Chem12 CPT Review (PART ONE)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/90
Last updated 3:17 PM on 12/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
1
New cards
alkanes
* ane
* non-polar
* van den waal forces
* low m and b point
* combustion reactions
* non-polar
* van den waal forces
* low m and b point
* combustion reactions
2
New cards
alkyl halides
* bromo, chloro, iodo, fluoro
* alphabetical order
* alphabetical order
3
New cards
alkenes
* -ene
* double bonded carbons
* unsaturated
* double bonded carbons
* unsaturated
4
New cards
alkynes
* -yne
* triple bonded
* unsaturated
* triple bonded
* unsaturated
5
New cards
stereoisomers
* same # of atoms bonded, different formation
6
New cards
cis-/trans- isomerism
* cis- same side
* not balanced
* trans- opposite side
* balanced
* not balanced
* trans- opposite side
* balanced
7
New cards
markovnikov’s rule
* the attraction of H to other H atoms
* in reactions, the atoms being replaced must be closest to the most amount of H as possible
* in reactions, the atoms being replaced must be closest to the most amount of H as possible
8
New cards
aromatic hydrocarbons
* -benzene
* phenyl-
* unsaturated
* ring shape
* 3 double bonds
* liquid @ room temp
* non-polar
* insoluble in water
* does not undergo addition reactions
* phenyl-
* unsaturated
* ring shape
* 3 double bonds
* liquid @ room temp
* non-polar
* insoluble in water
* does not undergo addition reactions
9
New cards
aliphatics
* hydrocarbons lined up in a straight line
* not a pleasant odour
* burn with non-sooty flames
* some unsaturated, some saturated
* not a pleasant odour
* burn with non-sooty flames
* some unsaturated, some saturated
10
New cards
aromatic
* ring structure
* pleasant odour
* all unsaturated
* burn with sooty flames
* pleasant odour
* all unsaturated
* burn with sooty flames
11
New cards
alcohols
* -ol
* contains hydroxyl group (OH)
* polar
* higher b points than alkanes
* soluble in water
* made through the hydration of alkenes
* contains hydroxyl group (OH)
* polar
* higher b points than alkanes
* soluble in water
* made through the hydration of alkenes
12
New cards
primary alcohols
* bonded to 1 other carbon chain
* makes aldehydes
* makes aldehydes
13
New cards
secondary alcohols
* bonded to 2 other C chains
* makes ketones
* makes ketones
14
New cards
tertiary alcohols
* bonded to 3 other C chains
* non-reactive (NR)
* non-reactive (NR)
15
New cards
e__th__ers
* -oxy//-ane
* 2 carbon chains stick together by an oxygen
* b points higher than alkanes, but lower than alcohols
* good solvent
* c-o bond makes them polar
* alkyl groups make them non-polar
* 2 carbon chains stick together by an oxygen
* b points higher than alkanes, but lower than alcohols
* good solvent
* c-o bond makes them polar
* alkyl groups make them non-polar
16
New cards
thiols
* -thiol
* contains sulfhydryl group (SH)
* contains sulfhydryl group (SH)
17
New cards
carbonyl group
* C double bonded to an O
* C=O
* C=O
18
New cards
aldehyde
* -al
* carbonyl group @ the end of the C chain
* strong, pungent smell (like roses)
* polar & soluble in water
* b points are high
* \[O\] to make carboxylic acids
* carbonyl group @ the end of the C chain
* strong, pungent smell (like roses)
* polar & soluble in water
* b points are high
* \[O\] to make carboxylic acids
19
New cards
ketone
* -one
* carbonyl group in the middle of the chain
* strong, pungent smell (like roses)
* polar & soluble in water
* b points are high
* carbonyl group in the middle of the chain
* strong, pungent smell (like roses)
* polar & soluble in water
* b points are high
20
New cards
carboxylic acid
* -oic acid
* C double bonded to an O, & same C bonded to an OH
* very polar
* H bonding
* m point is high
* made from the \[O\] of an aldehyde
* C double bonded to an O, & same C bonded to an OH
* very polar
* H bonding
* m point is high
* made from the \[O\] of an aldehyde
21
New cards
e__st__ers
* -oate
* fruity/floral smell
* 2 chains being bonded by an O and C
* C has a double-bonded O on the other side
* less polar and soluble than carboxylic acids
* b points are lower
* made from alcohols and carboxylic acids
* fruity/floral smell
* 2 chains being bonded by an O and C
* C has a double-bonded O on the other side
* less polar and soluble than carboxylic acids
* b points are lower
* made from alcohols and carboxylic acids
22
New cards
ami**n**es
* -amine
* N present to connect chains
* strong, fishy smell
* polar
* not very soluble
* higher b and m points
* N present to connect chains
* strong, fishy smell
* polar
* not very soluble
* higher b and m points
23
New cards
primary amines
* N attached to 1 alkyl group
* made from an alkyl halide reacting with ammonia
* made from an alkyl halide reacting with ammonia
24
New cards
secondary amines
* N attached to 2 alkyl groups
* made from a primary amine reacting with an alkyl group
* made from a primary amine reacting with an alkyl group
25
New cards
tertiary amines
* N attached to 3 alkyl groups
* made form a secondary amine reacting with an alkyl halide
* made form a secondary amine reacting with an alkyl halide
26
New cards
ami**d**es
* -amide
* 2 chains joined by a N bonded to a C which has a double bonded O
* N-C=O
* mildly soluble in water
* made from:
* carboxylic acid reacting with ammonia
* OR a primary amine reacting with a secondary amine
* 2 chains joined by a N bonded to a C which has a double bonded O
* N-C=O
* mildly soluble in water
* made from:
* carboxylic acid reacting with ammonia
* OR a primary amine reacting with a secondary amine
27
New cards
general polymers
* polymer: large molecule that is built from monomers
* monomers: one of the repeating units that make up a polymer
* copolymers: different types of monomers combined to form a polymer chain
* can be joined through addition or condensation
* natural polymers: polymers made entirely of living things (ex. glucose, DNA, proteins)
* synthetic polymers: made artificially to have desirable properties, or to serve a specific purpose (ex. polyester)
* they undergo either addition or condensation reactions to perform certain actions
* monomers: one of the repeating units that make up a polymer
* copolymers: different types of monomers combined to form a polymer chain
* can be joined through addition or condensation
* natural polymers: polymers made entirely of living things (ex. glucose, DNA, proteins)
* synthetic polymers: made artificially to have desirable properties, or to serve a specific purpose (ex. polyester)
* they undergo either addition or condensation reactions to perform certain actions
28
New cards
natural polymers
* peptide bonds- produced when condensation reactions between amino acids build protein polymers
* protein structure- the sequence of amino acids in a protein
* nucleic acid- store and transmit genetic information
* nucleotides- monomers of nucleic acid
* 5 carbon sugar
* nitrogen-containing organic base
* phosphoric acid molecule
* protein structure- the sequence of amino acids in a protein
* nucleic acid- store and transmit genetic information
* nucleotides- monomers of nucleic acid
* 5 carbon sugar
* nitrogen-containing organic base
* phosphoric acid molecule
29
New cards
synthetic addition polymers
* the result of a reaction between monomers of an unsaturated hydrocarbon
* plastics - synthetic polymer that can be molded into shape and will retain that shape when cooled
* Low Density Polyethylene- branched molecule, synthesized by adding a small amount of compounds that have multiple double bonds
* High Density Polyethylene- blow moulded products, mostly straight chain, can pack more tightly
* plastics - synthetic polymer that can be molded into shape and will retain that shape when cooled
* Low Density Polyethylene- branched molecule, synthesized by adding a small amount of compounds that have multiple double bonds
* High Density Polyethylene- blow moulded products, mostly straight chain, can pack more tightly
30
New cards
synthetic condensation polymers
* polymer made through many condensation reactions
* ester linkages- a polymer formed by a series of esterification reactions, a copolymer
* amide linkages- formed from a reaction between a carboxylic acid and amine
* ester linkages- a polymer formed by a series of esterification reactions, a copolymer
* amide linkages- formed from a reaction between a carboxylic acid and amine
31
New cards
alkane reaction (1)
* substitution
* alkane + H(cl/br/f/i) → alkyl halides
* alkane + H(cl/br/f/i) → alkyl halides
32
New cards
alkene reactions (3)
* alkene + 2H₂ → alkane
* alkene + H₂O → alcohol
* alkene + H(cl/br/f/i) → alkyl halide +~~H₂O~~
* alkene + H₂O → alcohol
* alkene + H(cl/br/f/i) → alkyl halide +~~H₂O~~
33
New cards
alcohol reactions (6)
* 1° alcohol + \[O\] → aldehyde
* 2° alcohol + \[O} → ketone
* 3° alcohol + \[O\] → **NR**
* alcohol + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
* alcohol + (cl/br/f/i) → alkyl halide + H₂O
* alcohol →*heat*→ ether + H₂O
* 2° alcohol + \[O} → ketone
* 3° alcohol + \[O\] → **NR**
* alcohol + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
* alcohol + (cl/br/f/i) → alkyl halide + H₂O
* alcohol →*heat*→ ether + H₂O
34
New cards
aldehyde reactions (2)
* aldehyde + \[O\] → carboxylic acid
* aldehyde + 2H₂ → alcohol
* aldehyde + 2H₂ → alcohol
35
New cards
carboxylic acid reactions (3)
* carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester + H₂O
* carboxylic acid + \[O\] → amide
* carboxylic acid + amine → amide
* carboxylic acid + \[O\] → amide
* carboxylic acid + amine → amide
36
New cards
ester reaction (1)
* ester + acid/base → carboxylic acid + alcohol
37
New cards
alkyl halide reactions (3)
* alkyl halide + ammonia → 1° amine
* alkyl halide + 1° amine → 2° amine
* alkyl halide +2° amine → 3° amine
* alkyl halide + 1° amine → 2° amine
* alkyl halide +2° amine → 3° amine
38
New cards
__**UNIT CHANGE**__
\--------------
39
New cards
Democrutis-present Atomic Theories
* around 400 BC
* atom was founded by hypothesizing that matter cut into smaller and smaller pieces would eventually become indivisible
* atom was founded by hypothesizing that matter cut into smaller and smaller pieces would eventually become indivisible
40
New cards
John Dalton
* reintroduced the atom
* the billiard ball
* elements consists of atoms
* atoms cannot be created destroyed or divided
* atoms of the same element have identical size, mass, and properties (which is FALSE)
* the billiard ball
* elements consists of atoms
* atoms cannot be created destroyed or divided
* atoms of the same element have identical size, mass, and properties (which is FALSE)
41
New cards
JJ Thompson
* discovered the electron (negatively charged subatomic particle)
* plum pudding model
* cathode ray tube
* vacuum-like tube that spits out particles to measure the deflection of the beam of light
* concluded the atom is a negatively charged electron inside a positively charged “shell”
* plum pudding model
* cathode ray tube
* vacuum-like tube that spits out particles to measure the deflection of the beam of light
* concluded the atom is a negatively charged electron inside a positively charged “shell”
42
New cards
Robert Milikan
* mass of the electron
* calculated the mass by using charged oil in a can and saw how fast or slow the oil would drop from level to level
* calculated the mass by using charged oil in a can and saw how fast or slow the oil would drop from level to level
43
New cards
Henri Becquerel
* radioactivity
* uranium is capable of emitting energy, particles, or waves that travel through space
* 3 types of radioactive emissions
* alpha particles (He)
* beta particles (e⁻)
* gamma rays
* uranium is capable of emitting energy, particles, or waves that travel through space
* 3 types of radioactive emissions
* alpha particles (He)
* beta particles (e⁻)
* gamma rays
44
New cards
Ernest Rutherford
* the nucleus
* gold foil experiment
* alpha particles were fired at a thin gold sheet to measure how often they would deflect (1 in 8000)
* Rutherford concluded
* the atom has a nucleus: a dense, positively charged center made of proteins
* electrons orbited the nucleus
* gold foil experiment
* alpha particles were fired at a thin gold sheet to measure how often they would deflect (1 in 8000)
* Rutherford concluded
* the atom has a nucleus: a dense, positively charged center made of proteins
* electrons orbited the nucleus
45
New cards
James Chadwick
* the neutron
* when calculating the nass of the nuclei, Chadwick notices there was an imbalance and discovered neutral particles to make-up for the imbalance
* positive nucleus containing neutral particles called neutrons
* when calculating the nass of the nuclei, Chadwick notices there was an imbalance and discovered neutral particles to make-up for the imbalance
* positive nucleus containing neutral particles called neutrons
46
New cards
Classical Light: Huygens
* light is a wave
* refraction, reflection, and defraction
* refraction, reflection, and defraction
47
New cards
Classical Light: Maxwell
* electromagnetic spectrum
* made of magnetic and electric fields
* made of magnetic and electric fields
48
New cards
Classical Light/Quantum: Hertz
* photoelectric effect
* the colour of light determines the energy of electrons emitted
* shortwave electromagnetic radiation
* the colour of light determines the energy of electrons emitted
* shortwave electromagnetic radiation
49
New cards
Quantum: Planck
* light behaves as a particle
* blackbody: perfectly black object that does not reflect any light & emits various forms of light as a result of very high temps.
* light is emitted in bursts of discrete quantities of energy, rather than continuous flow
* quantum energy/quanta
* blackbody: perfectly black object that does not reflect any light & emits various forms of light as a result of very high temps.
* light is emitted in bursts of discrete quantities of energy, rather than continuous flow
* quantum energy/quanta
50
New cards
Einstein
* photons
* EM radiation is a stream of particles called photons (units/packets of light energy)
* quantum theory
* the energy of a photon has to be above the threshold frequency, otherwise, no electrons are ejected
* EM radiation is a stream of particles called photons (units/packets of light energy)
* quantum theory
* the energy of a photon has to be above the threshold frequency, otherwise, no electrons are ejected
51
New cards
Bohr’s Model of the Atom
* spectroscopy → invented by Bunsen & Kirchoff
* used to study light passing through a plate and prism to create different coloured lights and emissions
* dark light spectrum
* start with white light & pass through a gas & analyze what’s left
* absorption spectrum
* lower to higher level
* bright line spectrum
* when a gas is exposed to an electric current then passed through a prism to emit light
* emission spectrum
* higher to lower level
* used to study light passing through a plate and prism to create different coloured lights and emissions
* dark light spectrum
* start with white light & pass through a gas & analyze what’s left
* absorption spectrum
* lower to higher level
* bright line spectrum
* when a gas is exposed to an electric current then passed through a prism to emit light
* emission spectrum
* higher to lower level
52
New cards
Successes & Failures of the Bohr Model
* gives a reasonable explanation for Mendeleev’s periodic law; periods result from the filling of electron energy levels
* the max. # of electrons in each energy level corresponds to the elements in each period of the periodic table (2,8,8,18)
* it explained the line spectrum of H
\
* could not predict the spectra of ions of more than 1 electron
* the max. # of electrons in each energy level corresponds to the elements in each period of the periodic table (2,8,8,18)
* it explained the line spectrum of H
\
* could not predict the spectra of ions of more than 1 electron
53
New cards
Bohr’s postulates
* An electron in an atom revolves in certain stable orbits without emitting radiant energy.
* Each atom has certain definite stable orbits.
* Electrons can exist in these orbits.
* Each possible orbit has definite total energy.
* Each atom has certain definite stable orbits.
* Electrons can exist in these orbits.
* Each possible orbit has definite total energy.
54
New cards
Quantum Mechanical Model: Louis De Brogilie
* electrons have wave-like properties
* if light behaves like a particle, a particle should also be able to behave like a wave
* if light behaves like a particle, a particle should also be able to behave like a wave
55
New cards
Quantum Mechanical Model: Erwin Schrodinger
* used math and stats to combine De Brogilie’s and Einstein’s theories of light
* energy levels
* everything has wavelengths
* energy levels
* everything has wavelengths
56
New cards
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
* it is impossible to know the exact position/location & speed of any electron @ any given time
57
New cards
Orbits vs. Orbitals
* orbitals- the region around the nucleus when an e⁻ has a very high probability of being found
* 2 electrons
* 3D
* distance from the nucleus varies
* no set paths
* orbits
* 2n² electrons
* 2D
* distance from the nucleus is fixed
* path is elliptical or circular
* 2 electrons
* 3D
* distance from the nucleus varies
* no set paths
* orbits
* 2n² electrons
* 2D
* distance from the nucleus is fixed
* path is elliptical or circular
58
New cards
principal quantum number
* principal, n
* describes the size & energy of an orbital
* differences between energy levels are not =
* describes the size & energy of an orbital
* differences between energy levels are not =
59
New cards
secondary quantum number
* secondary, l
* describes the shapes of sub shells of the main energy level
* values of **l** describe the shape and energy of an atomic orbital
* s=0, p=1, d=2, f=3, g=4
* describes the shapes of sub shells of the main energy level
* values of **l** describe the shape and energy of an atomic orbital
* s=0, p=1, d=2, f=3, g=4
60
New cards
magnetic quantum number
* magnetic, m
* describes the orientation in space relative to other orbitals
* m₁ is equal to the # of orbitals
* +l or -l are integral values (including 0)
* describes the orientation in space relative to other orbitals
* m₁ is equal to the # of orbitals
* +l or -l are integral values (including 0)
61
New cards
spin quantum number
* spin, ms
* describes the spin
* possesses only 2 values; either +1/2 or -1/2
* describes the spin
* possesses only 2 values; either +1/2 or -1/2
62
New cards
Pauli exclusion principle
* no 2 electrons have the same 4 quantum numbers
* each has 2 arrows (+ and -)
* each has 2 arrows (+ and -)
63
New cards
Aufbau principle
* an energy level must be filled before moving on to the next higher level
64
New cards
Hund’s rule
* each orbital at the same energy level must have 1 electron in ut before any orbital can contain 2 electrons
65
New cards
electron energy diagrams
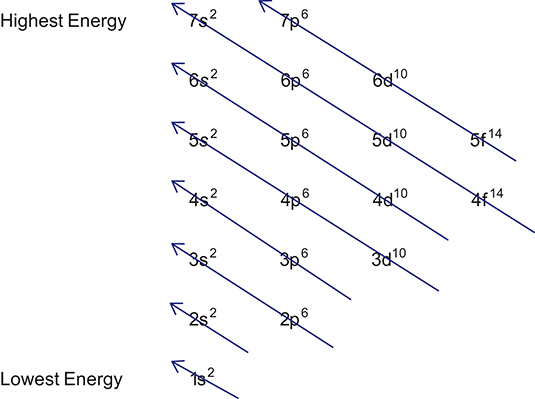
66
New cards
ionic compounds
* the electrostatic attraction between opposing charged ions
* isoelectric- have the same # of electrons (Xe, I⁻, Cs⁺)
* isoelectric- have the same # of electrons (Xe, I⁻, Cs⁺)
67
New cards
molecular compounds
* the attraction of electrons from 1 atom to the nucleus of the other
* covalent bond occurs when atoms share electrons
* covalent bond occurs when atoms share electrons
68
New cards
Lewis Theory of Bonding
* atoms and ions are stable if they have a stable octet of electrons (or in pairs)
* duet rule- a H atom from a stable configuration when it shares 2 electrons in order to obtain a full valance shell
* octet rule- many atoms are more stable when they are surrounded by 8 e⁻ to achieve a full valance shell
* lone pair- a pair of e⁻ that is not involved in bonding
* duet rule- a H atom from a stable configuration when it shares 2 electrons in order to obtain a full valance shell
* octet rule- many atoms are more stable when they are surrounded by 8 e⁻ to achieve a full valance shell
* lone pair- a pair of e⁻ that is not involved in bonding
69
New cards
VSEPR Theory
* valance shell electron pair repulsion theory
* based on the distance of electeons and their pull & push factors
* based on the distance of electeons and their pull & push factors
70
New cards
VSEPR: linear
* AX₂, AX₁, AX₂E₃
* equal repulsion to pull
* equal repulsion to pull
71
New cards
VSEPR: trigonal plannar
* AX₃
* 3 bonds, no lone pairs
* 3 bonds, no lone pairs
72
New cards
VSEPR: tetrahedral
* AX₄
* 4 bonds
* equal forces
* 4 bonds
* equal forces
73
New cards
VSEPR: trigonal pyramidal
* AX₃E₁
* 3 bonds, 1 lone pair
* 3 bonds, 1 lone pair
74
New cards
VSEPR: bent/v-shaped
* AX₂E₂
* 2 bonds, 2 lone pairs
* 2 bonds, 2 lone pairs
75
New cards
VSEPR: seesaw
* AX₄E₁
* 4 bonds, 1 lone pair
* 4 bonds, 1 lone pair
76
New cards
VSEPR: t-shaped
* AX₃E₂
* 3 bonds, 2 lone pairs
* 3 bonds, 2 lone pairs
77
New cards
VSEPR: square pyramidal
* AX₅E₁
* 5 bonds, 1 lone pair
* 5 bonds, 1 lone pair
78
New cards
VSEPR: square plannar
* AX₄E₂
* 4 bonds, 2 lone pairs
* 4 bonds, 2 lone pairs
79
New cards
VSEPR: octahedral
* AX₆
* 6 bonds, no lone pairs
* 6 bonds, no lone pairs
80
New cards
types of bonds (3)
* int**ra**molecular- the chemical bond within a compound
* int**er**molecular- the force that causes 1 molecule to be attracted to another molecule
* van der waal forces- types of intermolecular forces
* dipole dipole, H bonding, london dispersion
* int**er**molecular- the force that causes 1 molecule to be attracted to another molecule
* van der waal forces- types of intermolecular forces
* dipole dipole, H bonding, london dispersion
81
New cards
dipole dipole bonds
* polar molecules
* positive end and negative end line up to electrostatically join
* positive end and negative end line up to electrostatically join
82
New cards
H bonding
* strong dipole dipole
* H covalently bonded to N, O, or F
* increases b points
* important in biology for life to continue
* H covalently bonded to N, O, or F
* increases b points
* important in biology for life to continue
83
New cards
london dispersion
* non-polar molecules
* increases b points
* increases b points
84
New cards
physical properties dependant on intermolecular forces
1. m points
2. b points
3. viscosity
4. solubility
5. binding affinity
6. surface tension
7. adhesion
8. hydrophobicity
9. elasticity
85
New cards
types of solids (4)
* ionic
* metallic
* molecular
* covalent network
* metallic
* molecular
* covalent network
86
New cards
ionic solids
* metal + non-metal
* hard and brittle
* dissolves in water
* high m point
* v strong bonds
* hard and brittle
* dissolves in water
* high m point
* v strong bonds
87
New cards
metallic crystals
* closely packed metal atoms connected by electrostatic interactions and free-moving electrons
* shiny/sheen
* good conductor of heat and electricity
* malleable
* hard
* not all the same properties
* shiny/sheen
* good conductor of heat and electricity
* malleable
* hard
* not all the same properties
88
New cards
electron sea theory
* explains why metallic solids dont always have the same properties
* the valance electrons of the metal move around freely, which explains why properties are always different
* the valance electrons of the metal move around freely, which explains why properties are always different
89
New cards
molecular crystals
* complex
* intermolecular forces determine its structure and properties (london dispersion)
* low m points
* less hard
* does not conduct electricity well
* intermolecular forces determine its structure and properties (london dispersion)
* low m points
* less hard
* does not conduct electricity well
90
New cards
covalent network crystals
* interwoven bonds and structure (v strong bonds)
* electrons do not move freely
* v high melting points
* v hard
* not v good conductors of electricity
* carbon, diamonds, graphite, buckyball, carbon nanotubes, quartz
* electrons do not move freely
* v high melting points
* v hard
* not v good conductors of electricity
* carbon, diamonds, graphite, buckyball, carbon nanotubes, quartz
91
New cards
semi-conductors
* a substance that conducts a slight electric current @ room temp but has increasing conductivity @ higher temps
* full valance shell
* non- conductors usually
* n-type: conductivity significantly increases when dipped in arsenic (e⁻ get excited and jump a shell)
* p-type: conductivity significantly increases when dipped in boron (valance e⁻ are lost)
* full valance shell
* non- conductors usually
* n-type: conductivity significantly increases when dipped in arsenic (e⁻ get excited and jump a shell)
* p-type: conductivity significantly increases when dipped in boron (valance e⁻ are lost)