Lecture 23: Thin Lenses
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
23.7, 23.8, 23.10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What are thin lenses
those whose thickness is small compared to their radius of curvature
types of thin lenses
converging or diverging
light rays parallel to the principle axis are brought to … by a … lens
a focus
converging
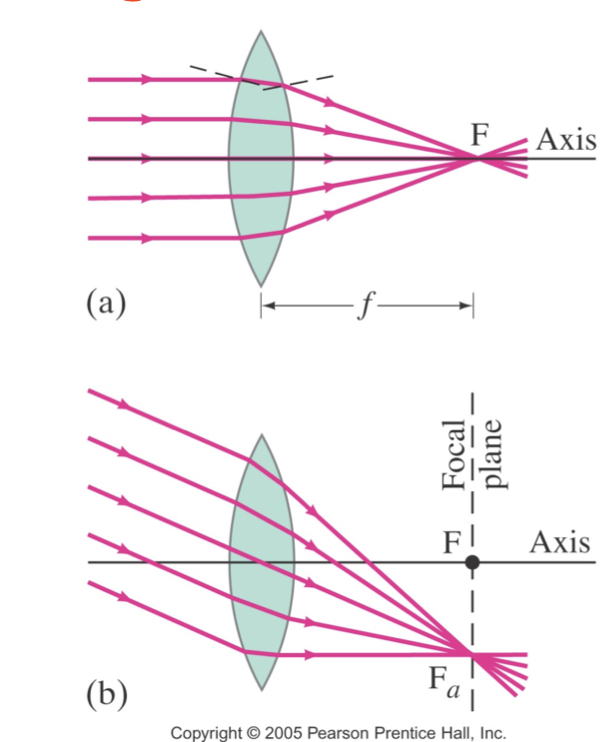
no matter whether the right rays are parallel to the principle axis or not
they will always focus on a line through the focal point
line is called the focal plane
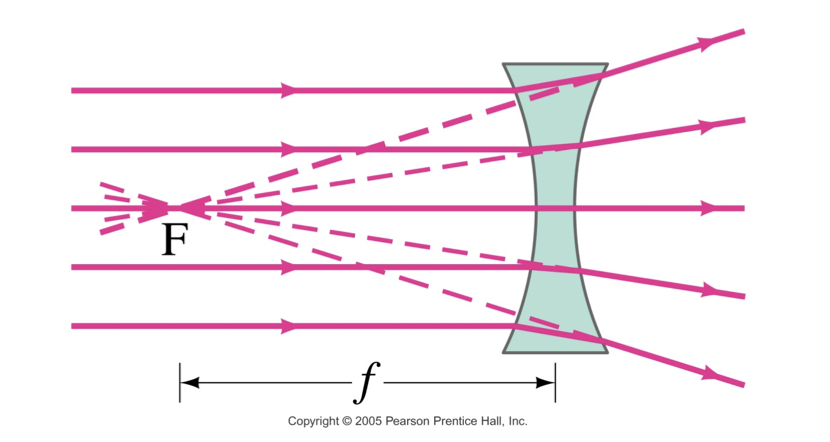
diverging lens make … light diverge
parallel
the focal point is that point where the diverging rays would converge if projected back
refractive power of a lens is the inverse of
its focal length in metres
refractive power is measured in diopters (D), this unit is used in optometry
P = 1/f(m)
eg) what is the power of a lens whose f = 50 cm
P = 1/f(m) → 1/0.5 = 2 D
Lens equation
same as the mirror equation but sign convention is different
1/do + 1/di = 1/f
magnification = m = hi/ho = -di/do
SIGN CONVENTION
+f = convex
-f = concave
SPHERICAL MIRRORS
-f = convex
+f = concave
1.7 m tall person is standing 2.5 m in front of a camera of f = 0.05 m, fine the image distance, magnification and image height
1/do + 1/di = 1/f
1/2.5 + 1/di = 1/0.05
di = 0.051 m → real since positive
m = hi/ho = -di/do = - 0.051/2.5 = -0.02 → image is inverted as magnification is negative
hi = (-0.02)x1.7 = -0.035 m
virtual image is always
upright
real image is always
inverted
convex lens makes…
real image when do > f
virtual image when do < f
concave lens always makes…
virtual image no matter where the object is located
lens makers’ equation
this equation relates the radii of curvature of the two lens surfaces and the index of refraction to the focal length of the lens
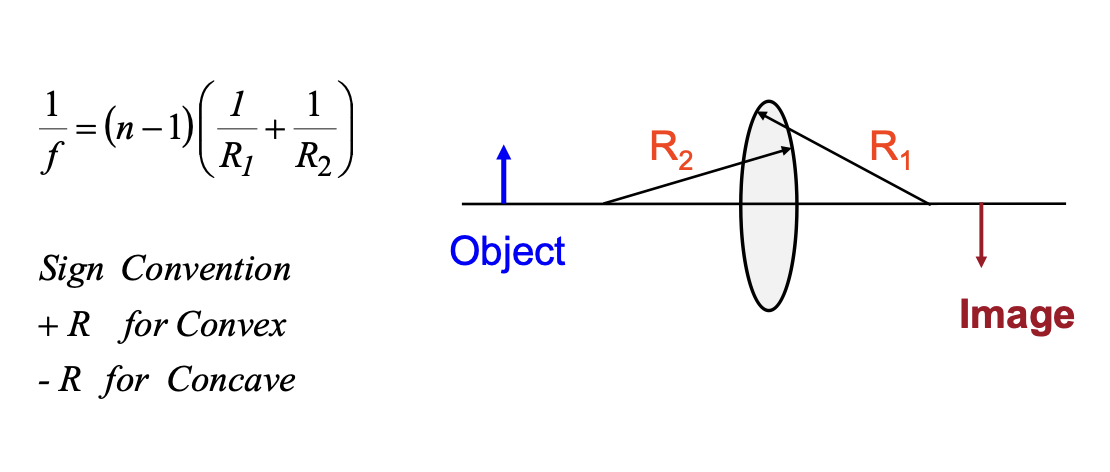
The glass lenses shown below has R1 = R2 = 42 cm and n = 1.65
Find their focal length
converging lens
1/f = (n-1)(1/R1 + 1/R2)
1/f = (1.65 -1)(1/42 + 1/42)
f = +32 cm
diverging lens
1/f = (1.65 -1)(1/-42 + 1/-42)
f = -32 cm