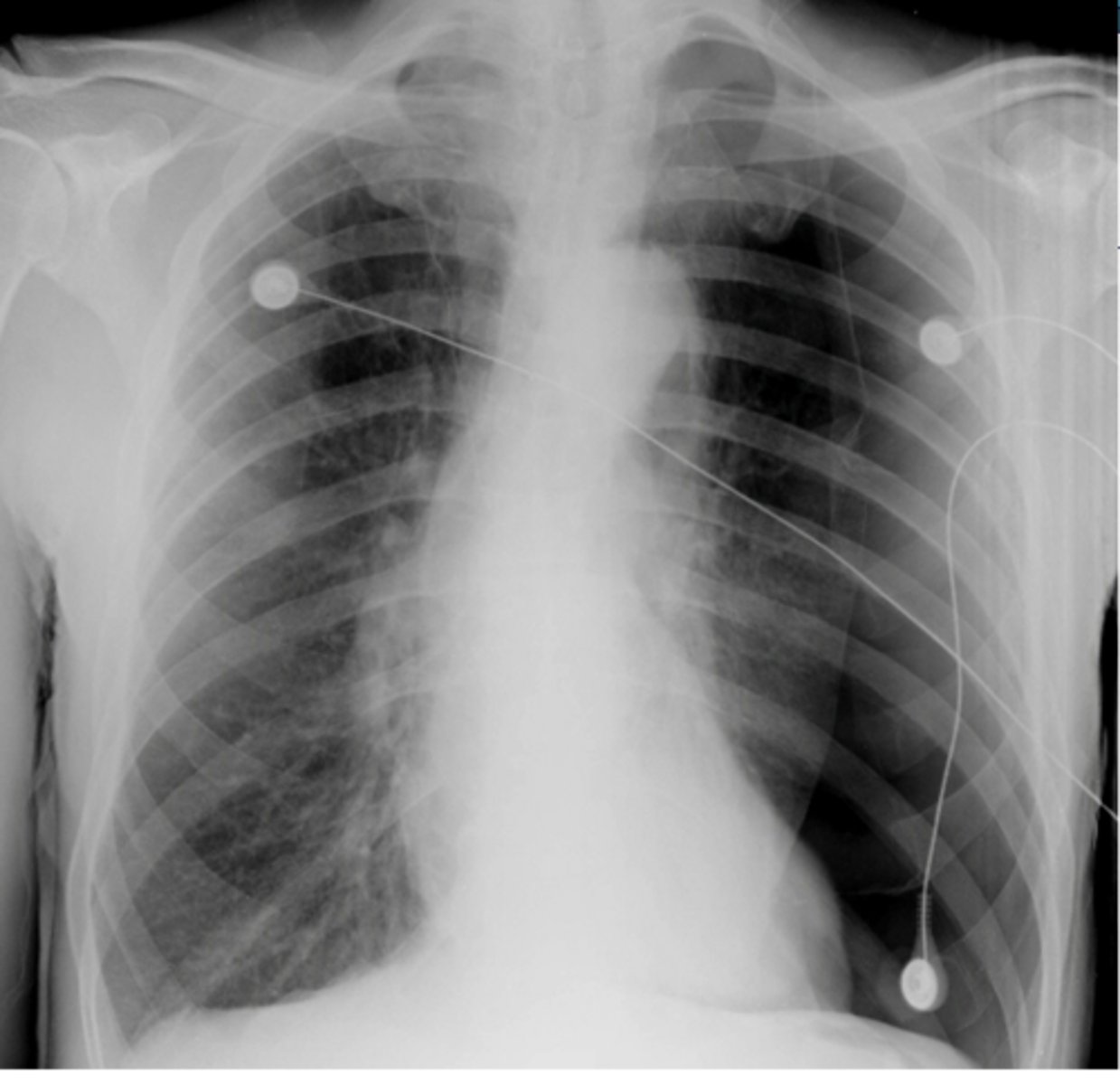
L sided moderate pneumothorax
Dx
-mediastinal shift
-less density (darker)
-sharp line if non-tension pneumothorax
3 key findings for pneumothorax
Seems like biggest difference is shift of mediastinum
Difference between tension and moderate pneumothorax
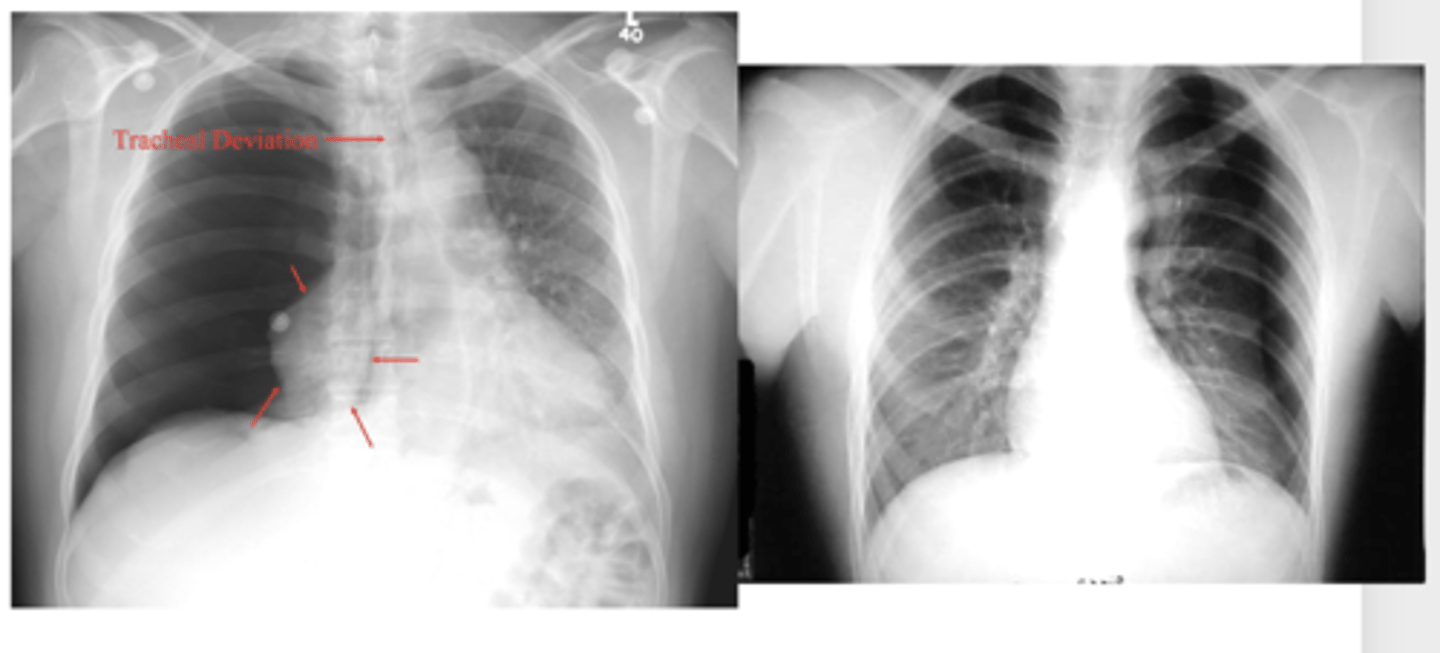
refer to picture
ID findings in red
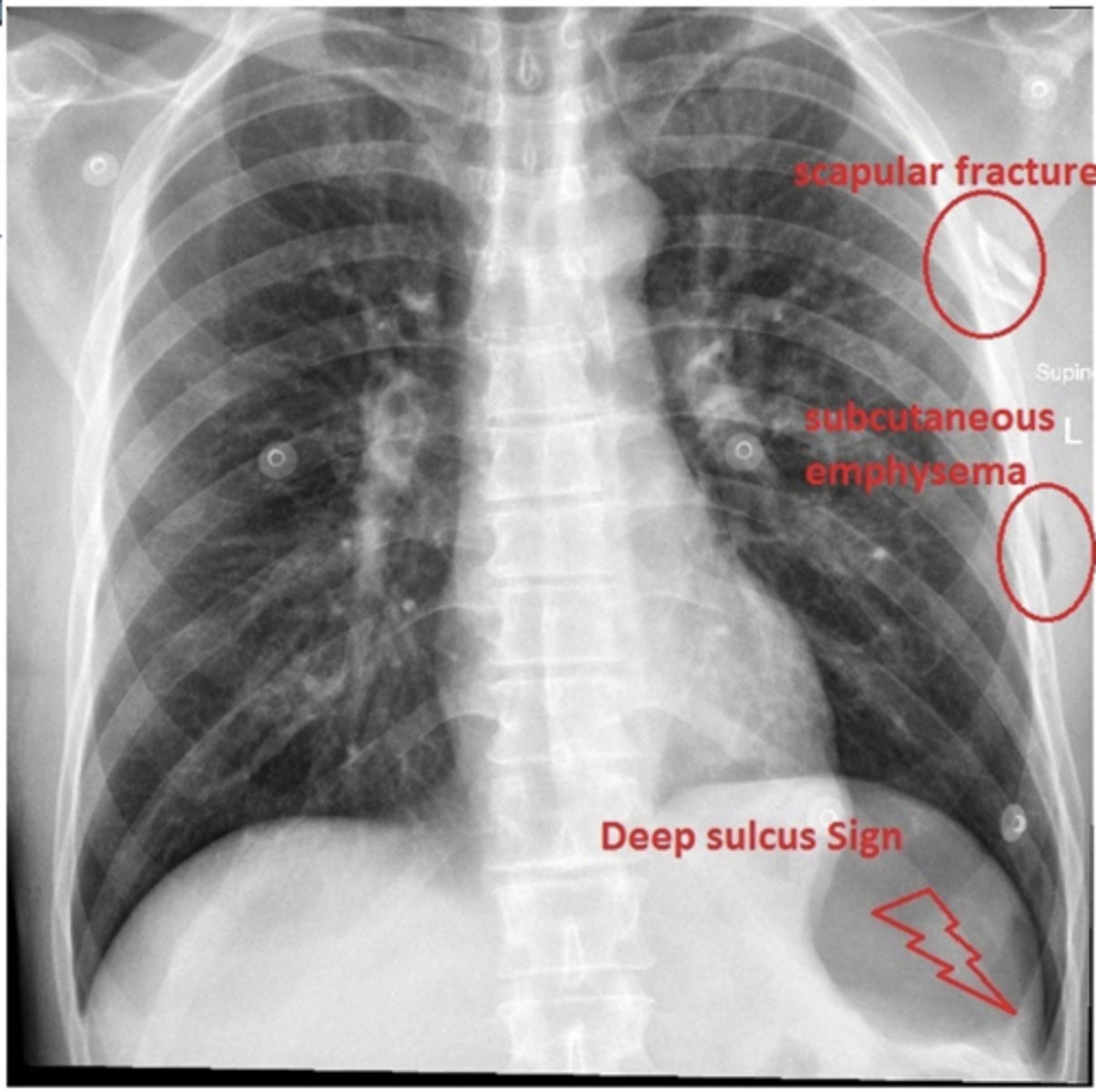
Pneumothorax (caused by stabbing)
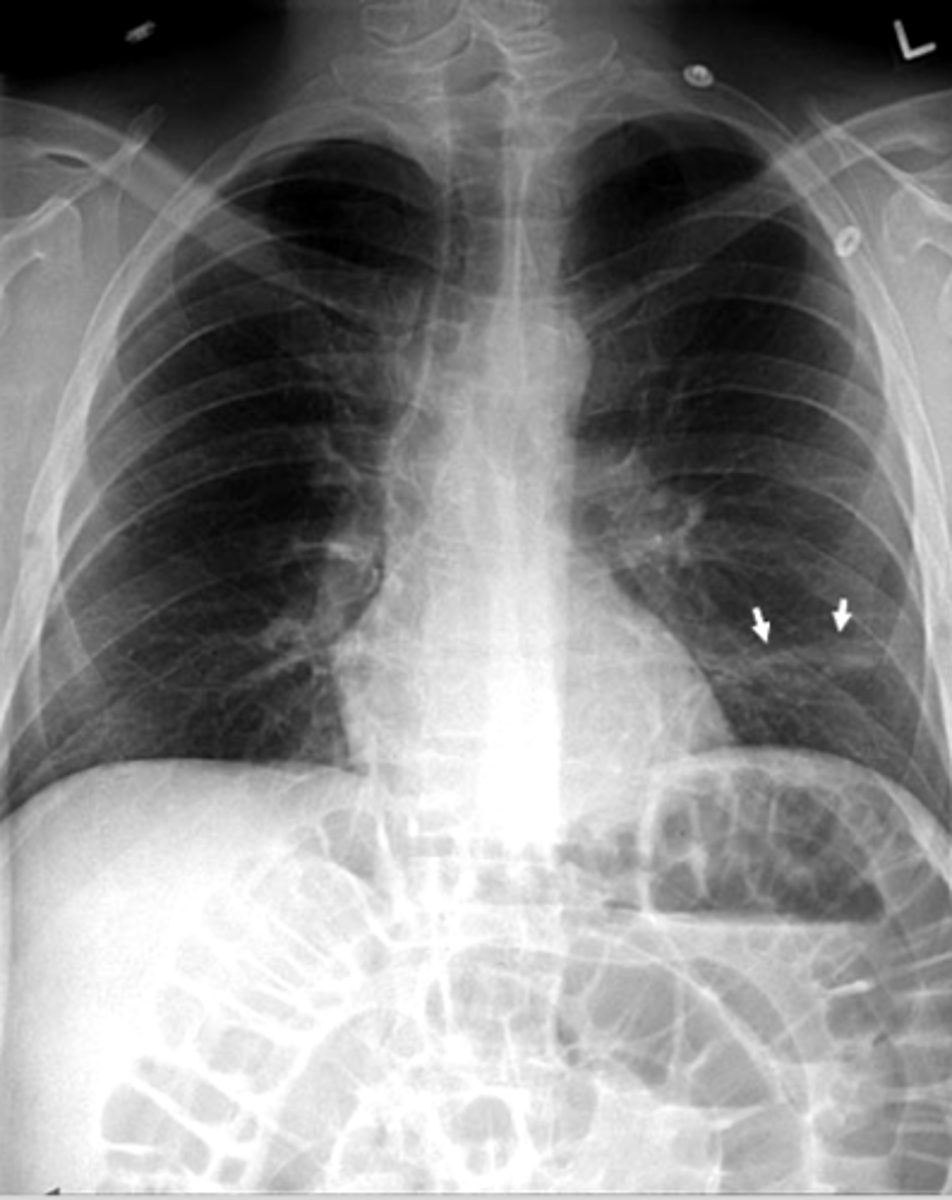
visceral pleural line in the left chest (white arrows).
horizontal line along the base of the left hemithorax, which represents an air-fluid level (black arrows), showing that the patient has a hemopneumothorax.
2 key findings in this x-ray and dx
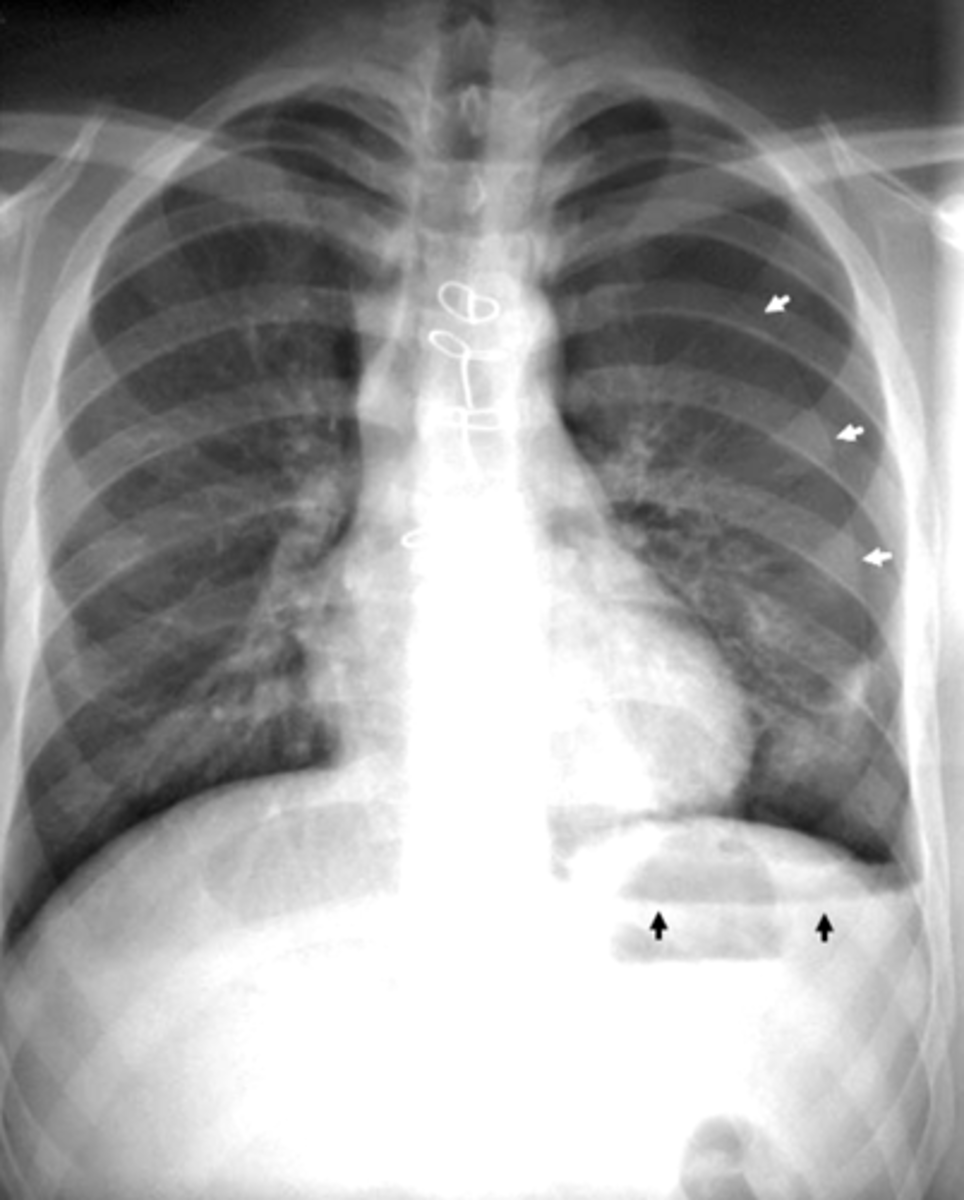
•Pneumomediastinum aka mediastinal emphysema - is air or gas in the space between your lungs (mediastinum).
•Spontaneous or secondary cause (injury or illness)
Leads to increased pressure
What is pneumomediastinum?
Pneumomediastinum
-increased pressure results in pushing down of mediastinum and pushing up of diaphragm
Dx
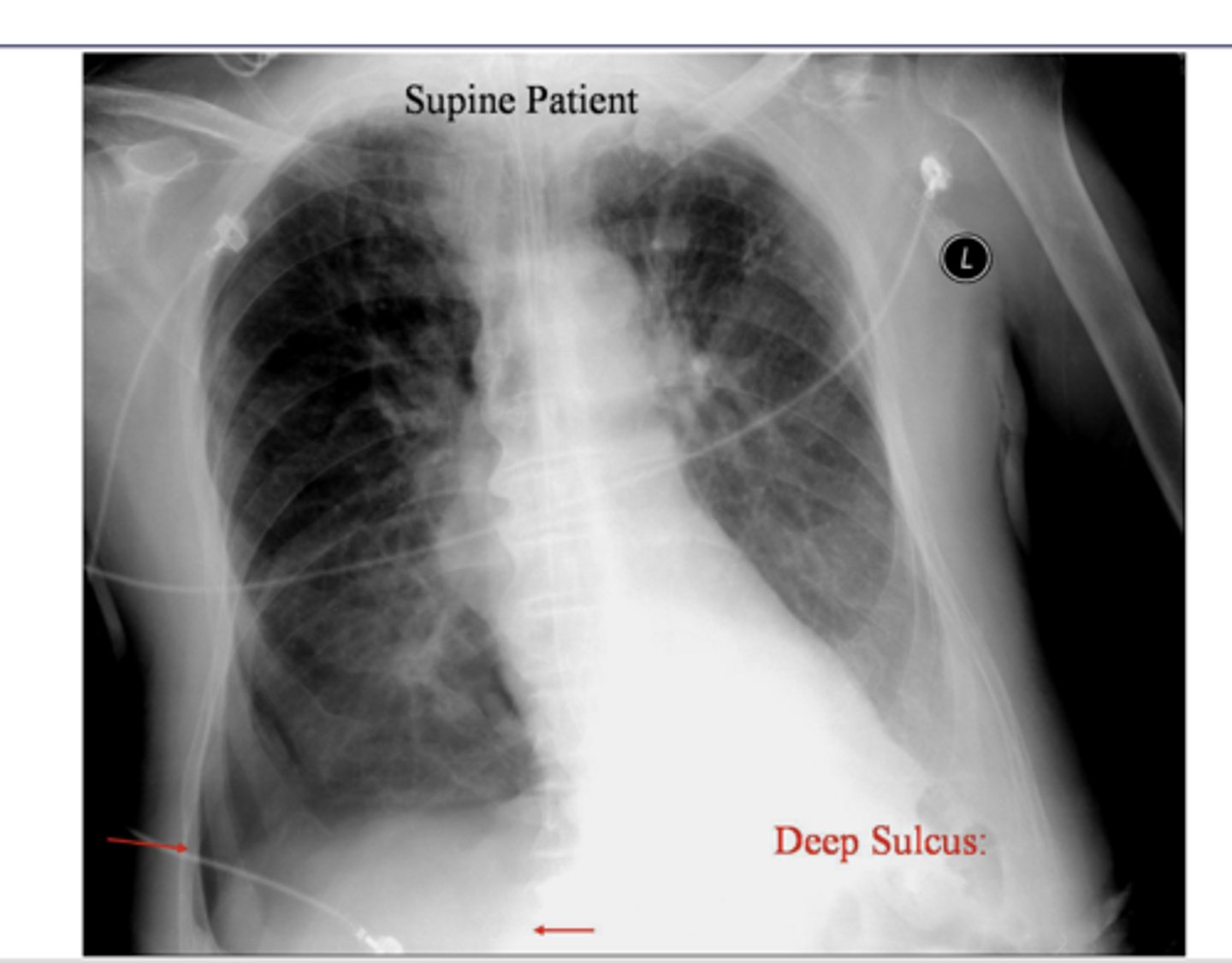
When pt supine, xray findings support pneumothorax
It represents lucency of the lateral costophrenic angle extending toward the hypochondrium
What sign is this?
-Severe injury (trauma) to your chest.
-Surgery.
-Rupture of the small sacs of your lungs
-Tear in your airways or gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
-Infections
-Excessive coughing, sneezing, vomiting and other body functions that increase pressure in your chest suddenly.
-Bearing down while going to the bathroom.
-Pushing during childbirth.
-Scuba diving
-Mechanical vent.
Common causes of pneumomediastinum
pneumomediastinum - i literally dont know why,
dx
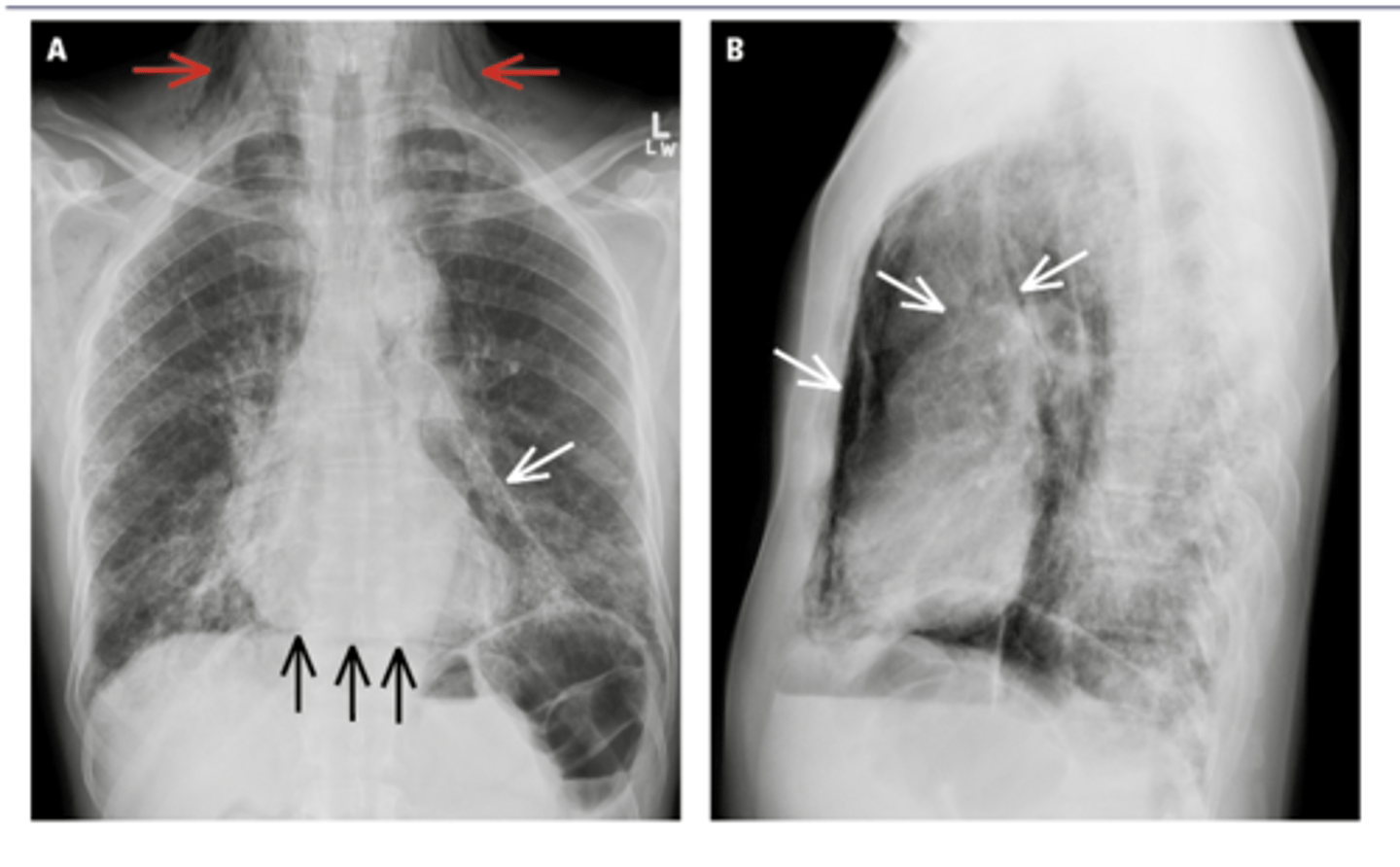
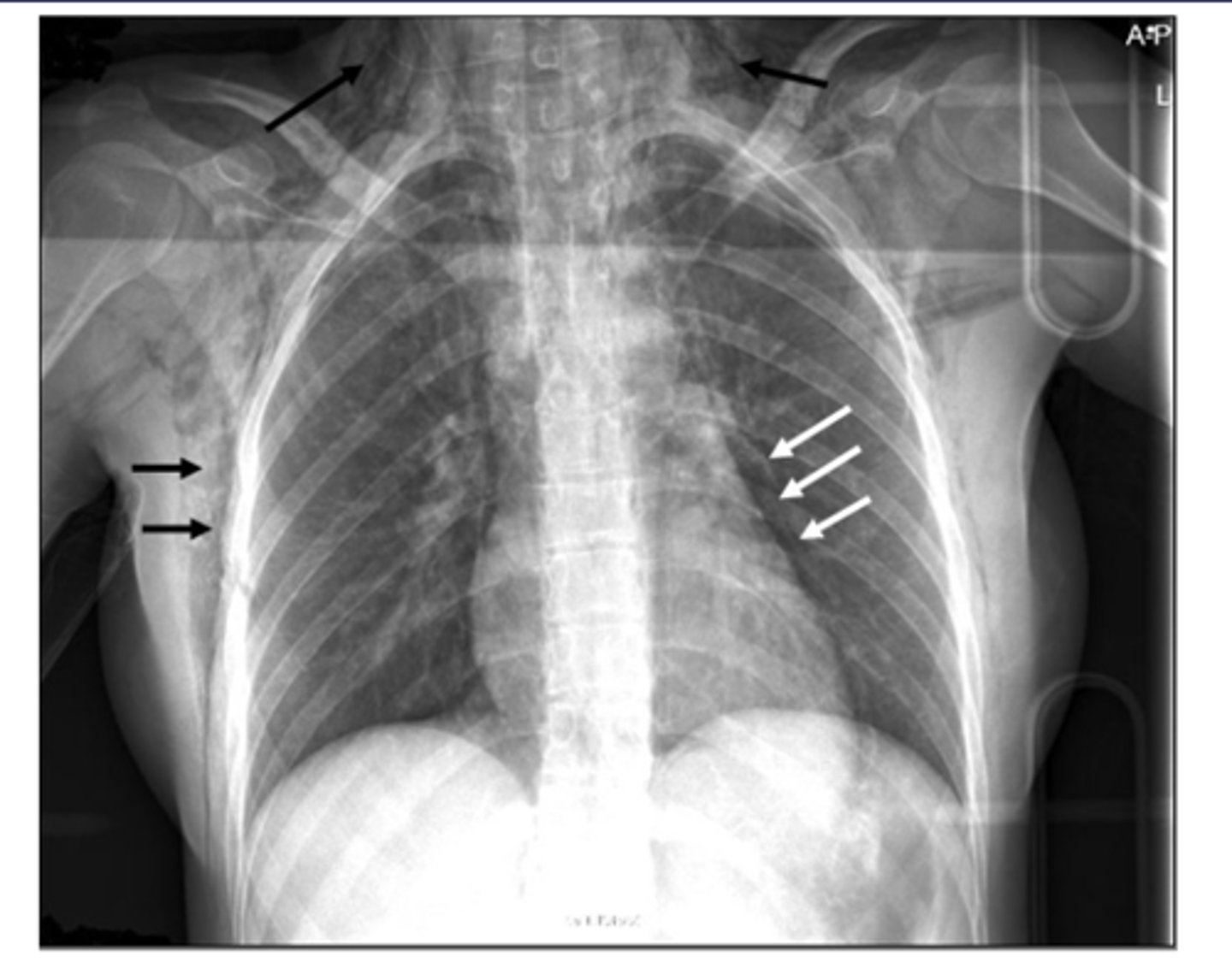
Black arrows: subcutaneous emphysema. White arrows: pneumomediastinum
ID black and white arrows
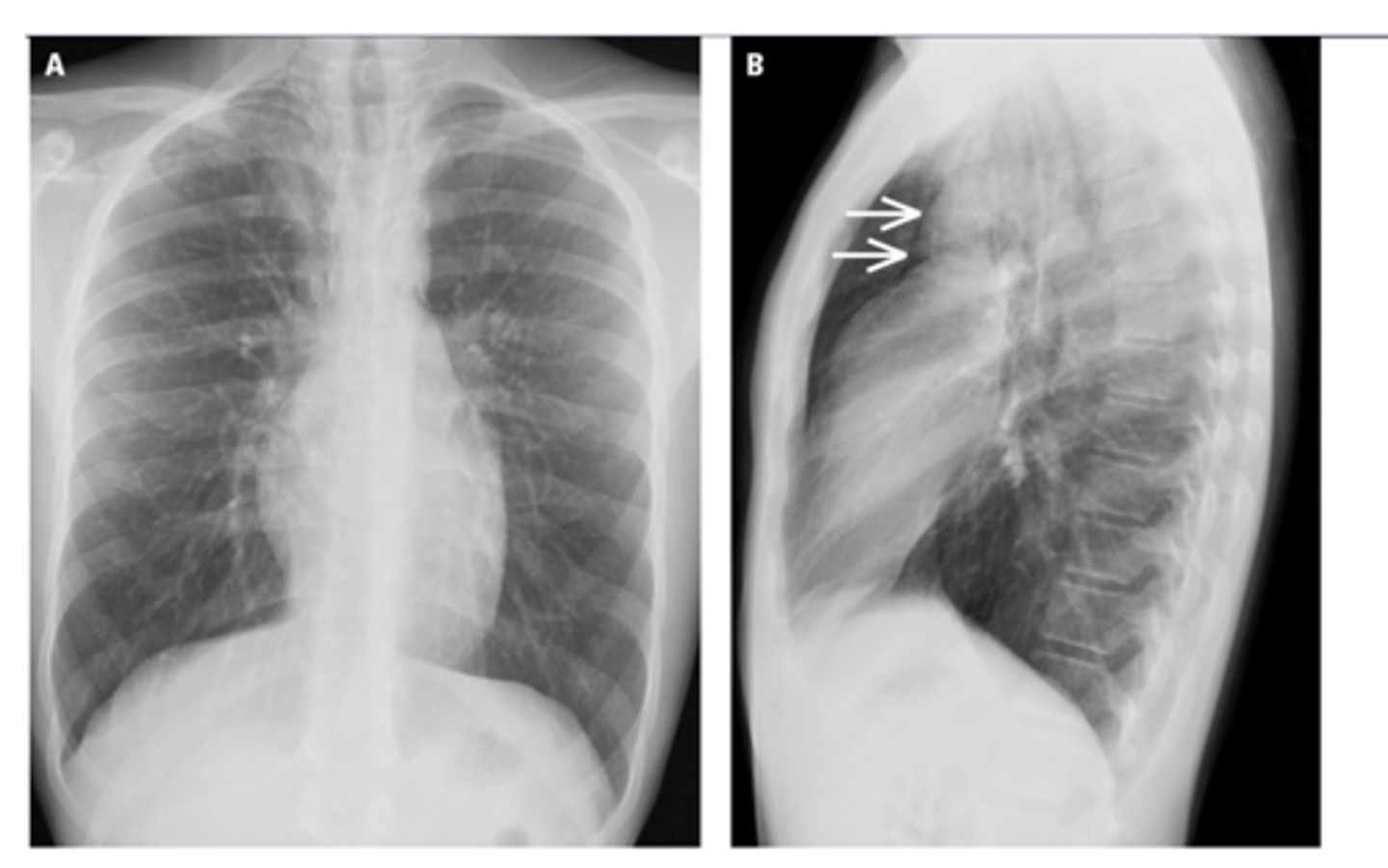
Blunting of costrophenic angle when upright
Fluid along lateral chest wall (gravity)
**normal diaphragm border obscured by pleural effusion
What are findings that indicate pleural effusion?
-Congestive heart failure (CHF) - bilateral effusions with cardiomegaly
-Pneumonia - 40% have a small effusion
-Pancreatitis - L sided effusion
-Cirrhosis - R sided effusion
-Malignancy - massive effusion
Causes of pleural effusion
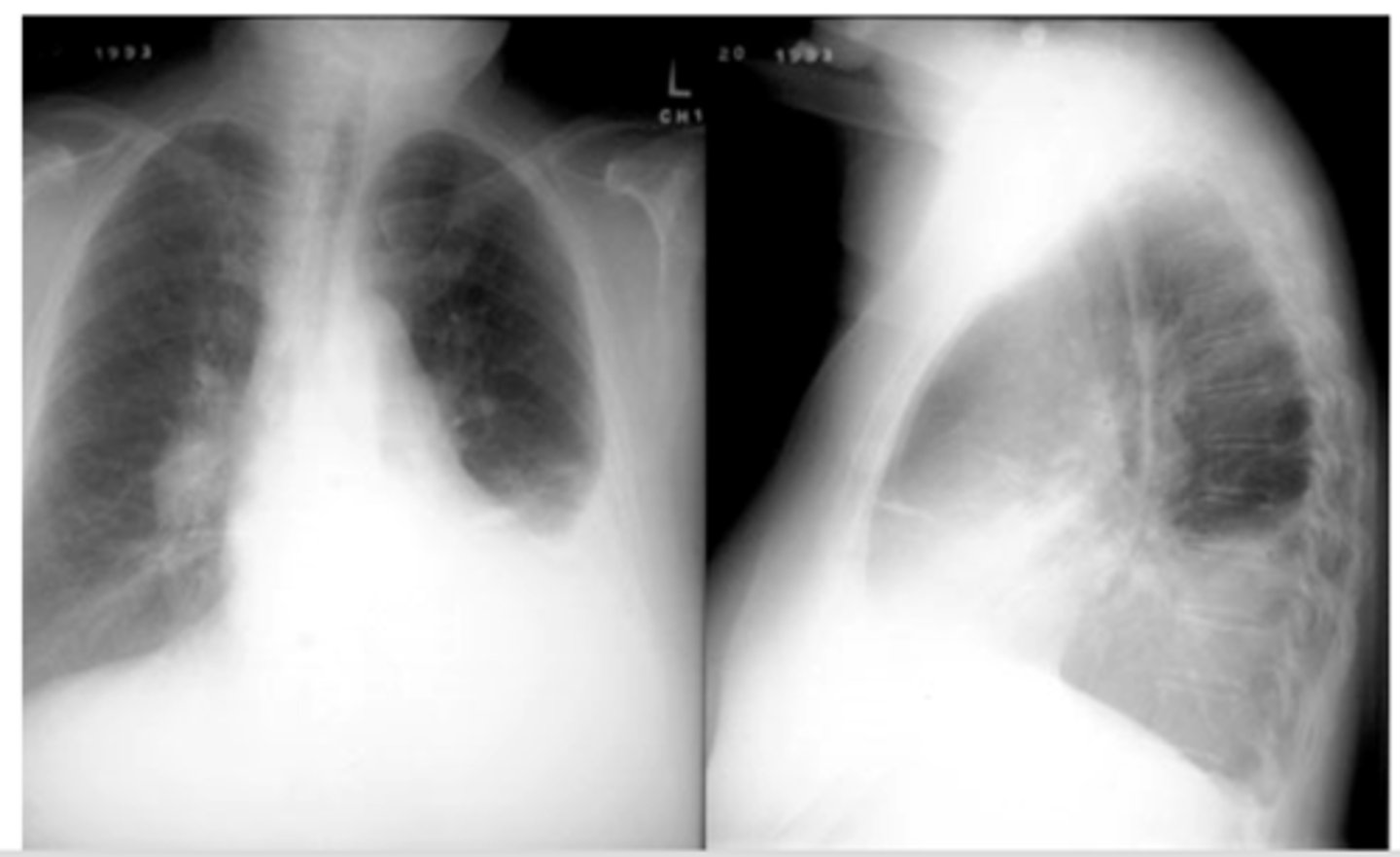
Pleural effusion
-fluid build up is pushing the mediastinum laterally which causes the t spine to be more visible
-can use lateral decubitus position to confirm presence of effusion/fluid
Dx
pus in pleural space
What is empyema?
Fluid is more viscous so...
1. Fluid doesn't move as freely and less affected by gravity
2.sharper line of demarcation
What is the main differentiator between empyema and emphysema on x-ray?
CT is best study
What is best study for empyema?
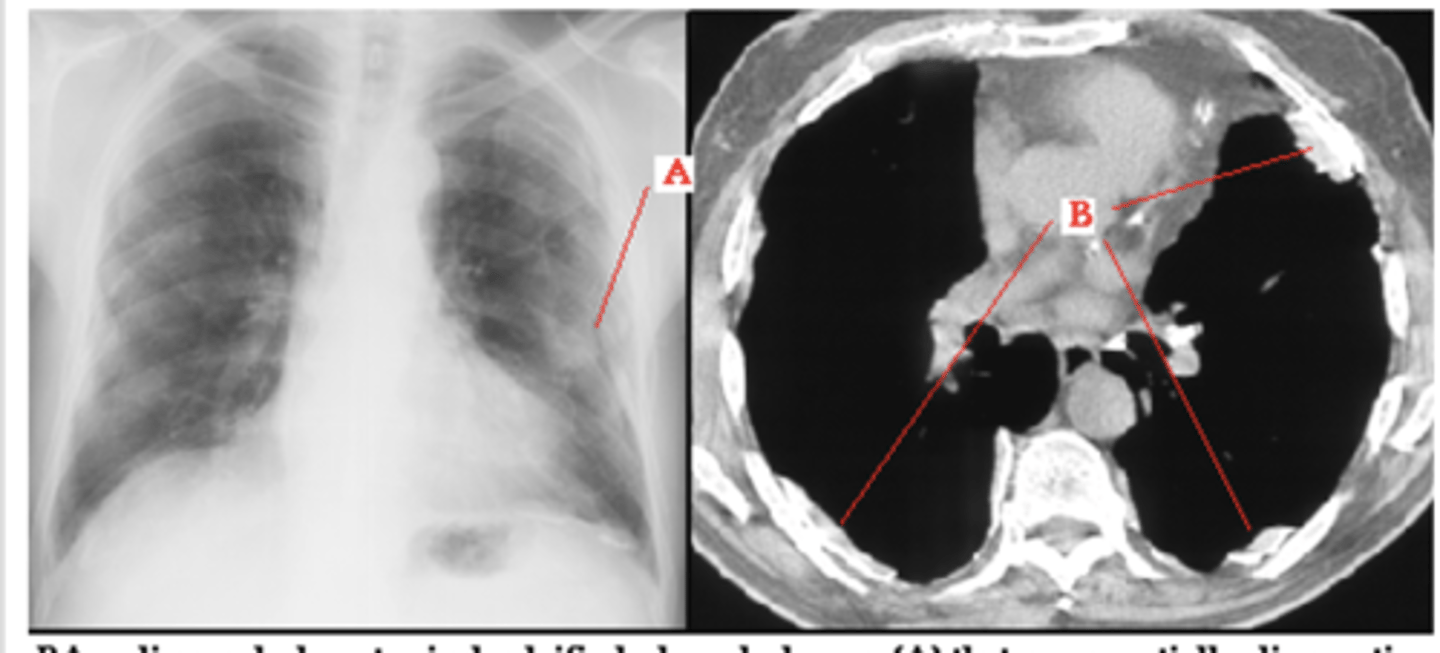
pleural calcifications - asbestos exposure (asbestositis will be bilateral)
Dx - what is the most common cause of this finding? Bilateral or unilateral?
Mesothelioma - A mesothelioma is a primary malignant neoplasm of pleura
It occurs in patients with prior exposure to asbestos.
It has no correlation with cigarette smoking
Dx. What is the most common cause of this finding?
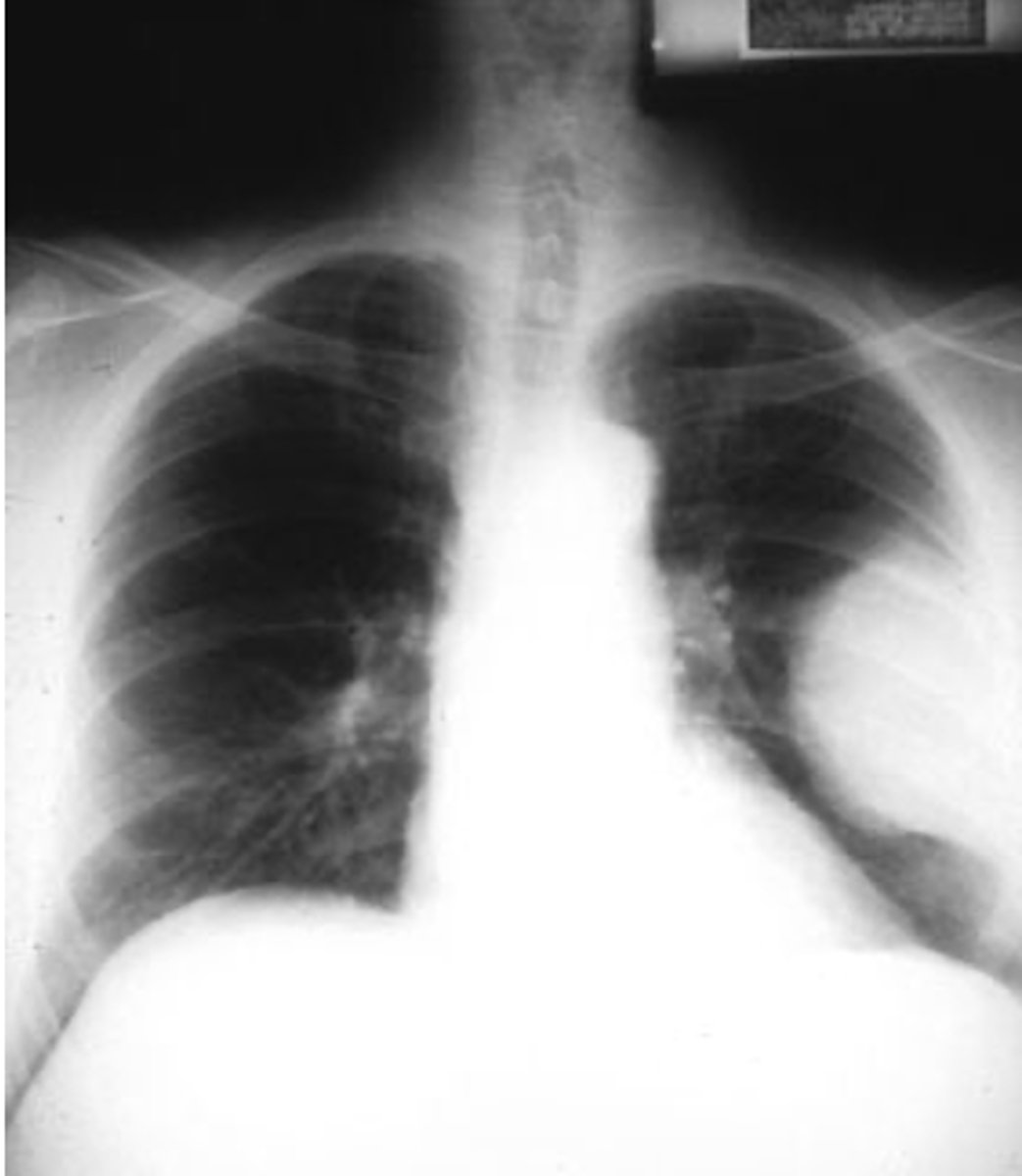
Diaphragmatic rupture
o Usually due to trauma – more common on the left side. Can be a post-op complication of upper GI surgery.
o Most common appearance is loops of bowel in the lower chest cavity (R lung in pic)
-Can cause mediastinal shift
Dx. What is the most common radiologic finding for this dz state?
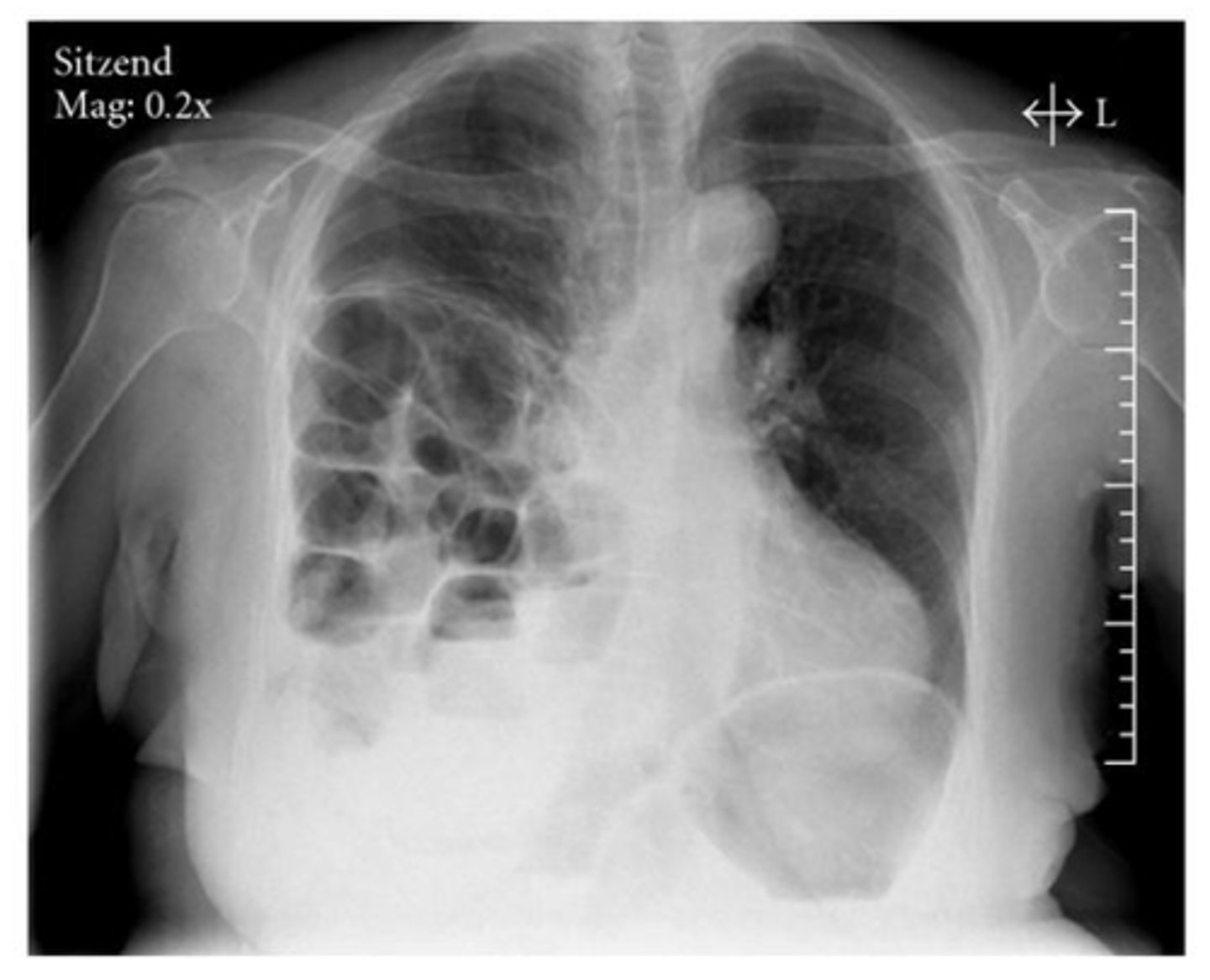
Diaphragmatic rupture
Dx
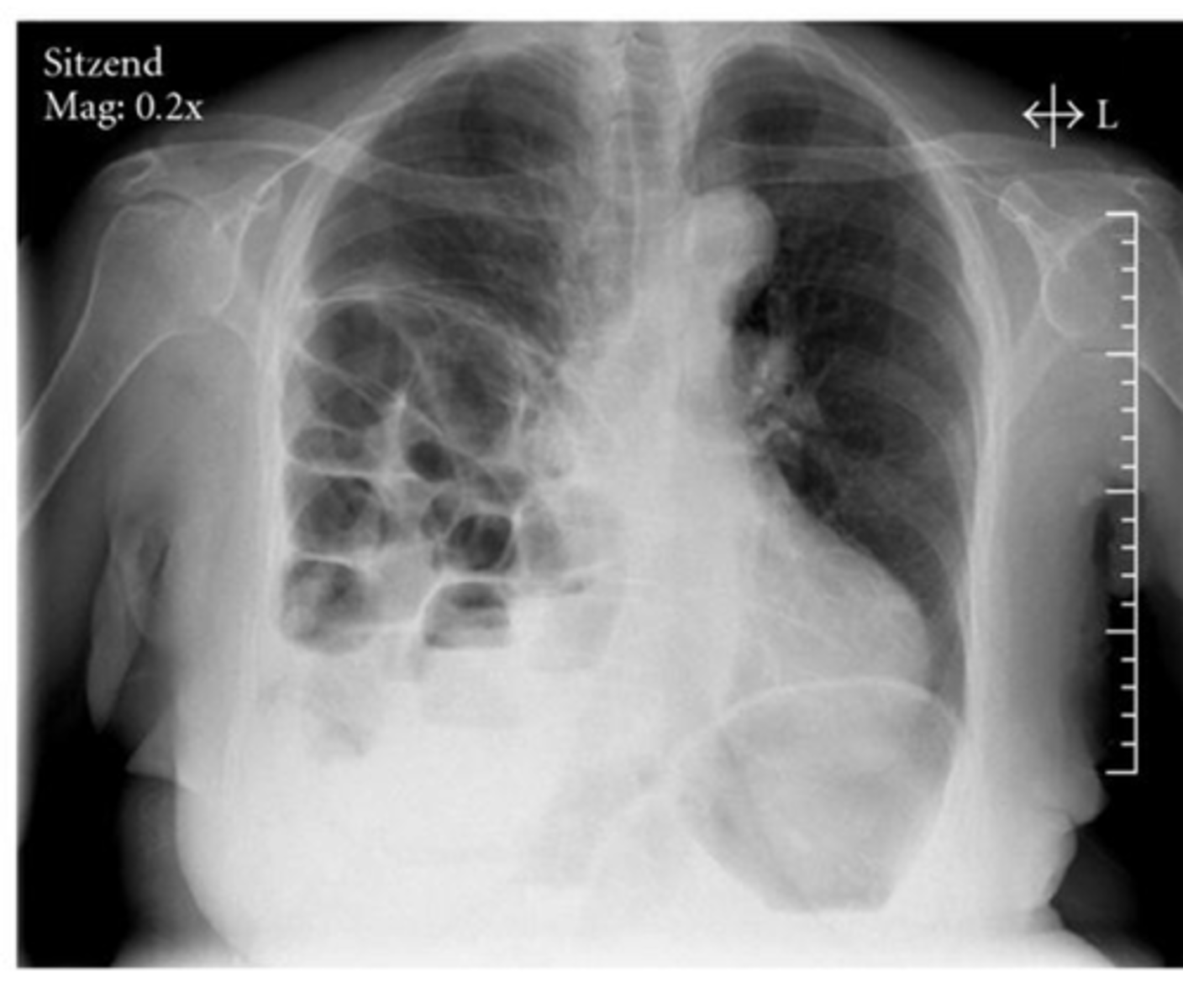
Diaphragmatic rupture/hernia
-GI goes to area of least resistance
Dx
o dyspnea if your exam is abnormal or if the patient is over 40 years old or is at risk for early cardiovascular disease.
o In most cases, you would not be wrong to get a CXR.
When is CXR inficated for chest pain or dyspnea?
Yes, CXR ois indicated for diagnosis and progression.
Is CXR indicated for CHF?
No, not really!
Is CXR indicated for HTN?
If it's true hemoptysis, yes
oMost common cause is bronchitis, however a neoplasm or PE is possible.
oIf CXR is normal and pt is low risk for cancer, CT scan is next step.
oIf patient is at risk for cancer then bronchoscopy is indicated.
Is CXR indicated for hemoptysis?
1. Mild: increased fluid into vasculature and seen by increased markings in upper lobes
2. Mod: Kerley B lines in lateral basilar regions
3. Severe: pulmonary edema – bilateral perihilar and basilar alveolar infiltrates
Kerley B lines (arrows) are horizontal lines in the lung periphery that extend to the pleural surface. They denote thickened, edematous interlobular septa often due to pulmonary edema
Radiological findings - CHF mild vs moderate vs severe
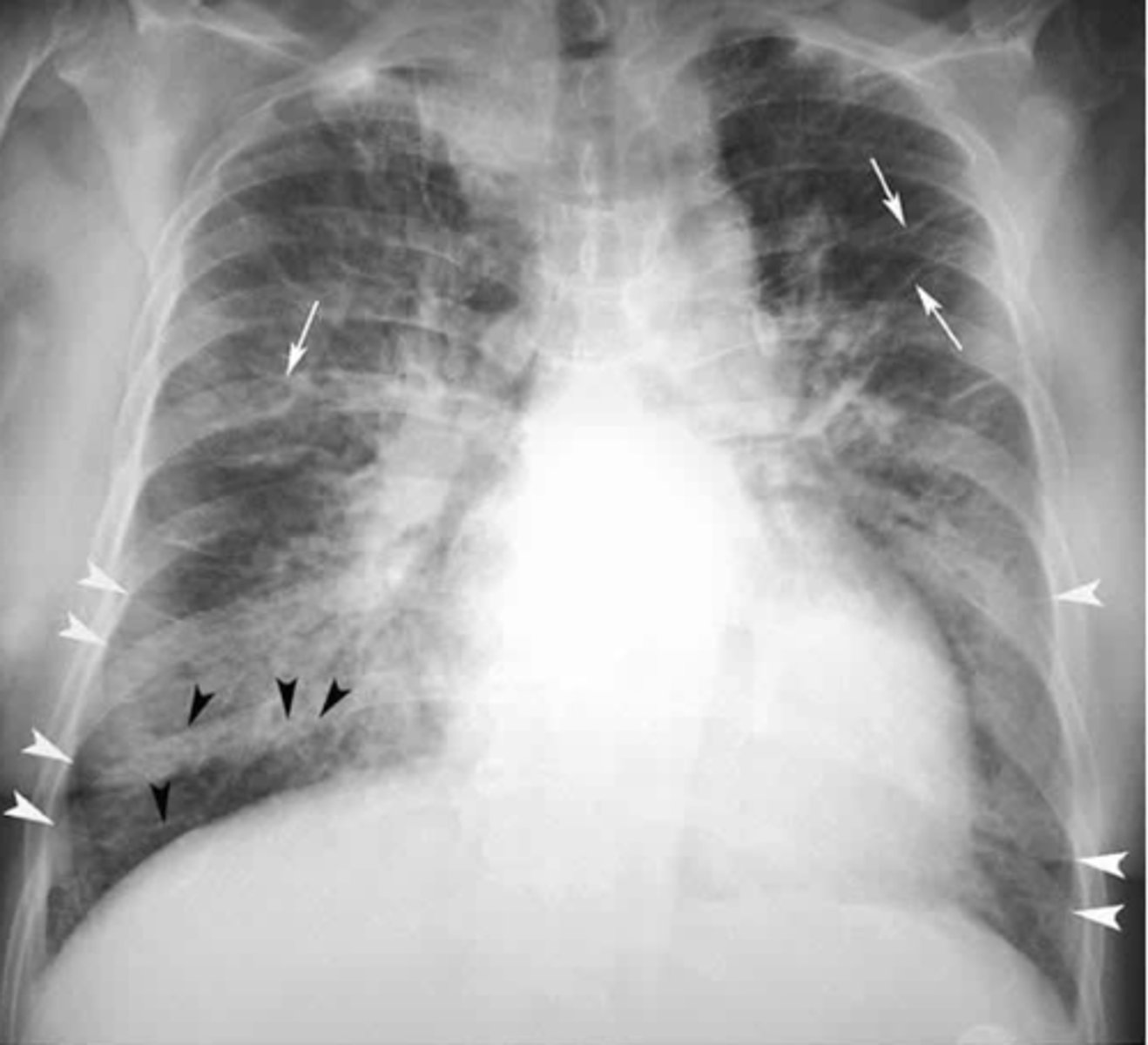
Moderate CHF with:
-redistribution of pulmonary vasculature (pulm vasculature should not be visible at all, esp in apices, but they are visible here)
-cardiomegaly and L sided pleural effusion
Dx - what kind of CHF is this?
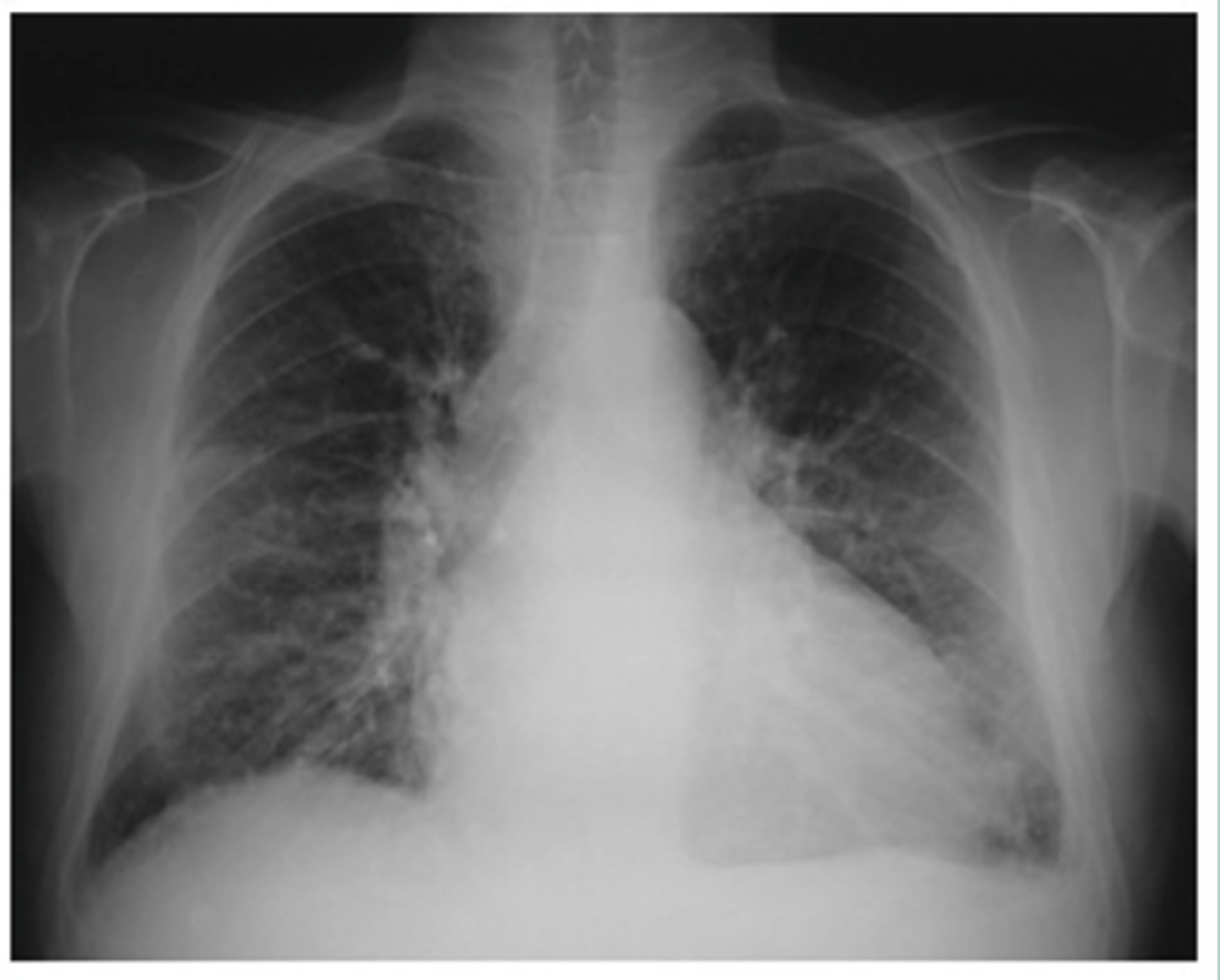
Mild to moderate CHF with redistribution of pulmonary vasculature, indistinct hila, mild cardiomegaly and Kerley B lines.
What signs on radiograph indicate CHF?
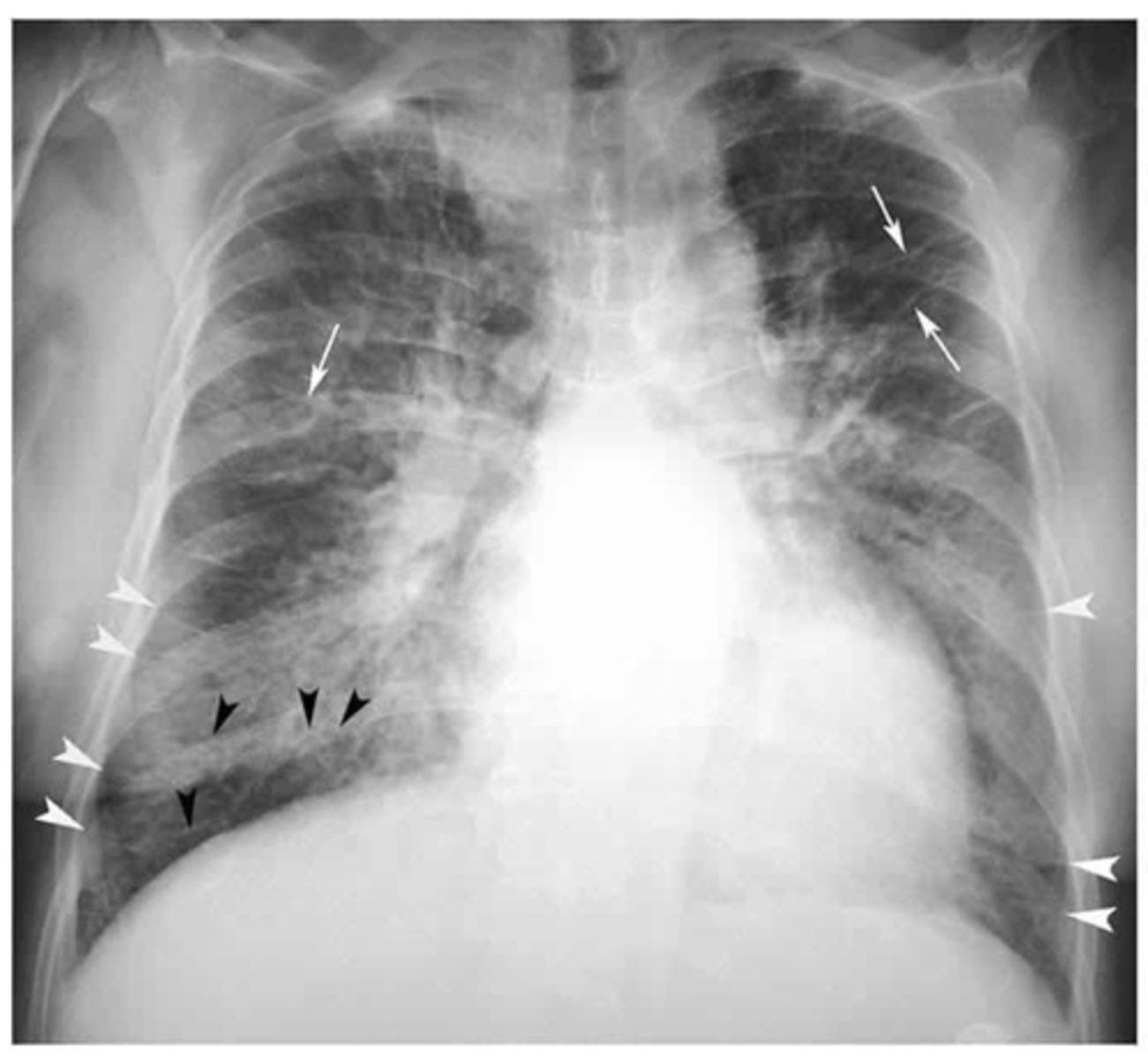
alveolar infiltrates
What does "fluffiness" on CXR indicate?
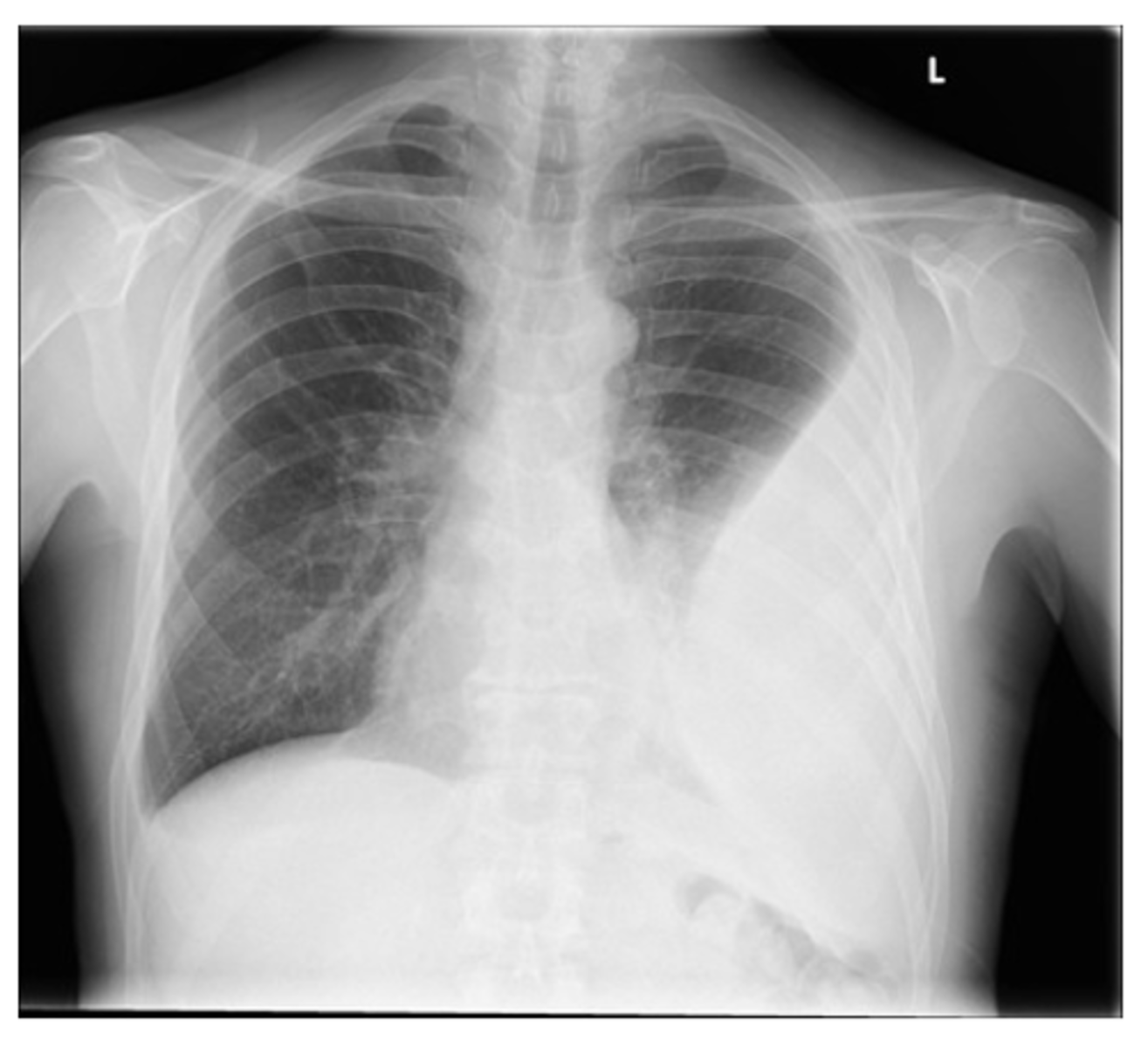
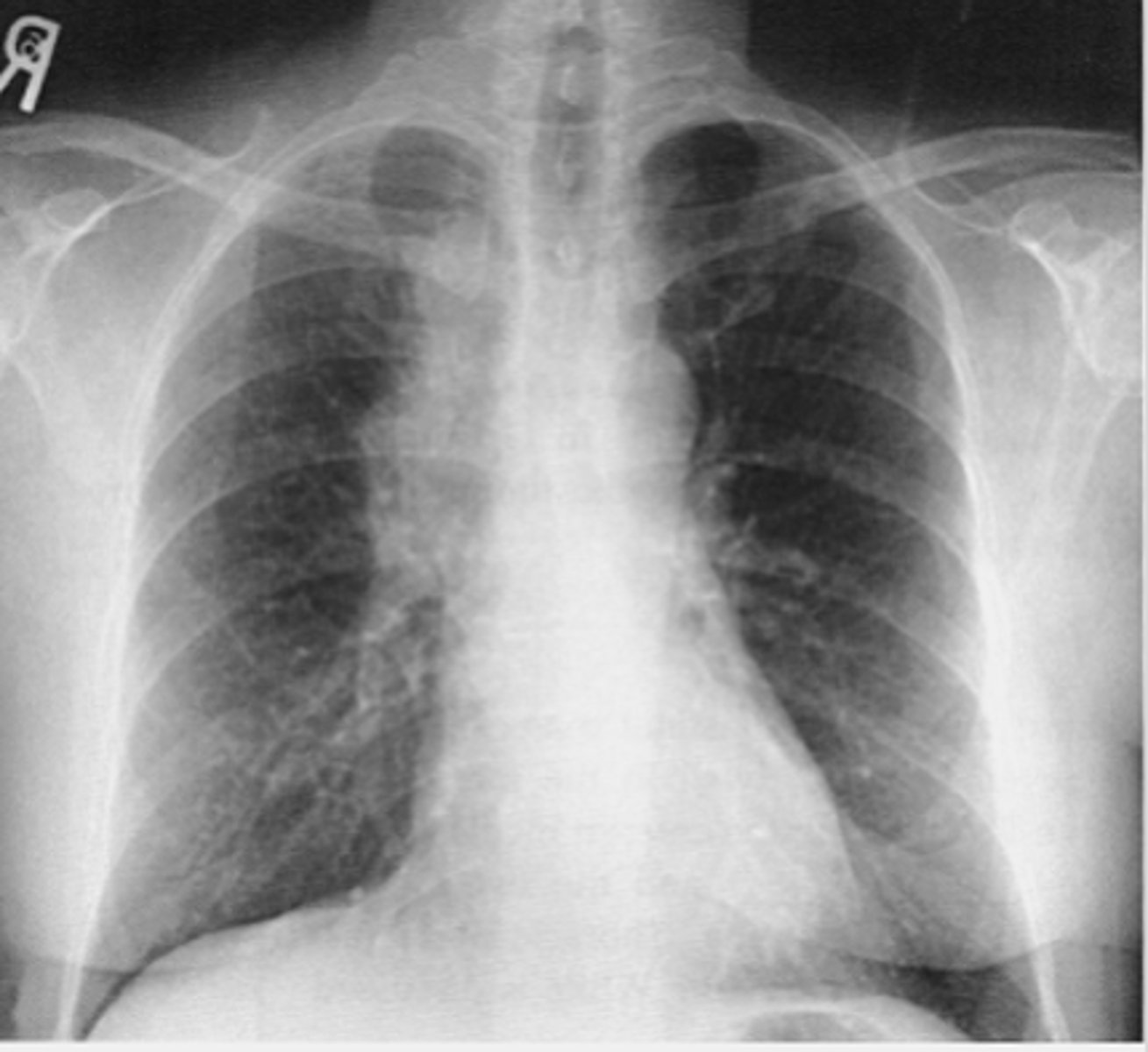
Left image: Thymoma in patient with Myasthenia Gravi
-Focal lesions are caused by masses
-Diffuse lesions are caused by infection, bleeding or infiltrating tumor
Identify focal vs diffuse mediastinal lesions. What do focal lesions typically indicate and diffuse lesions idnicate?
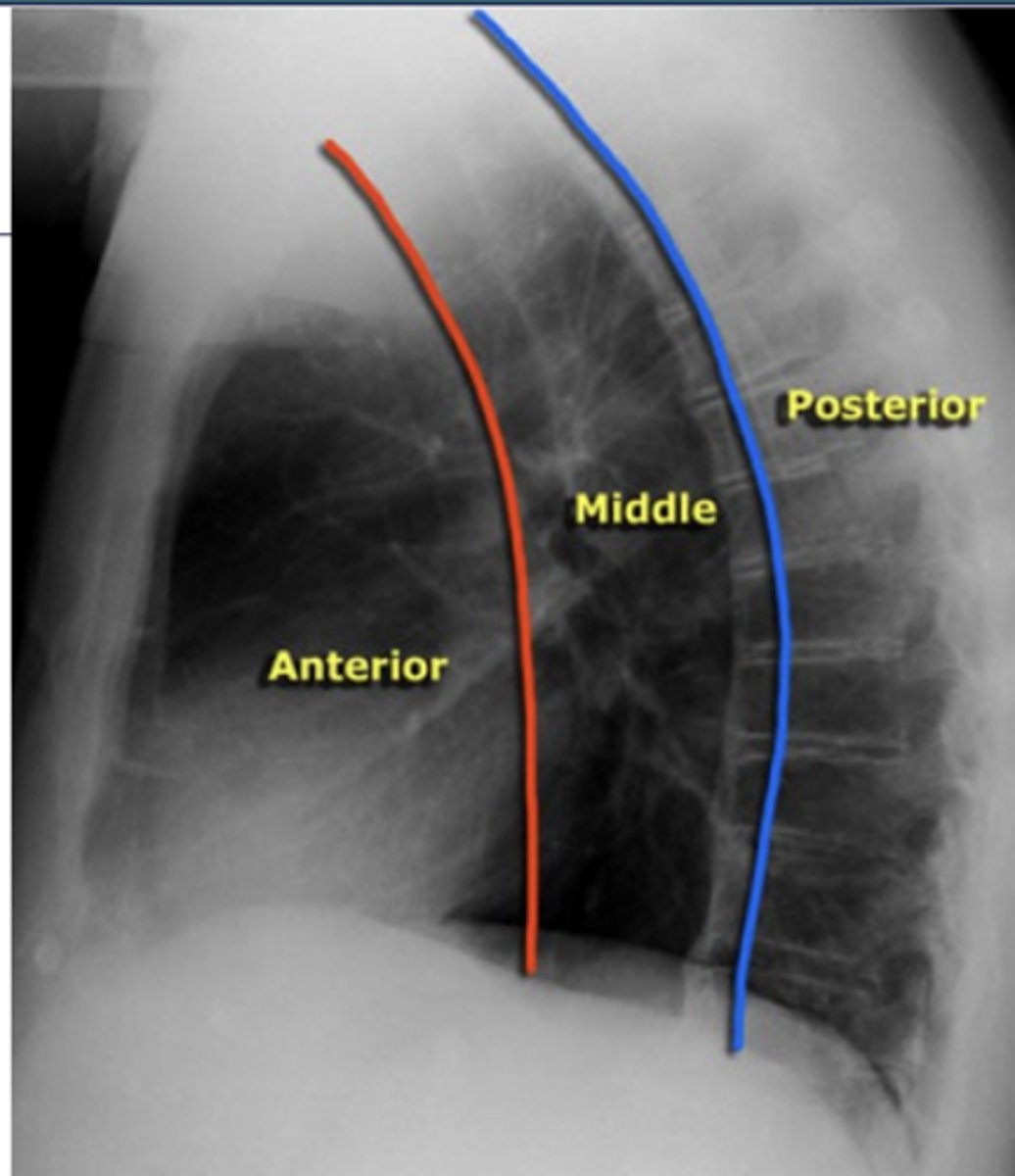
ascending aorta, aortic knob, heart, lymph nodes, thyroid, and thymus
What structures are located in the anterior mediastinal compartment?
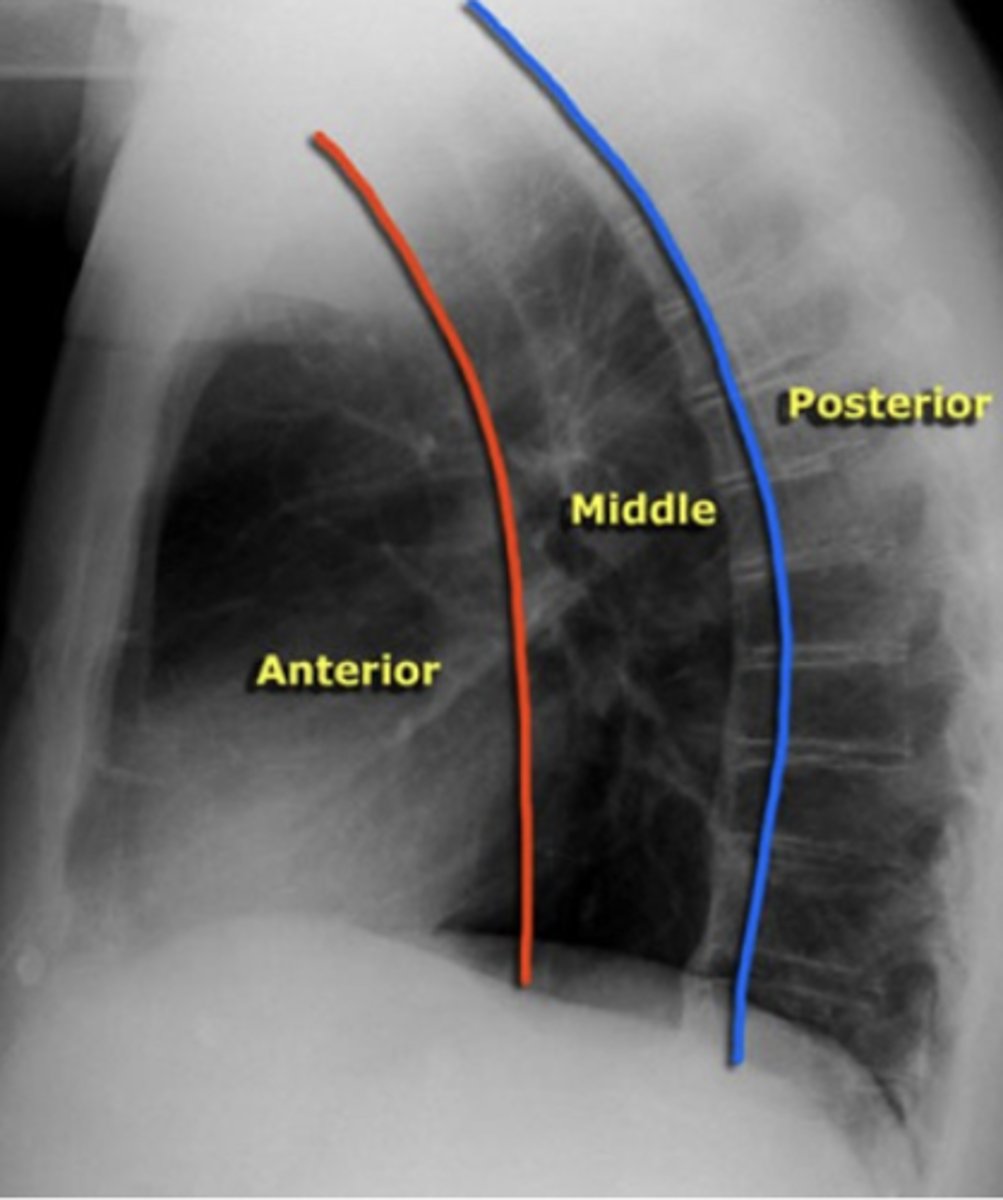
esophagus, trachea, lymph nodes, and aortic arch
What structures are located in the middle mediastinal compartment?
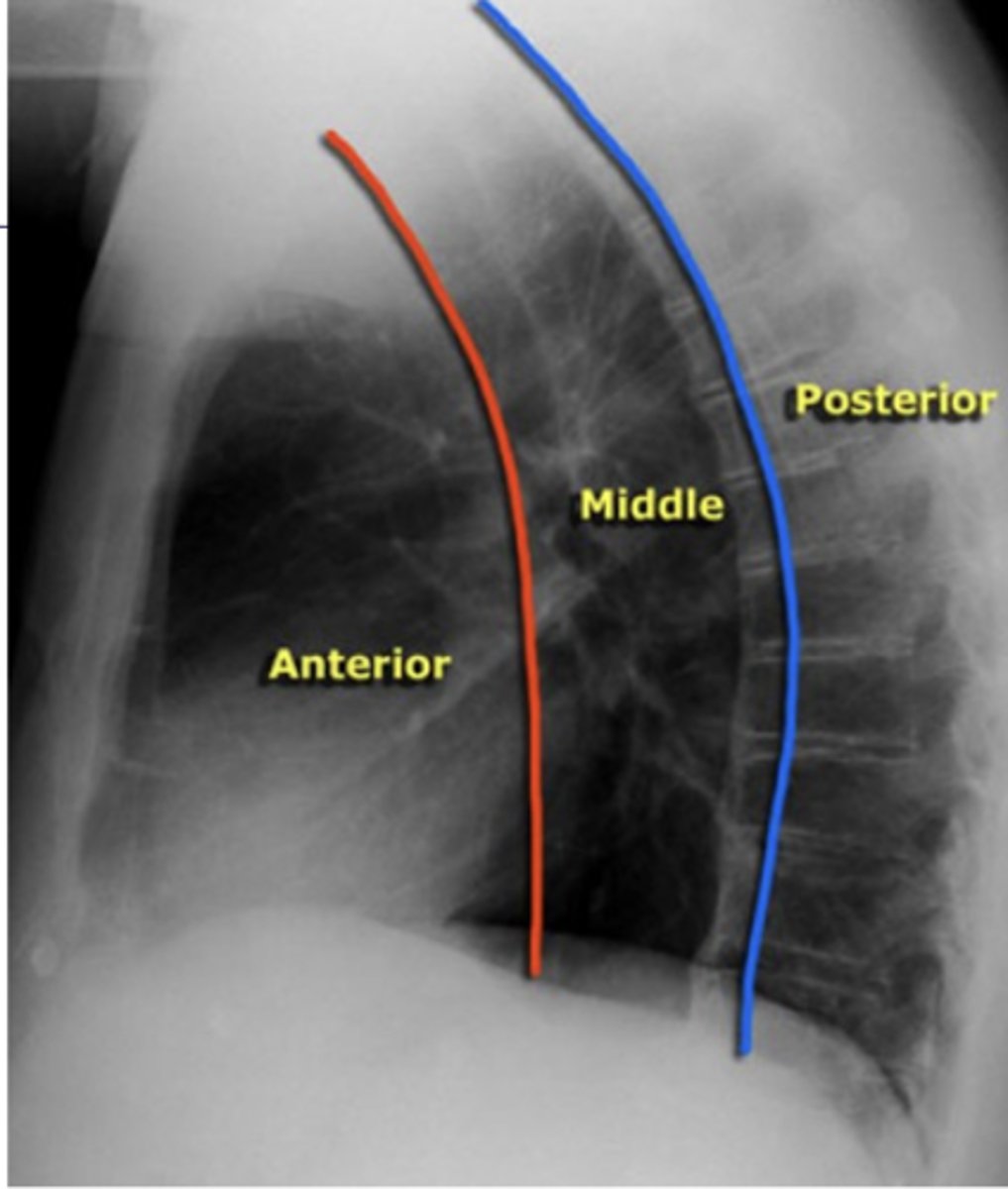
descending aorta, lymph nodes, spinal nerves, and vertebral bodies.
What structures are located in the posterior mediastinal compartment?
thymoma
-no need to interpret image
What is the most common anterior mediastinal mass?
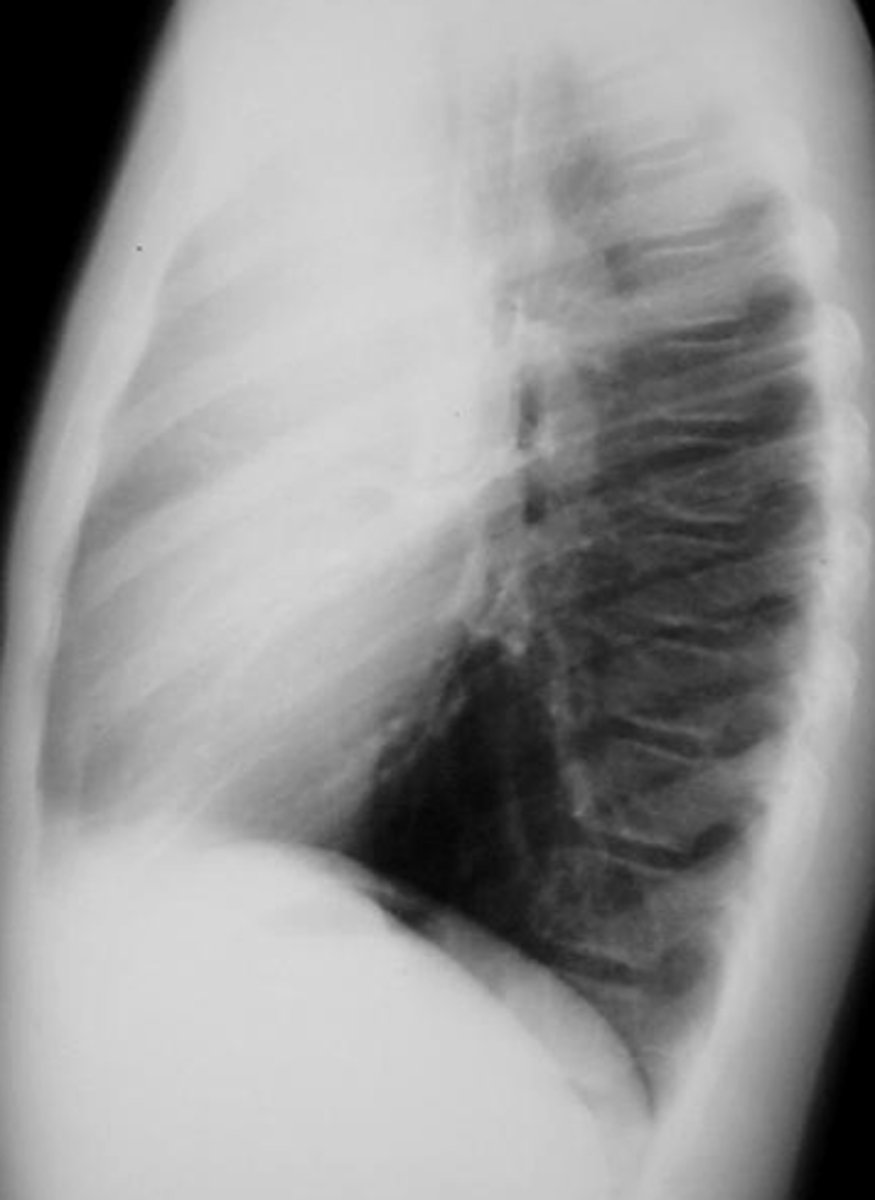
enlarged lymph nodes
Mass obscuring the right tracheal border - lymphadenopathy
What is the most frequent cause of a middle mediastinal mass? What finding on this x-ray would indicate this dz?
middle
What compartment is this lesion in?
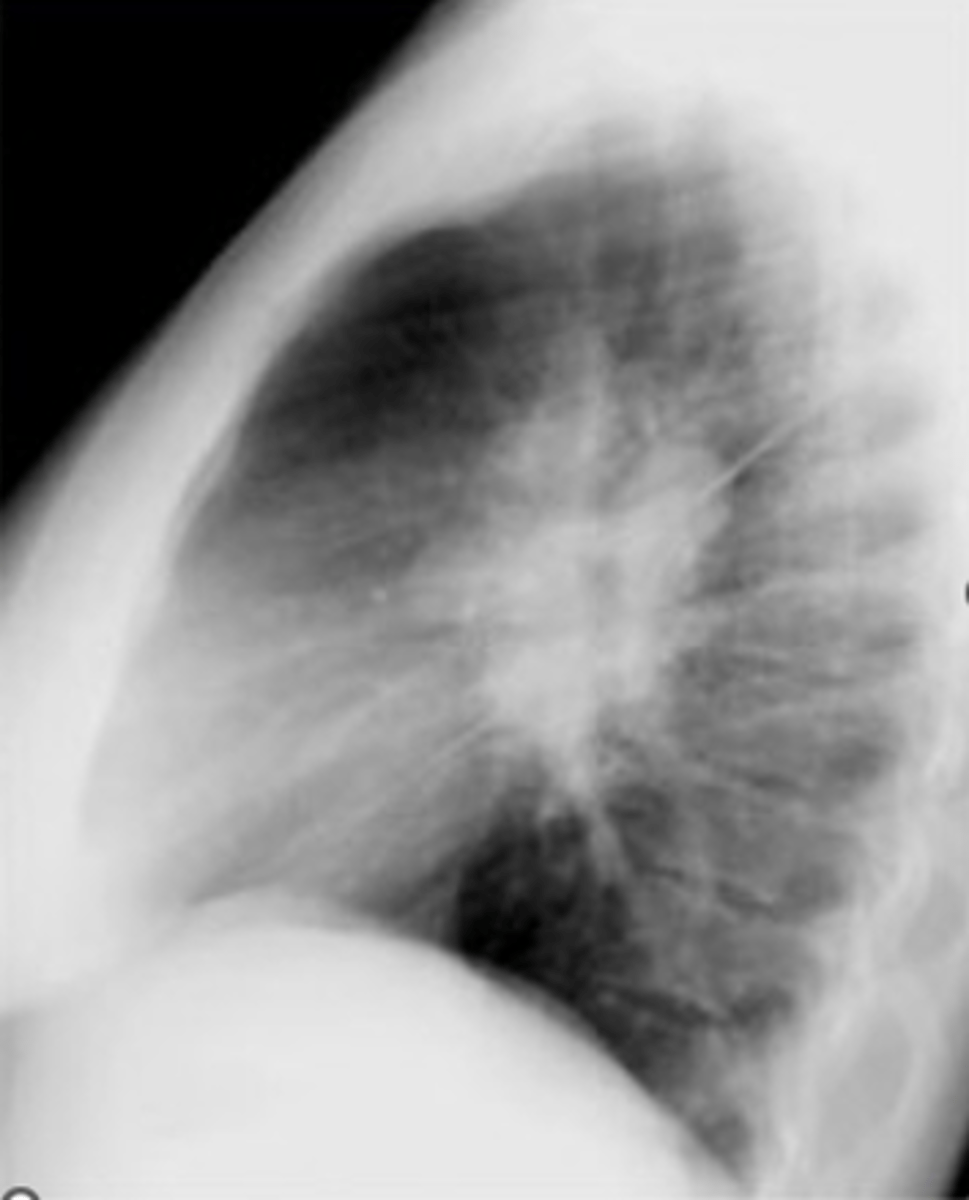
ganglionic lesion
-posterior compartment because neurogenic
-Posterior mediastinal masses can show a double density over left side of heart.
dx
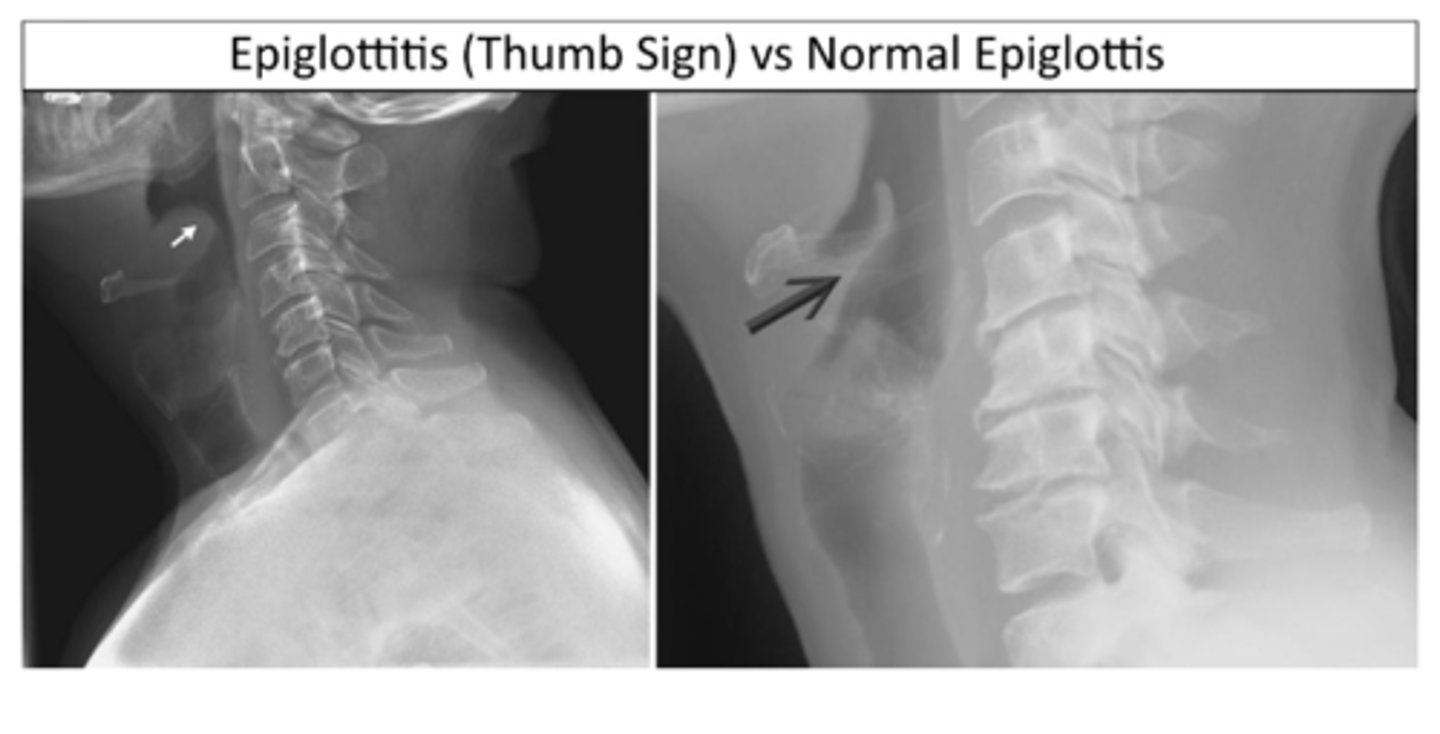
thumb sign (L)
-indicates inflammation of epiglottis
Classic radiologic finding for epiglottitis (ID L or R)
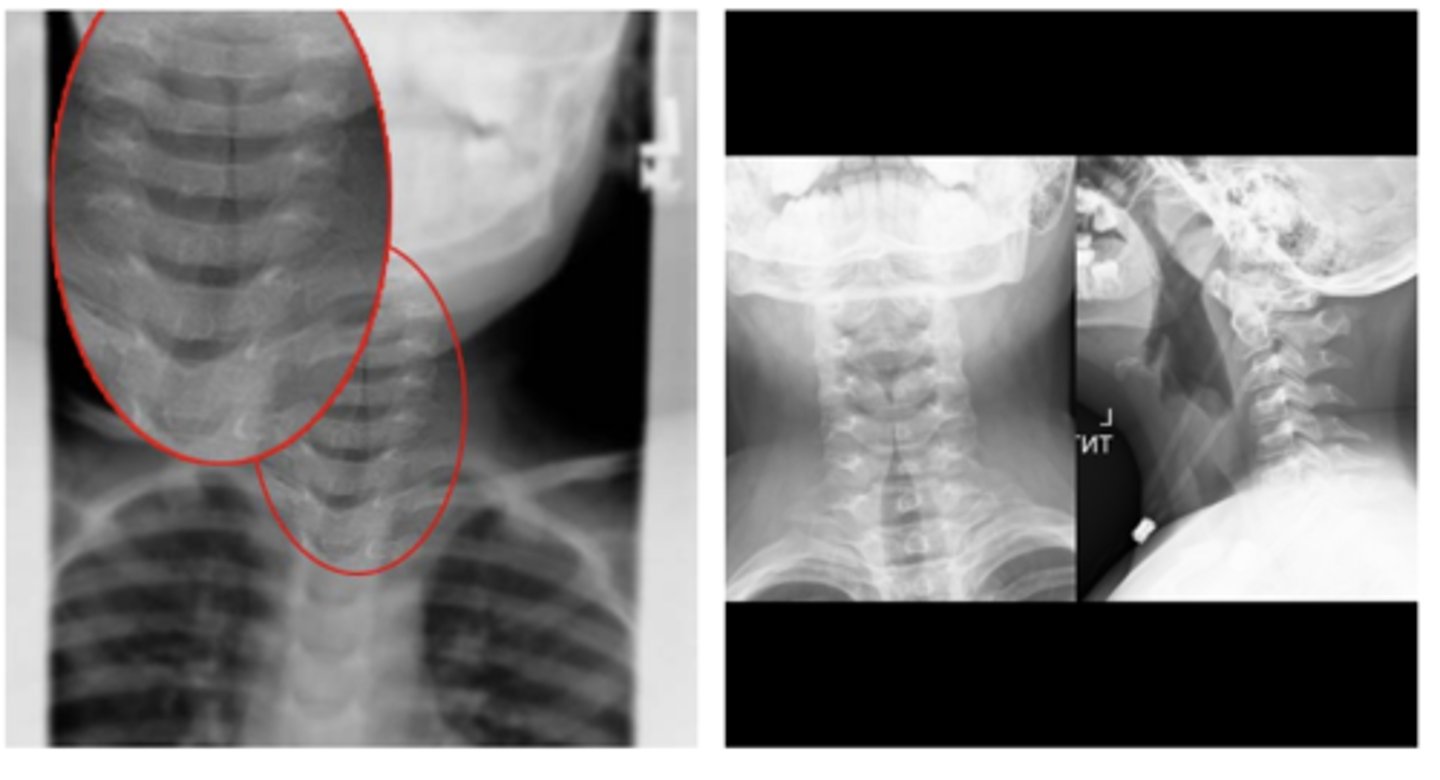
Croup "steeple's sign"
oNarrowing of the trachea due to edema
oCauses: Respiratory Syncytial Virus, Human parainfluenza virus (HPIV-1)
ID abnormality - what dz is this indicative of?
oUsually 6mo-3years old, up to 15 years old
oS/S: Inspiratory stridor, hoarse voice, barky seal-like cough, fever, runny nose
Who does croup typically affect? What are typical S/S