Language, Speech, Reading & Writing
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Expressing Emotion
neural activation related to emotional pathways include the firing of facial muscle causing them to contract in associating with experienced emotion
Emotions (6)
surprise
anger
disgust
fear
happiness
sadness
Echoing Expressions
mimicking facial expressions and emotions
Mirror Neurons
specialized neuron that facilitates human understanding of the intention underlying actions
association of body language, facial expression, and emotional meaning
Grammar
obedience to a set of rules for using words/phrases
Syntax
arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences
Prosody
utterances of the appropriate emotional valence by varying pitch, stress, intensity, and rhythm
Speech - Muscles (4)
larynx
pharynx
mouth
tongue
Glottis
vocal cords
Speech - Function
air expelled through lungs
accelerate as it goes through glottis
Glottis - Function
decreased pressure, folds close
increased pressure, folds open
varies between 100-400 Hz
Speech - Left Brain
articulates language
comprehension
word recognition
syntax language
Speech - Right Brain
recognition of tone
rhythm
stress of speech
speaker identification
gesture recognition
prosody
Wada Test
patient is given short acting aesthetic into internal carotid artery
patient is given series of language/memory tests or neuro examination
determined which side of brain responsible for certain vital functions (speech and memory)
Areas of Language (2)
wernicke’s area
broca’s area
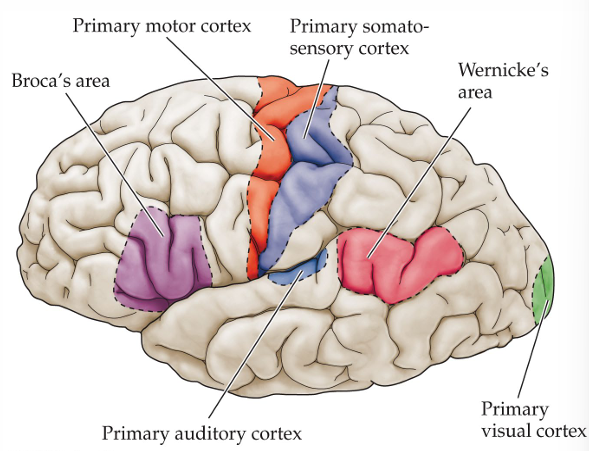
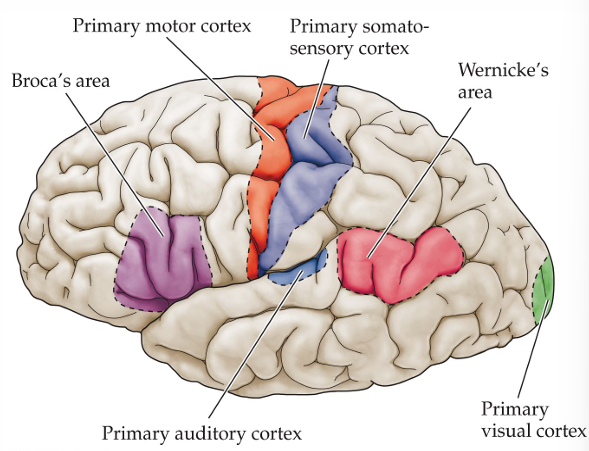
Wernicke’s Area - Location
temporal lobe (pink)
Wernicke’s Area - Function
receptive
understands and comprehends language
Broca’s Area - Location
frontal lobe (purple)
Broca’s Area - Function
expressive
speech articulation, moves mouth to form words
Geschwind’s Territory - Location
temporal lobe
near wernicke’s area
(green)
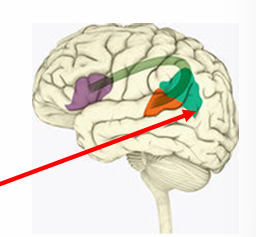
Geschwind’s Territory - Function
sight, sound, and body come together to form meaning and comprehension
high level cognition
Arcuate Fasciculus
nerve fibers that link wernicke’s and broca’s areas
Broca’s Aphasia
language cannot be expressed
language can be interpreted
Wernicke’s Aphasia
language cannot be interpreted
language can be expressed (may not make sense)
Conduction Aphasia
arcuate fasciculus is damaged
cannot produce appropriate responses to heard communication
Global Aphasia
inability to comprehend or express language
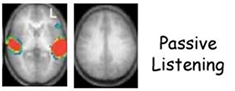
Passive Listening
visual cortex activated when reading
not listening to understand
Active Listening
listening to understand
wernicke’s, broca’s, and geschwind’s areas activated
Left Hemisphere Aphasia - Sign Language
problems with sign production
problems with sign comprehension
Right Hemisphere Aphasia - Sign Language
problems with emotional tone, visuospatial processing and emotional processing
Amygdala
processes emotional tone
Auditory Cortex
tone and rhythm analyzed
Listening Pathway
auditory cortex → amygdala → (left hemi) wernicke’s area → inferior frontal cortex → anterior temporal lobe → memories in frontal lobe
Cerebellum
times control of speech production
Speech Pathway
wernicke’s area → arcuate fasciculus → broca’s area → motor cortex → cerebellum
Reading & Writing - Brain Involvement (5)
Visual Cortex
Visual Word Recognition Area
Auditory Cortex
Broca’s Area
Temporal lobe
Reading & Writing - Visual Cortex
visual image of text is processed and sends information along recognition route to language areas
Reading & Writing - Visual Recognition Area
evolved to discriminate visual details for text discrimination after training
Reading & Writing - Auditory Cortex
text is broken down into sounds so it can be “heard”
reader is able to know the word by its sound
Reading & Writing - Broca’s Area
links written word to spoken word
Reading & Writing - Temporal Lobe
matches words to meanings via memories
Mixed Non-Fluent Aphasia
limited, effortful speech
comprehension more limited than those with broca’s aphasia
Dyslexia
language development disorder where individuals have brain changes in areas where words are translated from visual symbols into sounds
more gray matter
cannot analyze and remember the sounds contained in words
Dyslexic Treatments
tutoring ways to remember spelling
audio books
spell-checkers
voice-recognition programs
Dyslexia - Issues
phonemic awareness
decoding (sounding out words)
fluency (reading speed & accuracy)
comprehension (understanding what is read)
Dyslexia - Signs
difficulty spelling simple words
reluctance to read aloud
mixing up the position of sounds in a word
confusing letters with shapes
Dyslexia - Left Hemisphere
less active
responsible for language processing
Dyslexia - Right Hemisphere
more active
responsible for visual and spatial processing
Dyslexia - Matter
less white matter in the left hemisphere
Dyslexia - Broca’s Area
grammar processing and speech production
compensating more for people with dyslexia
Dyslexia - Parietotemporal Lobe
decodes phonemes and assembles words
crucial for reading
affected by dyslexia
Dyslexia - Occipitotemporal Lobe
word form area
rapid word cognition and fluent reading
reduced activity in this area
Phonological Dyslexia
most common
difficulty with phonemic awareness and decoding
affects cognitive functions like memory and attention
Surface Dyslexia
difficulty with sight word recognition and spelling irregular words
Rapid Naming Dyslexia
difficulty with quickly naming objects or colors
Mixed Dyslexia
combination of multiple types of dyslexia