Unit 3 ALL - Bio
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Evolution
any change in relative frequencies of alleles in a population’s gene pool
Selection pressure
an external force which drives changes in the frequency of traits within a population (disease, predation, etc)
Inheritance
the process by which genetic information is passed from parent to offspring
Fitness
how well an organism can survive and reproduce
Homologous structures
common ancestry, different functions
Analogous structures
different ancestry, same function
Speciation
the evolutionary process by which new, distinct species arise from an ancestral population, caused by reproductive isolation
Geographic Isolation
when two populations are separated geographically
Behavioral Isolation
when two populations that were once able to interbreed evolve in courtship rituals/behavior
Cladogram
a diagram that shows how different groups of organisms diverged from common ancestors
Natural selection
the process by which organisms with variations most suited to their environment survive and reproduce
Variation
the differences in characteristics within a population or species
Adaptation
any heritable characteristic that increases an organisms ability to survive and reproduce
Coevolution
when two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution
Divergent evolution
two or more related species evolve in different directions from a common ancestor, leading to new species
Convergent evolution
when two unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
Reproductive isolation
when a species’ gene pool gets split because members stop breeding with other members
Temporal isolation
when two or more species reproduce at different times
Trait
a specific, heritable characteristic or feature of an organism
Vestigial Structures
structures that have lost all/most of their original function through evolution
arms race
organisms develop ways to resist “weapons“, a result of evolution in response to natural selection
directional selection
occurs when individuals at one end of curve have greater fitness than anywhere else
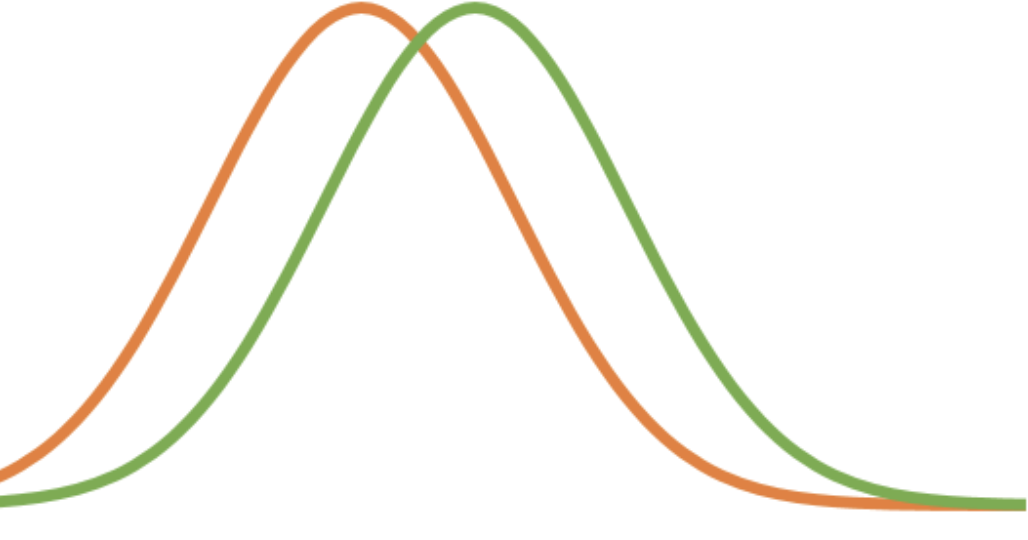
stabilizing selection
occurs when individuals near center of curve have greater fitness than either end

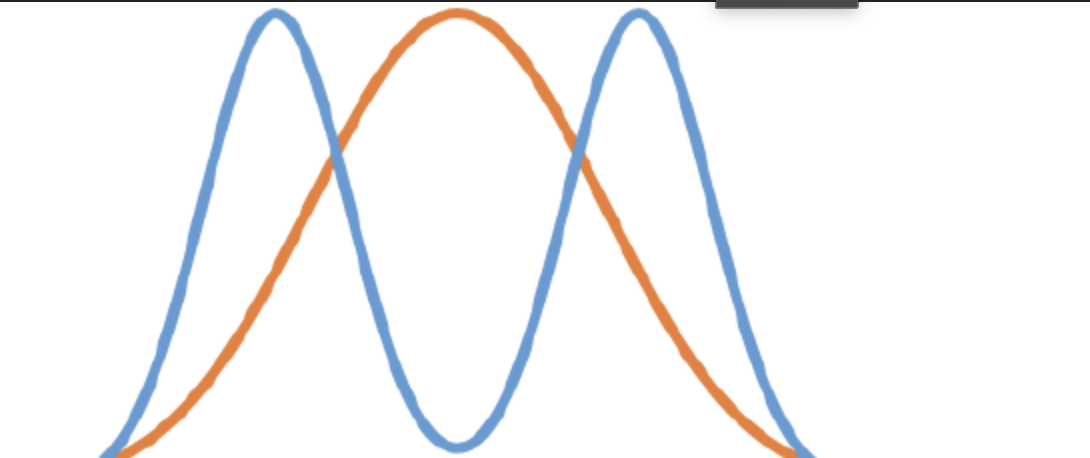
disruptive selection
occurs when phenotypes at both upper and lower ends of curve have greater fitness than the middle
genetic drift
random change in allele frequency, can cause allele to become more/less common in a population
genetic bottlenecks
a change in allele frequency following dramatic reduction in the size of a population
founder effect
allele frequencies change because of a migration of a small subgroup of a pre
genetic equilibrium
when a population is not evolving, allele frequencies in its gene pool are not changing
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
allele frequencies in a population should remain constant unless one or more factors cause these frequencies to change
Nonrandom mating
a factor where genes for traits selected for/against are not in equilibrium
sexual selection
when females select mates based on size, strength, coloration, etc.
small population size
a factor where genetic drift mainly effects small populations and evolution happens more easily
gene flow
the movement of genes into or out of a population
mutations
can introduce new alleles in a gene pool, causing evolution