Sympathetic, Parasympathetic, and Somatic Nervous System
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
The nervous system has two anatomical divisions. What are they?
central nervous system
peripheral nervous system
The central nervous system is located where?
brain and spinal cord
The peripheral nervous system is located where?
outside of the brain and spinal cord
The peripheral nervous system has two functional divisions. What are they?
somatic nervous system
autonomic nervous system
The somatic nervous system controls what type of movements?
voluntary
How many neurons are involved in the somatic nervous system?
one
There are 3 types of sensory receptors. What are they, and what differentiates them?
tactile-touch
nociception-pain
proprioception-length changes (tendons/ligaments)
Where are the tactile and nociception receptors located?
skin, cornea, mucosa, hair/feather follicle, connective tissue
Where are the proprioception receptors located?
tendons, ligaments, muscles, joints
In the afferent path of the somatic nervous system, what are the steps?
ventral/dorsal branch of spinal nerve>spinal nerve>spinal ganglion>dorsal root>dorsal horn
In the efferent path of the somatic nervous system, what are the steps?
ventral horn>ventral root>spinal nerve>ventral/dorsal branch of spinal nerve
How many neurons are needed in the visceral (ANS)?
two (pre and post ganglionic/synaptic)
Sympathetic effects on:
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Digestive
Urinary
Reproductive
Cardiovascular +
Respiratory +
Digestive -
Urinary -
Reproductive -
Parasympathetic effects on:
Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Digestive
Urinary
Reproductive
Cardiovascular -
Respiratory -
Digestive +
Urinary +
Reproductive +
Actions such as fighting, running, hunting, and stress/fear are examples of which system?
sympathetic
What is the sympathetic trunk?
located below thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, formed by ganglia connected by axons, with a group of visceral ganglia connected below
Where do the sympathetic nuclei live?
thoracic and lumbar segments of the spinal cord
2 neurotransmitters are needed at the pre and post ganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system. What are they?
1 (pre): acetylcholine
2 (post): norepinephrine
Are spinal nerve roots unidirectional or bidirectional?
unidirectional
Is the spinal nerve uni- or bi-directional?
bidirectional
Somatic afferent neurons go to what area of the spinal cord?
dorsal root
Visceral afferent neurons go to what area of the spinal cord?
dorsal root
The somatic efferent neurons come from what area of the spinal cord?
ventral horn
The visceral efferent neurons come from what area of the spinal cord?
lateral horn
What are the communicating branches?
axons that connect the spinal nerve with the sympathetic trunk
Are the communicating branches uni- or bi-directional?
bidirectional
What are the 3 target tissues of the sympathetic nervous system?
axial (neck) and limbs smooth mm. and glands
heart, smooth mm., and glands of thorax, abdomen, and pelvis
head smooth mm. and glands
The vertebral nerve carries what type of fiber, and where does it lead?
postganglionic fibers
cervical spinal nn.
In the sympathetic pelvic libs, describe the path the neurons take.
What structures does the ansa subclavian connect? How did it get its name?
communicating branch between cervicothoracic and middle cervical ganglia
fibers go around the subclavian
What are splanchnic nerves, and where will the neuron synapse?
axons from preganglionic neurons
visceral ganglia
ONLY PREGANGLIONIC NEURONS
What are the hypogastric nerves?
runs parallel to aorta and internal iliac aa. to the pelvic plexus
CARRIER PRE AND POST GANGLIONIC
Actions like eating and sleeping are what system?
parasympathetic nervous system
How does the pre and post ganglionic neurons of the sympathetic pathway compare to those of the parasympathetic?
parasympathetic has a longer preganglionic, sympathetic has a longer postganglionic
What are the 2 neurotransmitters required for a pre and postganglionic neurons in the parasympathetic nervous system?
1 (pre): acetylcholine
2 (post): acetylcholine
What is an intramural ganglion?
a ganglion within the wall of the target organ
The parasympathetic nervous system takes place where?
cervical and sacral segments
An erection is an example of what nervous system, while ejaculation is what nervous system?
parasympathetic
sympathetic
A parasympathetic signal sent from the cranial portion is sent from where?
brainstem
A parasympathetic signal sent from the sacral portion is sent from where?
ventral horn of spinal cord
The dorsal and ventral vagal trunks are made up of what branches?
right and left dorsal/ventral branches
The ventral vagal trunk brings synapses to what organs?
ventral portion of stomach and spleen
The dorsal vagal trunk brings synapses to what organs?
dorsal portion of stomach and spleen
liver
gallbladder
pancreas
kidneys
small and large intestines (until transverse colon)
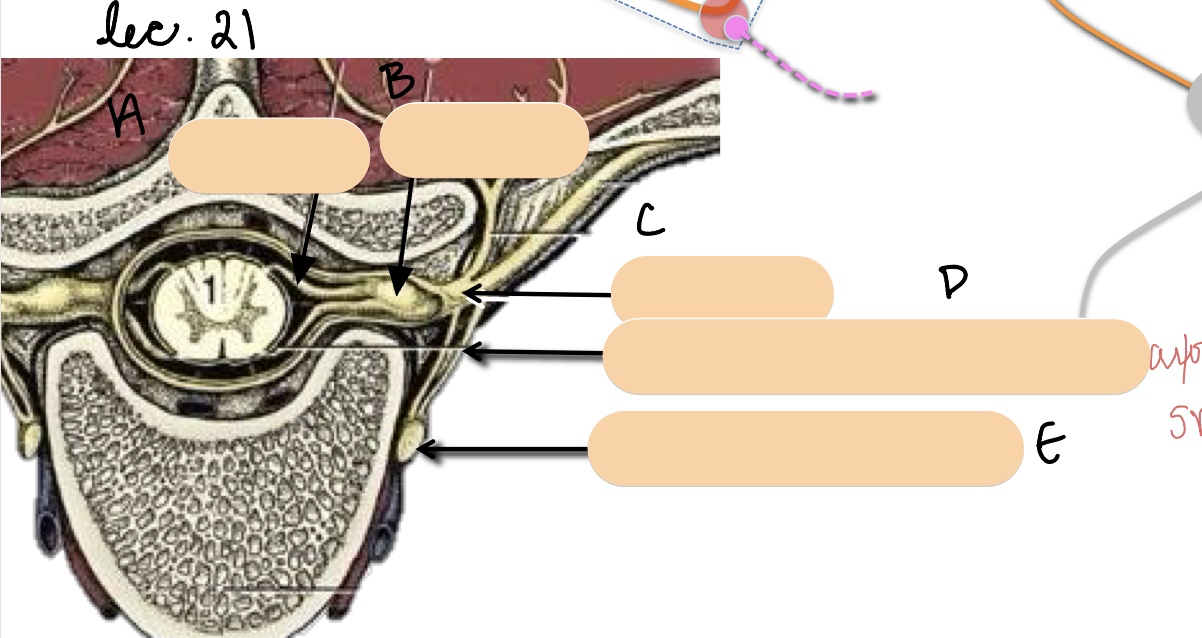
Name the structure(s) represented by a, b, and c.
dorsal root
spinal ganglion
spinal nerve
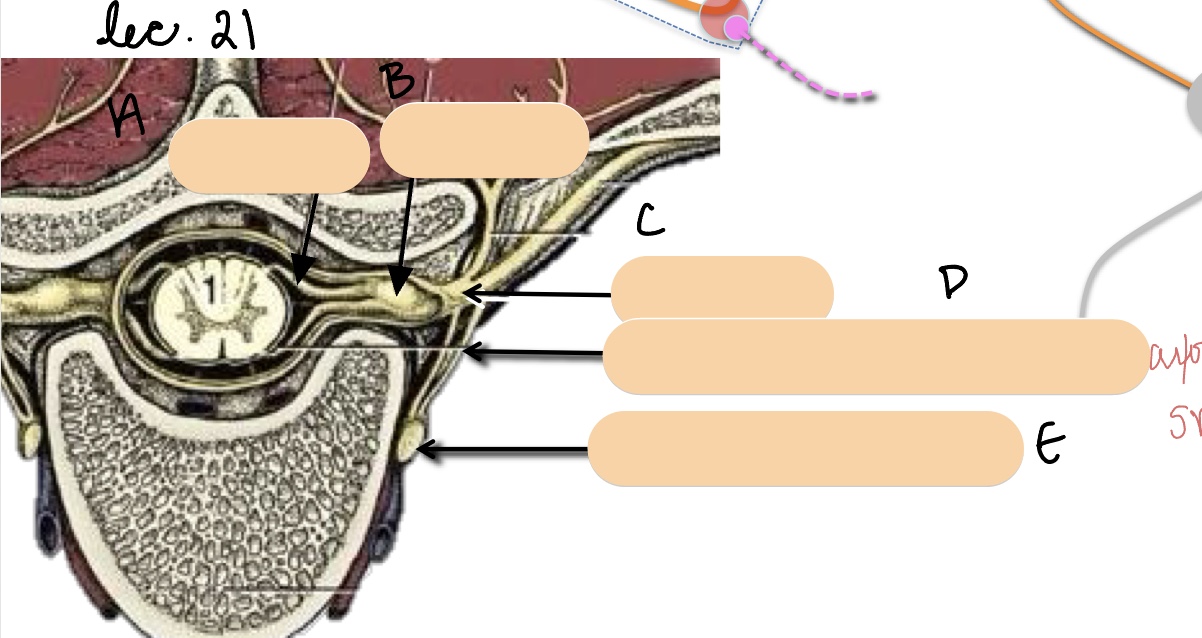
Name the structure(s) represented by d and e.
communicating branches
sympathetic trunk
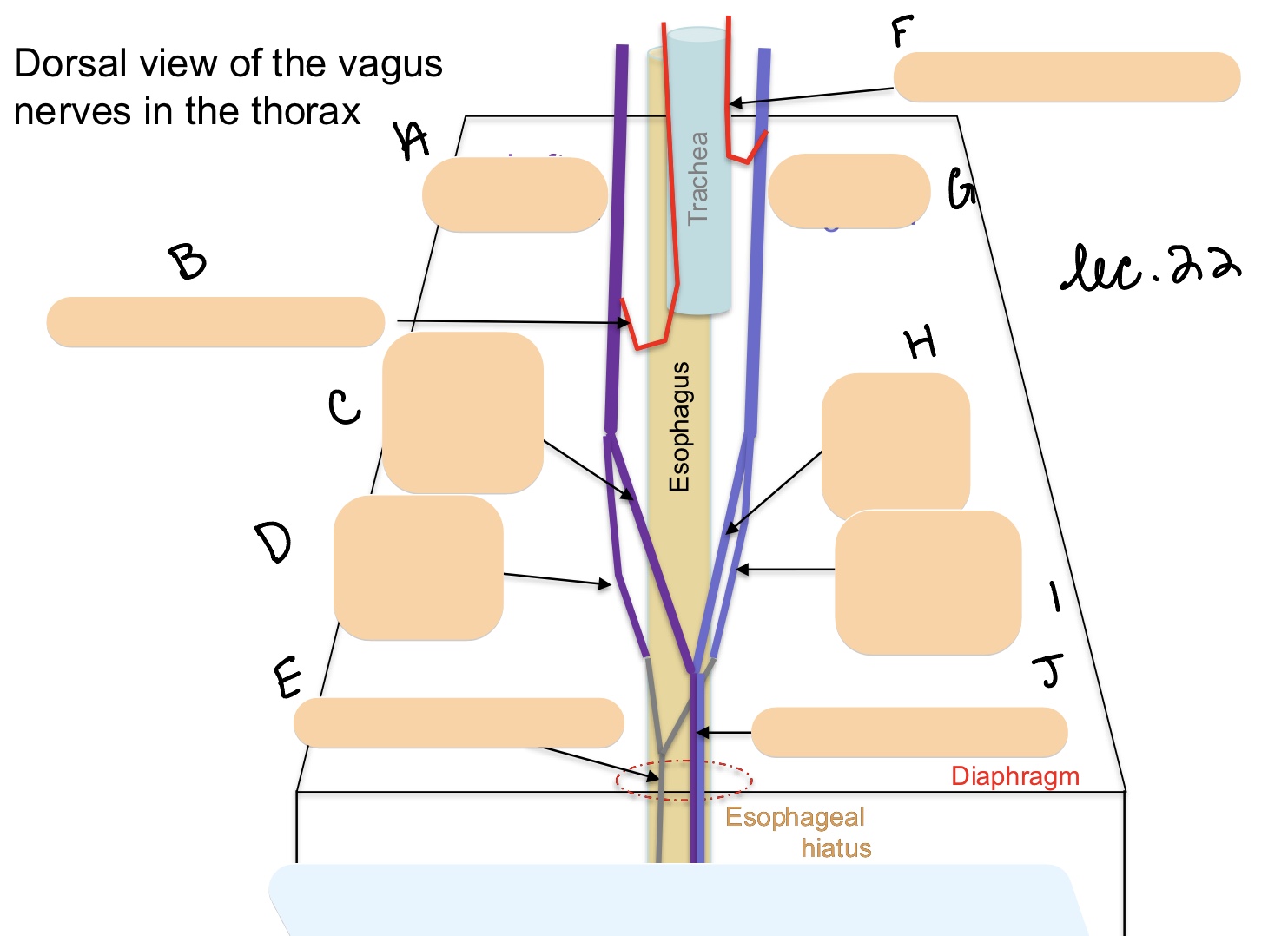
Name the structure(s) represented by a, b, and c.
left vagus n.
left recurrent laryngeal n.
dorsal vagal branch
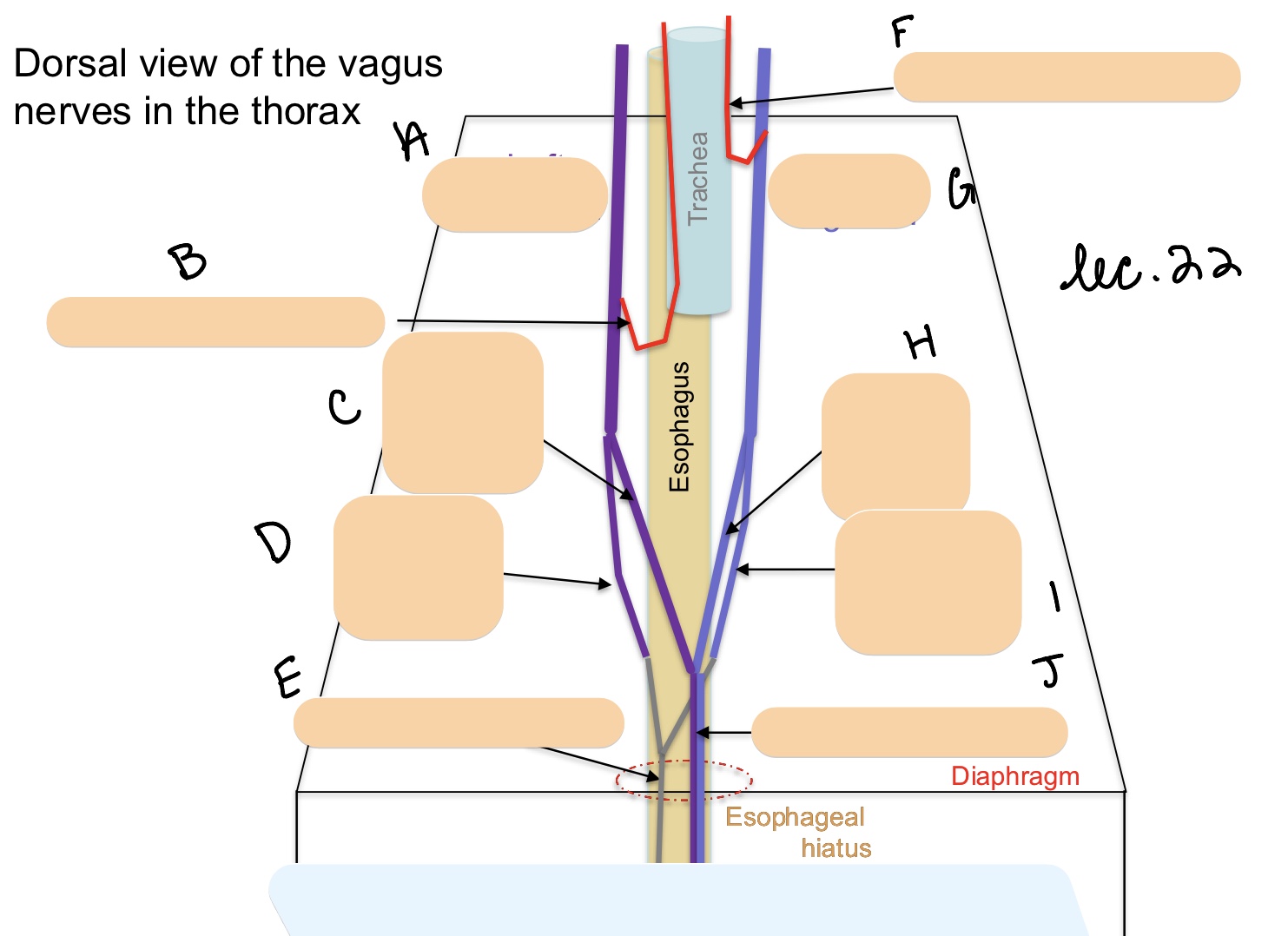
Name the structure(s) represented by d, e, and f.
ventral vagal branch
ventral vagal trunk
right recurrent laryngeal n.
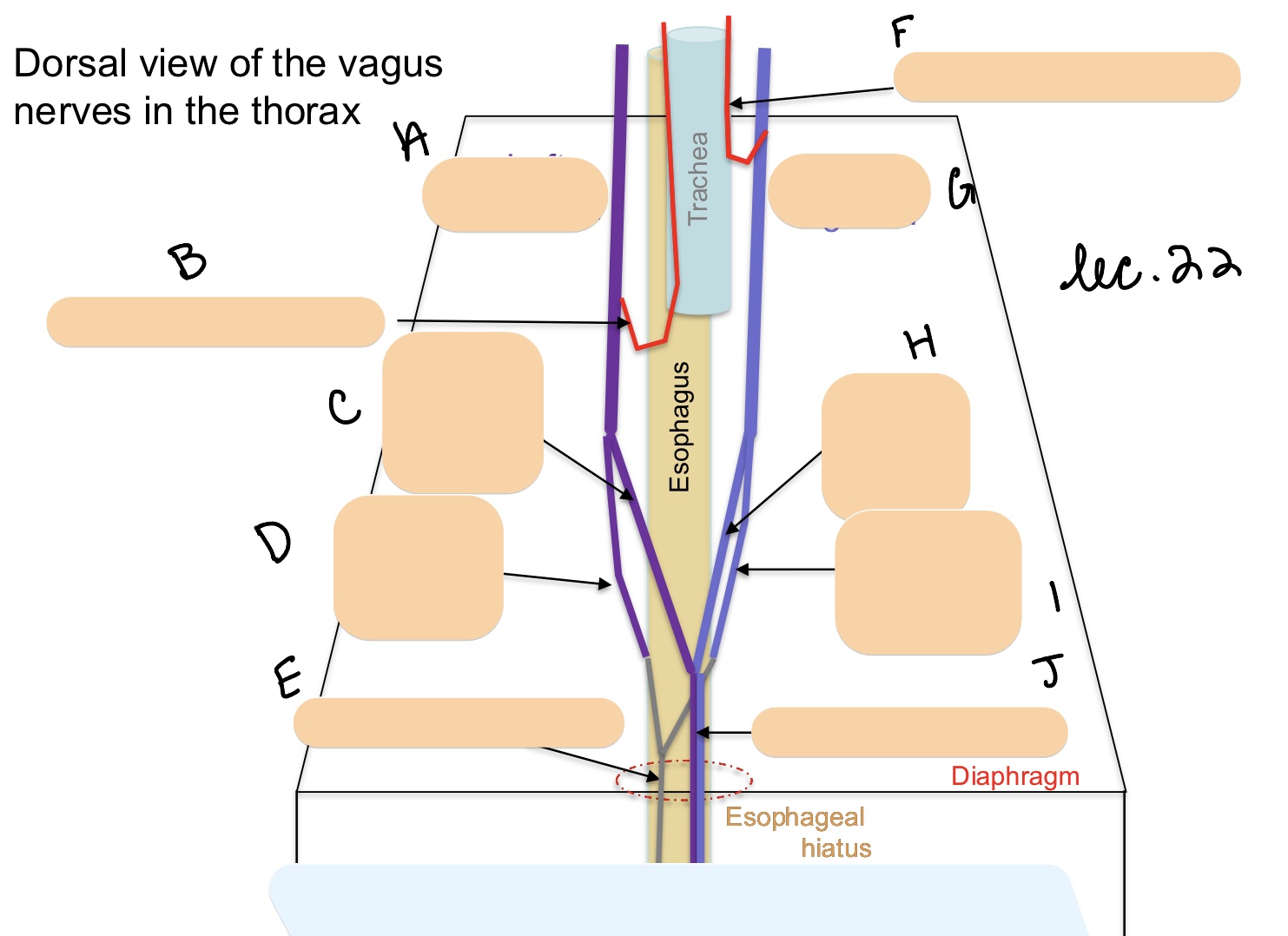
Name the structure(s) represented by g, h, I, and j.
right vagus n.
dorsal vagal branch
ventral vagal branch
dorsal vagal trunk
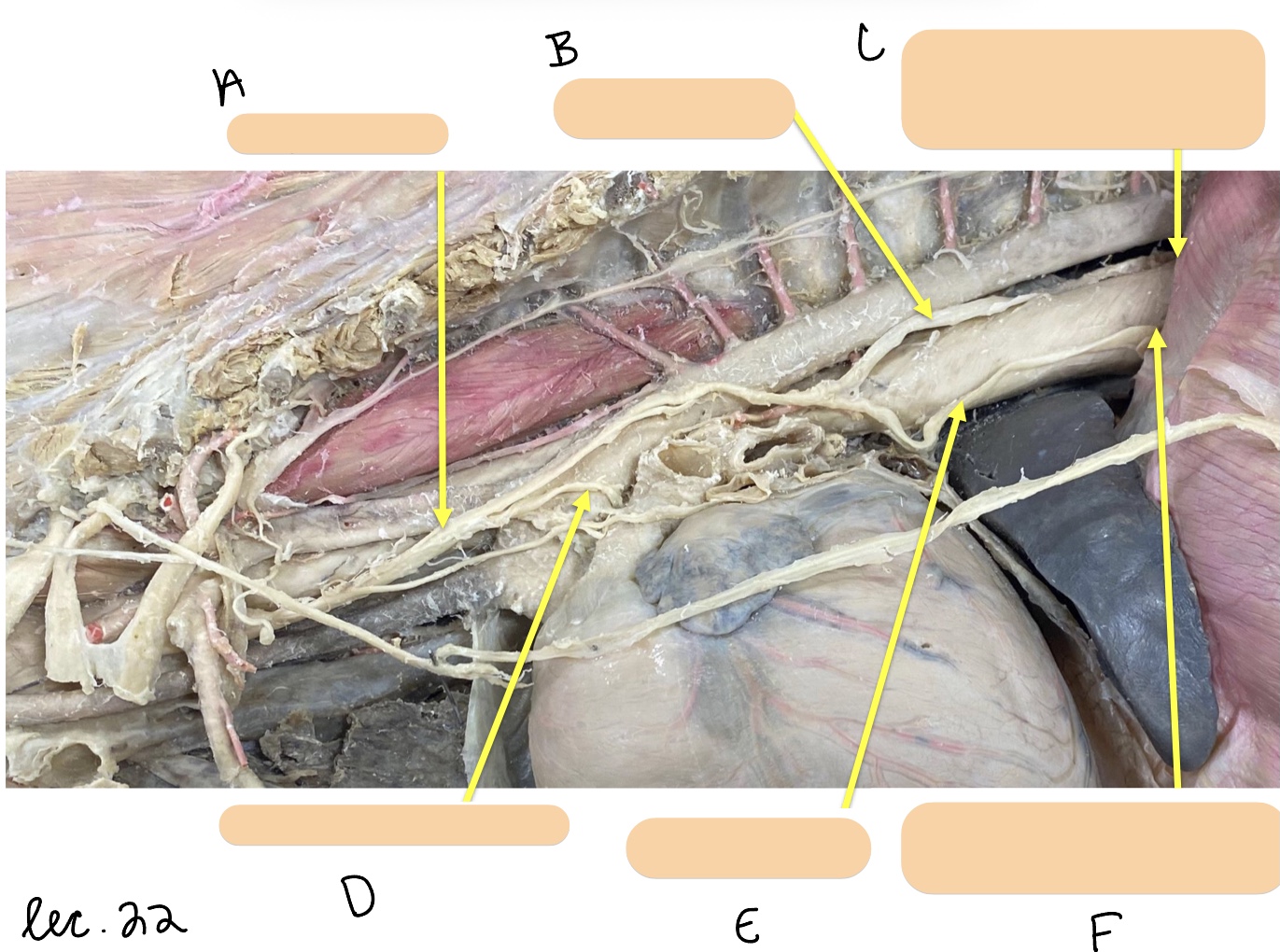
Name the structure(s) represented by a, b, and c.
vagus n.
dorsal branch of vagal n.
dorsal vagal trunk
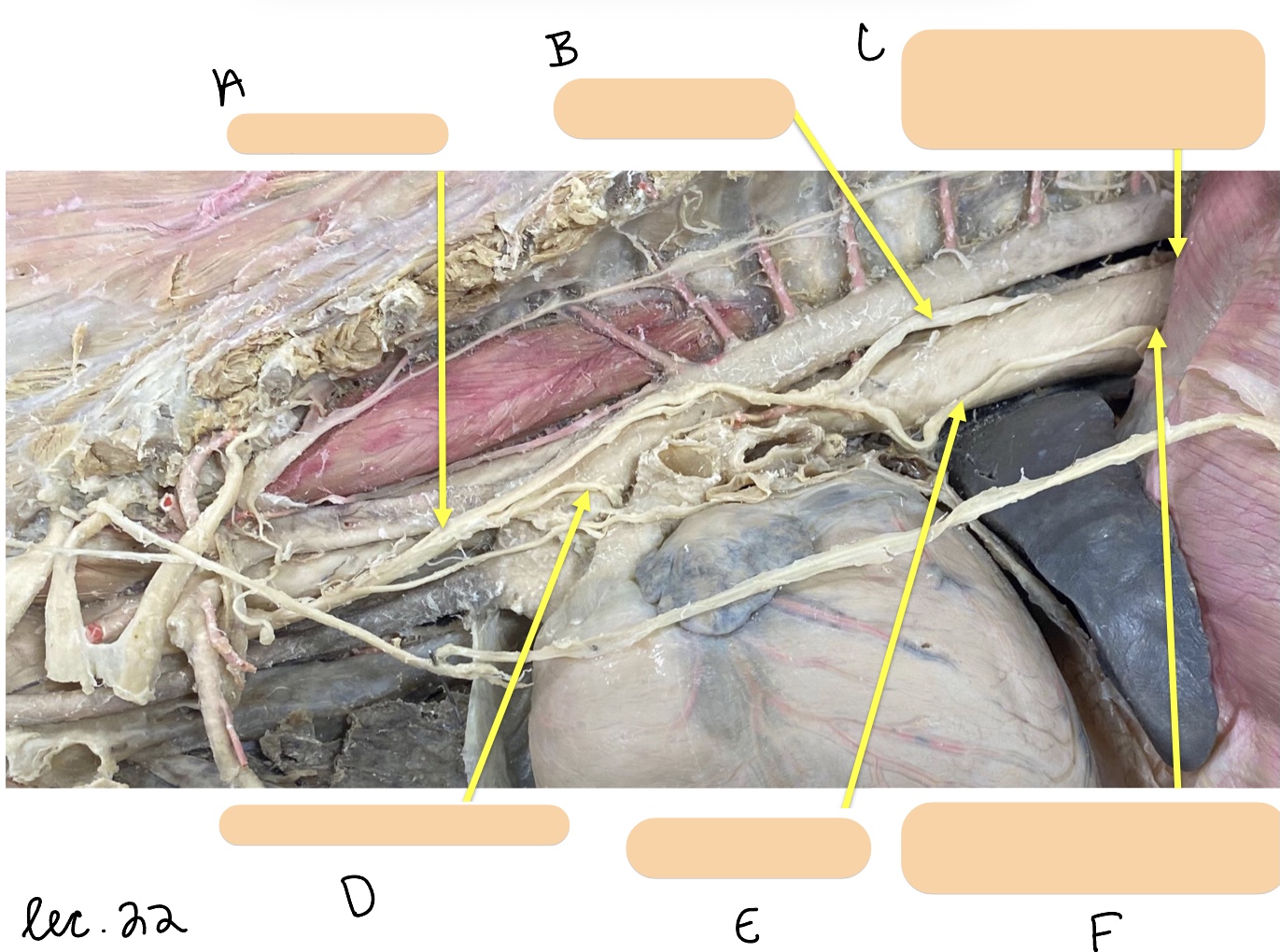
Name the structure(s) represented by d, e, and f.
recurrent laryngeal n.
ventral branch of vagal n.
ventral vagal trunk
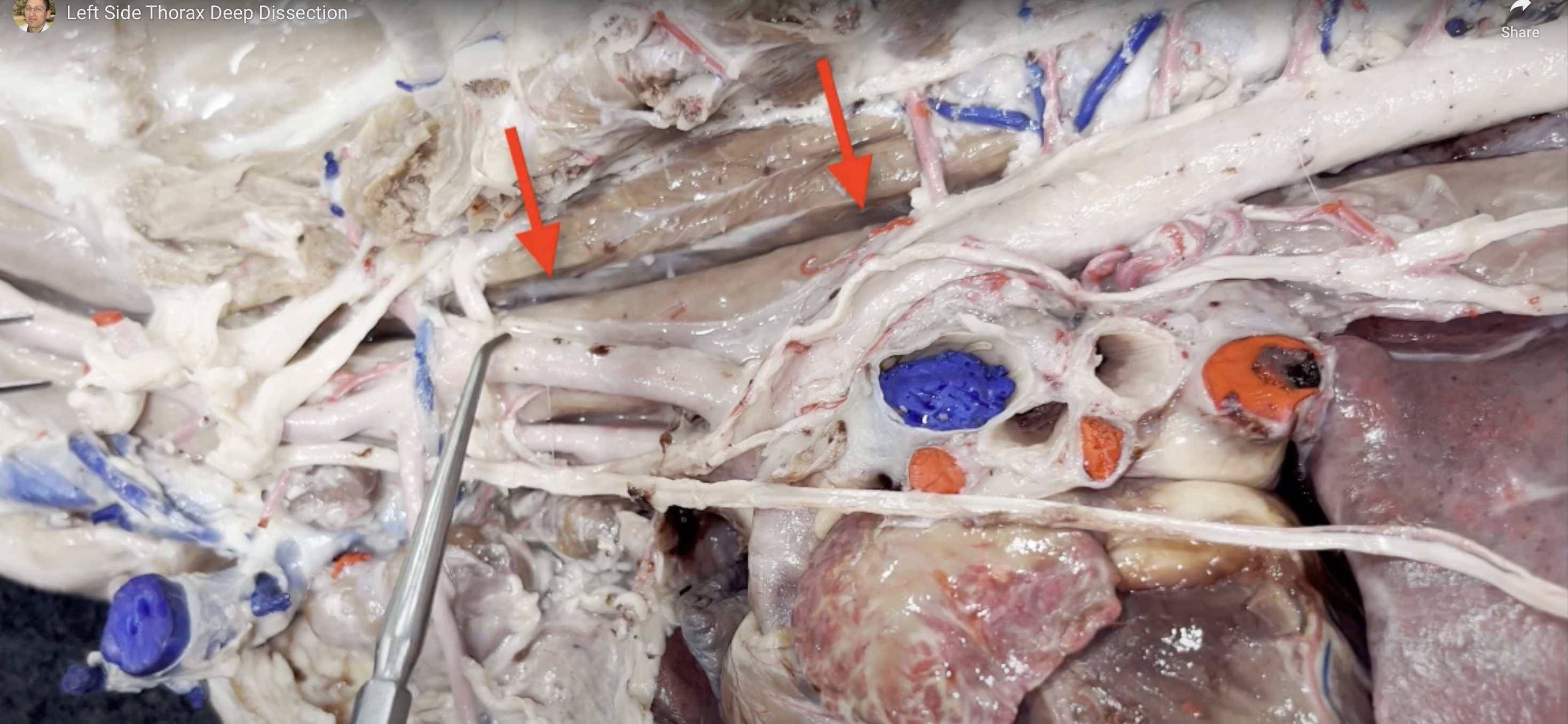
Name the structure(s) represented by the arrows.
sympathetic trunk