AP Bio Unit 6 Molecular Genetics
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- DNA vs RNA Structure - DNA Replication (Enzymes and how DNA gets copied) - DNA --> RNA --> Protein (transcription + translation) - Operons (How bacteria control their genes: epigenetics, Transcription initiation complex, RNA processing, MicroRNA) - Restriction enzymes (Restrictive enzymes, PCR, gele electrophoresis)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Timeline of Genes to Proteins
DNA → RNA → Protein
DNA amino pairs
AT
CG
RNA amino pairs
AU
CG
DNA Structure
Double Helix - 2 strands
RNA Structure
1 strand
DNA duplication (Replication)
5’ - TTTTTACGTTAATGGC - 3’
….?
5’ - TTTTTACGTTAATGGC - 3’
3’ - AAAAATGCAATTACCG - 5’
DNA Replication Summary
Why? Create 2nd set of DNA prior to cellular reproduction.
When? S phase of interphase.
Where? Eukaryotes Nucleus.
How? ENZYMES
Result? Semi-conservative strand
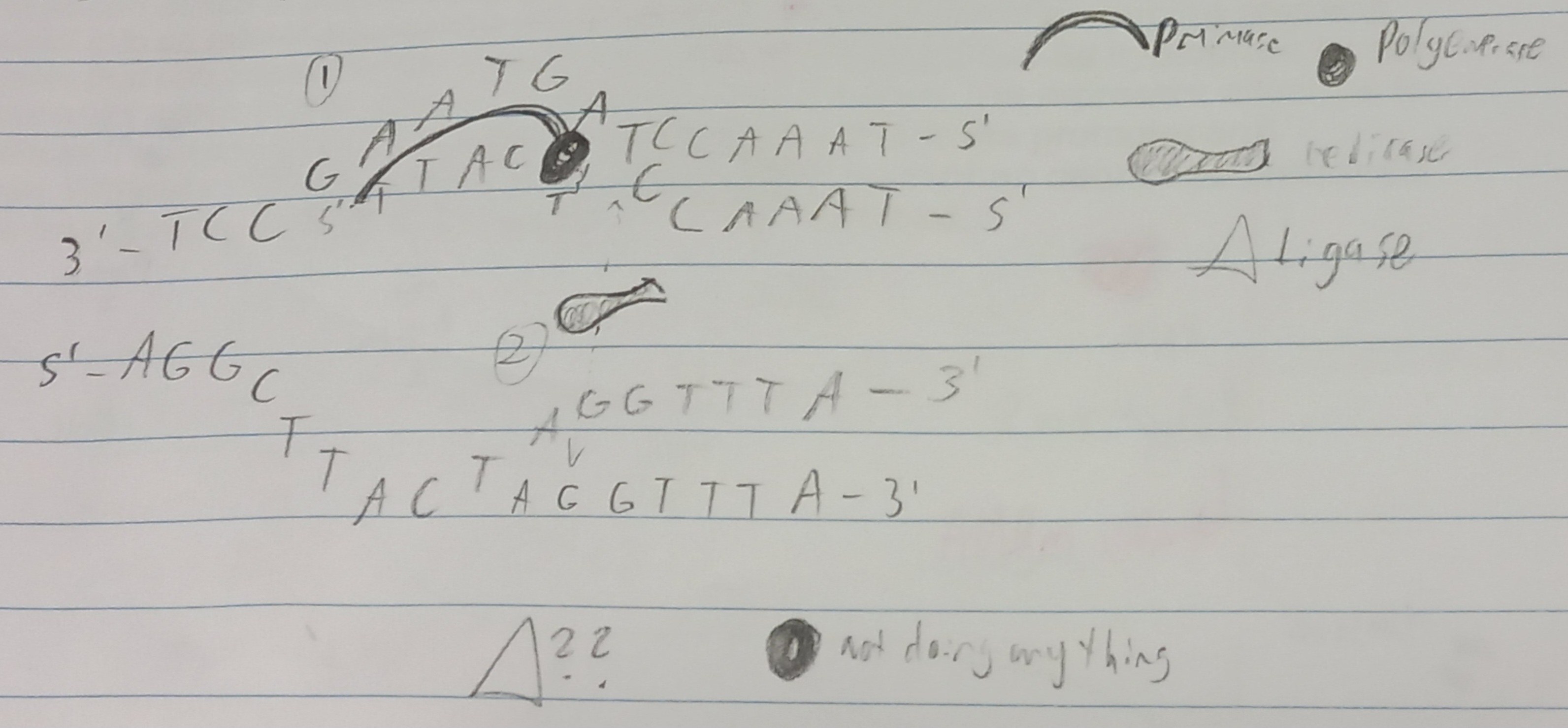
DNA Replication Enzymes
helicase - unzipper / strand separator
topoisomerase - snips and prevents super coiling
primase - directions for DNA made out of RNA primers
DNA polymerase - builder of new DNA chain that attaches at 3’ end(s)
DNA ligase - glue connects enzymes
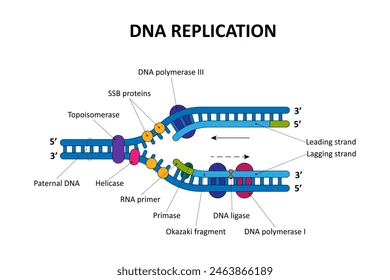
Helicase Enzyme
unzipper / strand separator
Tipoisomerase Enzyme
snips and prevents super coiling
Primase Enzyme
directions for DNA
made out of RNA primers
DNA Polymerase Enzyme
builder of new DNA chain that attaches at 3’ end(s)
Ligase Enzyme
glue connects enzymes
Transcription in Prokaryotes
transcription happens for one strand of mRNA and the translation happens before transcription is over.
more than one protein can be produced during translation
Transcription in Eukaryotes
transcription happens for one strand of mRNA and the translation happens after transcription is over.
usually only on protein is produced
DNA to RNA (Transcription)
5’ - TTTTTACGTTAATGGC - 3’
….?
5’ - TTTTTACGTTAATGGC - 3’
3’ - AAAAAUGCAAUUACCG - 5’
That is an mRNA molecule
RNA to Proteins (Translation)
3’ - AAAAAUGCAAUUACCG - 5’
…?
3’ - AAAA-AUG1-CAA2-UUA3-CCG4 - 5’
met1-Gin2-Leu3-Pro4
That is an amino acid sequence
Operons
structure for turning genes on & off
regulate genes
how prokaryotes control protein production
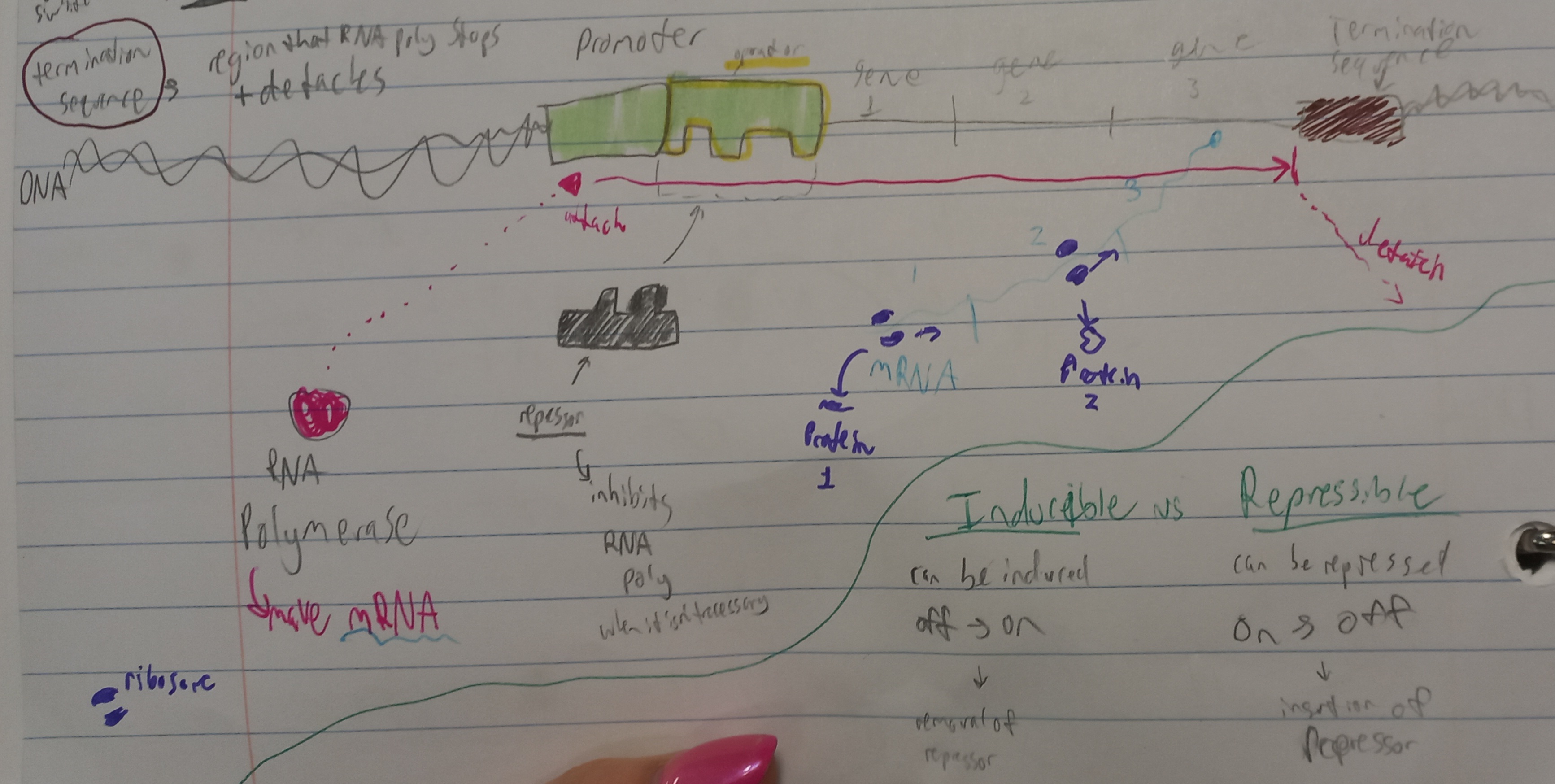
Operon Pieces
RNA polymerase - makes mRNA
promoter - region that RNA polymerase attaches to
Operator - on
Repressor - off (attaches to operator and blocks RNA poly)
Termination sequence - region where RNA polymerase stops and detaches
Inducible
Can be induced
Off →On
Removal of repressor
Repressible
Can be repressed
On → Off
Insertion of repressor
Transcription Initiation Complex
facilitate the binding of RNA polymerase to the DNA strand
start synthesizing mRNA based on the DNA template
transcription factors that help recognize the promoter sequence and stabilize the RNA polymerase before the actual transcription process begins
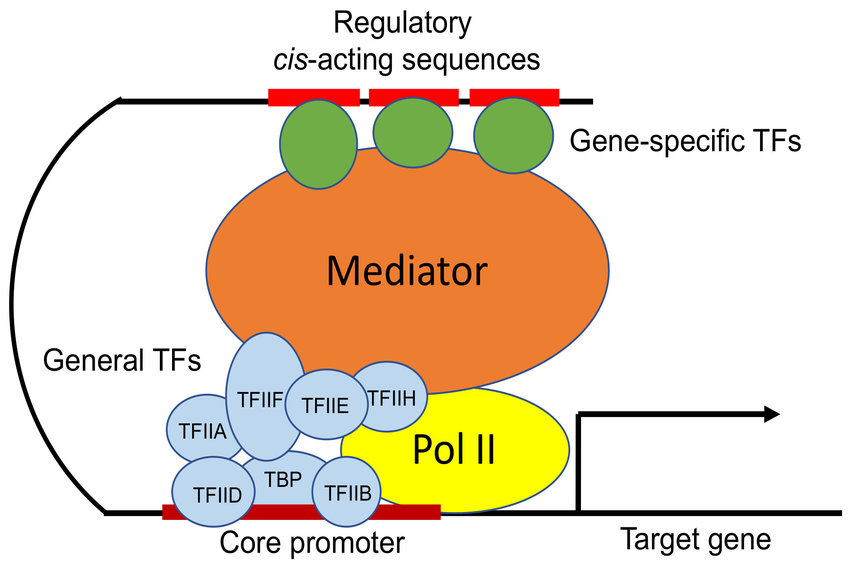
Transcription Factors + Mediator Proteins
When bound to the promoter, they help the RNA Polymerase move onto the operon / genes etc…
micro RNA
short, non-coding RNA molecules that block RNA polymerase
Differential Gene Expression
same genomes, but difference in expression of gene
expressed = on
not expressed = off
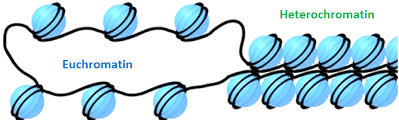
Euchromatin
loosely bound DNA genes that can be loosened by aceytl groups where RNA poly can pass through
“on”
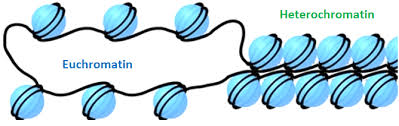
Heterochromatin
when the genes and dna are too tightly wound, preventing RNA poly from going through
“off”
Histone Acetylation
loosen the chromatin to let the RNA poly through
(temporary)
DNA Methylation
DNA gets marked and blocks the transcription because it’s tightening, preventing RNA poly from readin it
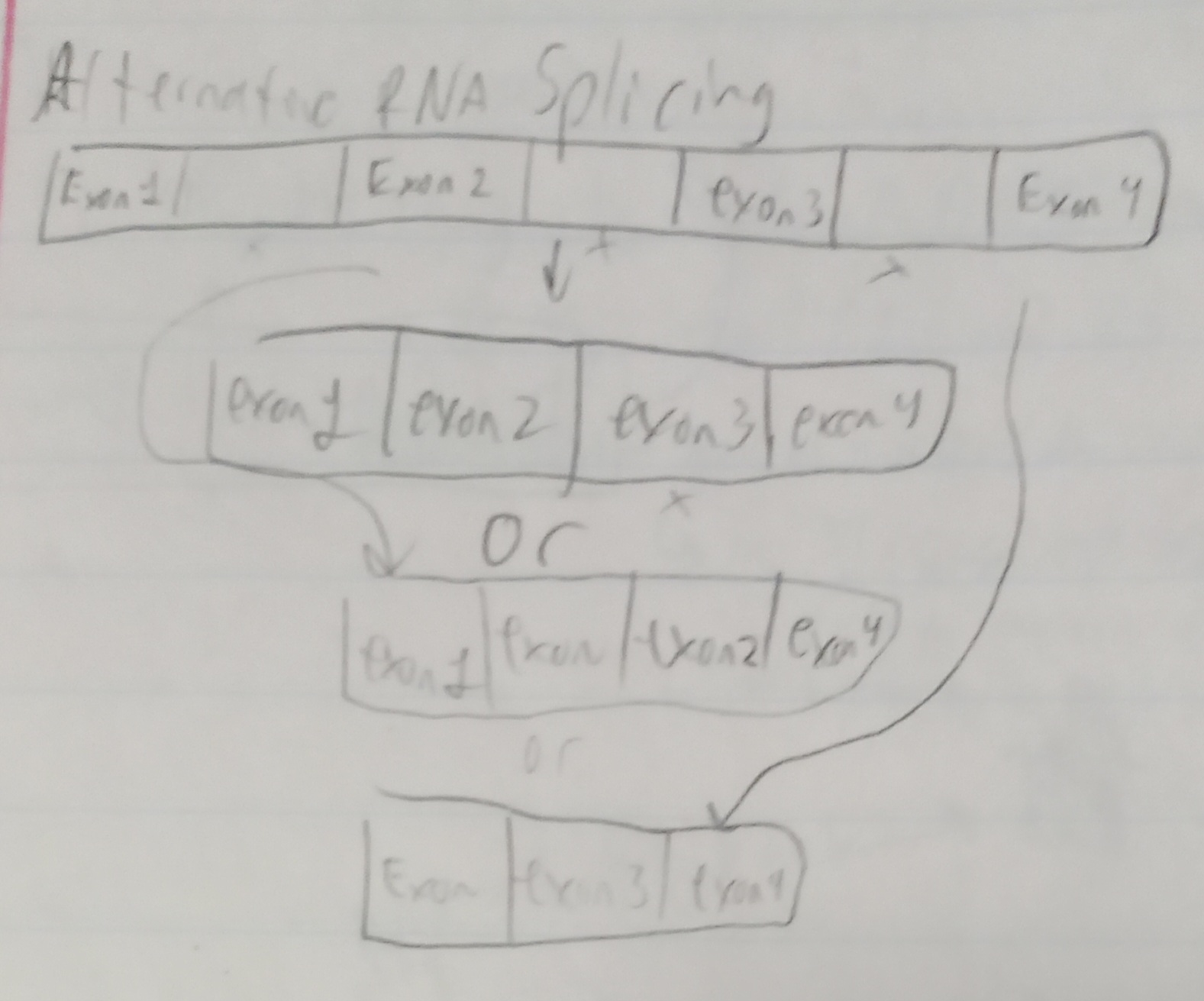
Alternative RNA Splicing
The process of variants from different exons being kept
2(# of exons) - 1
Technologies for Genetic Modifications
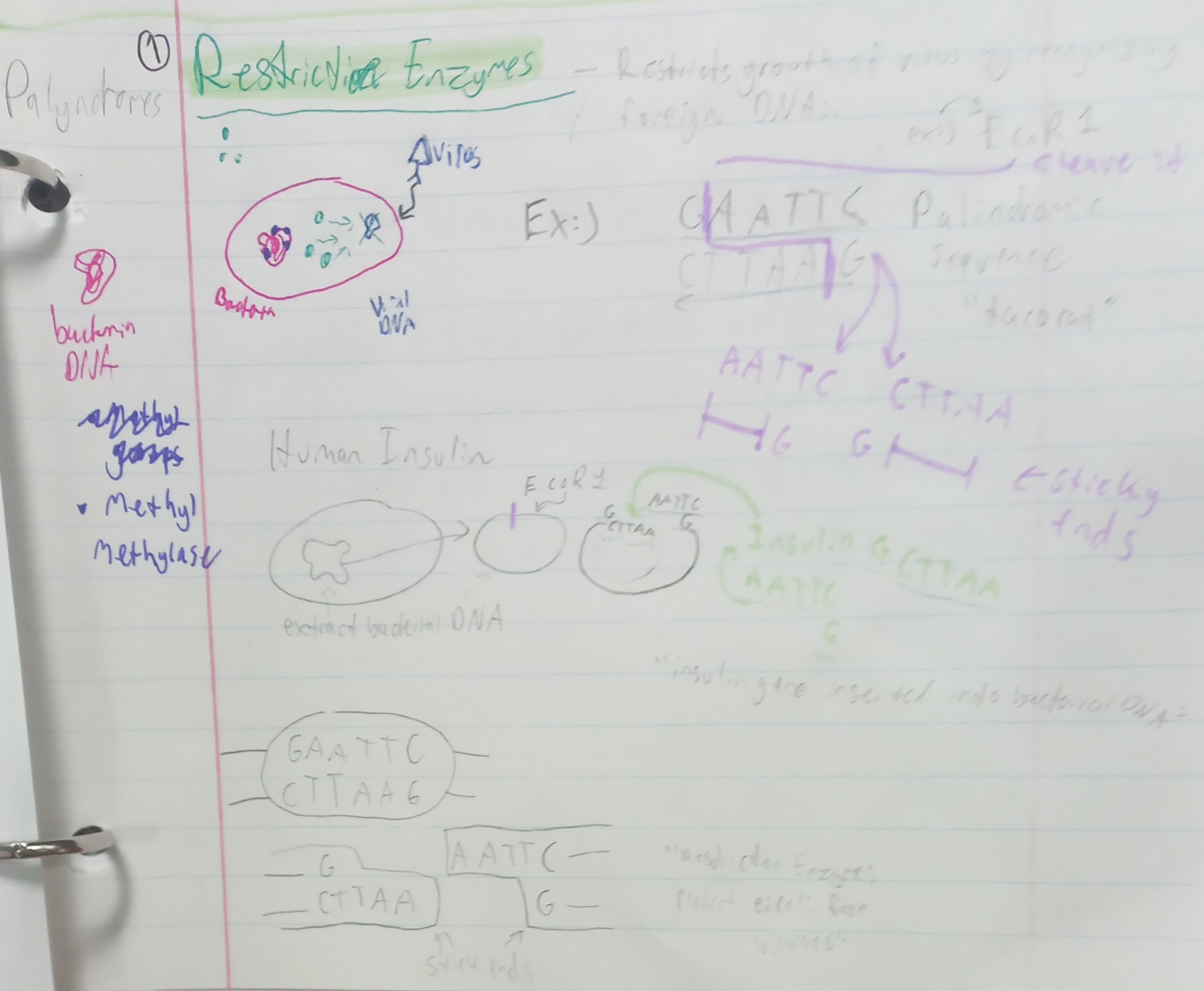
Restriction Enzymes - cuts DNA at specific sequences and creates multiple segments
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) - Generates Millions of Copies
Gel Electrophoresis - separating the segments / molecules and making gaps to analyze
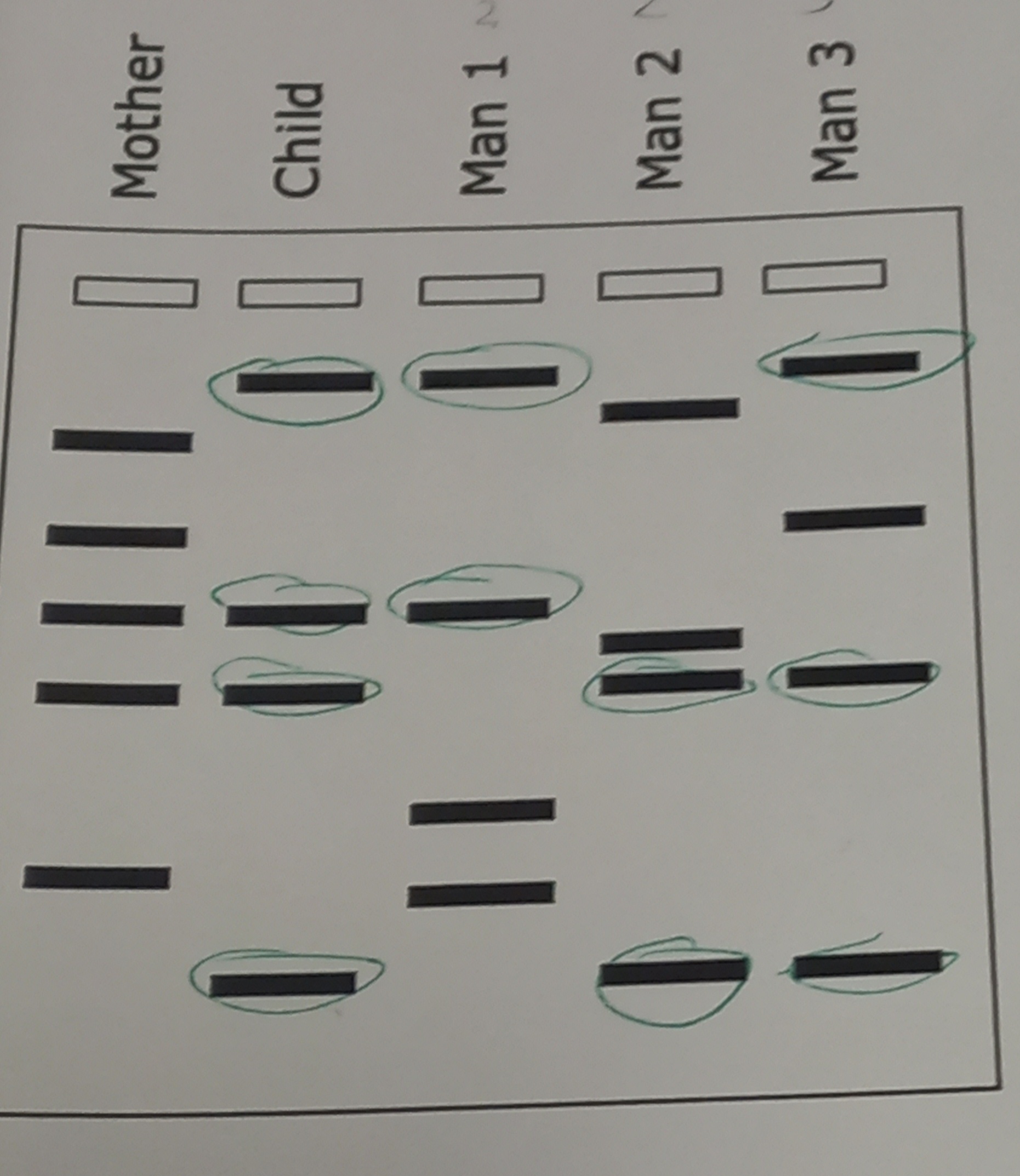
Restriction Enzymes
cuts DNA at specific sequences and creates multiple segments
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
Generates millions of copies of the DNA segments
To visualize DNA bands
Gel Electrophoresis
separating the segments / molecules and making gaps to analyze
DNA is Negative, so it will go toward the positive
Direction Impactors
Charge → goes to opposite
Size
Small = Far / Fast
Large = Less Far / Slow