Zonation
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What are the different zones on the shore?

What two species are dribble spawners and what does that mean?
Fucus and Postelisa releases gametes onto the rock when the tide first returns
How do bands form?
spores mix by crashing waves
biotic and abiotic stressors prune back populations restricting their distributions
leave behind banded zonation pattern
What defines the upper limit of speceis?
primarily abiotic
high light
high temperature
low/freezing temperatures
snow/ice
high desiccation stress
osmotic shock from rain
limited access to nutrients
wave action (higher upper limits where waves splash)
What defines the lower limit of a species?
primarily biotic:
herbivore grazing
competition
fouling y other algae (diatoms, epiphytes)
desiccation cleaning- get overgrown easier
some abiotic factors:
light quality
When the tide recedes, how might algae resist light stress?
adjust pigmentation
calcification
grow in the shade, crevice, or under another organism
When the tide recedes, how might algae resist desiccation stress?
saccate morphology (halosaccion)
turf morphology (corallina vancouveriensis)
cell wall polysaccharides retain water
— red: carrageenans and agarans
— brown: alginates
dry out then rehydrate
what does low tide (midday) in the summer expose algae to?
bright sun, desiccation, and thermal stress
what does low tide (midday) in the winter expose algae to?
low temperatures, osmotic stress, snow fall
What is the equation for measuring seaweed hight?
seaweed height = tide height + beam height - laser
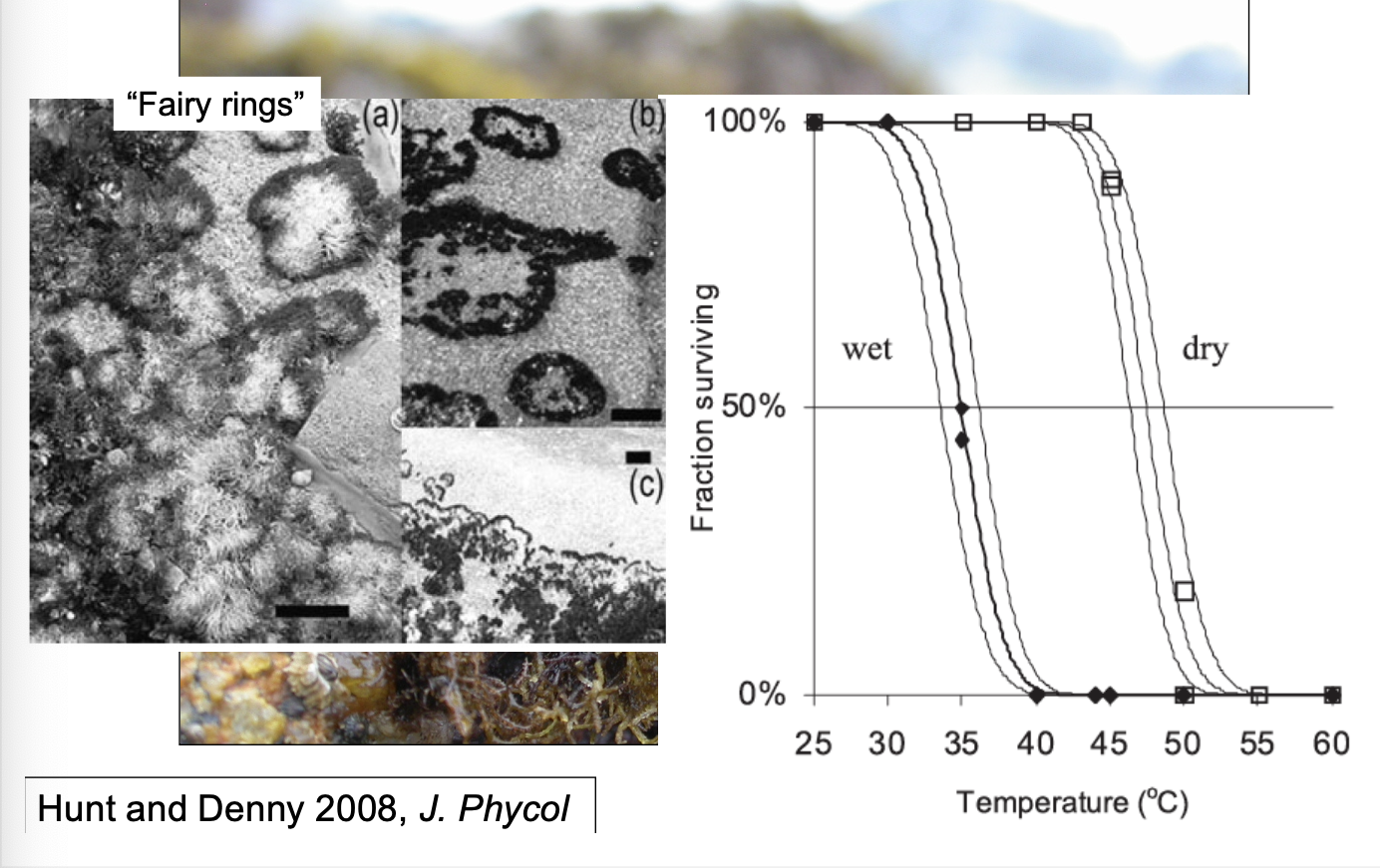
How do Endocladia use desiccation to resist temperature stress?
leave behind “fairy rings”