isomers chapter 4
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
isomers
Different compounds
that have the same molecular
formula.
constitutional isomers
Isomers that have the same
molecular formula but
different connectivity – their
atoms are connected in a
different order.
conformational isomers ( conformers )
isomers that have the same connectivity but differ ONLY BY rotations about single bonds.
Newman projections
look at the image from left to right, the first carbon chain that appears is on top, and the last is on the back
carbons bonded together are not visible in newman projections
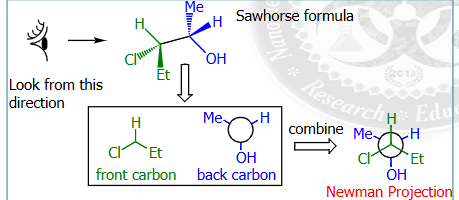
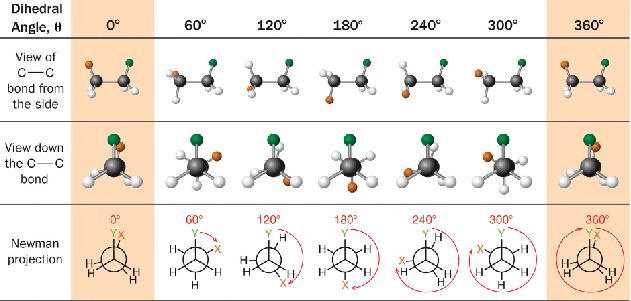
dihedral angle
angle of rotation corresponding between the C-x or y bonds as they appear in the newman projections, basically the bonds that are not hydrogen
conformational analysis
the plot of a molecules energy as a function of that bonds dihedral angle
such as eclipsed conformation - where its kind of an off angle, or staggered where they are at equal distances
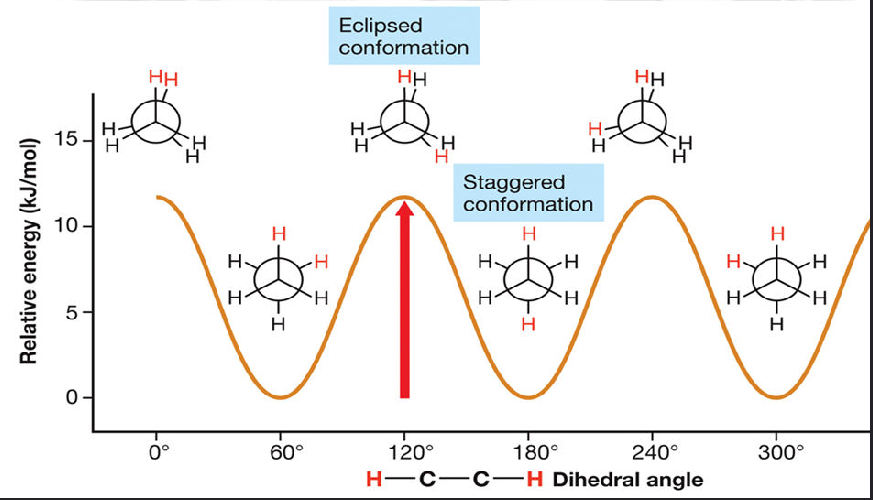
which is more stable, staggered or eclipsed molecules
staggered are more stable because electron repulsion is at a minimum,
what is torsional strain? which type of molecules ( staggered or eclipsed ) have higher torsional strain?
torsional strain is an increase in energy that arises in an eclipsed conformation
ring strain
increase in energy due to geometric contrainst on a ring structure
angle strain and ideal angle for hybridized Carbon rings
makes a significant contribution to ring strain because the ideal bond angle for a sp³ hybridized C is 109.5 degrees
steric strain
occurs when atoms or groups of atoms are in the same space
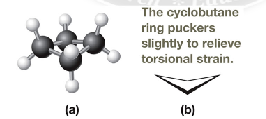
Describe how cyclobutane looks
slightly puckered with interior angles of 88 degrees, Basically a square that is slightly bent. see image.
describe how cyclopentane looks
envelope conformation that is slightly puckerd at the end. Bonds range from 102 to 106 degrees
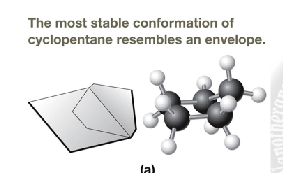
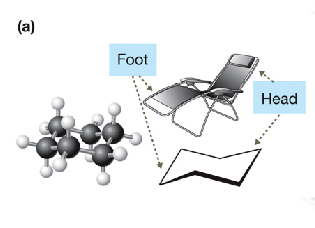
describe how cyclohexane looks
almost no ring strain, looks like a chair formation
ring strain is calculated from what? How?
heat of combustion → ring strain energy =[ (observed heat of combustion)] - (expected heat of combustion)
![<p>heat of combustion → ring strain energy =[ (observed heat of combustion)] - (expected heat of combustion) </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ff139914-9d60-474a-80b5-9bd49dc42810.png)
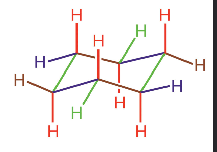
describe axial and equatorial hydrogens
equatorial bonds line in the plane that is defined by the ring
axial bonds are perpendicular to the plane
SEE IMAGE - red shows axial bonds, and green shows equatorial bonds
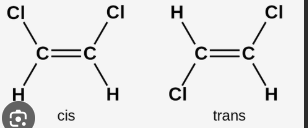
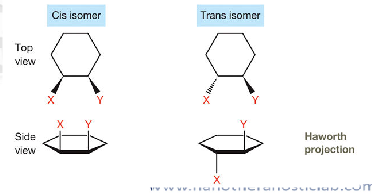
describe cis and trans isomers
differ by physical properties and stability
Physical properties differ:
Cis often has a higher boiling point (more polarity).
Trans often has a higher melting point (more symmetry).
Stability differs:
Trans is usually more stable than cis (less steric strain).
In short:
Cis = same side
Trans = opposite sides
see example of cis vs trans isomer in haworth projections
image example
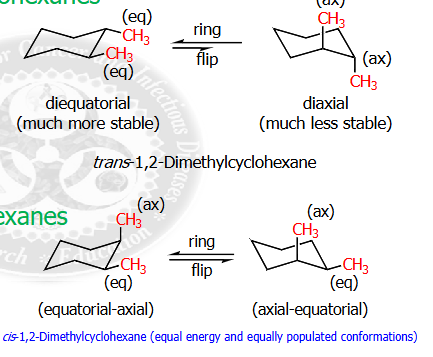
explain the difference between diequatorial vs diaxial
diequatorial is much more stable that diaxial, ,
equatorial - axial and axial -equatorial are moderately stable
constitutional isomers ( aka structural isomers)
share the same molecular formula but differ in their connectivity
what are the rules for identifying constiuttional isomers
1. For each molecule, identify the parent chain or ring. This is the longest
continuous chain or ring of carbons that contains any C=C double and C≡C triple
bonds.
2. Number the carbons in the chain or ring. Make sure that:
• The carbon atoms involved in the double or triple bonds receive the lowest numbers,
or, if there are no such multiple bonds, the first substituent is attached to the lowest-
numbered carbon.
3. Establish the relative connectivity along the parent chain or ring. The
molecules must have different connectivities, and be constitutional isomers, if
they differ in:
• The size of the parent chain or ring.
• The numbers assigned to the carbons involved in the multiple bonds.
• The numbers assigned to the carbons to which any substituent is attached.
• The identities of the substituents attached to the same-numbered carbon.
• Otherwise, the molecules have the same connectivity and are not constitutional
isomers
explain how the melting point and boiling point are affected by the constitutional isomers’ structure
melting point is more affected by molecular symetry, the more symetrical it is, the higher the melting point,
boiling point is more affected by surface area _> longer chains have higher LDF’s → higher boiling points
What is Index of hydrogen deficiency and how to determine it
Give the formula for it.
Each double bond contributes 1 to a molecule’s IHD.
Each triple bond contributes 2 to a molecule’s IHD.
* Each ring contributes 1 to a molecule’s IHD
IHD =( max # of H’s - Actual # of H’s)/2
or better represented by ( ( 2*{carbons} +2 - (number of hydrogens) + (number of nitrogens ) - Number of hallogens))/2.
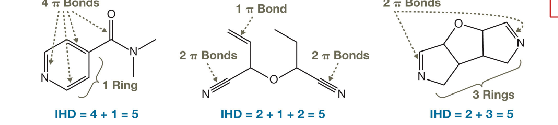
describe how to draw isomers
deterine the IHD, deterines the number of double or tripple bonds required as well as rings
draw all possible unique structures without H’s or halogens
add double bonds or tripple bonds to achieve the total IHD
add halogen atoms at various location to generate as many unique connectivities possible