Ecology Midterm 1
1/273
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
274 Terms
What is Ecology?
The scientific study of the interactions between organisms and their environment.
What are the three ways to think about ecology?
Systems and Processes
Large and small scales
Variety!
Where is the word Ecology from?
Greek
oikios = living relations
ology = study of
What part of the definition sets Ecology apart from Biology
Ecology is the study of organism AND their environment.
What are 4 methods of Ecology overview / list
observational
experimental
statistical
theoretical
Expand on the observational method
going out into the field and collecting data such as going suba diving and collecting coral densities
Expand on the experimental method
This is setting up an experiment. It helps to have a more controlled environment and to have to control in changing different factors
Expand on the stats method
This is mainly done on a computer and involved models, analyzing data, regressions, etc.
expand on theoretical method
This is more math focused so using data to work through theories but not actually going and collecting data from the field.
What are the four venues in Ecology overview / list
laboratory
in silico
mesocosms
natural environments
Expand on the laboratory venue
This is tests done in a lab, either experiment or take samples from field to test onE
Expand on in silico venue
This is things done on the computer such as stats and math
Expand on mesocosms venue
these are similar to setting up a mini environment to control. Such as a big bucket add water plants and fish to mimic a lake
Expand on natural environment venues
This is similar to field work where you go out into the natural world and collect data
for example how a certain plant is surviving and can view after rainfall, drought, etc.
What are the levels of organization
individual (alligator)
population (group of alligators)
community (group of alligators and plants and land)
ecosystem ( take the community but add in weather such as sun and rain)
landscape (multiple ecosystems)
biosphere (collection of all ecosystems and biodiversity)
What factors determine the physical environment
climate, weather, air and water circulation patterns.
What is the habitable zone
the distance from the sun where water in liquid
e.x. the earth gets enough radiation and warmth but not so much that the water evaporates
What is the biosphere
Zone of life on the earth (wet and fuzzy layer)
between the lithosphere (earth’s surface crust and upper mantle) and the atmosphere
The life contained is diverse and overwhelming
Generally what is the ratio between known species and undiscovered
Today ~1.8 million species are known but there is ~12 million existing today yet undiscovered.
Are the more species on earth or more stars in the sky?
There are more species on earth and most have never been fossilized
Environmental controls on the distribution of water?
Climate determines environmental bands determines where species are found
What is the foundation of life on earth
H2O
delete
delete
The distribution of life is determined by what
H2o and environment
What are the different parts that make up climate
temperature and precipitation
long term description of weather events
trends are predictable
includes averages and variations, scales of decades to centuries
What does weather tell us
Short term description, what we are experiencing in the moment (hurricane, atmospheric river)
What is the main different between weather and climate
Weather is short term and climate is long term
Climate is _____, but trends are_____
dynamic(a lot is going on), predictable
What drives climate?
Incoming solar radiation
Why is the sun important
the sun is the driving force behind our climate
General path of heating the earth
Sun radiation is absorbed by the earth (49), some is initaily reflected then we have heat that leaves (114). in general it needs to be equal. So some radiation leaving is reflected back for example by green house gasses
How is the heat in and heat out equalized in heating the earth
More heat is leaving when cooling but greenhouse gasses help reflect the heat back
What are 4 reasons why the earths climate system is dynamic
Heating is uneven in space
Heat locations changes throughout the year (axial tilt = seasons)
Radiation at equator drives atmospheric circulation cells
Maintained by pressure gradients caused by adiabatic temperature chage
Earths climate is dyanamic explain why heating is uneven has an impact
The angle of incidence of the solar radiation is different. This is how radiation hits the planet
How is heating uneven at the equator
radiation hits the earth perpendicular, making it more direction and intense
How is heating uneven at the poles
radiation hits on the oblique so at an angle then spreads out over a larger area. This is less direct and less concentration. Also longer path through atmosphere, rays get reflected
How does the distance radiation takes to the earth affect it
The longer the path the more rays will get reflected resulting in less intense radiation
The sun warms ____ resulting in the ground heating the ____
the ground, air
What is a result of the heating locations changing throughout the year
Seasons!
What causes seasons?
The tilt of the earths axis
When the earth is tilted towards the sun what results
Increase in intensity, more direct, warmer
When the earth is tilted away from the sun what results
decrease intensity, less direct, cooler
When the N. Hem is tilted ____ and the S. Hem is tilted ___ the sun N is winter and S is summer
N away
s towards
Why does distance from the sun not produce seasons?
The earth is not perfectly round so path is not perfect, it revolved ~30hm/s the sun is not in the perfect center of orbit. The impact of the tilt overpowers any impact from the distance from the sun
Energy surplus at ____ latitude
Energy deficit at ____ latitude
Low (equator)
High (poles)
What are three things that results from the uneven distribution of solar radiation
atmospheric circulation
Precipitation patterns
Distribution of biota
The physical environment determines the _____ of life
Location
Increasing the angle of incident results in
a dilution of radiation
What is the earths tilt for Fall and Spring
Parallel to the sun, they are transition seasons
More energy is gained than lost at the ___
More energy is lost than gained at the ___
More energy is gained than lost at the low altitude equator
More energy is lost than gained at the high altitude poles
What drives atmospheric circulation
This is driven by the unequal distribution, so the equator (low latitude) surplus and poles (high latitude) deficit
What is adiabatic temperature change
Change in temperature without change in thermal energy
The thermal energy amount__ __ __ and just ___ and ____
The thermal energy amount STAYS THE SAME and just EXPANDS and CONTRACTS
relationship between pressure and temperature at constant Volume
proportional
relationship between V and T at constant P
proportional
relationship between P and V at constant temperature
inverse
relationship between T and humidity / water content
proportional
Does warmer or colder air hold more water
Warmer air holds more water
Air is under ____ which changes with ___
Air is under pressure which changes with altitude
In adiabatic temperature what happens to warm air
warm air rises, the pressure decreases resulting in the volume increasing and cooling occurs
this is exapanding
often resulting in rain because it can no longer hold has must water
Thermal energy __ temperature
= or ≠
≠
What does energy mean
The molecule speed
What does heat (temperature) mean
The sum/result of collisions between molecules
Adiabatic cooling (process)
As volume increases (expansion) there is more room for the molecules and few collisions, this decreases temperature
As air temp decreases there is a lower saturation point, water vapor condenses and can not longer be help we get precipitation
thermal energy is CONSTANT just changes by expansion or compat
What is humidity
Fraction of air that is water vapor
Talk through Adiabatic temperature changes
Warm air is less dense than cool air so the warm air rises above
as the warm air rises, it expands and cools
as the air cools water vapor condenses to form couds
Air circulation
Unequal incoming solar
radiation sets up zones
of adiabatic cooling and
warming
This drives airflow
around the planet,
which distributes water
What mechanisms distributes water
Airflow around the planet
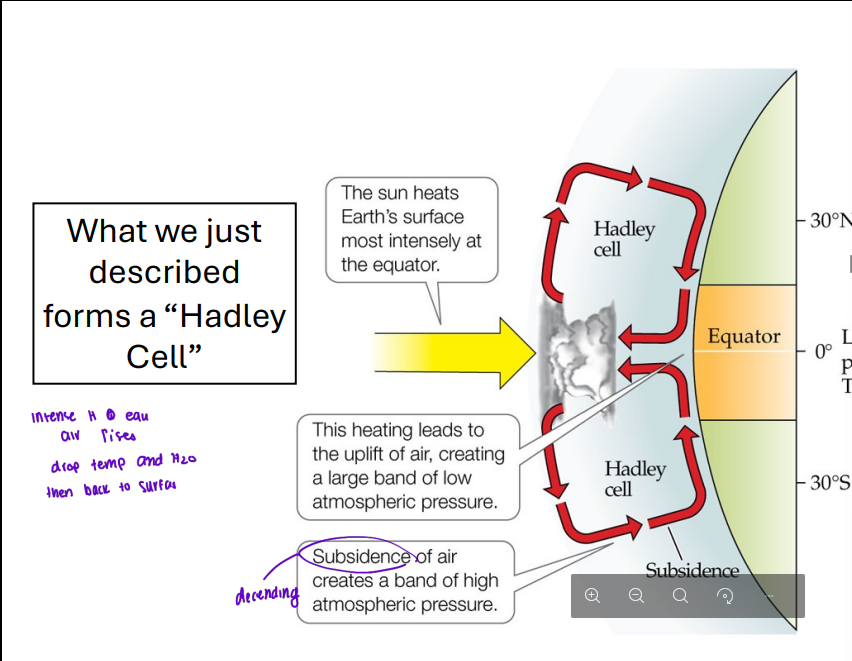
Air circulation at the equator
solar radiation heats the surface and the air
this warm air is wet and buoyant
warm air rises and expands and cools ( P↓, V↑, T↓). This is adiabatic cooling, then there is rain resulting in tropical rainforests
low pressure zone
after air cools, it stops rising and splits N to S
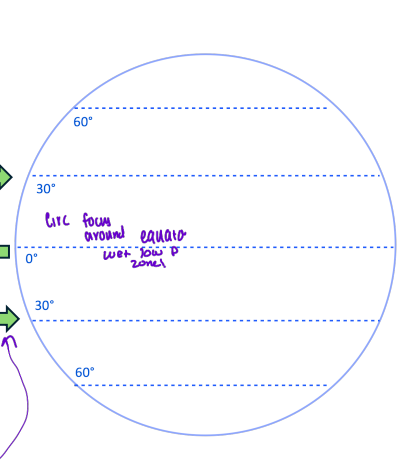
How do we get tropical rainforests
when the warm air rises and cools, the ability to hold water decreases and rains at the equator
Air circulation at 30 N/S
This air is cold and dry (from the equator) and sinks and warms (P↑, V↓, T↑) = adiabatic warming
the warmer the better the ability to hold moisture the the air picks up moisture from the surface = deserts
This is a high pressure zone (air is pushed down)
Air then splits and runs towards low P zone
Hp and dry here
What gradient does air flow
High pressures to low pressures
Hadley cells
The flow of air at the equator
Air circulation at 60 N/S
Air is warm and moist, this air meets air from the poles and rises because it is relativly warmer, (P↓, V↑, T↓) rises, expands, and cools, this produces temperate rainforests, low pressure, adiabatic cooling
Air circulation at poles (90)
air is cold and dry, so it descends, air sinks and warms (P↑, V↓, T↑) adiabatic warming
DRY (deserts), high pressure
If low pressure we or dry
Wet
Is high pressure wet or dry
dry
What is the cell name at the equator
Hadley
What is the cell name mid latitude
Ferrell
What is the cell name at the poles
Polar cells
What pattern is important for winds
The H to L pressure patterns
Winds flow from areas of ____ pressures to ____ pressures
High, low
Prevailing winds
Consistent patterns of air movement at the earths surface. (H to L / dry to wet)
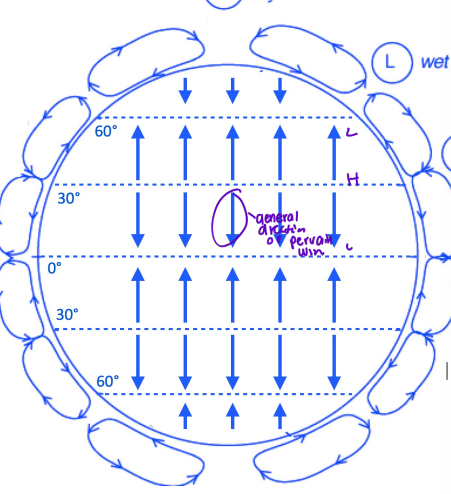
Coriolis effect
prevailing winds appear deflected due to earths rotation
Coriolis effect: What way does the winds move in N. Hem
clockwise
Coriolis effect: What way does the winds move in S. Hem
counterclockwise
Coriolis effect impacts not only air, but ___ ___ __
any moving particle like water, baseball
Coriolis effect: does the poles are equator have a longer distance to travel in the same amount of time
The poles have a longer distance to travel
Coriolis effect: If you have a larger distance what happens to your speed
Your speed increases
Air moves at different ___ depending on ___
Speeds, location
Coriolis effect: explain how it looks
When going from high pressure to low such as 30-0 the speed is slower at the high pressure (short distance traveling) so it looks like it falls behind
when going from 30 to 60, 30 is going faster so the winds push forwards leaving behind the 60 winds
Trade winds
Historical importance in the
transport of goods
on equator counterclockwise`=
Westerlies
Moves from west to east
Easterlies
Move from east to west
How are wings generally named
From whew they originated
How are circulation cells sustained
Pressure gradients (low to high) that result from adiabatic cooling
Moving air is ____ by the spin of the earth. this is called ____
deflected, coriolis
Winds force shallow ____ ____
ocean current, coriolis further deflects the water
Ocean currents impact regional climates: Example
The gulf stream brings warm water to N.Europe / scandinavia
also impacts the growth at location