IGCSE Economics - Trading blocs
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Trading blocs
A group of countries that come together and form agreements to promote trade and economic cooperation among themselves.
Trading blocs around the world
APEC (exports: $12.47 trillion, imports: $12.55 trillion)
EU (exports: $7.49 trillion, imports: $8.11 trillion)
BRICS (exports: $5 trillion, imports: $4 trillion)
NAFTA (exports: $3.23 trillion, imports: $4.55 trillion)
ASEAN (exports: $1.95 trillion, imports: $1.88 trillion)
GCC (exports: $1.1 trillion, imports: $691 billion)
SAARC (exports: $567 billion, imports: $935 billion)
MERCOSUR (exports: $448 billion, imports: $388 billion)
COMESA (exports: $182 billion, imports: $257 billion)
SACU (exports: $141 billion, imports: $131 billion)
5 types
Preferential Trade Areas
Free Trade Areas
Customs Union
Common Market
Economic Union
Different stages of economic integration
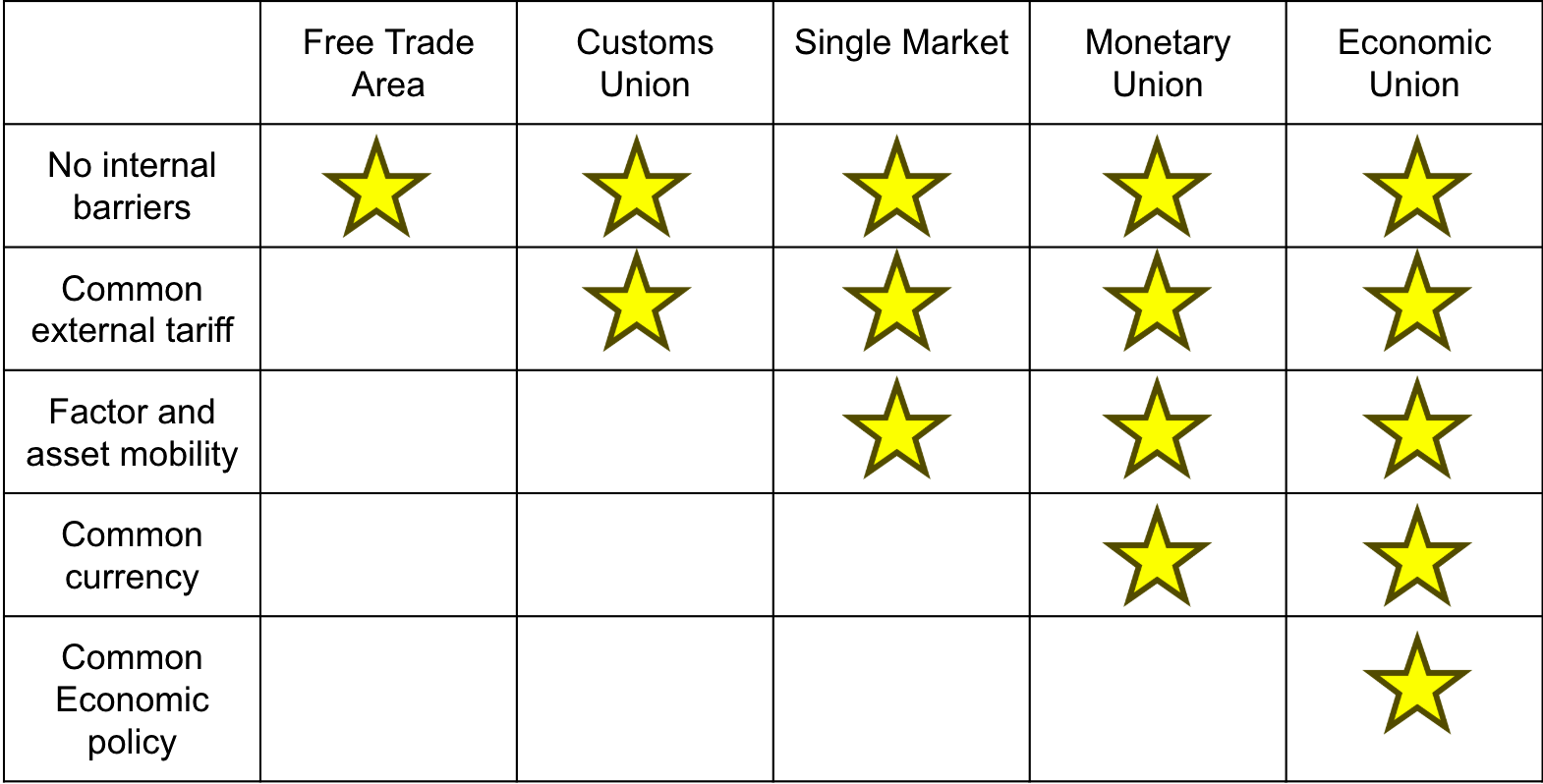
Free trade Area
An agreement formed by a group of like-minded countries that agree to reduce trade barriers, such as tariffs and quotas
Customs Union
Group of countries that apply one common system of procedures, rules and tariffs for all or almost all their imports, exports and transiting goods.
Single Market
Allows for people, goods, services and capital to move around a union as freely as they do within a single country
Monetary Union
A group of countries that share a common market where goods, services, capital, and labor can move freely. Uses a common currency, eliminating the need for exchange rate fluctuations within the union.
Economic Union
An agreement between two or more nations to allow goods, services and workers to move over borders freely. (EU)
Why do trading blocs exist
Remove all barriers to trade and gain all the benefits of trade
Competition
Efficiency (resources allocation)
Economies of scale
Macroobjectives (e.g. Unemployment)
Trading bloc membership
Immigration
Membership fees
Trade
Immigration
More factors of production —> increases PPC
- Lowers wage rate (Increase supply of labour)
- Creates unemployment for local citizens
Membership fees
Gains for developing countries
- Cost to more developed countries - support less developed countries
Trade
Increased trade with member countries (benefits of free trade)
- Reduced trade with non-member countries
- Local businesses face greater competition (reasons for protectionism)
Trading bloc
causes domestic firms to lose out to foreign competition
On balance trading blocs will benefit economies, however with BREXIT, there can be loss of sovereignty (power) to other countries
Countries are far more interdependent in trading blocs (problematic in financial crisis 2008-9 where economic failure can spread)