Classifications of Abortions
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
sponteneous abortion
What does SA stand for
Therapeutic abortion
What does TA stand for
True
T/F: miscarriage is synonymous with spontaneous abortion
25%
What is the natural pregnancy loss rate
5-12 weeks
When in the pregnancy does majority of spontaneous abortions occur
Maternal, fetal, fetal and maternal (both)
What are the three major categories of factors causing spontaneous abortion
50%
What is the risk of a spontaneous abortion when the mother becomes pregnant beginning at age 45 or older
Genetic (50-70%)
What is the most common fetal factor causing spontaneous abortions
Rh incompatibility
What is an example of a fetal and maternal factor causing SA
Mother is Rh- and fetus is Rh+
When does Rh incompatibility occur
Vaginal bleeding, cramping, dilated cervix, uterine contractions
What are the four major clinical signs for a spontaneous abortion
Heavy bleeding with cramps
What type of vaginal bleeding is 3 times more likely to be because of a miscarriage compared to the other types of bleeding
50%
What percent of women that have vaginal bleeding during pregnancy will lose the pregnancy
PROM and preterm labour
If the patient does not miscarry when experiencing vaginal bleeding, there is a 17% chance they will have complications such as _______________ and ___________________
Cervix, vagina, or uterus
Where else can vaginal bleeding come from, if not coming from the pregnancy
Bleeding with viable IU pregnancy and heart beat seen
What is a threatened abortion
Embryo present but no heart beat detected
What is an embryonic demise
Uterus is non gravid
What is a spontaneous abortion with no retained parts
Less then half
How much of the total uterine cavity should the gestational sac occupy at 6 weeks
Half
How much of the uterine cavity should the gestational sac occupy by 8 weeks
Entire uterine cavity
How much of the uterine cavity should the sac occupy by 10 weeks
B (inner to inner)
Which is the correct measuring technique for yolk sac
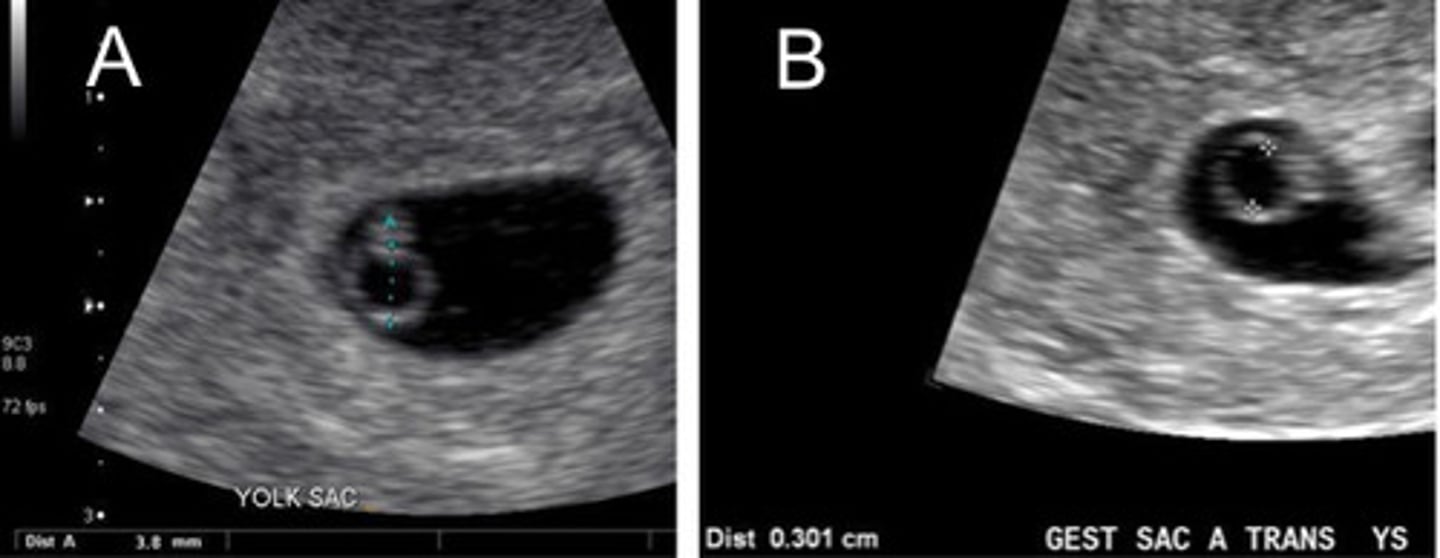
There is something wrong
What does it usually mean when you can not see the embryo/fetal pole by a MSD of 25mm
12 w 6 d
When in the pregnancy does a normal intrauterine pregnancy ultrasound reduce the risk of loss by 1-2%
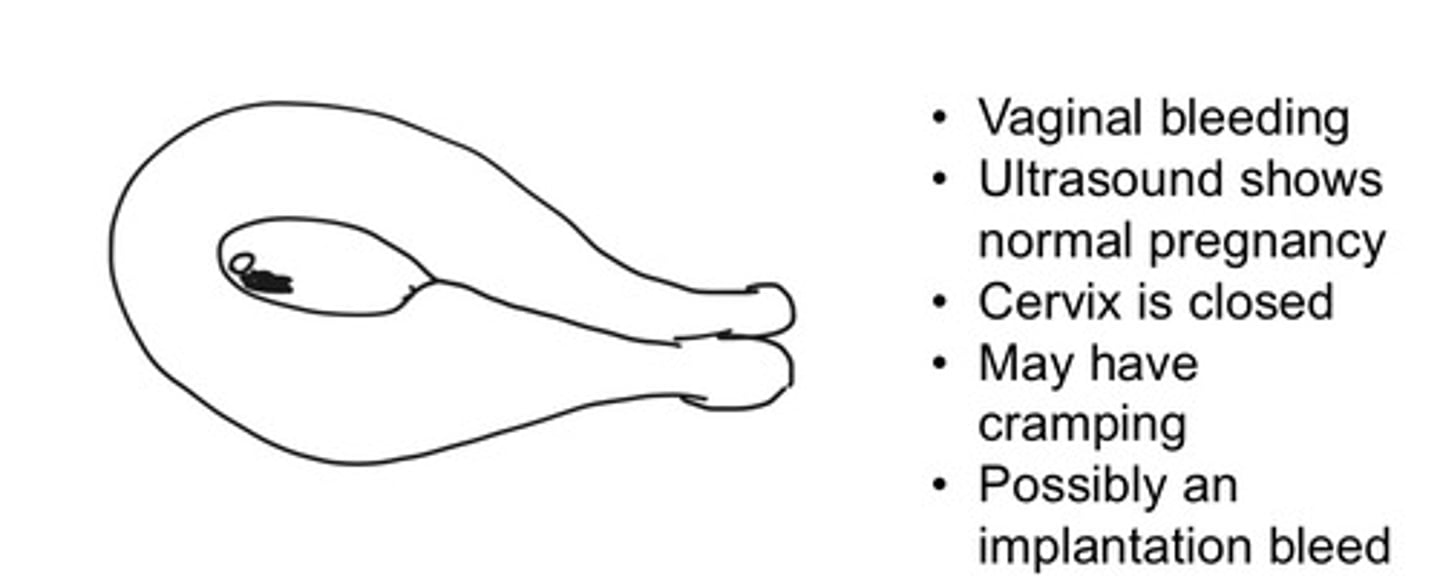
Threatened abortion
Vaginal bleeding in a pregnancy less than 20 weeks
Closed
Is the cervix closed or open if the patient has a threatened abortion
Implantation bleeding
What may be a possible explanation of a threatened abortions
Document location relative to GS, image ins 2 planes, measure in 3 dimensions
How do you document a sub chorionic hemorrhage
Less than 90bpm
What fetal heart rate becomes worrisome
Less than 5mm
A MSD to CRL measurement becomes concerning when it is :
Measurement less than 6mm or calcified
When do we become concerned about the yolk sac
Irregularly shaped
When do we become concerned about the gestational sac
Abnormal, less than 5mm
Is this MSD to CRL normal or abnormal
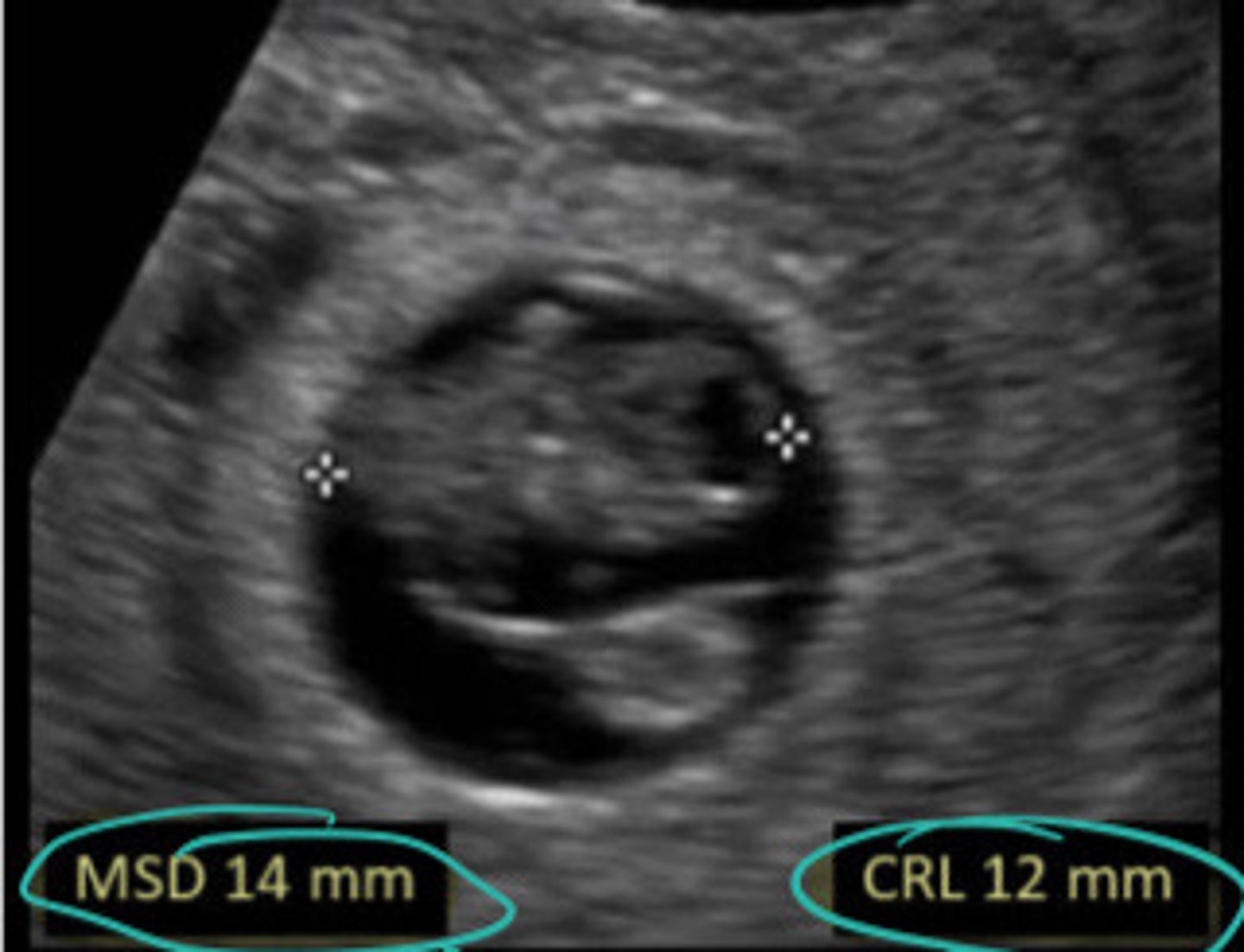
Anembryonic pregnancy
A pregnancy which failed prior to the development of an identifiable embryo
Blighted ovum
What is another name for an anembryonic pregnancy?
Bleeding with positive pregnancy test but no embryo
What may indicate a anembryonic pregnancy
Less than 20mm
What does the MSD have to be in order to be an anembryonic pregnancy
It is breaking down
What can a gestational sac that has an irregular shape indicate
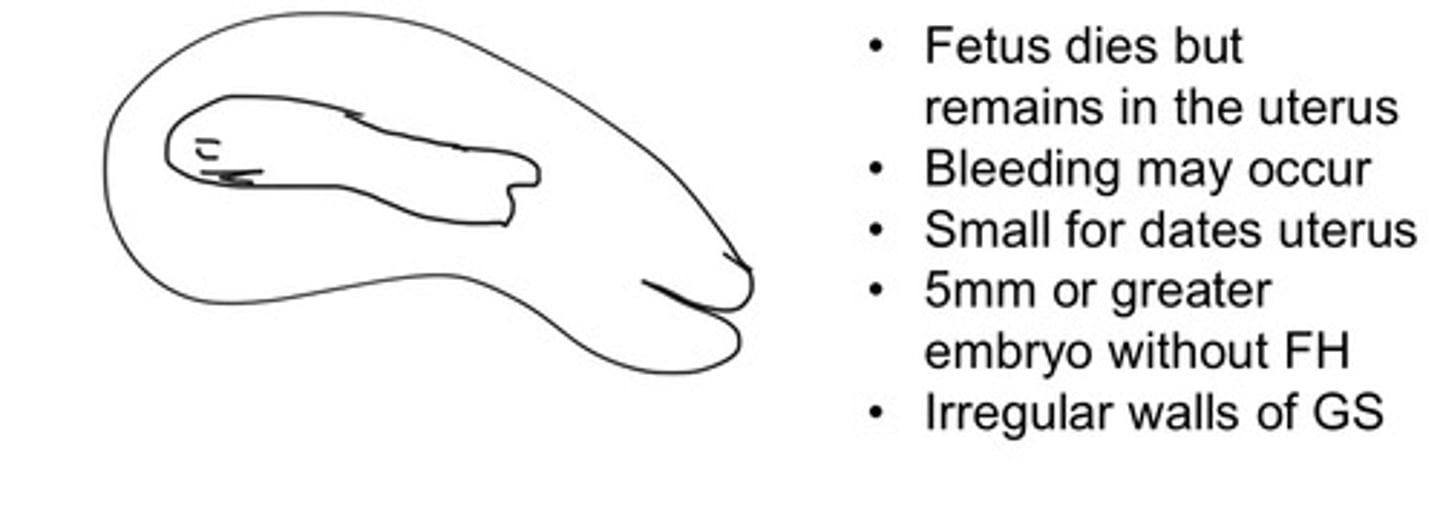
Embryonic demise
An early failed pregnancy that remains in the uterus
Missed abortion
What is another term for embryonic demise
5mm or greater embryo without FH
What are the characteristics of an embryonic demise
Bleeding and small for dates
What are the two major symptoms of embryonic demise
10-14 weeks
When in the pregnancy is embryonic demise often discovered
No FH, macerated fetus, Spaulding sign, irregular walls of GS
What are some sonographic indicators of an embryonic demise
Embryo not as bright as we would expect
What indicates an echopenic fetal pole
Overlapping of skull bones
What is the spalding sign
In process of disintegration
Why would the gestational sac have irregular walls when suspicious of an abortion
Put colour doppler over heart of fetus
How can we confirm a fetal demise
Inevitable abortion
Failed early pregnancy that is in the process of being expelled from the uterus
Active bleeding and an open cervix
What symptoms indicate an inevitable abortion
Low in uterus
Where would the sac be in an inevitable abortion
No vascularity surrounding GS with Doppler and
What are the two major sonographic characteristics of an inevitable abortion
Dynamic EV scan
What may help determine is the GS moves or not
Incomplete abortion
A spontaneous abortion in which some products of conception remain in the uterus
Enlarged uterus, empty/poorly define GS, internal echoes no resembling a fetus
What are some sonographic characteristics of an incomplete abortion
Let nature take its course
What is the first step of treatment for an incomplete abortion/embryonic demise
Induce abortion
If doing nothing is not working, what is the next step of treatment for an incomplete abortion
Dilation and curettage
What is D & C
Less than 14 weeks in pregnancy
When would the patient be treated with a D & C
Dilate cervix and remove contents
In simple terms, how is a D & C preformed
Dilation and evacuation
What is D & E
Indication of labour
What is D & E also know as
Prostaglandin or hypertonic saline urea
What is used to induce labour
More than 14 weeks in the pregnancy
When would the patient be treated with induced labour
Risk of complications from D&C when over 14 weeks
Why are patients that are over 14 weeks induced into labour instead of D&C
Complete abortion
all products of conception are expelled and bleeding/cramping has decreased
Empty/enlarged uterus, may see some blood within endometrium
What are some sonographic characteristics of a complete abortion
3 or more consecutive abortions
What are habitual abortions
Luteal failure, retroverted uterus, DES exposure, unicornuate uterus, chromosomal abnormalities
What may cause habitual abortions
Progesterone
What does the corpus luteum secrete
Infection as a result of abortion
What is a septic abortion
Pain, fever, bleeding, discharge
What are some symptoms of a septic abortion
Thick endometrium, air shadowing, increased endometrium echoes
What are some sonographic characteristics of a septic abortion
Personal reasons or fetal abnormalities
In Alberta, TA can be performed up to 21 weeks for:
Any fetal abnormality
In Alberta, TA can be performed from 21w 1d - 23w 6d weeks for:
Lethal fetal abnormalities
In Alberta, TA can be performed from 24 weeks to term for:
Date of pregnancy, diagnosis of masses or malformations, locate IUCD, guide procedure
What are some of roles of a sonographer before/during TA
Diagnosis of potential complications
What is role of the sonographer after TA
Threatened abortion
Classify this abortion
Anembryonic pregnancy
Classify this abortion
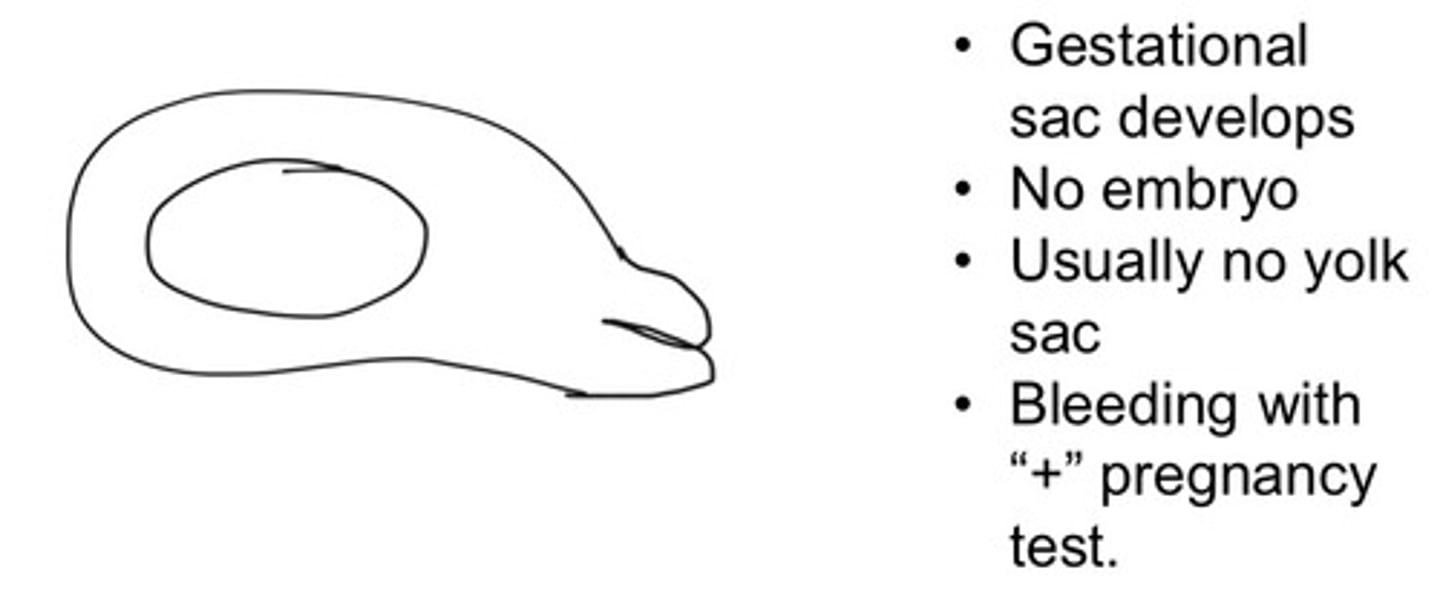

Embryonic demise
Classify this abortion
Inevitable abortion
Classify this abortion

Incomplete abortion
Classify this abortion
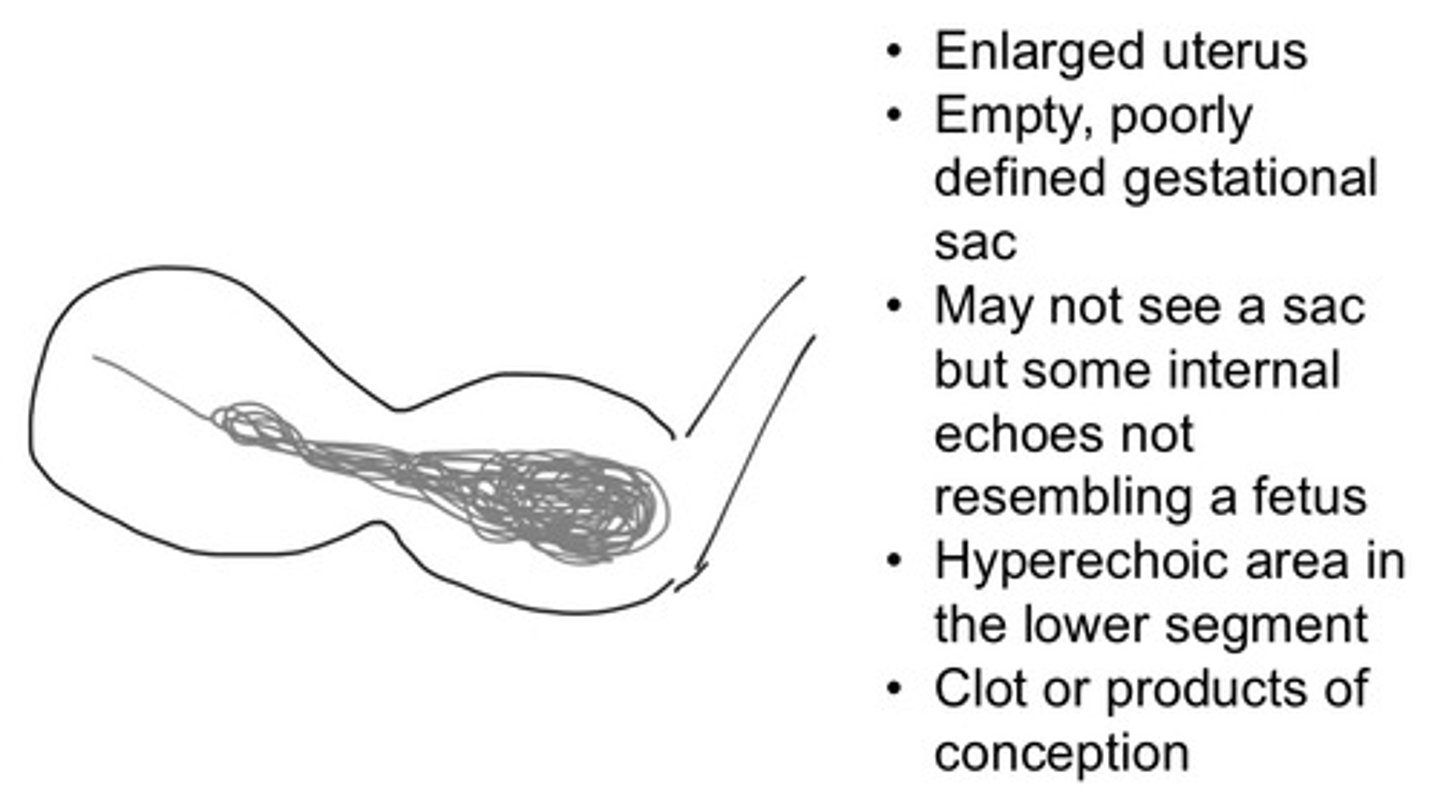
Complete abortion
Classify this abortion
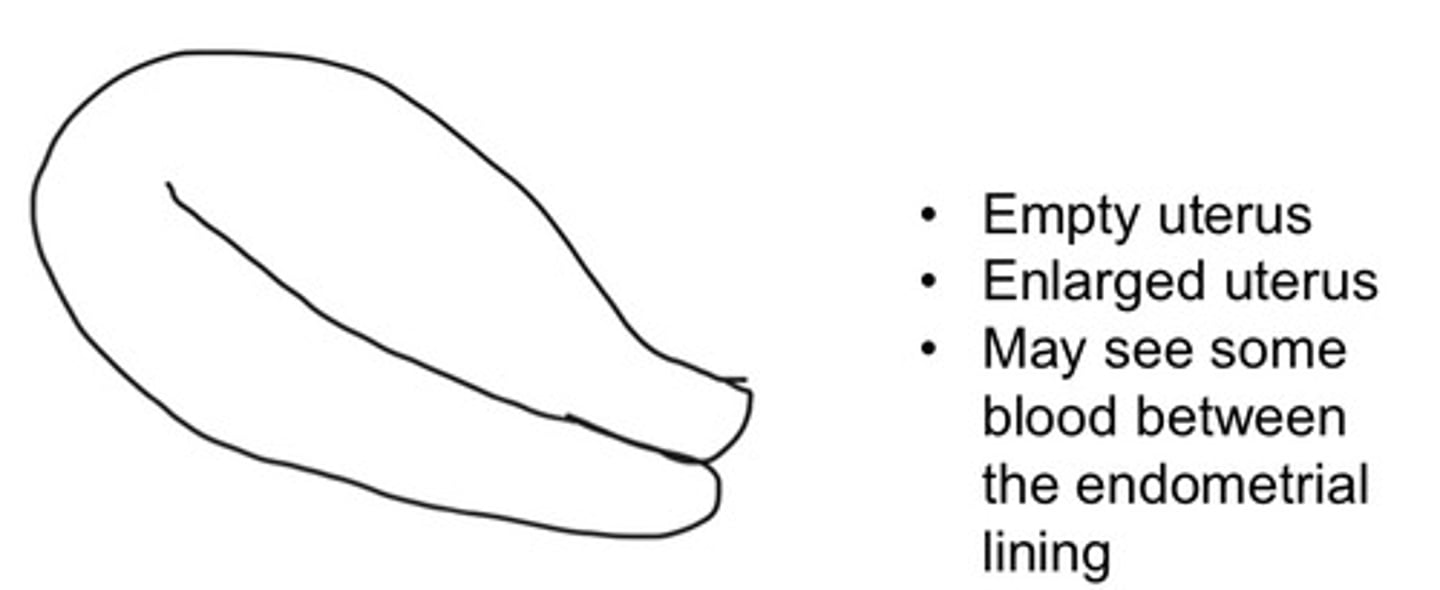
5mm
When should you be able to detect a fetal heart rate
Absent YS or embryo when should be seen, absent FH, abnormal morphology of GS or YS
What are the diagnostic criteria for a IUP failure/abortion