AP Bio Exam Prep
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Hydroxl
R-O-H (polar,
methyl
R-Ch3 (non-polar)
carbonyl
Aldehydes= O=C-R-H
(polar, both)
Ketones= O=C-CR-R
carboxyl
O=C-R-OH (polar acidic)
amino
R-N-H (polar, basic)
phosphate
R-O-P-OH-OH=O (Polar, acidic)
Sulfhyrol
R-S-H (polar)
Cis
elements on same side
trans
elements on opposite sides
Carbonyl group
C=O
Chitin
Arthropods + fungi, FOR STRUCTURE
A long-chain polymer that primarily makes up the exoskeletons of arthropods and cell walls of fungi.
Cellulose
Plants, STRUCTURE
A long-chain polymer that makes up the primary structural component of plant cell walls, providing rigidity and strength.
Starch
Plants, ENERGY STORAGE
A polysaccharide that serves as the primary energy storage carbohydrate in plants, consisting of long chains of glucose units.
Glycogen Carbs
Animals, ENERGY STORAGE
The primary energy storage carbohydrate in animals, glycogen is a polysaccharide composed of glucose units and found mainly in the liver and muscle tissues.
Dehydration synhesis
Pulls out water, covalent bonds from creation of H20
+H20
Hydrolosis
breake bonds and water apart
OH in formula
Base pairs
A and T (DNA)
A and U (RNA)
C and G
Polar=
hydrophillic
non-polar
hydrophobic
Purines
A and G
2 bonds, 2 carbon rings
Pyrimidines
C, T, and U
3 bonds, 1 carbon ring
Glycosidic linkage happens with the macromolecule…
carbohydrates
Glycosidic Linkage is…
a type of bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
-it also joins two monosaccharides togtether and you can use water to break them
In a phospholipid bilayer the heads are… and the tails are…
heads=hydrophillic
tails=hydrophobic
Straight fats (trans, saturated)
Solid in room temp, more compact due to single bonds between carbon atoms.
Bent fats (cis, unsaturated)
liquid in room temp, kinks, double bonds
what type of carbohydrate bonds store energy
C-H
Steroids
4 fused carbon rings
Omega 6 is considered… Omega 3 is consdiered…
Omega 6=good
Omega 3=bad
Trigylceride
Glycerol backbone and 3 fatty acid tails
Nucleic acids
used for storage and transmission of genetic information, made up of nucleotides
chloestroal
fatty substance, maintains hormones, 4 ringed carbon, increases membrane fluidity
what type of bond holds polypeptides together
peptide bonds
covalent bonds
electrons shared, two non-metals, stronger than hydrogen bonds
Cohesion
sticks to eachother, hand + hand
Adhesion
Sticks to other things, Hand + Table
Ionic bonds
electrons transferred, metal and non-metal, polar
trace element
only need a little to maintain life
Polar bonds are ___ charged
oppostily charged
non-polar bonds are ___charged
evely charged
Capillary Action
A result of water molecules having an ADHESIVE force; narrower the diameter=farther the water will rise
If an element has 8 electrons it is considered…
non-reactive
Sweat cooling=
absorption of heat by breaking bonds
Carbs ratio
C H2 0=1:2:1
Water condensing=
temp increases, release of heat by FORMING hydrogen bonds
Hydrogen (water especially) bonds are stronger when…
when there is less to bond with
proteins
amino acids, polypeptide chains (peptide bonds), central carbon bound to a hydrogen, an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a variable R group.
Water has ___ heat capacity and surface tension
high
Forming bonds…
releases energy
Cations (positive) usually have___ electrons
Anions (negative) usually have ___electrongs
Cations=1 or electrons
Anions=7 or 6 electrons
Sweat cooling=
absorption of heat by breaking hydrogen bonds
Cofactor (dealing with enzymes)
Something that binds with something to help an anzyme bind to the substrate
A non-protein compound that is essential for the activity of an enzyme, often assisting in catalysis or regulation.
Competitive inhibitor
looks and acts similar as a substrate, can bind to an enzyme, prevents substrate from beingsing to the enzyme
A substance that binds to an enzyme's active site, preventing the substrate from binding and thereby inhibiting the enzyme's activity.
Induced fit
Binding of substrate changes the shape of enzymes active site
Amino acids always have a __group
carboxyl group
a hydrocarbon chain is…
hydrophobic
Primary structure
peptide bonds (covalent), linkage of amino acids, structure dictates function
Secondary Structure
Hydrogen bonds (between backbone atoms), folding of polypeptide chains into regular paterns, alpha helix (spiral)
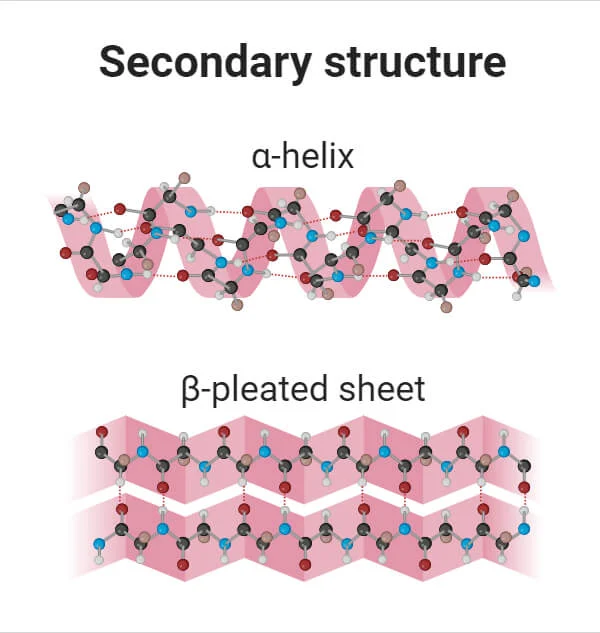
Tertiary Strucutre
Covalent bonds (R-group interactions), the overall 3D shape of a single polypeptide chain, Disulfide bridges, determines the proteins specific function (like active sites on enzymes)

Quantenary structure
Disulfide Bridges, 3D, various interactions, the structure formed when two or more polypeptide chains come together, also helped together between R-grouo of different chains.
NH2 is a…
base
Polar molecles are
hydrophillic
Alpha-carbon
a carbon that is next to a functional group attached to
-hydrogen
-R-group (side chain)
-Amino (NH2)
-Carboxyl
C-terminus
end of amino acid chain terminated by a free carboxyl (-COOH) group
what does a high temperature do to proteins
it causes them to denature and risks them not being able to refold
(low temp causes them to freeze while they're cold)
N-terminus
very 1st nitro
Elements in proteins, carbs, nucleic acids, and lipids?
Proteins= C, H, O,
(phosphorus never, sulfur sometimes)
Carbs=C,H,O (1:2:1)
(nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur never)
Nucleic acids=C, H, O, N, P (THINK DNA)
(sulfur never)
Lipids=C, H, O
(nitrogen and sulfur nevermind phosphorus sometimes)